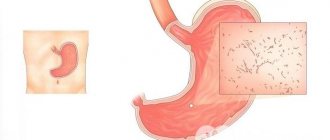
Autoimmune gastritis is a rare case in the practice of gastroenterologists. This specific type of gastritis has not been fully studied. The mechanism of occurrence and development of this disease is complex, as in other cases of occurrence. Autoimmune gastritis, or gastritis type A, occurs only in 7–10% of cases, according to rough estimates by doctors.
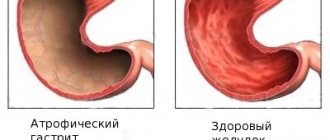
Type A gastritis is an autoimmune disease, the distinctive feature of which is the transient atrophy of the gastric mucosa, with the death of a large mass of cells. In such a case, the immune system perceives the cells of the gastric mucosa as foreign agents and begins to actively produce antibodies against them. Many doctors note that the disease is transmitted at the genetic level, becoming a consequence of genetic mutations. Antibodies produced by the immune system begin to fight gastromucoprotein, a secretion that protects the stomach from various inflammatory infections.
Gastritis type A
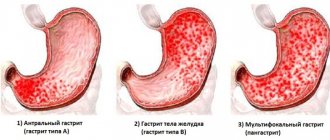
When an autoimmune process occurs, the bottom and body of the stomach are affected. As a result, the production of gastric juice and other important components involved in digestion is significantly reduced. With autoimmune gastritis, the development of vitamin B-12 deficiency is observed. The phenomenon is associated with a decrease in the content of the Castle factor in the body, which is responsible for the normal absorption of the vitamin.
Chronic autoimmune gastritis
As a rule, gastritis, which occurs as a result of autoimmune processes, becomes chronic. Autoimmune chronic gastritis is a disease that leads to complete atrophy of the gastric mucosa. In the early stages, the disease is focal, later spreading to the surface of the stomach tissue. In addition, anemia occurs, with a pronounced deficiency of vitamin B-12. More often, autoimmune chronic gastritis is accompanied by other autoimmune thyroid diseases.
The chronic form of autoimmune gastritis requires long-term and systemic treatment. Patients often need to take medication periodically throughout their lives. Type A gastritis is an insidious and cunning disease that even gastroenterologists are not always able to distinguish from other, less severe forms of gastritis. Additionally, we note that this type of gastritis is difficult to diagnose. The disease is often confused with Helicobacter pylori gastritis; the symptoms and treatment are not very different from infectious gastritis.
Possible complications
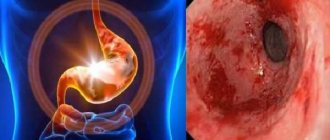
If the disease is not treated promptly, atrophy of the mucous membrane will only progress and the symptoms will intensify. As a result, adenocarcinoma may occur. Also, a careless attitude towards health leads to iron deficiency anemia and polyhypovitaminosis.
Thus, if a person suddenly notices that his stomach is gurgling, heartburn appears, bad breath and other strange manifestations of the body occur, then he should consult a doctor as soon as possible. This often indicates the development of autoimmune gastritis, untimely treatment of which leads to serious complications.
Autoimmune gastritis is a rare case in the practice of gastroenterologists. This specific type of gastritis has not been fully studied. The mechanism of occurrence and development of this disease is complex, as in other cases of occurrence. Autoimmune gastritis, or gastritis type A, occurs only in 7–10% of cases, according to rough estimates by doctors.
Type A gastritis is an autoimmune disease, the distinctive feature of which is the transient atrophy of the gastric mucosa, with the death of a large mass of cells. In such a case, the immune system perceives the cells of the gastric mucosa as foreign agents and begins to actively produce antibodies against them. Many doctors note that the disease is transmitted at the genetic level, becoming a consequence of genetic mutations. Antibodies produced by the immune system begin to fight gastromucoprotein, a secretion that protects the stomach from various inflammatory infections.
When an autoimmune process occurs, the bottom and body of the stomach are affected. As a result, the production of gastric juice and other important components involved in digestion is significantly reduced. With autoimmune gastritis, the development of vitamin B-12 deficiency is observed. The phenomenon is associated with a decrease in the content of the Castle factor in the body, which is responsible for the normal absorption of the vitamin.
Causes of autoimmune gastritis
The nature and mechanisms that trigger autoimmune gastritis are mysterious. Modern science is not able to give a complete and comprehensive answer to the question. However, selected facts about the disease are known. Individual causes that activate autoimmune processes in the body are named.
Autoimmune inflammation
Genetics
An important factor in the development of the disease is genetics. The area of genetic disorders remains not fully understood, but doctors say that 10% of the occurrence of the disease is associated with genetic disorders. If a relative in the patient’s family suffered from a disease, the patient exhibits similar symptoms, it is likely that “bad genes” are to blame for the disease.
Autoimmune system
Your own immune system can sometimes do a bad job. If a person has a hereditary predisposition to the occurrence of gastritis A, under certain conditions, if processes in the human immune system are disrupted, the occurrence and progression of chronic autoimmune gastritis is possible.
It happens that there is no inheritance in the form of “bad genes”, but a person still develops this rare type of gastritis. The processes are mysterious, but doctors suggest that the cause of the development of the malaise is other previously acquired autoimmune diseases of the thyroid gland.
Hard food and bad habits
Two additional factors that can lead to gastritis are too hard food and bad habits. With mechanical damage from pieces of food or aggressive exposure to harmful substances contained in nicotine or alcohol, autoimmune processes in the stomach begin to develop. This happens more often if the person’s genotype reflects prerequisites and innate predisposition.
How does this pathological process proceed?
With this disease, the human digestive system begins to eat itself. In other words, the immune system, by producing specific antibodies, destroys the normal cells that make up the gastric mucosa. This leads to a decrease in the acidity of gastric juice, food stops being digested and its rotting begins, and beneficial substances are not absorbed either into the tissues or into the general bloodstream. A person, after eating, feels quite severe pain in the lower abdomen. Because of this, he stops eating anything, and after some time dystrophy and anorexia develop.
Symptoms
The symptoms of this rare disease are similar to those of other forms of gastritis.
When first occurring, patients suffer from:
- Heaviness, pain, other discomfort in the stomach after eating;
- Persistent flatulence;
- Strong and loud rumbling;
- Nausea regardless of meals;
- Unstable stool;
- Heartburn, belching.
At the stage of exacerbation of a previously existing disease, the following can be observed:
- Constant fatigue;
- Migraine;
- Sweating;
- Weight loss;
- Pallor;
- Low pressure.
To identify autoimmune gastritis and make a clear diagnosis, a full diagnosis is required.
Clinical picture
Clinical signs of fundic atrophic gastritis occur when the number of parietal cells is below the borderline norm, and the stomach stops producing hydrochloric acid in the required volume. The patient is concerned about the following characteristic symptoms of the pathology:
- heaviness and feeling of fullness in the stomach after eating;
- belching;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- decreased appetite;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- bowel dysfunction;
- heartburn.
Atrophic gastritis is prone to rapid progression, so the lack of timely measures taken leads to impaired absorption of nutrients. The body does not receive the necessary vitamins and minerals, against the background of which vitamin deficiency and its characteristic manifestations develop:
- dehydration, dryness, peeling of the skin;
- visual impairment;
- increased bleeding;
- hair loss;
- fatigue;
- fragility and delamination of nail plates, etc.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of chronic gastritis is made by collecting anamnesis from the patient. More research will be needed to definitively confirm the autoimmune nature.
- Immunological analysis, including detection of the presence of antibodies in the blood;
- General and biochemical blood test;
- Determination of the level of secretion in the stomach:
- Complete fluoroscopy of the entire gastrointestinal tract;
- FGDS;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- Blood test to detect vitamin B-12 deficiency.
A full range of examinations prescribed by a doctor will help to accurately determine the presence of gastritis A.
Treatment of autoimmune gastritis
The cause of the disease is at the genetic level. So far the disease cannot be cured. Treatment of autoimmune gastritis is aimed at eliminating symptoms and discomfort in the stomach and maintaining normal functioning of the organ.
Medications
For severe stomach pain, gastroenterologists usually prescribe painkillers: No-shpa, buscopan, papaverine. To stimulate the digestive processes, Mezim, Creon, Pancreatin are prescribed as preparations containing enzymes. If the patient is bothered by heaviness, heartburn or nausea with vomiting, it is recommended to take the drugs Cerucal, Motilium, Smecta.
If the acidity of the stomach is sharply reduced or rotting is observed, medications based on hydrochloric acid are prescribed. Sometimes acid is prescribed in its pure form: it must be taken in the form of drops before meals, several times a day. Folic acid is a must. It is recommended to take a course of B vitamins.
Diet and nutrition
The most important factor in the treatment of autoimmune gastritis is proper nutrition. As in the treatment of other forms of gastritis, doctors recommend strictly following a special diet. Without a diet, treatment with pills alone will not give results.
Products that irritate the mucous membrane are completely excluded from the daily diet. Removed from the menu: strong coffee, hot herbs, spices, chocolate products, buns, pastries, sausages, various canned goods. Fatty meat is prohibited; it is quite possible to replace the product with chicken, beef or rabbit.
What to do during an exacerbation
Autoimmune gastritis requires specific treatment. On the first day, it is advisable to completely abstain from food, especially if the patient has severe pain. It is acceptable to drink clean water, non-hot tea, and still mineral water.
Then, from the second day, it is allowed to gradually include porridge, jelly, mashed potatoes and soft-boiled eggs in the diet.
A strict diet is necessary only in the first days of an exacerbation. Then you will need to gradually soften and adjust. To make it easier for the stomach to cope with food, solid and liquid food should be separated. If, for example, porridge is eaten, it is recommended to drink tea after at least 1.5 hours. You should be careful about the combination of foods you eat. If the patient has dined on a protein meal, it is not recommended to immediately mix it with a carbohydrate meal. For example, if a person eats cottage cheese or meat, it is worth digesting what was eaten first, then taking on flour products.
As a rule, liquid food is digested and absorbed faster and leaves the stomach earlier. After the liquid, the process of breaking down solid protein foods occurs. Fats that remain in the stomach longer than others are digested last. Coarse fiber is difficult to digest, especially for a sick stomach during periods of exacerbation.
The basis of nutrition is the focus on reducing spasms, pain and inflammation of the mucous membrane. The food is chosen varied, replenishing the body's needs for nutrients and vitamins. It should be easily digestible for the stomach and not damage the walls thermally or mechanically.
In chronic autoimmune gastritis, characteristic secretory insufficiency is observed. Food is enriched with vitamins and stimulates secretion.
Dietary nutrition for exacerbation of gastritis
The temperature of the cooked food and the mechanical or chemical damage caused by food to the gastric mucosa become important. For example, very cold or too hot food will have an irritating effect on the walls of the stomach, which will negatively affect the treatment process as a whole. Recommended food should not be colder or hotter than human body temperature.
The method of preparing food, its grinding, and consistency have a mechanical effect on the gastric apparatus.
Traditional methods of treatment
They can be used in parallel with drug therapy. Juice obtained from potatoes or cabbage leaves is effective and safe. It is better to prepare the drink right before drinking. A single dose is 150 ml, which should be drunk on an empty stomach or before bed.
Aloe juice has a positive effect. It makes it possible to stop inflammatory processes and accelerates the process of regeneration of mucosal cells. To protect the stomach from aggressive influences, you need to mix the plant juice and egg white in equal proportions. You should drink it three times a day, a tablespoon before meals.
Prevention and prognosis in treatment
In most cases, the treatment prognosis is quite encouraging. Even with a complex form of type A gastritis, it will be possible to achieve noticeable success and long-term remission of the disease. To prevent autoimmune gastritis from recurring, a number of rules are followed. Follow a special diet, do not eat foods that can have a negative effect and provoke a new exacerbation, consult a gastroenterologist who can help you choose mineral water. It is recommended to periodically resort to resort and sanatorium treatment. Eat foods enriched with vitamin B.
Measures to prevent gastritis can be public or individual. Public ones are aimed at improving the quality of water or food in catering establishments. Individual ones are aimed at eliminating harmful foods from the diet, giving up bad habits, and rationally taking medications.
Autoimmune gastritis is considered a serious disease that is difficult to treat. It is forbidden to self-medicate, this will lead to the opposite results. Treatment of this form of gastritis is indicated under the supervision of professionals.