What it is
Nodular fibroids are one of the types of benign uterine tumors. This tumor consists of several nuclei. Unfortunately, fibroids are almost impossible to detect through a gynecological examination in the first stages of development. The neoplasm also does not cause pain. Therefore, the tumor is often diagnosed already in the late stages of formation.
A nodular type tumor develops in the environment of healthy tissues, gradually beginning to put pressure on the body of the organ.
Women who have experienced or are experiencing serious hormonal changes are at risk for this disease. For the most part, these are middle-aged women on the verge of menopause (from 33 to 45 years).
Why is it developing?
Nodular fibroids are considered a hormone-dependent tumor, so the main reason for the development of pathology is a change in hormonal levels in the female body, namely an increase in estrogen and progesterone hormones. Because of this, hyperplastic changes occur in the cells of the muscular layer of the uterus.
The growth of the tumor causes the absence of pregnancy and lactation. Every month, a woman’s body prepares for conception, and when this does not happen for too long, a malfunction may occur, which triggers the formation of fibroids. At risk are patients with late puberty (the norm is up to 15 years), irregular menstrual cycles, heavy and prolonged periods, dissatisfaction with sexual relations and abstinence from them.
Most often, women aged 25 to 55 experience the disease. During this time, the body has already suffered certain pathologies, disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine and other systems, and has been exposed to stressful situations. The development of uterine fibroids is facilitated by a decrease in natural immune defenses.
Diagnostics
A tumor that has affected a large volume of tissue can be identified during examination in a gynecological chair by palpation of the uterus. The specialist will identify the formation of atypical relief, bumps and deformed areas.
More informative diagnostic methods are also used:
- ultrasonography;
- MRI;
- CT;
- laboratory research methods (sampling and interpretation of urine and blood tests);
- Dopplerography.
The most accurate picture is revealed by hydrosonography. This is a type of ultrasound test that works on the uterine body, which is filled with fluid.
Types of nodular fibroids
The classification of nodular fibroids is based on the geography of the location of nodes in the body of the uterus:
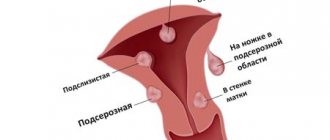
- nodes of the submucosal space (bordering the muscular wall and the mucous layer of the organ; these neoplasms reach very large sizes and can descend to the vaginal tract);
- nodes of the muscle space (such nodes develop in a layer called the myometrium);
- subserous (nodules have a thin base or “leg” of small size, which ensures adhesion of the large head of the node to the uterus; the neoplasm develops at the junction of the myometrium and the outer membrane of the uterine body, i.e. the myomatous neoplasm is located under the membrane of the visceral peritoneum).
Fibroids are also correlated with weeks of pregnancy based on the size of the node. Small nodular fibroids do not cause a pronounced enlargement of the uterus, while large tumors can lead the organ to a state characteristic of the last weeks of gestation.
Classification of myomatous formations
Depending on the location of myomatous nodes in the uterus, there are:
- Submucosal nodes, which are located at the border of the muscular layer and the mucous membrane (inner layer of the uterus). Such nodes grow into the uterine cavity and, reaching large sizes, can descend through the cervix into the vagina. A large submucosal nodular myoma is also called a nascent myomatous node.
- Intermuscular nodes that are located in the thickness of the myometrium. Such nodes grow outside the uterine cavity.
- Abdominal nodes, which are located at the border of the myometrium and the outer lining of the uterus. Such knots are characterized by a small base compared to the size of the knot itself - a “knot on a leg.”
Depending on the size, nodular uterine fibroids are usually classified according to weeks of pregnancy (enlargement of the uterus, which is characteristic of each week of pregnancy), for example, nodular uterine fibroids 9 weeks, 12 weeks, 18 weeks, etc.
Certain classifications of fibroid nodes are based on various criteria for assessing fibrous formations. Judging by size, there are large (over 6 cm), medium (in the range of 4-6 cm) and small (up to 2 cm). The form of neoplasms can be diffuse (when the node does not have a clear outline, and the myometrium grows diffusely) or nodular (single or multiple myoma formations of a smooth, round shape).
The placement of fibroids relative to other layers of the wall of the reproductive organ distinguishes the following types of fibromatous neoplasms:
- Subserous - develops on the outer part of the uterus, grows towards the peritoneum.
- Submucosal (submucosal) - originates under the thin mucous membrane (endometrium) inside the uterus.
- Interstitial (intermuscular) - nodes form inside the muscle layer, that is, the walls of the uterus.
- Intramural (intramuscular) - the tumor appears in the middle layer of muscle tissue.
- Subserous-interstitial – a tumor of the interstitial type that develops towards the peritoneum.
- Intraligamentary (interligamentous) - develops between the broad ligaments of the uterine body.
A special form of pathology is calcified fibroid, in which tumor formation occurs in the calcium membrane. Static, slowly progresses, responds poorly to drug therapy.
Reasons for appearance
The main reason for the development of uterine fibroids is hormonal imbalance. An imbalance in the formation of estrogen and progesterone causes hyperplasia in the myometrial layer. That is why doctors advise adjusting hormonal status under the strict supervision of specialists in order to avoid the development of concomitant pathologies.
It is also widely believed in the scientific community that nodular uterine fibroids can be caused by the fact that a woman ignores the reproductive function of the body. Those. If, over a sufficiently long period of time, the uterus renews the endometrium, but conception does not occur, the cells begin to change and develop into a tumor.
Other causes of uterine fibroids:
- genetics (very often fibroids develop in those women whose close relatives also struggled with a tumor of the uterine body);
- damage to the uterus (damage to the integrity of the uterine cavity can be caused by abortions, surgeries, diagnostics, and even gynecological examinations);
- physical inactivity (lack of physical activity);
- late birth;
- previously suffered inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system;
- stress and insomnia;
- bad habits (smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages and taking prohibited substances);
- disturbances in the body's metabolic processes.
Cases of fibroids occur more in women of reproductive age, when hormonal levels are at their peak. After menopause, the pathology is no longer observed, and previously formed fibroids in patients at the menopause stage begin to decrease.
The lack of regular sex, as well as the lack of orgasm during regular sex, negatively affects the reproductive system: stagnation forms, which over time can provoke pathology.
Diabetes mellitus, coupled with active excess weight gain, can also lead to tumor formation. This reaction of the body to obesity is due to the fact that a certain amount of hormones is produced in adipose tissue.
Complications
- torsion of the legs of nodular uterine fibroids;
- necrosis of nodular uterine fibroids;
- degeneration of fibroids into a malignant tumor;
- infertility;
- miscarriage;
- anemia.
Myoma formations of large and medium sizes become the culprits of painful sensations. By exerting pressure on nearby organs and blood vessels, fibroids provoke disruptions in their functioning. For example, lymphostasis, which is accompanied by stagnation of lymph in the system, develops as a result of compression of the lymph nodes.
Often, multinodular fibroids are aggravated by additional diseases of the reproductive system. Pathology occurs in combination with:
- endometriosis (adenomyosis), when the tissues lining the uterine cavity grow into its muscle layer;
- erosion of the cervix, which develops against the background of a tumor;
- various forms of endometrial hyperplasia;
- adenomatous polyps.
Such “duets” add unpleasant symptoms to a woman and need to be treated urgently. There are complications that are dangerous to life and health. These include necrosis of tumor tissue, purulent processes, and the birth of a myomatous node. Cell death occurs due to torsion of the stalk and malnutrition of the neoplasm. Accompanied by symptoms of intoxication of the body (nausea, vomiting, fever).
A large tumor puts pressure on neighboring organs. Compression of the bladder leads to disruption of the kidneys; when exposed to the rectum, constipation, hemorrhoids, and inflammatory processes in the intestines appear. It should also be taken into account that as a result of torsion of the leg of the node without medical assistance, necrosis develops, which can result in peritonitis. In addition, it should be taken into account that there is a risk of the tumor degenerating into a malignant formation.
One of the serious complications of nodular uterine fibroids is infertility or the inability to bear a child. An enlarged tumor can interfere with the patency of the fallopian tubes. If pregnancy does occur, there is a huge risk of miscarriage. But in case of cervical fibroids, large tumors, or rapid growth, the pregnancy should be terminated.
Symptoms
A small nodule does not cause any deviations in the body’s condition from the norm, so in the early stages a woman may not even be aware of the tumor. But during an examination in a gynecological chair, pathology can be detected.
Actively developing uterine nodular fibroids begin to bring painful discomfort and unpleasant sensations, and also manifest themselves in the form of a number of symptoms:
- too long or heavy periods;
- pain in the lower abdomen, pulling sensations or a feeling of heaviness;
- spotting not related to menstruation;
- frequent urge to “relieve need”;
- change in the relief of the abdominal wall;
- edema processes affecting the legs and hips;
- weakness;
- apathy and drowsiness;
- problems with conception;
- dizziness (if you suddenly change position, your vision begins to darken);
- migraine;
- loss of appetite;
- loss of healthy complexion (pallor is associated with anemia).
Try to immediately contact a gynecologist if you find yourself with more than 3 symptoms from the list. After all, treatment of nodular fibroids at the initial stage is a procedure with minimal intervention in all processes of the female body. But later stages require serious and often risky measures.
Detailed description of the disease
The development of nodular fibroids is characterized by the formation of single or multiple nodes, which are localized in the thickness of the myometrium. The initial stage of the disease has no obvious signs and does not make itself felt for a long time.
A benign formation develops on healthy tissues, so changes in processes in the body can lead to the development of negative phenomena and the subsequent formation of oncology. Timely detection of fibroids requires immediate and effective treatment.
The main reason for the formation of nodular fibroids is considered to be a change in the level of hormones in the female body, which leads to disruption of many processes. The disease is often diagnosed in menopausal women, when the reproductive system suffers serious disruptions.
Drug treatment to prevent fibroid growth
Treatment for fibroids depends on how the symptoms of the disease manifest. If the symptoms are very mild or not visible, the woman is simply put under the supervision of a doctor and adjusts her lifestyle (giving up bad habits, increased stress, baths and solariums).
If symptoms appear, but the woman’s discomfort can be classified as “moderate,” hormonal therapy is prescribed:
- antagonists (suppress the natural production of estrogen, thus stopping the development of the tumor);
- tranexamic acid (affects platelets in the blood, stopping their breakdown);
- oral contraceptives (prevent the growth of tumors and provoke a reduction in small fibroid nodes).
Surgery
If six months after diagnosis and treatment were started, regression of the myomatous nodes is not observed, the woman is referred for surgery. The reason for prescribing surgery may be complications and untimely detection of fibroids (uterine size from the 12th week of pregnancy).
Surgical intervention for pathology can be of two types:
- radical (removal of the tumor along with the uterus);
- selective (removal of only myomatous nodes, without violating the integrity of the uterus).
Methods for surgical removal of fibroids:
- uterine artery embolization (a minimally invasive operation in which a catheter is inserted into the patient through the femoral artery and then the blood supply to the fibroids is blocked using polyvinyl alcohol);
- FUS ablation (neoplastic tissue is subjected to controlled heating through the abdominal wall using focused ultrasound; the result of the operation is the destruction of fibroid tissue);
- myomectomy (removal of fibroids under anesthesia in an operating room, through an access in the abdominal wall);
- hysterectomy (removal of the uterine body under general anesthesia).
Treatment of multinodular uterine fibroids
When choosing a treatment method, the woman’s age, her plans for childbearing, the severity of clinical signs, the location of the nodes and their total number are taken into account. May consist of medications, surgical interventions of varying volumes. Gynecologists rarely recommend folk remedies for this disease.
Drugs
If a woman plans to become pregnant after treatment, she is prescribed tablets with a low hormone content (Marvelon, Charozetta). This method is indicated for small nodes. The Mirena spiral helps reduce the intensity of blood loss. It contains a hormone from the group of gestagens (similar in action to progesterone), which is released in small quantities directly into the uterine cavity.
If the goal of therapy is to reduce the nodes for further removal, then the patient is recommended to administer drugs that stop menstruation. They transfer the body into a state of artificial menopause. Their therapeutic capabilities for multiple fibroids are limited, since the effect will be temporary, and after discontinuation, re-growth is observed. For young women, these medications (Zoladex, Diferelin) should not be used for more than 3 months.
One of the new methods is the use of drugs that block progesterone receptors - mifepristone (Ginestril), ulipristal (Esmiya). On an individual basis, medications that counteract pituitary hormones (Danazol) and estrogens (Tamoxifen) can be prescribed.
Operation
In case of severe blood loss, rapid growth of fibroids or large tumors, surgical treatment is prescribed. The operation is also indicated for complications: infertility, miscarriages, pain, compression of the intestines, bladder, torsion of the leg of the node.
If a subsequent pregnancy is possible, they try to preserve the uterus - the node is removed or a substance is injected that clogs the uterine arteries that feed the fibroid (embolization). If childbearing is not planned, as well as in case of adenomyosis, signs of malignancy, radical removal of the uterus and cervix or supravaginal cutting is performed.
Traditional methods
There are many recipes that are designed to stop the growth of fibroids. In practice, this method does not help get rid of the tumor, and the time for gentle types of surgery or drug treatment is lost. Therefore, the use of herbs should be agreed upon with a gynecologist. Most often they are recommended as a hemostatic agent for asymptomatic fibroids.
Treatment with traditional methods may include:
- Infusion of nettle leaves, shepherd's purse (a tablespoon per glass of boiling water, leave for 20 minutes) a third of a glass three times a day. Start drinking 5 days before menstruation and continue until it ends.
- Water pepper extract 25 drops 3 times a day for bleeding.
- Alcohol extract from the septa of walnuts, especially with reduced thyroid function (50 walnuts and 100 ml of 70-proof alcohol, leave for 10 days) 15 drops 3 times a day. Drink for 2 months.
- Broccoli and green tea in the form of food products, as well as dietary supplements based on them - Indinol, Epigallate. The course of treatment is 3 months.
We recommend reading about the signs of cervical fibroids. From the article you will learn about the causes and classification of cervical fibroids, symptoms of the pathology, diagnosis and treatment options.
And here is more information about whether fibroids can develop into cancer.
Multiple uterine fibroids cause bleeding, pain, and anemia. Its consequences include infertility and miscarriage, complications during childbirth. When combined with adenomyosis, the disease is even more severe. Its symptoms depend on the location, size and number of nodes. Ultrasound is usually prescribed for detection.
Treatment can be medicinal, but for large and complicated nodes, surgery is required - the tumor, uterus are removed, or a substance is injected to block the feeding vessel during embolization of the uterine artery.
https://youtu.be/QiuaHPuiSsk
Folk recipes
Traditional methods can help control uterine fibroids by affecting its growth and development. Herbal preparations, which are a natural source of certain hormones, have a pronounced positive effect.
- tincture with boron uterus (you need to boil a couple of spoons of boron uterus raw material in 350 ml of water for 15 minutes, then infuse the decoction for another 3 hours);
- tincture of marina root (mix dry root and vodka in a 1:1 ratio, then keep the mixture in a dark place for 7 days);
- tincture of red brush (pour boiling water over a couple of tablespoons of the raw material and leave for an hour).
Celandine and tartar also help well in treating pathology with folk remedies.
Treatment with folk remedies
It is not recommended to treat uterine fibroids on your own; improper therapy can cause uterine bleeding and enlarged nodes. After consulting a doctor, if the patient has no contraindications, traditional methods of treatment can be used.
Traditional medicine recipes can only be used if the fibroid is small, if the tumor has grown to a large size, treatment can only be surgical.
The most common method is herbal medicine; the following herbs are used to reduce tumor size:
- hog uterus;
- red brush;
- celandine;
- prickly tartar.
Tinctures, decoctions and teas are prepared from herbs. It must be remembered that it is strictly forbidden to apply hot compresses to the abdomen and other warming procedures, as this can provoke a sharp growth of tumors and bleeding.
To reduce estrogen levels, you can ingest flaxseed oil , it has an anti-inflammatory effect, is an antioxidant and normalizes the body's hormonal levels.
Propolis is known for its benefits in the treatment of female diseases; you can purchase vaginal suppositories with propolis in the pharmacy chain, and you can take an alcohol tincture based on a beekeeping product orally.
Treatment with traditional methods is long and requires patience, but sometimes surgery can be avoided in this way.
Important! You should not rely only on home remedies for treatment; herbal medicine can be used in parallel with medications and only after consultation with a doctor.
https://youtu.be/L7WRB0k8IZo
Compatibility with pregnancy
This pathology in most cases is incompatible with pregnancy, since fibroids cause temporary infertility or miscarriages.
The compatibility of fibroids with pregnancy depends on what kind of nodular form is observed in the woman. If at the time of conception the expectant mother already had a tumor in the uterus (submycotic type), then the risk of miscarriage is very high. But with subserous fibroids, it is quite possible to carry a child to term under the supervision of doctors.
But in some cases, doctors may recommend that a woman refuse to give birth:
- fibroids in the cervix;
- pathology in advanced form;
- too rapid progress in the development of the tumor.
Pregnancy and multinodular uterine fibroids
If the nodes are located closer to the outer surface of the uterus and are small in size, then normal conception and pregnancy are possible. In this case, the fibroid itself can either increase or decrease along its course, or the size of the nodes stabilizes.
However, infertility is a common manifestation of fibroids. This is due to the following reasons:
- lack of release of the egg from the follicle due to hormonal imbalance (ovulation does not occur);
- decreased patency of the cervical canal (viscous mucus);
- insufficient contractility of the fallopian tubes;
- the structure of the endometrium is disrupted - the fertilized egg cannot attach or is quickly rejected.
Those women who begin to develop pregnancy often suffer from complications:
- high uterine tone causes miscarriage in the early stages;
- after the 1st trimester, the risk of placental abruption and impaired blood flow to the fetus increases;
- bleeding, premature birth;
- a large tumor disrupts blood flow to the fetus, which can cause malformations;
- the labor period is characterized by weakness and unsynchronous contractions of muscle fibers;
- After childbirth, prolonged bleeding and slow recovery of the normal size of the uterus are observed.
Visitor reviews
Review #1
I had surgery for multinodular fibroids at about 12 weeks. It was successfully removed and there were no relapses. A year later she became pregnant. She refused preliminary hormonal therapy herself, since at the consultation they warned that hormones can shrink the smallest nodes (which will not be detected during surgery and will then cause a relapse).
Review #2
She treated myoma with hormonal drugs in combination with traditional methods. I can’t say for sure which method gave a positive result, but I got rid of the tumor.
Review #3
She was treated with regular birth control pills, which were prescribed by the doctor. But these pills didn’t help my older sister and she had to undergo surgery. When it comes to treating fibroids, everything is very individual.
Forms
Depending on the degree of growth of the nodes, a simple and proliferative course of the disease is distinguished, in which rapid cell division occurs and the tumor increases. Based on the location of fibroids, the following classification of its varieties is determined:
- subserous fibroids located in the abdominal region;
- submucous tumor, which is mainly localized near the uterine mucosa;
- interligamentous tumor of intraligamentary type;
- intermuscular myoma of interstitial type.
The nature of tumor formation can be single or multiple, which is visualized by ultrasound.
Nodular fibroids in combination with endometriosis
The formation of nodular fibroids in the presence of endometriosis develops with a sharp change in the hormonal background of a woman. This phenomenon often occurs during unregulated sexual contacts and frequent gynecological operations in the form of abortions.
When immunity decreases, excess cells penetrate the muscle structure and begin to grow into the body of the uterus, which is accompanied by the appearance of a tumor. Therefore, to prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle and visit a gynecologist in a timely manner.
The symptoms of fibroids in combination with endometriosis are the same as with the development of a single tumor. Diagnosis is carried out through a certain number of studies and, after a doctor’s conclusion, surgical intervention is recommended.
The operation depends on the location and extent of the tumor. In this case, after the manipulation, treatment is prescribed as maintenance and restorative therapy. They mainly use medications that artificially induce menopause for a certain period of time. After complete recovery, the woman is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle with moderate sexual contact and the absence of bad habits.
Course of nodular fibroids and adenomyosis
There are often cases of simultaneous development of fibroids and adenomyosis. Both pathologies are of benign origin and develop against the background of negative changes in the body associated with hormonal imbalance and the presence of chronic gynecological diseases.
Treatment of fibroids and adenomyosis involves the use of conservative methods of therapy, mainly in the initial stages of the development of the disease. If the size of the tumors is quite impressive, then surgical intervention is required to remove the pathology or completely eliminate the reproductive organ.
At the same time, the treatment methods for both tumors have similar directions, but their approval requires the opinion of the attending physician. Prescribing adequate treatment requires an accurate diagnosis and location of tumors in the uterine cavity. The most effective method for eliminating diseases is the use of surgery.
Small nodular fibroids
The presence of nodular fibroids up to 2 cm in size is considered a small formation by generally accepted standards, and this pathology is subject to conservative treatment. They mainly use hormonal agents to stabilize the functioning of the reproductive system. Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are also used.
Nodular myoma of small size requires constant monitoring, so if it increases, more radical methods should be taken and the progressive tumor should be eliminated. When planning a pregnancy, the average size of the formation can cause infertility or cause miscarriage in the early stages.
Disease Prevention
The most important contribution to preventing the development of fibroids should be regular (every six months) examinations by a gynecologist.
And, of course, it is important to plan your pregnancy correctly and use contraception so that in the future you do not have to resort to artificial termination of pregnancy.
Additional preventive measures:
- proper nutrition and taking vitamins;
- giving up bad habits;
- control and fight against excess weight;
- dosed physical activity.
Even if there is a hereditary factor, you can avoid the occurrence and development of the disease if you adhere to the right lifestyle and a competent approach to organizing sexual relations in a couple.