Removal of kidney stones is carried out depending on the chemical nature of the neoplasm, its size, the general condition of the patient and many other factors. If the diameter of the stone is small, conservative therapy is used, which includes taking medications, physical activity and a special diet that promotes the evacuation of the stone from paired organs. If it is impossible to cope with the pathology conservatively, surgical intervention is prescribed, which is carried out in various ways. The choice of type of operation depends on the size of the tumors, their composition, and the general condition of the patient.
Indications for surgery
Surgery may be performed in the following cases:
- Ureteral obstruction. This problem requires an immediate solution, so the use of conservative therapy, which gives a slow effect, is not acceptable.
- Increasing renal failure, acute renal failure. If these symptoms are ignored, serious consequences, including death, are possible.
- Pain that cannot be controlled with medication.
- Purulent inflammation.
- Kidney carbuncle. This is the name given to the site of purulent necrosis caused by stones.
- The patient's desire to undergo surgery.
Depending on the degree of damage, the methods of surgical intervention may vary:
- Unilateral urolithiasis. Localization of stones in one kidney makes it possible to preserve the functions of the genitourinary system in case of unsuccessful surgery.
- Bilateral urolithiasis. If the location of the stones is established, the operation can be performed on two kidneys simultaneously. Otherwise, it is carried out in two stages, with a break between them of 1-3 months.
What triggers the formation of gallstones
The location of the gallbladder organ is next to the liver. He takes responsibility for the accumulation of bile secretion in his sac.
It is produced by the liver. If there is no bile, the gastrointestinal tract will not be able to process food. When the secretion enters the intestines, it breaks down food for its beneficial properties. If the gallbladder and liver are not able to work harmoniously, this effect will not be achieved.
Stones will form when one of these organs fails to function normally.
The thing is that bile is not able to move in a timely manner; it can stagnate and change its constituent characteristics. To date, several mechanisms for the occurrence of pathology are known. This is an metabolic and inflammatory process.
Exchange mechanism
If there is a failure of the liver metabolic process, this is a consequence of a person’s unhealthy diet and improper eating regimen. Internal pathologies that occur in the human body can also affect the failure.
Inflammatory mechanism
The appearance of stones in such a situation will depend on changes in the pH composition of bile. There is an increase in acidity.
The inflammatory process disrupts the functionality of the organ, as well as the protective properties of protein fractions. In this case, bilirubin begins to crystallize, and a primary calculus appears.
A build-up of bile components is observed around it, and as a result, a stone is formed.
Types of surgery
The following methods for removing stones are distinguished:
- Lithotripsy. The stone is crushed by exposure to ultrasound through the skin, after which it is removed through the ureter or catheter to the outside.
- Endoscopic operations. A special instrument, an endoscope, is inserted through the ureter or urethra and approaches the location of the stone. Removal is carried out through it.
- Open surgery. Involves direct incision of the kidney and surgical removal of salt deposits.
- Resection. The operation is a type of open, but involves partial removal of the kidney.
Lithotripsy
The essence of the procedure
Since its discovery and introduction into practice (in Russia - in the late 90s of the last century), lithotripsy has earned recognition and taken a leading place in urolithiasis surgery. It eliminates the trauma of surgical intervention and the risk of infection, since the effect is performed percutaneously without any incision.
The essence of the method is based on the effect of ultrasound on various environments of the body. It spreads freely in the soft tissues of the body without causing any harm. When ultrasound encounters a dense salt deposit, it creates cavities and microcracks in it, which leads to a violation of the integrity of the stone.
Modern lithotriptors are generators of ultrasonic shock waves; depending on the country of origin, they can be driven by an electromagnetic, electrohydraulic, piezoelectric element, or even a laser. However, there are no significant differences between them. Visual control of the location and condition of the stone can be carried out using x-rays or ultrasound.
Indications and contraindications
Lithotripsy is performed to remove small stones (up to 2 cm), the localization of which can be unambiguously determined by one of the indicated methods, from living kidneys. In the fifth and final stage of urolithiasis, using this removal method can be dangerous. Note. Some authors (O.L. Tiktinsky) believe that even with large coral deposits it is possible to use ultrasound. But in this case, constant monitoring of the location of all their fragments and readiness for additional endoscopic surgery is necessary.
Surgery is not performed in the following patient conditions:
- Pregnancy.
- Injuries to the musculoskeletal system that do not allow you to take the correct position on the couch.
- The patient's body weight is above 130 kg, height is more than 2 m or less than 1 m.
- Blood clotting disorder.
Progress of the operation
At the very beginning of the use of the technique, general anesthesia was widely used, but today it is obvious that in most cases it is not necessary and doctors limit themselves to epidural anesthesia. Analgesics are injected into the lumbar spine. They begin to act within 10 minutes, and the duration does not exceed 1 hour. In emergency cases and when epidural anesthesia is contraindicated, they are administered through a vein.
The operation is performed in the prone position on the stomach or back, depending on the location of the stone. In the second case, the patients legs will be raised and secured. After the onset of anesthesia, a catheter is inserted into the ureter, through which a contrast agent enters the kidney for better visualization. The patient will not feel any discomfort.
If the stone is larger than 10 mm, a needle is inserted into the renal pelvis. Through the puncture, the formed channel expands to the required diameter, which allows you to place a tube with a tool in it to extract sediment fragments. This lithotripsy is called percutaneous or percutaneous. Smaller stones, after crushing, are excreted in the urine - a remote version of the technique.
A catheter inserted into the ureter is filled with saline solution . It is designed to facilitate the passage of the ultrasonic wave and protect neighboring tissues from unwanted effects. The device is located at the exact location of the stone projection. When it acts, the patient feels soft, painless tremors. Sometimes several approaches are required to break the stone.
Important! In rare cases, the patient may experience pain of varying degrees of intensity during the procedure. You must remain calm and not move. You should report pain to your doctor.
With non-invasive lithotripsy, the patient moves to the ward after the operation and the end of anesthesia. There he is asked to urinate into a jar in order to control the removal of stone fragments. Unpleasant sensations are possible. There may be blood in the urine - this is normal; it is formed as a result of sand scratching the epithelium of the ureter. The release of salt residue may take up to several days after surgery. With percutaneous lithotripsy, the stone will be removed through a tube, but parts of it may be passed out in the urine.
After 2 days, the doctor performs an ultrasound of the kidneys to study their condition. If the operation is successful and there are no complications, the patient is sent home.
Symptoms of urolithiasis
The disease is asymptomatic for some time. The first manifestation of the pathology is pain in the lumbar region. Painful sensations can be very different: in some cases the pain is not expressed, in some it is unbearable, radiating to the lower abdomen, accompanied by nausea and even vomiting. There is often blood in the urine. At times, urination can be very painful. In this case, the liquid has an extremely unpleasant odor and its consistency changes. In some cases, a pebble can block the ureter and cause stagnation of urine. This is a very dangerous condition in which severe intoxication of the body occurs. Small pebbles and sand often come out during urination.
It is important to show the stone to a specialist to find out its chemical composition. Having an idea of the type of stone, the doctor will be able to prescribe proper nutrition and treatment.
Urinary stones are divided into the following types:
- urates – formations from uric acid;
- oxalate – formations from oxalic acid lime;
- phosphate – formations from calcium phosphate;
- carbonate - formations of calcium carbonate.
Read
Healthy foods and vitamins for the kidneys
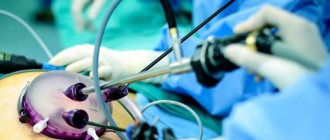
Endoscopic operations
Depending on the location of the stone, the endoscope can be inserted into the urethra (urethra) or higher into the bladder, ureter, or directly into the kidney. The lower the deposits are located, the easier the operation is. It is performed under general anesthesia or intravenous anesthesia to remove stones up to 2 cm. Indications are:
- Ineffectiveness of lithotripsy;
- Long-term presence of a stone in the path of the ureter;
- “Stone paths” (residual formations) after exposure to ultrasound.
The operation, despite its apparent simplicity, requires a highly qualified surgeon and high-quality modern equipment. A urethroscope is inserted into the patient's urinary canal. This device consists of a tube with a mirror that allows the surgeon to directly detect stones. Once the tube reaches them, they will be removed. The most modern technique is laser removal of kidney stones. The action of the beam is transmitted through a special fiber, which is inserted into the urethroscope.
In some cases, the installation of a stent is required - this is a catheter that prevents compression of the ureter (obstruction). It is placed for up to several weeks. Removal also occurs without incisions using an endoscope.
How do stones pass out?
For stones up to 1.5 cm in size, therapy is aimed at dissolving and removing the remains of the formation. For this purpose, special drugs are prescribed. When stones leave the gallbladder, their movement can provoke colic. This process occurs gradually, sometimes over several hours:
- First, the stone with bile gets to the beginning of the duct, which causes its blockage.
- Under the influence of bile pressure, the mouth of the duct stretches and the stone gradually continues to move further. At this moment the person feels severe pain.
- When the calculus enters the duodenum, the patient’s condition returns to normal, and dramatic relief occurs.
- The pebble leaves the body along with feces.
Open surgery
In recent years, this type of intervention has been performed extremely rarely. Indications for it are:
- Constant relapses;
- Large stones that cannot be removed in any other way;
- Purulent inflammation.
Open surgery is performed under general anesthesia and is abdominal . This means that it affects the body cavity. Excision occurs through all layers of tissue. The presence of a stone in the renal pelvis is considered favorable. This reduces the invasiveness of the operation. It is also possible to open the ureter and remove the stone from there.
The modern option for performing the operation is laparoscopy. Removing the stone through a small incision. A camera is inserted into it to transmit images to a large screen. Laparoscopic stone removal is carried out only for special indications and is often replaced by endoscopic operations.
When is it necessary to remove stones?
Stones up to 0.7-0.8 cm in size can be treated with stone-dissolving drugs. It is recommended to remove stones surgically if:
- frequent renal colic;
- blockage of the renal pelvis;
- disruption of urine outflow;
- purulent inflammation of the kidney tissue;
- ineffectiveness of conservative treatment.
There are different ways to remove stones - with dissection of the renal tissue (parenchyma) or pyelocaliceal structures, through laparoscopy or open access, with contact or remote crushing. The surgeon chooses the appropriate treatment method taking into account:
- type of stones - their chemical composition, diameter, shape;
- age of the patient;
- associated complications;
- contraindications to radical and minimally invasive operations;
- location of stones.
Conservative treatment is recommended for relatively small stones - up to 0.8 cm. Surgery is prescribed for complicated nephrolithiasis, large stones, and decreased performance.
Removal of part of the kidney
Indications and contraindications
This operation allows you to save the organ, which is especially important if you have only one working kidney. Resection is performed in the following cases:
- Multiple (multi-locular) stones located at one pole of the organ.
- Constant relapses of the disease.
- Necrotic lesions.
- The last stages of urolithiasis.
Important! A contraindication is the patient's serious condition, if doctors assume that the operation may aggravate it.
Progress of the operation
Resection is performed under general anesthesia. The patient is placed on his healthy side, under which a cushion is placed. The surgeon makes an incision. After this, he pushes the underlying layers of tissue apart. A clamp is applied to the part of the kidney with the ureter to prevent bleeding, since this is where the maximum concentration of blood vessels is located.
After this, the affected area is excised. The edges are stitched. A drainage tube is removed from the kidney. After this, the wound is sutured. The drainage tube remains in the kidney for 7-10 days after surgery; after this period, provided there is no separation of pathological contents, it is removed.
Methods for diagnosing pathology
Today, medical scientists have achieved a truly great breakthrough. To determine gallstone pathology, many methods are used.
All of them are distinguished by their reliability. Only the most important thing will be the analysis and examination of the person who came with complaints.
You should consult a gastroenterologist. An experienced specialist will conduct a thorough inspection. Thanks to this, he will be able to understand how serious the patient’s problem is.
The specialist is able to determine the enlargement of the gallbladder, as well as the degree of sensitivity of the organ.
Of course, it is worth understanding that only through a thorough and attentive analysis of all clinical manifestations can an accurate diagnosis be made.
For these purposes, it is also sometimes necessary to resort to additional methods of examining a person.
This time it will be impossible to do without an ultrasound. Also, specialists often send cholecystography for analysis. These methods allow you to clarify existing changes in the area of the gallbladder and understand whether there are stones in it.
Plus, urine and blood tests are prescribed. Sometimes laboratory tests of gallbladder bile may be required. For such purposes, specialists use the method of duodenal intubation.
Complications
Each of the described types of operations may have a different probability of undesirable consequences, but in general they can be presented in the form of the following list:
- Relapses. Recurrent stone formation is not uncommon with urothiasis. The operation only combats the consequences, but does not eliminate the cause. That is why it is important in each specific case to find out why urolithiasis developed, to give the patient recommendations for lifestyle changes, diet and, possibly, taking medications.
- False relapses. This is the name given to the remaining unremoved stone fragments. This outcome of the operation is becoming less and less common due to the improvement of methods of its implementation and constant monitoring of its progress.
- Infection. Even with minimally invasive operations such as endoscopic ones, there is a risk of pathogens entering internal organs. To prevent infection, a course of antibiotics is prescribed even if the patient is in good condition.
- Acute pyelonephritis is inflammation of the renal pelvis. It occurs due to the displacement of stones, prolonged residence of their fragments in the kidney and the accumulation of infiltrate (fluid) around them.
- Bleeding. Most often occur during open operations. To prevent them, irrigation of the kidney with a solution containing antibiotics is used.
- Progression, exacerbation of renal failure. For prevention, hemodialysis (connection to an artificial kidney machine) is used before and after surgery.
- Heart rhythm disturbances, hypertension (high blood pressure). The complication occurs more often after ultrasonic destruction of stones due to an incorrect assessment of the patient’s condition.
Who is at risk
Women are most often affected by cholelithiasis. Doctors explain this by frequent childbirth and taking hormonal drugs. Favorable conditions for the appearance of stones most often include:
- Surgery to cut the vagus nerve and remove the lower part of the ileum.
- Sudden weight fluctuations.
- Lack of fiber in the daily diet.
- Cool climate.
- Some drugs can provoke the appearance of stones: Octreotide, Cyclosporine and others.
- In some cases, cholelithiasis is inherited. Therefore, if one of the parents had cholelithiasis, you should be careful and undergo an ultrasound examination every two years.
- People with diabetes and cirrhosis of the liver are also at risk.
Excessive consumption of fried, smoked and salty foods has an adverse effect on health and provokes the appearance of cholelithiasis. Constant stress also harms the organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
Cost of surgery for urolithiasis, carried out under compulsory medical insurance
The most common type of intervention is lithotripsy. It is carried out in most clinics and medical centers dealing with urological diseases. The average price is 20,000 rubles. The operation is free of charge only for persons under 18 years of age in public medical institutions.
According to the compulsory health insurance policy, endoscopic, open surgeries and kidney resections are usually performed in hospitals. The first type of procedure in private clinics costs from 30,000 rubles. The price does not include medications necessary for rehabilitation and a place in a hospital. Open abdominal surgeries are rarely performed in private clinics; the price must be determined privately. The cost of partial kidney removal starts from 17,000 – 18,000 rubles and can reach 100,000 rubles. The price is shown only for the procedure.
Prevention and nutrition
There are products that can remove excess cholesterol from the body, and, therefore, prevent the formation of stones. These include fermented milk products and whole milk. And also buckwheat and oatmeal, green tea. Doctors strongly advise not to ignore breakfast.
Like any other disease, cholelithiasis is easier to prevent than to cure. People who already have stones are recommended to exclude smoked meat and fish, onions, garlic, chocolate, and butter from the daily menu. And also reduce to a minimum the consumption of vinegar, hot peppers and fried meats, which contain huge amounts of cholesterol. During the period of exacerbation of the disease, it is prohibited to drink alcohol.
Patient reviews about the operation
The largest number of reviews on the Internet are devoted to lithotripsy. Many patients were satisfied with the result. As a rule, the following negative aspects are noted:
- High price. Often the decision to undergo surgery must be made suddenly and as soon as possible. Not every patient has a reserve of several tens of thousands of rubles.
- Painful sensations during surgery. This happens quite rarely, and patients note that the discomfort cannot be compared with the agony of renal colic.
- Risk of relapse and lack of guarantees.
With other operations to remove kidney stones, especially those performed free of charge, patients are concerned about the tactics of the chosen treatment. Not every doctor explains to the patient the essence of his actions and prescriptions, especially when it comes to elderly patients or their relatives. The wrong choice of the type of surgical intervention and the lack of improvement are usually difficult for people entering a medical facility.
Urolithiasis is a common disease that develops as a result of the combined action of many factors. And although modern methods of surgical treatment can successfully solve this problem, the latest developments in the field of ultrasonic crushing are not available to everyone. The outcome of treatment cannot always be predicted, and with any type of therapy the risk of relapse remains. Therefore, if there is a predisposition to the disease or its presence in relatives, all measures must be taken to prevent urolithiasis.
Consequences of gallstone disease
The formation of stones occurs in stages:
- Violation of the properties of bile. It is quite difficult to detect problems at this stage, since no clinical symptoms are observed. The problem is diagnosed during an ultrasound, which detects an increase in cholesterol. A biochemical examination of bile can show a decrease in the volume of bile acids.
- The latent stage is characterized by an asymptomatic manifestation of the disease, but with visible stones on ultrasound.
- The third stage is characterized by biliary colic of varying duration, mainly in the evening hours.
- At the fourth stage, various complications of cholelithiasis are diagnosed: acute cholecystitis, an inflammatory process in the gallbladder, hydrocele of the gallbladder is formed when the duct is completely blocked. Bile, with all its might, trying to break out, begins to be absorbed into the walls of the bladder. It, in turn, increases. The inflammatory process is quite sluggish, no pain symptoms occur, as the walls atrophy and stop contracting; bubble perforation. If there is a large accumulation of bile, the gallbladder may rupture and the entire contents will enter the abdominal cavity, causing peritonitis; an abscess inside the liver, when pus begins to accumulate in the organ; gallbladder cancer. The presence of stones in the organ is a predisposing factor for the development of a tumor; subhepatic jaundice appears when the common bile duct is blocked by a stone. Symptoms include discoloration of stool, since bile cannot enter the intestines. And the darkening of urine up to a brown color is associated with an increase in bilirubin.
Gallstone disease is an epidemic of our time. The way people live is to a greater extent to blame: poor nutrition, non-compliance with eating schedules, ignoring the body’s signals about the presence of problems. Therefore, if the first symptoms of the disease appear, you should undergo an examination to prevent surgical intervention to remove the gallbladder.