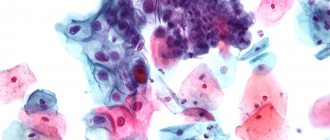
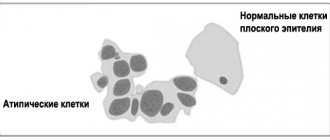
This type of cancer usually develops in the lower part of the uterus, which connects to the vagina. This disease affects women of all age groups.
The dangerous thing is that at an early stage of the disease, cervical cancer is asymptomatic. The chances of successful treatment increase if the problem is detected in the early stages. We list 10 main signs of this disease that you definitely need to pay attention to.
Frequent fatigue and weakness
Another cause for concern may be constant fatigue, weakness and lack of energy even after a long rest. When a cancerous tumor appears, healthy red blood cells are replaced by white blood cells to fight the disease. This causes anemia, one of the symptoms of which is constant weakness and fatigue. At the same time, the amount of oxygen in the body decreases, which leads to chronic fatigue that does not go away even after long sleep.
Uterus and development of malignant process
The uterus is the most important component of the reproductive system. It is a hollow smooth muscle organ, unpaired, pear-shaped, in women of childbearing age with an average length of 5 to 9 cm. According to its structure, the uterus itself is divided into sections: the cervix, body and fundus; and its wall consists of three layers: perimetry, myometrium and endometrium (internal mucous membrane of the organ).
The appearance of symptoms and signs of uterine cancer occurs as a result of mutation of endometrial cells that begin uncontrolled abnormal division, leading to the appearance of a tumor. Along with the growth of the tumor, the process of spreading of malignant cells begins, first through the lymph nodes, then through the blood vessels to vital organs (kidneys, liver, lungs).
Symptoms and signs of uterine endometrial cancer depend on the degree of pathological disease. Conventionally, according to the size of the tumor and the affected area, the process is divided into four stages:
| On first | The neoplasm is localized within the mucosa and gradually begins to grow into the muscle layer |
| On the second | The tumor affects not only the myometrium, but also spreads to the cervical area |
| On third | Malignant cells begin to damage nearby lymph nodes (pelvic, lumbar) |
| For stage 4 | Characterized by damage to the inguinal lymph nodes, pelvic organs (ovaries, bladder, etc.) and the appearance of distant metastases |
Damage to other organs leads to disruption of their work and the vital functions of the entire organism, because malignant cells displace healthy ones, but, due to their immaturity, are not able to perform their functions. The development of a malignant process irreversibly leads to death if the first signs and symptoms characteristic of uterine cancer are not detected in a timely manner and special treatment is not started.
Vaginal bleeding
Many representatives of the fairer sex diagnosed with cervical cancer suffer from regular vaginal bleeding. Neoplasm cells affect tissues, and new capillaries appear, which are eventually damaged, causing bleeding. They can occur between periods, during sexual intercourse, after menopause, and even after a routine gynecological examination. Bleeding occurs not only when the uterus is affected by cancer, but also when there is an imbalance in the hormonal sphere, infections of various etiologies, and inflammation. If abnormal vaginal bleeding occurs, you should immediately contact your gynecologist.
Oncology treatment
At the very beginning of the disease, when there are no characteristic symptoms, cervical carcinoma is treatable. For different forms of the disease, methods such as:
- laser therapy;
- removal of the affected area;
- cryodestruction;
- removal of the cervix.
Stage 1 treatment begins with intracavitary radiation irradiation. For stage 2-3 carcinoma, surgical intervention is necessary. To perform the operation, the woman’s age, the presence of metastases, and tumor growth are taken into account. If cancer cells have grown in the lymph nodes, the uterus is removed along with the affected areas of other organs.
If stage 4 carcinoma is detected, when the tumor has grown as much as possible throughout the organs, they undergo a course of radiation and chemotherapy.
It is important to know that self-medication is unacceptable under any circumstances! It should be remembered that early diagnosis means successful treatment of carcinoma with virtually no serious consequences!
Regular visits to the gynecologist will help to detect any pathologies in time and begin timely treatment. With effective treatment of grade 1-2, mortality is about 5%, with grade 3-4 it increases, but even at the last stage it is possible to recover. Be attentive to your health and you can avoid many serious diseases.
Pain during intimacy
Painful sensations during sex can also be symptoms of cervical cancer, which should not be neglected. They indicate that the oncology is already progressing, and the cancer cells have spread to nearby reproductive organs. In addition to pain, in this case, very often you also feel a strong unpleasant odor from the vaginal opening. But it is worth paying attention to the fact that pain during intimacy is often associated with various infections, sexually transmitted diseases, inflammation, etc. In any case, this phenomenon should not be ignored.
Pregnancy with uterine cancer
During pregnancy, atypical changes in tissues are difficult to determine. The tumor does not grow throughout the entire period of pregnancy. However, with uterine cancer, pregnant women may experience miscarriage, placental abruption, fetal death, and heavy bleeding. Here doctors begin immediate delivery with further extirpation of the organ. If a woman has undergone a full course of therapy and a positive effect is noticeable, she can become pregnant over time. Hormone therapy sessions that stabilize healthy reproductive activity will help restore reproductive function.
Life expectancy is calculated depending on the stage of detection of the pathology and the level of sensitivity to hormonal levels. The hormone-dependent type guarantees a five-year survival rate in 85-90% of cases, patients live more than five years. The autonomous type in the elderly reflects 60-70%. Stage 3, regardless of the form of cancer, reduces the duration of over five years to 1/3 of patients, and stage 4 to 5% of patients.
Vaginal discharge
It is considered normal if a small amount of fluid is released from the vagina without any special odor or color. But when the discharge increases sharply and begins to smell unpleasant, it means that the uterus is functioning with certain disturbances, including the development of oncology. In addition, discharge can be caused by various infections, endometriosis, bacterial vaginosis, candidiasis (thrush) and other problems. In cases of cervical cancer, watery, brownish mucus mixed with blood often comes out of the vagina. If such a symptom occurs, you should immediately see a doctor.
Cervical cancer treatment
Based on the clinic’s experience, it is possible to preserve the uterus and the possibility of childbearing with precancerous changes in the cervix. For cervical cancer, radiation therapy and surgical treatment - extended extirpation of the uterus and appendages - are equally widely used.
Treatment depends on the stage of the disease. In the early stages of cervical cancer, surgical treatment is preferred. During the operation, the uterus is removed. Sometimes the operation must be supplemented by removal of the pelvic lymph nodes. The issue of removing the ovaries is decided individually; with an early stage of the tumor in young women, it is possible to leave the ovaries. No less important is radiation treatment. Radiation therapy can either complement surgical treatment or be an independent method. In the early stages of cervical cancer, the results of surgical and radiation treatment are almost the same. Chemotherapy can be used to treat cervical cancer, but unfortunately, chemotherapy options for this disease are significantly limited.
At stage 0
Cancer cells do not spread beyond the surface layer of the cervix. Sometimes this stage is even considered a precancerous condition. Such a tumor can be removed in different ways, but with organ-preserving interventions, the risk of recurrence remains in the future, so regular cytological smears are indicated after surgery.
| Treatment methods for squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix, stage 0 | Treatment methods for cervical adenocarcinoma, stage 0 |
| Cryosurgery is the destruction of a tumor using low temperature. Laser surgery. Conization of the cervix - excision of a cone-shaped area. Loop electroconization of the cervix. Hysterectomy. It is also used in case of relapse of a malignant tumor after the above interventions. | Hysterectomy. In some cases, if a woman plans to have children, conization may be performed. In this case, an important condition is a negative resection margin according to biopsy data. Subsequently, the woman should be observed by a gynecologist, and after childbirth a hysterectomy is performed. |
The choice of treatment method is always made individually by the attending physician.
At stage 1a
- microinvasive cervical cancer - extirpation of the uterus and appendages is performed.
In cases where the tumor grows into the blood and lymphatic vessels, removal of the pelvic lymph nodes is also indicated. If a woman plans to have children, organ-conserving surgery is possible. In stage Ib
—the cancer is limited to the cervix—external or intracavitary irradiation (brachytherapy) is performed, followed by extended extirpation of the uterus and appendages. In some cases, surgery is initially performed, followed by external gamma radiotherapy.
At stage 2
cervical cancer - involvement of the upper part of the vagina, possible transfer to the body of the uterus and infiltration of the parametrium without transfer to the pelvic wall - the main method of treatment is radiation therapy. Chemotherapy may also be prescribed, usually with the drug cisplatin or its combination with fluorouracil. In this case, surgical treatment is rarely performed.
In the 3rd stage of cervical cancer - transition to the lower part of the vagina, infiltration of the parametrium with transition to the pelvic bones - radiation therapy is indicated.
At stage 4
(transition of cancer to the bladder, rectum or distant metastasis) only palliative radiation is used. In patients with advanced stages of cervical cancer with metastases, treatment is palliative, and chemotherapy may be used. In most cases, the chemotherapy regimen involves using one of the platinum drugs (carboplatin or cisplatin) in combination with gemcitabine (Gemzar), paclitaxel (Taxol), or topotecan.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7 (495) 151-14-53
Pain in the uterus
Pain in the pelvic area is far from uncommon in women. Cramps are common during your period. They are most often not associated with any serious health problems, but only accompany changes in the body during menstruation. But if pain in the pelvic area continues for a long period, then it may be a symptom of cervical cancer. In this case, severe pain syndromes occur at any time of the month. Severe and constant pain indicates that the cancer is already actively developing, and it is important to begin treatment immediately.
Diagnostic methods
Cancer is a terrible diagnosis, so when going to the doctor, many patients unconsciously downplay the extent of their health problems and do not name all the symptoms present. The specialist involved in examining the patient is faced with difficult tasks, and the first place here is occupied by identifying hidden signs of cancer, or those symptoms that the woman does not want to talk about.
So, if a woman turned to a gynecologist, then to determine the causes of her symptoms of illness, the doctor:
- performs a visual examination of the cervix using a special mirror;
- takes a smear for cytological examination;
- uses colcoscopy;
- recommends donating blood for a biopsy;
- refers the patient to a vaginal ultrasound;
- the area of the cervix that aroused his suspicion is visible on the x-ray;
- recommends doing a CT and MRI, and conducting additional laboratory tests.
If signs of cancer are identified and confirmed, an additional study is performed to assess the level of spread and the number of metastases.
A healthy cervix has a pleasant pink tint, its structure is almost uniform. If there is a malignant formation, an ultrasound machine will show the presence of small ulcers and a change in the color of this organ.
To confirm or refute the preliminary diagnosis, a Schiller test, ultrasound of the kidneys, liver, X-ray of the lungs, examination of the condition of the bladder and rectum, as the organs closest to the uterus, are performed. Patients are often prescribed intravenous urography, which allows them to determine the functionality of internal organs compressed by a malignant tumor. The main goal of diagnosis is to identify pathology. It is possible that not everything is as bad as it seems to the patient and the doctor himself. Sometimes test results reveal the most unexpected problems, among which cancer is not even present.
If a malignant tumor is suspected, almost all vital organs are examined. To prevent an identified disease, the symptoms of which a woman did not even suspect, from becoming a cause of severe shock and stress, it is necessary to undergo examination by a gynecologist approximately once every six months. The disease can be diagnosed immediately upon its appearance and its terrible consequences for the body can be prevented. The risk group for developing cervical cancer includes young women who lead a promiscuous lifestyle, as well as middle-aged women who have reached menopause. It is important to remember that many diseases get younger over the years. Malignant tumors are no exception, therefore girls should be regularly examined from the moment they enter into first sexual relations. The unique ability of cancer not to announce its presence for several months and even years is a problem that the best scientists in the world are working to solve.
Unpleasant sensations when urinating
Cervical cancer can cause discomfort when urinating. This is one of the most obvious and common symptoms of such a dangerous disease. Discomfort includes a fairly strong burning or pain when emptying the bladder. These sensations appear when cancer cells have already managed to occupy surrounding organs. If these types of symptoms appear, it is important to immediately consult a doctor. Unpleasant sensations while visiting the toilet can also occur due to urinary tract infections or sexually transmitted diseases.
Causes of the disease
Currently, cervical carcinoma has not been fully studied by specialists, since it is difficult to establish the cause of its origin, and it is practically untreatable. Negative factors increase the likelihood of development and put you at risk, such as:
- venereal diseases;
- promiscuous sex life;
- hypertension;
- contraceptives;
- overweight;
- alcohol, smoking, drugs;
- diabetes;
- cervical erosion;
- herpes, papillomaviruses on the genitals;
- menstrual irregularities;
- social status, poor hygiene;
- ruptures during abortion, childbirth.
Pain in lower extremities
Women whose uterus is affected by cancer often experience pain, weakness and severe discomfort in the legs. The spread of cancer cells interferes with normal blood flow, causing pain and swelling. Of course, it is not only the diseased uterus that is to blame for the appearance of such symptoms. Pain in the lower extremities can be caused by fatigue after a hard day at work, late pregnancy, varicose veins, diabetes and other reasons. Pain caused by cervical cancer is most often constant and only increases over time. Later, back pain is added to them. To accurately determine the nature and cause of pain in the legs, you need to go to the doctor.
Causes
Oncologists have not yet established the reliable reasons for the development of a malignant neoplasm in the body of the uterus, but taking into account long-term statistics, they were able to identify some factors that can provoke the appearance of this disease in women. These include:
- Endometrial hyperplasia is a pathology that manifests itself in the form of thickening of the endometrium due to constant cell division. In the early stages, it is not a malignant process, but if treatment is not started, it can easily develop into one.
- Obesity - as practice shows, women with increased body weight are at increased risk of developing uterine cancer.
- Women whose periods began before the age of 13 or last until the age of 55, and those who do not yet have children, are more susceptible to developing uterine cancer.
- Quite long-term use of estrogen-based oral contraceptives, especially if they are not balanced with progesterone.
- A history of radiation therapy aimed at treating cancer in the pelvic area.
- Heredity - if there are women in the family with uterine cancer, the risk increases by 2 times.
- HPV is the human papillomavirus, one of the most important causes of cancer.
The above factors do not mean that their presence will be 100% the cause of cancer development. But women who have them should monitor their health more closely, and if any alarming signs appear, seek advice from a gynecologist so that the specialist can timely identify cancer at an early stage.
Dramatic weight loss
This is one of the main signs of any oncology. Cervical cancer is no exception. With it, a woman can also lose weight dramatically, without any particular reason. During cancer, the immune system fights the problem with all its might. The body releases large quantities of proteins called cytokines. They destroy fats very quickly, which entails weight loss, regardless of diet.
First signs
The first symptoms that may indicate uterine cancer: abnormal bleeding from the vagina, leucorrhoea, pain in the pelvis and lower abdomen, bleeding after sexual intercourse. There is also an increase in the duration and intensity of menstruation in young girls, and vaginal bleeding during menopause. When the tumor continues to grow and affects neighboring tissues, a lot of secondary symptoms appear, such as: lower back pain, leg pain, swelling, urinary dysfunction.
Statistically, the earliest symptoms and signs of uterine cancer begin to appear in the form of bloody discharge from the uterus itself. If blood appears during or after sexual intercourse, a woman should think about the possible presence of a malignant process in her cervix or in the uterus itself, and seek advice from a gynecologist. In addition, it is necessary to pay attention to bleeding from the genitals in the absence of menstruation for more than six months. In the postmenopausal period, bleeding should be the first sign of a serious abnormality, which requires immediate consultation with a doctor and examination for uterine cancer. At a young age, the first symptoms of oncology may be atypical discharge of bloody masses that appear spontaneously, without any temporal order, as well as disruption of the normal menstrual cycle.
In addition to bleeding, abnormal white discharge may be a sign of cancer. At the very beginning of the malignant process, they may have the appearance of a colorless liquid, in very scanty quantities, without affecting the frequency of menstruation. Over time, as the disease progresses, bloody impurities begin to join such secretions, which is why they take on the appearance of ichor and have a sharp and unpleasant odor. The presence of discharge of this nature indicates that the neoplasm has entered the stage of decay and uterine cancer is developing with particular activity.
The third and final symptom of uterine cancer is pain. When a woman begins to experience severe pain, this means that the tumor has reached the stage of inoperability, and it will no longer be possible to remove it through surgery. The cancer has already left the uterine body and has affected the pelvic and abdominal organs.
As with any other type of cancer, during uterine cancer a woman may experience typical signs of this disease. She notices a rapid weight loss that occurred without any reason, chronic fatigue and weakness in the body, and poor appetite.
Loss of urinary control
Pregnant women or those who consume large amounts of liquid find it quite difficult to control urination. If this symptom appears without any reason, then you should pay close attention to your health. This may be a sign of cervical cancer. Most often, loss of control over urination indicates that the disease has already spread beyond the localized area and has affected the bladder. Women with cervical cancer often have blood in their urine.
Today, cervical cancer is curable if we pay attention to the disease in its early stages. To this end, women of reproductive age are required to undergo gynecological examinations at least once every three years. In addition, it is advisable for girls from 12 to 26 years of age to be vaccinated against the human papillomavirus. It is very important to give up smoking and other bad habits that increase the risk of developing this dangerous disease.
Stages
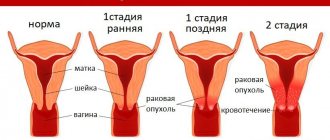
The first signs of cervical cancer depend directly on its type and stage, as mentioned above. Experts have identified at least 4 stages of cancer development in this part of the female body:
- Precancerous. Histological examination will show the presence of cancer cells that have not yet had time to penetrate the epithelium. Timely treatment allows you to get rid of not only the symptoms of the disease, but also its cause. Most specialists guarantee a complete recovery.
- Stage 1 cancer. Malignant cells penetrate the epithelium to a depth of 4-5 centimeters, but the tumor is still small and does not extend beyond the cervix. At this stage, possible signs are bleeding from the uterus and severe pain in the lower abdomen.
- Stage 2. The malignant tumor metastasizes and leaves the cervix. The pain intensifies, my back begins to ache, and anemia occurs. The disease at this stage is considered relatively curable.
- Stage 3. The tumor affects the pelvic walls and the upper part of the vagina. The prognosis is unfavorable, the patient loses strength, heavy bleeding occurs, and anemia develops.
- Stage 4. Metastases affect the pelvic organs and lymph nodes, and their active spread throughout the body is observed. The survival rate of women whose disease has reached this stage is low.
Unfortunately, in a number of cases, patients turn to a doctor precisely at the moment the disease moves to stage 4, which suggests a high degree of danger to life from cervical cancer. The clinical picture at this stage is so unfavorable that nothing can be corrected. The bleeding practically does not stop, anemia begins, the lower extremities swell, the pain is sharp and does not stop even at night.
Stages and their lifespan
Oncologists distinguish several sequential degrees of uterine cancer:
- At the first stage, tumor formation is located directly in the uterine body. The probability of recovery is about 80-90%;
- At the second stage of the oncological process, the tumor formation penetrates beyond the boundaries of the uterine body and affects the cervical canal (cervix), however, nearby organs are not affected. Recovery occurs in approximately ¾ of cases;
- At the third stage of cancer, the oncological process spreads to the appendages and vagina. Survival rate is about 40% of patients;
- At the fourth stage of uterine body cancer, tumor processes spread beyond the pelvic region, the formation grows into the intestinal and bladder tissues. Survival rate – no more than 15%.
Diagnosis of endometrial cancer
The following methods are used to diagnose endometrial cancer:
- Pelvic physical examination: Your doctor will examine your uterus, vagina, and nearby organs to check for masses or changes in shape or size.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound machine uses sound waves that are inaudible to humans. These waves are reflected from areas of different densities. This creates an image of the uterus and nearby organs. This picture may show an endometrial tumor. To obtain a clearer image, ultrasound examination can also be performed transvaginally (when an ultrasound probe is placed in the vagina).
- Hysteroscopy: the use of a thin, flexible tube that is placed into the vagina. At the end of this tube there is a camera that displays an image of the uterus. In this way, the doctor can examine in detail the condition of the uterus and endometrium.
- Biopsy: This is the removal of tissue and further examination of it to look for cancer cells. Typically a thin tube is used that is placed into the uterus through the vagina. A thin layer of tissue is scraped from the wall of the uterus, and then a pathologist examines this tissue under a microscope. Often a biopsy is the only way to accurately diagnose a malignant tumor of the uterus.
Make an appointment with an oncologist-gynecologist
Organ structure
To make the process of pathology more understandable, let’s say a few words about the structure of the female reproductive organ. Visually, the uterus looks like an inverted pear (see photo). At the top there is a wide “pear-shaped” base - the fundus of the uterus, to the bottom (towards the vagina) there are:
- body;
- isthmus;
- Cervix.
The tissue that makes up the organ is formed by 3 layers:
- endometrium - a mucous layer facing inward (on top the endometrium is lined with epithelial cells);
- myometrium - muscle (middle) layer;
- perimetry - the outer shell.
Diagnostics
The diagnostic process for uterine cancer begins with a gynecological examination using speculum. The patient is then sent for an ultrasound examination, which reveals the true size and structure of the uterus, as well as the structure and thickness of the endometrium.
The photo shows what uterine cancer looks like on ultrasound diagnostics
Often, curettage and histological examination of the resulting biomaterial are performed. This procedure is performed using general anesthesia in a hospital setting.
When analyzing for the detection of tumor markers for uterine cancer, the following markers are used:
- CA 72-4;
- CA 125;
- Carcinoembryonic antigen;
- HCG or human chorionic gonadotropin.
Thanks to the introduction of tumor marker tests into gynecological oncology practice, it was possible to save the lives of many patients.
Is it possible to cure the disease?
The success of treatment is closely related to the timing of cancer detection. When detected at an early stage, the disease can in most cases be cured, and it is often possible to even preserve the ability to bear children.
The further the process goes, the lower the effectiveness of possible treatment.
If the cancer has not grown beyond the cervix and is located in a small area, the operation is limited to conization of the affected cervix, the appendages and uterus remain intact. In this case, the woman can maintain reproductive function.
If the situation is complicated by a large spread, the uterus is amputated with or without the ovaries. Additionally, lymph node dissection may be performed.
Surgery is combined with chemotherapy or radiation therapy at the doctor's discretion. It has been proven that the combination of these methods with surgery gives a favorable result. Radiation and cytostatic effects can be prescribed before or after surgery.
There are three methods of treating cancer.
- surgical;
- radiation therapy;
- chemotherapy.
Surgical exposure
(conization and trachelectomy) consists of surgical removal of a damaged area of tissue or organ (several organs). The problem of effectiveness lies in the relationship between the required radicality of the operation (it is advisable to remove as much of the area as possible to prevent the spread of cancer) with its traumatic impact.
The more the body’s resources are preserved at the time of surgery, the easier and more successful the recovery process after it is. In the later stages of the disease, the method is not used, since the life expectancy of patients after the operation does not exceed the life expectancy without it.
Doctor's advice
Cervical cancer is a tumor leading to loss of reproductive function and disability. It is possible to protect yourself from this disease by regular examination by a gynecologist. Women should not die from diseases of visible localizations!
Olga Zorina Pregnancy and childbirth, Gynecologist, Gynecologist-endocrinologist
Radiation therapy
Cell destruction occurs through radiation. Limitations in the use of the method are associated primarily with the degree of prevalence of the malignant process and the volume of affected tissue. The maximum effect is in the middle and early stages.
In the later stages, therapy is not applicable, since the dose required to completely destroy the entire volume of pathological foci exceeds the limit that is safe for the body and becomes destructive.
Chemotherapy
Specific method of influence. It consists of using drugs that are cellular poisons, that is, leading to the death of any cells. The principle of application is based on the fact that actively reproducing cells die faster than others.
The main flaw of the method is the fundamental impossibility of selective action. The impact is not targeted at the source of the disease, but on the entire body. But at the final stages of the disease with widespread metastasis, the use of other methods is impossible, and chemotherapy remains the only available remedy.
Possible complications
The complete lack of treatment for cervical carcinoma leads to the penetration of cancer cells into the deeper layers of the organ, the spread of metastases and disruption of the functioning of internal organs.
Complications of carcinoma include:
- blood clot formation;
- sepsis;
- peritonitis;
- cancer exhaustion;
- pyelonephritis;
- pneumonia;
- uremia;
- female infertility.
Do not forget that endometrial cancer of the uterus has a high probability of recurrence.
What puts you at higher risk
Let's look at the factors that contribute to the development of uterine cancer:
- the presence of bad habits in women, in particular smoking and drug addiction;
- indiscriminate change of sexual partners (read about effective contraception here);
- early onset of sexual life;
- hormonal disorders (consultation with an endocrinologist will help correct them);
- obesity;
- impossibility of conceiving/giving birth to a child for various reasons before the age of 30;
- hypertension;
- ovarian pathologies (treated by a gynecologist);
- diabetes;
- abortions;
- acute liver diseases;
- weakening of the body's protective functions.
Stages of endometrial cancer
Stage 0 - Pathological cancer cells are found ONLY on the lining of the inner layer of the uterus; this tumor is called carcinoma of the uterus in situ.
Stage I - The tumor has grown through the mucosa into the endometrium. Sometimes the tumor grows into the myometrium.
Stage II - The tumor has grown into the cervix.
Stage III - The tumor has grown through all layers of the uterus and invaded neighboring organs: the vagina and lymph nodes.
Stage IV - The tumor has grown into the bladder or intestines. Or the tumor cells have spread to distant parts of the body: the liver, lungs or bones.
Treatments for uterine cancer include surgery, chemotherapy, and hormonal therapy. A combination of these methods is often used.
The difference between pathology and fibroids
In the photo: uterine fibroids
Myoma is a benign tumor, and this is its main difference from uterine cancer. But it is necessary to understand that the primary symptoms of these diseases are similar. In addition, if you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner and late detection of fibroids, it can develop into oncopathology (observed in 1.5 - 2% of all cases). More information about fibroids is described here. Therefore, only a comprehensive examination of the patient, including:
- UAC;
- examination by a gynecologist;
- curettage of the uterus;
- Ultrasound and MRI of the pelvic organs.
Prevention and prognosis
The causes of cancer are not fully understood today, so there are no specific preventive measures.
To prevent uterine endometrial carcinoma from developing, you must follow simple rules:
- rules of personal hygiene;
- lifelong cessation of bad habits;
- body weight control;
- careful planning of pregnancy, which will help avoid abortion;
- complete exclusion of unprotected sex and promiscuity;
- early detection and full treatment of any gynecological diseases, chronic pathologies that are fraught with the development of carcinoma;
- proper and balanced nutrition;
- constant strengthening of the immune system;
- taking medications only in strict compliance with the recommendations of the attending physician;
- moderate but daily physical activity;
- prevention and treatment of STDs;
- regular visits to a gynecologist and a general preventive examination at a medical institution.
The prognosis is considered conditionally favorable, since even after surgery, the five-year survival rate varies from 45 to 87%. Stage 1 cervical carcinoma has the most favorable prognosis - complete recovery is observed in 80%. Life expectancy of 5 years with stage 4 cancer is only 5%.
Consequences
The neglect of the oncological process can significantly threaten the safety of life, and very often, in the absence of adequate treatment, death occurs.
In the early stages of uterine cancer, doctors try to preserve the female reproductive organs and fully restore their functioning. But after such operations, adhesions often form and various seals form on the walls of the vagina and uterus. In more complex situations, women have their uterus, vagina and ovaries completely or partially removed, which in turn entails an irreversible loss of the possibility of childbearing, as well as changes in the patient’s hormonal levels. Therefore, to normalize further life activity, women after surgery are prescribed hormonal medications.
It should be noted that chemotherapy, which is always used in the treatment of uterine cancer, also negatively affects all internal systems of the body. It will take at least 3 years to restore the correct functioning of all affected functions.
And finally, if you suddenly hear a terrible diagnosis from a doctor, do not forget: a disease diagnosed in the early stages is not a reason for despair. It can be successfully treated, and modern medicine gives the young woman every chance to become a happy mother in the future.
You can ask your gynecologist a question here.
For more information about the causes and symptoms of uterine cancer, watch the video:
This article has been verified by Olga Zorina, a current qualified physician, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Rate how helpful this article was
4.9 28 people voted, average rating 4.9
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!