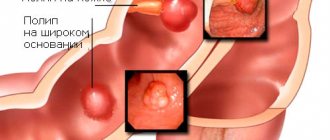
Lymphocytic gastritis is one of the forms of this disease. Very rare. Elderly people are at risk; it rarely occurs in young children. It is worth noting that women often experience this type of gastritis than men.
Diagnostics: main methods
Life expectancy and prognosis for gastritis in cats depends on how early the disease was identified, the correct medications and other therapeutic measures were selected. It is strictly forbidden to give any medications to your pet until an accurate diagnosis has been established. If you have unpleasant symptoms of stomach inflammation, contact your veterinarian. The specialist will collect anamnesis and conduct a visual examination of the pet. To clarify the full clinical picture and prescribe treatment, a number of diagnostic procedures are required:
- ultrasound diagnostics of the gastrointestinal tract;
- laboratory testing of blood and urine;
- stool analysis;
- endoscopic examination;
- X-rays with contrast agent;
- biopsy.
Return to contents
Causes of stomach lymphoma
The precursor of this neoplasm is lymphoid tissue located in the mucous membrane in the form of individual lymphocytes and clusters of cells. Under certain conditions (for example, with chronic gastritis caused by Helicobacter pylori infection), such accumulations form lymphoid follicles, in which areas of atypia may appear. Taking into account the fact that in 95% of patients with gastric lymphoma, various strains of Helicobacter pylori are detected during examination, this infection is considered as one of the main causes of this pathology.
Along with Helicobacter pylori, the development of various types of gastric lymphomas can be provoked by other factors, including contact with carcinogenic substances, prolonged stay in areas with increased levels of radiation, previous radiation therapy, taking certain medications, excess ultraviolet radiation, nonspecific decrease in immunity, immune disorders in AIDS, autoimmune diseases and artificial suppression of immunity after organ transplantation operations.
Necessary treatment
Effective drugs
If gastritis in an animal is associated with chronic renal failure, a deviation from the liver, then it is necessary to treat the underlying disease. After a comprehensive diagnosis, veterinarians prescribe gastroprotectors for cats and other tablets indicated in the table:
Pain relief medications
| "Spazmolgon" | |
| "Baralgin" | |
| "Belladonna" | |
| Medicines to stop vomiting | "Metoclopramide" |
| "Anzemet" | |
| "Zofran" | |
| "Prochlorperazine" | |
| "Atipamezole" | |
| Medicines for high acidity | "Gastal" |
| "Ranitidine" | |
| "Omeprazole" | |
| Pharmaceuticals with an enveloping effect | "Almagel" |
| "Phosphalugel" | |
| Digestive Enzymes | "Pepsin" |
| "Trypsin" | |
| "Mezim forte" | |
| "Pancreatin" | |
| Antibiotics | "Sinulox" |
| "Ampicillin" | |
| "Kefzol" | |
| "Biseptol" | |
| "Cefamezin" |
Treatment of gastritis in a cat can be carried out at home, after consulting with a veterinarian. Flax seeds, blueberries, and oak bark have a positive effect on the process of restoration of the gastric mucosa.
How important is diet?
All veterinarians agree that if gastritis worsens, it is better not to feed your pet for the first 2 days, so as not to cause negative symptoms and complications. A pet can only be given something to drink if it so desires. After 2-3 days, you can feed him light food, and the portion should be 3 times less than usual. The amount of food is increased gradually, taking into account the pet's condition. It is important that the dishes are at room temperature. This is necessary so as not to provoke additional damage to the mucous membrane. Cat food for gastritis is prepared separately without adding salt and spices. Fatty meats, spicy, fatty and smoked foods are prohibited.
Lymphoma of the stomach
Gastric lymphoma is a malignant non-leukemic neoplasm that originates from lymphoid cells in the wall of the organ. It usually has a relatively benign course, slow growth and rare metastasis, but the degree of malignancy of the tumor may vary. Most often located in the distal part of the stomach. Not associated with damage to peripheral lymph nodes and bone marrow. Gastric lymphomas account for 1 to 5% of the total number of neoplasias of this organ. Typically develops over the age of 50. Men are affected more often than women. In the initial stages, the prognosis is favorable. The average five-year survival rate for gastric lymphomas of all stages ranges from 34 to 50%. Treatment is carried out by specialists in the field of oncology, gastroenterology and abdominal surgery.
Prevention measures
To avoid having to give Ranitidine for cats and other drugs against gastritis, you need to carefully monitor your pet’s diet. The temperature regime of the food consumed is no less important. It is worth regularly carrying out deworming procedures and performing other vaccines. It is recommended to comb the fur so that it does not get into the cat’s stomach and cause gastritis.
Avanesova Marina Shamirovna - veterinarian, surgeon, endoscopist, Department of Anatomy and Histology of Animals named after. Professor A.F. Klimova.
Currently, lymphocytic-plasmacytic enterocolitis occurs quite often. One of the most common signs of this pathology is chronic diarrhea, vomiting and resulting weight loss in dogs. Middle-aged and older animals are most often affected. Gender doesn't matter.
LPE is the most common form of IBD (inflammatory bowel disease). In turn, IBD may have other forms of cellular infiltrates, such as eosinophilic gastroenteritis, granulomatous enteritis, and chronic histiocytic ulcerative colitis.
LPE is a chronic, idiopathic, inflammatory bowel disease characterized by diffuse infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells into the gastrointestinal mucosa, resulting in diffuse inflammatory reactions of the intestinal mucosa. An increased number of lymphocytes and plasma cells causes a reaction in the lymphoid tissue, which causes a disruption in the conductivity of the intestinal wall.
The etiology of the occurrence and pathogenesis of this disease remains completely unknown, but it is believed that there are several factors that cause damage to the intestinal mucosa: the reaction of the immune system, the abnormal immune response of the mucous membrane to various environmental antigens (bacterial, food) lead to allergic reactions, with in which the body's immune system attacks its own cells and organs.
Prolonged exposure to an antigen causes prolonged inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, as a result of which proteolytic and lysosomal enzymes are released, cytokines are produced, secondary immune complexes are activated, and a large number of oxygen radicals are formed. Delayed gastric emptying can also lead secondary to inflammation of the gastrointestinal mucosa. Genetic factors may also influence the development of LPE. Bassenji, Shar Pei, Wheaten Terrier, and German Shepherd have a hereditary predisposition to this disease. The most severe hereditary form of LPE has been described in the Basenji.
LPE most often affects the small intestine, but the large intestine may also be affected. In some cases of damage to the large intestine, bile acids may be to blame. Bile acid malabsorption plays a role in the diagnosis of LPE. Bile acid malabsorption is the inability of the intestine to completely absorb bile acids. Bile carries toxins and waste products out of the body and helps the body metabolize fats. Bile acids that reach the colon can lead to diarrhea.
In addition, diseases related to IBD pathologies can cause thromboembolic lesions, polyarthritis, kidney stones, dermatological diseases and immune-mediated anemia.
The differential diagnosis includes other causes of inflammatory bowel disease: infectious diseases, infiltrating inflammatory diseases (eg, eosinophilic, granulomatous enteritis), tumors (lymphoma, leiomyomas, leiomyosarcoma), as well as other diseases such as lymphangiectasia, gastrointestinal motility disorders and exocrine pancreatic insufficiency.
Diagnosis of LPE : By hematologic examination, initial diagnostic findings may include neutrophilic leukocytosis with a left shift, microcytic anemia, hypoproteinemia, hypoalbuminemia, hyperglobulinemia, lymphopenia, hypocalcemia, and hypercholesterolemia. Bile acid values should be assessed to rule out possible hepatic causes of gastrointestinal disease.
Additional diagnostic tests that should be performed to rule out these diseases may include urinalysis to rule out a renal cause for protein loss, stool analysis (Giardia sp., Salmonella sp., Campylobacter sp., Clostridium sp.), folic acid testing, and cobalamin (bacterial overgrowth), TLI - test for trypsin-like immunoreactivity (exocrine pancreatic insufficiency).
Severe forms of IBD and LPE can lead to peritoneal effusions; their classification will require laparocentesis or laparoscopy to collect material for cytological examination, as well as x-rays and ultrasound diagnostics.
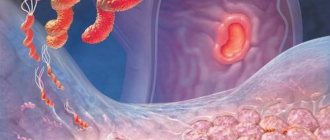
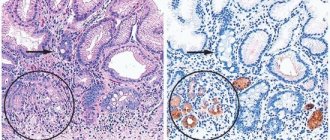
Endoscopic diagnosis plays an important role in the diagnosis and treatment of this disease. Using endoscopy of the upper and lower gastrointestinal tract, it is possible to visualize the condition of the mucous membrane, villi of the duodenum (color, swelling, vascularization, lesions of the mucous membrane in the form of erosions or ulcers, straightening of folds, infiltrates, etc. (Fig. 1). For pathological changes, an increase in looseness and granularity of the mucous membrane is visualized (Fig. 2), a decrease in the vascularization of the submucosal layer, and in some cases the appearance of erosions.
Rice. 1 Damage to the duodenal mucosa in LPE
An unbalanced diet or sudden changes in diet can cause digestive disorders in your pet. Such failures are fraught with the appearance of such an unpleasant pathology as gastritis. In cats, the symptoms and treatment of the disease are similar to those in humans, but there are a number of differences in the rules of treatment and preventive methods. Let's talk about them.
Causes of lymphocyte infiltration
The function of intraepithelial lymphocytes is to collect and transmit information about the properties of food entering the stomach to cells of the immune system, which have a cytotoxic effect against bacteria supplied with food. For what reason lymphocytes mistakenly recognize the organ’s own cells as dangerous and attack them, disrupting and destroying the structure of tissues is unknown.
These processes are classified into the group of autoimmune (distorted immunity) diseases. There are hypotheses according to which the factors causing lymphocytic gastritis are:
- the bacterium Helicobacter, capable of attaching to the gastric epithelium, creating its own colonies, damaging and creating chronic inflammation and causing an active reaction of lymphocytes to them;
- disruption of metabolic processes in the body, delay in the elimination of waste and toxins;
- hormonal imbalances leading to pathological manifestations;
- complications of infectious and viral pathologies.
People who are susceptible to one of the above reasons: often suffer from colds, take medications on their own without a doctor’s prescription, thereby injuring the gastric mucosa, breaking its protective barriers, suffer from gastritis, do not relieve them with medication, and neglect the rules of a healthy diet. So, they are at risk.
Gastritis in a cat: etiology and pathogenesis
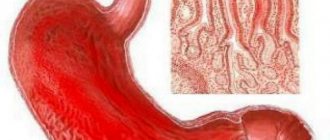
The term “gastritis” means acute inflammation in the mucous membrane and gastric walls. The pathology is characterized by disruptions in the motor-secretory activity of the organ.
All animals are susceptible to stomach diseases, regardless of age and breed characteristics. If not treated in a timely manner, the disease can develop into more serious disorders of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract - oncology, erosive and ulcerative formations.
When the disease occurs, the mucous membrane and walls of the stomach are deformed
Mechanism of disease development
To find the correct approach to treating the disease, you need to understand the features of its development.
The mechanism of pathology formation
Causes of the disease
The appearance of pathology is facilitated by many factors, the first place among which is unbalanced nutrition.
Constant stress is considered a factor provoking the disease
Table 1. Possible causes
| Provoking factor | Description |
| Diet mistakes |
|
| Stressful situations | Emotional stress negatively affects the transmission of nerve impulses to the brain. This contributes to disruptions in the formation of enzymes and gastric juice |
| Use of medications | Depending on the characteristics of the pet’s body, medications can irritate the mucous membrane and provoke the development of gastritis. Taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is especially dangerous |
| Hairballs | Wool that enters the body during washing irritates the membranes of the organ and contributes to the formation of the inflammatory process. |
| Diseases | KSD and renal failure are fraught with disturbances in protein metabolism, which causes inflammation of the mucous membrane. Liver pathologies, bad teeth, and gum disease often lead to secondary gastritis. Vitamin deficiency and lack of useful mineral elements negatively affect the production of hydrochloric acid |
| Poisoning | Household chemicals or expired products, when entering the body, provoke inflammatory processes, which can lead to gastritis. |
| Bacterial infections | Bacteria of the Helicobacter family lead to the development of disease not only in humans, but also in cats |
| Worm infestations | Parasites produce toxins that irritate the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract |
Symptoms of helminthic infestation in cats
Read more about deworming cats in a special article on our portal.
The multi-stage organization of the digestive process causes a variety of causes that contribute to the occurrence of inflammation.
The activity of Helicobacter pylori leads to gastritis
Types of gastritis
The disease is systematized according to many signs. One of the main classifications is based on the nature of the inflammatory process. Based on the characteristics of the pathology, gastritis is divided into the following types:
- Exudative. This type includes fibrinous, catarrhal, serous and purulent.
- Alternative. This type includes erosive-ulcerative and necrotic.
In addition, diffuse gastritis is observed, and if one or several areas are damaged, focal gastritis is observed.
According to the nature of the secretion of gastric juice, they are distinguished:
- hypoacid (with low acidity);
- hyperacid (with increased);
- normacid (indicators within normal limits).
The origin of the disease can be primary or secondary.
The clinical picture of the disease is determined by acidity levels and the degree of damage to the mucous membrane
In addition to the listed classifications, there is a more detailed division into forms of gastritis.
Table 2. Forms of gastritis
| View | Characteristic |
| Uremic | Characteristic for pets suffering from kidney failure. If the organ does not function properly, urea is not excreted from the body and accumulates in the stomach. The toxic product concentrates in the gastric juice, provokes swelling of the mucous membrane and the inflammatory process |
| Eosinophilic | Manifestations of allergies or the presence of helminths increase the content of eosinophils in the mucosa. Cells produce substances that cause disturbances in gastric tissue |
| Endogenous | Occurs as a result of insufficient production of pepsin, gastric juice and iron deficiency. The lack of these elements leads to the formation of inflammatory processes |
| Hypoxemic | Poor supply of gastric tissue with oxygen leads to inflammation of its walls. This type of disease occurs with prolonged hypoxia and pathologies of the cardiovascular system. |
The acute form is characterized by frequent vomiting
According to the degree of manifestation, the disease is divided into the following types:
- Spicy. It is developing rapidly. The symptoms are clearly visible. Occurs after eating too hot or cold food and stale foods.
- Chronic. Formed as a result of prolonged exposure to irritating factors on the mucous membrane. Symptoms are mild. The phases of the disease alternate, smoothly flowing from attenuation to exacerbation of inflammation.
In both acute and chronic types, both the gastric mucosa and the tissues attached to it undergo pathological changes. This is fraught with neuro-reflex disruptions in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
What happens with lymphocytic gastritis
A rare form of chronic gastric disease is characterized by a non-standard development pattern. Inflammation in the lymphoid type of pathology is not the result of a destructive process in the lining of the stomach due to irritation, but a response to the opposition of lymphocytes.
Local immunity in the stomach is responsible for lymphoid tissue, consisting of special cells, among which there are lymphocytes of varying degrees of maturity, as well as clusters of follicles.
After the penetration of leukocytes (infiltration) and a further increase in their number in the cells of the gastric epithelium, autoimmune reactions develop, which gives the right to speak of lymphoid gastritis as a separate stage of lymphocytic.
By protecting a segment of the damaged area of the stomach, lymphocytes attack inflammation, saving the body. Under the influence of provoking factors, lymphocytic follicles grow, this leads to uneven thickening of the gastric folds.
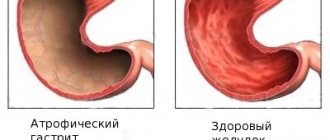
Due to impaired production of gastric juice, foci of atrophy are formed, which results in the development of benign lymphoma.
Symptoms of the disease
The variety of existing types and forms of pathology complicate its early diagnosis. Considering this fact, owners of furry pets should become familiar with both the symptoms that appear in the initial stages of the pathology and those characteristic of certain types of disease.
One of the main symptoms of gastritis is loss of appetite.
- Decreased appetite. The cat may completely ignore the food or experience discomfort after eating it.
- Emotional decline. The animal loses interest in games and spends most of its time lying down.
- Stool disorders. Undigested food remains are found in feces.
- Nausea and vomiting. The structure of the vomit is foamy, interspersed with bile.
- Mucous membranes of the oral cavity. The tongue becomes covered with a white coating. A repulsive odor appears from the mouth.
- Peritoneum. The stomach gets hard. When palpated, painful sensations and rumbling occur.
- Condition of the coat. The hair becomes dull. The animal looks unkempt.
- Body mass. The pet quickly loses weight and looks lethargic.
Symptoms
There are no characteristic complaints with lymphocytic gastritis, but even its latent course is endowed with certain symptoms. Since immune cells are involved in the process of inflammation, there may be a reaction from the lymph nodes and a slight increase in body temperature. Digestive disorders occur individually in each case; general complaints may look like:
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- frequent low-grade fever;
- lack of appetite;
- feeling of heaviness in the epigastric region;
- distortion of taste sensations;
- belching , heartburn , bloating after eating;
- various types of pain in the hypochondrium, in the stomach area;
- hunger pains after sleep.
If you experience any discomfort before or after eating, you should consult a gastroenterologist. Taking measures on your own does not bring any cure for lymphocytic pathology. Treatment, without determining the form of gastritis, can lead to the development of tumors and the degeneration of one’s own cells into malignant ones.
Diagnosis of pathology
Digestive system disorders are not always a manifestation of gastritis. Diarrhea can be a consequence of food poisoning, for example. To make a correct diagnosis, the veterinarian does a series of examinations.
For diagnosis, the following activities will be required:
- comprehensive inspection;
- taking anamnesis;
- examination of urine, blood and feces;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- detection of gastric acidity.
If the pathology is in an advanced stage, endoscopy and tissue biopsy of the stomach walls are performed.
Ultrasound is one of the informative methods for diagnosing the disease
Risk factors
Risk factors are the causes of inflammation of the stomach of any form:
- Irregular intake of dry food with long breaks;
- frequent meals with fatty, vinegary, fried foods, using spices and seasonings;
- regular consumption of fizzy drinks containing dyes and preservatives;
- poisoning with chemical or medicinal reagents;
- abuse, frequent irritation of the gastric mucosa with alcohol and nicotine.
If the lining of the stomach is healthy, without erosions, ulcerations, proportional production of gastric juice and dynamic gastric motility are observed, and there are no failures in the diet, then the chance of developing any gastritis is minimized.
Treatment of pathology
Self-treatment without appropriate doctor's instructions can negatively affect your pet's health. Medicines used for humans are not always suitable for use in animals. Therefore, the use of any drugs is possible only as prescribed by a specialist.
Treatment of the disease is possible only under the guidance of a veterinarian
Drug therapy
Since the pathology is characterized by discomfort in the abdominal area, actions should be focused on relieving pain. In parallel with this, it is necessary to launch the mechanism for restoring the mucous membrane.
- To eliminate pain, “Baralgin” and “Spazgan” are used. Belladonna-based products have a softening effect.
- A decoction of flax seeds, Almagel and Phosphalugel protects the mucous membrane.
- Vomiting is stopped with the help of Metoclopramide, Atipamezole, Anzemet, Prochlorperazine and Zofran.
- Astringents are actively used. This function works well with products containing tannin, blueberries, bismuth and oak bark.
- If the acidity is high, Ranitidine and Omeprazole are prescribed; if the acidity is low, an artificial analogue is prescribed.
- In case of insufficient production of digestive enzymes, Pepsin, Pancreatin and Trypsin are prescribed.
- In case of dehydration, infusion therapy is carried out. For this purpose, Ringer's solution or saline is administered. Regidron is welcome.
- If gastritis of bacterial origin has been diagnosed, antibacterial therapy is prescribed - Ampicillin, Cefamezin, Sinulox, Kefzol, Sulfadimethoxine and Biseptol.
- To support the immune system, vitamin therapy is carried out, based on the consumption of vitamins B6 and B12.
"Baralgin" is often used to relieve pain
To activate protective resources, immunomodulators are used. They increase resistance to negative effects and accelerate the restoration of damaged tissues.
Medical nutrition
To quickly cure the pathology, in addition to drug therapy, you should transfer your pet to a therapeutic diet.
- Feeding regimen 5 times a day in small portions.
- The diet is based on porridges and soups cooked in water.
- Cottage cheese and yogurt are introduced into the diet gradually, monitoring the cat’s condition
- It is advisable to feed boiled chicken and veal, cut into small pieces.
- The amount of fish consumption is reduced.
- If acidity is high, focus on rice and oatmeal porridge, potatoes and carrot juice.
- For low acidity, meat soups, low-fat cottage cheese and beet juice are recommended.
- The transition to industrial medicinal feed is encouraged.
If your pet's diet was based on ready-made food, preference should be given to the option developed for the treatment of eating disorders in animals.
Fresh milk should be excluded from the diet plan
- milk;
- canned food;
- sweets;
- baking;
- smoked meats;
- lamb, duck and pork.
Feeding food from the table is not recommended.
It is not advisable to feed canned cat food during the treatment period.
Type of disease
The representative of the local immunity of the stomach is lymphoid tissue. It consists of a number of cells (fibroblasts, reticular, plasma cells, lymphocytes of varying maturity, and others) and is represented by single or group follicles (limited clusters).
Lymphoid gastritis does not occur like all inflammations, due to a specific reason for irritation and destruction of the stomach lining, but in response to the natural fight carried out by lymphocytes. What is lymphoid gastritis? We can say that this is a certain stage of lymphocytic. After infiltration of leukocytes, their number further increases, and autoimmune reactions develop.
It is also called lymphofollicular gastritis; it always occurs against the background of chronic inflammation, concentration of lymphocytes, in the segment of the damaged area of the stomach. Initially, it provides the process of saving the body, then the lymphocytic follicles grow, unevenly thicken the physiological gastric folds, disrupt the production of juice and can create areas of atrophy, leading to benign lymphoma.