Vision defects can be corrected with glasses, contact lenses, surgery and laser correction. The last method of eliminating visual pathologies is the most effective. It provides excellent vision and is rarely accompanied by complications. Let's find out what the essence of this treatment method is, how the operation takes place and how long it lasts.
In this article
- When is laser vision correction prescribed?
- When does a person need to sign up for laser vision correction?
- Contraindications to laser vision correction
- How is laser vision restoration surgery performed?
- Are there complications after laser correction?
- How long does laser vision correction surgery take?
- Laser vision correction techniques
- Laser correction of vision pathologies: advantages
When is laser vision correction prescribed?
Laser vision correction today is a very popular technique for correcting refractive errors. Unlike surgery, laser treatment is absolutely painless and safe. With its help, it is possible to achieve almost one hundred percent vision. Laser correction allows many people to forget about glasses and contact lenses for many years or forever. This procedure is prescribed for the following visual pathologies:
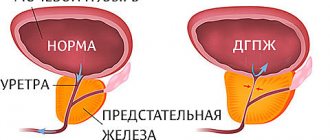
- Myopia or myopia (from −1 diopter). With this disease, light rays are focused in front of the retina, as a result of which a person has difficulty seeing what is at a distance from him. The operation is performed when the reading is no higher than −1 diopter. Usually this degree of myopia is not corrected even with glasses and contact lenses.
- Farsightedness or hypermetropia (up to +6 diopters) is a refractive error caused by a decrease in the size of the eyeball. Light rays appear behind the mesh shell. The patient sees well into the distance, but objects close to the eyes appear blurry.
- Presbyopia (age-related farsightedness) is a pathology that occurs in people after 40 years of age. Almost every person who has reached the specified age encounters it. This happens due to the natural aging of the body and all its organs and structures, including the lens of the eye. Over the years, it becomes less elastic and it is difficult for it to change its shape when looking from distant objects to close ones and vice versa. The first symptom of presbyopia is difficulty viewing small objects (for example, the type in a book) at close range. If presbyopia develops against the background of myopia, a person will need several pairs of glasses - for distance and for near.
- Astigmatism (up to 4 diopters) is a visual pathology that results from curvature, change in the shape of the eyeball, cornea or lens. Light rays fall on several points of the retina and form a blurred image. A person has to constantly squint to see anything. Often, astigmatism is accompanied by myopia or hypermetropia.
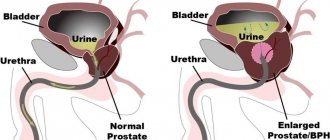
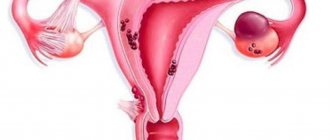
Removal of uterine fibroids
Uterine fibroids are a benign tumor that forms from muscle tissue. The incidence rate of this pathology is quite high. Small tumors do not require emergency surgery. Most gynecologists take a wait-and-see approach - regular examinations by a doctor to monitor the growth of fibroids.
It is necessary to urgently remove fibroids in cases where there is active growth. The acceleration of this process indicates that malignant cells appear in the tumor, which stimulates its growth.
Surgery to remove fibroids can be performed in two ways: laparoscopic and laparotomy. The laparoscopic approach is more modern and less invasive, so most women prefer it. Endoscopic surgery has many benefits.
The only disadvantage of laparoscopic surgery is the narrow view, which is why the myomatous node on the uterus may go unnoticed. At the same time, after laparoscopic surgery, a woman can go home a few days later. Most often, endoscopic intervention is performed for small myomatous nodes (less than 3 cm in diameter)
During laparotomy surgery, access is through a Pfannenstiel incision (a transverse incision on the anterior abdominal wall just above the symphysis pubis). In rare cases, a lower median laparotomy is performed. The laparotomy method is used for large tumors.
The surgery itself to remove fibroids is called myomectomy. If the intervention is performed using a laparoscope, then the operation to remove uterine fibroids lasts no more than 1 hour. When performing abdominal surgery, the time required to remove fibroids may be shorter.
These figures are approximate and may vary.
Intravenous, epidural, endotracheal, or local anesthesia may be performed.
When does a person need to sign up for laser vision correction?
All of the above diseases can be corrected with glasses and contact lenses. However, if a person wants to get rid of the need to wear them, select them and systematically adjust their optical power, he agrees to laser surgery. In some cases, patients have to do this. This is due to a profession that does not allow you to wear contact lenses and glasses: we are talking about firefighters, military personnel. Laser vision correction as the only opportunity to play sports is becoming necessary for many athletes.
Wearing glasses during sports activities is dangerous and inconvenient, as they can break, fall off the face, fog up, and contact optics are not compatible, for example, with water sports. Laser correction is for such people a chance to work fully and do what they love.
Contraindications to laser vision correction
Laser vision correction is a very safe and absolutely painless procedure. However, it is not available to everyone. There are a number of limitations that are revealed during a thorough examination of the patient. Contraindications can be relative or absolute. The first include:
- eye infectious diseases of the visual organs;
- dry eye syndrome in the initial and middle stages;
- severe lagophthalmos (failure to close the eyelids);
- viral keratitis. The laser can provoke the appearance of the herpes virus and cause an exacerbation of keratitis during the rehabilitation period;
- low sensitivity of the cornea. This is a symptom of neurotrophic diseases;
- glaucoma in one form or another;
- congenital cataract;
- mild corneal dystrophy;
- retinal detachment;
- autoimmune diseases during exacerbation;
- severe deterioration of vision over the past six months (it is necessary to find out the reason for the progression of the disease);
- young age. Until the age of 18, a person’s eyes are in the formative stage, so laser correction is inappropriate, since vision after 18 can improve without treatment;
- diabetes mellitus (depending on each specific case);
- pregnancy and lactation period.
Absolute contraindications
The above pathologies and conditions are temporary. Absolute forever exclude the possibility of prescribing the procedure:
- fourth degree glaucoma;
- severe corneal dystrophy;
- progressive cataract;
- last stage of diabetic retinopathy;
- keratoconus (thinning of the cornea and its taking on a cone-shaped shape);
- incurable blindness;
- chronic infectious diseases that greatly affect the functioning of the immune system (HIV);
- severe psychiatric pathologies.
Today, these contraindications are absolute, but the development of technology is expanding the possibilities for laser vision correction. Thus, some relative restrictions, for example, diabetes, were previously absolute.
Recovery period
How the implantation of the artificial lens will proceed will depend on the correctness of postoperative rehabilitation. At an early stage, it is important to protect the eye from infection. To do this, within 5-7 days it is prohibited:
- wash your hair;
- wash your face in the usual way;
- touch your eyelids with bare hands that have not been pre-treated with antiseptics;
- go outside without an insulating eye patch.
In addition to this, it is necessary to instill antiseptic drops under the eyelid every day for 10 days and carefully monitor eye hygiene.
During the period from the first to the 20th day of rehabilitation, it is important to avoid any phenomena that could provoke blood flow to the face, especially to the operated eye. These include:
- bending forward;
- visits to baths and saunas;
- lifting weights over 3 kg;
- gymnastics and other types of sports activities.
To avoid accidentally injuring the operated eye
, it is advisable to sleep on your side with the healthy eye for the first week. If the intervention was bilateral, it is recommended to sleep on your back. The duration of sleep should be at least 8 hours a day, and the duration of continuous work with active involvement of vision should not be more than half an hour.
Don't forget about nutrition
which will help you recover faster after surgery. Ophthalmologists claim that it suppresses the immune system, and therefore the risk of infectious and inflammatory complications remains high for up to 3 months. To avoid them, it is recommended to include more fresh vegetables and fruits in your diet, which contain vitamins and microelements. Additionally, you can take vitamin complexes that your doctor recommends, or natural immune stimulants, for example, Eleutherococcus. You should give up alcohol, fatty and spicy foods, carbonated drinks and energy drinks for at least 3-4 months.
How is laser vision restoration surgery performed?
There are several laser techniques that differ from each other in a number of parameters. In general, the essence of any technique comes down to the following:
- the surgeon uses a scalpel or the laser itself to form a corneal flap from the epithelial layer of the cornea;
- then the doctor removes this corneal flap, as during PRK surgery (photorefractive keratectomy), or moves it to the side, as during LASIK (laser-assisted keratomileusis);
- the cornea is evaporated by a laser beam until it acquires the correct shape;
- the flap, if it was not removed, returns to its original place.
In some cases, the surgeon installs a bandage lens on the eye - a hydrogel bandage that promotes rapid healing of the cornea and prevents bacteria from entering the eye. The patient does not need to prepare thoroughly and for a long time for the operation. Two weeks before vision correction, he stops wearing optics. This is necessary for the cornea to take its natural shape. Two days before the procedure you should not drink alcohol. It negatively affects the blood vessels of the eye.
On the day of the procedure, the patient needs to wash his hair and face. Make-up, cream and make-up are not allowed. Fragments of cosmetics can get into the eye and cause inflammation. The doctor will give all the necessary instructions that must be strictly followed. Any operation is associated with risk. If you do not follow your ophthalmologist's instructions, the risk of complications increases. In addition, the doctor may cancel the procedure.
Vascular stenting - heart surgery
Heart surgery - stenting - may be prescribed in cases of narrowing of the coronary vessels (stenosis). In such a life-threatening condition, the blood supply to the heart and the supply of oxygen and nutrients to it are disrupted.
Essence of the disease
Coronary vessels are the vessels that deliver oxygenated blood (arterial) to the myocardium (the middle muscular layer of the heart, which makes up its main part). Due to the narrowing of the coronary vessels, coronary heart disease develops - a violation of the cardiac blood supply, and heart failure may develop in the future. At first, there are no clinical manifestations of stenosis. This condition manifests itself in the presence of coronary artery disease or heart failure with the following symptoms:
- pain in the heart area;
- shortness of breath with light exertion;
- swelling of the lower extremities;
- Arrhythmia is a heart rhythm disorder.
Stenosis develops due to the accumulation of cholesterol plaques in the arteries. Cholesterol plaques are accumulations of cholesterol (a naturally occurring fatty alcohol), calcium, connective tissue waste, and fat.
Narrowing of blood vessels can lead to blockage and acute myocardial infarction, when the restriction of blood supply to the myocardium cannot be compensated, and ischemic necrosis of the myocardial area occurs. Manifested by symptoms such as:
- severe pain in the chest (in patients with diabetes mellitus there may be no pain);
- pain or discomfort radiating to the shoulder blade, arm, throat, stomach;
- increased sweating;
- dyspnea;
- heart failure.
Coronary stenosis is diagnosed using the following examination methods: ECG (electrocardiography) - a method of recording the electrical activity of the heart, showing disturbances in heart contractions; ultrasound examination of the heart (EchoCG); Dopplerography of the vessels of the neck and head, MRA (magnetic resonance angiography); CT (computed tomography); Coronary angiography is an X-ray examination with the introduction of a contrast agent through a catheter through the femoral artery, which, by filling the coronary arteries, allows one to determine the degree of vasoconstriction, the location and duration of the process.
Indications for surgery
Stenting is indicated for patients with the following pathologies of the cardiovascular system:
- Myocardial infarction in the early stages.
- Acute coronary syndrome.
- Progressive angina.
- Stable angina in case of low quality of life.
- Early post-infarction angina if attacks develop during treatment of myocardial infarction.
- High risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- High risk of death.
There are conditions under which the operation is not permitted:
- Diffuse (scattered) stenosis of the coronary bed, that is, the absence of local narrowing where a frame could be installed.
- The diameter of the stenotic vessel is less than 3.0-2.8 mm.
Stenting procedure
For the first time such a procedure was carried out in 1986. Previously, treatment of coronary heart disease was possible only through coronary artery bypass surgery (the creation of a shunt to bypass a narrowed section of a blood vessel). But, 10 years after such heart surgery, in half of the cases, repeated coronary artery bypass grafting became necessary, since the shunt became stenotic. In such cases, stenting is a safer alternative to bypass surgery.
A catheter is inserted through the femoral or radial artery, and a conductor is inserted through it, with the help of which a stent is installed at the site of stenosis (narrowing) - a tubular metal frame placed on a special balloon. At the site of narrowing, the balloon is inflated, straightening the stent and thus expanding the walls of the vessel. Then the balloon is removed, and the stent remains, strengthening the walls of the vessels. Stenting is a more advanced technique of balloon angioplasty, when only a balloon was inserted into the narrowed lumen, inflating the walls of the vessel. But after such a procedure, stenosis often resumed after 3-6 months. The stenting method reduces the possibility of recurrence of stenosis. The procedure is carried out under local anesthesia and lasts about 30-40 minutes; the patient does not feel pain, only slight discomfort in the area where the artery is punctured.
Preparation for surgery and postoperative recovery
If stenting is necessary, the patient is prescribed anticoagulants - substances that reduce blood clotting and prevent the formation of blood clots. Before the procedure, patient preparation is indicated, which consists of stopping certain medications and prohibiting food intake for 8 hours before stenting.
After the operation, a pressure bandage is applied to the puncture site. After 24 hours the patient can move, and after 7 days he is discharged if there are no complications. For complete recovery, you must follow all the doctor’s instructions: limit physical activity for a week, perform special exercises, follow an anti-cholesterol diet, take prescribed medications.
Advantages of the stenting method:
- no blood loss;
- speed of the procedure;
- rapid postoperative recovery;
- reducing the likelihood of re-stenosis,
- minimal risk of complications compared to other surgical interventions.
But, despite the positive qualities of this technique, stenting is still considered a surgical intervention, and a stent is a foreign body, so there is a risk of negative consequences after such a procedure on the heart. Possible complications:
- myocardial infarction;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- vessel dissection;
- angina attack;
- thrombosis – the formation of blood clots in blood vessels, preventing the free flow of blood through the circulatory system;
- hematoma;
- false or true aneurysm;
- restenosis, that is, repeated narrowing of the vessel walls;
- an allergic reaction to a substance introduced with the catheter (usually iodine) or to the frame itself.
Types of stents
The material from which the stent is made is stainless steel, but the production of stents is constantly being improved - today there are about 400 models made of various alloys.
The possibility of re-narrowing of blood vessels is significantly reduced when using stents coated with a polymer substance containing antitumor cytostatic drugs. They have healing properties, slowing down the division of cells that form atherosclerotic plaques, and are aimed at reducing the risk of new stenosis. In addition, the coating prevents the body from reacting to a foreign body. The disadvantage of this type of frame is the longer healing of the inner wall of the vessel, which can cause stent thrombosis. Therefore, when using a drug-coated device, a longer course of anticoagulants is prescribed. The installation of such a stent is contraindicated for persons with intolerance to its components, the presence of a peptic ulcer, or the need for surgery within a year after stenting.
The operation of coronary stenting allows the patient to significantly improve his health. But in order to maintain it and preserve the effect of surgical treatment, it is necessary to follow certain rules: stop smoking and alcohol, observe moderate physical activity, limit the consumption of foods containing cholesterol, avoid stress and nervous strain.
Sources: https://nailsgid.ru/operatsii/operaciya-na-serdce-stentirovanie.html https://urexpert.online/trudovoe-pravo/bolnichnye/oplachivaemye-dni/v-zavisimosti-ot-zabolevaniya/infarkt-i -invazivnye-procedury.html
Are there complications after laser correction?
The likelihood of complications is very low. After PRK they occur in 2-5% of cases, and after LASIK - in 1-5% of cases. In the first days and weeks after the procedure, side effects may appear that do not affect visual acuity:
- blurred vision at night. Most often, the complication occurs in patients with pupils that are wider than the average norm;
- infection. May develop due to the patient’s failure to comply with hygiene in the postoperative period;
- painful sensations. Lasts until the cornea heals;
- lacrimation in the first three days after correction;
- dry eye syndrome associated with drying out of the cornea after laser evaporation. It is treated with eye drops;
- photophobia in the first 48 hours;
- Drooping of the upper eyelid (ptosis) is a very rare complication that goes away without treatment after a few days.
There are a number of complications that lead to decreased vision:
- poor-quality cut of the flap;
- ingrowth of epithelium under the flap;
- overcorrection or undercorrection (the doctor removed more or less tissue than planned);
- keratitis is an inflammatory disease of the cornea that leads to vision impairment.
Almost all of these complications, except keratitis, require repeated vision correction. They appear within a few months. There are even more severe side effects that occur extremely rarely and lead to a severe decrease in visual function:
- displacement, loss, damage to the corneal flap in the first month after the procedure as a result of mechanical trauma;
- diffuse lamellar keratitis. The reasons for its occurrence after laser correction are not exactly known, but treatment of the disease should begin as early as possible, as it leads to clouding of the cornea and serious vision loss.
Complications after laser vision correction, as already noted, are rare. The entire procedure and its consequences are completely controlled by the doctor. The patient only needs to follow his instructions exactly.
What is cholecystectomy
The gallbladder (GB) is a pear-shaped organ located under the liver. It is designed to accumulate bile and send it into the duodenum. Poor nutrition, unhealthy lifestyle and metabolic disorders lead to gastrointestinal diseases. The organ and ducts can become inflamed and clogged with stones. In such cases, surgery to remove the gallbladder is prescribed.
Regardless of the method of removal, all operations are called cholecystectomy. To indicate the type of intervention, a qualifying word is added - laparoscopic, abdominal, mini-access, single-port.
Although the organ is not vital, the intervention is performed by surgeons with extensive clinical experience. Improper removal of the gallbladder can lead to serious consequences: bleeding, damage to the liver and nearby organs, and effusion of bile.
How long does laser vision correction surgery take?
15 minutes before the procedure, a local anesthetic is instilled into the patient’s eyes. During these 15 minutes, the doctor tells the patient about how the operation will proceed and what needs to be done. The laser action takes about 20-60 seconds depending on the damage. In total, the procedure lasts from 10 to 30 minutes on one eye.
The duration of the operation depends, among other things, on the technique. LASIK is done in 5-7 minutes. Usually, laser vision correction is performed on both organs of vision on the same day. PRK takes about 10-15 minutes on one eye.
After the operation, the person operated on remains in the clinic for 1-3 hours and is sent home. The doctor instructs him on what can and cannot be done after the correction, and sets the time for the next examination. The duration of the operation may depend not only on the degree of pathology that needs to be corrected, but also on the methods used by the doctor.
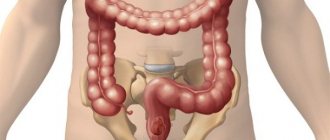
If pathological factors are identified (atypical location or presence of adhesions)
During the operation, it is possible that the surgeon may detect adhesions. They are often a consequence of previous surgical interventions. In addition, access to the abdominal cavity may reveal other pathologies of tissues or organs. Then the surgeon decides to eliminate the identified pathologies. Accordingly, the time allotted for the operation will increase exactly in proportion to the number of pathologies. If the surgeon discovers an atypical location of appendicitis, then the time for surgical treatment will increase significantly. The complexity of this phenomenon lies in the fact that the atypical location is very difficult to diagnose, and therefore can only be detected during surgical procedures. An hour and a half is allotted to perform such an operation.
Localization of pain during inflammation of the appendix
Reference! An atypical location of the inflamed appendix is observed in almost 30% of patients.
There may be additional factors that influence the duration of surgical procedures. For example, the age of the person being operated on. If a child under three years of age is placed on the operating table, the operation will last at least two hours. This is explained by the fact that these babies have not yet fully formed their immune system, so the possibility of complications cannot be ruled out.
Video - What are the complications of appendicitis?
Laser vision correction techniques
There are two main types of laser vision correction surgery: PRK and LASIK. The second technique is constantly being improved, newer methods are appearing that are even safer and faster. LASIK modifications:
- Super LASIK (Super LASIK) is a procedure performed according to the individual characteristics of each individual patient. This operation gives very high results, since it uses a topographic examination of the cornea. Using a topographer, the eye is scanned and the resulting map is transferred to an excimer laser installation for correction. The operation is almost completely automated. It lasts 7-10 minutes on one eye. The laser takes 1-1.5 minutes to operate.
- Femto Lasik (FemtoLASIK). In this procedure, a corneal flap is created using a femtosecond laser. This allows surgery to be performed on very thin corneas. The doctor performs correction of one eye in about 10 minutes.
- Epi LASIK (Epi LASIK). This technique involves creating a flap along the natural interface between the layers of the cornea. The correction lasts as long as the standard LASIK procedure, but the recovery period after Epi LASIK is longer.
- Presby LASIK (PresbyLASIK) - laser correction of presbyopia. During the procedure, the surgeon uses a laser to create a shape of the cornea that is similar to the design of multifocal lenses. Thanks to this, after treatment the person sees well at close and long distances.
In terms of the time it takes the doctor to perform the operation, the techniques practically do not differ from each other. The doctor prescribes a particular procedure depending on the indications and financial capabilities of the patient.
Home care
The bandage should be changed, taking into account the doctor's recommendations. You should not shower until the wound has completely healed. Painkillers are used as prescribed by the doctor. After a month, the patient will be able to return to normal life. You will need to visit the clinic 2 weeks after discharge. To prevent the rehabilitation period from being prolonged, it is necessary to follow a diet. The patient must give up bad habits.
Diet
You need to eat several times a day, portions should be small. Therapeutic nutrition can reduce the burden on the gastrointestinal tract. During the recovery period, you should not eat salty, spicy, fatty, or pickled foods. It is worth giving up alcohol. No smoking. Your diet should include boiled potatoes, pumpkin casseroles, and oatmeal; boiled beets are allowed in moderation. In the future, the doctor can review the diet and make the necessary adjustments.
Laser correction of vision pathologies: advantages
Now you know how the correction works, what the indications are for it, how long the operation lasts and whether there are complications. Despite the presence of the last point, this method of correcting refractive errors has a number of undeniable advantages:
- correction of any vision pathology;
- safety and painlessness;
- a small number of contraindications;
- short recovery period compared to surgery;
- speed of implementation;
- performed on an outpatient basis. You don’t have to stay in the hospital; it’s enough to take a day off or a few days off from work;
- stability of results.
The shape that the cornea takes on during laser vision correction lasts for life. In some cases, if there is no progressive myopia, the person will never need to wear glasses again.
Trachelectomy
Removal of the cervix is one of the rarest gynecological operations. Usually, doctors practice extirpation of the uterus along with the cervix and appendages, or supravaginal amputation of the uterus.
Trachelectomy is the removal of all or part of the cervix. Trachelectomy is performed in the presence of the following pathologies:
- Cervical cancer. It is worth noting that this malignant disease is most often diagnosed in the early stages. This is due to the fact that all women undergo a smear for cytological examination during preventive examinations. Atypical cells appear even at stages 0-1 of cervical cancer, when it is possible to perform a gentle operation and completely get rid of the problem.
- Cervical erosions. A fairly common pathology of the cervix is various erosions. They can cover a fairly large area of the organ, which creates a risk of bleeding. (