Gravidar, or retrochorial, hematoma is a common gynecological disease. It is formed during pregnancy in the early stages of gestation, i.e. in the 1st trimester. When the chorion separates from the endometrium, blood vessels rupture. Blood pours into the resulting space, which leads to the formation of a hematoma (bruise).
What is retrochorial hematoma
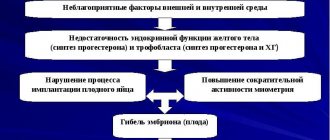
Pathology is an accumulation of blood clots in the gap between the membrane of the fertilized egg and the wall of the uterus. When the disease occurs, detachment of the chorion from the uterine wall occurs. Retrochorial (gravid) hematoma is a consequence of the threat of interruption of gestation or destruction of the walls of the uterine vessels by chorionic villi during the growth of the membrane of the fetal egg.
The insidiousness of the disease is that it creates a vicious circle: a growing clot increases the risk of miscarriage, and the ongoing threat of pregnancy failure contributes to increased hemorrhage. The chorion transforms into the placenta over the course of pregnancy, this happens around the 16th week. Based on the timing of pregnancy, the pathology is divided into retrochorial and retroplacental hematoma. Depending on the course, the disease is classified into mild, moderate, and severe.
Why does the disease occur?
The causes of retrochorial hematoma during pregnancy, contributing to its formation (including retromnial hematoma during early pregnancy - in the first 8, 11, 13 weeks), are presented in large numbers. The formation of a clot is equally influenced by hereditary predisposition, disruption at the hormonal level, the presence of a disease of a chronic or infectious type, increased physical or emotional stress.
The stages of formation of a neoplasm are as follows:
- Influencing predisposing factor.
- The beginning of the separation of the egg, where the fetus is located, from the uterine wall.
- Rupture of a blood vessel.
- Formation of a space where a neoplasm is localized, similar to a hematoma.
According to the results of scientific studies, in 65-70% of cases when such a neoplasm was diagnosed in pregnant women, thrombophilia was detected along with this condition. It is equally rare for women to have a history of coagulation dysfunction.
Among the factors predisposing to the formation of a neoplasm are the following:
- injury to the abdominal organs, which affected the female organ (damage as a result of an unsuccessful fall, etc.);
- failure at the hormonal level;
- abnormal formation of fetal organs and systems;
- failure of the immune system;
- the presence of severe depression, systematic stress, nervous shock;
- excessive physical activity;
- engaging in professional activities that require interaction with harmful chemicals (including inhalation of their vapors);
- inflammation developing in a complex in the female genital tract;
- oncological process in any organ;
- the presence of an infectious disease, the route of transmission of which is sexual;
- ultraviolet and radiation exposure on a constant basis;
- severe toxicosis during pregnancy;
- high or low blood pressure;
- unhealthy lifestyle (smoking abuse, drinking alcohol, taking drugs);
- developing heart and vascular disease;
- diabetes;
- impaired blood clotting function;
- living in an unfavorable ecological environment;
- ongoing diseases in the vessels of the organ.
We recommend additional reading: How to get rid of edema during late pregnancy and why they are dangerous
Causes
The causes of gravid hematoma are similar to the factors that provoke the risk of miscarriage. The source of the problem is currently not fully understood. Some of the prerequisites for the occurrence of hemorrhage between the fetus and the uterine wall do not depend on the pregnant woman; they can only be corrected with medication. Other causes can be eliminated by changing lifestyle and diet. General factors that provoke the formation of hematoma:
- mechanical impact on the uterine area (injuries, bruises);
- strong physical activity, especially heavy lifting;
- negative industrial impact (radiation, noise, vibration, etc.);
- smoking, drinking alcohol or using drugs;
- stressful situations.
Pathological conditions can lead to the development of gravid hematoma. This:
- hormonal system disorders (progesterone deficiency);
- genetic abnormalities in the development of elements of the fertilized egg;
- infantilism or abnormalities of the internal genital organs;
- inflammatory or tumor pathologies of the uterus (endometriosis, fibroids, endometritis);
- STIs (sexually transmitted infections);
- systemic diseases (collagenosis, lupus erythematosus);
- pathologies of the blood coagulation system;
- vascular diseases;
- toxicosis in early and late stages;
- sudden changes in blood pressure;
- chronic somatic pathologies.
How to identify pathology
Diagnosis is quite simple and painless: a hematoma is detected during a routine ultrasound examination.
For details, a 3D ultrasound is usually prescribed: thanks to a three-dimensional image, the doctor can determine where exactly the blood is collecting and whether there is a risk of damage to the placenta. If a stage 1-2 retrochorial hematoma has been detected, then an ultrasound scan will have to be performed once every 2 weeks to track the dynamics of the pathology.
But a retroplacental hematoma on an ultrasound machine monitor may look like a thickened placenta, which slightly complicates the diagnosis. A specialist may suspect pathology if the hypoechoic zone is > 2 cm in size.
To confirm concerns, an ultrasound using Doppler is prescribed. A simply thickened placenta will have uniform blood circulation, but the hematoma will take the form of a flat dark stripe, since the neoplasm does not have its own blood flow.
It is almost impossible to identify pathology on your own based on some external signs. New growths (especially small ones) do not cause bleeding. Only with the development of a retroplacental hematoma may blood discharge and leakage of amniotic fluid appear.
Symptoms
Any unpleasant manifestations during the period of bearing a child should be a reason for an immediate visit to your gynecologist or calling an ambulance. When it comes to maintaining a pregnancy, you cannot hesitate for a second. The most dangerous is the last stage, because it can lead to intrauterine death of the child. A pregnant woman urgently requires hospitalization. Signs of gravid hematoma depend on the severity:
- At the initial stage, the pathology is asymptomatic. Often, a retrochorial hematoma without discharge or discomfort is detected during a routine visit to the gynecologist during an ultrasound scan. There are cases when an asymptomatic hematoma is discovered after the birth of a child. Remnants of clots from old hemorrhage can be observed on the placenta when it comes out.
- Nagging pain and brown discharge with retrochorial hematoma signal a more severe phase of the pathology. Just don’t panic; perhaps brown vaginal discharge indicates spontaneous resorption of the clot or stopping bleeding. The process of spontaneous resorption takes from 15 days to 2 months.
- Sharp cramping pain, localized in the lower abdomen or lower back, as well as the discharge of scarlet blood from the genital tract are signs of detachment of the fetus from the mucous surface of the uterus. Due to a sharp decrease in blood pressure, a woman may faint. The appearance of bright red blood indicates the growth of a gravid hematoma, which leads to termination of pregnancy. Or this sign may indicate that the clot has just formed and requires immediate treatment.
- Bath during pregnancy: how to take the procedure in the early and late stages
- Hemorrhagic syndrome - types and causes. Symptoms and consequences of hemorrhagic syndrome in children and adults
- Treatment of hemorrhoids 4 degrees
Clinical signs
The symptoms of a hematoma directly depend on its shape and degree. In medicine, there are mild, moderate and severe degrees of pathology:
- With a mild degree, the woman feels normal and may not feel any symptoms. The presence of a bruise is detected by ultrasound or after childbirth. There are no pathological discharges from the genital tract.
- The average degree is characterized by nagging or aching pain in the lower abdomen, which can radiate to the leg or lumbosacral region. A characteristic sign of pathology is spotting red or brown discharge. Ultrasound also shows abnormal fetal heartbeat.
- In severe cases, the pregnant woman suffers from acute pain in the abdomen or back that cannot be tolerated. Blood pressure can drop sharply, resulting in dizziness and fainting, general weakness and loss of strength, blurred vision, a state of “intoxication,” increased sweating, and numbness of the extremities. There is copious bloody discharge from the vagina, which may occur before bleeding.
A woman should be able to independently assess the shade of discharge from a hematoma:
- clear or light white color is normal;
- brownish streaks or impurities that appeared in the early stages indicate that the hematoma is small in size and does not affect the formation of the fetus;
- a rich brown tint or the color of “meat slop” indicates that the hematoma is resolving on its own or is coming out as the blood coagulates;
- scarlet or burgundy discharge indicates open bleeding that is currently occurring. That is, the hematoma continues to increase in size and poses a real threat of termination of pregnancy.
Severe placental abruption usually causes severe bleeding and pain.
Signs according to ultrasound
The main method for diagnosing gravid hematoma is ultrasound examination of the uterine cavity and membranes of the ovum. There are several reasons to suspect pathology; the specialist makes a final conclusion only after a complete examination of the pregnant woman. Signs of the presence of hemorrhage in the space between the chorion and the uterine wall:
- Local compaction of the uterine wall indicates an increase in the tone of the uterus. Tension of the uterine muscles may occur during vaginal examination with an ultrasound machine. In such a situation, it is better to resort to the use of a transabdominal sensor, which is used to conduct ultrasound through the anterior abdominal wall. If muscle tone persists, this indicates a risk of miscarriage.
- The presence of a cavity filled with bloody fluid. On the monitor, this may appear as a dark spot that is located between the chorion and the wall of the uterus.
- A change in the shape of the fertilized egg to teardrop-shaped or scaphoid occurs due to pressure on the embryo from the hematoma.
Tumor treatment
It is important to identify retrochorial hematoma during pregnancy at the stage of organization, when measures can still be taken to completely cure it. To do this, they carry out the necessary tests and examinations to determine the diagnosis.
During treatment, lifestyle needs to be changed: a pregnant woman is advised to rest more and not expose herself to physical overload and emotional shock. Sexual activity is strictly prohibited.
Will a caesarean section be required?
If a retroplacental hematoma is present during pregnancy and placental abruption is observed, and the pregnancy period exceeds 22 weeks, a cesarean section is performed.
For most women, there is a favorable outcome and the child’s life is saved. Premature newborns are placed in an intensive care unit, where measures for further nursing are carried out.
Medication treatment of retrochorial hematoma during pregnancy
It is possible to cure retrochorial hematoma during pregnancy. It is enough to identify the pathology in a timely manner and begin therapeutic procedures. Initially, measures are taken to stop the growth of the tumor and normalize blood circulation in the affected area.
We recommend further reading: What to do if your legs start to swell during pregnancy
Hormonal support is important, which contributes to the normal bearing of the baby and its birth on time. With this diagnosis, doctors prescribe the following medications:
- hormonal drugs, for example, Duphaston or Utrozhestan, which are prescribed for uterine tone;
- preparations with folic acid and myeroelements A, E in the composition, which are involved in the proper formation of the fetus, also help to increase the volume of oxygen;
- homeopathic tablets, for example, Sulodexide or Wobenzym;
- medications that normalize platelet clotting, for example, Dicynon;
- taking magnesium supplements, for example, Magne B6, is necessary if the tone of the uterus increases;
- drugs with an analgesic effect, for example, No-shpa;
- drugs that improve the functioning of the placenta, for example, Actovegin;
- medications that help normalize the emotional state, for example, Valerian or Motherwort.
The above drugs are absolutely safe for the baby developing in the womb and the woman carrying him.
How does a small retrochorial hematoma come out during pregnancy?
It is difficult to say how a retrochorial hematoma occurs during pregnancy and during what time. The data is influenced by the size of the tumor, concomitant pathologies and the characteristics of the general health of the pregnant woman. The approximate duration of release is 2-2.5 weeks.
The exit of a neoplasm in a pregnant woman is indicated by the presence of a specific discharge from the vaginal cavity. The normal process is characterized by a small volume of bloody exudate released. Some women have a nagging pain syndrome.
How does a hematoma heal?
During treatment of hematoma during pregnancy, it is important to follow the recommendations of your doctor. This is the only way to avoid negative consequences. Resorption of the hematoma occurs painlessly, without taking into account the size of the ovum, that is, at different stages of pregnancy.
Diagnostics
If a gravid hematoma is suspected in a pregnant woman, the doctor collects an anamnesis, interviews the patient about her well-being, and performs a gynecological examination. Detection of clots during hemorrhage in the space between the fetus and the wall of the uterus, clarification of the size of the hematoma and the location of the clot is possible only with ultrasound examination. To make a reliable diagnosis, you will need not only hardware, but also laboratory diagnostic methods:
- blood test for coagulation (establishing the concentration of fibrinogen, prothrombin and other factors);
- blood chemistry;
- general blood and urine analysis;
- hormonal profile (amount of progesterone);
- vaginal smear (examination of microflora, exclusion of STIs);
- Ultrasound of the uterus and ovum (transabdominal, vaginal method);
- CTG (cardiotocography), fetal Doppler (in late pregnancy).
Danger for the expectant mother and baby
If a woman during pregnancy adheres to all the recommendations and prescriptions of the gynecologist, there is no threat to the life of the fetus. Even if there is an outflow of blood from the chorionic section, but the pregnant woman adheres to the correct lifestyle and carries out the necessary treatment, the hematoma will resolve within 15-35 days.
During the entire period of pregnancy, the woman’s health condition is carefully monitored. If appropriate measures are not taken in a timely manner, the area increases with exfoliation of the chorionic section, which can be explained by incessant bleeding.
We recommend additional reading: Is it possible to eat lingonberries during pregnancy, leaves and decoction of lingonberries for edema
The consequences of retrochorial hematoma for a woman during pregnancy and for a child (baby in the womb) are often unpredictable. Among them:
- premature termination of pregnancy (in other words, miscarriage);
- cessation of embryo development in the womb or death;
- hemorrhage in the uterus;
- failure in the development of organs and systems of the embryo;
- the formation of such a neoplasm at a later stage, as a relapse of the pathology.
If pathological exudate begins to be released during pregnancy, pain symptoms occur in the lower abdomen, such clinical manifestations should alert the woman and cause a visit to the doctor. In the first 3 months, the state of discomfort indicates this condition and other problems requiring emergency treatment.
Treatment of retrochorial hematoma
Drug treatment of retrochorial hematoma during pregnancy is carried out by an obstetrician-gynecologist. Therapeutic measures are carried out in a hospital or at home - it all depends on the stage of the pathological process. Treatment continues throughout the period of risk of miscarriage. The course of therapy lasts at least a month with preventive actions in the most vulnerable periods of gestation (12–14, 20–24, 28–32, 36–38 weeks). Complex treatment of gravid hematoma includes:
- drug therapy;
- prohibition of physical activity or heavy lifting;
- stabilization of emotional state;
- temporary cessation of sexual activity;
- changing diet and lifestyle.
Drug therapy for hemorrhage in the space between the chorion and the uterine wall gives quick positive results. The following groups of drugs will help stop the pathological process and maintain pregnancy:
- Sedatives (Phytosedan collection, motherwort or valerian tincture, Novo-Passit and others). Natural sedatives will help maintain a normal psycho-emotional state.
- Drugs and vitamins that improve uteroplacental blood flow (Curantil, Actovegin, folic acid, vitamin E, Ascorutin). The drugs have a vasodilating effect, due to which they quickly normalize blood circulation and eliminate tissue hypoxia.
- Hemostatic drugs (Ditsinon, Vikasol). Hemostatics are used to prevent or stop uterine bleeding in cases of gravid hematoma.
- Antispasmodics (Papaverine, No-shpa, Drotaverine, Magne B6). The drugs reduce uterine tone.
- Hormonal medications (Utrozhestan, Duphaston). Drugs that correct the balance of the endocrine system are prescribed only by a doctor, taking into account individual tolerance, dosage and duration of use.
- Analgesics allowed during pregnancy (Paracetomol, Ibuprofen and Voltaren can be taken only in the 1st and 2nd trimester).
Papaverine
According to its pharmacological action, the drug belongs to the group of myotropic antispasmodics and vasodilators; it is an opium poppy alkaloid isolated from vegetable oils. It is derived from the organic compound isoquinoline. Papaverine is an affordable and highly effective remedy for eliminating vascular spasms:
- Therapeutic effect: relaxes the smooth muscles of the blood vessels of the genitourinary system, reduces blood pressure.
- Indications for use: spasms of vascular smooth muscles, weakening of the tone of the uterine muscles.
- Ingredients: papaverine hydrochloride.
- Advantages: efficiency, safety, low price.
- Dosage: injections up to 4 times a day, tablets 3-4 times a day in small courses for 1-2 weeks.
- Side effects: increased blood levels of transaminases and the number of eosinophils, AV block, ventricular extrasystole, decreased blood pressure, drowsiness, sweating, allergic reactions, nausea, yellowness of the sclera and skin, constipation; thrombosis is possible with intravenous administration.
- Contraindications: individual intolerance, severe liver failure, AV block, glaucoma.
Askorutin
A combined vitamin preparation that restores the deficiency of vitamins C and P is a means of stabilizing the elasticity and strength of capillaries. In addition to the main effect, Ascorutin additionally strengthens the immune system. The drug is a preventative against colds and infectious diseases, which is especially important during pregnancy, because taking antibiotics is undesirable:
- Therapeutic effect: strengthens vascular walls, reduces fragility and permeability of blood vessels, reduces platelet aggregation, takes part in redox processes, saturates the blood with oxygen, reduces platelet aggregation, has an anti-inflammatory effect and antioxidant effect.
- Indications for use: prevention or treatment of vascular fragility, which prevents bleeding, fetal hypoxia, and edema.
- Ingredients: ascorbic acid, rutin.
- Advantages: the vitamin complex is harmless, well absorbed by the body, and has an affordable price.
- Dosage: 1 tablet 2 times a day.
- Side effects: dyspeptic type disorders, feeling of heat, headache.
- Contraindications: hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, diabetes mellitus, urolithiasis, predisposition to the development of thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, blood hypercoagulation.
Chime
A myotropic vasodilator has an inhibitory effect on platelets, which prevents varicose veins, which are observed in many women after bearing a child. Immunomodulatory properties are achieved by activating the synthesis of interferon, so the drug is effective against influenza and ARVI. Curantil is a medicinal product, so it should be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the characteristics of the pregnant woman’s body:
- Therapeutic effect: improves blood circulation and oxygen exchange in cells, strengthens the walls of blood vessels, dilates blood vessels.
- Indications for use: placental insufficiency, convulsions, swelling, headaches, high blood pressure.
- Ingredients: dipyridamole, lactose monohydrate, gelatin, potato starch, magnesium stearate, calcium carbonate, polyvidone K 25, gelatin, sodium carboxymethyl starch (type A), colloidal anhydrous silicon dioxide.
- Advantages: wide spectrum of action (immunomodulator, antiplatelet agent, improvement of uteroplacental blood flow);
- Dosage: 3 times a day, 1 tablet containing 25 mg of dipyridamole.
- Side effects: feeling of internal heat, fever, general weakness, dizziness, heart rhythm disturbances.
- Contraindications: decreased blood clotting, gastric or duodenal ulcers, cardiovascular disease, liver and kidney pathologies.
- Use of the drug Actovegin during pregnancy - indications and instructions for use, composition and analogues
- Treatment and consequences of cerebral edema in children and adults
- Aescusan - instructions for use, release form, indications, side effects, analogues and price
Lifestyle change
If the pregnant woman does not have scarlet-colored bleeding or pain, the attending physician may allow the patient to undergo therapy at home. To do this, the woman will need to remain in bed, undergo regular examinations and follow all doctor’s orders. Most of the time, a pregnant woman who has a gravid hematoma should be in a supine position. Several times a day, it is recommended to place a cushion under the lower back to ensure the outflow of blood from the pelvic organs.
Any worries or worries are strictly unacceptable. Emotional stress with such a diagnosis can provoke increased bleeding and loss of the child. Intimate relationships should be temporarily suspended until complete healing. You will also have to change your diet in favor of light, but highly nutritious foods. If the woman’s condition is stable without complications, and the treatment gives positive results, then short walks in the fresh air are recommended for the pregnant woman.
Nutrition
A woman diagnosed with gravid hematoma needs to exclude foods that cause gas formation in the intestines. The basis of the diet should be protein foods in combination with vegetables, fruits, and herbs. Do not get carried away with foods that thin the blood (beets, cherries, strawberries, raspberries and others). To avoid constipation, it is necessary to maintain a daily drinking regime. Meals should be small to avoid overloading the gastrointestinal tract.
Treatment
In most cases, treatment of retrochorial hematoma is carried out in a hospital setting.
When the accumulation of blood is small and does not pose a threat, the pregnant woman may be allowed to undergo a therapeutic course at home. To relax the muscle tone of the reproductive organ, a woman needs to lie quietly in a horizontal position. Bed rest is necessary so that the body can mobilize its reserves and direct them to fight pathology. Hypertonicity in early pregnancy can be treated with:
- Magne-B6;
- Papaverina;
- No-shpy.
If the hematoma is located on the fundus of the uterus, the woman is recommended to lie on her back with her legs elevated. This position normalizes blood circulation in the pelvic organs and also promotes the release of blood clots.
During the entire period of pregnancy, a woman should not expose herself to nervous strain. Getting enough sleep helps improve your well-being and improve your health.
During the treatment period, the patient is contraindicated in any physical activity and sexual intercourse. It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that cause flatulence and contribute to constipation.
To stop bleeding, the following may be prescribed:
- Vikasol;
- Ascorutin;
- Dicynone.
If the hemorrhage has formed high at the fundus of the uterus, which often makes it impossible to empty the hematoma through the vagina (in the form of brown spotting), with the correct treatment, the bruise will resolve. The healing process can only be seen using ultrasound. For this reason, the patient's condition is constantly monitored. Once a week, the woman undergoes a routine ultrasound scan.
Important information: Why does a hematoma of the auricle appear in humans and how to treat a bruise on the ear
If the therapy gives positive results, then resorption or emptying of the hematoma occurs within a month. For the remainder of the pregnancy, the woman should regularly visit the gynecologist.
Consequences
Detection of gravid hematoma at an early stage allows you to maintain pregnancy and bear a healthy child. If you miss time and do not carry out timely treatment, then a disastrous outcome is possible. Alarming signs that the detachment of the ovum has reached critical proportions are uterine bleeding and sharp cramping pain. Detachment of the fertilized egg by 1/3 of its own size threatens with serious consequences, such as:
- intrauterine fetal death;
- spontaneous termination of pregnancy;
- unfulfilled miscarriage (frozen pregnancy);
- chronic oxygen deficiency in the fetus during intrauterine development;
- anemia in the pregnant woman and the embryo;
- delay and abnormal development of the child inside the womb;
- relapse of pathology in late pregnancy.
Possible complications and consequences for the body
The danger of a hematoma directly depends on its size and location. If the hemorrhage covers more than 40% of the area of the fetal membrane, and its volume exceeds 20 ml, then the following consequences are possible:
- disturbance of nutrition and oxygen exchange of the chorion (placenta);
- fetal hypoxia;
- uterine tone;
- intrauterine growth retardation;
- slowing down the increase in coccygeal-parietal size;
- frozen pregnancy;
- miscarriage in the early stages or premature birth in later stages;
- severe internal bleeding, which in rare cases is fatal for a woman.
The most dangerous consequence is considered to be “Kuveler’s uterus”. Placental abruption occurs, which causes hemorrhage into the endometrium and necrotic processes (tissue death). In this case, a uterine resection is performed, which makes it impossible for the woman to become a mother again.
Kuveler's uterus is characterized by placental abruption in pregnant women ahead of schedule
How to recognize the disease symptoms of the disease
The symptoms of hemorrhage depend on its severity.
There are 3 forms of hematoma:
- Light form. It is characterized by a slight accumulation of blood in the tissues and is asymptomatic. The disease is detected during examination using ultrasound. The doctor’s task is to determine the causes and stabilize the patient’s condition, to prevent further aggravation of the process. During childbirth, the obstetrician must puncture the amniotic sac using a special instrument.
- Medium severity. It manifests itself as pain in the lower abdomen, yellow or brown discharge. With this form, severe bleeding does not occur, the physiological functions of the fetus are disrupted, including heart rhythm. Natural childbirth is not recommended.
- Severe form. The expectant mother constantly experiences severe pain, general weakness, and spotting. This condition threatens the patient and her child, and therefore requires stabilization in a hospital setting. Delivery is carried out by caesarean section several days or weeks earlier than the due date.
An obstetrician-gynecologist makes an accurate diagnosis after a comprehensive examination based on the results of blood and urine tests and ultrasound diagnostics. It is possible to conduct additional bacteriological and virological studies, Doppler measurements, hormonal levels, etc.
When to suspect
Signs of a hematoma in the area where the fertilized egg is attached in pregnant women are not always obvious. Sometimes it is a “find” during a planned ultrasound in the 1st trimester
But more often the detachment manifests itself clinically, although the woman does not always pay due attention to the symptoms
The general state of health does not change even with significant detachment for a short period of time. A slight decrease in blood pressure, dizziness, weakness, and a decrease in signs of toxicosis (if expressed) may appear. The main symptoms are pain in the lower abdomen and discharge.
Pain
The pain caused by a hematoma in the uterus during pregnancy is nagging, similar to menstrual pain. They can be constant or occur only in the evening, after overwork. They become cramping when the miscarriage begins.
Discharge
Discharge during detachment can be normal - whitish or mucous. Bloody ones appear when the hematoma is emptied. If it is small in size or located far from the cervix (for example, in the fundus), there will be no bloody or even brown discharge.
The intensity of the discharge depends on the size of the hematoma: from barely noticeable pinkish, brown, brown to heavy bleeding with clots. A hematoma is dangerous with the following discharges during pregnancy.
- If they intensify. They were light or brown and not abundant, but gradually become bright and scarlet, which indicates the progression of detachment.
- If clots appear. They talk about a large area of detachment.
The hematoma may not be accompanied by discharge, but it may be large. In this case, the fertilized egg most often dies.
Detachment can be suspected if a pregnant woman has nagging pain in the lower abdomen and bleeding appears. But a reliable diagnosis can only be made using ultrasound. Especially if two sensors are used - abdominal and vaginal
At the same time, it is important to monitor the state of the detachment over time every three to seven days.
Treatment of hematoma during early pregnancy
The procedure for treating internal bleeding is carried out on an outpatient or inpatient basis exclusively under the supervision of a gynecologist. Self-medication with any medications is contraindicated.
Despite the fact that retrochorial pathology is formed only in the first trimester, basic supportive measures are carried out throughout the entire period before birth. The main treatment is the entire period of threatened miscarriage (on average 1 month). At peaks in the risk of miscarriage and premature birth, therapeutic measures are repeated.
Conservative therapy:
- Stop bleeding and stabilize. Dicynone, vikasol;
- Induction of uteroplacental exchange. Curantil, folic acid, vitamin and mineral complexes;
- Hormonal prevention. Duphaston, utrozhestan;
- Relaxation of uterine tone. Magnesia, drotaverine, papaverine;
- Stabilization of the emotional background. Novopassit, seduxen.
Secondary recommendations:
- Correction of the power system. All foods and drinks that cause gas formation, stool consolidation, and enhance intestinal motility are excluded;
- Prohibitions. Sexual contact, physical activity, heavy lifting, stress;
- Bed rest. The woman spends most of her time horizontally with her legs raised.
Who is at risk?
The main risk group for the potential development of retrochorial pathology in the uterus includes women in the first trimester of pregnancy with a history of the following problems:
- High risk of injury to the abdomen and uterus due to various reasons;
- Predominance of Th-1 response in the general immunological profile;
- Acquired or hereditary thrombophilias, including those caused by anti-hCG sensitization or antiphospholipid syndrome;
- Chronic DIC syndrome;
- Severe arterial hypertension of any nature;
- Compatibility of mother and father according to HLA antigens of the second group;
- Regular bacterial or viral infection;
- Chronic endometritis at any stage.
What types of hematomas are there?
Based on the nature of hemorrhage, pathologists in the uterus distinguish several types:
- Subchorionic is the earliest possible hematoma of the uterus during early pregnancy.
- Retrochorial - the result of detachment of the chorion from the wall of the uterus and filling the cavity with blood.
- Retroplacental is a pathology of the second trimester, characteristic of 15 weeks.
- Retroamniotic - filling with blood the cavity formed by the walls of the uterus and the amniotic capsule.
- Subamniotic - looks like retroamniotic, but occurs at a later date.
- Intrauterine - occurs when the walls of the uterus are damaged.
When assessing a possible threat to the mother and baby, the size of the hematoma is important. They indicate the severity of damage to perinatal structures.
Retrochorial
The chorion is the layer that lines the inside of the uterus in the first half of pregnancy. Over time, it gradually transforms into the placenta. When certain negative phenomena appear in the body of a woman or child, detachment of the fertilized egg occurs. The resulting cavity is filled with blood clots that enter from the blood vessels supplying the uterus. This is a retrochorial hematoma of the uterus. During pregnancy, such a pathology is possible.
The severity of the pathology and future pregnancy prospects depend on the area of hemorrhage. Detachment of a third of the fertilized egg is a bad sign. It threatens the death of the fetus in the uterine cavity. The exact mechanism of the phenomenon still remains a mystery. The process of shedding the outer membrane of the fetus or placenta and filling the cavity with fluid is called a transthecal hematoma. During pregnancy, the membrane can begin to peel off at any stage. If this occurs in the later stages and poses a threat to the child’s life, then a cesarean section is used. The main indication for such a decision is fetal viability.
We recommend further reading: What to do if your legs start to swell during pregnancy
Subchorionic
Subchorionic hematoma is the most common abnormality during early pregnancy. The condition is dangerous due to the spontaneous release of the embryo. At the first problems in the body: nagging pain in the lower abdomen and brownish discharge, you should quickly contact an obstetrician-gynecologist. If the size of the hemorrhage is small, then it is necessary to monitor its development.
Retroplacental
This form of hematoma is typical for the second trimester. The placenta, as an organ, is formed only in the sixteenth week. Retroplacental hemorrhage occurs in the vessels of the placenta and is characterized by a number of signs, both from the health of the mother and from the behavior of the fetus.
A woman complains of severe pain in the lower abdomen. Bloody discharge appears and the tone of the uterus increases. These are considered dangerous symptoms. The hematoma stimulates the reproductive organ to get rid of the fetus. For the embryo this does not go unnoticed. The child's heart rate increases, which is replaced by bradycardia. He seems to sense danger and reacts with fear.
Retroamniotic and subamniotic
Retroamniatic hematoma does not show any external signs. This diagnosis is made by ultrasound at approximately 12 weeks. Most often, it does not threaten the normal course of pregnancy. This type of hemorrhage refers to interthecal hematomas: blood accumulates between the amniotic membrane and the wall of the uterus. The diagnosis requires constant monitoring. This is necessary in order to promptly prevent the growth of hemorrhage.
Subamniotic hematoma is not dangerous. If it is small, 3-4 mm, it resolves on its own or comes out in the form of blood clots.
Intrauterine
This pathology occurs when the fetus grows and the walls of the uterus are weak. The organ cannot withstand stretching and is damaged by the blood vessels that simply pierce it. Among all hemorrhages, this hematoma is the most dangerous. Life-giving moisture penetrates into the reproductive organ, which can lead to tissue necrosis. With a uterine hematoma, it is possible to deliver and protect the fetus, but the woman requires urgent hospitalization.
Hemorrhage is a result of the development of the uterus and fetus. Occurring in the last trimester of pregnancy, it can destroy the unborn baby. If the process progresses, they resort to caesarean section or artificially induce labor. This helps save the life of a little person.
Important aspects
Brown and brown vaginal discharge is considered a favorable symptom. This means that the hematoma does not progress, and there is a high probability of continuing the pregnancy. The appearance of scarlet discharge should alert a woman. This phenomenon indicates an increase in the size of the RG and increases the risk of miscarriage and fetal death.
Any bleeding from the genital tract is a reason to see a doctor. The help of a specialist is extremely necessary in such situations:
- increased bleeding;
- the appearance of blood clots in the secretions;
- the occurrence of severe cramping pain in the lower abdomen;
- decreased blood pressure;
- loss of consciousness;
- absence of fetal movements (after 18 weeks).
In any of these situations, you need to urgently call an ambulance.
The doctor advises how to cure the disease
In case of uterine hemorrhage, the patient must observe a special regime of physical activity. The medical specialist prescribes drugs that stop hemorrhage, help strengthen the vascular walls and resolve the clot.
The expectant mother needs to rest more, avoid any stress or emotional stress. For general weakness, constant pain in the lower abdomen, and bleeding from the vagina, the doctor may prescribe bed rest.
Pay attention to your diet, choosing foods that help normalize intestinal functions. It is unacceptable to consume foods that provoke flatulence and increase peristalsis.
You will have to give up smoked, spicy and salty foods, and carbonated drinks. It is necessary to eat boiled cereals and liquid soups, lactic acid products, steamed meat and fish.
Drug therapy involves the use of Actovegin, Curantil, Vikasol, Wobenzym, Dufatson, folic acid, vitamin C and other drugs.
Combinations of drugs are selected by the attending physician depending on the type of pathology, its size, the general condition of the patient and the duration of pregnancy:
- Actovegin. Used to prevent fetal hypoxia, improves tissue oxygenation and energy metabolism.
- Vikasol, dicynon, tranexam. They have an antihemorrhagic effect, improve blood clotting, and help stop bleeding.
- Duphaston or Utrozhestan. Chemical analogues of the pregnancy hormone progesterone. They are prescribed to normalize hormonal levels and prevent miscarriage.
- Papaverine and No-shpa. Used to reduce uterine hypertonicity.
- Magnesia - used to lower blood pressure, eliminate the consequences of placental abruption and delay the development of the child.
The presence of infectious diseases that provoke fragility of the walls of blood vessels requires the use of antiviral or antimicrobial drugs - Cefazolin, Tamiflu, Amoxiclav, Ampicillin
These medications should be used with great caution, carefully choosing the dosage
If the interthecal hematoma takes a long time to come out, Wobenzym is prescribed. It has a stimulating effect on the immune system, accelerates the resorption and emptying of a blood clot, and prevents the appearance of local edema.
Any pathology in a woman’s body during pregnancy causes her stress, so to prevent the consequences of anxiety, it is recommended to use mild herbal-based sedatives.
Uterine hematoma in the first trimester of pregnancy features
The uterus is an organ of the female reproductive system in which the fertilized egg is fixed after conception and the further development of the unborn child. In the fertilized egg, the embryo is surrounded by the amnion and chorion. Amnion is a water membrane that protects the embryo from mechanical damage. The chorion is the outer membrane of the fetus, which performs the most important functions:
- provides breathing and nutrition to the fetus;
- removes metabolic products;
- participates in the formation of the unborn child’s immunity;
- regulates the hormonal levels of a pregnant woman.
The embryo is surrounded by two membranes: the chorion and amnion
After the 16th week of pregnancy, the chorion transforms into the placenta, which functions in a similar way.
If there is a partial detachment of the chorion (placenta) from the walls of the uterus, then a diagnosis of “uterine hematoma” is made.
Placental abruption is a type of uterine hematoma
With a uterine hematoma, the vessels and tissues of the organ are damaged. Also, when the disease occurs, a pathological cavity is formed in the uterus, which contains blood inside.
Causes of the disease
The following factors can trigger the development of the disease in early pregnancy:
Women with multiple pregnancies also have an increased likelihood of developing a uterine hematoma.
Types of uterine hematomas in the first trimester
Depending on the location, uterine hematoma can be of the following types:
- retrochorial. Formed between the chorion and the muscular layer of the uterus;
- subchorionic. Mainly localized in the chorion;
- subamniotic. Affects the amnion area;
- retroamniotic. Located outside the amnion.
Clinical signs of pathology
Symptoms of uterine hematoma depend on the degree of pathology:
- In a mild form, there are no obvious signs. Only minor symptoms may be observed: discomfort in the abdomen and perineum, dizziness, general weakness. With this form of the disease, small depressions form in the chorion, which are filled with blood clots. Mild stage placental abruption can be diagnosed during pregnancy only using ultrasound. Often, pathology is discovered after childbirth has taken place.
- With an average degree of the disease, the symptoms become more “bright”: light bleeding appears from the vagina, the woman feels severe pain in the perineum, groin and lower abdomen. Moderate disease requires urgent medical treatment.
- The severe stage of the disease is characterized by severe uterine bleeding, unbearable pain in the lower abdomen and perineum, a strong drop in blood pressure, pale skin, and increased sweating. Critical symptoms: fainting, limb cramps, difficulty breathing. In such a situation, medical assistance should be provided immediately.
FAQ
Below are the most pressing questions regarding common pregnancy pathologies and qualified answers to them.
How does a hematoma come out during pregnancy?
The process of natural release of retrochorial hematoma is the formation of irregular, scanty, spotting-type discharge with dark red or brown tints.
If the pathology is confirmed by laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods, and is regularly monitored, then such discharge is the norm and a positive symptom, indicating the start of the process of emptying the designated localization naturally.
In this case, intense bleeding with bright red discharge and secondary manifestations (tugging feeling and pain in the abdomen) is a symptom indicating the need for immediate hospitalization of the patient.
Can it resolve on its own?
With its small size, stable condition and absence of external symptoms, quite often the hematoma remains unnoticed until childbirth, especially if the woman for some reason did not undergo routine ultrasound examinations.
However, this does not mean that the pathology “dissolves.” In any case, the accumulation of biological fluid comes out - either naturally before/during childbirth, or as a result of a cesarean section.
Is it placed for preservation if there is a hematoma in the uterus?
They are sent for preservation if there is a risk of miscarriage or early labor, which can be caused by a hematoma. If the pathology is stable, small in size, and gradually resolves naturally, then outpatient therapy and regular diagnostics are prescribed, without the need to transfer to a hospital setting.
The main indications for urgent hospitalization are:
- The presence of stable/unstable dynamic tone of the main female sexual organ;
- Pain syndrome in the lower abdomen;
- Vaginal discharge of bright red shades.
What is hidden behind such an incomprehensible and frightening name, retrochorial hematoma?
A hematoma, in general, is coagulated blood or any fluid of the human body that has accumulated in some localized place of the human body. Retrochorionic means that a blood clot has formed behind the shell of the egg, the chorion. This can happen during the first three months, until the chorion transforms into the embryonic organ, the placenta.
Retrochorial hematoma during pregnancy indicates that the chorion has begun to be rejected, a void has appeared between the reproductive organ and the amniotic sac, which has filled with blood.
Evolution of pathology
The evolution of pathology can occur in two ways. Small hematomas can resolve on their own over time without causing any adverse consequences. Pregnancy proceeds normally, and there are no threats to the development of the embryo.
The opposite situation is observed with severe detachment of the chorion - there is a high probability of an increase in the volume of formation and separation of the fertilized egg from the decidua, which is accompanied by severe bleeding and leads to spontaneous abortion.
Retroamniotic hematoma
Detection of retroamniotic hematoma on ultrasound occurs in the early stages, in the first trimester. The very name of the disease suggests that it is a hematoma formed between the wall of the uterus and the amniotic membrane.
The amniotic membrane or aqueous membrane is what the fetus contains in the womb, i.e. these are the walls of a certain reservoir that contains the fetus and amniotic fluid (amniotic fluid). The main task of the amniotic membrane is to produce amniotic fluid and prevent infections from entering, as well as protecting the baby from external factors.
In fact, this type of hematoma does not pose any threat to the fetus, because the baby is protected by the amniotic sac.
For a pregnant woman, the presence of a retroamniotic hematoma leads to spotting and, in severe cases, bleeding. The consequence may be a deterioration in the woman’s general health: dizziness, nausea, weakness, etc. With proper treatment, this disease resolves quickly and does not lead to serious complications.
Prevention
To avoid problems with pregnancy, a woman should be regularly examined by her doctor and listen to his advice. When visiting a gynecologist for the first time about pregnancy, you should answer all questions truthfully - this will help avoid unnecessary problems. Be sure to take the necessary tests in a timely manner.
Habits and lifestyle play a big role. While carrying a child, you should try to avoid provoking factors, come to your appointment on time, and take care of the well-being of the pregnancy. Walking in the fresh air is beneficial. Physical activity should be feasible. It is necessary to pay attention to proper nutrition, rich in vitamins and microelements. If any alarming symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a specialist.
Features of the pathology
Retrochorial hematoma is more often diagnosed, as a result of which the fertilized egg along with the embryo partially moves away from the uterine cavity. Accompanied by impaired blood flow, the formation of a space filled with blood clots or fluid. The main symptoms are sharp pain in the lower abdomen, which can radiate to the lower back. Smearing yellow discharge is observed, and after a while brown discharge appears.
After 16 weeks, when a hematoma forms, a woman may feel a deterioration in her general health, discomfort and abdominal discomfort. If you seek medical help immediately, there is a chance to save the pregnancy.
Consequences of uterine hematoma
Any hemorrhages in the uterus are always very dangerous, not to mention bleeding during pregnancy.
The threat of a hematoma depends entirely on its size. The most dangerous are formations with a volume of more than 15 ml; they occupy about 45% of the territory in the uterine cavity. Because of this, the growth of the embryo slows down and the likelihood of its detachment increases. The coccygeal-parietal size of the fetus slows down its development for more than 2 weeks. Proper treatment of retrochorial hematoma gives the pregnancy a chance to develop normally in the future.
The most dangerous complication of any bruise in the uterus is uteroplacental apoplexy or premature placental abruption. As a result of heavy bleeding, the endometrial layer of the uterus can become filled with blood, it will penetrate into the abdominal cavity, and the blood-soaked tissues of the reproductive organ will begin to die. As a result, doctors may decide to remove the uterus, and this is the most difficult test in a woman’s life.
The outcome of such bleeding with hematomas is very difficult to predict. Sometimes they lead to death not only of the child, but also of the pregnant woman herself. This is why it is so important to be sensitive to all manifestations of pregnancy. You need to react to every abnormal sensation, and at the first symptoms of pathology, run for medical help. Effective therapy gives a woman a chance to carry and give birth to a healthy baby.
Diseases
Retrochorial hematoma of the uterus during pregnancy can develop as a result of diseases that are associated with blood clotting disorders. And often this is a pathological condition such as thrombophilia. This genetic pathology is characterized by increased formation of blood clots.
And although in most cases the disease is mild and does not cause much discomfort in patients, it is very difficult for pregnant women to bear a child with this diagnosis. There is always a risk of placental insufficiency, including placental abruption.