Functions
Features of the structure and function of the appendix include the following aspects:
- The organ performs a protective function. Its cavity contains lymphoid tissue, which plays an important role in the immune system of the whole body;
- Restorative function. Participates in the process of restoration of intestinal microflora after poisoning, illnesses, and taking medications;
- It is a reservoir of beneficial bacteria. As stool moves through the intestines, the appendix remains to the side. This fact has a positive effect on the microflora in the organ. As a result, this process allows positive bacteria, E. coli, to actively multiply. This reservoir has an invaluable effect during the restoration of normal microflora in the intestine;
- Influences human development. According to some medical data, the location of the appendix, as well as its main functions, allow the child to develop normally and improve intellectual development.
Based on the above functions, we can conclude that the structure and functions of the appendix play an important role in the human body, and are not a rudimentary appendage that turned into an extra part of the intestine during human evolution. However, according to practical data from doctors, after removing this part of the intestine for some reason, a person’s health does not worsen.
The body continues to provide stable resistance to infectious and viral diseases. The development of dysbacteriosis has never been noted. This fact is explained by the adaptation of the whole organism to the environment, as well as compliance with the doctor’s recommendations after organ removal. Proper nutrition during the rehabilitation period allows the body to “understand” what happened and adapt to such work.
- Protective. The appendix contains a large amount of lymphoid tissue, which is actively involved in the immune response.
- Restorative. Participates in the normalization of intestinal microflora.
- "Storage" for beneficial bacteria. As a rule, there is no reflux of feces into the appendix, which has a beneficial effect on the microclimate of the appendix and promotes the active reproduction of positive microorganisms. The appendix is a reservoir for E. coli. It preserves the original microflora of the large intestine.
- Influence on human growth and development. The medical literature indicates that the preservation of the appendix in childhood has a beneficial effect on the physical and intellectual development of the child.
From the above functions, we can conclude that the appendix undoubtedly plays an important role in human life. However, after its surgical removal, the person’s condition does not worsen - the body is still able to give an immune response, and the development of dysbacteriosis does not occur. This can be explained by human adaptation to the environment.
Proper nutrition, a healthy lifestyle, consumption of dairy products and preparations containing bifidobacteria and lactobacilli balance the relationship between opportunistic and beneficial microflora. It is worth considering the fact that some people may not have an appendix from birth, which will not have a significant impact on their immunity.
Why does a person have an appendix? This question has been asked by doctors for a long time.
At the beginning of the 20th century, a “list of useless organs” was even compiled from 180 “rudiments”, which included the appendix, tonsil, spleen... The appendix was classified as a dangerous rudiment that causes appendicitis.
Famous biologist I.I. Mechnikov believed that it was necessary to remove not only the cecum, but also all the large intestines of a person, because It is there that putrefactive processes occur that poison the human body. And the British surgeon William Lane even began performing similar operations on his patients until he was criticized. Now doctors are proposing, instead of a “list of useless organs,” to create a list of little-studied organs.
Many years of research have shown that the appendix plays an important role in the human body. Today, the appendix has three main functions:
- protective;
- secretory;
- hormonal.
Why can the appendix become inflamed?
There is no single point of view, and there cannot be one. The spring decrease in immunity, helminths, foreign bodies, and food debris may be to blame for this. Also, any inflammatory process in the body, be it a sore throat or a sore tooth, can lead to inflammation of the appendix. In any case, inflammation occurs due to the fact that the artery in the appendix is of a terminal type, so when it becomes inflamed, blood clots immediately form here, clogging the artery.
Because of this, the blood supply to the appendix stops, its walls become thin, and pus passes through them into the abdominal cavity. It all starts with inflammation of the mucous membrane of the appendix, then the inflammation spreads to all layers of the appendix, after which ulcers appear on its mucous membrane. At the last stage of appendicitis, gangrenous, the wall of the appendix dies, and the contents of the appendix enter the abdominal cavity. Gangrenous appendicitis can lead to peritonitis. Usually this stage begins on the second day after inflammation.
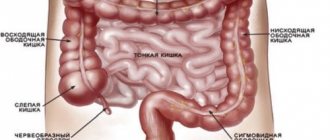
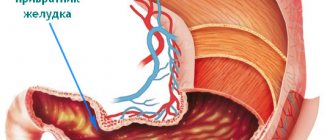
Location and structure
The appendix extends from the medial-posterior surface of the cecum below 3 cm from the point where the small intestine enters it and is covered by peritoneum on all sides. Its length, on average, is 9 cm, in diameter it reaches up to 2 cm. The lumen of the appendix in some people, in particular in the elderly, can become overgrown, causing inflammation - appendicitis. This condition requires urgent hospitalization as it can be fatal.
We recommend reading:
Proctosigmoiditis: how is the pathology manifested and treated?
Depending on how the cecum is located, there are several options for the normal location of the appendix:
- Descending. It occurs most often (50% of cases). When the appendix is inflamed, it is worth keeping in mind that it is in close contact with the bladder and rectum.
- Lateral (25%).
- Medial (15%).
- Rising (10%).
The appendix opens into the cecum through the opening of the appendix and has a mesentery that extends from its beginning to its end. Its mucous membrane has a large amount of lymphoid tissue, and the general structure is the same as that of the cecum - serous, subserous, muscular, submucosal and mucous layers.
Why does a person need an appendix?
Despite the fact that the appendix is attributed to a number of vestiges, as an organ that has lost its main function, it is very important. Before answering the question of why a person needs an appendix, it should be understood that its absence, at a minimum, leads to disturbances in the digestive processes. However, not only the organs of the gastrointestinal tract suffer from the removal of this appendage.
Today, several important functions of the worm-shaped organ are known:
- Lymphoid formations are located under the mucous membrane of the appendix cavity. It contains a large number of lymphatic follicles that perform a protective function. In other words, when we cut out a healthy organ, we lose part of the body's immune system. There are accumulations of lymphatic formations in many other rudimentary organs, for example, in the spleen, thymus, tonsil, but there are most of them in the appendix.
- The secretory function of the organ is that it secretes amylase and lipase, which improve intestinal motility and promote the decomposition of starch.
- Hormones released by the appendage help the intestines during digestion.
- Due to the fact that there is a very small lumen between the appendix and the cecum, digestive products do not enter the appendix. Favorable microflora constantly reigns there. Therefore, if, after illness or stress, a person loses beneficial bacteria, the necessary microorganisms are supplied from the appendix, which repopulate the intestines. This helps prevent dysbiosis.
What are the main symptoms of appendicitis
First of all, it is pain, dull and constant. It starts in the upper abdomen, and then slowly goes down. The most painful area in this case is the so-called McBurney's point, which is located just above the anatomical location of the process itself, that is, between the anterior superior iliac spine and the navel.
In this case, a limp is possible, and the pain increases with coughing, any shaking on the bus, and even when walking or bending. When a person lies on his back, it is difficult for him to lift and straighten his right limb, and the anterior abdominal wall is very tense. Vomiting is also possible, but it is one-time. The temperature is rising, but not much.
However, sometimes acute appendicitis is disguised as poisoning or other gastrointestinal diseases. In this case, high fever, vomiting, and nausea are possible. In any case, the most accurate diagnosis can only be established by a doctor, ultrasound and blood test (the more leukocytes there are, the more likely it is appendicitis), so an ambulance should be called at the slightest suspicion of inflammation of the appendix
Also sometimes there is such a thing as chronic appendicitis, in which pain appears periodically. Sometimes this disease is classified as a duodenal ulcer, cholecystitis or pyelonephritis. When exacerbated, the disease is similar to acute appendicitis. The difficulty is that with such appendicitis peritonitis is possible.
Incisions for appendectomy
1. Volkovich - Dyakonov - McBurney (oblique incision in the right iliac region with muscle spreading)
2. Lennander (pararectal)
3. Sprengel (transverse)
4. Median laparotomy for widespread peritonitis
5. Laparoscopic removal.
1. Ligature (sometimes used in children), during laparoscopic operations.
2. The stump of the appendix, previously tied with catgut, is immersed in the wall of the cecum with purse-string and 2-shaped sutures.
3. Immersion of the unligated stump into the lumen of the cecum with purse-string and 2-shaped sutures (almost never used).
To remove or not to remove the appendix
For modern doctors, this question no longer arises. Sometimes the appendix takes the entire blow from the infection, and an inflammatory process develops - acute appendicitis. If surgical intervention is not undertaken, there is a risk of complications: peritonitis and abscess may develop. In this case, there is a threat to the life and health of the patient; there is only one solution: remove.
In recent years, acute appendicitis has been diagnosed by doctors more and more often, which is associated with poor diet, weakened human immune system, and poor environment.
Intestinal diseases accompanied by diarrhea contribute to dysbiosis. In such cases, patients who have undergone surgery for appendicitis receive effective conservative treatment, including prebiotics and probiotics that normalize the intestinal microflora.
Nature does everything intelligently. The human body does not contain anything unnecessary or random. Modern medicine continues to study the features of the appendix; the question of “is it needed” is no longer raised. Today there is only one conclusion: the appendix should be removed only in case of acute appendicitis. It is important to remember that this organ is an important defender of human immunity.
Based on all of the above positive properties of the appendix, it should be concluded that it is not a superfluous organ. Therefore, the answer to the question whether a person needs an appendix is obvious. Undoubtedly, it is needed, and it is not worth removing it for prevention. In this case, you can deprive your body of additional protection and other necessary functions.
It’s another matter if inflammation of the vermiform appendix occurs. Then the question of surgery to remove appendicitis is acute. Appendicitis is considered the most common surgical disease of the intestinal tract, and inflammation is often accompanied by complications. Some complications are considered life-threatening, so doctors of the last century recommended removing even a healthy appendix for prevention.
Among the complications of appendicitis, the most dangerous are:
- abscess;
- peritonitis;
- pylephlebitis;
- abdominal ulcers.
Today, with a timely visit to the hospital, a successful operation (which is one of the simplest ones) and compliance with the doctor’s recommendations, complications after appendicitis can be avoided. In addition, as a rule, acute appendicitis has pronounced symptoms, due to which the need for medical care arises immediately.
Diversification of inflammation with other diseases
Due to the diversity of the clinical picture of appendicitis, differential diagnosis is necessary based on the exclusion of the following diseases:
- acute inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- right-sided formation of kidney stones;
- reproductive system diseases (inflammation of the appendages, ovarian cyst, ectopic pregnancy);
- perforation of a gastric or duodenal ulcer;
- acute inflammation of the pancreas;
- acute gastroenteritis;
- Crohn's disease.
Acute appendicitis is a disease with a fairly rapid progression, requiring immediate diagnosis and implementation of appropriate surgical treatment. It is especially dangerous for older people, whose risk of postoperative death is 5-10%. Most often this occurs in cases of perforation of the appendix and inflammation of the peritoneum.