At high temperatures, anyone feels unwell. A small child, unlike an adult, is not able to endure prolonged headaches, so parents try to bring down the fever with medications.
Medical experts recommend that children take paracetamol. It is the most effective and safe for the child’s body.
Paracetamol tablets for children are discussed in detail below: instructions for use, how to give them to children.
The article is for informational purposes only. Before use, be sure to consult a specialist.
Instructions for use
Instructions for the use of paracetamol tablets for children recommend taking the drug orally with plenty of liquid 1-2 hours after a meal (taking immediately after a meal leads to a delay in the onset of the drug effect). The tablet drug is prescribed to a child only after two years of age, not earlier.
It is very difficult for any child to swallow tablets, so parents try to crush them and disguise them with sweetened water, but not every child willingly takes the bitter powder.
Does Paracetamol help with headaches?
The analgesic copes well with aching, sharp, lingering headaches. Paracetamol is very effective for blood pressure: after taking the medicine, it begins to dilate blood vessels, making them elastic, flexible, restoring blood flow. For migraines and other types of pain, the drug relieves pain by reducing the synthesis of cells responsible for unpleasant sensations. The drug is taken only with water. Tea, coffee, carbonated drinks can cause liver problems.
The recommended dosage is no more than 1000 mg per dose. You are allowed to take no more than 4 times per day, unless otherwise prescribed by your doctor. The product is convenient to use for any category of patients: suppositories and syrup are suitable for children over 3 years old; tablets are suitable for teenagers and adults. It is better to contact a specialist so that he can select the form of the medicine and prescribe the dosage in accordance with age and weight category.
- Powder for colds: list of effective drugs
- Remedy for poisoning: the best medicines for children and adults
- How to get rid of pain during menstruation - the best analgesics. Tablets and methods for severe menstrual pain
Dosage
The drug is prescribed at a temperature of at least 38 degrees that occurs for various reasons (flu, infection, virus, post-vaccination reaction).
The dosage of tablets at a temperature is determined taking into account the age of the patient.
- The regulated dosage for children aged 3 to 6 years is 150-200 mg. Pediatricians, without further ado, prescribe one tablet at a time. For skinny kids, half is enough. The permissible maximum is 800 mg / day (no more than 4 pieces).
- For older children (from 6 years of age), the dose is increased to 1.5-2.
If the fever does not subside, the medicine is given again. The minimum interval between doses is 4 hours.
It is strictly forbidden to use this product in parallel with other drugs containing paracetamol.
About efficiency
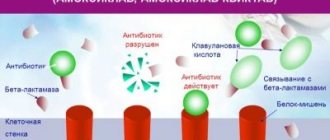
Dispensing Paracetamol without a doctor's prescription, the possibility of using it without consulting a specialist - all this is possible due to the peculiarities of the pharmacological activity of the main component of the drug. The substance affects the human body differently than other painkillers; it inhibits the production of prostaglandins, mediators of the inflammatory process, while affecting COX-3. The central effect due to this mechanics is explained by the properties of the drug as an antipyretic and analgesic. In the selective mode, the active component weakly inhibits COX-2, but this effect is quite insignificant, and therefore is not taken into account when it is necessary to work with the source of tissue damage.
Clinical studies on this issue have clearly confirmed the effectiveness of the use of Paracetamol to combat acute and chronic pain syndrome. There is reliable evidence of significant results of use after surgery.
Action, reviews
Paracetamol tablets provide analgesic and antipyretic effects; its anti-inflammatory activity is weakly expressed. The mechanism of action is to suppress the production of prostaglandins, which are responsible for the inhibition of the thermoregulation center and the development of the inflammatory reaction.
Active absorption of paracetamol occurs in the small intestine, then through the bloodstream it is transported to the tissues and organs of the body, distributed in its liquid media, excluding adipose tissue and cerebrospinal fluid.
About 25% of paracetamol forms a bond with blood plasma proteins. Glucuronidation and sulfation in the liver ensure the elimination of about 80% of the active component, at the same time, paracetamol and glucuronide sulfate are formed, which are metabolized by the kidneys. An intermediate product of the metabolism of an insignificant amount of paracetamol is paraaminophenol, which further participates in the synthesis of methemoglobin, which explains the toxic effect of paracetamol in overdose and long-term use. No more than 5% of paracetamol in unchanged form is excreted during urination.
40 minutes after taking paracetamol, its highest concentration in the blood is recorded.
The half-life of the substance lasts about 2-4 hours in healthy people; in those suffering from pathological conditions of the liver, this period is longer - within 8-12 hours.
Reviews from specialist doctors
A good antipyretic drug, but in terms of analgesic effect it copes worse. The duration of its antipyretic effect is 7-8 hours, analgesic - about 5-6 hours. It is recommended to strictly adhere to dosages, since the drug is hepatotoxic. There are many analogues with different names, carefully look at the composition so as not to take the same paracetamol twice.
An excellent antipyretic agent, tested more than once in practice. Allows you to quickly reduce high fever and chills. The effect occurs within 8-10 minutes. after administration (through the mechanism of sweating) and continues for quite a long time. You will have to sweat a lot after taking it. Suitable for typical diseases accompanied by high fever.
A good antipyretic drug from the group of antipyretics. Suitable for use in different age groups. Different release forms make it easier to use in children. In personal practice, the administration of the drug was not accompanied by adverse side effects. Excellent price and availability of the drug in the pharmacy retail chain.
Reviews from people
Children's paracetamol tablets are very effective for reducing fever and as a pain reliever. When a child is small, for various reasons his temperature rises, and paracetamol very quickly helps to reduce it. I've been giving my baby paracetamol almost from the cradle. It does not cause allergies or any reaction. Plus, paracetamol has a calming effect, and after using it, the child sleeps peacefully and sweetly. Of course, when he sleeps, I periodically check his temperature. Despite its inexpensive price, paracetamol copes with its task more effectively than its expensive analogues. Therefore, I confidently recommend paracetamol to children at a very early age.
When we encountered a fever when our daughter was two years old, the first aid kit was immediately replenished with antipyretics. Nurofen worked well, but with a strong fever it only lasted about three hours. The hope remained in alternating it with paracetamol. So, it didn’t help at all, didn’t relieve the pain at all, even though the temperature froze at the same level. I had to spend three hours rubbing. For two years, paracetamol has never been able to bring down the fever one degree. I took another company and candles - everything is useless. The doctor said that with white fever, heat transfer is difficult, and this greatly aggravates the likelihood of a decrease in temperature, but without vascular spasms, paracetamol did not help.
When the temperature rises, we always use paracetamol for children. I know that many people refuse it because it supposedly does not bring down the temperature, but for my children these pills always work flawlessly. After application, the temperature begins to decrease within half an hour, sometimes you have to wait about an hour. Another reason for choosing this medicine was its low price. Why overpay for the same drug if the expensive analogue is no better.
Video
Below is a short video review about the drug paracetamol.
Release form
Paracetamol for children has various forms of release: syrup, suspension, rectal suppositories, tablets.
Paracetamol tablets
If it is possible to purchase another form of medication for your child, it is better to do so. Paracetamol tablets are contraindicated for children under 2-3 years of age. Some doctors say that children under 5 years old should not be given paracetamol tablets.
Children's paracetamol (tablets) is available in a dosage of 200 mg. The only advantage of this form is the price. In order for the child to take the tablet, it must be crushed. You may not like the taste, so it is recommended to mix it with honey or sweet jam.
All indications and contraindications for paracetamol tablets are identical to other forms of release. The interval between taking tablets should be at least 6 hours. Single dose:
- 10-15 mg/kg body weight;
- but not more than 60 mg/kg body weight per day.
Paracetamol in syrup
There is syrup and suspension of paracetamol. The difference is that syrup is a dosage form containing sugar and alcohol. Therefore, some sources contain information that syrup should not be given until 2 years of age, although some manufacturers’ instructions recommend starting from 6 months.
Indications for use: hyperthermia for viral infections (influenza, ARVI), childhood infections (measles, scarlet fever, rubella, mumps, chicken pox, etc.); pain of various origins: arthralgia, myalgia, neuralgia, toothache, headache; injuries, burns; post-vaccination syndrome.
Contraindications are:
- individual intolerance to paracetamol or other components included in the syrup;
- impaired liver and kidney function, leukopenia, age up to 6 months;
- congenital hyperbillirubinemia.
The peculiarity of using the children's form of paracetamol is that it can enhance the effect of indirect anticoagulants and chloramphenicol.
A hepatotoxic effect is possible when taking rifampicin, phenytonin, barbiturates and antidepressants.
Suspension
The consistency is very similar to syrup and does not contain alcohol. The maximum concentration in the blood can be achieved within 30 minutes. up to 2 hours. Manufacturers claim that the suspension does not have a negative effect on the gastric mucosa. Indications for use are identical to tablets and syrup.
Side effects may include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, allergic reactions, changes in blood counts - leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, pancytopenia, methemoglobinemia.
The use of the suspension simultaneously with other drugs, as well as for more than 5 days, must be agreed with a doctor and blood counts monitored.
Dosage with a measuring spoon at the rate of 10-15 mg/kg body weight.
Rectal suprositories
Available for children in a dosage of 0.8; 0.17; 0.33 g. This is convenient for those parents whose children categorically refuse to take medications. They are especially convenient for babies from 3 months. Maximum concentration in the blood after 30-120 minutes. If we compare liquid paracetamol and suppositories, the former act faster.
Suppositories are used:
- 0.8 at the age of 3-12 months;
- 0.17 from 1-6 years;
- 0.33 from 7-12 years.
The intervals between the use of paracetamol should be at least 4 hours, but 6 hours is better. If the temperature rises before the specified time, then you can give, for example, Nurofen. On average, paracetamol “holds” the temperature for 4-6 hours.
If a child has a hot head and body, and cold feet, this is “white” hyperthermia. Then you need to give the child no-shpa. If the temperature rises frequently or is high, it is better to call an ambulance.
Contraindications
The list of contraindications is small compared to other drugs. This includes:
- individual intolerance;
- age up to 2 years;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract with the formation of ulcers and erosions, gastric bleeding, inflammation, active bleeding;
- progressive pathologies of the kidneys, liver, severe forms of failure of these organs;
- intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs;
- hyperkalemia (increased potassium levels in the blood).
Reception features
The drug in question and all painkillers made on the basis of paracetamol are intended for one-time use. It is strictly forbidden to take such medications on a regular basis. The body may get used to the flow of the analgesic, which is extremely undesirable.
In case of discomfort or any minor problem, it is not recommended to take the drug. Paracetamol is intended to relieve pain in an emergency when the patient has a fever. The main purpose of taking such a medicine is temporary relief of the condition, allowing you to wait for the doctor to arrive or get to the appointment yourself. If the condition has not improved after half an hour, it is not recommended to take the pills again.
Paracetamol as a pain reliever for pain should be taken no more than four times a day. Excessive intake may cause nausea and vomiting. An overdose is indicated by general weakness, the patient quickly gets tired. Excessive intake of Analgin and Citramon manifests itself with similar symptoms. It is worth remembering that the latter is made on the basis of paracetamol and other components, and the combined composition is more dangerous for the liver. Paracetamol is considered less aggressive than Citramon.
Side effects
When taking the drug, there is a risk of the following side effects:
- allergic reactions (skin rashes, itching, urticaria, Quincke's edema);
- nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain;
- hepatotoxic effect;
- agranulocytosis, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia;
- anaphylactic shock (rare);
- impaired renal function, oliguria, anuria, proteinuria, interstitial glomerulonephritis;
- urticarial rash on the conjunctiva and mucous membranes of the nasopharynx;
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome;
- toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome);
- bronchospastic syndrome;
- aseptic pyuria.
Pharmacological properties
A non-narcotic analgesic, it blocks cyclooxygenase (COX) 1 and COX 2 mainly in the central nervous system, affecting the centers of pain and thermoregulation. In inflamed tissues, cellular peroxidases neutralize the effect of paracetamol on COX, which explains the almost complete absence of anti-inflammatory effect. The absence of a blocking effect on the synthesis of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues determines the absence of a negative effect on water-salt metabolism (sodium and water retention) and the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract.
Pharmacokinetics. Absorption is high, time to reach maximum concentration (TCmax) is 0.5-2 hours; maximum concentration (Cmax) - 5-20 μg/ml. Communication with plasma proteins - 15%. Penetrates the blood-brain barrier. The therapeutically effective concentration of paracetamol in plasma is achieved when administered at a dose of 10-15 mg/kg. Metabolized in the liver (90-95%): 80% enters into conjugation reactions with glucuronic acid and sulfates to form inactive metabolites; 17% undergoes hydroxylation to form 8 active metabolites, which conjugate with glutathione to form inactive metabolites. With a lack of glutathione, these metabolites can block the enzyme systems of hepatocytes and cause them. The CYP2E1 isoenzyme is also involved in the metabolism of the drug. The half-life (T1/2) is 1-4 hours. It is excreted by the kidneys in the form of metabolites, mainly conjugates, only 3% unchanged.
Overdose
Due to parental oversight, many children find where the pills are hidden. Sometimes they think of trying them. What happens if you take 10 Paracetamol tablets at once? Everyone knows the answer; of course, an overdose will occur.
The active ingredient paracetamol is safe for children if the dosage is calculated correctly. Ten tablets are 2000 or 5000 mg of the active ingredient. Plus, keep in mind that they also contain additional substances that are unsafe for health in large quantities.
Taking 10 tablets can cause liver toxicity.
And the child is likely to develop toxic hepatitis, which over time turns into cirrhosis. The consequences of an overdose can be fatal for a child. As for liver recovery after paracetamol, you will have to undergo more than one course of treatment, which will include not only drugs and IVs, but also blood transfusions. As you can see, paracetamol is dangerous for newborns, school-age children and adolescents if the dosage is not observed, especially when taking a large amount of the active substance. That is why the pharmaceutical factories that produce the medicine write in the instructions that the drug should be stored out of the reach of children. In case of overdose, there is a risk of the following symptoms:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness;
- impaired renal function;
- pale face;
- hives;
- skin rash (appears first on the cheeks);
- sharp pain in the abdominal cavity;
- Quincke's edema.
How to take Paracetamol for a cold
Everyone understands that it is necessary to treat colds in a timely manner. Otherwise, serious complications may occur. At the initial stage of development, colds are characterized by weakness and increased fatigue. With ARVI, the temperature often rises, chills, cough, runny nose, and sneezing appear. Pain in the joints and muscles also occurs.
You can minimize the manifestations of all these symptoms and stabilize the condition with the help of Paracetamol. But at the same time, the drug should be used exclusively during complex therapy.
Almost always, the drug in tablet form is prescribed for the treatment of adults and children over 12 years of age. An important condition in the second case is that the child must weigh more than 49 kg, otherwise it is difficult to choose the dosage.
Due to the fact that there are other forms of the medicine, it can be prescribed to treat young children:
- The suspension
is approved for use in the treatment of children under one year of age. It is quickly absorbed, and thanks to the fact that the kit includes a special dispenser syringe, it is easy to maintain the required dosage. - The syrup
is used to treat children after one year. For the correct dosage, use a special dispensing spoon, which is included in the kit. Rejection of the drug in a child is rarely observed, since the syrup contains flavoring additives, most often imitating the taste of strawberries or bananas. - Rectal suppositories
are used for young children when there is a rise in temperature. This allows you to stabilize the baby’s condition before the ambulance arrives.
In most cases, when treating a cold, the medicine is taken by adults, 1 tablet 4 times a day. The course of treatment should not exceed three days. This time is usually enough to stabilize the condition. If you manage to bring down the temperature earlier, then you should stop using Paracetamol.
When using an antipyretic drug, it is important to completely abstain from alcoholic beverages. Otherwise, the load on the liver will increase significantly, which can cause negative consequences.
Analogs
Typically, paracetamol, if taken correctly, does not cause side effects, but in some situations reactions of individual intolerance or allergies appear. Most often, an allergy to paracetamol develops in a child, because his immune system is not yet fully formed and is not ready to fight back some foreign substances.
If the product does not work, there are decent replacement options:
- Nurofen (active ingredient: ibuprofen). This medication is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, it lowers fever better and does not have a negative effect on the liver. The only contraindication is acute painful kidney conditions.
- Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) is a good pain reliever and has antipyretic properties. Not suitable for children. Changes platelet aggregation, greatly thins the blood. Has less toxic effects on the liver and kidneys.
- Diclofenac is a good pain reliever, but does not lower the temperature. Has strong anti-inflammatory properties.
Other drugs for severe pain are ketanov, nalgesin, nise, indomethacin.
Paracetamol for the treatment of nursing mothers and children
Paracetamol can be taken once by a mother while breastfeeding.
If a nursing mother needs to relieve pain, doctors recommend paracetamol. It minimally passes into milk (less than 0.25%) and does not harm the child with a single use.
Breastfeeding women with toothache should take the drug immediately after feeding. Its highest concentration in a woman’s blood is achieved half an hour after administration.
It is advisable to avoid feeding during this time. Feeding a child becomes safe a few hours after taking the drug, when it is eliminated from the body.
If a child over three years old has a toothache, you can give him half a tablet of medicine. After this, you must urgently consult a dentist to eliminate the cause of the pain.
Characteristics of the drug
Paracetamol belongs to the group of non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs with pronounced antipyretic and analgesic effects. The anti-inflammatory property of the drug is noted due to the inhibition of the synthesis of prostaglandins and other inflammatory mediators, and the antipyretic effect is manifested due to a decrease in the excitability of the thermoregulation center, and the effect of Paracetamol is observed throughout the entire time until the drug substance is eliminated from the body.
The onset of action of the drug is observed, on average, after 20-30 minutes and continues for the next 3-4 hours .
After 4-5 hours, the medicine is completely eliminated from the body by the kidneys, which is the main priority among other medications of similar action. The maximum concentration in the bloodstream is observed after 50-90 minutes.
The variety of release forms of Paracetamol allows its use in complex therapy for patients of all age categories. That is, each defined form is used as follows:
- the suspension is prescribed for the treatment of children from 1 month to a year, because a child at this age swallows liquids better, and the medicine contains no additives other than Paracetamol and excipients;
- syrups that have a sweetish taste are used for children older than one year and up to the age of 6-8 years, that is, until the child learns to swallow tablets and capsules;
- The tablet form of Paracetamol acts more slowly and is recommended for older children and adults who can swallow it without difficulty;
- suppositories with Paracetamol are good to use for all age categories, because, unlike oral forms of the drug, they do not have a negative effect on the gastric mucosa and have a more prolonged effect over time, which is excellent for nightly use;
- The capsule form of Paracetamol can be used by everyone, but for children for whom sweet syrups and suspensions are contraindicated, you just need to open the capsule and mix the powder with water or honey.
If Paracetamol does not work and does not reduce the temperature, you can take an Aspirin or Analgin tablet after 30-40 minutes. You should not combine these drugs unless absolutely necessary, since they are quite irritating and can provoke the development of gastritis or gastric ulcer.
special instructions
If elevated body temperature persists after 3 days of taking paracetamol, and pain persists after 5 days of using the drug, you should definitely consult a doctor.
With long-term use of Paracetamol-UBF, monitoring of peripheral blood parameters and the state of liver function is required.
Paracetamol is not recommended to be taken simultaneously with alcoholic drinks, or for patients prone to chronic alcohol consumption. In patients with alcoholic hepatosis, the risk of liver damage increases during drug therapy.
When conducting a study on the quantitative content of glucose and uric acid in plasma, false results may be obtained.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and complex mechanisms
There is no data confirming the negative impact of Paracetamol-UBF on the ability to concentrate attention or perform movements quickly and accurately.
Drug interactions
Effect of paracetamol on other drugs:
- increases the effect of anticoagulants;
- reduces the effect of uricosuric drugs;
- increases the risk of developing bladder or kidney cancer in patients receiving salicylates;
- reduces the secretion of diazepam;
- slightly increases the excretion of lamotrigine;
- increases the risk of developing analgesic nephropathy and renal papillary necrosis, the onset of end-stage renal failure in patients receiving non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for a long time;
- increases the likelihood of a slight or moderate increase in prothrombin time in patients receiving anticoagulants;
- may enhance the myelosuppressive effect of zidovudine. There is a known case of severe toxic liver damage.
The effect of other drugs on paracetamol:
- inhibitors of microsomal oxidation (including cimetidine) - reduce the risk of hepatotoxicity;
- cholestyramine and anticholinergics - reduce absorption;
- ethinyl estradiol and metoclopramide - increase absorption;
- activated carbon – reduces bioavailability;
- probenecid – reduces clearance;
- rifampicin and sulfinpyrazone - increase clearance;
- barbiturates – reduce effectiveness;
- diflunisal – increases plasma concentration and the risk of hepatotoxicity;
- isoniazid and phenobarbital - may enhance toxic effects;
- myelotoxic drugs – increase the manifestations of hematotoxicity;
- hepatotoxic drugs, ethanol, inducers of microsomal enzymes in the liver (tricyclic antidepressants, barbiturates, phenytoin, phenylbutazone, rifampicin) - increase the production of active hydroxylated metabolites of paracetamol, which increases the risk of developing severe intoxications even in the case of a slight overdose;
- carbamazepine, primidone, phenobarbital, phenytoin, oral contraceptives - accelerate elimination and, as a result, reduce the effect.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
It is known that paracetamol is able to penetrate the placental barrier and in very small quantities into breast milk. Experimental studies did not reveal teratogenic, embryotoxic or mutagenic effects. During clinical experience with the drug, no negative effects on fetal development were noted.
Paracetamol-UBF 500 mg tablets can be used during pregnancy and lactation in cases where the expected benefits outweigh the potential risks.
Indications for use
What is paracetamol tablets used for? Drug therapy using paracetamol is prescribed by a doctor in the following cases:
- Severe toothache.
- Migraine.
- Myalgia, menalgia, arthralgia.
- Infectious fever.
In addition to pain, paracetamol is used for intolerance to salicylic acid and its derivatives, and can be used for chickenpox.
Paracetamol in combination with other medications
Often, for certain diseases, experts prescribe the use of this composition in combination with other medications. Let's look at the main points related to this:
- this should be allowed only with the appropriate recommendation of a specialist after the examination;
- the drugs must be suitable for simultaneous use and not contain relevant contraindications;
- use in such a combination is not allowed in the presence of certain pathologies and functional abnormalities;
- before taking it, be sure to find out about the side effects and any contraindications present;
- in practice, quite often this component is present in other stronger painkillers.
In modern pharmaceuticals there are a number of drugs that contain Paracetamol. Quite often, this component can be combined with Tramadol, codeine and dihydrocodeine. Here we are talking about stronger drugs that are used for serious disorders and pain in a person suffering from a certain disease.
How does this drug work?
Paracetamol has an effect on the human brain, namely on its pain and thermoregulatory centers. It stops cyclooxygenases (enzymes that cause fever) in the central nervous system and has virtually no negative effect on the gastric mucosa. The drug also has a very weak anti-inflammatory effect. Therefore, it is not used for pain with severe inflammation.
Paracetamol is indicated for the symptomatic treatment of pain of various origins of mild to moderate intensity:
- headache;
- toothache;
- neuralgia;
- back and joint pain;
- menstrual pain.
This medicine is produced in the form of tablets, suspensions, syrups, and also in the form of suppositories.
Correct use of the product:
- The tablets should be taken orally with plenty of water (at least 100 mm). If you take the tablet with warm milk, it will work faster. Do not take the drug with tea or coffee. These two drinks contain a large amount of caffeine, so the metabolism of the drug in the body may be disrupted. Paracetamol should be taken 1-2 hours after meals to make the drug more effective. If the medicine is taken immediately after a meal, its absorption into the blood slows down, and accordingly, its effect on the body slows down. If you use Paracetamol before meals, it can lead to problems associated with the gastrointestinal tract. Paracetamol begins to act in about 15-30 minutes, the maximum effect is achieved after 2 hours. In some cases, the effect may not occur for two hours or more. This is due to severe cramping or low fluid intake. Let us remind you that Paracetamol should be taken with plenty of water - only then will it act quickly enough. If you take it without drinking it, it may not work. Its dosage is prescribed by the attending physician. It is completely eliminated from the body 6 hours after the last dose of the drug.
- Paracetamol syrup in appearance is a yellow viscous liquid, sweet with a tart taste and a fruity smell. In this form, the medicine is prescribed to children from several months to 6 years old, since it is difficult for children to swallow the tablet. After taking the medication, the active components are absorbed by 90%, which provides a quick result and the child soon feels relief. The effect of the drug occurs within 30-40 minutes. The medicine is completely eliminated one day after its last use.
- The main difference between a suspension and a syrup is the absence of alcohol and lower sugar content. The medicine is a viscous liquid of pinkish color with a pleasant, fruity aroma. The active ingredient here is Paracetamol. Excipients are glycerin, methyl parahydroxybenzoate, liquid sorbitol, xanthan gum, citric acid. The suspension or syrup must first be shaken, then poured into a measuring spoon and swallowed with plenty of water.
- Candles. In the form of a suppository from white to white with cream or white with a yellowish tint, solid torpedo-shaped. The main substance here is Paracetamol, and the excipient is a solid fat base. Main advantages: no dyes, longer lasting effect compared to syrups and suspensions, applied rectally.