Most people do not pay attention to health and nutrition. Due to non-compliance with the rules of a proper diet, digestive tract disorders develop. As a result, a person develops hyperplastic gastritis or other inflammation of the stomach. The disease has characteristics of its course, symptoms and manifestation factors. To prevent the development of the disease, you need to know about its signs.
What kind of disease is hyperplastic gastritis?
In clinical gastroenterology, hyperplastic gastritis is considered a rather rarely detected pathology of the stomach, which, among chronic gastric diseases, accounts for about 3.7-4.8% of diagnosed cases.
Hyperplastic gastritis is a rare form of chronic gastric disease.
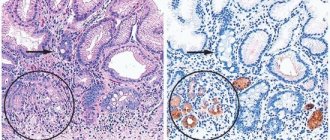
When areas of increased mitosis of the cells of the mucous membrane lining its cavity are identified as a result of an endoscopic examination of the stomach, gastroenterologists can make a diagnosis of hyperplastic gastritis.
Experts call such risk factors for the development of hyperplastic gastritis as:
- eating disorders;
- allergies to certain foods;
- deficiency of essential vitamins;
- toxic effects of alcohol and carcinogenic compounds, severe renal failure and hyperglycemia.
And when treating hyperacid gastritis and gastroesophageal reflux disease with the help of potent drugs that inhibit acid secretion (Omeprazole, Pantoprazole, Rabeprazole, etc.), the risk of increased growth of polyps that appear in the areas of the main glands and foveoli (gastric pits into which the ducts of the glands emerge) increases. . Probably, this localization of the pathological process is due to the fact that regeneration of the gastric mucosa when it is damaged occurs precisely due to the cells of the mucosa covering the areas of the gastric pits.
The symptoms of hyperplastic gastritis are not specific and vary greatly, but gastroenterologists include in the list of possible clinical manifestations of this pathology: heartburn, belching with a rotten taste, plaque on the back of the tongue, nausea, increased gas formation, pain in the epigastric region (aching, pressing or cramping), vomiting .
The main method on which the diagnosis of hyperplastic gastritis is based is endogastroscopy (endogastroduodenoscopy). Endoscopic instrumental diagnostics allows not only to visualize pathologically changed areas of the gastric mucosa, but also to perform a biopsy: take tissue particles for subsequent histochemical examination. X-rays, ultrasound of the stomach, and electrogastrography are also used.
The main method on which the diagnosis of hyperplastic gastritis is based is endogastroscopy
Advanced hyperplastic granular gastritis threatens the development of gastric ulcers and even cancer. Giant hypertrophic gastritis leads to hypochlorhydria; experts note the ability of this form of pathology to degenerate into a cancerous tumor of the stomach. With focal hyperplasia of enterochromaffin-like mucosal cells, gastric carcinoma can also develop. Polypous hyperplastic gastritis, according to some data, becomes malignant in almost 20 cases out of a hundred.
The most common consequences and complications of hyperplastic gastritis:
- changes in the structure of the gastric mucosa with atrophy of varying severity;
- damage and reduction in the number of parietal cells, decreased acid synthesis and deterioration of the digestive functions of the stomach;
- atony and impaired gastric motility, leading to persistent dyspepsia and partial gastroparesis;
- hypoproteinemia (drop in serum protein levels);
- anemia;
- weight loss.
https://youtu.be/VSoI4pldph4
Hyperplastic gastritis
Hyperplastic gastritis is a rare form of chronic gastric disease. The concept of “hyperplastic gastritis” includes a disparate group of diseases that are not based on an inflammatory process, but on primary hyperplasia of the gastric epithelium. Each of these diseases is quite rare; in general, the group of hypertrophic gastritis accounts for no more than 5% of all chronic gastric diseases.
At the moment, the causes of the development of hyperplastic gastritis are unknown. The disease is considered polyetiological. Most often, the development of hyperplastic gastritis is associated with malnutrition, hypovitaminosis, chronic intoxication of the body caused by alcohol, drugs, smoking and lead poisoning. In addition, data obtained during research indicate that the disease can occur against the background of metabolic disorders and disorders of neurohumoral regulation.
Sometimes the development of the disease is associated with the patient having a food allergy. When allergens influence the mucous membrane, its permeability increases, as a result of which epithelial dysplasia occurs, against the background of which a significant amount of transudate sweats into the gastric cavity. Such processes are accompanied by significant loss of protein, which is considered one of the classic signs of this form of gastritis.
With all types of hyperplastic gastritis, bleeding from the gastric mucosa is possible, which can lead to gradual anemia
Some experts note that hyperplastic gastritis is an anomaly in the development of the stomach or a special variant of a benign tumor, as a result of which the cells of the gastric epithelium begin to rapidly divide, which is accompanied by a significant thickening of the mucous membrane of this organ.
With all types of hyperplastic gastritis, bleeding from the mucous layer of the stomach may develop, which can lead to gradual anemia. Patients complain of increased fatigue, weakness, and loss of strength. With significant protein loss, peripheral edema may occur. Due to the fact that the causes of the disease have not been established, it is impossible to develop effective measures to prevent hyperplastic gastritis.
Treatment of hyperplastic gastritis
There is no etiotropic treatment, since the causes of the disease are not fully understood. Symptomatic therapy depends on the manifestations of the pathology. In case of increased acidity, antisecretory drugs are prescribed; in case of atrophy development, replacement therapy with natural gastric juice is prescribed. If endoscopic examination reveals multiple erosions or a peptic ulcer, therapy will be consistent with gastric ulcer disease. A diet rich in proteins and vitamins is indicated.
Surgical treatment is carried out when polyps are detected (removal of gastric polyps during endoscopy), as well as in case of resistant hypoproteinemia, frequent recurrent bleeding (partial or complete resection of the stomach). All patients diagnosed with hyperplastic gastritis must be registered at a dispensary and undergo endoscopic examination twice a year for timely detection of oncopathology.
Forms of hyperplastic gastritis
https://youtu.be/jsQCTQlmRso
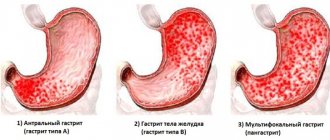
Chronic or acute hyperplastic gastritis is one of the most severe forms of gastritis, a disease that affects the gastric mucosa. During the disease, the mucous membrane grows, the lesions are localized in certain parts of the organ, or the pathology spreads to the entire stomach cavity. There are several forms of hyperplastic gastritis.
Granular hyperplastic gastritis
The pathology concerns small foci of the gastric mucosa, which resemble grains in appearance - this can be seen during an FGS examination. Usually the damage is located on the front wall, in rare cases it appears on the back wall. Differentiated as antral hyperplastic gastritis.
Chronic or acute hyperplastic gastritis is one of the most severe forms of gastritis, a disease affecting the gastric mucosa
Giant gastritis or Ménétrier's disease
It is characterized by multiple benign neoplasms in the form of adenomas. In most cases, erosions are detected on their surface. The disease spreads to the antrum. Warty gastritis - as the name suggests, the neoplasms are single and shaped like warts. It also leads to degeneration of the gastric antral mucosa. With polypous gastritis, areas of atrophy alternate with polyps and hypertrophic folds. In most cases, neoplasms are localized on the posterior wall of the stomach.
Antral hyperplastic gastritis
There is also such a thing as antral hyperplastic gastritis. The antrum is the junction between the stomach and the intestine, and its main physiological function is to reduce the acid level in the bolus before it moves into the intestine. But a drop in pH also reduces the bactericidal properties that gastric juice has. And this, in turn, allows pathogenic bacteria to multiply, and therefore they most often choose the antrum.
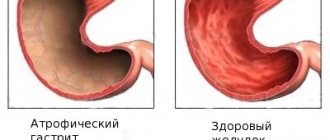
Atrophic hyperplastic gastritis
Atrophic hyperplastic gastritis is the most dangerous type of the disease. The onset of this form of the disease occurs without pronounced symptoms and can subsequently develop without pain. This is a very dangerous sign - it indicates the initial stage of degeneration into cancer.
With antral atrophic gastritis, the mucous membrane becomes inflamed in the pyloric section of the stomach, which extends into the intestine. Gradually, the atrophic process spreads to the entire organ. The glands located in the pyloric region are replaced by fibrous tissue, and protective mucus ceases to be produced, which leads to damage to the entire organ by hydrochloric acid.
With atrophic hyperplastic gastritis, large areas of hyperplasia occur, and degenerative changes cover the antrum. There is a risk of this form of disease degenerating into gastric carcinoma.
Forecast
When atrophy is combined with hyperplasia, the pathology is dangerous, mainly due to the risk of malignancy of the polyps that appear in the stomach. The development of cancer is considered a dangerous complication, but even in this case, the individual characteristics of the unfavorable process should be taken into account. The risk is much lower if the disease is detected at the initial stage - that is, with the development of primary symptoms in the form of nausea, loss of appetite, heaviness in the abdomen and belching.
In the absence of malignant transformations of polyps, the patient’s life is not threatened by the disease.
If you follow your doctor's recommendations, follow a regular diet, and treat exacerbations in a timely manner, the prognosis is relatively favorable.
Despite the lack of possibility of complete recovery, the pathology can go into long-term and stable remission.
Atrophic hyperplastic gastritis
This is a chronic disease that is characterized by an enlargement of the gastric mucosa. Atrophic hyperplastic gastritis is dangerous and very common. The disease cannot be called a clinical form, since only during examination in an endoscopic room can one see the structure of the mucous membrane of the gastric tract.
Of course, during gastritis, unnoticed, low-specific symptoms of gastritis may appear, but there are cases that this type of disease is completely asymptomatic. One of the most important signs of the disease can be considered pain in the stomach, which manifests itself after eating. The pain is paroxysmal and intermittent. Pain usually appears after eating certain foods. Depending on how much hydrochloric acid is present in the stomach, the patient may experience belching and heartburn.
To establish the symptoms of atrophic hyperplastic gastritis, not only laboratory data are used, but also instrumental studies. This is very important, since with severe neglect or with the use of improper therapy, atrophic hyperplastic gastritis can last from six months to several years. Doctors associate this type of gastritis with chronic inflammatory processes, so older people are more likely to suffer from the symptoms of the disease. The disease is preceded by bacterial gastritis, which can be easily treated if detected in time.
Gastropathy in children
In childhood, this disease ranks second after ARVI. In this case, the disease usually occurs suddenly and progresses rapidly. Gastropathy can be observed in infancy during the transition to artificial feeding or as an allergic reaction to food. The disease is also often provoked by infections, medications, infant formula and expired products.
Gastropathy is manifested by weakness, anxiety, pain in the abdomen, lack of appetite, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting. The acute form often becomes chronic, characterized by pain and a feeling of discomfort in the stomach.
How to treat hyperplastic gastritis
The hypertrophic (hyperplastic) type of gastritis is said to occur when, during the inflammatory process, the mucous membrane grows and thickens. Subsequently, these changes lead to functional failure of the gastric mucosa, therefore this form of the disease is called a precancerous condition.
Regarding digestion for gastritis, the first point in treatment is always a therapeutic diet
In this regard, it is important to properly treat gastritis in order to prevent further restructuring of the wall of the digestive organ.
When it comes to digestion, the first point of treatment is always a therapeutic diet. In such a case, it is necessary to take an increased amount of protein, which, due to malabsorption, enters the body in small quantities. In addition, it is important to eat food often and in small portions so that it has time to be digested. The portion should be warm to prevent additional injury to the organ.
Hyperplastic gastritis also requires the prescription of enveloping drugs, which include Almagel. It is necessary to reduce the aggressive effects of gastric juice on the stomach wall.
For the same purpose, medications related to proton pump blockers (for example, omeprazole) are additionally prescribed. If almagel envelops the stomach, protecting its wall, then omeprazole and similar drugs block the receptors, and gastric juice is produced in smaller quantities. The use of astringents is also shown, among which are tannin, tanalbin, bismuth derivatives and vicalin.
Causes and risk factors
Different types of the disease are currently diagnosed frequently. Doctors divide the causes of the disease into internal and external. These include:
- Poor diet, consumption of alcohol and nicotine, coffee, infections,
- Insufficient secretion of enzymes in the body that are needed for digestion,
- Long-term use of medications, burns and other injuries,
- Reflux of bile into the stomach, stagnation,
- Incomplete blood supply to the stomach due to the formation of internal pathologies,
- Genetic predisposition.
Diet and treatment for hyperplastic gastritis of the stomach
Depending on the nature of the pathology of the mucous membrane, several types of hyperplastic gastritis are distinguished, including: warty; polyposis; giant hypertrophic; grainy.
The first of them is manifested by the fact that the lining of the gastric mucosa is covered with growths in the form of warts, the second type is characterized by the appearance of polyps, the third - enlarged folds of the organ. The granular type of hyperplastic gastritis is characterized by the presence of oval tubercles from 3 to 5 millimeters.
In addition, the hyperplastic inflammatory process can be diffuse or limited depending on the localization of pathological changes throughout the entire wall of the stomach or only in one area.
In severe cases, surgical treatment is prescribed in the form of resection of the stomach or part of it.
This type of gastritis is considered the most dangerous, being, in fact, a benign tumor, which, in the presence of constant stress, non-compliance with diet, sleep and lack of adequate treatment, can degenerate into a malignant one.
Proven factors contributing to the development of a disease such as hyperplastic gastritis are nicotine and alcohol addiction, work in hazardous industries and long-term intoxication.
Considering that this disease occurs with signs of gastritis with reduced acidity, its treatment usually consists of components such as:
- drug therapy;
- gentle diet;
- physiotherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- phytotherapy;
- treatment with gastroenterological mineral waters.
Drug therapy usually consists of prescribing:
- antibacterial agents;
- painkillers and antispasmodics in the presence of pain;
- proton pump inhibitors;
- antacids that normalize the content of hydrochloric acid;
- astringents for diarrhea.
After completing the therapeutic course, usually 1.5-2 months later, it is necessary to undergo a re-examination to determine the effectiveness of the treatment.
In severe cases, surgical treatment is prescribed in the form of resection of the stomach or part of it. Chronic hyperplastic gastritis, the treatment of which is selected individually for each patient, requires subsequent mandatory medical supervision due to the possible transition to stomach cancer. After completing the therapeutic course, usually 1.5-2 months later, it is necessary to undergo a re-examination to determine the effectiveness of the treatment.
Diet in the treatment of hyperplastic gastritis
The most important role in the treatment of hyperplastic gastritis is played by the diet that is selected by the doctor. As a rule, the following are excluded from the diet:
- alcohol;
- meat and fish broths;
- fresh baked goods;
- chocolate, cocoa and coffee;
- spices, seasonings, pickles;
- fatty, smoked, fried and salty foods.
It is necessary to follow the regime, eating small portions 5-6 times a day. Food must be cooked by boiling, stewing or steaming and served warm. The therapeutic diet should be followed even after completion of the course of therapy and persistent disappearance of the symptoms of the disease for at least 1-2 months. This will reduce the risk of relapse of hyperplastic gastritis.
Prevention
Preventative measures are important both before the onset of the disease and after treatment. The measures are quite simple:
- undergo regular examinations and consult a doctor;
- eat right, avoid overeating and obesity;
- avoid stressful situations;
- play sports and do physical activity, but in moderation;
- give up bad habits.
It is easier to prevent any disease than to treat it later, don’t forget about it. Lead a healthy lifestyle - this will reduce the risk of developing dangerous diseases.
Why is hyperplastic gastritis dangerous?
Chronic hyperplastic gastritis is characterized by hypertrophy of mucosal tissues, they compress full-fledged cells and prevent them from fully developing.
This is how atrophic hyperplastic gastritis turns out - a disease without any special symptoms at the very beginning. The difficulty in diagnosing this disease is that at the very beginning it is often asymptomatic, and only later, when polyps appear, the patient may complain of:
- pain in the epigastric region, abdominal pain radiating to the lower back or shoulder blades;
- belching with an unpleasant odor;
- stool instability - either constipation or diarrhea;
- bloating;
- increased salivation;
- nausea, sometimes vomiting (by the way, vomiting can also be of nervous origin);
- a sudden increase in body temperature is a sign of internal bleeding, and sometimes patients notice blood in the stool.
The most important role in the treatment of the hyperplastic form of the disease is played by the diet, which in this case is selected only by the doctor.
For doctors, the situation is more familiar when atrophic gastritis occurs in older people; a decrease in gland function with age is considered normal. But atrophic and even hyperplastic gastritis is a completely different matter. This problem can strike at a young age. Then the prognosis will depend on a timely diagnosis and proper treatment.
Diagnostics
After a physical examination and a general history, the following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- clinical blood test (anemia);
- liver tests;
- serum amylase and fecal elastase (to rule out pancreatitis);
- Helicobacter tests (urease breath test, stool PCR and serological blood test);
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- FEGDS is mandatory for an accurate diagnosis.
FEGDS of the stomach