Most often, patients are diagnosed with acute hemorrhoids, characterized by striking manifestations. If the signs of acute deviation are not quickly eliminated, then chronic hemorrhoids will soon arise. In the acute phase, the patient’s body temperature rises, hemorrhoids appear, which bleed and hurt. The acute form of hemorrhoids requires medication or surgical treatment, as well as diet.
International classification, differences from clinical
Statistical records of hemorrhoid cases are carried out in accordance with ICD-10 (additions adopted in 2014). It does not contain the names “acute” and “chronic”. All types of the disease differ in their connection with prolapse of nodes and bleeding. The most suitable species for compliance with the Russian clinical classification are included in code K64:
- Partial (segmental) thrombosis of the vessels surrounding the anus is a common pathology. Characteristic symptoms: moderate sensation of pain, release of hemorrhoids, inflammation, swelling of the skin and sphincter, detection of blood clots in stretched veins. All symptoms last for 3–4 days, then remission occurs, followed by repetition.
- Diffuse thrombosis - differs from segmental thrombosis in the extensive area of damage near the anus, accompanies and aggravates inflammation of the external nodes, is accompanied by intense pain, inability to defecate, severe swelling of the sphincter, and cyanosis of prolapsed nodes.
- Hematoma (collection of blood) in the perianal space is rare. The symptoms of the pathology are similar to segmental thrombosis. The development is caused by rupture of veins due to high intra-abdominal pressure. An internal “bruise” forms.
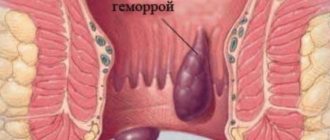
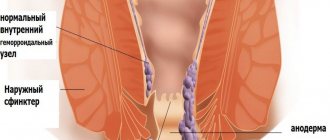
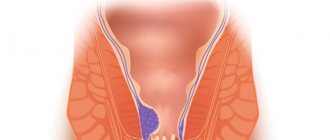
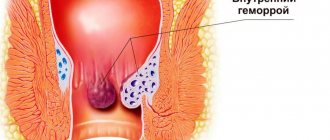
Russian proctologists continue to divide the disease into acute and chronic. The anatomical types of hemorrhoids do not cause controversy: external, internal and combined. An acute process can develop in any type of node.
So far, none of the proposed classifications has been accepted in all countries.
For practicing doctors, it is important to divide the severity of symptoms into degrees:
- I - small painful bumps are detected inside the canal and under the skin, tight to the touch, thrombosis is detected without symptoms of inflammation;
- II - characterized by intense pain, swelling and redness of the skin, sphincter, increased compaction, thrombosis is accompanied by inflammation within the node;
- III - characterized by significant inflammation, the process moves from the nodes to the surrounding tissues, the wall of the node becomes necrotic.
Development of hemorrhoids in acute form: causes
Since the main mechanism of acute hemorrhoids is thrombosis and strangulation of nodes, we will analyze the probable causes of these disorders.
The tendency to thrombus formation appears from the moment the walls of the caverns are stretched. The process causes local release of pro-inflammatory pest substances (kinins). They contribute to the parietal adhesion of platelets. Stagnation of blood reduces the speed of blood flow, so favorable conditions are created for the formation of a blood clot.
Blood clots form in both internal and external nodes. It is believed that the pain syndrome causes blood clots to press on the nerve endings in the vessels.
Incarceration is the most common cause of acute internal hemorrhoids. Sagging nodes descend into the anus and irritate the external sphincter muscle. A reflex contraction occurs. Increased tone does not allow the hemorrhoidal lump to move back into place. The base of the node is compressed, creating a mechanical obstacle to the outflow of blood. The liquid part escapes into the surrounding space, creating swelling. Stretching causes severe pain.
General symptoms
The appearance of symptoms of an acute condition in patients is preceded by general signs of hemorrhoids. Sometimes they are weakly expressed, unstable, and can be clarified by leading questions from the doctor. Most often, patients note:
- pain during bowel movements;
- itching of the skin around the anus;
- blood on top of stool;
- the appearance of painful lumps in the perineum under the skin.
The symptoms are not considered specific, since they occur with other diseases of the anorectal area. Correct assessment is of great importance in making a diagnosis.
Bleeding - occurs in 76% of patients. Blood is found on toilet paper, drips into the toilet, and in a severe stage of the pathology flows out in a stream from the anus.
When internal nodes are damaged, hard feces damage the epithelial wall of blood vessels, bleeding is painless, accompanied by the feeling of a foreign body inside the canal.
A painful reaction is most often caused at the stage of infringement or with significant growth of external nodes. Itching and irritation of the skin occur due to the release of mucus and failure of the external sphincter. Prolapse (prolapse) to the outside is observed in 44% of patients.
Important! Infringement of the internal node causes spastic contraction of the sphincter. At the same time, it is accompanied by thrombosis in external formations. There is a sudden pain in the skin area around the anus due to the abundance of nerve endings. The condition is called "acute hemorrhoidal crisis."
The nature of the pain is described as “pulsating, twitching.” They are constant and worsen with movement and coughing. The patient cannot go to the toilet due to severe exacerbation. There are differences in the symptoms of damage to internal and external nodes:
- acute internal hemorrhoids cannot be examined without special devices; excruciating pain is detected upon palpation of the anal canal;
- with acute external hemorrhoids, the external altered node is visible in the anus area, it is dense, swollen, bluish in color, painful to the touch;
- rupture of the node is accompanied by bleeding, while the tension subsides, therefore the pain decreases;
- the spread of inflammation is indicated by symptoms of intoxication (fever, nausea, weakness, vomiting), rapid deterioration of the condition.
A sign of hemorrhoidal necrosis is a change in color from bluish to black. During this period, it is especially dangerous to try to push the knots into place manually. The patient cannot be treated at home; urgent hospitalization in a hospital is required, removal of dead tissue, otherwise sepsis may develop in the coming hours.
Etiology of exacerbation
The progression of the disease begins with untimely treatment of the chronic form.
The main causes of exacerbation of rectal pathology are:
- excessive consumption of fatty, salty, smoked, pickled foods, carbonated liquids, fast food, semi-finished products;
- binge eating;
- abuse of bad habits;
- alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- impaired blood circulation during prolonged sitting or lack of active life;
- performing intense physical exercise;
- lifting large objects;
- genetic predisposition;
- pregnancy, postpartum period.
An incorrect daily diet increases blood flow to the pelvic area, as a result of which hemorrhoids increase in size and swell. Hard and liquid stools are irritants of the rectal mucosa, leading to an inflammatory process. Chronic and acute hemorrhoids occur with excessive exercise and regular sitting as a result of disruption of natural blood circulation.
During pregnancy, women experience an enlarged uterus, which puts pressure on the veins of the nearby rectum, which causes stagnation of the anal canal. Lifting large objects provokes prolapse and pinching of nodes - dangerous signs of the acute stage of hemorrhoids.
Diagnosis of the disease
It is mandatory that the proctologist examines the patient’s perineum in a supine position with the knees pressed to the chest as much as possible or on a special chair. The doctor must determine the color of the node, the possibility of prolapse, density, pain, the condition of the wall of the rectum and the skin around the anus.
Anoscopy is the most accurate diagnostic method; it helps to examine internal nodes, determine their size, location, and displacement. Using an anoscope device, minimally invasive methods of influencing cavernous formations are carried out.
Treatment of acute hemorrhoids
In case of acute hemorrhoids, it is necessary to begin treatment as early as possible to avoid complications. Depending on the patient’s condition and the appearance of the nodes, a method of drug therapy is selected, or surgery is immediately recommended. It is important not only to relieve pain faster, but also to use medications that normalize blood circulation in the rectal area.
First aid
In case of intense pain, you must call an ambulance. If the patient is at home, it is recommended:
- lay him down with his pelvis raised;
- use any suppositories with anesthesin, adrenaline;
- put a fingertip or a rubber glove (with bandaged fingers) filled with water in the refrigerator freezer to make ice suppositories; they are inserted into the anus to narrow the blood vessels;
- cool boiled water and apply cold lotions with napkins or cotton swabs.
If knots fall out, you should never try to set them back yourself.
Regime and diet
In the first days of an acute process, the patient needs bed or semi-bed rest. If the condition is assessed by the doctor as stage III, then treatment is carried out in the surgical or proctology department of the hospital on an inpatient basis.
A restrictive diet is prescribed (according to Pevzner, table No. 4). Any irritating substances (alcohol, hot seasonings, spices, pickles, fried and smoked meats) are excluded from the diet.
During an exacerbation, it is recommended to retain stool for three to four days by using a slag-free diet (egg white omelet, low-fat meat broth, rolled boiled meat, slimy porridge, white crackers). It is recommended to drink plenty of fluids (rosehip decoction, sweetened weak tea, liquid jelly).
Important! It has been established that in 70–80% of cases with thrombosis of hemorrhoids, rapid inflammation is observed and spreads to the surrounding subcutaneous tissue, the skin around the anus. Therefore, patients need effective local and general anti-inflammatory treatment.
Pain therapy
Locally, for pain relief in acute hemorrhoids, it is recommended to apply cold lotions to the inflamed nodes for the first 2 days, moistening cotton balls in a weak solution of potassium permanganate. Replace tampons every 15 minutes. The procedure is performed within two hours. Repeat 2-3 times a day.
How and with what to treat
Drugs
Treatment of hemorrhoids in the acute stage involves complex treatment. First, you need to relieve the pain that prevents you from having normal bowel movements. If a person has constipation, then it is necessary to do enemas. The table shows the main medications used for acute hemorrhoids.
| Release form | Drug name |
| Ointments | "Proctosan" |
| "Relief Ultra" | |
| "Troxevasin" | |
| Heparin ointment | |
| "Bezornil" | |
| "Levomekol" | |
| "Aurobin" | |
| "Gepatrombin" | |
| "Posterizan" | |
| Rectal suppositories | "Proctosan" |
| "Posterizan Forte" | |
| "Nizhpharm" | |
| "Natalsid" | |
| "Gepatrombin" | |
| "Ginkor Procto" | |
| "Procto Glivenol" | |
| Pills | "Diclofenac" |
| "Movasin" | |
| "Nise" | |
| "Movalis" |
Return to contents
Surgery for acute hemorrhoids
Surgical removal of hemorrhoids is also carried out using a scalpel.
If local medications and tablets for acute hemorrhoids do not provide the desired result or are contraindicated, then the problem is eliminated through surgery. During surgical therapy, a scalpel, ultrasound devices, and a surgical laser are used. The procedure is painful, so general anesthesia is performed first. There are several types of surgery:
- Classic hemorrhoidectomy. This method is used in particularly severe cases, but has good results.
- Transanal hemorrhoidal dearterilization. During this surgical procedure, hemorrhoidal arteries are sutured using an ultrasonic sensor.
- Operation Longo. Using a circular endostapler, the surgeon excises the damaged area and stitches it in a circle. Thus, the nodes are tightened and returned to their previous position.
Doctors' recommendations
After suffering a hemorrhoidal attack followed by surgery, we can talk about the prognosis of achieving long-term remission. But it is impossible to completely overcome the disease. It depends on the patient how quickly a re-exacerbation occurs. Proctologists recommend:
- do not forget to come for examination 2 times a year;
- take phlebotonics medications in courses of 2 months every six months;
- control your diet - exclude all foods that contribute to constipation and a rush of blood to the intestines (alcohol, fried meat, spicy seasonings, pickles), add a portion of vegetables and fruits, dairy products;
- walk more, do swimming, do fitness, do not do hard work, ride a bicycle, horse riding is not recommended;
- perform exercises daily to strengthen the pelvic muscles;
- take care of hygiene, in addition to the morning and evening toilet of the anal area, it is necessary to wash the anal area after each bowel movement; you will have to carry wet wipes with you to work;
- it is better for women to prepare and undergo preventive treatment before pregnancy;
- refuse anal sex.
If signs of exacerbation appear, you should consult a doctor. If you have no previous experience, you cannot start herbal treatment on your own. A consultation with a proctologist will help you understand the choice of the most suitable means.
Prevention
When hemorrhoids worsen, the pain is unbearable - the patient is unable to move or sit. Relieving pain is not easy. More attention needs to be paid to disease prevention.
- If you have a history of anal fissures and hemorrhoids, replace laxatives with products that have a laxative effect.
- Add substances that stimulate regeneration and counteract infection to suppositories and ointments.
- Include prunes and dried apricots in your diet. Will help avoid unnecessary constipation.
- Avoid alcohol, tea, coffee, flour products - pathogens of the digestive system that cause spasms of blood vessels.
- Add fiber to your food, which is necessary for the development of intestinal microflora.
- Train your abdominal muscles without allowing pathologies of the circulatory system to develop.
- Drink plenty of water, distributing it evenly throughout the day. With a lack of fluid, some thickening of the blood in the hemorrhoidal veins and intestines is possible.
- Avoid stress. Nervous explosions provoke spasms of the muscle structure. Use mild sedatives. Drink soothing herbal teas.
A diagnosis of acute hemorrhoids and inflammation of the nodes requires fighting. Contact your doctor at the first call and methodically follow medical instructions for the treatment of acute hemorrhoids.
When a person eats wisely, pays attention to physical activity, and controls his well-being, acute hemorrhoids go far and long.