Examination
Gynecologists use two methods for research:
- Visual – carried out manually by a doctor on a gynecological chair.
- Carrying out an ultrasound using a transvaginal sensor is a more reliable method; it determines the size up to mm. Typically performed in the second trimester.
Favorable results of gynecological examination:
- length of the cervix during pregnancy is more than 36 mm.
- Dense to the touch.
- Closed external opening. For the organ of a woman giving birth again, penetration of the fingertip is allowed.
Based on the resulting sum of estimates of size, location and density, 3 degrees of maturity are distinguished:
- Immature – total value 0-2 points.
- Not mature enough – final score 3-5 points.
- Mature – the sum of points is more than 6.
How can an ultrasound procedure help with pathologies?
Many women often neglect systematically going to ultrasound examinations. Such tactics of behavior are fundamentally wrong. Ultrasounds should be done regularly. The attending gynecologist talks about this when he tells his patient the news about her pregnancy.
It is extremely important to control the length of the cervix. Only ultrasound can detect abnormalities. A serious disorder is a short cervix . Sometimes its size in the early stages is critical (from 2 to 10 cm). Immediately after the ultrasound diagnosis, the woman is referred for a consultation with the treating gynecologist.
If the doctor sees that the cervix is short, and this poses a threat to the development of the fetus, then he can advise the woman on the following options for getting out of the situation :
- compliance with bed rest and complete absence of stress;
- hormone therapy;
- use of a specialized gynecological ring (pessary);
- suturing the cervix.
The choice of a specific method of dealing with this problem depends on the patient’s lifestyle, the presence of concomitant pathologies, the duration of pregnancy and many other factors. The doctor may also advise the woman to go to a maternity hospital for preservation . This way, the pregnant woman will always be under the control of doctors and medical personnel.
In addition, the gynecological department carries out special physiological procedures that strengthen the cervix . Sometimes, with a short cervix, the doctor prohibits the patient from getting out of bed even to go to the toilet. In this case, the woman lies on her back, and her legs are slightly raised up. This position prevents the cervix from descending further. However, such a regimen is prescribed only in the first and second trimesters and exclusively in particularly critical situations .
Starting from the 7th month, the doctor already allows you to get up and walk a little. The main task of a pregnant woman is to protect herself from stress and physical activity, and also to follow all the recommendations of her gynecologist.
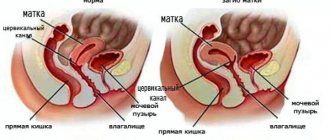
Short cervical length
A shortened value indicates a threat of miscarriage or premature birth. If this happens before the 37th week (the baby is fully formed and capable of independent life), a diagnosis of isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI) is made. Circumstances influencing the early reduction of ICI can be congenital or acquired. Probable reasons:
- Hormonal disorders.
- Infectious diseases, inflammatory processes.
- Surgery before conception.
- Past childbearing trauma.
- Multiple births.
- Large child.
- Polyhydramnios or low amniotic fluid.
If such a pathology is detected, the mother in labor requires complete rest and constant medical supervision.
Long cervix
Lengthening is not so risky for the health of the baby, but it can cause complications when labor begins. Causes:
- Individual anatomical features.
- Surgical intervention.
- Psychological factor.
Causes
- a short cervix may be a consequence of the anatomical structure of the female body;
- - a consequence of hormonal changes in the body caused by pregnancy. The pathology is especially pronounced in the second trimester;
- deformation of the cervix caused by previous abortions, surgery or multiple births;
- lack of the hormone progesterone;
- stressful situations, fears, worries;
- diseases of the uterus and cervix of an infectious and inflammatory nature, as a result of which the tissues of the organ are deformed and scarring occurs;
- deformation caused by uterine bleeding.
Examination and diagnosis of isthmic-cervical insufficiency It is possible to diagnose isthmic-cervical insufficiency with maximum accuracy in the second half of pregnancy, namely in the period from 14 to 24 weeks.
- Examination by a gynecologist. At the appointment, the specialist assesses the condition of the cervix, the presence of discharge and its nature, as well as the size of the external pharynx. In a healthy state, the cervix should be tight, have a deviation in the backward direction, the external pharynx should be tightly closed and not allow a finger to pass through.
- Ultrasound examination using a special sensor. In the first trimester, diagnosis is carried out with a transvaginal probe; in the future, transabdominal examination is used. Based on the diagnostic results, the specialist decides on further treatment methods that will allow you to maintain the pregnancy.
Norms by week of pregnancy
Changes in the uterine muscle begin to occur after conception:
- Due to the rush of blood, the color changes from pinkish to bluish.
- The structure becomes softer.
- Lowering occurs and mobility increases.
- The cervical canal becomes narrower.
- A mucus plug appears.
The volume and length of the cervix during pregnancy begins to increase in the early stages. With normal development, the parameter increases in segments:
- 4-8 weeks - normal value is at least 20 mm, external changes are noticeable, and slight asymmetry is characteristic.
- 8-12 – value 30-36 mm.
- 12-15 – the coefficient increases to 38 mm and approaches the value that accompanies the favorable course of the process.
- 16-20 – maximum value 40-45 mm.
- 21-28 – dimensions remain the same. A reduction of up to 35 mm is acceptable.
- 29-36 – reduction to 33 mm.
Next, the maturation of the uterine muscle begins and preparation for the process of the birth of the baby.
Changes in the cervix during pregnancy
Fertilization affects the functioning of a woman’s entire body. The changes are especially pronounced in the reproductive system. Internal organs adapt to the needs of the fetus. Some changes are considered normal , others – pathology. Only the treating gynecologist can determine which disorder is dangerous and which is absolutely harmless after carrying out a series of diagnostic procedures.
In the first trimester, the cervix changes color. Instead of light pink, the epithelium becomes bluish. This is explained by the fact that the branch of blood vessels is expanding, which in the future will nourish the placenta with all the necessary substances. In addition, the length and width of the uterine cervix changes . The muscle layer grows to hold the baby. This becomes the reason that already in the first months the cervix may be somewhat larger. In this case, the cervical canal closes more tightly than usual.
In the first trimester, the cervix lowers and becomes softer. The cervical canal produces several times more mucus. This is necessary in order to prevent the penetration and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms in the uterine cavity.
The most important indicator that gynecologists focus on is the length of the cervix .
The size of the muscle canal can be determined using ultrasound. The data obtained will help to understand whether there is a threat of miscarriage or premature birth. The doctor gives the patient recommendations based specifically on the quantitative indicators of the examination of the uterine cervix. The main task of a pregnant woman is to strictly follow the doctor’s instructions in order to bear a healthy and strong baby.
Cervical length by week of pregnancy table
The normal length of the cervix during pregnancy described in the previous paragraph corresponds to generally accepted medical standards, however, within their limits, the coefficients may vary in correlation with the weekly period and the individual characteristics of the expectant mother.
- 10-14 - for women in labor expecting a baby for the first time, the typical measurement is 35.3 mm, for multiparous women - 35.6 mm.
- 15-19 – 36.5 m during the first pregnancy, 36.7 mm during the subsequent pregnancy.
- 20-24 – 40.4 mm and 40.1 mm, respectively.
- 25-29 – parameters for first-time mothers are 40.9 mm, for women with experience – 42.3 mm.
- 30-34 – 35.8/36.3 mm, respectively.
- 35-40 – 28.1/28.4 mm, respectively, for “beginners” and “experienced”.
The most informative coefficient for gynecologists is the normal length of the cervix during pregnancy at 24 weeks. Deviations of the coefficient from the medical rule indicate potential early birth and the risk of miscarriage.
Cervical length at 32 weeks of pregnancy
Particular attention is paid to the expectant mother in the last trimester. At the 32nd segment of 7 days, the child is almost formed, the womb is in the shape of a circle, closed. The uterine muscle remains at a value of 40-50 mm. Shortening is a risk of potential pathologies.
Cervical length at 33 weeks of pregnancy
The indicators differ minimally. At this stage, the premature birth of a baby is likely if observed at 14-24 days. Since the baby is already formed, this does not pose a great danger, but caution and medical supervision are required.
Cervical length at 35 weeks of pregnancy
At this stage, the baby is fully formed and begins to actively gain weight. The body begins intensive restructuring and prepares for birth. The mother's womb is enlarged to the maximum, the cervix matures, shortens and becomes more elastic, forming the birth canal of the baby. During this period, false contractions occur.
Description of the organ
The cervix is
not just a component of the reproductive system, but is considered an important component of the female body, without which full childbearing and natural childbirth are impossible.
What does the cervix look like during pregnancy? It is a hollow muscle, the front part of which can be seen during an examination of a woman in a gynecological chair.
Usually her condition is assessed using a mirror, which provides correct information about the development of the fetus.
Where is the cervix located? It is located in the vaginal cavity in the lower part of the pelvis.
Because of this, the uterus itself is not visible during manual examination; it can only be seen during an ultrasound.
The normal size of this organ is 3.5-4.5 cm , however, during pregnancy this figure may change slightly.
What does the cervix look like during pregnancy? After conception, it becomes more flattened. There is also a change in its color, which becomes bluish rather than pale pink. The part that is located in the vaginal cavity is called the external os. If a woman has not had childbirth, it is completely closed; in patients who give birth repeatedly, it is capable of allowing 1 finger through.
Attention!
A short or long cervix should remain tight during pregnancy, because its main task is to hold the baby in the womb until labor begins.
As soon as a woman begins contractions, the external os will begin to shorten and smooth out, turning into a ring. As a rule, after the start of the first contraction, it begins to gradually open from 2 cm to 10 - in this case, it will be easy for the baby to be born through it.
If the organ begins to open before 36 weeks, it can end in disaster, since the consequences for the baby are unpredictable.
What is the norm for the weeks of the cervix, why is the organ shortened immediately after conception, and is it possible to lengthen it. It all depends on the structure of the female genital organs. If the size of the uterus is smaller than normal, then the pharynx will be short and narrow. In this case, not every woman can fully bear a child. To avoid unpleasant consequences for the baby, doctors need to take measures to maintain normal fetal development.
On the eve of childbirth
14-15 days before the onset of labor, the uterine muscle rapidly matures. Normal organ examination data for this stage:
- Shortening up to 1 cm;
- Soft muscle structure;
- The internal pharynx began to open;
- Position in the center relative to the pelvis.
An indicator much higher than normal indicates that the woman’s womb is not ready. Hormonal imbalances can cause immaturity, which is accompanied by tightness and a closed throat. If such indicators persist by the 40-41st estimated period, then labor is induced by medication or a cesarean section is performed.
https://youtu.be/zBdP-QH3tb8
Causes of early organ contraction
The main reasons for the pathological condition of the cervix and isthmus of the uterus, due to which they lose the ability to withstand intrauterine pressure and hold the growing fetus in its container, can be divided into two main groups:
- functional;
- traumatic.
Functional ones include hormonal imbalance (excess androgens, progesterone deficiency). Traumatic is any injury in the area of the isthmus or cervical cavity resulting from surgery, medical abortion, or trauma. Any intervention that leads to muscle rupture and replacement with scar (connective tissue) can impair the organ’s ability to contract properly.
According to the heredity factor, we can distinguish:
- hereditary (predisposition to miscarriage associated with genetic changes leading to hormonal imbalances);
- acquired reasons.
Acquired factors can become an additional impetus for the development of ICN, these include:
- inflammatory diseases of the reproductive organs (mainly associated with STDs);
- emotional and psychological factors (the impact of stressors is either chronic or one-time, but very strong);
- exposure to chemicals (for example, medications).
A doctor can notice a decrease in length at the time of a gynecological examination. That is why women in the gestational period are not recommended to skip routine examinations.
Organ characteristics
Checking the condition of the unfolding organ is the key to successful pregnancy. After all, if it is weak, the child will not be able to stay normally in the uterine cavity as it grows, which will ultimately lead to early birth. However, it is not necessary to check the baby’s condition at every visit to the gynecologist; several times when the gynecologist needs to examine the patient are sufficient. An examination should also if the patient has complaints.
There are several ways to determine the condition and size of the cervix during pregnancy week by week, namely:
- Manual inspection, which is recommended to be carried out on a chair.
- Conducting an ultrasound, where a transvaginal sensor will be used, inserted into the vaginal cavity.
During a manual examination, the doctor needs to assess the softness and also check the condition of the organ:
if it is soft and slightly open, this indicates the readiness of the organ. Besides,
this signals the onset of labor in the last weeks or a miscarriage in the 1st and 2nd trimester.
However, more often the pharynx begins to open as the baby grows, when he has already gained weight.
To understand whether pregnancy is proceeding normally,
need to be assessed:
- the length of the organ, which should be more than 3.5 cm,
- the pharynx must be completely closed and its structure dense
.
Assessment of the condition of the cervix based on ultrasound results is considered more reliable, since the sensor will show the length strictly in mm. An ultrasound will also help assess the density of the organ, which is important for the normal bearing of the baby. What is it - an indicator with which it is possible to assess the possibility of opening when certain factors act on the organ. Particular attention is paid to the color, which is bluish-red when the baby is pregnant.
This is interesting! When does the corpus luteum appear in the ovary: what is it?
Even more interesting:
Sores around the head
Mouth ulcers hiv
Can the cervix lengthen during pregnancy? No - the exception is the last weeks of gestation, when the fetus puts a lot of pressure on the external os. In this case, it will either open or become a little longer.
Little uterus
The small size of the reproductive organ is considered a clear violation of it, leading to its improper functioning. Unfortunately, not every woman with hypoplasia (the so-called disease) is able to bear a fetus, since the reproductive system and components of the small pelvis are not able to hold the child.
If a woman has a small reproductive muscle , a shortened cervix during pregnancy will not allow her to fully bear the fetus.
What is the danger of shortening the cervix
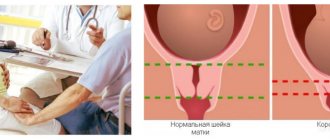
Shortening of the cervix is otherwise called effacement. It can cause the development of cervical insufficiency. This pathology is fraught, because in such a situation, the fetus simply will not stay in the uterus. It is heavy and presses down, the short neck opens under its pressure, and premature labor begins. In order to diagnose a woman with cervical insufficiency, the cervix must be shortened to a length of less than 25 mm. Also an alarming symptom is the opening of the internal pharynx. As doctors note, children born due to this pathology are extremely premature and often die immediately.
The development of ICI can be recognized by bursting pain in the vaginal area. They can often radiate to the lumbar and groin area. But it also happens that a woman does not experience any symptoms, and this is fraught with unexpectedness in the course of the situation.
If there is such a problem, the lady is offered a whole range of therapy. It includes:
- Hormonal therapy: offered in a course and prescribed exclusively by a doctor
- Installation of an obstetric pessary
- Stitching the neck
This helps to artificially delay the labor process so that the baby is not born prematurely. As a rule, such artificial barriers are removed at 38 weeks of pregnancy - at this time the fetus is considered full-term. As a rule, after such a measure, the woman begins active labor. If rupture of water is noted, the sutures and ring should be removed immediately, regardless of how far along the pregnancy is.
The procedure for installing a pessary is not the most pleasant. After this, you should remain in bed. Doctors also suggest that the woman take a number of medications that will relieve tension from the uterus. Moreover, despite the fact that the expectant mother with a pessary leads an extremely sedentary lifestyle, doctors still have to constantly ensure that the ring does not move and performs its protective functions.
Suturing is a kind of operation. It is performed accordingly - using anesthesia. However, such intervention is not recommended to be carried out earlier than the second trimester, because anesthesia does not have the best effect on the condition of the baby. During this operation, the uterine canal is not completely closed - it is simply left narrowed to maintain drainage between the uterus and vagina.
Unpreparedness of the cervix for childbirth
Another problem that awaits women is the lack of biological readiness of the body for childbirth after 37 weeks. This is evidenced by maintaining a cervical length of more than 3 cm during full-term pregnancy. The neck remains tight and the throat is closed. Such a cervix is called immature and indicates serious hormonal problems in the body.
What to do if at 40-41 weeks the cervix still does not ripen? In such a situation, the cervix is prepared with special preparations based on prostaglandin. If therapy does not bring the desired effect within several days, a planned caesarean section is performed.
Reasons for deviation from the norm
The following factors can provoke an abnormal condition:
- endured stress,
- tissue dysplasia,
- abortions/miscarriages,
- difficult birth,
- large fruit,
- polyhydramnios,
- conception that occurred immediately after childbirth,
- injury,
- hormonal imbalances,
- surgical or medical procedures.
Pregnancy in the cervix
If the fertilized egg attaches in this place, then its development will not occur. The embryo will remain viable for a maximum of 5 weeks, after which it will be rejected. With this pathology, women experience severe bleeding, which can be stopped with the intervention of doctors.
Attention! The cause of pregnancy in the cervix is most often an early abortion or surgical manipulation in the uterine cavity. The abnormality is diagnosed during an ultrasound, after which the patient is referred to a gynecologist or surgeon.
Short neck
With a shortened cervix, women undergo special manipulations, during which sutures are placed (up to 28 weeks). Refusal to timely cerclage will lead to the following consequences:
- spontaneous abortion,
- infection of the fetus (intrauterine),
- gap,
- rapid birth.
Long neck
The disease can be congenital, caused by an abortion, surgery, or gynecological diseases. A long cervix opens slowly and poorly during childbirth, which increases the risk of fetal hypoxia.
Erosion
In almost 70% of examined patients, erosion is detected. The reasons lie in trauma to the mucous membranes, hormonal imbalance, sexually transmitted diseases, etc. During pregnancy, the pathology is not treated, as it often goes away on its own after delivery.
Ectopia of the cervical epithelium: effective methods of therapyClassification of ovarian cystadenoma - surgical intervention and prognosisAlmag for the endometrium - use for endometriosis and fibroidsMethods of infection with thrush - how you can get sick
Dysplasia
With this form of the disease, epithelial changes occur. In the absence of timely treatment, an oncological process may develop. The reason lies in low immunity, bad habits, chronic inflammation, and the HPV virus.
Attention! Most often, the disease is detected in women under 35 years of age. The pathology has a negative impact on the pregnancy process and often provokes premature birth.
How and why measurement occurs
The parameters of the cervix are measured in two ways - on a gynecological chair using a mirror and colposcope, and using ultrasound diagnostics.
With a manual examination, the doctor can determine the condition of the external pharynx, the density of the cervix and the closure or opening of the cervical canal.
An ultrasound measures the length and also provides a more accurate idea of the condition of the internal os (the junction with the uterine cavity), which cannot be examined by other means.
When registering, the doctor conducts a manual examination, and at the same time, smears of the vaginal flora are taken for analysis. In the first trimester, a woman also undergoes colposcopy; it provides more information than a regular speculum examination.
Measuring the length of the cervix is advisable only after the 20th week of pregnancy, when the baby begins to actively grow and the load and pressure on the cervix increases.
Up to 20 weeks, the length of the cervix varies among different pregnant women, much depends on individual values. However, by week 20, the dimensions of the lower part of the uterus in different women reach common average values, and the length becomes diagnostically important.
In mid-pregnancy, ultrasound is usually done transabdominally , placing the scanner probe on the pregnant woman's abdomen, examining through the anterior abdominal wall. If there is a suspicion of lengthening or shortening of the cervix, as well as other anomalies, the doctor uses an intravaginal ultrasound method, in which a sensor is inserted into the vagina. Through the thinner vaginal wall, the cervix is clearly visible.
Control over the size and other parameters of the cervix is necessary to make sure that the child is not in danger of being born prematurely, that there is no threat of intrauterine infection, which also becomes possible if the cervical canal opens slightly or opens completely
During the entire period of bearing a baby, a healthy woman undergoes cervical examinations four times. If there is cause for concern, then diagnostics will be prescribed more often, as many times as necessary.