In recent years, representatives of the fairer sex have increasingly had to deal with various pathologies. The reason for this may be promiscuous sex life, failure to give birth at a certain age, hormonal imbalances, poor lifestyle, and so on. Many diseases have to be treated surgically. Of course, every woman is afraid of getting on the surgeon’s table. Especially when it comes to the future of her reproductive function. This article will discuss a procedure called hysteroresectoscopy. What this is will be described below. It is also worth saying about the conditions and methods of carrying out such an operation.
Minimally invasive methods of treating gynecological diseases
In recent decades, minimally invasive surgical interventions have gained great popularity. These include hysteroresectoscopy. The operation allows you to reduce the time of treatment in the hospital and recover faster after all procedures. Minimally invasive treatment uses microscopic instruments. Most often, the surgeon controls them autonomously. In this case, control is carried out using special optical instruments.
Minimally invasive treatment is not always used. Before doing this, the doctor must carefully assess all the risks. Sometimes it is impossible to carry out such manipulation. In this case, a conventional laparotomy is prescribed.
https://youtu.be/S9pGE0YShAE
Preparation for hysteroresectoscopy
The preparatory process begins with a complete clinical examination of the female body and a series of laboratory tests of biological fluids. In the latter case, we are talking about general blood and urine tests, a smear for vaginal flora, tests for hepatitis, HIV and syphilis. It is also necessary to take a biochemical blood test. Other diagnostic methods are:
- fluorographic examination;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- ECG.
Hysteroresectoscopy involves careful preoperative preparation: it is necessary to clean the intestinal cavity; for this, doctors perform a cleansing enema. Afterwards you should not eat anything, given the upcoming anesthesia. Before surgery, you need to completely empty your bladder, wash yourself thoroughly, and be sure to shave the hair in the perineum and pubic area. The hysteroresectoscopy procedure should be performed on days 5-7 of the cycle, when the patient’s critical days end.
- Homemade soaked apples. Recipes for soaking apples in jars and barrels for the winter with photos
- How to treat fingernail fungus
- How to boost your child's immunity
Pros of the procedure
The minimally invasive treatment method avoids many complications. Thus, during abdominal surgery, the patient always experiences an adhesive process in the pelvic area. Some women experience pronounced symptoms of this pathology, while others more easily tolerate the presence of adhesions.
Using tools in a self-contained manner avoids major injuries. Women no longer have to worry about leaving unsightly and large scars on their bodies. The use of this technology leaves only small and invisible scars.
The main advantage of the minimally invasive treatment method is that the woman must remain in the hospital for a minimum amount of time. After some interventions, the patient can go home within a few hours. However, the time required for the procedure itself may increase slightly. This is due to the fact that the doctor does not have direct access to the diseased area and works “blindly”.
Disadvantages of the procedure (possible complications)
The minimally invasive method of treating gynecological diseases also has a number of disadvantages. However, they are minor compared to the benefits described. Among these are:
- risk of damage to neighboring organs when inserting instruments and optics;
- bleeding that leads to the need for laparotomy;
- the ability to remove pathology not completely;
- the addition of infections and so on.
It must be remembered that abdominal surgery can lead to the same consequences. That is why, when choosing a particular treatment method, it is worth considering all the risks and benefits.
Flaws
To understand what it is, what capabilities hysteroresectoscopy has, and in what cases it is recommended for patients, you should better understand the consequences and possible complications after its use.
The postoperative period may be characterized by the following deviations from the norm:
- the development of infections in the uterine cavity (can be caused by instruments);
- injury to organs located near the uterus;
- unsuccessful elimination of polypous formations;
- bleeding, to eliminate which abdominal surgery is used.
According to experts, almost all deviations are not associated with a violation of the technique, but are a consequence of forced intervention in the body and its vital processes. Even despite possible adverse consequences, hysteroresectoscopy is considered the safest and most harmless method for removing polyps and has many significant advantages. However, each specific case has its own nuances and, therefore, the need to perform the procedure is determined only by a specialist. He is responsible for the qualified and successful course of the operation and postoperative period.
Hysteroresectoscopy: what is it?
This manipulation is one of the minimally invasive procedures. It is performed within the walls of a hospital. However, in some cases, a woman can go home within a few hours.
In most cases, preliminary anesthesia of the body is necessary during a procedure called hysteroresectoscopy. What it is? Anesthesia is the use of anesthesia. It can be local, general or epidural. It all depends on the complexity of the pathology, the wishes of the patient and the capabilities of the clinic.
Hysteroresectoscopy today makes it possible to treat many diseases that just a few decades ago required the complete removal of the reproductive organ or dissection of its walls. This manipulation is increasingly used by modern clinics and young specialists. Perhaps, in a few years, hysteroresectoscopy of the uterus will become one of the most common manipulations and will be a priority over laparotomy and laparoscopy.
Contraindications to hysteroresectoscopy
Operative hysteroscopy has a number of contraindications:
- fibroids with a diameter of more than 10 cm;
- presence of scars, endometriosis;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- desired intrauterine pregnancy;
- lactation period;
- inflammation of the genital organs;
- severe heart and vascular diseases;
- pulmonary, liver and kidney failure;
- the presence of acute or chronic diseases during the period of exacerbation;
- blood clotting pathologies;
- malignant tumors of the uterus;
- stenosis of the cervical canal.
Before the upcoming operation, a number of studies are performed. This will allow you to assess the scope of the intervention and identify possible contraindications to the procedure.
Indications for manipulation
So, you have become acquainted with the concept of hysteroresectoscopy (what it is). Now it’s worth finding out who is being assigned this manipulation. The main indications for intervention are the following conditions:
- fusion of the walls of the reproductive organ caused by genetic abnormalities or inflammatory diseases;
- the formation of adhesions inside the uterus for various reasons;
- fibroid treatment;
- neoplasms that appear on the walls of the uterus (papillomas, cysts, tumors);
- some pathologies of the cervical canal and so on.
Before the manipulation, the doctor always assesses the risks. In some cases, preference is still given to laparoscopy or laparotomy.
Indications
Prescribed if the following pathologies are suspected:
- inflammation of the endometrium in the uterine cavity;
- various types of adhesions and adhesions in the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes;
- remnants of the fertilized egg or membranes after termination of pregnancy;
- oncological neoplasms;
- violation of the integrity of the walls of the uterus after cleansing or abortion;
- intrauterine pathology of fetal development;
- pathologies of the menstrual cycle;
- abnormal development of the uterus;
- the occurrence of vaginal bleeding after menopause;
- infertility;
- monitoring the condition of the uterine cavity after termination of pregnancy or hormonal therapy.
Indications during surgery:
- benign tumors in the uterus;
- adhesions and synechiae in the uterus;
- polyps:
- excessive growth of the endometrium;
- removal of the intrauterine device.
It is carried out exclusively according to the doctor’s indications after a comprehensive examination of the genital organs and tests.
Contraindications for manipulation
Not all patients can undergo hysteroresectoscopy of the uterus. Contraindications for the operation include the following situations:
- infectious diseases of the pelvic organs, in particular the reproductive organ;
- bleeding of unknown etiology;
- severe pain in the abdominal cavity associated with pathology;
- some heart, liver and kidney diseases;
- pregnancy;
- colds and so on.
All of the above contraindications can be divided into absolute and conditional. Some of them categorically prohibit the use of this method of treatment. Others allow the use of a resectoscope after some correction.
Indications for use
Before operating on a patient, a set of measures, tests and examinations is provided that the doctor will need to familiarize himself with the clinical picture and condition of the patient in each specific case.
Polyps can cause severe pain and heavy bleeding in women. In cases where, when they are detected, the pain increases significantly, then there is a possibility that the patient has an additional and serious gynecological pathology. The operation is carried out only after a serious examination. It will be necessary to use all possible research methods and identify the cause of this symptom, and based on the final data, make a decision on performing hysteroresectoscopy.
How is the procedure performed?
During manipulation, high-tech methods of monitoring the operation of devices are used. At the very beginning of the procedure, the woman is given an anesthetic. After this, the patient falls asleep (with general anesthesia) or stops feeling pain (with local or epidural anesthesia). Next, the doctor begins to insert the devices.
First, the cervical canal and cervix expand. A resectoscope is inserted into the cavity of the reproductive organ. This device is equipped with a special camera that displays the image on a large monitor, and the necessary tools for the operation. The doctor controls the entire process that occurs in the cavity of the reproductive organ.
Immediately after inserting the device, a small amount of solution is supplied. This fluid improves visibility and allows the walls of the uterus to slightly stretch. Thanks to this, the treatment will be carried out more efficiently.
Hysteroscopy and hysteroresectoscopy
In their work, almost all gynecologists most often encounter pathologies of the cervix.
The disease can be diagnosed at any age.
But what pathologies do women encounter most often? What equipment and what procedures allow for timely diagnosis and treatment of these ailments?
The most common pathologies of the uterine cavity
The development of a particular pathological process depends on various reasons: hormonal imbalance, injury, etc. Modern women most often encounter the following pathologies:
- Endometrial hyperplasia. This disease develops as a result of reasons such as infections, hormonal disorders, and genetic factors.
- Endometrial polyps. They are fibrous, glandular and mixed.
- Intrauterine synechiae. This disease occurs as a result of inflammatory processes, as well as intrauterine interventions (surgical interventions on the uterus, curettage after a frozen pregnancy, abortion).
- Partitions of the uterine cavity. The septum can be complete or incomplete. With a complete septum, women very often cannot get pregnant. If the septum is incomplete, complications may arise during pregnancy.
- Internal endometriosis. According to statistical information, this pathology most often develops in women over 35 years of age.
Hysteroscopy and hysteroresectoscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of pathologies of the uterine cavity
To diagnose and treat intrauterine pathologies, procedures such as hysteroscopy and hysteroresectoscopy are used.
Hysteroscopy has occupied a special place in practical gynecology. This procedure has become mandatory in gynecological hospitals, and not only in large medical institutions. Hysteroscopy allows you to visually examine the uterine cavity using an optical system. The study can be control, surgical and diagnostic.
Hysteroscopy has the following advantages:
- Provides the opportunity to implement curettage under video control. Thanks to this, it is possible to eliminate the formation of treated areas.
- Provides an opportunity to assess the condition of the mucous membrane by visual examination before taking material for biopsy.
- Safety, since the risk of damage to the walls of the uterus in this case is minimized.
After this procedure, some women experience vaginal discharge. They are due to the fact that the mucous layer of the uterus was damaged. Most often, the discharge is not heavy and passes very quickly.
When performing this procedure, for example, material can be taken for a biopsy, various formations can be removed, control over the absence of residues after an abortion, and control over the abortion.
Hysteroresectoscopy is a low-traumatic surgical procedure that takes place under short-term intravenous anesthesia. Most often, this operation is performed for uterine fibroids. It can also be performed for other pathologies of the uterus.
Hysteroresectoscopy provides the opportunity to take a comprehensive approach to the treatment of cervical pathologies. Moreover, in this case, comprehensive correction and therapy is carried out, as well as complete sanitation of the genital organs from existing ailments. All this is possible during one procedure.
Hysteroresectoscopy has the following advantages:
- good tolerability of the operation,
- no scars after surgery,
- the opportunity to return to a normal lifestyle in the shortest possible time.
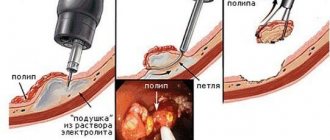
Removal of a polyp in the uterus
This operation is performed in the following way. After introducing the device, the doctor detects a pathological formation. All available tools are directed to it and work begins. Using a device that looks like a curette, the polyp is excised along with the stalk. After this, the base must be coagulated. Most often, laser or medications are used for this.
Removal of a polyp in the uterus occurs quickly and without any consequences. Many clinics guarantee no relapse with proper therapeutic correction after the procedure.
Treatment of fibroids
Hysteroresectoscopy of fibroids has become one of the life-saving procedures for women who want to give birth to a child. If earlier laparotomy and laparoscopic methods were used to treat pathology, which required dissection of the walls of the reproductive organ, then with the development of technology everything has changed. This manipulation allows you to avoid incisions on the uterus, which lead to scar formation. Most representatives of the fairer sex, after manipulation, successfully bear children and give birth on their own.
During the procedure, the myomatous node is cut off with a small depression. After this, the damaged surface is processed. Also, during work, the doctor has the opportunity to carefully examine the remaining cavity of the reproductive organ. Small nodules may be detected and removed immediately. This avoids repeated surgery.
Treatment of uterine pathologies
If there is a septum in the organ cavity or adhesions have formed, the device detects them and makes a dissection. This manipulation allows you to assess the condition of the walls of the organ and, if necessary, correct other pathologies.
A few decades ago, the septum in the uterus was not removed in any way. Women with such education who were carrying a child were at risk. Now everything has changed. With the development of medicine, representatives of the fairer sex can not only eliminate the disease, but also prevent its relapse.
Contraindications
The hysteroresectoscopy method is not recommended for everyone. The operation should be postponed if diagnosed:
- inflammation caused by infections of the reproductive system;
- inflammation detected in the uterine cavity, ovaries, tubes or vagina;
- infections not related to the reproductive system (influenza, ARVI, pneumonia);
- severe pain;
- seemingly unreasonable, intense bleeding.
An exacerbation of certain chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system, liver or kidneys can become a serious obstacle to the operation. Exacerbation of existing pathologies is considered individually and in each specific case the decision is made by the doctor.
Polyps cause discharge, but if they are excessive in nature, then removal will not solve the problem. It is not recommended in the presence of an adenomatous neoplasm during menopause. In this case, it is advised to amputate the uterus, since this type of polyp is a harbinger of cancer and is fraught with relapse. The feasibility of the operation is determined by the gynecologist.
Postoperative period
Like any other operation, hysteroresectoscopy causes discharge. However, they don't last long. If after laparotomy, which requires dissection of the walls of the uterus, bleeding can continue for up to two weeks, then after hysteroresectoscopy, discharge is observed for only a few days. This avoids massive bleeding and infection of the wound.
After the procedure, the woman goes to the ward, where she comes to her senses. The effect of anesthesia is short-lived, and after a couple of hours the patient can go home. Only in some (more severe) cases does the fairer sex remain in the hospital for several days.
After hysteroresectoscopy, it is necessary to carry out treatment. Depending on the pathology, it can be antibacterial, antimicrobial, immunomodulatory and hormonal. If the patient wishes to conceive a child, then it is worth informing the doctor. In this case, a milder therapy is selected, which does not exclude the possibility of pregnancy.
Main advantages
Hysteroresectoscopy is performed quite often. This is due to the undeniable advantages of this treatment method:
- The operation belongs to the category of minimally invasive. It is well tolerated by ladies of all ages and does not require a long rehabilitation period;
- after the procedure, the woman can quickly return to her normal activities;
- hysteroresectoscopy does not affect reproductive functions in any way: pregnancy is possible after the operation;
- after the intervention there will be no scars or scars left on the body. This is important not only from an aesthetic point of view: any open surgery is fraught with serious complications, for example, inflammation of the postoperative suture. Naturally, due to its specificity, hysteroresectoscopy does not have such a drawback. This refers to the main differences between minimally invasive interventions.
https://youtu.be/nN3q4yynJL4
Recovery after surgery
As a rule, a woman can go home on the second day after such an intervention. However, the full rehabilitation period is about 14 days. At this time, there may be quite unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen, and bloody discharge may appear. This should not be scary: such symptoms indicate restoration of the uterine mucosa. Treatment in this case is not required: after the postoperative period ends, they will disappear on their own.
To avoid various infections, a woman needs to take antibiotics prescribed by a doctor for some time. If the pain after hysteroresectoscopy bothers you severely, you can take analgesics.
For about three to four weeks after the intervention, the woman needs to follow simple rules:
- do not lift heavy things;
- do not engage in strength sports and do not overload;
- bathe only in a cool shower, refusing hot baths;
- avoid douching;
- don't get too cold.
You should not be sexually active for a month. If you are planning a pregnancy, ask your doctor when you can start trying to conceive. If the purpose of hysteroresectoscopy was to remove a polyp or myomatous node, it is additionally required to take hormonal medications that speed up the process of postoperative recovery of the body. There is no point in refusing to take them. There are many prejudices that relate to this group of drugs, however, it should be remembered that the doctor prescribes drugs in a certain dosage, which is not capable of causing harm to the patient. If you feel unwell after taking hormonal pills, contact a specialist to adjust your treatment regimen. You cannot change it yourself or replace medications!
Complications
Hysteroresectoscopy relatively rarely causes complications. However, in some cases, patients have:
- gas embolism of the uterine vessels. This happens extremely rarely and is due to the fact that the gases used to expand the uterus enter the bloodstream;
- perforation of the uterine wall. Such a complication can develop if surgical intervention is performed carelessly by insufficiently qualified specialists. If the doctor damages the uterine wall, massive bleeding develops, which leads to fainting. In this case, immediate restoration of circulating blood volume and other resuscitation measures are required;
- hematometra, that is, spasm of the uterine walls. This causes heavy bleeding, in some cases life-threatening for the patient;
- with severe damage to the uterine mucosa, infertility may develop.
However, there is no need to fear. Reviews indicate that serious complications rarely develop after surgery. To protect yourself, you should find a good specialist who has considerable experience in performing such operations, and also do not hide the presence of chronic diseases from your doctor.
Patient opinions
Hysteroresectoscopy has only positive reviews. Women say that manipulation allows not only to remove the pathology, but also to conduct additional research. All materials obtained during the operation are sent for histology. Based on the diagnostic results, a more accurate diagnosis is made, allowing the correct treatment to be prescribed.
Patients also note that a procedure called hysteroresectoscopy is quite expensive. The price of manipulation in a private clinic can vary from 10 to 50 thousand rubles. In public medical institutions, treatment is provided free of charge, but currently not all hospitals have the necessary equipment and specialists qualified in this field.