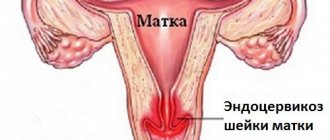
Histological examination: when is it necessary?
Histology in gynecology is one of the popular and effective methods for diagnosing the disease today. For example, for various gynecological diseases associated with the uterus, endometrial polyps, endometritis, histology is simply irreplaceable. Part of the tissue, obtained aspirate (scraping) from the uterine cavity, has highly informative material that will allow you to determine the presence or absence of oncology.
If you consult a doctor in time and identify the problem, treatment can be started at an early stage and then it may be possible to avoid surgical intervention.
There are many reasons why histological examination of the tissues of the uterine cavity is indicated.
- the need for a detailed study of fetal tissue during pregnancy; blurred colposcopic general picture; hyperplastic conditions of the endometrium and cervix; acyclic bleeding; cytology results are negative; bleeding during menopause; examination of the tissues of the cervix, endometrial mucosa and uterine cavity in case of a frozen fetus; identifying the causes of tumor formation; after curettage of endometrial polyp, endometritis, etc.
A gynecologist can also prescribe histology if the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- incomprehensible, causeless pain in the lower abdomen; prolonged bleeding; roughness and irregularities on the mucous membrane of the organ; leukoplakia; the presence of any type of tumor; other abnormalities detected during a general gynecological examination; to establish the state of the endometrium in the required phase of the menstrual cycle.
Sample materials are taken under anesthesia by scraping or cutting off a piece from the desired area.
Significance in gynecology
Histology analysis
necessary when the following situations occur:
- frozen pregnancy;
- birth of a deceased child;
- permanent endometritis;
- questionable symptoms during colposcopy;
- tumors on the uterus;
- bleeding during;
- infertility;
- histology in gynecology after curettage.
If the fetus died in the early stages, the gynecologist performs curettage to determine the cause of the miscarriage or fading. After eliminating the pathology, the patient has a chance for a successful course of subsequent pregnancies. What a histological examination shows: the presence of diseases that prevent successful pregnancy.
These include:
- hormonal disorders,
- genital infections,
- endometrial abnormalities.
Control of the endometrium after curettage
The operation is performed before the onset of the planned menstruation to identify altered cells. If during the manipulation there is a suspicion of oncological pathology, an express study is carried out , the results of histology will allow the operation to be adjusted.
Important!
Histological diagnostic methods in gynecology make it possible to identify the causes of infertility, miscarriage and detect tumor cells before the onset of clinical signs of the disease.
Analysis transcript
If the analysis was carried out in a state institution on the direction of a gynecologist, then the woman will learn the results of the histological examination at a doctor’s appointment.
In a private clinic, the histology transcript is given to the patient on three forms. A woman who does not have a medical education should not try to understand the records.
Many histology results are written in Latin. It is reported what research methods were used - composition of solutions, brand of dyes. A long list of items in the conclusion does not mean that this
Badly.
The doctor who deciphered the analysis describes everything he saw: pathological changes and tissues that correspond to the norm. What is histology in
diagnosing gynecological diseases is an informative way that helps the doctor draw a conclusion about the state of health, prescribe treatment and preventive measures. The conclusion does not contain recommendations for the treatment of the detected disease. VKontakte
Histological examination is one of the most accurate methods for identifying diseases of the female reproductive system. Reliable diagnostics are carried out by professionals using the latest equipment, which eliminates errors and the need to repeat the procedure. Histology of the uterus is carried out on the basis of tissues taken by biopsy, the cells of which are later examined.
Histology: scraping and aspirate
Why is scraping done? A scraping for histology is taken from the uterine cavity and cervical canal to: establish the cause of problems with conception, uterine bleeding of unknown etiology, determine the hormonal level in the body, find out whether there are malignant neoplasms.
The scraping is taken like this: the uterine cavity and vagina are united by the cervical canal, which goes through the cervix. The canal and organ cavity are lined with mucous membrane. First, using gynecological instruments, by cleaning they try to get the mucous part without touching the layer underneath it.
They can also do a test scraping, in which a small piece of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal or some areas of the uterine cavity is collected. As a rule, they do a complete cleaning and take all the material obtained (the doctor must indicate on the test tube where the highly informative material was taken from). Curettage is performed using painkillers.
Aspirate is a gentle method. Vacuum aspiration is performed to obtain the contents of the uterine cavity. Today, improved and modern vacuum-type syringes are used for this method. Using a syringe, the contents are collected, and the mucous part is less injured. There are no preparation measures, vacuum aspiration is carried out in a antenatal clinic by a gynecologist, the procedure lasts only a few minutes and no painkillers are needed.
Before the study, the doctor prescribes:
- taking a smear of vaginal microflora; general blood analysis; coagulogram; analysis for the presence of infections; cytology; tests for syphilis, HIV infection, hepatitis; colposcopy.
If there is any inflammation or infection, the procedure is postponed until complete healing.
Indications for the study
The reason for prescribing an analysis may be pain in the lower abdomen, abnormal menstrual cycle, or discomfort during sex. This research method is used for pathologies of the cervix, the main reproductive organ. A timely examination will give a chance to begin therapy in the early stages of the disease. In some situations, a smear for histology allows you to avoid surgical intervention. Diagnosis of the cervix is carried out if the presence of leukoplakia, abnormal cells, or uneven tissue surfaces is suspected.
After the analysis, an ectopic or frozen pregnancy, malignant or benign neoplasms can be detected. Diagnosis is made in case of chronic inflammatory process in the endometrial area, acyclic uterine bleeding, hyperplasia, suspected cancer of the uterine mucosa. The study is prescribed when a polyp or fibroid is detected.
The technique is used to identify various abnormalities and pathologies. Histological analysis is a study of the endometrium, a study of the structure of the fetus. The study allows you to study the exact structure of any tissue. Diagnostics are prescribed after curettage for various indications, for any abnormalities identified through a routine gynecological examination of the woman’s reproductive system in a chair.
Research in a medical laboratory
Immediately after receiving highly informative material, it is sent for analysis. Before starting a full and thorough study, it is necessary to prepare it.
- the material is dehydrated, which then makes it possible to compact it; prepare the necessary sections; stained with specially designed preparations; placed in a conservative environment.
Absolutely all tests are examined in a medical laboratory under an electron microscope. The selected material is illuminated by a beam of electrons. Such a microscope allows you to magnify information material by 106 times. The duration of the analysis is from 5 to 10 days.
Preparation of material for analysis
The manipulation is carried out in stationary conditions. Material for research is selected by biopsy - taking prints, smears, films or tissue sections
. For each method, instructions have been developed, the exact execution of all points of which is mandatory. A tissue sample is fixed with ethanol or formaldehyde, sectioned, stained, and examined using an electron microscope.
To conduct studies under light, fluorescent, phase-contrast or scanning magnifiers, complex preliminary preparation is required. Tissue sections are placed in a specialized balm or filled with paraffin. Material collection
from various organs or textures is carried out using a punctate needle, trepanation, or aspiration method.
The selected material goes through the following processing steps:
- Fixation with formaldehyde or alcohol. Proteins coagulate, enzymes are inactivated, the cell dies, but does not disintegrate.
- Wiring. The sample is dehydrated and impregnated with paraffin.
- Filling. The container with the prepared material is filled with a hot liquid that hardens at room temperature. A solid formation is created, which can be conveniently divided into thin layers using a microtome.
- Cutting. Different thicknesses are recommended for different microscopes.
- Mounting. The slice is placed on the surface of warm water, and from there onto a glass slide to avoid wrinkles.
- Coloring.
- The final stage. The prepared section is covered (enclosed) with a protective film of Canada balsam or its equivalent. The drug can be stored for a long time.
How many days is the analysis done? This is a labor-intensive process that, together with decryption, takes from 7 to 10 days.
Endometrial polyp curettage: histology of material
Removal of a uterine endometrial polyp is sometimes simply necessary. After the operation, the excised material is necessarily sent for histological examination. Such an analysis will help determine the nature of the polyp and its possibility of degeneration into cancerous tumors.
A polyp is a benign neoplasm that affects the cavity and walls of the uterus. The size of the polyp can be from 2 to 5 mm, and sometimes several centimeters. The reason for the formation of a polyp is the proliferation of the mucous layer of the endometrium.
They do not always need to be removed; they can resolve on their own. Removal of a polyp is carried out not only for therapeutic purposes, but also to find out whether the formation has a predisposition to cancer.
Attention! Histology will help to identify precancerous formations in the early stages, and this significantly affects the healing process!
When a polyp is curetted in a private clinic, the patient receives the results in person. The specialist deciphers the research results.
Method of carrying out after organ excision
Conization of the cervix involves excision of tissue. The analysis allows us to identify the presence of pathology at an early stage and begin timely treatment. The obtained materials must be sent for histological examination. Tissue collection occurs using several methods:
- knife;
- laser;
- loopback.
The first method of collecting material is practically not used, since it can lead to serious consequences. Loop conization is often used. If during a previous examination the doctor diagnosed cancer, this research method is prohibited. The examination shows the presence of a malignant formation, polyp, cyst, cervical hypertrophy, dysplasia. After conization, some complications may occur, such as endometriosis on the cervix.
Timeframe for analysis
In fact, each clinic or medical institution, when asked how long a histological examination takes, gives its own reasoned answer. On average, this is approximately 5 to 10 days after the information material is received.
Also, the timing depends on whether the institution has its own medical laboratory for analysis. Of course, if there is, the terms are minimal. If the analysis is ordered from another laboratory, delivery alone may take about 3 days.
There is also express diagnostics, which is carried out directly in the operating room itself. Sometimes during surgery there may be obvious suspicions of oncology, then the tissues are examined in a short time. If the result is positive, the operating surgeon must perform an extended removal, taking into account the rules for excision of cancerous tumors.
Only a specialist deciphers the tests; a person without a medical education will not be able to understand anything, since the result is in Latin.
Some people are concerned about the question: can such analyzes be erroneous? As a rule, histology is an accurate analysis and errors occur extremely rarely. If all the rules for collecting, preparing, processing and examining tissue are followed, then there can be no error.
When is cervical histology indicated?
Histology is carried out after the initial diagnosis of the genital organs. This method is used to confirm a diagnosis that the doctor suspected during a mirror examination, ultrasound and colposcopy. The study makes it possible to distinguish benign tumors from cancer.
Tissue for examination is collected using diagnostic curettage or aspiration biopsy. In this case, biological samples are taken from the cervix and uterine cavity. The test identifies atypical cells and determines the stage of the pathological process.
Cervical histology is prescribed for the following indications:
- signs of pathologies during examination in the mirrors;
- affected areas of the cervix during hardware studies (,);
- infection with human papillomavirus (HPV);
- poor cytogram results;
- keratosis of the squamous epithelium of the cervix;
- long-term treatment of inflammation of the cervical canal with medications;
- performing polypectomy;
- suspicion of and;
- foci of endometriosis (proliferation of the endometrium of the uterus);
- identification of any tumors and growths of the cervical canal;
- the appearance of signs of cervical dysplasia (the first changes in the cells);
- bleeding after menopause;
- , miscarriages, frozen pregnancy;
- (abundance, change in color and consistency of discharge);
- hereditary factor (cervical cancer in close relatives).
Treatment of the tumor is prescribed only after receiving the results of the histological test. To assess the effectiveness of treatment, the analysis is repeated. This allows you to adjust doses and medications.
What is histology?
Histology is the science of the state of the body at the tissue level.
The analysis is closely related to cytology (the study of cells) and embryology (the study of the structure of the fetus) and allows one to study the exact structure of any tissue, so it is often prescribed to identify various abnormalities and pathologies.
To conduct a histological examination, a small piece of tissue is taken from a person: sometimes it is just a smear or print, but it can also be a thin section directly from the organ being examined.
The study lasts on average 5-10 days (in rare cases, urgent histology is performed from 1 to 24 hours, but it is less reliable) and is carried out in 7 stages:
- Fixation - the tissue fragment is treated with a liquid that prevents the breakdown of cells and structures so that the material does not rot during the study. Wiring - the material is dewatered for compaction. Embedding - The tissue is impregnated with paraffin or another embedding preparation to prepare a solid block for sectioning. Cutting - using special equipment - a microtome - the solid block is cut into the thinnest plates. Staining - sections are laid out on glass slides and stained with special preparations to determine different tissue structures (DNA, RNA, cytoplasm, etc.). Conclusion - the prepared sections on glass slides are covered with a second layer of glass with the medium necessary to preserve the material for a long time. Research - the resulting histological preparations are studied by histologists or pathomorphologists using an electron or light microscope.
In gynecology, histology is usually prescribed to study tissues of the fetus, uterus and cervix.
In the USA, many people are vaccinated against HPV, but in our country few people know about it; you can use the link to fill in your knowledge gaps.
Diagnosis and treatment of pathological formations
To diagnose uterine fibroids, it is important to undergo a gynecological examination in a chair using mirrors, as well as additional examinations and tests.
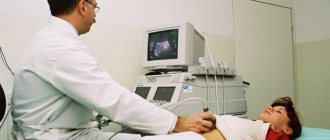
To establish an accurate diagnosis, an ultrasound examination is prescribed, it will help determine the location and size of the nodes. It is performed with a full bladder.
An effective method for diagnosing uterine fibroids is hysteroscopy. This procedure is carried out using a special device and allows you to examine the uterine cavity. This method helps to determine the size of the tumor and its location and to perform a biopsy or curettage.
To exclude pathology of the cervix, a histological examination is performed. After which treatment for the disease is prescribed. Depending on the form and severity of the disease, conservative or surgical treatment is prescribed. But more often a combined method is used to avoid relapse of the disease.
Drug therapy is recommended if:
- Myoma no more than 12 weeks of pregnancy.
- Presence of small subserous nodes.
- For some reason, surgery is contraindicated.
With this treatment, the patient is prescribed hormonal drugs, but individually for each woman.
Combined contraception will help stop the growth of formations and even reduce their size. The course of such treatment should be at least three months.
For small fibroids, gestagens are prescribed. Agonists help normalize hormonal balance in the body by reducing estrogen hormone in the blood.
But if the disease progresses, surgical intervention is performed, this is done for the following indications:
- Myoma has grown to a huge size (more than 13 weeks of pregnancy).
- There was profuse bleeding.
- The fibroid nodes began to grow rapidly.
- Infertility or premature termination of pregnancy.
- Necrosis of the node.
Complete removal of the uterus is more often performed for women who already have children and are no longer planning a pregnancy; the fibroids have grown to large sizes, with pronounced clinical manifestations.
But more often, modern methods are used to remove fibroids, which allow preserving a woman’s reproductive organs:
- Laparoscopy - this procedure is performed to diagnose the disease and simultaneously remove the tumor. The operation is performed under local anesthesia, the woman does not feel pain.
- Hysteroscopy - removal of pathology is carried out through the vagina.
After surgery, hormonal therapy is prescribed. You should avoid physical activity and abstain from sexual intercourse for two months. To avoid complications, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations by a specialist.
Histological examination of a frozen pregnancy or after a miscarriage
A frozen pregnancy in the medical sense is the same miscarriage, it just hasn’t happened yet.
In both cases, the doctor cleanses the uterus to avoid rotting of the embryo in the female body, which can lead to inflammation and severe illness. The extracted material (placenta) must be sent for histological examination.
Histology after a miscarriage, together with testing for viruses, hormonal imbalances, etc., helps determine the exact cause of spontaneous abortion or fetal death in the womb. Knowing the cause will help you avoid recurrence of problems in your next pregnancy.
Complication of uterine fibroids
Without specific treatment, a woman may experience serious problems:
- As fibroids grow, they can put pressure on other pelvic organs, interfering with their normal functioning.
- Hemorrhages lead to hematomas, which become inflamed, which contributes to the formation of cysts.
- Torsion of the leg of the node provokes necrosis, which requires urgent surgical intervention.
- Uterine fibroids disrupt the functioning of the reproductive organs, which leads to infertility or premature termination of pregnancy.
- Severe blood loss causes anemia.
With this diagnosis, a woman should follow a number of recommendations to prevent the development of the disease and complications:
- Follow a nutritious diet, consume more fiber and vitamins. Monitor your weight, because obesity can trigger the development of the disease and complications.
- Limit visits to baths and saunas, avoid prolonged exposure to the hot sun.
- Do therapeutic exercises, but avoid physical overexertion. You can use yoga to stay fit.
- Learn to relax, avoid constant stress and psychological tension.
- Stop using tampons.
In order to prevent uterine fibroids, it is important to promptly treat gynecological diseases and infectious diseases that are sexually transmitted.
Have sex regularly, avoiding abortions; for this you need to use contraception and monitor the hormonal balance in the body.
Even if nothing bothers a woman, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations by a gynecologist.
Histology for determining gynecological oncological diseases
It can be very difficult to determine the presence of cancer - often in the initial stages they are asymptomatic, so it becomes almost impossible to notice and manage to prevent their development. However, with regular visits to the gynecologist, it is possible to recognize the emerging disease. During the examination, the doctor will notice symptoms that the woman does not feel and will prescribe a histology of the affected organ.
The study allows not only to identify the pathology, but also to carry out the correct treatment: histology shows the category of the neoplasm - benign or malignant.
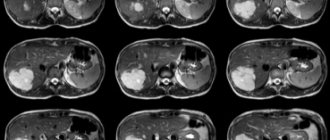
Histology of the uterus
To prescribe uterine histology, more noticeable symptoms and other studies (ultrasound, blood tests, etc.) . Symptoms for which histology is prescribed include:
- prolonged bleeding; causeless pain in the lower abdomen; leukoplakia; irregularities on the surface of the organ; neoplasms on or inside an organ and other symptoms related to tumor diseases.
Under sterile conditions under local anesthesia, the doctor uses gynecological instruments to cut out a piece of the tumor directly from the uterus. The tissue is sent to the pathology laboratory, where it is examined.
If abnormal tissue areas are detected, appropriate gynecological oncological treatment against cancer is prescribed. If the tumor tissue is homogeneous with the tissues of a healthy uterus, then the disease is benign (most often it is fibroids) and it can either be treated or wait until it goes away on its own (in some cases it does) - the gynecologist reports the exact decision.
Ovarian histology
It is carried out to determine the contents of cystic neoplasms on the ovaries or the type of tumor growths. To select the material, a puncture (puncture) is used through the abdominal cavity.
For many women, “these days” do not go as they should; at this address you will find out how long they should last from a medical point of view.
And by following the link you can find out ways to stop your period altogether.
Histology of the cervix
If inflammatory, precancerous or oncological diseases of the cervix are suspected, the gynecologist sends a small piece of it for histology.
The study helps determine the presence of erosion, dysplasia, flat condylomas, cancer and other diseases of the cervix, so that the gynecologist can prescribe correct and effective treatment.
The material is collected in the same way as from the uterus, but there is no need to dilate the cervix.
Other types of histology in gynecology
For histological examination to identify health problems in the female reproductive system, endometrial tissue, part of the mucous membrane from the cervical canal, and fluid from cystic formations in the vagina taken by puncture can be sent.
Indications for diagnostics
Quite often, histological studies are prescribed by gynecologists for the following diseases:
Inflammatory processes in the uterine cavity or neoplasms that have arisen there. Sudden and prolonged bleeding in a woman, an increase in the size of the organ itself, or detected polyps in the uterus are indications for a histological examination of this organ. Pieces of pathological tissue are taken for analysis either through a simple intervention - a biopsy, or all the material removed after surgery is sent for research.
Determining the causes of missed pregnancy or miscarriage. The loss of a child at any stage of pregnancy is a huge stress for a woman. To avoid a repetition of this traumatic situation, immediately after curettage, a histological examination of the tissues of the frozen fetus is performed, which allows us to confidently determine the reasons for what happened.
Multiple ovarian cysts. Histology is carried out to identify the causes of the formed growths and study the contents of these cysts.
Changes in the cervix. A huge amount of histological material is sent for research precisely for the purpose of early detection or complete exclusion of pathologies of this organ. Often, it is the early detection of cervical cancer that determines the favorable outcome of this terrible disease. Therefore, when receiving a referral for a procedure through which histological material will be taken, you should immediately undergo this examination.
Carrying out analysis
Tissue sampling for histological examination can only be performed by an experienced doctor, since the final result of the study will depend on the level of his skill. The analysis should be taken from the most changed area. Most often, tissue is collected using a biopsy. This is a simple and virtually painless procedure, after which the woman is immediately able to return to her previous daily routine.
// 10
The day before the intervention, you should not have sexual intercourse, douche, or use medications in the form of tablets and suppositories used vaginally.
Obtaining and interpreting histology results
The study of the cells of the taken material is not carried out by a gynecologist or even by an operating surgeon. Only a highly qualified pathologist has the right to conduct this study. The results of the analysis cannot be given to the patient earlier than 10 days after the cells are collected, since the procedure for preparing and staining the tissue itself takes a certain time.
There is also express diagnostics. Its results are ready in a few hours, however, this method is not so informative and is carried out mainly before surgical interventions in order to indicate the extent of the operation.
Often, upon receiving the histology results, patients become frightened when they see a large number of unfamiliar terms and try to make a diagnosis on their own. In fact, the interpretation of the results is the responsibility of the attending physician, and there is no need to delve into unnecessary terminology
The patient should also be aware that the chosen diagnostic laboratory is important in the preparation of histology results. The result of the analysis largely depends on the competence of the pathologist examining the tissue - he must have appropriate experience in conducting histological studies, and the laboratory itself where the analysis is sent must have high-quality equipment. Only with such a combination of two factors can you safely trust the conclusion handed out to you.
Histology in Moscow
You can take histology tests not only at the clinic, but also at various paid centers. In Moscow these are:
Source: https://ginomedic.ru/ginekologiya/diagnostika/gistologiya-v-ginekologii.html
Histology: analysis transcript
When filling out a sheet with research results, they use medical terms that are difficult for ordinary people to understand, and often the most unpleasant things from these terms are written in Latin.
The histology results are sent to the gynecologist, and based on them he will make a diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment. It is not recommended to decipher the analysis yourself, so as not to make yourself think about terrible diseases.
Almost all diseases today are curable, so it is better to rely on a doctor and his experience.
Sources:
http://aginekolog. ru/zdorove/matka/soskob-iz-polosti-matki-na-gistologiyu. html
http://1ginekologiya. com/info/gyn/gistologiya-v-ginekologii. html
How is cervical histology taken?
Tissue collection for histology is carried out by a gynecologist. The procedure consists of several stages:
- Stage 1.
The woman is located in a gynecological chair or on a couch. First, the doctor performs a standard examination in mirrors. This is necessary to identify the area of tissue damage. It is from these areas that samples are taken for analysis. - Stage 2.
Next, the doctor stains the tissue of the cervical canal with a special reagent (usually an iodine solution). Since the cervix is lined by several types of epithelium, they are colored differently. The squamous epithelium has a lighter shade, and the cylindrical epithelium is painted in a dark color. - Stage 3.
At the junction of different types of epithelium (high-risk area), the doctor removes tissue fragments. To obtain the material, the gynecologist uses one of the medical instruments. A hollow needle, aspiration syringe, radio wave loop or electric knife can be used. All instruments must be sterile. using a radio wave loop is the least traumatic because it does not cause bleeding. - Stage 4
. After tissue collection, the injured area is treated with an antiseptic. Treatment is performed to prevent the development of infection. The doctor also takes measures to stop bleeding if tissue is removed with a needle or syringe. If the bleeding cannot be stopped, the wound is sutured.
Normally, a woman will experience bleeding from the vagina 2-3 days after the procedure. They go away on their own and painlessly. If bleeding persists for more than 3 days, you need to consult a gynecologist.
The biopsy may be uncomfortable. This is due to tissue injury. At the request of the patient, the doctor can use local anesthesia before taking the material.
After the biopsy, the woman does not require hospitalization and can return home.
For quick recovery after cervical tissue collection, doctors recommend:
- exclude sexual intercourse for 10-12 days;
- avoid physical activity and heavy lifting for 7-10 days;
- stop douching for 2 weeks;
- use a shower for intimate hygiene;
- do not take medications without consulting a doctor;
- Avoid visiting saunas and steam baths for 10-14 days.
What is it prescribed for?
Histological examination is a microscopic examination of biomaterial taken from the patient’s pathological focus. This is the most accurate method for detecting dangerous cells; it is a mandatory procedure in examining a patient with suspected cancer. The value of its results is incomparable to ultrasound or x-rays.
Objectives of histological examination:
- establishment, confirmation, clarification or refutation of serious diagnoses;
- detection of oncology at an early stage;
- confirmation or refutation of the malignancy of neoplasms;
- establishing the stage and dynamics of the tumor process;
- discovery of the most effective drugs for further treatment;
- checking the effectiveness of therapy by analyzing changes in tissues;
- diagnostics of the condition of organs in severe pathologies, for example, cirrhosis of the liver;
- obtaining data for a planned operation, etc.
To receive detailed advice, you must make an appointment with a specialist at the medical center. The doctor will determine the advisability of a biopsy and the type of intervention.
The price of the study directly depends on the complexity of the procedure.
Such procedures are planned in advance (except for urgent biopsies during surgery). Manipulations of taking biomaterial for research require patient preparation.
The biopsy is performed under anesthesia, so you should not eat or drink before the procedure. It is necessary to do a blood test to check for a number of infections. The patient is given recommendations regarding the exclusion of certain drugs several days before the study.
Clinics use several ways to take biopsy material for histological examination.
| № | Biopsy sampling technique | Description |
| 1 | puncture | Taking material with a thick hollow needle by puncture of the pathological focus. As a result of the manipulation, columns of tissue are obtained. |
| 2 | Invasive | Cutting off part of an organ or tumor during surgery. |
| 3 | Aspiration | Suction of contents with a vacuum from pathological formations, for example, uterine fibroids or nodes in the thyroid gland. |
| 4 | Excision | Excision of an entire organ or neoplasm followed by cutting out fragments from it for analysis. |
| 5 | Plucked | Taking a sample with special biopsy forceps during bronchoscopy, colonoscopy, FGDS, etc. |
| 6 | Curettage | The procedure of scraping from the walls of natural and pathological cavities, for example, the uterus. The resulting material is sent to the laboratory. |
| 7 | Smear | Used most often in gynecology. Involves taking a smear from the mucous membrane. |
In medicine, there are other methods of collecting biomaterial for histology.