Assessment of UHM indicators (the abbreviation stands for uterine fundal height) is one of the most important diagnostic measures during pregnancy. Firstly, the indicator under consideration allows us to determine the age of the developing baby, secondly, to assess the condition of the fetus, and thirdly, to assume the presence of various types of deviations in the child’s development.
In sexually mature women, the uterus in normal condition has a length of up to 8 cm, of which about 2.5 cm is at the cervix. As the child develops, the size of the uterus also changes, and by week 40 it can reach about 40 cm. The weight of this organ also increases - before conception it is approximately 50 g, and by the third trimester it increases up to 4 kg.
Size of the uterus during pregnancy by week (table): why the size does not correspond to the timing
Based on the dynamic development of the uterus and the height of its fundus, the doctor assesses the successful course of pregnancy. How to correctly measure the changing size of an organ? What deviations affect the increase? What to do if there is a threat of miscarriage?
The uterus of a nulliparous woman has very modest dimensions: 5.0 – 6.0 cm in length; 3.4 – 4, 0 – in width. Its weight is about 50 grams. Over 9 months of gestation, the organ undergoes enormous changes, increasing in size, thinning, reaching a weight of up to 4 kg along with the fetus. This transformation, recorded weekly in a special table of indicators, constitutes the dynamic course of pregnancy.
- Measurements using the Leopold method Fundal height of the uterus in the early stages
- When can an organ be measured?
- Uterine wall thickness
- Uterus sizes by week
How is the uterus structured and functioning?
It may seem that the uterus is simply a muscular sac that contains the fetus, and at the time of birth it simply pushes it out. In fact, the uterus is quite complex.
The wall of the uterus consists of serous and mucous membranes , between which muscles are actually located. The muscle layer, in turn, consists of three thinner layers, the fibers of which are located in different directions: two layers in the longitudinal and one, the middle one, in the circular.
This device allows the uterus to stretch and then forcefully push out the fetus.
The uterus is regulated by both the nervous system and hormones.
It is hormonal regulation that is the weak point with which most disorders in the functioning of the organ are associated. Problems occur especially often after the age of thirty, when the amount of hormones produced by the ovaries begins to gradually decrease. In youth, hormones are released in normal quantities.
Problems also often arise when there was an operation on the uterus, and because of this, a scar appeared there that does not stretch, unlike muscle tissue. Surgeries on the uterus in the past are one of the most common problems associated with an increase in the size of this organ.
https://youtu.be/JlqskWAsyOU
Method for measuring the uterus during pregnancy
The measurement is carried out using the “Leopold technique” - a special obstetric technique.
- The measurement is carried out with an empty bladder.
- The woman lies on her back on the couch.
- Raising your hand from the pubic area along the midline of the abdomen, you feel the area where the dense tissue becomes soft and loose - this is the border of the uterus, called the bottom.
- Using a soft ruler, measure the distance from the pubic bone to the bottom.
With physiologically correct development, the distance in centimeters coincides with the period established in weeks. Possible error: 1 – 2 cm. This calculation is applicable up to 37 – 38 weeks. Later, the uterus settles into the pelvic cavity in preparation for childbirth.
In the first weeks, pregnancy manifests itself only with slight tension - an increase in the tone of the uterus. Its walls soften, which promotes stretching and increase in mass. But the organ is located within normal boundaries, so it is impossible to measure its size using the described method.
No visual changes are observed until 6 weeks. The fact of conception is established using hCG analysis and a urine test. Monitoring the correct formation of the placenta and embryo is carried out by ultrasound examination.
Only from the 12th week the uterus extends beyond the symphysis pubis and can be felt in the lower abdomen. From this point on, weekly growth measurements are taken and development dynamics are monitored.
Fetal growth causes changes in several directions. They all have a role in controlling proper development.
The uterus is a muscular organ. Conception stimulates active growth of myocytes. During the first half of gestation, the wall of the organ thickens 3–4 times; further increase, in the second half of gestation, occurs due to stretching of the muscle fibers. Around the middle of the term, the thickness of the wall is 3.5 - 4 cm. By the end of the third trimester, during the period of intensive growth of the child, the wall thins to 1 - 0.5 cm.
The volume of the organ increases 400 times at the time of delivery. In multiple pregnancies, these indicators are even higher, and the thinning of the wall is stronger.
In thin ladies, a noticeable increase in the abdomen can be observed as early as 6 weeks of pregnancy. First, changes occur in the anteroposterior direction, and the uterus takes on the shape of a ball. Later, transverse growth begins. By 8 weeks, the volume of the organ doubles, and by 10 weeks, it triples.
In the early period, the fertilized egg is located in one of the halves of the uterus, which causes visual asymmetry of the abdomen. As it develops, the embryo fills the entire cavity, and the abdomen becomes uniform. It matters in which part the embryo is attached. If its introduction occurred on the posterior wall of the cavity, the abdomen is hardly noticeable, but if on the anterior wall, a round protrusion is visible in the early stages.
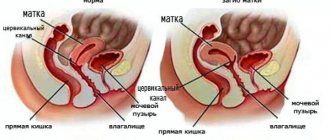
The location of the uterus and its parameters change depending on the anatomical features of the organ. In pre-pregnancy life, a woman may not be aware of any abnormalities. But during the development of the embryo, an anatomically abnormal uterus can become a threat to pregnancy.
- The intracavitary septum is a strand of connective tissue that divides the uterus lengthwise or crosswise.
- Bicornus is the presence of a paired uterine cavity connected by a narrow passage at the cervix.
- Hypoplasia - a small uterus is often accompanied by an anatomically narrow pelvis, which makes natural childbirth problematic.
Attention! These features do not affect a woman’s daily life in any way, but pose a threat during pregnancy.
The enlargement of the organ occurs gradually, which allows the female body to adapt to the new reality. The growing fetus compresses the surrounding tissues, forcing you to change your usual lifestyle.
Each stage of development is accompanied by conventional boundaries:
- Week 8. The uterus increases to twice its original size, but obvious visual changes are not yet observed.
- Week 12. The uterus protrudes above the symphysis pubis; this is the peak period of pregnancy toxicosis.
- Week 14 The organ increases to 12 cm, the first movement is felt.
- Week 16 The size of the organ is 14–15 cm. All vital structures of the embryo are fully formed. The upper border of the uterus can be felt in the midline between the womb and the umbilical fossa.
- Week 18. The organ increases to 18–19 cm and moves closer to the umbilical cavity.
- From 20 weeks, the height of the uterine fundus is set at 20 cm and increases by a centimeter every subsequent week.
After 36 weeks, the size of the organ changes slightly - 5-2 mm per week.
A woman can independently determine the boundary at about 12 weeks. It will be felt as a small painless lump above the symphysis pubis. In the presence of pathologies (fibroids, fibroids), the organ enlarges faster. During multiple pregnancies, the size of the uterus increases at a faster rate.
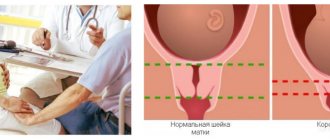
Not only the uterine cavity, but also the cervix undergoes changes. From the moment of conception, it lengthens, softens, and changes color. Its length reaches 4.0–4.5 cm. Subsequently, a gradual shortening of the canal is noted.
The following parameters indicate the successful development of pregnancy.
Important! Rapid shortening of the cervix is a threat to full pregnancy. Such progress is especially dangerous for a period of up to 34 weeks.
Fundal height of the uterus is measured weekly, starting at 14 weeks. The data is recorded in the patient’s individual table to monitor the dynamics. A physiologically normal pregnancy corresponds to the following indicators.
At week 38, the height of the uterine fundus is no more than 32 cm, and the fetus descends into the pelvic cavity.
All described sizes vary within 2–3 cm and depend on many factors:
- Genetically determined embryo weight. A large fruit adds several centimeters, but the positive dynamics remain.
- Position of the fetus in the cavity. With longitudinal presentation, the height of the fundus is less than with transverse presentation.
- Pelvis width. With a narrow pelvis, the uterus is located higher.
- The amount of amniotic fluid. Polyhydramnios increases the volume and size of the organ.
- Frozen pregnancy, in which there is a lack of dynamics.
- Several embryos.
Toxicosis, the occurrence of infectious diseases, and low weight gain play a negative role.
During a multiple pregnancy, the abdomen grows rapidly; it can protrude above the symphysis pubis as early as 10–11 weeks. When measuring VMR, the parameters have a gap of 5–7 cm. By the peak indicator (36–38 weeks), the upper limit is at a distance of 42–48 cm above the symphysis pubis.
The stretching of muscle fibers and skin is much stronger, and labor occurs earlier - at 36–37 weeks. With multiple pregnancies, the cervix becomes shorter and denser. And its physiological shortening occurs more quickly.
Methods for maintaining pregnancy with uterine exhaustion and cervical shortening
The cervix is a dense muscular ring that holds the fetus in the cavity and prevents it from slipping into the vagina. Throughout the entire gestation period, the cervix is in good shape, gradually shortening. By the time labor begins, it opens, releasing the baby's head.
If the cervix weakens earlier, this threatens spontaneous miscarriage and fetal death. Therefore, a woman is offered to strengthen the cervix in one of two suitable ways:
- Sutures are applied in a circular manner. The procedure is performed at 14–26 weeks, and the sutures are removed just before the birth process. Cerclage – suturing – has its contraindications:
- cervix dilated by more than 4 cm;
- inflammatory process;
- integrity violation.
Cerclage prevents premature birth, but has a number of side effects: localized hemorrhages, tears in the cervical tissue, rupture of the uterine wall.
- The application of a pessary is used when the cervix is exhausted to prevent spontaneous miscarriage. The device is a silicone ring placed on the lips of the cervix. The ring evenly distributes the load on the organ, normalizes blood supply and tissue nutrition. Prevents untimely dilatation of the cervix. The pessary is installed in the late stages of gestation (28–34 weeks) when there is a threat of fetal rejection.
The height of the uterine fundus does not always correspond to the indicated period. Deviations can be significant, although the date of conception is set correctly. Why does this situation arise?
Placental insufficiency leads to a delay in the formation of the embryo, as a result – to reduced dynamics. This condition is caused by the presence of hypothyroidism in the mother, long-term debilitating toxicosis, and severe viral infections.
The opposite situation is the increased size of the uterus in relation to gestational age. A common diagnosis is polyhydramnios - an increased amount of amniotic fluid. It occurs as a result of infection with an intrauterine infection (herpes, cytomegalovirus and others). It has been noted that polyhydramnios occurs in women with a history of surgical or spontaneous abortion.
During a dynamically developing pregnancy, the upper border of the uterus fits within the allotted weekly norms reflected in the table. But if deviations occur, do not panic; non-compliance with accepted indicators does not indicate fetal pathology. There are many reasons why the size of the uterus exceeds or falls short of normal. It is necessary to conduct an examination and adjust the timing and condition.
Size of the uterus by week of pregnancy - normal indicators in the table and reasons for deviations
From the moment of conception until birth, the size of the fetus gradually increases. The growth of the uterus observed during the weeks of pregnancy is a normal physiological process. Based on the dynamics of this indicator, an experienced gynecologist monitors the changes in the mother’s condition and the development of the embryo, can promptly notice any complications or pathologies that have arisen and take measures to eliminate them. Measurements are taken and recorded by a doctor during regularly scheduled examinations; from the second trimester, a woman can perform them independently, at home.
What is the size of the uterus by week of pregnancy
The dimensions of the uterus in nulliparous women average from 4.5 to 7 cm in length and from 4.5 to 6.5 cm in width, thickness - 3.5-4 cm. Individual parameters may deviate from the physiological norm by 2-3 see. After pregnancy and implantation of the embryo, the organ begins to enlarge (under the influence of fetal growth), continuing until the last prenatal weeks. By birth, the size of the uterus reaches 33-40 cm.
By changing the location of the uterus and its growth parameters, an experienced specialist can determine the duration of pregnancy, the nuances of its course, and the characteristics of fetal development. To track the dynamics of organ enlargement, at each scheduled examination, the gynecologist takes measurements of the volume of the abdomen and the width of the pelvis. With the beginning of the second trimester, the indicator of the height of the uterine fundus (VSD or VDM) is introduced.
The height of the uterine fundus by week of pregnancy is the distance between the pubic symphysis and the highest point of the organ, measured with a regular centimeter tape. On average, this figure corresponds to the period - from 8-9 cm in the eighth to ninth week, to 35-40 cm in the fortieth. Deviations may indicate a multiple pregnancy (with increased values) or pathologies (improper position of the fetus, slow development, oligohydramnios). The method of such diagnostics is indicative only in dynamics; one-time measurements are not informative.
Fundal height of the uterus by week, how to determine:
- at the beginning (in the first weeks), the gynecologist can determine its size only through a gynecological examination - through the vagina, palpating it;
- at 11 and 12 weeks, the VSD of the uterus reaches the pubic symphysis;
- from the 14th week it can already be felt through the abdominal wall, because its dimensions already extend beyond the pelvic region;
- A fairly common method for determining height measurements and assessing the fundus of the uterus is measurement using a centimeter tape. The expectant mother is in a supine position, and her leading gynecologist measures the distance from the symphysis pubis to the fundus of the uterus;
- The obtained data is recorded in a log in order to monitor further developments.
- size of the height of the uterine fundus by week (measurements from the 8th week of pregnancy): 8-9 weeks - about 8-9 centimeters, 10, 11, 12 and 13 weeks of pregnancy - from 10 to 11 cm, at 14-15 weeks - from 12 to 13 cm, at 16-17 weeks - from 14 to 19 cm, at 18, 19, 20 and 21 weeks - from 18 to 24 cm, at 39-40 - from 35 to 40 cm (more details see below for meanings).
- The VSD (fundal height) of the uterus corresponds to approximately one week of pregnancy.
By the way, if during an examination the gynecologist notices deviations from the norm in a larger direction, this may mean that the patient is carrying twins or triplets. To a lesser extent - a woman experiences oligohydramnios, a transverse or oblique position of the fetus, or slow development of the baby. The height of the uterine fundus must be measured constantly in order to monitor the dynamics of the results.
Important!
The given average statistical dimensions of the height of the uterus may not correspond to reality, because Before pregnancy, each woman's uterus has an individual size.
Features of changes in the uterus during pregnancy
The process of organ enlargement occurs gradually, measuredly, and therefore does not normally cause the woman any discomfort. Nagging pain and other unpleasant symptoms occur against the background of sprained ligaments or the formation of adhesions during polyhydramnios, multiple pregnancies, or due to scars after previous surgical operations. The size of the uterus depends on the trimester and changes as follows:
- First trimester. The uterus is located behind the pelvic bone and is shaped like a pear. In the sixth week, the size of the organ reaches the volume of a chicken egg, in the eighth - that of a goose egg. By the end of the trimester, the uterus takes on a round shape and increases three times its original size.
- Second trimester. The organ is centered in the pelvic region, acquires symmetry, and begins to be palpated through the abdominal wall as it emerges from behind the pubic bone.
- Third trimester. The organ again takes on the shape of an egg, stretching towards the bottom. The uterine cavity increases 500 times compared to the beginning of pregnancy, the weight of the organ changes on average from 50 g to a kilogram (muscle fibers lengthen, thicken, and the vascular network develops).
The height of the uterine fundus increases week by week in each trimester in parallel with the development of the fetus. It goes through the following main stages:
- 8-9 weeks of obstetric period - the average volume of the organ corresponds to a goose egg, it cannot be felt through the abdominal wall.
- 10-13 – the organ rises above the pubic bone; The activity of the functions of the placental system increases, the corpus luteum gradually disappears. The fetus develops its vascular system and begins to make its first movements. VDM - about 11 cm.
- 14-16 – completion of the formation of the internal organs of the embryo. The uterus reaches a size of 14-15 cm. At week 16, the position of the fundus height reaches the middle between the navel and the top of the pubic bone.
- 17-19 – the fetus develops its immune system, limbs, and cerebellum. The organ increases in size to 19-20 cm.
- Week 20 and beyond - the gap between the fundus of the uterus and the pubis reaches 21 cm, then this figure increases by an average of 1 cm per week. The VDM is located approximately two fingers' length below the navel.
- 23-24 – the weight of the fetus reaches 0.6 kg or more, its muscles and bones develop, and the respiratory system is formed. VDM – 24 cm.
- 28 – VDM is about 28 cm, located 2-3 cm above the navel.
- 29-30 – the size of the organ reaches 31-32 cm.
- 32 – the uterus is located in the center between the navel and the xiphoid process of the sternum, the IMD is about 34 cm.
- 38 – gradual descent of the organ begins, accompanied by strong pressure on the diaphragm and stomach.
- 40 – the size of the uterus ranges from 32-34 to 40 cm, depending on the physiological characteristics of the mother’s body, the size of the fetus, and a number of other factors.
Indicators of the height of the fundus and the size of the uterus are physiological, therefore deviations from the fixed norms within 2-3 cm in most cases arise due to the characteristics of the mother’s body and the individual nuances of the course of pregnancy. The dynamics of changes in the size and position of the organ in accordance with different periods are presented in the table:
Source: sovets.net
Height of the fundus of the uterus during pregnancy, table and description
The initial measurement begins at 8-9 weeks, when the uterus changes its shape and becomes like a goose egg. It is from this period that it can be felt, because it extends beyond the pelvis and has a new position - just above the pubis. In addition, it is at this time that the corpus luteum begins to disappear gradually, and the placenta begins to work actively. The baby, despite his small size, is already moving, and blood vessels are beginning to form in his body. At 10-13 weeks, the length of the pregnant woman’s uterus reaches approximately 10-11 cm. The body tries to cleanse itself, due to this toxicosis increases. The height of the uterine fundus at 14-16 weeks already reaches approximately 15 cm. By this period, all organs of the fetus are already formed. The uterus changes its position and is already in the gap - from the pubic part to the navel. At 17-18 weeks, the UMR of the uterus = 19 cm. For this period, the mother has already formed the placenta, and her baby has the immune system, all limbs and the cerebellum. Half term is 20 weeks. The height of the uterine fundus by week corresponds (approximately) to the period of pregnancy of a pregnant woman. The uterus is located 1.5 fingers below the navel. The weight of the fetus at 22-24 weeks is 550-610 grams. His lungs begin their formation, and his muscles and bones begin to develop. The size of the uterus reaches 23 cm. The height of the uterine fundus at week 28 = 28 cm. The VSD is already located above the navel, about 1.5-2 fingers. The beginning of the third trimester is 29-30 weeks. The UMR of the uterus is slightly longer than the term, approximately 31 cm. At this moment, many women complain of high blood pressure and this is not surprising, because The uterus has greatly increased in size. 9 months of pregnancy and 32 weeks, the length of the uterus is 32 centimeters. At week 36, the fundus of the uterus rises again and reaches the line of the costal arches. Pregnancy is approaching its logical onset; you only have to wait 2-3 weeks before meeting your baby. At week 38, the baby’s weight reaches 2200 kg, although in some cases it may not be much more. A woman experiences heartburn due to the fact that the uterus puts pressure on the digestive organs, because its length is 32 cm. Preparation for childbirth is the 40th week. IMD - 34 cm. Such a pregnancy is usually called full-term. The woman needs to prepare for childbirth and for the first meeting with the baby.
Why can the height of the uterine fundus differ from the average from week to week? Several factors can have an impact:
- child's weight;
- the structure of the expectant mother (height, weight);
- fetal position;
- a pregnant woman is bearing 2 or more children;
- amount of amniotic fluid.
Why is the fundus of the uterus during pregnancy lower than the statistical norm? Factors:
- Mom’s figure is curvy and her pelvis is wide;
- little amniotic fluid;
- the gestational age does not correspond to the actual one;
- possible delay in fetal development.