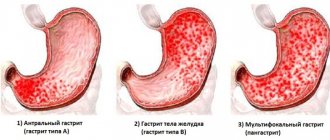
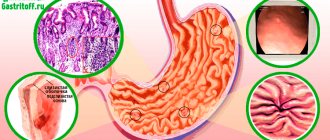
Perhaps the most common type of gastritis is diffuse gastritis. With this form of the disease, the entire mucous surface of the stomach becomes inflamed evenly, without specific foci or ulcers. This diagnosis is heard “right and left”; there is neither a certain age nor any other classification by which one can determine those most susceptible to the disease. Schoolchildren, elderly people, office workers, and people engaged primarily in physical labor are equally susceptible to this disease.
It is important to start treatment of diffuse gastritis in a timely manner.
Due to the rather long and gradual development of the disease, the initial stages remain without treatment, and patients come to doctors already with a fairly advanced disease. To prevent this from happening, you need to understand what symptoms indicate the need for urgent medical advice.
Typology
There is a classification of this type of gastritis, which is a consequence of acute and chronic forms of the disease:
- diffuse superficial gastritis;
- diffuse chronic;
- diffuse subatrophic;
- diffuse antral.
The superficial (moderate) form is characterized by mild inflammation of the gastric mucosa without the presence of wounds, erosions, or cicatricial deformities. When this type of disease is detected, there is no disruption of the digestive organ. The initial stage of the inflammatory process is revealed only by the results of an ultrasound examination. Untimely treatment of active superficial gastritis leads to the development of the disease.
A chronic type of inflammation of the stomach is characterized by structural changes in the surface of the digestive organ. A long period of the disease is a consequence of disruption of the stomach. Untimely treatment of chronic gastritis leads to an ulcer or the formation of a malignant tumor.
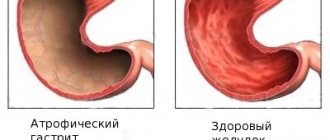
The atrophic form of the disease is characterized by noticeable damage to the gastric mucosa: wounds, erosions. As a result of the progression of this type of gastritis, the damaged cells of the mucous membrane die off. Lack of timely treatment can lead to the development of a subatrophic form of the disease.
The antral form is characterized by the production of hydrochloric acid in the lower section between the stomach and intestines. As a result of the inability to neutralize the acidity in the mucous membrane, cell death occurs in this part of the digestive organ.
Complications
If left untreated, diffuse gastritis causes serious complications that are dangerous to life and health:
- reflux gastritis. With this gastropathology, the contents of the stomach are thrown back into the esophagus, which irritates and corrodes the mucous tissue. A pathological process develops with the formation of erosions and ulcers;
- stomach ulcer. The disease takes a long time to treat and requires constant monitoring by a gastroenterologist;
- stomach cancer. The most dangerous complication that can lead to death.
Causes
There are reasons that contribute to the development of the diffuse form of gastritis:
- unhealthy diet - eating spicy, fatty, fried, smoked, salty foods;
- lack of proper sleep and rest;
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- smoking;
- food poisoning;
- taking medications on an empty stomach;
- disruptions of the gastrointestinal tract due to previous surgical interventions of the digestive system;
- penetration of the bacterium helicobacter pylori into the body, causing the spread of infection;
- stress instability, overstrain.
Poor nutrition, lack of sleep, stress are factors that negatively affect not only the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, but also the systems and organs of the body. The combination of symptoms leads to the progression of the disease.
Symptoms
As mentioned earlier, each disease has its own symptoms. Basically, diffuse changes are accompanied by the following symptoms:
General symptoms
- Stool disorder
- Decreased appetite
- Feeling of stomach emptiness
Acute pancreatitis
- Hypotension
- Acute stomach
- Nausea
- Vomit
Chronic pancreatitis
- Pain in the right hypochondrium
Lipomatosis
- Pain
- May be asymptomatic
- Indigestion
Fibrosis
- Possibly asymptomatic
- Symptoms of pancreatitis
- Weight loss
Symptoms
In the presence of a diffuse type of gastritis, there are certain symptoms characteristic of the inflammatory process of the stomach of other forms. Signs can appear both in aggregate and individually.
- pain syndrome;
- nausea and vomiting;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- weight loss;
- unstable stool: constipation, diarrhea.
The appearance of pain is the first factor signaling a disruption in the functioning of systems and internal organs. At an early stage of the disease, infrequent spasms are observed. As inflammation progresses, the duration and intensity of pain in the stomach area increases. Attacks are typical after eating food at any time of the day.
Nausea occurs immediately after eating due to the release of a small amount of gastric juice due to the affected mucous membrane. As the disease progresses, patients experience vomiting. After the release of undigested food, the patient feels improvement, pain dulls.
The inflammatory process disrupts the usual function of the digestive organ and gastrointestinal tract, and as a result negatively affects the physical condition of a person - weight loss. Malfunction of the intestines is the cause of the unstable nature of the stool: rapid digestion or delay in the passage of food.
In severe forms of the disease, which is characterized by the death of mucosal cells, heartburn, increased gas production, belching, fatigue, and frequent dizziness are observed.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is made according to the usual scheme: the doctor first prescribes gastroendoscopy - a study using a small camera placed in the stomach, which transmits an image to a monitor. This is one of the methods for differential diagnosis of gastritis. After carefully studying the image, the doctor finds foci of inflammation, determines the type of gastritis and can roughly name a treatment regimen.
Then urine, stool and blood tests are prescribed. In some cases, an ultrasound examination of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity may be required. This set of simple studies gives the doctor an absolutely complete picture regarding the etiology of the disease. After the diagnosis is made, a treatment regimen is determined and a diet is prepared for the patient.
It is important to understand that only a doctor can give you the correct diagnosis. No amount of logical speculation regarding one’s diagnoses will give the patient such a picture as an endoscopy and a set of tests. Self-medication often aggravates the picture and makes further treatment more difficult and less effective.
Treatment methods
Diffuse gastritis requires immediate treatment at the first appearance of symptomatic signs. Timely assistance will help avoid serious complications. Treatment of any form of diffuse gastritis can be carried out in several effective ways:
- medications;
- traditional methods;
- following a diet.
Medicines
As medications, preference should be given to antispasmodic, analgesic, anticholinergic drugs that relieve discomfort, as well as drugs that suppress nausea and diarrhea. To combat high stomach acidity, it is necessary to use antacid medications.
To prevent the possible spread of the inflammatory process due to the penetration of harmful microorganisms, it is recommended to use antibacterial agents.
All medications should be used after consultation with a gastroenterologist, who prescribes treatment in accordance with the form and severity of diffuse gastritis.
ethnoscience
Treatment should begin with the elimination of disturbing symptomatic signs. Traditional therapy methods can reduce pain syndromes and prevent discomfort in the stomach. In case of severe form and progression of the disease, you should not self-medicate. Traditional methods are suitable only for superficial and non-advanced chronic diffuse gastritis.
Recipes include:
- chamomile;
- aloe;
- mint;
- calamus;
- plantain;
- St. John's wort;
- licorice;
- caraway;
- linen;
- Linden;
- fennel;
- roots.
Herbal infusions and decoctions have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. There are proven recipes that help relieve pain, nausea and heartburn.
An infusion to prevent unpleasant sensations is made from 1 teaspoon of mint and calamus (root), 2 tablespoons of St. John's wort, plantain, 1/3 spoon of cumin (seed). The herbal mixture is poured with several glasses of hot water and infused for 12–13 hours. Two tablespoons of the resulting drink should be drunk before meals. The infusion should be taken until the formation of heartburn stops.
To relieve severe pain, make an infusion of 1 tablespoon of licorice, ½ teaspoon of mint, 3 tablespoons of linden, fennel. The resulting herbal mixture should be poured with 1 liter of water and boiled until it boils. For mild forms of gastritis, it is recommended to drink ½ glass on an empty stomach in the morning and at night.
A decoction based on flax helps relieve spasms and pain. A few tablespoons of seeds are poured into hot water and boiled until boiling. Freshly prepared decoction should be consumed immediately. The drink cannot be stored. Another product is prepared based on flax: add a few tablespoons of seeds to boiling refined vegetable oil and cook.
The resulting liquid must be infused for at least 7 days. One teaspoon of flaxseed oil per day before each meal is an excellent remedy for relieving symptomatic signs of chronic diffuse gastritis.
Chamomile and aloe are universal remedies that have anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and analgesic effects. Infusions from medicinal plants help eliminate heartburn and cramps.
Juices based on root vegetables - carrots, potatoes - are suitable for the treatment of chronic types of diffuse gastritis. You should drink half a glass of the drink before each meal on an empty stomach for several weeks. Juice from root vegetables prevents burning in the stomach and reduces pain.
Traditional medicine methods are not recommended to be combined with the use of medications in order to avoid serious consequences.
Diet
Proper nutrition for diffuse gastritis is an important component of treating the disease. Complex therapy is the path to recovery. For the most effective results with diffuse gastritis, you should follow the following diet:
- refusal of fatty, fried, smoked foods, processed foods, food dyes, preservatives, coffee, sweet products, bread;
- inclusion in the diet of cereals, cereals, soups with vegetable broth, boiled or steamed lean meat, fish, and natural fermented milk products.
Fractional meals should be organized: throughout the day, eat 5-6 times in small portions. Dishes should be at medium temperature; it is not recommended to eat foods that are too hot or cold to avoid irritation of the mucous membranes.
Diet
With diffuse gastritis, diet is a very important component of treatment. Its basis is table No. 2 . Everything spicy, fried, dyed, smoked, sour, and salty is completely excluded from the diet. The food you eat should be smooth, warm, but not hot or cold.
The menu is designed in such a way that it provides the body with sufficient nutrients, as well as vitamins and minerals. Food should activate the production of gastric juice and digestion.
The diet should include boiled or steamed vegetables, meat, eggs, and fish. Purees, mousses, jelly, and compotes are prepared from fruits.
In case of exacerbation of diffuse gastritis, as well as in the atrophic type of gastritis, it is necessary to adhere to diet No. 1a for the first few days. It is even more gentle and prohibits the intake of food that stimulates the production of gastric juice. All food should be consumed grated or pureed.
Preventive actions
To prevent stomach disease, it is recommended to give up bad habits, start leading an active lifestyle, and monitor your diet. Regular medical examination and visits to a gastroenterologist will help avoid complications of the inflammatory process.
Inflammation of the stomach is a common disease. Gastritis is characterized by the same symptomatic signs. To treat the diffuse form, you should follow a therapeutic course: the use of medications, adherence to dietary nutrition. A healthy lifestyle, playing sports, giving up bad habits is the key to health.
We recommend: Is it possible to have cranberry juice, jelly and juice for gastritis?
Prevention and prognosis
The prognosis will depend on how timely treatment was started. In the initial stages, therapy gives a pronounced positive result. At the stage of atrophic gastritis, treatment will make life easier for the patient, but will not fully restore the condition of the organ to its previous level.
To prevent the development of diffuse gastritis, you need to follow simple recommendations that will help maintain overall health:
- adjust your diet and monitor your weight;
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- spend more time outdoors;
- control medication intake;
- Regularly undergo preventive examinations with your doctor.
Which doctor treats diffuse gastritis?
It is possible to get rid of diffuse gastritis, but only if all the doctor’s instructions are followed. First of all, you should go for a consultation with specialists such as a gastroenterologist and nutritionist. To make an accurate diagnosis, the patient is initially interviewed. Important questions in this case may be:
- How long has the patient been experiencing symptoms of the disease?
- Are there any other complaints?
- When does this discomfort most often occur, after what dishes?
- Have there been any attempts at self-medication?
- Do you have problems with stool?
- Have similar manifestations happened before?
- Do you have a history of chronic illnesses?
All these questions are very important for the attending physician; they will allow you to prescribe adequate treatment. But first, the patient must undergo an examination to make an accurate diagnosis:
- ultrasonography;
- FGS;
- general blood analysis.