What does hysterosalpingography determine?
Hysterosalpingography is a method of medical examination of the uterus for the internal condition of tissues and fallopian tubes for patency. In practice, two types of GHA are used:
- Using ultrasound
. It is used primarily to determine abnormalities in the uterine cavity, the presence of developmental anomalies, lesions, erosions and other probable causes of infertility.
It is most often possible to detect spots and other destructive changes using GHA with ultrasound. Usually, after such abnormalities are detected, additional examinations and tests are prescribed to accurately determine the type of lesion and prescribe therapeutic measures. The choice of the type of HSG is determined by the doctor depending on the goals and possible suspicions, in particular, in case of female infertility.
HSG can cause painful complications, so after the procedure it is necessary to follow good hygiene and doctor's recommendations for recovery.
The procedure can be prescribed if polyps, fibroids, adenomyosis, polycystic disease, endometriosis, etc. are suspected. Infertility is usually the indication for diagnosis. Before the procedure, a comprehensive examination is carried out.
Diagnostic process
Before the actual procedure in women, a smear test for flora is required to determine the absence of inflammation and other abnormalities. The diagnosis itself proceeds as follows:
- The patient is immersed in the gynecological chair.
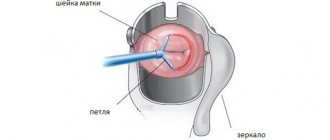
- A speculum is placed in the vagina. A catheter and contrast agent are inserted through it.
- An ultrasound and (or) X-ray machine is connected to the work.
The process can bring discomfort and pain. Therefore, a local anesthetic is used before inserting the catheter. The examination result will be obtained immediately on the screen or using images, depending on the choice of technology. If in this case one or more spots are detected, the doctor will make a preliminary conclusion and prescribe additional studies.
Causes of spots and their types
White, red, or dark spots may appear on the screen or pictures. Each of them indicates the occurrence of a separate deviation. In this case, the spots can be almost invisible and do not cause discomfort to the patient.
Spots in the uterine cavity do not always require mandatory treatment.
During the HSG procedure, a contrast agent is injected, which also forms spots.
If it fills the uterine cavity, this indicates patency of the fallopian tubes. This result can be considered positive and does not require additional intervention.
Leukoplakia
It is a separate symptom indicating keratinization of individual cells of the uterine cavity. Causes:
- Development of the papilloma virus
. It manifests itself in the formation of convex neoplasms of a grayish tint. The danger is the further development of infection and the degeneration of the spot into a malignant tumor. - Hormonal imbalance
. It can cause keratinization of cells, but is not a prerequisite for the appearance of oncology, and therefore does not pose a danger.
Also, spots can form due to infectious lesions, decreased immunity, traumatic damage to the membrane, or previous surgery. For diagnosis, tests for the presence of infections and hormone levels are used. A biopsy of the affected area is also required.
Cervicitis
The main prerequisite for the development of the lesion is sexually transmitted infection. In this case, the patient experiences:
- nagging pain in the abdominal area;
- discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- pain during sexual intercourse and urination.
The formation of a spot indicates scarring of the tissue affected by the infection. The formation is rarely subjected to radical removal. Antibiotics and other medications are usually required. Both sexual partners are treated.
Eritoplakia
It is an atrophied and thickened layer of the uterine epithelium, formed by a red dense spot. The etiology of the lesion is not completely clear; the disease itself is rare. Upon visual examination, the doctor may detect a reddish area of the mucosa with a thin upper layer of epithelium, through which blood vessels are visible.
Eritoplakia in itself is not considered a dangerous lesion, but requires therapy. For this purpose, the procedure of cryodestruction, laser treatment, and conization is used. Further, constant monitoring is required to prevent relapses.
Ectopia
The lesion is otherwise called pseudo-erosion. A common cause of formation is menstrual irregularities in women of childbearing age. Ectopia without complications does not require mandatory treatment; in such situations, observation is necessary. In other forms, conservative or radical therapy is carried out.
Ectopia can be congenital or acquired.
As ectopia progresses, painful symptoms do not appear. There may be an increase in the number of white spots on the surface, as well as the appearance of reddish discharge. The presence of hyperemic areas requires treatment.
Ectropion
The formation is a small area of the uterine mucosa, everted to the surface due to damage to the muscle fibers. These processes are possible during surgical treatment of lesions, abortions, and childbirth. Tissue ruptures are among the complications after complex diagnostic procedures.
Ectropion is classified as a type of pseudo-erosion. The progression of the condition is usually not accompanied by unpleasant symptoms and pain. Complex cases of damage are treated. For this purpose, surgery is used.
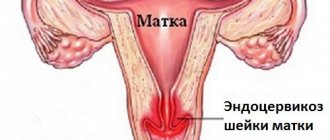
Endometriosis
The progression of the lesion is accompanied by the growth of tissue, similar in structure to the endometrium, in the vaginal cavity (normally, the endometrium should be located exclusively in the cavity of the uterus itself). Such processes arise as a result of traumatic injuries, diagnosis, and biopsy. Sometimes endometriosis becomes a complication after childbirth.
Unpleasant symptoms do not appear with the development of endometriosis. Bloody discharge may appear after sexual intercourse, before and after menstruation. When a lesion is detected, mandatory treatment is not always required. But a biopsy is necessary to exclude malignancy.
Why does it occur
The causes of the development of retrocervical endometriosis have not been fully identified. There are five theories of the occurrence of this pathology.
Hormonal
The hormonal theory is based on the negative impact of increased estrogen levels on the body. This can occur under conditions of normal progesterone levels (absolute increase). A relative increase is observed when estrogens remain normal, but progesterone levels are reduced.
Immune
Against the background of altered immunity, the formation of phagocytic cells that destroy the excessively growing endometrium decreases. Unlimited growth leads to its spread to tissues not adapted for this.
Implantation
The spread of the uterine layer occurs during its transfer with menstrual blood through the cervical canal. In the presence of a number of factors unfavorable for the reproductive system, the immune response of the woman’s body decreases . As a result, the endometrium is introduced (implanted) into the epithelium of the cervix. However, this process requires an increased level of estrogen. That is, without a hormonal imbalance, implementation does not work.
Metastasis theory
This theory is based on the idea that endometrial cells spread hematogenously to organs not intended for the presence of such cells. They are introduced and serve as a source of tissue formation similar to a benign tumor.
Modern theory
Modern medicine considers the simultaneous coincidence of several unfavorable factors as the cause of the formation of cervical endometriosis. The conditions for the development of pathology include the influence of the following:
- a decrease in the overall immune response, which leads to insufficient destruction of these types of cells that enter other organs;
- heredity;
- surgical treatment of the uterus, abortion and curettage, rough cauterization of erosion;
- hyperestragenemia (increased estrogen in the blood);
- changes in the structure of the cervix;
- iron deficiency in the blood caused by impaired absorption or insufficient dietary intake;
- chronic pathological processes of a woman’s reproductive or urinary system;
- imbalance in nutrition, obesity and consumption of large amounts of meat and milk;
- long-term use of intrauterine contraception;
- endometriosis of the cervical stump, which often occurs after supravaginal amputation of the reproductive organ;
- unfavorable factors of the external environment, especially the increased content of heavy salts.
Important! Cervical endometriosis develops against the background of a hormonal disorder (discrepancy between estrogen levels and progesterone levels). Initially, the pathology is benign, but there is a high risk of degeneration into a malignant neoplasm. Treatment is necessary.
Read more Nipple thrush symptoms
Treatment of spots in the uterine cavity
The choice of treatment methods depends on the accurate diagnosis. In such situations, one of three options is usually used:
- observation (in this case, the patient undergoes periodic examinations, auxiliary treatment may be used in the form of vitamins and hormonal-normalizing agents);
- conservative therapy (includes taking hormonal drugs, eliminating systemic lesions that cause changes in the uterine cavity, using local medications);
- surgical intervention (includes coagulation, laser therapy, cryotherapy, cauterization, radio wave non-contact surgery).
Observation is recommended for uncomplicated endometriosis, leukoplakia without pathological causes, and ectopia. Additionally, maintenance therapy may be offered, including taking vitamins A, E, C, group B. It is also recommended to consume foods and dietary supplements with Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids. A restorative diet rich in fiber, fresh vegetables and fruits is recommended.
The form of conservative therapy is developed individually and directly depends on the causes of the lesion. Typically it includes:
- antibacterial local drugs and oral agents;
- antiviral medications;
- antifungal medications;
- immunostimulants;
Often, vitamin complexes and diet are also prescribed as a supplement. Probiotics are used to restore vaginal microflora. Systemic diseases that have become prerequisites for the development of uterine pathology are considered and eliminated separately. Surgical methods are described in the table.
| Treatment method | Description | Peculiarities |
| Thermocoagulation (cauterization) | Exposure to temperature on the affected area | The procedure is simple, leaves virtually no traces and does not cause complications. The disadvantage of the method is the difficulty in determining the depth of the lesion to remove the formation |
| Cryodestruction | Exposure to liquid nitrogen | In most cases, treatment is well tolerated by patients, but sometimes prolonged discharge may occur. A nitrogen sensitivity test is required before surgery to prevent allergies. |
| Radio wave surgery | The destruction and elimination of pathological tissues is carried out through non-contact exposure to the affected area by a wave | The patient does not feel pain or experience any other unpleasant sensations, and a scar forms at the site of the lesion |
| Laser | Laser exposure followed by heating the affected area | The method is painless and can affect the deep layers of the epithelium without causing bleeding or leaving a scar. |
The most radical and painful is surgical removal of the uterus under general or epidural anesthesia. The method is indicated for cancer lesions and can be combined with chemotherapy. After the operation, a recovery period is indicated, including a diet based on healthy eating rules, taking antibacterial medications and vitamins. A doctor's supervision is also necessary to prevent complications.
Important things to remember about uterine health
To determine the form of the lesion and the reasons for its appearance, it is necessary to undergo not only HSG, but also other examinations and tests. Not all neoplasms are subject to therapeutic measures, but in some cases it is possible that benign tumors may transform into malignant ones. To eliminate the lesion, conservative and radical measures are used separately or in combination.
In a healthy state, the cervix has the classic color of the normal mucous membrane - light pink, uniform. Any deviations from the norm most often indicate some kind of pathological process. So, during inflammatory processes or infections, the mucous membrane becomes hyperemic and has a rich red tint. What do the white spots that appear on the cervix mean? It is quite difficult to unambiguously determine the cause of this phenomenon: the symptom may indicate several diverse gynecological pathologies.
Characteristics of background processes
Even in teenage girls, the gynecologist can see displacement of the columnar epithelium during examination. After colposcopy, it becomes clear that it is bright red in color. However, it is impossible to paint it with Lugol's solution. This condition is often called pseudoerosion or ectopia. It can be congenital or acquired. But these are not yet precancerous conditions of the cervix, so such erosions do not require treatment. You just need to monitor them regularly.
Read more Fetal position during pregnancy
If the patient's mucous membrane of the cervical canal everts onto the vaginal part of the cervix, then this condition is called ectropion. This is a combination of scar deformation of cervical tissue and pseudo-erosion. Upon examination, the doctor may see a deformed neck with a slit-like or gaping pharynx with red areas of columnar epithelium. Often they can have a transformation zone.
Another background process is leukoplakia, the name of the disease is translated as “white spot”. With this disease, the stratified epithelium becomes locally keratinized. In this case, infiltrates form around the stromal vessels. Leukoplakia can be simple, then it is classified as a background process. If atypical cells appear with this disease, then we are talking about precancer.
Another disease is erythroplakia, but it is quite rare. This name literally translates as “red spot”. In this condition, the stratified epithelium atrophies and thins down to several layers. Intermediate cells disappear. Vessels are visible through the thinned epithelium, so the areas look like red spots.
Also, during examination, the doctor can see growths covered with epithelium. They are called polyps. These are bright pink formations that can be leaf-shaped or oblong. They hang from the throat of the cervix.
Leukoplakia
Often, whitish spots on the cervix are evidence of leukoplakia. This is not an independent disease, but rather a symptom indicating keratinization of the epithelial layer. Despite the fact that the disorder may not cause obvious discomfort, it occurs against the background of other pathological processes in the genital area.
There are three forms of leukoplakia:
At the initial stage, small flat light gray spots appear. They do not cause discomfort; they can only be noticed during a gynecological examination. In the absence of proper treatment, the disorder can progress, turning into a warty form. In this case, the cervix becomes uneven, lumpy, white spots rise above the solid healthy epithelium.
Possible reasons
It is almost impossible to accurately determine the causes of leukoplakia.
The integumentary epithelium of the cervix normally becomes keratinized and should not have a white color. In most cases, pathology occurs in women who suffer from hormonal imbalances, especially regarding estrogen levels.
Flat or simple leukoplakia is considered the most favorable type of keratinization in terms of cancerous degeneration. Such white spots are often the result of improper healing of the site of destruction when the cervix was subjected to physical treatment due to benign pathologies.
Verrucous or verrucous leukoplakia is a consequence of active human papillomavirus infection. The human papillomavirus with a high risk of carcinogenesis can lead to malignancy of the area of excessive organization of the cervical epithelium.
Violations can also be caused by:
- bad habits;
- disruption of the endocrine or immune systems (hypothyroidism, hyperfunction of the adrenal cortex);
- infectious diseases of the gynecological tract;
- ovarian dysfunction (PCOS);
- trauma and damage to the mucosa.
Treatment options
Treatment methods are selected individually based on the patient’s age, the severity and shape of the white spots that affect the cervix, and reproductive functions. The gynecologist makes the final decision after a detailed examination, which includes:
- PCR tests for STIs, including varieties of human papillomavirus;
- extended colposcopy;
- biopsy if necessary;
- cellular composition of white spots on the cervix - scraping for cytogram;
- tank culture of genital tract secretions or Femoflor analysis.
First of all, the factor that provoked the appearance of spots and changes in the mucous layer should be eliminated.
The white plaques themselves can only be removed surgically. The following methods are used:
- laser coagulation;
- radio waves;
- conization;
- cryotherapy.
Chemicals with a cauterizing effect are used less frequently. Treatment should be carried out five days after the end of menstruation. If the patient is pregnant, therapy is postponed.
Cervicitis
In some cases, white spots appear in certain forms of cervicitis, an inflammatory process that affects the vaginal segment of the cervix. The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- dull or nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- pathological discharge, mucous or mucopurulent consistency, which has an odor different from normal;
- pain during urination;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse.
Pathology is caused by sexually transmitted infections. They lead to the formation of erosion, which in some situations becomes an area of keratinization - a white spot.
Human papillomavirus
HPV – non-enveloped DNA – containing a virus from the papovavirus family. Human viral pathogens are divided into 5 groups.
Viruses from alpha groups are capable of penetration into the epithelium of the cervix with the subsequent development of precancer or cancer.
Betta, gamma, etc. persist in skin cells.
Genome size is 8000 nucleotide pairs.
HPV does not have a lipoprotein shell, which makes it stable and resistant to adverse factors.
The virus does not have a specific risk group, or all people who are sexually active can be included in the risk group.
According to data provided by the World Health Organization, 75% of women of reproductive age have had an episode of HPV infection at least once in their lives. This prevalence of the virus is determined by social, economic, hygienic, and behavioral factors.
In Russia, positive results when tested for HPV are detected in 45% of women, while, in addition to human papillomavirus infection, other sexually transmitted infections are detected.
The peculiarity of HPV is that after entering the body, the virus can persist for a long time (be in a dormant state), but as soon as the immune system malfunctions, viral pathogens begin to actively multiply, and it is then that symptoms of papillomavirus infection appear.
A viral pathogen is able to “deceive” the immune system due to its properties:
• absence of viremia, • limitation of the replication cycle by the epithelium, • absence of cytolysis, • local immunosuppressive (immunosuppressive) effect of specific viral proteins.
Cervical papilloma caused by HPV is dangerous because it can cause the development of cervical and anogenital cancer.
It should be noted that the ability of HPV to lead to the development of cancer is very variable.
Table of papillomaviruses of different types
Based on their oncogenic potential, papillomaviruses were conventionally divided into 3 groups:
• unable under any circumstances to lead to tumor pathology – non-oncogenic • in certain circumstances, cancer may develop – low-risk oncogene viruses. • under certain conditions lead to malignancy, are a confirmed cause of cervical cancer - oncogenic.
Cyst on the cervix
A cyst is a benign neoplasm that forms in the cervical canal or in the area of the vaginal part of the cervix. It consists of glandular cells that are filled with fluid and visually resemble convex white spots.
Such spots are not leukoplakia. The neoplasm can be single or have multiple manifestations. When the cyst reaches a size of more than one and a half to two centimeters, which is extremely rare, the pathology is characterized by the following signs:
- bloody, bloody, brown discharge;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse.
A cyst can be diagnosed during examination using a gynecological speculum or ultrasound.
During the examination, the state of hormonal levels is necessarily assessed and smears are examined for urogenital infection. The pathology does not pose any particular danger and, as a rule, requires only observation. Large cysts that are prone to growth are recommended to be opened.
Cervical papillomatosis
Papilloma is a benign tumor resulting from a disruption of the structure of the integumentary epithelium due to changes in the structure of cells. The cause of the disease is the human papillomavirus, which is transmitted in three ways:
- during sexual intercourse;
- when carrying out medical manipulations in violation of the rules of the sanitary and epidemiological regime;
- from mother to child during childbirth.
After infection, the virus can “dormant” for a long time, and only when the body’s immune defenses are suppressed does the cervix become covered with white papillomas. The apex of each condyloma has an area of excess keratinization, which gives it a whitish tint, causing cervical papillomatosis to look like a white spot. This area of the cervix is not considered leukoplakia. Papillomas are initiated by HPV with a low risk of carcinogenesis, unlike leukoplakia
On the neck, papillomas can be flat or pointed. Flat papillomas are considered the least favorable in terms of oncology. A significant role in the degeneration of such lesions into cancer is played not only by the state of immunity, but also by the vaginal biocenosis.
As the pathology develops, the formations can be grouped, forming one large growth that looks like a white spot.
Symptoms
With genital or flat condylomas, certain symptoms occur:
- unpleasant odor of vaginal discharge;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- sensation of itching and burning in the vagina;
- spotting after sexual intercourse;
- slight pain in the lower abdomen.
If any of these symptoms occur, you should visit a gynecologist.
If a gynecologist discovers white spots on the cervix, he will conduct a detailed examination to differentiate between papillomatosis and leukoplakia.
Necessary therapy
If the diagnosed white spots on the cervix are papillomas, treatment methods are selected individually for each patient. Certain factors matter:
- age of the patient;
- type of detected HPV;
- cytology test results;
- type of neoplasm;
- immune status.
If necessary, physical or chemical removal of formations is carried out. Antiviral drugs are used to suppress the activity of the virus itself. For the best result, general strengthening therapy with vitamins is carried out.
Symptoms of papilloma virus and causes of appearance in the cervix
The cause of infection is intimate contact with an infected person. The infection is transmitted only through sexual contact, regardless of the type of contact. Infection is possible through oral, anal and genital contact.
During sexual intercourse, microtraumas of the urogenital tract occur. The virus penetrates into the deep layers of the dermis. Infection through household contact with strains that cause the appearance of malignant neoplasms in the reproductive system is unlikely.
For a long time, HPV remains dormant in the body. When the immune defense decreases, the virus attacks, and condylomas appear in the genital area, urethra, and perianal fold.
When growths appear on the vulva or vaginal opening, the following symptoms develop:
- itching;
- burning;
- difficulty defecating and urinating when papilloma is localized in the urethra or rectum.
When the formations are localized on the cervix, there are no symptoms. Pain and the appearance of traces of blood in the vaginal secretion indicate an active cancer process.
Dysplasia
Cervical dysplasia is a background pathology, which is characterized by changes in the epithelium of a pathological atypical nature. The disease is a precancerous process, but in the initial stages it can be successfully treated. Visually, dysplasia looks like areas of excess tissue growth with partially hyperemic areas and flat white spots that partially cover the cervix.
The disease does not have pronounced symptoms, but bloody discharge and discomfort during sexual intercourse can cause concern. Timely diagnosis is complicated by hidden symptoms. Most often, dysplasia is discovered only during a routine examination.
- symptoms of an acute inflammatory process;
- itching;
- burning;
- mucous or mucopurulent discharge with an unpleasant odor.
Pathology has no age restrictions. Women of reproductive age are at particular risk. The disease can develop even during pregnancy. To eliminate the possibility of white spots turning into cancer, it is necessary to undergo a full course of treatment.
Possible reasons
Dysplasia occurs when the differentiation of epithelial cells is impaired. The epithelium of the cervical uterus consists of five layers, the ancestor of which is the germinal basal layer of undifferentiated cells. HPV with a high risk of carcinogenesis affects this layer. As a result, the entire surface epithelium becomes atypical. Areas of white spots or leukoplakia in the area of dysplastic lesions of the cervix are a warty appearance, which is dangerous due to the increased likelihood of degeneration into cancer.
The provocateurs of such violations are:
- insufficient activity of cellular and humoral immunity;
- presence of bad habits;
- chronic diseases of the genital area;
- hormonal problems;
- STI;
- trauma to the cervix;
- heredity.
In rare cases, the pathology goes away on its own without medical intervention.
Treatment
When choosing appropriate therapy, the degree of the disease, the size of the white spots on the cervix and the general condition of the patient’s body are taken into account. Special attention is paid to individual risks of changes leading to the transition of dysplasia to cancer.
At the initial stages, concomitant or background diseases are treated and the normal vaginal microflora is restored. To restore the normal structure of the epithelial layer, eubiotics, probiotics and vitamins are used.
Considering the volume of the lesion, destruction is carried out by laser, liquid nitrogen, radio waves, but more often conization is performed.
The main task of any type of treatment is to eliminate the site of pathological changes and remove white spots with altered cells. The cervix should return to physiological normal.
A healthy cervix has a uniform pink color, but not saturated. If there are deviations from the norm, this may mean the presence of pathologies. White spots on the cervix are a fairly serious pathological condition that can mean the presence of several diseases and can degenerate into a malignant lesion. Such spots are also called leukoplakia. This pathology is characterized by keratinization of the epithelium.
Reasons for the development of dysplasia
Provoking factors also include:
– immune and hormonal disorders;
– the presence of erosive foci – the transition zone between flat and columnar epithelium, located on the outer part of the cervix, is dangerous;
– presence in the body of a highly oncogenic type of HPV.
The risk factors are the following:
– earlier onset of sexual activity by a girl at a time when the epithelium is not yet normally formed;
– long-term use of intrauterine and hormonal contraceptives;
– presence of sexually transmitted infections;
– poor nutrition with deficiency of vitamins C, A and beta-carotene.
It was also found that men’s hygiene also influences the occurrence of these female diseases. Smegma, which accumulates under the foreskin, can cause precancerous conditions of the cervix to begin to develop. This is due to the presence of carcinogenic substances in it, which during sexual intercourse fall on the cervix.
Causes
To date, scientists have not determined the exact causes of this disease in the female body. And yet there is a theory that such a dangerous manifestation as leukoplakia is directly related to hormonal imbalances.
Note! According to statistics, changes in the cervix are most often observed in patients with a history of infectious pathologies. For example, chlamydia, human papillomavirus, ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis, bacterial vaginosis, etc.
Additionally, inflammation localized in:
- Uterine appendages – adnexitis.
- Cervicitis - cervicitis.
- Endometrium in the uterus - endometriosis.
Diagnostics
The first diagnostic methods are laboratory tests. Due to the seriousness of the pathology, their list is quite expanded:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- cytological analysis of a vaginal smear;
- culture of the vaginal flora;
- blood and urine tests for hormones, including sex hormones.
A modern laboratory test is the polymer chain reaction. Using this analysis, it is possible to determine genetic disorders in the body.
An examination by a doctor is also important, as there may be, in addition to a white spot, a red spot on the cervix. In this case, diagnosis and treatment are prescribed individually.
The main effective diagnostic methods for the presence of white spots are colposcopy and cervical biopsy.
Colposcopy
This study is carried out using a special colposcope apparatus, which can be used to examine the vagina and cervix in detail. In this case, you can take biological material for a biopsy, or a smear for cytology.
Such a study helps to accurately examine the condition of the mucous layer and diagnose many gynecological diseases, including leukoplakia. With this pathology, using a colposcope, the doctor can see those spots that cannot be seen with the naked eye during a normal examination using mirrors.
When performing colcoscopy, Lugol's solution is also used. This is called the Schiller test. In this case, iodine-negative zones appear, that is, pathological foci that are not stained. It is considered normal if the mucous membrane is evenly colored after treatment with iodine.
Kolkospokia is effective in diagnosing precancerous transformation.
Biopsy and histology
Biological material is collected during colposcopy. During the biopsy, the cervical canal is scraped, namely, from the most suspicious place.
With histological examination, one can understand how deeply the pathological process has affected the epithelium of the cervix. Leukoplakia exhibits the following clinical picture on histology:
- The presence of a stratum corneum, and under it a granular layer;
- Epithelial proliferation;
- Thickened epithelium in pathological foci;
- Hyperkeratosis, etc.
Diagnostics: what examinations are needed for papillomavirus infection
Examination on a gynecological chair
If, during examination, a woman’s cervical erosion is visualized, then a diagnosis of HPV will be justified, since the cause of the formation of an ectopic defect may be papillomavirus infection.
Tests with acetic acid and Lugol's solution allow you to diagnose manifestations of papillomavirus infection.
After processing, pay attention to the presence of the following signs:
• acetate epithelium, • mosaic, • punctation, • presence of an atypical focus.
Papilloma on the cervix, after treatment with Lugol’s solution, acquires a coating similar to “semolina”.
A characteristic feature is the detection of cells with koilocytosis and dyskeratosis. In this case, we can assume the development of malignancy CIN (carcinoma in situ).
• Biopsy for cervical papilloma.
Carrying out a biopsy of the cervix and curettage of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal with subsequent histology is justified in the following cases:
1. after receiving atypical cells during cytological analysis, 2. with obvious signs of HPV infection, 3. with colposcopy (the oncogenicity of the virus is not taken into account here), 4. with minor changes in the cervix, but with available laboratory confirmed data on the presence of highly oncogenic HPV types.
Treatment
Leukoplakia is not a disease, but a symptom of many pathological conditions. Therefore, it is important to make a differentiated diagnosis carefully in order to prescribe effective treatment. First of all, it is necessary to remove the inflammatory process, if any.
When the cause of the white spots is identified, the following are prescribed:
- antibacterial drugs;
- antiviral agents;
- antifungal drugs;
- antitrichomonas drugs.
The group of drugs depends on the pathogen that provoked changes in the cervix. If blood tests show that there is a hormonal imbalance, then hormonal therapy is necessary. Additionally, you should take immunostimulating medications.
Other treatments are:
- Diathermocoagulation.
- Cryodestruction.
- Laser treatment.
- Radio wave treatment.
- Chemical coagulation.
During diathermocoagulation, pathological areas of the cervix are exposed to electric current. That is, this method can also be called cauterization, since after exposure to the electrode a burn occurs. The negative factor of this treatment is pain, activation of the inflammatory process of the uterus and vagina, the risk of heavy bleeding, and deformation of the cervix. In view of this, diathermocoagulation is used extremely rarely today.
Cryodestruction is a procedure during which the white spot is exposed to liquid nitrogen, that is, cold. This procedure is painless, and there is no bleeding during the procedure, and after healing there is no deformation of the cervix. But in rare cases, leukoplakia relapses.
Laser treatment is often used today. This is due to the painlessness and bloodlessness of the procedure. In this case, there is no direct contact of the device with the cervix, since the CO2 laser beam is applied. It evaporates fluid from the cells and they die. It is very important that after this a film forms on the treated surface, which prevents infections from entering the wound.
Radio wave treatment involves inserting a special electrode into the cervical canal. It emits radio waves that heat the pathological cells and thereby evaporate all the liquid from the cells. But this method requires a special Surgitron device, and it is not available in all hospitals and clinics.
Chemical coagulation is performed by treating the affected area with Solkovagin. It penetrates the tissue by only 2.5 mm, so this method is not effective for the atypical gross type of leukoplakia.
Treatment tactics
In cases where the doctor discovers problems with the cervix, he should tell you what needs to be done next. So, first of all, the specialist will perform a colposcopy, take material for cytological examination and, if necessary, offer a biopsy. A complete examination allows you to determine what causes cervical erosion. It is also important to do microflora smears to determine if there are any infectious diseases. It is mandatory to find out whether the patient has HIV, syphilis or viral hepatitis. In addition, the gynecologist can give a referral for examination for the presence of trichomonas, ureaplasma, HPV, chlamydia, mycoplasma, and gardnerella.
After this, you can begin treatment. Depending on the size, causes of appearance and other factors, the gynecologist will suggest cauterizing the cervix with electric current, performing cryodestruction, laser coagulation or using the radio wave method.
In some cases, simply observing the erosion is sufficient. This tactic is chosen in cases where it is detected in young nulliparous girls. Most often, their appearance is caused by hormonal changes.
Read more Spike on the sole of the foot treatment with folk remedies