Papillomas are pathological formations on the human body. Most often they appear in the form of warts or genital warts. It is noteworthy that such formations can appear on almost any part of the human body. If papilloma is caused by the HPV virus, then such a disease should be considered as oncogenic. The risk of developing a malignant tumor or cancer in this case is 80%.
Online consultation on the disease “Papilloma”. Ask a question to the experts for free: Dermatologist.
- Etiology
- Pathogenesis
- General symptoms
- Types of papillomas
- Pointed
- Squamous
- Nature of localization
- Breast papilloma
- Papilloma in the throat
- Cervical papilloma
- Papilloma on the tongue
Where do they come from - routes of HPV infection
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a very common DNA virus that is highly contagious and causes papillomatosis, i.e. the appearance of papilloma on the skin and mucous membrane. At their core, papillomas are benign formations that resemble warts that grow from epithelial cells. During development, they are able to affect not only the mucous layer, but also penetrate into the deeper layers of the skin.
Currently, more than 120 varieties of HPV are known, which differ in their contagiousness, oncogenicity and resistance to medications. The virus actively affects people of both sexes, regardless of age. It is almost impossible to completely remove it from the body, where it remains in a latent state for life even after treatment.
Moreover, after infection, the virus may not show itself for years, and the person does not even suspect its presence. As a result, more than 10 percent of all people become carriers of the infection, and during the most active sexual period (25–35 years) the number of infected people exceeds 50%.
How does infection occur? HPV is most often transmitted through sexual contact. It has been established that the probability of infection through sexual contact with a carrier of the infection exceeds 65 percent. Moreover, the risk of infection is the same for any method of contact (genital, oral, anal). At the same time, papillomatosis cannot be considered a disease transmitted only through sexual contact.
Most strains of the virus can be transmitted through contact and household contact, that is, through direct contact with the affected areas of the body of a sick person or through common objects. Infection is possible by shaking hands, kissing, using a swimming pool and public baths, using someone else's underwear, etc. Infection of newborns often occurs during childbirth if there is papilloma in the uterus, vagina and labia of the woman in labor.
Treatment at home
Treatment of papillomas at home, without a doctor’s prescription, is unacceptable. Thus, you can only aggravate the situation and give rise to the growth of infection throughout the body.
At home, treatment is possible only if the diagnosis does not reveal an oncogenic factor or suspicion of the formation of a malignant tumor.
In general, treatment at home means using local ointments and taking medications prescribed by a doctor. If HPV is not regarded as a precancerous condition, then hospitalization is not carried out.
Please note that self-treatment at home can lead to papillomitosis of the skin. In this case, papilloma formations will appear throughout the body. Therefore, treatment at home is only possible as prescribed by a competent specialist.
Only a competent specialist can tell you how to treat papillomas correctly. You should not self-medicate, trust advice from the Internet and “grandmother’s” methods without consulting a doctor.
Causes of occurrence, appearance on the body
Papillomatosis is an infectious disease, and the virus enters the body of a healthy person through one of the described routes. The risk of infection increases with the start of sexual intercourse too early, promiscuity, casual (unprotected) sex. However, the development of the disease occurs only when favorable conditions appear for HPV to emerge from its latent state.
The following provoking causes of papilloma are identified:
- immunodeficiency of a congenital or acquired nature, including HIV and AIDS;
- the postpartum period, when a woman’s body experiences the effects of hormonal changes and stress;
- diseases of the genitourinary system of a chronic nature, sexually transmitted diseases, venereal diseases;
- pathologies of the endocrine type, diabetes mellitus;
- active therapy with immunosuppressants;
- repeated artificial termination of pregnancy, long-term use of oral, hormonal contraception;
- exhaustion and physical weakening of the body;
- intoxication of the body, hormonal imbalance;
- long-term use of certain medications - cytostatics, antibiotics.
An incorrect lifestyle leads to the activation of HPV. Bad habits (excessive drinking, drugs) provoke the growth of papilloma. Poor nutrition, starvation diets, and vitamin deficiencies significantly weaken the body, reducing immune defense.
Treatment of skin tumors
If you find a growth on your body, contact a specialized doctor - a dermatologist, so that the latter can prescribe treatment. Do not attempt self-healing on your own, as some strains belong to the high oncogenic type group (this applies to both males and females).
HPV (human papillomavirus) with external signs in the form of neoplasms is not all. These growths can easily transform into malignant tumors, and this is already dangerous. It should be noted that the human papillomavirus remains in the body for the rest of your life. As a result, it is only possible to reduce activity, or in other words, bring the infection into a “dormant” state. But laser therapy will help completely destroy the mole absolutely painlessly.
Pay attention to external changes in the skin and visit doctors in a timely manner.
Take vitamin complexes and support your immune system. Follow certain rules and your health will be safe. In addition, the types of papillomas on the face, as we have already found out and whose photos can be seen on the Internet, are different and before resorting to removal, you need to find out what strain it is. A description of any can be found on the World Wide Web. The article has been verified by the editors
Symptoms
Once in the human body, HPV is most often suppressed by the immune system, and therefore does not manifest itself for a long time. When the immune defense is weakened, the virus integrates into the cells of the epithelial, basalt layer, changing the chromosomal structure. Accelerated cell division and their corresponding proliferation occurs, which gives external manifestation in the form of formations of various shapes (papillomas).
The skin can be affected on almost any part of the body. The most common location is on the genitals. Lesions can be found on the mucous membrane of the mouth, larynx, upper respiratory tract, intestines and other internal organs.
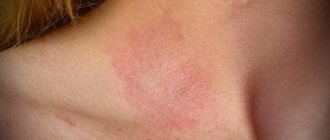
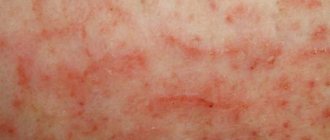
The symptoms and appearance of papilloma vary depending on their type, but some common features can be noted. Usually the formations do not show pain, but in some cases pain and burning are felt upon mechanical contact with the affected area. Atypical discharge may appear. The main sign of papillomatosis is the appearance of the growths.
Treatment
Treatment of papillomas depends on their location, etiology and form of HPV. Almost always, the removal of the shoots is carried out initially. If the nature of the localization allows, then papillomas are removed with liquid nitrogen.
Also in modern medicine, the radioknife method is used. Thus, painless removal of not only the process itself, but also its root system is carried out on the body. This method makes it possible to completely and permanently remove papilloma in this area of the body.
The above method is very often applicable in case of relapse of the disease in a person. Especially if a person tried to remove the formations on his own at home.
Laser removal of papillomas
In addition, surgical removal of papillomas on the body is possible using the following methods:
- electrocoagulation;
- laser removal;
- removal with a surgical scalpel.
In some cases, if there is no oncogenic factor, a local papilloma ointment can be used. Such a substance can only be prescribed by a doctor, after accurately determining the etiology of the disease. At the initial stages of the development of the disease, ointment for papilloma gives good results, even when used at home for treatment.
In any case, treatment of papilloma should be accompanied by drug therapy. But it is important to remember that there is no specific cure for papillomas. The doctor prescribes general-spectrum antiviral drugs. Therapy is also aimed at strengthening the immune system.
Treatment of papillomas at an early stage of development in most cases does not cause serious complications. But, this is only if HPV is not recognized as oncogenic.
What types are most common?
Papillomas are easily identified by their characteristic shape. Based on this feature, there are several types of formations:
- Warty type (warts) . They are generated by HPV 1–5, 10, 28 and 49. The main difference between viral warts and other formations of this type is their instability - they appear and disappear on their own, depending on the state of immunity. In color they are close to the shade of normal skin. The most common types are juvenile (flat) warts, plantar warts (spikes), and vulgar warts that appear on the hands.
- Condylomas of the pointed type . They are papillary growths provoked by HPV 6,11, 13,18, 35. The main localization areas are the genitals, anal area, oral cavity, lips, larynx, and respiratory tract. These condylomas can be single or multiple.
- Confluent condyloma acuminata . Nearby formations are able to join together to form a growth that looks like cauliflower. When using a magnifying glass, you can notice the presence in such formations of individual sharp elements with their own blood capillary. They can be differentiated using a weak vinegar solution - papillomas acquire a pearly white hue.
- Flat type papillomas . This variety indicates the existence of an old, chronic infection and significant cellular change. Formations can be of considerable size.
- Laryngeal papillomas . They are generated by HPV 11 and are characterized by a multiple nature. The affected area is the vocal cords.
- Papulosis bowenoid type . Papillomas look like small flat warts. As a rule, they are localized in the genital area and are caused by HPV 16, 33, 42, 54.
Research shows that the most common is HPV 16, which is detected in almost half of all cases. The second most common HPV 18 is significantly inferior to it (up to 10%).
When should papillomas be removed?
Papillomas can be removed without any complaints about the condition, even if the tumor is very small and does not threaten health in any way. Skin growths are a defect that many people want to get rid of.
Main indications for removal of papillomas:
- the location of neoplasms in a place where they are often damaged and inflamed under the influence of unfavorable external factors (temperature changes, high humidity, friction against clothing);
- active growth of papillomatous growths on the skin or in the mucous membranes of the genitals and oral cavity;
- disruption of the functionality of healthy tissues as a result of the growth of papillomas;
- high risk of malignancy, detection of potentially dangerous HPV strains;
- planning pregnancy, during which hormonal changes in the body occur, promoting the rapid growth of benign and malignant neoplasms.
If a doctor advises you to get rid of papillomas, you should listen to his opinion. The number of malignant tumors is growing every year, and this is an alarming fact. It is better to remove a benign tumor on time, because none of the doctors can say for sure that over time, papillomas will not turn into cancerous tumors.
Laser coagulation
Using a laser, you can remove papillomas on any part of the body, on the face and in the genital area. The method is characterized by maximum efficiency and safety. The laser evaporates pathological cells layer by layer, leaving no bleeding vessels. After removal, a small crust appears, which will gradually come off over several weeks.
Scarless healing is the main advantage of using this method. Many people refuse surgical treatment only because they are afraid of deterioration in the external condition of the skin on open areas of the body and face. Papillomas are prone to relapses, which can be prevented with the help of antiviral agents and immunocorrective drugs.
Cryodestruction
Freezing papillomas using low-temperature liquid nitrogen is almost as popular as the laser coagulation method.
The active agent is applied to the tumors using an applicator. Due to instant freezing, the neoplasm rarely turns white, but then hyperemia with slight swelling occurs. The area is covered with a dense crust, under which the process of epithelization begins. Necrotic areas are gradually replaced by healthy tissue. At the same time, no scar changes remain on the skin.
Electrocoagulation
Removal of papilloma using electric current is an affordable and proven method of surgical treatment. The electrocoagulator not only cuts off the neoplasm, but also seals the vessels and capillaries, preventing the release of blood from damaged vascular walls. Electrocoagulation is recommended to be combined with immunostimulating therapy and antiviral agents.
Radio wave treatment
Radio waves ensure the removal of benign tumors with minimal trauma. During the procedure, the radioknife coagulates the vessels. In combination with antiviral therapy, the method gives highly effective results. Immunostimulating drugs are prescribed for frequent relapses of papillomas and general weakening of the body.
Use of Solcoderm
Solcoderm is a cytotoxic drug that is often used to remove papillomas in women and men. The product contains a complex of acids. Additionally, the composition includes copper nitrate, which dries the tissue of genital warts, papillomas and warts.
Solcoderm allows you to painlessly remove small tumors. The drug is not suitable for the treatment of large papillomas and condylomas. After applying the product, the neoplasm dries out. If the papilloma is single, one use is enough. With multiple papillomatous growths, several applications are required. The break between procedures should be at least a week. Gradually, the neoplasm tissue becomes covered with a dense crust, which falls off after a few days.
Recovery of treated areas occurs quickly. There are no scars left on the skin. Large condylomas and papillomas gradually decrease in size, but usually it is not possible to achieve their complete disappearance with Solcoderm alone.
The final destruction of papillomavirus is impossible. Treatment is aimed primarily at getting rid of the main signs of the disease and preventing recurrence in the future. Removal of tumors does not exclude the transmission of HPV to contact persons, who most often already have human papillomavirus infection in a latent form. Papillomas pose the greatest danger to people with unfavorable heredity, when among close relatives there are cases of cervical cancer and other malignant pathologies.
It is important to pay attention to preventing the recurrence of papillomas. It necessarily includes the periodic use of interferons against the background of a measured lifestyle. It is recommended to abandon casual intimate relationships and use barrier methods of contraception that protect against human papillomavirus infection and its most aggressive form - genital warts. Girls and women under 45 years of age can be vaccinated. Vaccinations are available in almost all regions. In many areas today they are done completely free of charge. Vaccination can begin at 9 years of age.
How are they dangerous for men and women?
Despite the benign nature of papilloma, they pose a high health risk. Even simple warts on the body cause nervous overload due to their unpleasant appearance and the desire to hide them from prying eyes. The following manifestations caused by HPV can be noted:
- On the human body there are flat and common warts, butcher's warts (HPV 7), veruciform epidermodysplasia, Bowen's disease.
- On the genitals - genital warts, uterine flat papillomas, cervical dysplasia.
- On the internal membranes of the internal organs - epithelial hyperplasia of the oral cavity, recurrent type papillomatosis of the respiratory tract (HPV 6,11, 30), papillomas on the lungs.
The most severe complication is malignancy (malignancy) of the formation. Based on their oncogenicity, HPV is conventionally divided into 3 categories:
- without risk of transformation – HPV 1–5, 10, 28, 49;
- with a very low probability of cancer - HPV 6, 11, 34, 40–44, 72;
- with an average degree of oncogenicity – HPV 26, 35, –56;
- with a pronounced tendency to malignancy - HPV 16, 18, , 50, 61–64, 70, 73.
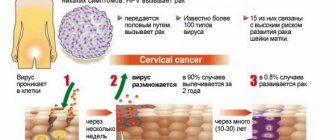
The overall risk of transformation of papilloma into a malignant formation does not exceed 1 percent, but the probability still exists and is quite real. The most common cause of cancer is the cervix in women and genital cancer in both sexes.
Types of papillomas
In official medicine, it is customary to consider the following main types of papillomas:
- threadlike;
- pointed;
- simple;
- flat papillomas;
- plantar.
Flat papillomas are most common on the palms and soles.
Pointed papillomas
During sexual intercourse, a virus enters the body and as a result, after some time, genital warts (a type of papillomas) form on the human skin. In some clinical cases, genital warts may eventually take the form of blisters with fluid. Later they burst and emit a sharp, unpleasant odor.
Of all the types of papillomas, it is the pointed type of formations that is the most dangerous. In most cases, genital warts are diagnosed as oncogenic - they can turn from a benign tumor into a malignant one. In addition, genital warts significantly worsen a person’s quality of life - they interfere with walking and sexual intercourse. Most often, removal of genital warts is carried out using liquid nitrogen.
Squamous papillomas
Squamous cell papillomas are the most common. Squamous cell papillomas do not cause any physical discomfort, but cause significant inconvenience in aesthetic terms. Squamous cell papillomas are localized on the sole, palms, and occasionally the back.
What happens if you get injured?
Patients are especially wary of papilloma injury, and this is quite justified. These formations are penetrated by blood capillaries, and mechanical stress damages them. As a result, bleeding begins, sometimes quite profusely. A wound that does not heal for a long time becomes a favorable environment for the proliferation of various pathogenic microorganisms, which increases the risk of infectious diseases.
The most traumatic location is the genitals. During sexual contact, damage to the papilloma is quite likely, especially if there is a pointed variety. In addition, one cannot fail to take into account that frequent damage increases the risk of oncological degeneration.
How is human papillomavirus transmitted?
The routes of transmission of human papillomavirus can be as follows:
- sexual;
- from mother to child during childbirth;
- contact;
- contact-household.
The main route of transmission is sexual. The infection can be transmitted to girls not only during unprotected vaginal and anal intercourse, but also during petting.
If a woman suffers from papillomavirus infection and there are condylomas or papillomas on the walls of the vagina or labia, then the child may also become infected with them during childbirth.
It is also possible to become infected with HPV through a handshake, personal hygiene items, pool water, sauna, etc.
Diagnostics
Papillomas have one important feature. The primary diagnosis is made quite simply - based on the results of the examination. In particular, the pointed variety is generally difficult to confuse with anything else. Other types of papilloma require clarification for complete differentiation. Diagnostic studies are mainly aimed at establishing the specific strain of the pathogen and the degree of its oncogenicity.
To obtain a complete picture, the following diagnostic studies are carried out:
- Colposcopy . The method is based on the use of a special microscope - a colposcope, which is capable of examining the cervical cavity. Microscopy allows you to clarify the presence, size and location of the formation.
- Biopsy . It involves taking tissue samples from the lesion. There are 2 main types of research. Cytology - a scraping is taken from the surface of the affected area, which is examined under a microscope. Changes that have occurred in the cellular structure are studied. Histology - a biopsy specimen in the form of a piece of tissue from the affected area is studied. The sample is subjected to layer-by-layer examination, treatment with special compounds and examination under a microscope. Such studies make it possible to identify a precancerous condition.
- PRC . The most informative way to diagnose papilloma is the PRC method. This technique allows you to establish a complete picture of the pathology, including identifying the specific type of pathogen.
These diagnostic studies make it possible to accurately identify pathology, the state of the immune system and the presence of complicating factors. Treatment, especially surgical treatment, can be prescribed only after a complete examination.
Types of skin growths
The appearance of a growth on the skin of the body is indicated by a decrease in the immune system. It is she who has a protective function and acts as a kind of barrier. When some type of human papillomavirus enters the body, the immune system does not allow HPV to take root. This has been proven by research.
Long-term medical practice has made it possible to divide all papillomas on the skin into three types:
- HPV is not an oncogenic type (such growths will not cause cancer, but will reduce immunity).
- The virus is not of a high oncogenic type (has a low threshold for the occurrence of pathology).
- Infection with oncogenic risk (due to a high threshold for oncology).
A sign of papillomavirus found on the skin is, although not a big thing, a cause for concern. Do not leave the growth unattended (especially in the genital area). To fully understand what type of tumor caused the appearance of the tumor, you should consult a dermatologist. To begin with, the doctor will perform a visual examination and, if necessary, write a referral for further tests and studies.
Do not start self-medicating if you have not figured out what type of papillomas you have - this can lead to irreparable consequences.
The number of existing neoplasms is in the tens. You need to understand what types of papillomas there are and remember that the entire range of growths presented is divided into five categories. They were divided according to symptoms, color range and risk of oncogenicity. We will cover each group in more detail later. Thus, the types of papillomas are divided into 5 types.
The first type is simple papillomas
Group I – simple papillomas. Another name is ordinary or vulgar growths. This type of papillomas is widespread. A clear sign is the appearance of a small growth on the skin. In the process of development of papillomas of any of the known types, it is transformed into a keratinized tubercle, dark in color. A common wart is localized on the skin, both in a single form and in entire groups. Favorite places for moles are the arms (inner and outer sides of the hands) and the lower part of the face (essentially the lips and chin).
It should be noted that there are plantar papillomas; they are practically no different in appearance from vulgar growths; only the keratinized outer shell reveals their identity. Such warts cause discomfort when walking. Getting rid of them is not easy, but it is quite possible at home.
The second type is flat
Group II – flat papillomas. A characteristic feature of the species is the appearance of growths in a group. They have practically no convexity and are dark in color. The location of distribution is the upper body. In some cases, they were observed in the genital area. Skin papillomas still belong to this group, and appear mainly in adolescence. Warts are localized on the neck, face and hands of young people. The main reason for its appearance is a failure of the immune system.
The third type is pointed
Group III – pointed papillomas on the face and other areas. Another name is condylomas. The main location of neoplasms is the mucous membranes. Most often, they affect the genitals and body, spoiling its appearance and affecting everything internally. It is these strains that belong to the oncogenic risk category. Marked by rapid development from one specimen to several in a short period. The method of penetration of condylomas is sexual intercourse. The presence of pointed moles is not advisable for pregnant women, as there is a possibility of infection of the baby. The latter can happen when the newborn passes through the birth canal.
The fourth type is filamentous papillomas
Group IV – thread-like peculiar papillomas on the body. In the scientific world they are called acrochord. A characteristic feature of neoplasms is the obligatory stalk that supports the mole itself. The age category is middle-aged people, and older women and men. Such growths are most often called senile growths.
The human papillomavirus develops in the body for many years, and only after a while it manifests itself as warts. Place of tumor formation: eyelids, neck, armpits, groin area and chest area. These growths are traumatic and often break off due to carelessness. This is a very dangerous phenomenon, so you should definitely show the wound to a doctor.
Fifth type - internal
Group V – internal moles. This subgroup includes all neoplasms that form on the internal organs of the body. These include condylomas located on the walls of the stomach and rectum. Growths in the mouth and throat, formations in the bladder. It is the presence of condylomas of this group that cannot be recognized independently, since this requires special diagnostics. But the presence of growths is revealed by pronounced symptoms. It is impossible to say with certainty how dangerous neoplasms are for the human body. Research work is carried out annually and constantly produces new results.
But one thing is clear: this fact cannot be ignored. For example, a growth in the bladder can lead to internal bleeding, or over time transform into a malignant tumor. Warts in the larynx area impair respiratory function and the ability to speak. By the way, the latter can also be localized in a newborn - so a pregnant woman needs to be especially vigilant.
How to treat?
In general, it must be taken into account that it will not be possible to completely get rid of HPV. The goal of treatment is to suppress the activity of the virus, remove papilloma, strengthen the immune system and the general condition of the patient. Depending on the stage of the pathology, the type of formations and their size, conservative or surgical treatment can be carried out.
Drug therapy
The basic treatment regimen for the pathology is based on the use of antiviral drugs. This technique is quite effective at the initial stage of the disease, when there are no complicating circumstances. The following drugs are prescribed as medications: Interferon, Cycloferon, Reaferon, Viferon, Leukinferon. They are aimed at stimulating the production of interferon in the body, which provides an antiviral effect.
Inducers of interferon synthesis act in the same direction - Neovir, Ridostin, Tamerit, Immunofan. To directly suppress HPV, the antiviral drug Alpizarip is used. To increase immune defense, nonspecific immunomodulators are recommended - Derinat, Wobenzym, Lykopid. The drug therapy regimen is individual in nature and is developed taking into account the results of the patient’s examination.
Another direction for the use of medications is the removal of papilloma. A positive effect is achieved when using Condilin, Solcoderm, Fluorouracil, Imiquamod. These agents provide necrosis of formations by blocking their nutrition or chemical burning of the affected tissues.
Hardware techniques
Surgical treatment involves removal or destruction of the papillomatous growth using hardware technologies. The following methods are distinguished:
- Cryogenic destruction . The destruction of papilloma occurs as a result of deep freezing using liquid nitrogen.
- Radio knife or radio wave excision . A narrowly directed wave with radio frequency plays the role of a thin scalpel. To generate such a beam, the Surgitron apparatus is used.
- Electrocoagulation or electric knife . The build-up is burned out using high frequency current.
- Laser exposure . It is considered one of the most effective methods, but requires special equipment that generates a laser beam.
- Surgical excision . This surgical operation is performed only in the presence of complications (including cancer) and is carried out using a scalpel.
The right to choose treatment technology remains with the doctor, who must take into account all factors. When treating the genitourinary system, it is important to preserve reproductive abilities. When diagnosing a precancerous condition, exclusion of further transformation of the lesion comes to the fore.
How to get rid of it using folk remedies?
Traditional medicine cannot eliminate the disease on its own, but in combination with antiviral therapy it can speed up the achievement of a positive result. The following folk methods are popular:
- Burning out with celandine juice . The abilities of this plant have been appreciated for a long time. In pharmacies you can purchase ready-made SuperClandestine.
- Compress made from leaves and juice of Kalanchoe or aloe . The course of treatment is long – about 50–60 days.
- Melissa infusion for internal use . Recipe – 100 g of raw materials per 100 ml of boiling water.
- Sage infusion is consumed 1 tablespoon 4-5 times a day. Recipe: 1 tablespoon of herb per 0.5 liters of boiling water.
Traditional medicine is not limited to these remedies. St. John's wort decoction, plantain infusion, treatment of the hearth with fir oil, cauterization with ammonia are used. It should be remembered that even the use of natural remedies should be agreed with a doctor.
Papillomas are benign formations, but their danger is expressed in the tendency of some types of pathology to degenerate. If signs of infection by the papilloma virus appear, you should consult a doctor, and only he can determine the need and treatment regimen. With timely treatment, the activity of the pathogen can be suppressed through conservative treatment.
Blackening of papilloma
If the papilloma turns black, then this is a sure sign of the beginning of the development of an infectious process in the body.
Papilloma can turn black in the following cases:
- injury;
- wearing tight underwear, which leads to chafing;
- trying to remove it yourself.
Blackened papilloma
If the papilloma turns black and falls off for no apparent reason, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Stages and degrees of papillomas on the body in women
Like any other benign tumor, papilloma develops on a woman’s body in several stages.
In this regard, the following stages of wart formation are distinguished:
- Stage 1 – uncontrolled division of squamous epithelium and formation of the papilloma root, which is asymptomatic and unnoticeable;
- Stage 2 - the formation of a wart head, which rises 1-1.5 mm above the general surface of the body, if located on the bends of joints, in the belt area, on the neck or under the armpits, it can cause a feeling of discomfort, chafing, and skin irritation;
- Stage 3 - a full-fledged flat, round or oblong neoplasm appears, which has a root, a stalk, a main body in the form of a head and blood supply due to the smallest capillary vessels connected to the rest of the epithelial tissues;
- Stage 4 – multiple proliferation of similar papillomas, which are formed as a result of cell division of an existing tumor (extensive papillomatosis is dangerous due to the high probability of malignant degeneration of one wart).
The stage of the skin disease is determined by a dermatologist during the examination of the patient. The treatment method is selected based on the diagnostic results, the type of papilloma and the degree of its development.
What is known about Gottron's papillomatosis
Gottron's carcinoid papillomatosis of the skin is a fairly rare dermatological pathology, the origin of which is unclear. It has a chronic course, and this disease is very difficult to treat. Its development is characterized by the appearance of extensive plaques on the skin surface. They reach large sizes - on average, about the size of a palm. These formations mainly affect the legs.
Diagnostic procedures are carried out by examining the patient, studying the medical history, and histological examination of tissues in the affected area. There is no etiotropic treatment as such, but symptomatic and supportive therapy has been developed (antibiotics, vitamins, antiseptics, and cytostatic agents are used).
Despite its threatening appearance, the formation rarely degenerates into cancer. But at the same time, the risk of secondary infection remains, and this can already provoke purulent inflammation, and, as a result, toxic shock and sepsis.
It is imperative to undergo treatment - the disease causes not only somatic, but also psychological problems. Over the years, it progresses, and also such a negative aspect as the unpleasant smell of growths is added.
Treatment of papillomas
Before starting treatment for papillomavirus, you should definitely see a doctor to find out the factors that triggered the onset of the disease.
Today there are enough treatment methods, so the doctor will determine which one is necessary for your case. There is no need to do this on your own, since if you choose the wrong method, you can only worsen the situation and allow the disease to spread throughout the body.
It is not allowed to remove papillomas yourself; this can lead to a lot of unpleasant consequences.
Drug treatment
By consulting a doctor at the first symptoms of HPV, the doctor will reduce the risk of infecting other people with the help of medication.
To combat viral infection, gynecologists and dermatologists recommend such remedies as:
- Isoprinosine - tablets have immunostimulating and antiviral effects. Allowed for use from three years of age. The average cost of 30 tablets is 900 rubles ;
- Likopid is a drug that has immunomodulator properties. The use of the drug in children under 3 years of age is prohibited. The average price of 10 tablets of 1 mg is 300 rubles ;
- Cycloferon is available in three forms: injection solution, tablets, ointment. To combat papillomavirus, tablets are most often prescribed. Contraindicated for use during pregnancy, lactation and children under four years of age. The average cost of 20 tablets is 350 rubles .
Isoprinosine
Lycopid
Cycloferon
Suppositories and suppositories for HPV are used when the spread of papillomas is visible in the genital area or inside, in the genital area.
Candles are:
- Rectal: Viferon - the drug is antiviral, immunomodulatory, and also inhibits the growth of pathological cells. Used after the first month of life. Cost from 270 rubles ;
- Genferon is a combination drug with interferon alpha-2. Has antiviral, antimicrobial, immunomodulatory effects. Approved for use by newborns. Cost from 290 rubles ;
- Panavir is a drug that artificially increases the nonspecific immune response and the production of its own interferons. Not used in children. Average price 1300 rubles ;
- Galavit - the active substance of the drug reduces intoxication and has immunomodulator properties. Do not use under 6 years of age. Cost from 440 rubles ;
- Betadine is an antimicrobial and antiseptic suppository, the main component of which is iodine. Contraindications: children's age. Cost from 360 rubles ;
Viferon
Genferon
Panavir
Galavit
Betadine
Kipferon
Any use of medications requires the supervision of your attending physician and careful study of the instructions for the drug.
Local treatment
Treatment of HPV can be carried out by local action exclusively on the neoplasm itself. There is a huge selection of drugs against papillomas in the pharmacy. All of them help dry out the growth, destroying its structure down to the roots, preventing its further spread.
Pharmacy drugs to combat papillomas:
- Feresol is a liquid for cauterizing warts and papillomas. Average price 360 rubles ;
- Dermavit - available in gel form. Average price 220 rubles ;
- Verrucacid is available in the form of an oily liquid with a special applicator. Average price 200 rubles ;
- Super cleanser is a powerful remedy; it literally burns away dead skin. Average price 30 rubles ;
- Lapis pencil - contains silver nitrate, which cauterizes growths. Average price 140 rubles ;
- Cryopharma is an aerosol and ointment that freezes papillomas and warts. Average price 600 rubles .
Feresol
Dermavit
Verrucacid
Super clean
lapis pencil
Cryopharma
Ointments are also used in complex treatment with other drugs.
Among them the most common are:
- Oxolinic ointment - average price 40 rubles ;
- Vishnevsky ointment - average price 40 rubles ;
- Viferon ointment - average price 160 rubles ;
- Panavir gel - cost from 180 rubles ;
- Levomekol ointment - average price 120 rubles ;
- Salicylic ointment - average price 20 rubles .
Oxolinic ointment
Vishnevsky ointment
Viferon ointment
Panavir gel
Levomekol ointment
Salicylic ointment
To achieve visible results when using any drug, follow the instructions: course of treatment, recommendations for use, number of applications per day, etc.
Hardware removal
Most patients pay little attention to the appearance of papillomas, and some still want to get rid of them, since the growths do not look aesthetically pleasing on the body and in most cases cause discomfort. Then, to eliminate them, a hardware removal method is used.
For example, they use methods such as:
- Laser removal is an operation that lasts only a few minutes. Using a laser device, the growth is burned out. Removal is painless, occurs without blood loss, and without inflammatory processes. The patient recovers quickly. During removal, local anesthesia is provided.
- Radio wave removal “Radio Knife” - high-frequency radio waves act on the growth and remove it without a trace, without leaving burns or injuring the skin around the affected area.
- Cryodestruction removal or removal with liquid nitrogen - using an applicator soaked in liquid nitrogen, a substance is applied to the growth for 1-5 seconds, the growth dries and falls off. This removal is quick and effective, but damage to surrounding tissue and pain may occur. This method is not used when removing large growths.
- Electrocoagulation removal - cauterization of soft tissues affected by papilloma with high-frequency current. If the growth is large, then local anesthesia is used during removal. When using this method, there is no bleeding or risk of infection.
- Cauterization with chemical means - these means act on the papilloma, cauterizing it, after which a crust appears at the site of the papilloma, which disappears several days after cauterization. The crust cannot be peeled off, as a scar may remain in its place.
Hardware removal of papillomas
The above methods are used when the growths are single and their size does not exceed 3 cm.
Surgical removal
Quite often, patients have growths over 1 cm removed surgically. Its only drawback is that after removing the growth, scars may remain in its place. Surgical excision is the oldest, simplest and most effective method and is performed under local anesthesia.
Surgical removal is prescribed if:
- there is a suspicion of degeneration of a benign papilloma into a malignant one;
- there is a risk of growth growth;
- the growth causes discomfort;
- if previously used methods were unsuccessful.
The patient must undergo a complete examination. If the growth is not malignant, the doctor will prescribe surgery to remove the papilloma.
Stages of the operation:
- The operating surgeon briefly explains to the patient the algorithm of his actions;
- Anesthesia is performed: local or general; More often, local anesthesia is used. And the general one is used if: there are large growths, papillomas on the head and face, the operation is performed on a child;
- The areas around the papilloma are treated with an antiseptic solution;
- The neoplasm is incised along the contour, slightly capturing part of the healthy skin;
- The cutting area is cleaned;
- If necessary, sutures are placed at the removal site.
If the doctor suspects the development of cancer cells or their changes, the excised tissue is sent for histological examination.
The results of the study are known already on the 7-10th day of the postoperative period. If an oncological type of papilloma is confirmed, inpatient treatment is performed.
The postoperative recovery period depends on the size of the papilloma being removed. This may take from 1 week to 2 months.
During this period, it is advised to refrain from:
- exposure to the sun;
- premature peeling of the crust from the operated area;
- getting the wound wet;
- do not allow the wound to interact with clothing;
- bleeding;
- Keep the healing area clean.
Surgical removal is more unpleasant than the other methods listed above, but is the most effective. If the removal was performed correctly and it was not a malignant tumor, then recurrence of the formation at this site is impossible.
It is advisable to postpone surgical intervention if signs such as:
- herpetic rashes;
- exacerbation of respiratory and chronic diseases;
- pregnancy and lactation period.
Treatment with traditional methods
It is useful to supplement the use of antiviral, anti-inflammatory and immune-strengthening drugs with folk remedies.
However, it is necessary to focus on what types of growths are prohibited from being removed independently:
- genital warts;
- growths and warts on the face;
- papillomas with signs of inflammation.
In other cases, it is quite possible to use treatment with traditional methods.
The most common folk methods:
- Banana - it should be mashed and the pulp applied to the growth;
- Celandine is considered the most effective remedy. It is necessary to treat the growth with freshly squeezed juice 3-4 times a day until the tumor completely disappears;
- Drying with cotton wool - dry cotton wool is applied to the growth and fixed with an adhesive plaster or bandage. The cotton wool needs to be changed after a shower. After about 3 weeks, the papilloma will dry out and disappear;
- White - egg white is applied to the papilloma several times a day until it completely disappears.
- Garlic. Apply the cut of a clove of garlic to the papilloma and cover with a band-aid. Change as needed. Use for 14 days;
- Potato juice - drink fresh juice orally, 100 ml 2 times a day for about 8 weeks;
- Castor oil - lubricate the skin around the papilloma with oil for a month;
- Apple juice - apply sour apple juice to the tumor 3 times a day until it completely disappears;
- Table vinegar - a ball is made from flour and vinegar and applied to the papilloma;
- Tea tree oil - lubricate the papilloma a couple of times a day.
Herbal medicine against papillomas is also known:
- St. John's wort decoction - in a ratio of 1:20. Take 0.5 cups half an hour before meals;
- Plantain infusion - prepared in a ratio of 1:20, take 4 times a day, using 1 tbsp of herbal tea per dose;
- Burdock infusion - in a ratio of 1:10, take 0.5 cups 4 times a day;
- Sage infusion - prepare 2 teaspoons of the herb and 0.5 liters of boiling water, take 1 tbsp. spoon every three hours.
To strengthen the immune system, a huge number of vitamin-rich methods for preparing folk remedies at home are known:
- Vitaminized recipe - juice from 4 squeezed lemons + 0.5 cups of aloe juice + 300 g of honey + 0.5 kg of walnuts (chopped). Mix everything and add 1 glass of vodka. Leave for 24 hours in the dark and cool. Use 30 minutes before meals 3 times a day;
- Fish oil - take 1 teaspoon per day orally;
- Herbal tincture - mix 150 g of lemongrass and nettle leaves, add 50 g of sage leaves. Brew a teaspoon of mixed herbs in a thermos, pour a glass of boiling water. Leave for two hours, strain. Consume after breakfast with a teaspoon of honey.
Also, do not forget to eat the healthiest foods to strengthen your immune system:
- honey;
- garlic;
- various berries;
- fruits and vegetables;
- spices such as cinnamon, ginger, turmeric.
Drink various herbal teas, fruit drinks, compotes based on fresh and frozen berries, as well as any freshly squeezed juices.
Diagnosis of human papillomavirus in women in gynecology
Skin rashes (condylomas, warts and papillomas) can be easily seen during external and internal gynecological examination (see photo).
Also, in the process of diagnosing HPV, colposcopy can be used - examination of the cervix with a special device - a colposcope, which allows you to enlarge the image several times and even display the image on a computer monitor.
But the most accurate diagnostic method is an analysis for the human papillomavirus, which is carried out using polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
PCR is used both to confirm the presence of human papillomavirus in the female body and to identify its type.
The “gold standard” for diagnosing HPV is the Digene Test, which determines the number of viral bodies in the body. Knowing the number of viruses in the body, you can estimate the risk of developing cervical cancer.
Also, all patients with suspected HPV are prescribed a cytological examination.
How does this happen?
- Through household items. Papilloma viruses can be transmitted if a virus carrier and a healthy person use the same toiletries and hygiene products. Sometimes even a simple handshake can cause infection.
- In public places. Baths, saunas, and swimming pools are especially dangerous in this regard, because pathogenic microorganisms tend to spread quickly in a humid environment. There is a chance that gym lovers will also get an unpleasant surprise. When visiting such places, you should especially carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene.
The risk of infection in these cases increases sharply if there is even minor damage to the skin. They become a kind of gate through which the causative agent of papilloma immediately enters the body.
- Autoinfection. Papillomas can appear in new places on the human body as a result of normal hygiene procedures (shaving, trimming nails). Even minor damage to the skin provides a comfortable environment for the introduction and reproduction of the virus.
What is papillomatosis
According to statistics, up to 70% of people of the so-called reproductive age are currently infected with the papilloma virus. And the problem is that it is sometimes difficult to detect the pathology: the disease often occurs latently and does not show obvious symptoms.
Human papillomaviruses are a group of viruses that includes 27 species and 5 genera, more than 600 strains . These viruses are armed with species-specific and type-specific antigens. They are not cultivated in cell systems. HPV is found in keracites; processes of productive infection and integration are not recorded.
Papillomatosis as a pathology can affect a person at any age. After infection, the virus does not activate immediately. The incubation period can be long - from two weeks to several years! But as soon as some catalyst occurs, it is like a trigger mechanism that turns on the activation of the virus in the body. And it begins to actively spread throughout the tissues of the human body. At this stage, the disease is no longer hidden - the clinical manifestations are obvious, the basal epithelial layer of the skin becomes infected.
When we say that scientists have identified more than 600 strains of HPV, this does not mean that there are so many types of the virus. There may be more: medicine continues to study the disease. One thing is good: not all strains are oncogenic, only a small part of them have these insidious properties.
Laryngeal papillomatosis: how it manifests itself
As already mentioned, most patients with HPV do not know about their illness or simply do not attach importance to papillomas that have arisen on the skin. It is virtually impossible to see papillomatosis of the throat at the very beginning of this disease: it does not cause any concern to the patient, and he does not go to the doctor. But if for a completely different reason the patient came to the ENT or dentist, the doctor may see a growth in the larynx. This is how papilloma is often discovered.
Such a growth is usually not associated with pain, but there are certain symptoms that patients often ignore.
Papilloma in the throat - symptoms:
- A feeling of “cottoniness” in the throat itself;
- Feeling as if food is not swallowed completely;
- It feels like something is scratching your throat while talking;
- The voice became muffled, the timbre changed slightly.
The doctor, having examined the mucous membrane of the throat, will see small growths there that have a mastoid shape. They may resemble ridges or tubercles, their surface is rough and uneven. The color is the same as the general color of the mucous membrane, sometimes a little lighter.
Laryngeal papillomatosis is considered a severe pathology that affects such body functions as breathing and sound production. Wide deformation of the tissues of the larynx threatens the life of the patient.
Laryngeal papillomatosis in children is most often diagnosed between the ages of one and five. If your baby's voice suddenly becomes hoarse, you should take him to the doctor. Further, the symptoms of the disease include a lump in the throat, trouble breathing, and a persistent cough - these can be permanent or temporary.
Attention! Papilloma in the larynx can be single, but the virus can cause multiple lesions. The disease becomes chronic. Localization occurs on the ligaments, on the laryngeal ventricles, on the uvula and in the subglottic zone, in the epiglottis.
Why does laryngeal papilloma occur?
As already mentioned, sexual transmission of the virus dominates. And oral sex in this regard poses the greatest danger - it is this that leads to HPV infection of the tonsils. Smokers, it should be noted, are at risk. But household transmission of HPV cannot be ruled out.
The doctor makes an assessment on the following points:
- What are the symptoms of the disease;
- Where is papilloma located in the throat;
- How much the mucous membrane is affected;
- What is the patient's age?
In children under five years of age, papilloma in the throat is formed during perinatal transmission of the virus; respiratory ailments less often lead to illness. For adults, it is most often sexual transmission. Chronic inflammations affecting the throat, hearing organs, and nose provoke activation of the virus in the body. Also, scarlet fever and measles suffered by children increase the risk of virus activation.
The catalyst for the disease to enter the active stage may be dependence on bad habits, as well as a decline in defenses.
How is tonsillar HPV infection diagnosed?
Unfortunately, there is no specific test that will detect papillomatosis of the throat at an early stage. An examination by an ENT specialist or even a dentist may be the moment when the doctor sees growths in the patient’s larynx. Most papillomas are found in people who have already complained of symptoms of infection.
The doctor examines the throat with a laryngoscope or pharyngoscope. There are special flexible forms of these instruments that improve the quality of diagnosis.
If the doctor evaluates the growth as suspicious, he will definitely send its tissue for a biopsy. Particles of papilloma are removed with a special hollow needle.
Cancerous damage to the throat can be indicated by problems with swallowing, a cough with blood discharge, a lump on the cheek or neck, or persistent hoarseness.
Numbness of the tongue, swelling or pain in the jaw, or a special coating on the tonsils may also indicate a malignant lesion. Don’t get excited, and if your voice becomes hoarse and it hurts to swallow, think about the worst. But if symptoms persist for more than two weeks, you need to get checked.
How to treat laryngeal papillomatosis
If the disease has a benign course, the patient will be given antiviral medications that will increase the patient’s immunity. And this will stop the spread of papillomas. But while the growths are there, they need to be removed. Even single papillomas are threatening in nature - they are a source of infection, which can only be stopped by removing it.
You should not take risks with laryngeal papillomatosis by choosing treatment using traditional methods. If the patient zealously insists on them, it is still worth discussing your choice with a doctor - most traditional methods are either ineffective or not effective at all, and often they aggravate the condition.
The malignant course of the disease is a different treatment. Doctors will assess the nature of the growths and prescribe an individual treatment regimen.
Important! Remember that papillomas in the throat are not always cancer or a risk of cancer. This may be the formation of a conditionally safe strain that does not pose a threat of a malignant course of the disease. But if you experience symptoms indicating papillomatosis, you need to go to the doctor to find out what is happening in the larynx. It is necessary to exclude the risk of cancer.
Possible complications
In the absence of adequate response and treatment measures for papillomatosis on the body, over time, a woman may encounter the following complications.
Possible complications:
- the appearance of similar warts on other parts of the body, which indicates an increase in viral activity;
- degeneration of a wart into a malignant cancerous tumor, which can lead to death;
- the occurrence of similar neoplasms in the cavity of the bladder, intestines, larynx, trachea, which will lead to disruption of their work, problems with urination, breathing, and digestive function;
- cervical cancer (scientific studies have shown that 80% of women suffering from this disease are infected with human papillomavirus;
- increasing the size of the wart, creating a cosmetic and aesthetic defect;
- injury to the neoplasm and bacterial infection entering the epithelial tissue.
To prevent the appearance of papillomas on the body of women, it is necessary to remember the causes of their occurrence. This will preserve the health of the skin and prevent the pathogenic activity of the papillomavirus from reducing the immune status. The disease itself is not life-threatening, but its presence can provoke the development of severe complications.
Article design: Anna Vinnitskaya
Special means
There are special remedies for warts and papillomas, but they do not provide any effectiveness or guarantee of recurrence. One of these products includes, for example, the Formu Clear patch and other similar patches.
Such products usually contain natural ingredients that counteract the virus to some extent.
Dog saliva
To get rid of a benign tumor using this method, you need to spread the wart with an even layer of sour cream. After this, the woman should approach the dog so that he licks the lactic acid product with his tongue.
After this, the papilloma is sealed with a medical adhesive plaster. Saliva cannot be wiped off the surface of the tumor. After 1 week, the patch can be removed. From this moment on, the wart will begin to crumble.
Cauterization with celandine
During the growing season of this plant (from late May to mid-June), you should pick off branches of celandine every day and burn the warts with poisonous yellow juice. The duration of therapy ranges from 10 to 30 days. Precautions should be taken to prevent juice from coming into contact with the mucous membrane of the mouth and eyes.
The effectiveness of using the above folk remedies for removing papillomas on the body has not been proven by official science. Women who used similar recipes were able to achieve the desired result and speak positively about these methods of therapy.
Other methods
The most effective way to treat papillomas is their complete removal.
The following methods are used for this:
- chemical burning – involves exposing the surface of the wart to aggressive solutions based on acids, potassium or sodium alkali;
Papillomas often occur on the body of women. There are many reasons for its appearance, but the main thing is to take care of your skin.
- electrocoagulation - the papilloma is cut and cauterized using a loop-shaped instrument, the metal end of which is under electric current (the treatment procedure is performed under local anesthesia);
- cryodestruction - a benign neoplasm is burned out using a liquid nitrogen solution (under the influence of low temperatures, epithelial tissue freezes and then falls apart);
- laser coagulation – excision of the papilloma is performed using positively charged laser particles, removing the main body of the wart and cauterizing its root system;
- Surgical removal is the traditional and most common method of treating a dermatological disease, which consists of excision of the wart with a scalpel and subsequent application of suture material.
All of the above methods for treating papillomatosis make it possible to remove benign tumors with minimal risk of relapse of the disease.
The average rehabilitation time ranges from 3 to 7 days. The safest method is laser excision and electrocoagulation. The most painful and traumatic method of treatment is traditional surgical removal of the wart.
Causes of papilloma
Here are the main causes of the disease:
- skin injuries;
- promiscuity;
- pregnancy;
- smoking;
- alcoholism;
- reduced immunity;
- endometriosis;
- hypovitaminosis;
- nervous tension, stress, depression;
- visiting bathhouses, saunas, beaches, etc.
Ways of infection with papilloma:
- household, contact (touch, shared towel, etc.);
- sexual;
- infection of newborns during delivery;
- from mother to fetus;
- self-infection (shaving, hair removal).
Types of formations
The HPV virus is represented by a microorganism that contains about 100 viral strains. Based on the type of this parasite, various types of formations arise, differing in external parameters and location on the body.
They traditionally form on the bladder, in the vaginal or genital area. After HPV is activated, moles appear within the body. They have several types.
Simple formations
These are phenomena that occur on the body when it is exposed to strains 26, 41, 63, 67. These are the most likely formations belonging to the benign group. The formation process starts with a slight burning and tingling sensation in a certain bodily area. The size starts from 1 mm and reaches a diametrical value of one centimeter. Favorite places of formation are fingers and palms.
Plantar warts
They appear during infection by viruses of types 1, 2, 4. These formations can be quite easily confused with calluses, but the presence of a warty disease can be confirmed by general signs. This is soreness and the absence of a skin pattern, because it persists on calluses. These formations may have a tendency to self-destruct, especially in children.
Flat papillomas
This name is due to the absence of their protrusion above the skin surface; it is only a couple of millimeters. The formations have a round shape, it is often elongated. These pathologies grow mainly in the area of the face, lips, and upper chest. In the fair sex, growths can be diagnosed in the cervical area. If several warts are nearby, they can merge and form groups of growths that are clearly visible on the body.
Thread-like elements
They grow on a thin stalk and have an elongated, elongated shape. Such growths appear during exposure to HPV 7 and 12. At the initial stage of growth in the localization zone, you can detect a small bump that gradually stretches out and begins to hang down. Typically, such growths form after 40 years, and gender does not matter. Most often they are located in the upper areas of the neck, in the armpits, and mammary glands. Trauma can lead to worsening of the mole.
Condylomas acuminata
These formations resemble papillae; they can be found individually or in entire groups. As growth occurs, the elements merge with each other, and their surface becomes similar to a cock's comb, the color of the formations being flesh-colored or pinkish. Condylomas can be caused by the progression of only those HPVs that are sexually transmitted. In the fair sex, the growths “capture” the vagina and cervix.
This is interesting: Treatment of warts and papillomas with medications: choice of medication
Squamous formation
The squamous epithelial element grows, causing this phenomenon. Most often, the disease develops in elderly people; it is characterized by a slow growth rate and formation in places that are most susceptible to injury. These formations have a wide base and are located on a very thin stalk, they are distinguished by a wide base and round shape, whitish or dark brown in color. The size of the formation can reach 1.5-2 cm.
Inverted forms
You can see what this type of papilloma looks like in the photo.
In another way, this formation is called a transitional cell growth and occurs exclusively in rare situations. Education has its own characteristics in terms of development:
- a clear location of localization - most often only the nose and paranasal sinuses are affected, the disease is localized in the maxillary, frontal sinus, and ethmoidal labyrinth;
- the unilateral nature of the lesion implies the growth of papilloma exclusively on one side of the nose, and it can be single or multiple;
- the likelihood of growth growing into bone-type structures entails the process of destruction of the walls of the orbit, nasal sinuses, and cranial bones;
- the likelihood of a relapse of the disease 5-10 years after undergoing an effective treatment process.
- Eliminates warts and papillomas.
- Strengthens immunity.
- Destroys human papillomavirus.
- Cleanses blood and lymph.
- Protects against the spread of the virus.
Find out details
This type of growth entails obvious nasal congestion and provokes deformation of the facial part of the skeleton. In 5% of cases the tumor is cancerous.
What are flat papillomas on the body
The photo shows flat papillomas on the arm and face
Flat papillomas are one of the types of neoplasms caused by papillomavirus. They can often be confused with moles, since such growths do not protrude too much above the surface of the skin. They are painless and do not cause any physical discomfort.
You can determine what kind of tumor is in front of you by finding photos of flat papillomas on the body on the Internet
Also pay attention to the following characteristics of growths:
- The size of the neoplasm is from 8 to 10 mm.
- They protrude slightly above the surface of the skin - up to 1 mm in height.
- They can have different colors, but most often they are flesh-colored or brown.
- They have a round shape without folds.
- The top of the buildup is flat.
- They have clear outlines.
- Usually they do not have keratinized skin, the surface is smooth and shiny.
- As a rule, they appear on the arms, legs, and face.
Flat papillomas can appear on the body in any person infected with HPV. As a rule, they appear in childhood or adolescence.
Papillomas are small growths on the body. Their color varies - from natural, matching the body, to dark brown. Neoplasms can appear in any anatomical area of a pregnant woman’s body, but they do not have a negative impact on the gestation and health of the fetus.
Symptoms of papillomas
Papillomas on the body (the causes of neoplasms in women are associated with infection by viral microorganisms) are single or multiple benign tumors that are easily identified by external signs.
Symptoms of papillomatosis in women manifest themselves as follows:
- the appearance of a small tubercle that rises above the general surface of the epithelium;
- enlargement of the wart root, which becomes larger every week;
- a foreign neoplasm appears on the body, characterized by a round, branched or cone-shaped shape;
- the main locations of papillomas on the female body are the armpits, inner thighs, neck, skin surface under the mammary glands, groin area, perineum, genitals, back, plantar part of the leg;
- in case of prolonged exposure to the surface of the wart, chafing and pain may occur;
- papilloma may have flesh-colored, yellowish, pink, brown shades, which is normal;
- attempts to remove the tumor on your own do not lead to a positive result, and the cut wart grows back.
The presence of symptoms such as a sudden change in the color of the wart to darker colors, the onset of an acute inflammatory process, the release of pus or sanguineous fluid, and attacks of pain are alarming signs that are not typical for papillomatosis. In this case, the degeneration of a benign tumor into a cancerous tumor cannot be ruled out.
Why are papillomas dangerous?
The papillomavirus itself is not dangerous to health, since it can “live in the body” for years and not manifest itself in any way. Health problems begin in the relapse stage, when warts begin to grow rapidly. When asked whether papillomas on the body are dangerous, the answer is definitely yes. Initially, these are benign growths on the skin, but in the absence of timely treatment and under the influence of pathogenic factors they can develop into malignant tumors, fraught with metastases. Potential complications are:
- Papilloma in the throat and tongue can lead to impaired breathing and attacks of suffocation.
- A growth on the clitoris or in the vagina leads to an inflammatory process in women.
- Papilloma on the skin or mucous membrane can lead to bleeding when injured.
- The formation of polyps, which in the human body are indicated to be removed promptly.
- Human papilloma when injured can lead to blood poisoning and death of the patient.
Maintaining immunity to prevent papillomas
It happens that you become infected, but papillomas do not appear.
If your immunity is good, this will happen.
In the vast majority of cases, this infection is transient.
You won't even know about it.
If the papillomavirus has established itself in the skin, then with a 90% probability, no later than in 2 years, it will no longer be there.
But for this, your immunity must be strong.
It is difficult to break it, but it is possible.
Here are the main reasons why the immune system becomes weaker:
- hypothermia and overheating;
- passive lifestyle;
- obesity;
- infection with other viruses;
- HIV;
- diabetes;
- any prolonged illness;
- injury;
- operation.
To strengthen your immune system, strengthen yourself, eat well, lead a healthy lifestyle, and get rid of bad habits.
You must be at a normal weight and have adequate physical activity.
If this is not the case, the immune system may deteriorate and papillomas may appear.
Effective treatment with traditional therapy
You can also treat warts on the stomach using folk remedies:
- To launch the body’s mechanism for fighting HPV, it is recommended to use the following recipe: you need to mix lemon balm, crushed plantain leaves, horsetail grass, nettle and dandelion root in equal proportions. Next you need to take 4 tbsp. l. herbal collection and pour one liter of cold water and boil for 10 minutes. The product is used in 3 tbsp. l. three times a day.
- You can quickly remove warts using this remedy: you need 100 g of potato sprouts, 100 g of celandine and 150 g of thuja shoots. All ingredients must be placed in a glass container and filled with medical alcohol. The alcohol level should be higher than the herbal tea level. The product should sit for two weeks. The growth should be lubricated 3-4 times a day. The course of therapy ranges from 7 to 14 days.
- To remove growths on the skin, you need to mix 100 ml of alcohol, 1 aspirin tablet, 5 drops of iodine and 3 drops of boric acid. The resulting product should be applied to the wart three times a day.
- To get rid of growths, you can wipe them with a mixture of dandelion juice and sour apple. Ammonia also helps a lot against such tumors.
- It is recommended to apply raw egg white to the warts every day for 1-2 months.
- You need to take a cabbage leaf, chop it very finely and squeeze the juice out of it. The resulting juice must be moistened with gauze or cotton wool, which is applied to the growth on the abdomen and secured with a band-aid. The compress is kept overnight.
- You need to peel and very finely chop two cloves of garlic, mixing it with 1 tsp. baby cream The resulting medicine is applied to the skin growth for 2-3 hours, wrapping the stomach with cling film. The course of treatment is one month.
Important addition: Antifungal agent Pharmtek MIKOSTOP spray - reviews
Is there specific prevention of human papillomavirus?
Today in our country two vaccinations against human papillomavirus in women are certified, namely: Gardasil and Cervarix.
These vaccines protect the body from HPV types 16 and 18, which most often cause cervical cancer. In developed countries of America and Europe, these vaccines are included in the vaccination schedule for girls. For example, in Germany, vaccination against HPV is indicated for all girls over 12 years of age. Vaccination is carried out in three stages.
In Russia, the vaccine can be purchased at pharmacy chains. The average cost of the drug is 7,200 rubles.
What is Buschke-Lowenstein papillomatosis?
This condyloma is rare, but more dangerous than many others - it tends to degenerate into squamous cell carcinoma. Treatment of the disease is also difficult. Even surgery does not provide protection against relapse.
Buschke's condyloma is a very large tumor, its tendency towards oncological transformation is fraught with the main danger. The tumor can appear at any age. But most often it forms on the penis of men. And this is not just papillomatosis on the head. This pathology does not always develop into cancer, of course, but the risks are really high.
If the immune system is weakened, if intimate hygiene leaves much to be desired, then the risks of degeneration increase. Predisposing factors for the appearance of the formation are considered to be narrowing of the foreskin of the penis, sexually transmitted diseases, hyperhidrosis, lichen ruber, and autoimmune diseases.
PCR analysis, a blood test for HPV, and a biopsy are used as diagnostics. But even by external characteristics it is not difficult to recognize condyloma; the areas of localization, as well as visualization, speak for themselves. Surgical treatment: how exactly to remove it depends, first of all, on the size of the growth.
In what forms can the virus exist?
Most people know about skin papillomatosis and also know about viral papillomatosis. But there are many options for the manifestation of the disease - and it does not only affect the skin, as those who believe that papilloma is just warts on the skin surface think.
Forms of viral existence:
- Episomal. This is the name given to the benign form, which exists outside the cellular chromosomes.
- Introsomal. And this is a malignant viral form in which the virus penetrates the cellular genome.
Only laboratory diagnostics can show what form of the virus is in each specific case. The treatment of papillomatosis depends on this.
What do papillomas look like and what types are there?
Types of skin neoplasms
Warts are multiplying growths on the human body. They are caused by the papilloma virus, which makes its way into the body through irritants or a weakened immune system.
Depending on the location on the body, appearance and germination period, there are more than fifty varieties of these growths. These are not necessarily benign neoplasms; a wart under human skin gives rise to new pathogens and worsening infections with the transition to oncology.
Location
There is no specific place of manifestation and reason for the appearance of small warts on the body; they spread everywhere. Particularly affected are those areas of the skin where it is easiest for bacteria to penetrate or where the skin is more delicate and more susceptible to damage. From the point of view of scientific findings, such evaluation criteria differ when warts appear.
- Carpal and elbow part;
- Kneecaps, feet, fingers;
- Warts on the back;
- cheeks and forehead;
- ankle, hands.
The most rarely affected are:
It is practically impossible to see warts on the hairy parts of the body, warts on the stomach and on the body in general. The full elimination of the problem begins as soon as the first growth is visible.
Causes of warts appearing on the body
Every person is susceptible to this disease; it is not completely known why warts appear on the body. Thanks to the nerve tissues in which the papilloma virus is retained, its spread is so local and can be susceptible to relapse.
There are 3 common types of papillomas.
- Common warts are about the size of a pea, flattened or slightly swollen, round and angular in edge, and quite hard to the touch. The color is skin-like or grayish-yellowish. Most often they occur on the back of the hand and fingers.
- Flat warts are small in size, weakly expressed, round, and have a fine-grained surface. Often multiple, located along the scratch line. Place of occurrence: back of the hand and face.
Surgical therapy
Skin papillomatosis involves surgical treatment, but it is only appropriate if the formation is more than a centimeter in diameter and there is a suspicion of its malignant nature or the threat of it. The doctor will remove the growth along with some surrounding tissue, and then apply cosmetic stitches to the wound.
The alternative is:
- Cryodestruction. The growth will be affected by low temperatures. This session is comfortable for the patient, it is painless, and no anesthesia is required. After the doctor treats the growth with liquid nitrogen, it will turn white, and then a blister will form in its place. Over time, the pathogenic cells will die. This is a good way to treat papillomatosis in gynecology, on the neck, on the eyelids, and in areas with sensitive skin.
- Electrocoagulation. The affected area is affected by high-frequency currents. The doctor places a special ring on the base of the formation or a narrow leg, and it cauterizes the tissue. After this action, the formation is simply removed. There will be no bleeding.
- Radiosurgical removal. A special device, a radio knife, removes the formation like a laser, leaving no traces.
- Laser removal. This method of therapy is considered the least traumatic. Damaged tissues are exposed to a carbon dioxide ray - this is how the liquid is evaporated, after which the tissues dehydrate, dry out, transforming into a dark crust. This crust comes off on its own after a few days. If papillomas are removed in this way on the eyelids, on the face as a whole, you need to make sure that UV rays do not reach the skin - this is fraught with pigmentation.
It is worth mentioning the method of chemical destruction - a composition with organic acids is applied to the neoplasm, it is they that eliminate the structure of pathogenic cells. If the patient has a low pain threshold, or if the growth itself is large, then either method may require local anesthesia.
After the operation, the patient must understand that such surgical intervention requires a rehabilitation period. This means that he needs to follow all the doctor’s instructions and disinfect the wound.
Doctors send the excised papilloma for histology, this allows us to exclude the presence of cancer cells in the removed formation.
What is HPV
This is one of the common infections that, once it enters the body, remains in it forever. The harmful effects and increased activity of HPV are observed only under the influence of provoking factors; otherwise, human papillomavirus predominates in a “dormant form” in the absence of alarming symptoms. Papillomavirus occurs equally in women and men and is contagious to others. Among potential complications, doctors do not exclude skin papillomatosis with frequent relapses.
Clinical manifestations of papilloma
The incubation period can last up to a year, but on average takes 3 months. If papillomas are provoked by a virus of high oncogenic risk, then malignant dysplasia forms within 5 years or more. The patient has time to remove tumors before tissue magnetization.
In most cases, human papillomavirus infection never manifests itself, but remains in the form of preclinical manifestations. Symptoms largely depend on the location of the tumors. The easiest to develop are skin papillomas, which are a cosmetic defect and practically do not cause any complaints. If the papilloma is large, it can be easily injured, in which case the tumor can become inflamed and bleed. But even if the papillomatous growths are not damaged, it is best to remove them in a timely manner in order to completely eliminate the risk of tissue malignancy under the influence of unfavorable factors.
Genital papillomas have striking clinical manifestations. At first, small flesh-colored papillary outgrowths appear on the mucosa, but gradually they grow and turn into formations that externally resemble a cockscomb or cauliflower inflorescences. Exudate constantly accumulates between papillomas in the genital area; the tissues remain moist for a long time and are easily damaged during friction with underwear or intimate contacts. Additionally, swelling of the mucous membrane appears, and an inflammatory infiltrate forms.
Papillomatous papillae are covered on top with stratified epithelium, with pronounced hyperplasia of the basal layer. Genital warts most often appear in areas of skin friction - the frenulum of the labia, clitoris, perineum, vaginal opening. In men, genital papillomas are localized mainly in the foreskin area. Neoplasms can appear in the urethra and distant parts of the urethra, causing symptoms of urethritis and severe pain during urination.
Active growth of genital papillomas is observed with hormonal disorders in pregnant women who suffer from a physiological decrease in immune activity. After childbirth, neoplasms usually disappear on their own. Giant genital warts put pressure on healthy tissues and contribute to their destruction.
Risk factors for the appearance of papillomas:
- frequent change of sexual partners and early onset of sexual activity;
- intimate contacts with people who have signs of genital papillomatosis;
- violation of intestinal microflora, the presence of diseases that suppress the activity of the immune system;
- development of immunodeficiency states;
- vitamin deficiencies;
- excessive insolation;
- hormonal disorders associated both with the course of a certain disease and with natural processes - pregnancy and menopause.
Treatment of papilloma
It is impossible to completely get rid of the virus. Warts are removed medicinally (Tebrofen ointment is prescribed - a local antiviral agent; intralesional administration of interferon) or surgically: electrocoagulation (a combination of electric current and high temperature), cryotherapy (liquid nitrogen), cryodestruction, chemical cauterization, laser therapy, excision of warts.
Taking multivitamins is also recommended.
Traditional methods of treatment: treating the rash with ammonia, celandine juice, dandelion, sour apples.
Decreased immunity
Once in the body, the virus cannot immediately take over, since at this moment the immune system is activated - the body’s ability to resist the introduction of any foreign agents.
As long as the immune system is functioning fully, performing its protective functions, the effect of the virus is suppressed. It turns out that the enemy is not completely defeated, but is weakened and in no condition to harm.
The insidious virus is waiting for the right moment to show itself in all its glory. This opportunity appears at the slightest weakening of the immune system.
What weakens a person's immune system?
- Chronic stress. Any stress is accompanied by the release of a large amount of hormones into the blood. It is a natural defense mechanism for mobilizing the body's physical forces and reactions. However, the functioning of the immune system is temporarily suppressed.
If stress is chronic, there is a constant suppression of the immune system, which is no longer able to fully perform its protective functions.
- Lack of sufficient rest . When a person rests, his body recovers. All physiological processes return to normal. Internal systems begin to work with renewed vigor, and the immune system is no exception.
- Unbalanced diet. If the body does not receive the required amount of valuable proteins, it will automatically begin to redistribute its existing reserves. First of all, the muscles will receive valuable material. But the immune system will be forced to be left without the elements it needs. If at the same time a lack of vitamins is discovered, a decrease in immunity is simply inevitable.
- Long-term illnesses, especially those accompanied by the use of antibiotics. In this case, the cells of the immune system are damaged and it becomes weakened. It is especially dangerous if the disease was not treated thoroughly, but only the symptoms were muffled with the help of quick-acting remedies. Long-term use of medications also sometimes leads to the papilloma virus receiving a signal to act.
- Bad habits. Smoking, alcohol abuse, use of narcotic and toxic substances and other similar addictions cause irreparable harm to the immune system and thereby contribute to the activation of the virus.
The listed factors deprive the body of a reliable protector and make it accessible to pros.
elimination of any viruses, including the human papillomavirus.
Hormonal changes in the body
Hormones are regulators of many reactions occurring in the human body. Failures that occur in the hormonal sphere for some reason provoke the appearance of neoplasms.
A number of studies indicate that human papillomavirus is hormone dependent. It is activated if changes occur in the body's metabolism of estrogen. Estrogen is a female sex hormone, so women are more susceptible to the appearance of papillomas due to hormonal imbalances.
- Pregnancy. Very often, the changes occurring in a woman’s body during this period activate the dormant virus. Papillomas can appear on the hands, face, neck, and armpits. Weight gain and sweating contribute to their more active spread. Clothing, which becomes increasingly tight during pregnancy, creates friction between the fabric and the body, which leads to the appearance of additional tumors.
- Adolescence. During this period, the body undergoes rapid hormonal changes associated with puberty. Against the background of such processes, in addition to traditional youthful acne, neoplasms may appear on different parts of the body in adolescents.
- Taking hormonal drugs. Some of them, as a side effect, disrupt the formation of skin fibers, thereby increasing the risk of unwanted growths on the body.
- Menopause in women . Women who have passed the age of 40 undergo major hormonal changes called menopause. Even an ideally healthy woman at this age runs the risk of discovering previously undetected neoplasms.
- Abortion, any gynecological diseases. The activity of all organs of the human reproductive system and its hormonal status are interconnected. Therefore, any problems in the reproductive system are risk factors that contribute to the activation of the papilloma virus.
Destructive treatment methods
Destruction of papillomas can be chemical (using trichloroacetic acid, Solcoderm, Feresol) and physical (laser coagulation, electrosurgical, radio wave methods, cryotherapy). The specific method for removing papillomatous growths is selected by the doctor, taking into account the location of the tumor, the number of tumors, the HPV strain and other important factors.
Destructive methods for removing papillomas are combined with the use of antiviral agents and immunocorrective therapy. Surgical excision with a scalpel is performed only for large papillomas and suspected tissue malignancy or if there are contraindications to minimally invasive surgical techniques.