Subatrophic gastritis is a rather serious disease characterized by severe inflammation of the gastric mucosa, death of the affected areas of the lining and the inability to produce hydrochloric acid. The main reason for the formation of the disease is the pathological effect on the body of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, but there are several other predisposing factors. These include genetic predisposition, autoimmune disorders, alcohol abuse, chronic stomach diseases and unnecessary use of medications.
- Etiology
- Varieties
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
Among the symptoms of subatrophic gastritis, there is disruption of the digestive system, which entails irregular bowel movements, vitamin deficiency, signs of dyspepsia, anemia, general weakness and severe fatigue of the body, as well as pallor of the skin and a significant decrease in body weight.
Diagnosis of this type of disease is similar to the methods for determining other types of gastritis. Includes laboratory tests, breathing tests and instrumental examinations of the patient. Treatment consists of taking medications, following a diet and using folk remedies.
Clinical picture
The peculiarity of subatrophic gastritis is that during examination, atrophied areas of the walls of the stomach or glands that produce hydrochloric acid and pepsin are detected.
When atrophy of individual parts occurs, the stomach cannot perform its functions normally; the damaged areas are replaced by epithelial and connective cells. The organ on the inside becomes inflamed and becomes thinner.
Most often, when a disease occurs, the level of acidity in the gastric juice produced decreases. With a more advanced degree of the disease, not only some part of the stomach, but also the entire organ can atrophy.
Thus, subatrophic gastritis is only the beginning of a disease that can be easily cured with proper timely therapy. The development of a chronic form should be prevented.
The most common causes of pathology:
- presence of the microorganism Helicobacter pylori;
- intoxication and chronic inflammatory processes;
- enterocolitis, pancreatitis and similar diseases;
- autoimmune processes in the stomach;
- medications used for a long time that damage the internal surface of the gastrointestinal tract;
- abuse of alcoholic beverages;
- genetic predisposition.
All these factors can trigger the onset of the disease, so people with these risk factors should be periodically observed by a gastroenterologist, and also be attentive to their health.
Essence of the disease
This pathology is characterized by a gradual process of atrophy of the internal tissues and glands of the stomach. In this case, there is a gradual death of cells that take part in the production of pepsin and hydrochloric acid. Areas of the gastrointestinal tract affected by the pathological process cease to produce gastric juice, and they are replaced by connective or epithelial tissue.
With this diagnosis, patients experience a decreased level of acidity. The atrophy process in this case can affect the entire stomach. If this disease is identified at an early stage of development, then it responds well to the therapeutic measures taken.
What symptoms occur and how is the disease diagnosed?
The disease has different degrees of severity. It comes in different intensities:
- Moderately expressed.
- Vividly manifested.
- Atrophic-hyperplastic.
With this disease, the attack falls on the parietal cells, and this reduces the secretory function of the stomach: the amount of pepsinogen, hydrochloric acid and gastromucoprotein produced decreases. These enzymes are needed for complete digestion of food.
The last of them affects the amount of vitamin B12 in the human body. If this vitamin is in short supply, anemia will begin to develop.
General symptoms of the onset of the disease:
- painful sensations in the abdomen, which intensify after a meal;
- frequent diarrhea with bloating, including after eating dairy products;
- the presence of a white coating on the surface of the tongue;
- lack of appetite and frequent belching with an unpleasant odor;
- feeling of heaviness, nausea and vomiting after eating;
- powerlessness, feeling of lethargy, constant drowsiness;
- anemia and dystrophy (weight loss);
- heavy sweating;
- pale skin, brittle hair and nails;
- vitamin deficiency and the consequences associated with it.
The signs of subatrophic gastritis are no different from those of other types of inflammation of the gastric mucosa, so only diagnostics will help determine the disease.
To clarify the disease, comprehensive examinations are carried out:
- gastric probing;
- measuring the level of acidity in the gastrointestinal tract using pH-metry;
- urease breath test to check for the presence of the microorganism Helicobacter pylori in the stomach;
- fluoroscopy of the digestive organ;
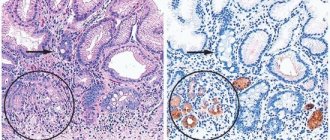
- pathological examination of a gastric tissue sample.
In this case, the examination is carried out by a gastroenterologist, but you should see a nutritionist for advice on proper nutrition.
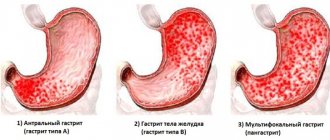
Kinds
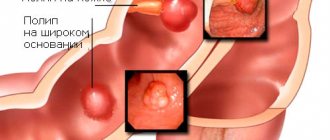
There are several types of disease:
- Surface. It can be called simple or catarrhal, since this is the initial stage of the disease. In this case, only the upper layer of the mucous membrane is affected by the disease.
- Antral. With this form of gastritis, doctors have to deal with increased acidity in the patient. The inflammatory focus is located in the antrum of the stomach, and not only it, but also the duodenum can be affected.
- Chronic. Gastritis is rare, but the most dangerous of all of these; its presence is considered a precancerous condition, since it can provoke the appearance of an oncological formation. The disease is associated with dysfunction of the immune system. It activates the formation of antibodies that destroy gland cells. The disease spreads to neighboring human organ systems as a result of intoxication. 10% of people with gastritis have this disease. In chronic subatrophic gastritis, in addition to the upper layer of the mucosa, tissues located in the deeper layers are also affected. Malfunctions occur in the entire digestive system. Without proper therapy, this disease leads to irreversible processes, and diffuse gastritis occurs.
Sometimes you can find mixed superficial and atrophic gastritis. Lack of therapy for this disease will lead to the onset of erosive gastritis, and then to an ulcer.
Reasons for the development of subatrophic gastritis
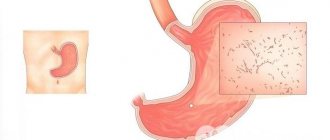
A common cause of this type of gastritis, like other types, is the Helicobacter bacterium. It multiplies and develops on the mucosal epithelium, causing inflammation in the affected areas, leading to the development of superficial gastritis. The main thing is to make a diagnosis in time to prevent further development of the disease.
The likely cause is genetic predisposition. In such cases, gastritis is rarely curable.
A number of possible causes of subatrophic gastritis:
- Poor diet, improper regimen. Eating large quantities of fatty, salty, fried foods. Long breaks between meals. Overeating or undereating.
- Consumption of large quantities of medications, antibiotics, which negatively affect human health.
- Frequent stress.
- Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages and cigarettes.
The causes of this form of gastritis do not differ from the causes of simple gastritis. However, subatrophic gastritis is more dangerous, the source of its occurrence is the border between the stomach and intestines, the place where food enters an alkaline environment. The disease is dangerous and can lead to obstruction of food into the intestines.
What is the treatment
How is the disease treated? This depends on the results of the patient's examination. Drug therapy is carried out during the period of exacerbation of gastritis, and during remission it is not prescribed.
Principles of effective treatment:
- Drug therapy.
- Proper nutrition and routine.
Food must be consumed in a crushed and warm state. The diet should primarily be based on the absence of rough food, which mechanically damages the gastric mucosa with sharp angles.
The disease requires complex therapy. It includes, in addition to medication and diet, physical therapy, proper sleep and rest, and physiotherapeutic procedures.
How is drug therapy carried out?
At the beginning of its development, the disease can be easily cured, regardless of what type of gastritis you encounter. Also, much in treatment depends on the cause that led to the development of the disease.
Treatment involves taking medications such as:
- Antibiotics. They prevent the development of the infectious and inflammatory process. Eradication treatment is prescribed to help a patient whose tests have shown the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. These are medications made from Amoxicillin and Clarithromycin.
- Substitutes. They are used for low acidity - insufficient levels of hydrochloric acid in the gastric juice. This is Pepsin, Pentagastrin.
- Antacid drugs. Doctors prescribe them in situations where acidity is high . These medications protect the walls of the stomach from the aggressive effects of hydrochloric acid, as they have an enveloping effect. Here are a few of them: Vikalin, Phosphalugel, Maalox.
- Anticholinergic drugs. Eliminates spasms of smooth muscles of the stomach and reduces the level of hydrochloric acid in case of increased acidity. These are Atropine, Platiphylline, Metacin.
- Multivitamin complex.
- Preparations containing iron.
- Immunomodulators.
Drug treatment is prescribed by a doctor after diagnosis. With subatrophic gastritis, the level of stomach acidity can be either lower than normal or elevated. The second is formed in the antral form of this type of gastritis.
Therapy should be aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease, normalizing the acidity of the stomach and the secretory activity of the glands.
Diagnostics
To establish a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to carry out instrumental and laboratory studies. But before prescribing them, the doctor needs to familiarize himself with the patient’s medical history and life history. This is required to search for possible causes of exacerbation of the chronic form of the disease. This is followed by a physical examination, which includes palpation and tapping of the anterior abdominal wall, as well as examination of the mouth.
Laboratory diagnostic techniques include:
- studying a blood test - necessary to identify changes in its composition, antibodies and gastrin levels;
- stool examination - performed to look for internal bleeding;
- conducting a series of breath tests for the presence of Helicobacter pylori bacteria in the body;
- Urine analysis will help identify concomitant diseases.
Instrumental diagnostic methods include:
- FEGDS with mandatory biopsy is a procedure for examining the condition of the mucous membrane and taking a small part of it for subsequent histological studies. It is carried out both for diffuse and antral lesions of the membrane;
- radiography with contrast – makes it possible to determine the size and activity of the stomach;
- Ultrasound and SCT of the abdominal organs;
- probing - to determine the acidity of gastric juice.
In addition, additional consultations with specialists such as a therapist and nutritionist are necessary.
Help from traditional medicine
Folk remedies can also alleviate gastritis; they are considered safe and effective methods of treating this disease.
- Rosehip decoction has a natural antibacterial effect on the body and does not cause it as much harm as chemical drugs. It disinfects the walls of the stomach and helps eliminate toxins.
- Chamomile also has a beneficial effect. Its decoction promotes a calming effect, has anti-inflammatory and relaxing properties and leads to an improvement in a person’s overall well-being.
- Other plants, as well as some vegetables, also have a pronounced positive effect in the treatment of gastritis. Herbs: calamus rhizome, sage, dandelion, peppermint, St. John's wort, calendula, plantain. Helping vegetables include white cabbage and potatoes. Their juice has medicinal properties.
It should be remembered that herbal decoctions can in some cases cause allergic reactions, so they should be taken with caution.
The role of proper nutrition and diets in the treatment of illness
For gastritis, diet and proper nutrition are very important components of treatment, without which it will be ineffective.
Proper nutrition in this case implies a gentle regime for the digestive organs and activates the secretion of glands. Products considered beneficial for gastritis:
- low-fat soups;
- eggs;
- stewed and pureed vegetables;
- lean boiled meat;
- porridge;
- fruit puree;
Unhealthy foods include fried and fatty foods (dairy products, fatty meats and fish), as well as pickled foods, raw vegetables and fruits, canned food, legumes, coffee, and sweets. Spicy and salty foods are also extremely undesirable. All these foods and dishes irritate the walls of the stomach, so you should avoid them.
Alcoholic drinks and smoking should be prohibited for people with gastritis.
During an exacerbation, it is necessary to follow a diet consisting of cereals, low-fat broths and soups. Food should be of uniform consistency. On the day when the patient suffered an attack, it is better to completely refuse food. This will reduce pain and relieve the gastrointestinal tract.
The period of following the diet after an exacerbation of the disease will last about half a month. At the end of this period, it is necessary to gradually include new foods in food.
Even after some time, it is advisable to eat dishes made from soft ingredients so that they contain vitamins (especially C, E and B), animal proteins, and microelements. This diet will promote remission.
What to do for prevention
The disease occurs in the presence of certain factors, and it will not be possible to have firm confidence that it will bypass you. Therefore, you should take a different route: you need to be attentive to your health, do tests from time to time, and go to an appointment with a gastroenterologist.
And also eat properly and in a timely manner, do not abuse alcohol and smoking, and avoid stressful situations.
Don't give subatrophic gastritis a chance to affect the walls of your stomach. If the disease does occur, start treatment without delay, get checked periodically and adhere to a healthy lifestyle.
Physiotherapy
When subatrophic gastritis is diagnosed, it is also treated with physiotherapy. It is used to reduce pain, improve stomach function, and stimulate cell regeneration. The procedures are contraindicated during exacerbations of the disease, in the presence of various neoplasms. During remission, paraffin compresses are made on the stomach. Magnetic field therapy , electrophoresis , and UHF are performed .
Homeopathy
Homeopathic medicines are also prescribed for treatment. The most effective products are those containing:
- antimony trisulphide;
- chilibukha;
- Activated carbon;
- meadow lumbago;
- arsenic anhydrite;
- metallic silver.
The release form of the drugs is in tablets. Plantaglucid , sea buckthorn oil, propolis and wormwood tinctures are also used for treatment