The placenta is an amazing organ that exists only while a woman is carrying a child. It connects two organisms: maternal and child. One of the most serious complications for pregnant women is separation of the placenta from the uterine wall in the early stages. This condition is a direct threat of miscarriage or fetal death if medical help is not urgently sought.
What kind of organ is this and what does it serve?
In non-professional language, this organ is also called “children’s place”, and from Latin the word is translated as “cake” . Both names reflect its essence in their own way. An organ that looks like a flat round disc is formed in the uterus in the earliest stages of gestation and provides the closest connection between the embryo and the mother’s body. At the same time, this organ is precisely “children’s” and not maternal. It is designed to provide a growing baby with everything necessary. The “child’s place” begins to form with the beginning of conception, performing for the embryo the function of the digestive organs, kidneys, lungs, and skin.
The following happens with the help of the placenta:
- delivery of oxygen to the fetal blood and removal of carbon dioxide back;
- saturation of the embryo with water, nutrients, vitamins;
- production of such important hormones as progesterone, hCG, prolactin, estrogens;
- constant work as an immune barrier that retains viruses and bacteria from maternal blood.
There are two sides to the “children’s place”: the maternal side and the child’s side. The baby is attached to his side by an umbilical cord, with two arteries and one vein inside to supply oxygen and nutrients.
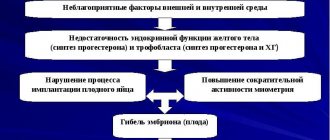
Failures in the functioning of this organ can have the most severe consequences for the mother and fetus. Such malfunctions are considered to be changes in size (too small or too large), changes in the structure itself, or incorrect place of attachment in the uterus. One of these dangerous disorders is premature placental abruption.
Consequences for the child
Premature placental abruption is a common cause of stillbirth in the last weeks of pregnancy. About 15% of children die from this pathology. The cause of death is the serious disorders that the fetus faces as a result of detachment of the placenta. These include hypoxia (oxygen deficiency) and other problems caused by prematurity in the case of preterm labor. The consequence of the pathology is often neurological disorders and developmental delays in the child.
Detachment during early pregnancy: what happens
Even in the early stages, the uterus and the “baby place” are connected to each other by special villi (chorion), and they are connected to the fetus by the umbilical cord. Detachment is said to occur when all the villi or some part of them are separated from the mucosa. Blood clots accumulate in this area, increasing the gap.
The uterus, like any muscular organ, is capable of contracting from time to time. But the “children's place” does not have muscle fibers. Therefore, in the early stages of pregnancy, with active uterine contractions, detachment of the ovum may occur. In later stages, placental abruption is a common cause of premature birth.
If this happens in small areas, there is hope to stop the process in a medical setting under close medical supervision.
Causes of premature detachment of a child's seat
Placental abruption is called its partial or complete separation from the uterine mucosa, which causes disturbances in its functioning or complete cessation of the organ’s functioning. There are three degrees of premature placental abruption:
- Minor peeling – less than 1/3. The chances of saving the baby and carrying the pregnancy to term normally remain high.
- Detachment by 50%. As a result of this rejection of the chorion, fetal hypoxia develops, which in itself is dangerous and can cause the death of the baby.
- Complete detachment. The fruit dies.
The causes of premature placental abruption can be a variety of factors, and sometimes finding out why this happened is a difficult task. Placental abruption is caused by:
- vascular problems caused by late gestosis or hypertension;
- abdominal injury due to impact;
- polyhydramnios;
- multiple pregnancy;
- hypovitaminosis;
- nephritis;
- chronic diseases of the endocrine system, such as diabetes.
In normal position
The way the baby's place is located can also affect its premature departure. However, it is not uncommon for premature abruption of the normally located placenta (PONRP) to occur. Such reasons for rejection include:
- the age of the mother is over 35 years, when it is possible to form an additional small placental part, which is easily torn off during delivery, after which complete detachment occurs;
- pathologies in the structure of the uterus, which include anomalies, synechiae, hypoplasia, cervical insufficiency, complications after abortions and operations, adenomyosis;
- hormonal imbalances caused by dysfunction of the ovaries or placenta;
- infectious diseases of both general and gynecological nature;
- incorrect lifestyle of a pregnant woman, bad habits and unbalanced diet;
- allergy;
- severe anemia;
- short umbilical cord;
- history of caesarean section.
With abnormal attachment
Many factors can provoke abruption of a normally located placenta, although in general only 0.1%–0.3% of expectant mothers face this problem. Another significant cause of chorion detachment may be an anomaly in its structure, attachment, development, as well as incorrect location of the placental organ itself.
For example, in the case of pregnancy after a cesarean section, the baby's place can be attached to the site of the postoperative scar. This increases the risk of placental abruption, which will occur until 8–9 months of pregnancy.
The second example of an abnormal location is attachment in the area of the myomatous node. Its tissues are much denser than the uterine walls, which makes placental attachment incomplete.
Placental abruption in early pregnancy: possible causes
Premature separation of the “baby place” is not a very common phenomenon; it accounts for about 1.5% of normal pregnancy . This condition in the early stages is caused by one of the following factors:
- intense contraction of the uterine walls;
- infection and subsequent inflammatory process in the membranes;
- vascular pathology (capillary fragility, impaired blood flow, excessive permeability of the walls);
- malfunctions in the functioning of body systems (endocrine, renal, cardiac pathologies);
- poor nutrition;
- autoimmune conditions: a rather rare condition in which the female body produces antibodies to its own cells;
- —pregnant woman’s allergies—to medications, donor blood;
- injury or blow to the stomach;
- drinking alcohol and smoking;
- multiple edema and subsequent gestosis, disrupting the functioning of all organs.
Consequences
Detachment affects not only the fetus, but also the pregnant woman. The severity of the consequences directly depends on the degree of detachment, as well as the time of initiation of treatment measures.
For a child
The most common complication in the fetus is hypoxia. In this condition, there is oxygen starvation of the fetus against the background of impaired transplacental circulation. In severe cases, fetal death occurs.
For mother
The main complications for a pregnant woman are:
- Kuveler's uterus (a condition accompanied by saturation of the uterus with blood due to massive hemorrhages);
- DIC syndrome (disruption of the coagulation system, against which a large number of blood clots form);
- hemorrhagic shock.
If left untreated, death may occur due to the development of shock.
Symptoms
It happens that the pathological condition passes without visible signs for the pregnant woman. But more often it is accompanied by two striking manifestations: bleeding and pain. A woman can notice them on her own:
- pain appears in the lower abdomen . The pain can be nagging, radiating to the groin or thigh area, or it can be cramping;
- bloody discharge from the genital tract is also a common symptom . If the blood is bright red, it means placental abruption occurred recently; dark blood discharge indicates that time has already passed since the separation. Undiagnosed internal bleeding is even more dangerous. In such cases, the life of the woman herself is at risk. Typically, external blood loss occurs when the edges of the “child’s place” are detached. If it is separated from the uterus in its center, then blood will accumulate inside.
Doctors distinguish between mild, moderate and severe forms of pathology:
- if the “baby spot” peels off slightly in some places in the early stages of pregnancy, then this process can be completely asymptomatic. The deviation is detected only by ultrasound;
- in the moderate form, increased tone of the uterus, tension and pain in the lower abdomen are felt;
- in severe cases, these symptoms include nausea, dizziness, vomiting, and bleeding from the genital tract.
Basic functions of the placenta
Let's take a closer look at the main functions:
- gas exchange;
- excretory;
- nutritious;
- hormonal;
- protective.
Oxygen from the mother's blood enters the fetus through the placenta, and waste carbon dioxide is released back. This phenomenon occurs according to physical laws - diffusion.
The excretory function of the placenta has one of the main significance for the life of the embryo: it removes toxic substances.
The protective properties of the placenta are expressed in the formation of local immunity, which prevents immune dissonance between the fetus and the mother. However, this protection is not omnipotent, and therefore cannot protect the baby from the harmful effects of alcohol and other adverse influences. Therefore, during pregnancy, it is prohibited to take almost all chemical medications, as well as most herbal mixtures.
Without the hormonal activity of the placenta, pregnancy would be impossible. The placenta performs the functions of an endocrine gland and produces hormones necessary for the functioning of the fetus and the female body:
- human chorionic gonadotropin;
- placental lactogen;
- prolactin;
- estrogen;
- serotonin;
- relaxin;
- others.
Gonadotropin supports the functioning of the membranes and activates the production of progesterone by the corpus luteum. Lactogen prepares the mammary glands to produce milk after the baby is born, and prolactin is responsible for milk production.
The hormone progesterone is necessary to prevent the fertilization of new eggs, and it is also responsible for the health of the uterine lining. Estrogen is also responsible for the development and repair of the uterine lining. The remaining hormones are directly involved in providing the fetus and mother with everything they need.
Placental abruption in early pregnancy: consequences
In the early stages, partial detachment from the walls of the uterus can threaten pregnancy loss if medical assistance is not provided. If separation from the mucous membrane occurs completely or over a large area, spontaneous abortion occurs.
If the stage of detachment of the ovum has just begun, doctors will try to save the pregnancy . The main thing is to seek help without delay. Then the pregnancy continues, and the lost area of contact with the uterine mucosa can be restored during the subsequent growth of the placenta.
Reviews
I encountered this situation at 18 weeks. Ultrasound showed the presence of partial placental abruption. Doctors admitted him to the hospital. They gave Dicinon and Duphaston. We were treated for about a month. After the control ultrasound, we were allowed to go home, prohibiting any exertion or stress. She gave birth to a normal healthy baby. For 2 pregnancies in a row I have been faced with abruption. My previous pregnancy was normal until 28 weeks, when I was diagnosed. We had a caesarean section at 32 weeks. My daughter was born premature, she spent a month in the maternity hospital. Its OK now. This year, already at the 14th week, a moderate abruption was diagnosed, we were hospitalized, and a control ultrasound revealed a frozen fetus.
Diagnostics
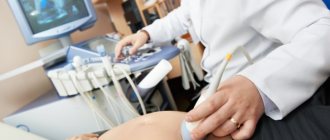
In the early stages, the doctor may suspect that placental abruption has occurred by conducting an ultrasound examination and excluding other diseases. For example, the cause of bleeding may be damage to the cervix, tumor, or infection. The doctor may suspect that this is placental abruption, and not something else, based on the following signs:
- bleeding that has begun (internal or external);
- the uterus is in increased tone;
- During the examination, a violation of the development of the embryo is detected, as a consequence of its oxygen starvation;
- During an ultrasound, blood clots were found in the placenta.
Even if a minor separation is suspected, hospitalization and urgent treatment measures are required. Therefore, you should not take any negative symptom lightly.
Causes
It is difficult to give a direct answer as to why partial or total placental abruption occurs. Experts identify predisposing factors that increase the risk of developing this disease.
During pregnancy these include the following:
- extragenital diseases (hypertension, kidney pathologies, severe anemia);
- endocrine diseases;
- preeclampsia;
- defects of the blood coagulation system;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- suffered falls, injuries.
During childbirth, risk factors include the following:
- use of oxytocin;
- multiple pregnancy;
- late rupture of membranes;
- polyhydramnios.
Expert review Olga Borovikova Thus, it is impossible to say exactly what causes complete placental abruption, but if a pregnant woman has one or more of the above factors, the risk of developing this pathology increases significantly.
Treatment
If a woman starts bleeding, and her lower abdomen hurts crampingly, then until the doctors arrive, she needs to go to bed without taking any medications.
If there is little blood loss, the doctor may prescribe bed rest and medications that relieve excess uterine tone. The most commonly prescribed antispasmodics are no-shpa and papaverine. Vikasol is prescribed to stop bleeding. Iron-containing drugs are selected as an antianemic agent. During treatment, blood clotting is continuously monitored. If in the early stages the size of the detachment is insignificant, treatment is started on time and carried out correctly, then the pregnancy continues.
Since it is difficult to determine exactly what provokes detachment in the early stages, it is impossible to indicate any special preventive measures to prevent this disorder. As for general measures, they include regular medical examinations, tests, good nutrition and a balanced daily routine.
Diagnosis of detachment
Placental abruption that occurs in the 1st trimester most often occurs without serious consequences. That is why it is important to diagnose the development of pathology in time, and then undergo an adequate course of treatment.
Ultrasound examination helps confirm and sometimes detect pathology. During the examination, a specialist can detect a retroplacental hematoma, as well as see destruction of subplacental tissues. In some cases, even blood clots are distinguished.
But at the beginning of the formation of pathology, such formation may be absent. In this case, the diagnosis is based on the method of excluding other probable diseases that have similar symptoms. It is carried out based on the following indicators:
- hypertonicity of the uterus;
- open bleeding or spotting;
- disorders in child development.
To rule out other possible diseases, the doctor examines the cervix and vagina during a gynecological examination. This allows you to exclude causes of bleeding or spotting, such as injuries to the genital organs, various infections or a tumor. The next step will be to order a full diagnostic examination, since it is possible to establish the true cause of the detachment only after a comprehensive study.
Pregnancy after placental abruption
Unfortunately, if during a previous pregnancy there was an untimely separation of the “baby place” caused by internal factors, then there is a possibility of a recurrence of the pathology. Repeated detachment is diagnosed in a quarter of subsequent pregnancies . To reduce the risk, the following is recommended:
- Even before the start of pregnancy, both the woman and the spouse need to undergo examination to identify diseases and infections. They must be treated before conception occurs;
- During pregnancy, sudden jumps in blood pressure should not be allowed; it must be kept under control;
- already in the early stages you need to attend all scheduled examinations and take the necessary tests;
- undergo ultrasound examinations prescribed by the doctor to identify abnormalities at the very first stage;
- be especially careful not to get injured, wear comfortable shoes, be careful when there is ice;
- keep in mind the possibility of allergic reactions; try to avoid them;
- any medications are taken only after consultation with a gynecologist.
Tactics of labor management in case of early placental abruption (before the birth of the child)
Departure of the placental place also occurs directly during childbirth. This happens when the first child of twins is born or labor is abnormal. With minor marginal placental abruption, when the condition of the woman and fetus remains satisfactory and the tone of the uterus is normal, natural childbirth can be carried out with constant monitoring of the condition of the fetus (via CTG) and the pressure of the woman in labor.
Amniotomy reduces bleeding and speeds up the birth process. During the entire delivery process, the doctor monitors the baby’s heartbeat and contractile activity of the uterus. In addition, central vein catheterization and infusion therapy may be prescribed. Epidural anesthesia is also relevant. Once the head appears, oxytocin is used to increase uterine contractions and reduce the severity of bleeding.
The tactics of labor management with progressive separation of the baby's place is determined by how far the baby has managed to advance. If it has reached the very exit, obstetric forceps are used in an anterior presentation, and in a pelvic presentation, the fetus is extracted by the pelvic end. Otherwise, when the fetus is still in the wide part of the pelvic cavity and above, an emergency caesarean section is required.
The main danger for a child with PONRP is acute hypoxia. Untimely obstetric care can result in antenatal fetal death.
Symptoms
What are the signs of premature placental abruption, how to determine the pathology? Any deviations during pregnancy must be immediately reported to the treating gynecologist or contact an ambulance in case of critical condition.
The most important symptom and sign of detachment is uterine bleeding. It is formed as a result of injury to the placental vascular network. The placenta does not separate from the lining of the uterus immediately, but gradually. First, a hematoma forms at the site of the break; an increase in the hematoma leads to further tissue breakage. As a result of these processes, heavy bleeding begins.
Doctors distinguish 3 forms of pathology:
- initial;
- moderate severity;
- critical (severe).
In a mild form, symptoms may be completely absent, and the pathology is determined only by ultrasound diagnostics. Sometimes pathology can only be detected during examination after birth. There is a slight indentation and blood clots on the bladder.
With moderate pathology, a woman feels dull pain in the lower abdomen, accompanied by slight bleeding. The expected heavy bleeding at this stage may not be present: this depends on the shape and size of the hemorrhage (hematoma). However, this condition already causes oxygen starvation in the fetus, which can be determined by the baby’s uneven heartbeat.
Severe hypoxia can lead (most often leads) to fetal death. The woman's condition is very serious, it is accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen. A woman may also experience severe weakness, sweating and dizziness to the point of fainting.
Signs of placental abruption:
- sweating;
- paleness of the skin;
- anxiety;
- severe pain in the lower abdomen;
- semi-fainting/fainting state;
- drop in blood pressure;
- decrease in body temperature;
- increased heart rate and shortness of breath.
The scarlet color of blood when discharged from the genital organs indicates a recent detachment of the placenta from the walls of the uterus.
In severe hypoxia, the fetal heartbeat cannot be heard and parts of the body cannot be palpated. The most important indicators of the course of the pathology: bloody discharge from the woman’s genital organs, increased uterine tone and lack of heartbeat in the fetus. The listed processes are accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, a feeling of fullness and severe discomfort.
Uterine bleeding
Placental abruption in the early stages is not always characterized by profuse bleeding; most often this condition is accompanied by small or moderate discharge. In rare cases, there is no blood loss at all. The amount of bleeding depends on several factors:
- blood clotting state;
- area of detachable shell;
- localization of the placenta breakage on the uterine mucosa.
There are cases of accumulation of blood discharge between the walls of the uterus and the placenta: with this clinical picture, vaginal discharge is not diagnosed. This is the most dangerous development of pathology of all, as internal hemorrhage occurs. Blood continues to ooze from the wound surface, but does not come out: a retroplacental hematoma is formed. This form of pathology is characterized by rupture of the placenta in its central part, while the edges continue to be connected to the uterine mucosa.
In medical practice, a similar condition is called Kuveler's uterus: this doctor was the first to describe the pathology. With Kuveler's pathology, the entire uterus is removed along with the dead fetus. This condition is extremely dangerous for a woman’s life, as it can lead to death.
Hidden uterine bleeding is the most dangerous.
Regional detachment accompanies the release of blood from the genital organs, so it is possible to detect the pathology in time and take action. Although this pathological picture is accompanied by slight blood loss. If pathology is detected in time, further detachment can be prevented.
Sometimes the clinical picture is accompanied by mixed bleeding: internal and external at the same time. It is impossible to accurately record the volume of blood loss in the latent form. When diagnosing, the doctor relies on the patient’s well-being, as well as blood pressure, pulse, etc. measurements.
Uterine tone and pain syndrome
Painful sensations accompany many pathological conditions in women. Rejection of the placenta causes dull abdominal pain. It can also be felt in the lumbar region, perineum or thigh. Most often, the pain syndrome occurs in paroxysms and is localized in a specific place. However, sometimes pain can manifest itself in the entire body of the uterus, and not in a separate place.
If there is hidden bleeding, the pain will be more pronounced than with open bleeding. This is due to the increased diameter of the internal hematoma formed between the uterine mucosa and the baby's place. When the doctor palpates the uterus, tension is detected: the organ is in good shape.
Fetal heartbeat
Lack of oxygen often leads to irreversible consequences and intrauterine fetal death. Hypoxia begins to appear when a quarter or more of the placenta is rejected. When a third of the area is separated, the fetus is no longer destined to survive: a form of oxygen deficiency is formed that threatens the life of the child’s body. However, most often the fetus dies when 50% of the amniotic sac is rejected.
Prevention of placental abruption
In order to avoid the development of pathology, preventive measures should be observed:
- Monitoring blood pressure throughout pregnancy. If you have hypertension, it is important when planning a child to normalize the indicators and neutralize the factors that contribute to their increase.
- Regular visits to the gynecologist and examination will help identify changes in the early stages, which will help maintain pregnancy. It is important to do an ultrasound examination every trimester, and more often if necessary.
- If you have a negative Rh factor and a high risk of developing a Rh conflict, you should take an injection of immunoglobulin and constantly do a blood test for antibodies.
- It is necessary to lead a correct lifestyle, first of all, by giving up smoking, drugs and alcoholism.
- It is necessary to reduce the risk of abdominal injury.
- It is important to promptly treat chronic diseases and stop their exacerbation.
- If gestosis develops, you should go to the hospital.
Placental abruption is a dangerous phenomenon that can cause fetal death or harm a woman’s health and her future ability to have children. If you follow preventive measures, regularly visit your doctor and undergo all diagnostic procedures, you can prevent this pathology.
How to prevent detachment in later stages
Prevention of pathology lies primarily in the correct approach to pregnancy planning. Before conceiving a child, a woman must cure all existing diseases, change her diet to a balanced and rational one, and give up all bad habits.
We recommend reading about gestosis during late pregnancy. From the article you will learn about the causes and forms of gestosis, its signs, the danger of the condition, and management of pregnancy. And here is more information about polyhydramnios during pregnancy.
The key to a successful pregnancy and childbirth is timely registration at the antenatal clinic and strict adherence to all medical recommendations. In no case should you refuse hospitalization if the gynecologist suspects placental abruption, since only timely measures can save the health and life of both mother and child.
Why does pathology occur?
Doctors find it difficult to determine for sure why premature rejection occurs. There is no specific cause; usually the etiology consists of several provoking factors. Typically, the causes often lie in systemic ailments and are combined in a complex of factors such as vascular and mechanical factors, bleeding disorders. Various factors predispose to the occurrence of rejection, including:
- Sudden fluctuations in blood pressure such as stress or fear;
- Parity, when there are many births and they occur at short intervals, while degenerative endometrial transformations occur;
- Endocrine diseases, when the walls of vascular canals change due to diabetes;
- High blood pressure due to vascular diseases, for example, glomerulonephritis or arterial hypertension;
- Fluctuations in blood pressure due to compression of the vena cava, especially if the patient spends a lot of time on her back;
- Post-term gestation, when the structures of the child’s place age and peel off;
- Autoimmune pathologies;
- Gestotic conditions such as vasculopathy coupled with bleeding disorders;
- The presence of cesarean section and other surgical interventions on the uterine body, in such situations, the baby's place is attached to the site of the scar, which causes unreliability of fastening, increasing the likelihood of rejection;
- Incorrect placental localization (too low or presentation of the baby's place);
- Presence of unhealthy habits in a pregnant woman such as smoking, alcohol abuse, etc.;
- Vasculitis of infectious-allergic origin;
- Age-related characteristics - over the years, the likelihood of difficulties increases noticeably, so pregnancy in women after 35 occurs with great complications;
- Blood clotting disorders of hereditary origin, predisposition to thrombosis;
- If the placenta has formed an additional lobe, which breaks off during the labor period, causing rejection;
- In the presence of congenital malformations of the uterine development, when, due to improper maturation, the placenta is not able to adhere entirely to the uterine tissues, and therefore is easily separated from them;
- Premature aging of the placenta;
- Allergy to blood plasma transfusion or intravenous infusion of colloidal solutions;
- Blunt traumatic injuries to the abdominal area due to a fall or blow.
In accordance with the course of placental abruption processes, progressive and non-progressive abruption are distinguished. In the first clinical case, the hematoma formation between the placenta and the uterine tissues grows, which aggravates the separation and complicates the condition of the baby and the pregnant woman. With non-progressive rejection, the damaged vascular channels are blocked by blood clots, internal blood loss stops, and pregnancy continues as normal.
Treatment of the disease
The choice of treatment depends on many factors: the degree of the disease, the general health of the pregnant woman, the duration of pregnancy, etc. A prerequisite for a favorable outcome is a constant stay in the hospital under the supervision of doctors before birth. At this time, fetal CTG, ultrasound and Doppler sonography are performed daily. This will allow you to monitor the child’s development and promptly identify the slightest changes.
Treatment for placental abruption includes:
- Maintain strict bed rest.
- Taking multivitamin complexes.
- Taking medications to reduce uterine hypertonicity (Papaverine, No-shpa, Drotaverine), treatment or prevention of anemia (Sorbifer), medications to prevent the formation of blood clots (disaggregants).
- If indicated, blood plasma transfusion is performed.
- Taking medications to normalize uteroplacental blood flow (Actovegin).
- Elimination of the causes that provoked the disease (hypertension, diseases of the endocrine system or kidneys, etc.).
For moderate to severe placental abruption, an emergency cesarean section is performed, regardless of the stage of pregnancy.
Diagnosis of the disease
If you experience abdominal pain, discharge and constant uterine tone, immediately contact a gynecologist for an examination and to identify the causes of such phenomena. As a rule, an accurate diagnosis does not cause any particular difficulties, since the clear symptoms speak for themselves.
To confirm the diagnosis, the following diagnostic procedures are performed:
- Ultrasound examination of the fetus, in which you can see placental abruption, assess the extent of the lesion and the volume of the retroplacental hematoma.
- CTG is a study of the baby’s heartbeat to ensure the absence of hypoxia and other pathologies.
Symptoms of detachment
In the last trimester, detachment is especially dangerous for the condition of the fetus, since by this time the formation of placental tissue is completed. In the early stages, damaged tissue can be replaced by new tissue, as new cells continuously grow. Infections and hormonal factors, important early in pregnancy, are less important in the last trimester. The state of the cardiovascular system of the expectant mother comes to the fore.
Detachment can be suspected by the onset of bleeding of any intensity, decreased fetal activity, or pain in the abdominal area. Detachment in recent weeks inevitably leads to fetal hypoxia.
With partial non-progressive detachment, there may be no symptoms. A woman who has received treatment gives birth at term. More serious problems arise with partial progressive detachment. In this case, both the fetus suffers from oxygen starvation and the woman herself suffers from massive blood loss. With complete detachment, the embryo dies almost immediately, as it remains without a source of oxygen.
Therapy
What should you do if signs of pathology are detected? If there is little time left before the predicted date of birth, you should give birth immediately, even if there is minimal rejection of the placenta from the uterus. The pathological picture can take an unpredictable form and provoke the death of the baby. In obstetric practice, caesarean section is used as an emergency method of delivery. If mother and baby feel comfortable, a natural birth is an option. However, a woman should be under constant supervision of an obstetrician so as not to risk the health of the fetus.
If the fetus is very preterm, the obstetrician weighs the degree of risk of a cesarean section and the possible progression of pathological placental rejection. In this case, the woman is placed in a hospital, where she is under constant supervision of medical staff. If there is a risk of fetal death, a caesarean section is performed, and the newborn is placed in a box for further development.
What measures are taken to prevent the development of a critical condition? Doctors take measures to stop blood loss, then administer medications to activate blood clotting. These are the most important medical measures to normalize the condition of the patient and fetus. The most appropriate method of delivery is then determined. It will depend on the following conditions:
- time of onset of pathology;
- volume of blood loss;
- well-being of the patient and fetus.
Under what circumstances can obstetricians allow vaginal birth? This is possible if:
- placental abruption has stopped, pathology does not develop;
- premature pregnancy (up to 36 weeks);
- gas exchange between the woman and the fetus is not impaired;
- slight blood loss.
To make sure that everything is fine with the fetus, ultrasound and other hardware examinations are regularly performed. They check the heart rate and the dynamics of blood flow in the placenta (Doppler). If a woman is allowed to carry her pregnancy to term and give birth on her own, she must still be in a hospital setting and adhere to bed rest. You should be prepared for this.
During inpatient treatment, drugs for blood clotting and relaxing uterine muscles, antispasmodics such as no-shpa, and iron supplements for anemia are prescribed. Treatment of concomitant diseases is also carried out. If, despite careful treatment and bed rest, blood is still released, a caesarean section is performed immediately.
What is the placenta
The placenta is an embryonic organ that consists of many blood vessels connecting the fetus to the mother. Between them there is a membrane that protects the child from harmful substances entering his body and promotes the release of his waste products into the mother’s blood.
The placenta is formed in the second week of pregnancy, when the fertilized egg has already fixed on the wall of the uterus. Over the next 10 weeks, it grows actively and reaches its maturity already at 12 weeks.
The placenta is responsible for the development of the fetus and takes part in many complex biological processes. Bearing a child depends on her condition.
Prevention
There is no special prevention to prevent organ detachment. It is important to avoid provoking factors.
It is worth giving up bad habits and not overworking yourself. You should not take any medications without first consulting your doctor.
Preventive measures:
- blood pressure control;
- regular visits to the doctor;
- completion of studies at the appointed time;
- walks in the open air;
- avoiding stress;
- injury prevention;
- good nutrition;
- healthy lifestyle;
- rest.
What is placenta
It is a temporary organ formed during pregnancy. With its help, a connection is formed between the fetus and the pregnant woman.
The organ appears on the 10th day after fertilization of the egg. It is often called a "children's place."
Functions of the placenta:
- protective - provides immune protection to the child;
- respiratory - carries out fetal breathing;
- hormonal - produces a number of hormones necessary for the normal development of the fetus;
- nutritious - vitamins and minerals pass through the blood into the placental vessels and to the unborn child;
- excretory - eliminates metabolites.
How doctors can help
At the end of pregnancy, the main therapeutic measure is to develop tactics for the most optimal method of delivery in order not to harm the health of the mother and the unborn child.
In most cases, childbirth becomes possible only with the help of an emergency cesarean section, but under certain conditions, while a woman is in the clinic, pregnancy can be maintained until the planned date of birth.
Pregnancy management tactics when placental abruption is detected in the last trimester depends on the following factors:
- whether the detachment occurred during pregnancy or during labor;
- how intense was the bleeding, how much blood was lost;
- can the fetal heartbeat be heard, are parts of the body identified during examination, and how does the expectant mother feel.
The advisability of placing a woman in the last trimester of pregnancy with a diagnosis of placental abruption in a hospital is determined by the following conditions:
- the gestational age should not exceed 36 weeks; if it is higher, then delivery is indicated, since the child at this stage is already fully viable, and further preservation can be fraught with significant risks for both the mother and the fetus;
- According to the results of ultrasound, it was determined that the detachment is not progressing, the area of separation from the uterine tissue is small;
- the woman has no complaints of poor health, the condition of the fetus does not cause concern;
- Vaginal bleeding is insignificant and blood loss is minimal.
If doctors nevertheless decide to place a pregnant woman in a hospital, she is prescribed strict bed rest and constant monitoring of the condition of the placenta and the unborn child is carried out. It is necessary to constantly monitor blood clotting indicators and conduct regular examinations using ultrasound and cardiotocography.
Drug therapy is indicated, which includes the following drugs:
- means to relieve uterine tone and vasospasm, for example, No-Shpa, Drotaverine, Magnesia and others;
- drugs to stop bleeding - Vikasol, Ascorutin, sodium etamsylate;
- vitamins, especially A, E and C;
- medicines to combat anemia, in particular preparations containing iron.
It is necessary to constantly monitor sugar levels and blood pressure.
Treatment of diseases that caused the emergence and development of the pathological process during pregnancy should also be carried out.
Expert opinion
Daria Shirochina (obstetrician-gynecologist)
If, despite the measures taken, the condition of the pregnant woman does not improve, and even minimal bleeding appears, urgent measures for delivery are necessary.
After childbirth, it is necessary to take measures to prevent recurrent bleeding, for which drugs that increase uterine contractions, for example, Oxytocin, are used. Transfusion of donor blood components is also indicated to stop bleeding and relieve symptoms of anemia.
Symptoms of placenta rejection
The symptoms that accompany the internal process of placental rejection may differ at different stages of pregnancy, including in the intensity of sensations.
For example:
- In the first trimester, most cases of detachment occur. With timely diagnosis, in most cases it is possible to improve the functioning of the placenta. During this period, the woman experiences discomfort in the abdominal area and bleeding of varying degrees.
- In the second trimester, the main symptom of the onset of placental rejection is an increase in the tone of the uterus, which is accompanied by tension and painful pulling sensations.
- In the third trimester, separation of the placenta is very dangerous, since the placenta's reserve of growth opportunities has already been exhausted. The symptoms are the most striking: pain, bleeding, pulling sensations; ultrasound shows a noticeable deterioration in the functioning of the fetus: it is inactive, noticeably suffering.
- Placental abruption during labor often leads to accelerated stimulation or emergency delivery.
The separation of blood can be external (the appearance of discharge) or internal, associated with the accumulation of blood in the resulting voids.