The danger of gastritis is high for every person who from time to time violates the principles of proper nutrition, experiences stress or drinks alcohol. Focal gastritis is a disorder that differs from other forms by affecting only one or several areas in the stomach. There are several types of this disease, and each of them requires the help of specialists.
Classification of forms of focal gastritis
The severity and type of course of the disease allows us to classify focal gastritis into different types:
- Chronic foveal . The disease enters a permanent stage and develops with poor quality or untimely treatment of acute gastritis. Since the inflammation is sluggish, the symptoms are usually blurred and do not cause such discomfort as in the acute stage.
- Catarrhal foveolar . The pathology is characterized by the first signs of focal hyperplasia - at this stage a tumor or polyps begins to form.
- Focal atrophic . Over time, the inflamed areas begin to atrophy, and the stomach glands lose function. Because of this, enzyme deficiency develops and digestion worsens.
- Non-atrophic foveal . With this disease, gland atrophy does not occur.
- Superficial gastritis . The initial form of the disease, accompanied by the first signs of inflammation. Most often, inflammation occurs in the epithelium at the junction of the stomach and intestines.
- Hypertrophic form . Benign formations and cysts form, and serious changes begin in the tissues, causing polyps and other disorders. The form affects different parts of the stomach, including the antrum.
- Subatrophic gastritis . Instead of benign formations, scars appear.
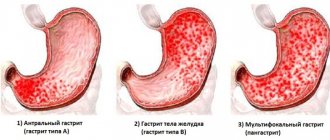
- Antral . A common form of focal gastritis in which the antrum is affected.
Any focal gastritis can be treated if the disease is detected in time and the development of foveal hyperplasia or a chronic form of pathology is prevented.
Classic manifestations of the disease
The clinical picture of focal gastritis depends on the severity of the inflammatory process, the number of pathological areas and the depth of the lesion. Mild stages of the disease are characterized by the appearance immediately after eating of discomfort and heaviness in the epigastrium, which is caused by the pressure of the food coma on the inflamed areas. Symptoms are often accompanied by bouts of nausea. If left untreated, the disease worsens and typical dyspeptic symptoms appear:
Reasons for the development of gastritis
The formation of focal gastritis is caused by many reasons, including activation of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. However, it is necessary to distinguish causes from provoking factors:
- a sharp decrease in immunity - occurs against the background of sluggish infectious and inflammatory processes, as well as due to other diseases;
- taking medications without the consent of a doctor - incorrect dosages and regimen of medications can lead to the development of the disease;
- gross violation of nutritional rules - a huge amount of store-bought products, fatty and spicy foods leads to illness. Overeating, late dinners, and improper nutrition can also trigger gastritis;
- drinking alcohol in large doses - alcohol irritates the mucous membrane and leads to its thinning over time;
- constant stress - nervous overstrain provokes various diseases, and focal gastritis cannot be considered an exception.
Other pathologies can lead to the formation of foveal focal gastritis: diabetes, metabolic disorders, heredity, endocrine disorders, weak immunity and autoimmune diseases. The age group should be highlighted separately - people over 60 years of age are especially susceptible to stomach diseases.
Provoking factors
The development of pathology is initiated by a combination of external and internal factors. A broader category is external factors that do not depend on heredity:
- infection of the stomach with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori; the bacterium is resistant to an acidic environment and can cause dangerous inflammatory processes in the form of atrophic and antral gastritis;
- problems with nutrition - overeating, lack of routine, abuse of fatty and smoked foods causes erosive, catarrhal, superficial gastritis;
- systematic intake of alcohol in large doses and over a long period of time has a detrimental effect on the stomach, provoking the formation of erosive defects on its walls; in persons with alcohol dependence, subatrophic and atrophic forms of inflammation are often diagnosed;
- long-term use of medications from the group of painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and antibiotics can negatively affect the condition of the stomach;
- Stress plays an important role in the occurrence of inflammatory diseases of the stomach.
Internal factors are associated with existing dysfunctions in the human body: hereditary predisposition, metabolic disorders, weakened immunity, autoimmune and endocrine diseases, infectious diseases, anemia. A certain role in the development of focal gastritis belongs to the age factor - people over 60–65 years of age are especially susceptible to inflammatory processes with tissue degeneration in the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms of focal gastritis
The disease has no specific signs, and the symptoms are similar to other forms. To distinguish them, it is important to consult a doctor for additional diagnostics. Here are the signs that worry a patient with focal gastritis:
- pain located on the left side under the ribs;
- fullness and heaviness in the stomach even with a small amount of food eaten;
- bowel irregularities, nausea, constant bloating or flatulence;
- loss of appetite;
- Unlike other gastrointestinal diseases, with gastritis intense pain always appears as soon as a person begins to feel hungry. After eating food, the symptom goes away;
- causeless weight loss;
- change in taste preferences;
- excessive saliva production;
- heartburn.
However, these signs may indicate the development of other diseases, which is why diagnostic procedures in identifying foveal gastritis are so important.
Signs
The main signs of focal gastritis are as follows:
- acute painful sensations in the stomach within half an hour after eating;
- constant feeling of heaviness;
- belching with a sour taste after eating;
- bowel problems (constipation or diarrhea);
- heartburn;
- bad breath;
- the presence of a sour-bitter taste in the mouth, regardless of food intake.
These symptoms are similar to other diseases of the digestive system, so an accurate diagnosis can be made after a full examination, which necessarily includes gastroscopy.
Diagnosis of the disease
To make an accurate diagnosis, the patient needs to undergo several instrumental examinations and pass all the tests prescribed by the doctor. For focal gastritis, it is most often recommended:
- general blood test - helps to find indirect signs of gastritis to prescribe further examinations;
- coprogram - studying the composition of stool helps to separate stomach diseases from diseases of the liver and pancreas;
- breath test - prescribed to determine Helicobacter pylori;
- ELISA analysis is an accurate method for determining bacteria in the body;
- FGDS is an endoscopic procedure with which the doctor visually assesses the condition of the stomach and mucous membrane.
In the process of FGDS, gastric tissue is often collected for subsequent histological analysis.
What it is
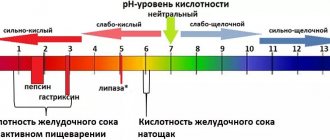
Antral gastritis is an inflammatory process occurring in the lower part of the stomach. The disease is caused by the active activity of Helicobacter pylori. The epithelium of the antrum is equipped with glands that secrete protective mucus that covers the walls of the stomach, the functions of which are disrupted when inflammation develops. Focal gastritis is characterized by point lesions of the mucous membranes. The disease is characterized by a chronic course.
With active life activity, Helicobacter pylori disrupts the production of bicarbonates, which alkalize food moving through the esophagus and stomach. Increased acidity contributes to the development of inflammation, causing severe pain and other symptoms characteristic of gastritis.
Treatment methods for focal gastritis
Treatment of focal disease requires an integrated approach. Without quality treatment and strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations, it is impossible to get rid of the disease. Therapy includes: taking medications, constantly following a diet, taking courses of physiotherapy if possible, increasing physical activity and using traditional recipes in remission.
Diet for focal gastritis
For therapy, a treatment table is prescribed, which imposes a complete ban on spicy foods, too salty dishes and pickled vegetables. Sweet pastries are prohibited, and citrus fruits and juices from them are in the acute stage. No one should eat strong tea and coffee, fatty meat, alcohol, or fried foods if they have gastritis.
Products that have a positive effect on health include: fermented milk drinks, cottage cheese, sour cream, boiled vegetables, lean protein and eggs, berries and non-acidic fruits, cereals, olive oil and up to 10 g per day of butter.
Important! You need to eat small portions up to 6 times a day, avoid long gaps between meals.
In case of exacerbation of focal gastritis, food is ground, fresh fruits and vegetables are excluded from the menu until the symptoms of the disease are smoothed out.
Drug treatment
Taking medications is necessary in the treatment of focal gastritis, but a doctor can prescribe them - independent use will lead to a deterioration in health. The following groups of funds are used:
- antispasmodics such as “No-Shpy”;
- means that improve motor skills - “Motilium”, “Cerucala”;
- agents that increase the production of gastric juice;
- Mezim type enzymes;
- means for reducing acidity - “Omezom”, “Ranitidine”;
- antibiotics to suppress the activity of Helicobacter pylori.
Probiotics are also prescribed, which protect the body from the effects of antibacterial substances. Be sure to use vitamins and complexes that increase immunity.
Traditional therapy methods
To treat focal gastritis, such effective remedies as sea buckthorn oil, decoction of flax and oat seeds, plantain, cabbage or potato juice are used. Your doctor will help you accurately determine the appropriate prescription.
Medicinal herbal preparations are highly effective, but you need to remember about their allergenicity. Such recipes can be used strictly under the supervision of a doctor.
Physiotherapy for the treatment of gastritis
Physiotherapeutic procedures are very effective in the fight against focal gastritis:
- Secretocorrective . They help restore the acidity of the stomach: magnetic therapy, the use of mineral waters internally and as baths.
- Vegetocorrecting . These procedures improve the condition of the body and the central nervous system. Aerotherapy is used.
- Anti-inflammatory . They use cryotherapy and UHF methods.
- Reparative - regenerative . These methods stimulate the healing of wounds on the mucous membrane. They use ultrasound, peloid therapy - mud applications on the back and abdomen.
- Antispasmodic . The most effective method is electrophoresis with drugs.
- Immunostimulating . This category includes SMV therapy (exposure to heat), laser therapy and magnetic therapy of the thymus.
Paraffin therapy and bathing with soothing infusions are also used. Physiotherapeutic treatment is highly effective, but requires long courses of implementation. The dosage and type of treatment are selected by the doctor.
How to diagnose the disease
Under no circumstances should you endure the discomfort brought by the disease! If the symptoms listed above are often observed, do not hesitate to visit a gastroenterologist. Superficial gastritis can occur unnoticed; it is recommended to examine the condition of the stomach at least once a year. The diagnosis is made based on the results of the examination and the results of examinations (scatological examinations of stool, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, fractional examination of gastric contents).
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs
The most widespread among diagnostic methods is fibrogastroscopy (abbreviated as FGS) - examination of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum using a flexible tube with a camera at the end (endoscope), inserted directly through the esophagus. Sometimes during the procedure, a small section of mucous membrane is removed for detailed analysis. The study can hardly be called a pleasant procedure, but FGS has high diagnostic accuracy.
Based on the results of the examination, the gastroenterologist will determine the stage of the disease. Highlight:
- Mild gastritis with a small number of cells affected by inflammation, inflammation is limited to the ventricular pits.
- Moderately severe gastritis, inflammation affects the middle section of the glands, following the superficial one, and the number of atrophied cells increases.
- The most severe form - severe gastritis is characterized by a large number of affected cells. The inflammatory process at this stage reaches the beginning of the muscle layer.
Complications and consequences of focal gastritis
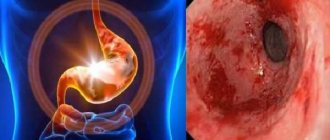
Prolonged course of the disease leads to the formation of ulcers and general deterioration of health. Inflammation of the intestines may develop, bleeding and other undesirable pathologies may occur. The worst consequence is cancer.
Gastric ulcer with focal acute chronic gastritis
Features of treatment of disorders after gastric resection
Taking into account that post-resection dumping syndrome often occurs in individuals with certain manifestations of neuro-vegetative dystonia, which largely determines the specific clinical symptoms of each attack (dumping attack), the importance of sedative
and
Tranquilizers.
Small doses
of Phenobarbital
(0.02-0.03 g 3 times a day),
Benzodiazepine derivatives, infusion of Valerian, Motherwort.
In cases where the dumping attack resembles a sympathetic-adrenal crisis, it is advisable to prescribe the GH blocker Pirroxan
(0.015 g 3 times a day before meals), as well as
Reserpine
(0.25 mg 2 times a day) and carefully
Octadine (Ismelin, Isobarin>
in an individually selected dose. The last two drugs have not only sympatholytic, but also antiserotonin action, and serotonin, released in excess by the mucous membrane of the small intestine and entering the blood, is given a certain importance in the pathogenesis of dumping syndrome.The course of treatment is 1.5-2 months.
The use of these drugs is contraindicated in patients with hypotension. According to T.N. Mordvinkina and V.A. Samoilova (1985), when taking Reserpine, dumping attacks were less severe and lasting. of Prodectin for therapeutic purposes.
(1 tablet 3 times a day), taking into account its antikinin effect.
Peritol
deserves attention in this regard (4 mg 3 times a day one hour before meals), as it has antiserotonin and antihistamine effects.
In order to slow down the evacuation of food chyme into the small intestine, you can resort to prescribing non-selective anticholinergics
(extract 100 g), vitamins. All dishes are prepared boiled, stewed or steamed.
Frequent, divided (6-8 times a day) meals often stop symptoms and even prevent the development of attacks, but it is not always practically feasible.
Hot and cold foods should be avoided as they are quickly evacuated; You should eat slowly, chewing your food thoroughly.
It is recommended to take liquid and solid foods separately (with an interval of 20-30 minutes) to reduce the possibility of the formation of hyperosmotic (hyperosmolar) solutions.
Patients with severe dumping attacks are advised to eat while lying down. Often, patients with dumping syndrome tolerate rough, mechanically poorly processed food better, especially 1-2 years after surgery. It is advisable to acidify foods; for this purpose, use a solution of citric acid (on the tip of a table knife in half a glass of water).
It must be taken into account that such patients are especially poorly tolerated
Many recommend that patients regularly keep a food diary.
Prevention of focal gastritis
With damage to the antrum, the development of atrophy or other processes, including hyperplasia, it becomes increasingly difficult to prevent relapses of gastritis. Therefore, prevention should be done in the initial stages and before the onset of the disease.
The main condition is adherence to the principles of proper nutrition and moderate physical activity. Strengthening the immune system in accessible ways will prevent the proliferation of Helicobacter pylori and increase the body's resistance to adverse factors. Of particular importance is giving up bad habits.
Focal gastritis, whether atrophy or partial damage to the antrum, requires complex treatment. But first you need to identify the cause of the disease, and for this the patient needs to visit a doctor and undergo the recommended diagnostics. Containing a disease at the initial stage is much easier than treating its consequences.
Types of pathology
Before treating inflammation, it is important to determine the nature of the lesion. In this regard, the following forms are distinguished:
- A focal process often occurs with increased acidity and is similar in course to superficial gastritis. Often diagnosed in women, especially with intolerance to certain foods. It is possible to relieve inflammation by consuming herbal infusions. At the same time, the erosive process requires the use of medications.
Focal gastritis occurs as a result of eating intolerant foods
- Moderate gastritis - symptoms of inflammation are mild. This form is often indicated by a cough that occurs when the esophagus is irritated. With the help of herbs, you can relieve unpleasant symptoms, but the atrophic process is not eliminated.
- Superficial gastritis with signs of atrophy - changes in tissue are minimal, but examination reveals signs of degeneration. Despite the mild course, proper treatment is required. An erosive process can develop as a complication.
- Antral gastritis occurs with damage to only the antrum. The appearance of scars is often provoked by erosive gastritis, which has not been fully treated. Pathology is indicated by belching, cough, heartburn, loss of appetite and body weight.
- Diffuse process - characterized by the appearance of individual areas of diffuse changes. At the same time, the pain increases, coughing and heartburn bother me. Herbal infusions only erase the clinic, but do not stop the process.
With atrophic gastritis, patients are bothered by heartburn
- Gastritis of the stump - occurs after gastrectomy. There are many reasons for the pathology. Inflammation of the stump can occur if asepsis is violated during surgery. Also a provoking factor is a violation of the diet by patients after the intervention. Gastritis can be mixed with atrophy and the formation of erosions.
Many people live after such operations by carefully following a diet. Ignoring the doctor’s recommendations can lead to inflammation of the stump, which occurs with a more pronounced clinical picture.
Preventive actions
To prevent the appearance of focal gastritis, a person will need to monitor his diet. It is better to exclude fried, salty, spicy foods from your diet. Add vegetables, fruits, and dairy products to the menu. In addition, the diet involves avoiding drinking coffee on an empty stomach, as well as smoking and alcohol-containing drinks. It is equally important to try to protect yourself from nervous tension and stress. Doctors recommend normalizing rest and sleep patterns so that the body does not become overtired.