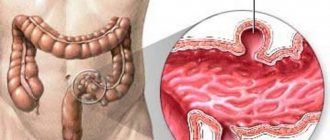
Colitis in a child may occur unexpectedly for parents. With this disease, the epithelial layer of the intestinal mucosa is affected. We are talking about a gradual deterioration and loss of the volume of the shell, as well as its restoration characteristics.
Due to food and the nuances of body structure, colitis is often observed in children. The risk of development cannot be excluded even in infants or kindergarteners.
Classification of the disease
Depending on the dystrophic changes in the intestine, colitis in children is divided into atrophic, catarrhal and erosive ulcerative colitis. Based on the nature of its course, the disease is divided into 4 types:
- spicy;
- chronic;
- nonspecific ulcerative;
- allergic colitis.
Each type of pathology is characterized by the reasons that provoke its development. Before prescribing treatment, the doctor identifies the factors that led to the onset of the disease.
Life expectancy with chronic colitis
In chronic colitis, life expectancy is impaired only when severe complications develop. Which is intestinal tuberculosis. As well as the presence of malignant pathologies.
Life expectancy is also influenced by the age of the patient. The older the patient, the greater the likelihood of developing severe consequences. The chronic process of this disease can manifest itself in different ways.
Periods of remission are followed by periods of exacerbation. Which helps to establish a certain clinical picture. And significantly reduces the patient’s life expectancy.
Causes of colitis in children
There are several sources of acute colitis. Most often it is provoked by such phenomena as:
- intestinal infections (we recommend reading: intestinal infection in a child: treatment);
- gastritis;
- enteritis;
- gastroenteritis;
- radiation exposure;
- gross flaws in nutrition;
- allergic reaction to certain foods.
Acute colitis in a child often develops into a chronic form. Long-term disease can be caused by:
- parasites;
- disordered eating;
- improper use of medications (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics);
- secretory insufficiency of the digestive glands;
- disturbance of intestinal microflora.
Along with this, inflammation of the intestinal mucosa can provoke mental disorders, VSD, congenital anomalies of organ development, physical inactivity, and bad habits in adolescents. A hereditary factor may also be a cause of the disease.
Causes of the disease
It is known that the disease is divided into several varieties, each of which has its own cause. For example, the development of acute intestinal colitis can be caused by various intestinal infections. It is believed that the disease can develop as a result of past illnesses such as:
- Acute gastritis.
- Enteritis.
- Gastroenteritis.
In addition to the above reasons, the following factors contribute to the development of symptoms of intestinal colitis in children:
- Genetics.
- Frequent stress.
- Worm infestation.
- Food poisoning.
- Violation of the proper functioning of the intestines during the neonatal period.
- Taking medications for a long time, often antibiotics.
- Improper diet and inadequate diet.
- Weak immunity.
- Bad ecology.
- Autoimmune diseases.
Based on the above, we can conclude that the disease can develop for completely different reasons.
In addition, similar causes and symptoms accompany Crohn's disease; only a highly qualified specialist can distinguish which disease a child is suffering from, make the correct diagnosis and prescribe effective therapy.
It is worth saying that this disease should not be neglected under any circumstances, since in addition to the complications listed above, it can lead to the development of rectal cancer.
Types and symptoms of the disease in childhood
The main clinical forms of pathology common in children are acute, chronic and nonspecific ulcerative colitis. Infants are often susceptible to an allergic form of the disease.
The older the child, the more difficult it is to determine inflammatory lesions of the intestinal mucosa. Often, parents consider the symptoms of the disease to be a temporary phenomenon and do not take measures to cure them.
Acute form
The symptoms of acute infectious colitis in children are extensive. It can be identified by the following manifestations:
- increased body temperature;
- weakening of the body;
- intense pain in the iliac region;
- nausea and vomiting;
- frequent urge to have a bowel movement (from 5 to 15 times per day, depending on the course of the disease);
- foamy and watery consistency of stool with a green tint (bloody and mucous inclusions are possible);
- drying of the skin;
- loss of appetite;
- a sharp reduction in the frequency of urination.
In acute colitis, rectal prolapse often occurs during bowel movements. The disease is also characterized by dry mucous membranes and sharpening of facial features.
Chronic form
The chronic form of colitis in children is characterized by alternating stages of exacerbation and periods of remission. In such cases, the symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- pain in the iliac region, concentrated on the right or left side;
- diarrhea;
- feeling of bloating and distension in the abdomen;
- sleep disorder;
- headache;
- weakening of the body, state of lethargy;
- irritability, sudden mood swings.
READ ALSO: Why does a 7-year-old child have a stomach ache near the navel?
With this type of pathology, the pain is aching in nature. After meals and before bowel movements, pain tends to intensify.
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis
Manifestations of nonspecific ulcerative colitis depend on the form, course of the disease, severity and age. Often found:
- diarrhea;
- liquid and foul-smelling consistency of stool with blood, mucous and purulent inclusions;
- frequent urge to have bowel movements;
- pain in the abdomen (in certain cases during meals);
- increased temperature with signs of poisoning of the body (with a severe disease);
- lack of appetite;
- bloating;
- weight loss;
- anemia.
An increased size of the liver, severe pain during bowel movements, and an increased urge to defecate at night are characteristic symptoms of the disease. Ulcerative colitis in children is rarely associated with constipation.
Allergic colitis
In newborns and infants under 1 year of age, this type of disease is extremely difficult to determine, since it has vague symptoms.
The main signs of allergic type colitis are:
- alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- watery consistency of stool mixed with blood, mucus and pus;
- flatulence;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- dehydration of the body;
- severe pain in the navel area (we recommend reading: how to treat pain in the navel area in a 7-year-old child?).
Allergic-type inflammation of the large intestine in an infant manifests itself in the form of frequent regurgitation, increased moodiness, and breast refusal. Babies press their legs to their tummy, which indicates the painful sensations they experience.
How to make a correct diagnosis?
Diagnosis of ulcerative colitis is very difficult. It requires careful medical history, laboratory and instrumental studies. To begin with, the doctor conducts a long conversation with the patient. Given the age, the child’s parents should take an active part in this conversation. Here is a list of questions to which it is recommended to know the answers:
- Does your child have abdominal pain? Where are they most often located? How does the child react to them (the severity of pain is assessed)?
- How often does the patient have stool (once a day)? Its consistency? Presence of impurities?
- Is defecation accompanied by bleeding? What is the intensity of blood flow?
- Do you have bowel movements at night?
- Is the child active during an exacerbation?
Further management of the patient consists of prescribing instrumental studies. In children, a colonoscopy with biopsy, gastric probing, and ultrasound of the abdominal organs are required.
Gastric endoscopy makes it possible to distinguish UC from CD, and also often reveals concomitant pathology.
Laboratory tests include complete blood count, liver enzymes, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, reactive protein, and ANCA antibody testing. In case of severe pallor and anemia, tests for ferritin and serum iron are prescribed. The doctor must examine the stool for infection.
Article on the topic: ischemic, spastic and mucous colitis of the rectum.
Diagnostic methods
If signs of disease are detected in a child, he should be shown to a pediatrician or gastroenterologist. A small patient is first given a blood test to detect leukocytosis and determine the number of red blood cells, hemoglobin and total protein. As a rule, such procedures as sigmoidoscopy, X-ray, colonoscopy, and histological examination help to make the correct diagnosis. Based on the examination results, the doctor prescribes optimal drug therapy.
Diagnosis and treatment of colitis
For an infant, colitis can cause the development of other diseases, for example, peritonitis. If you do not see a doctor in time, the symptoms become more severe and it is more difficult to determine an accurate diagnosis.
The purpose of diagnostic measures is to confirm or refute the presence of colitis and determine its type. To do this, the following procedures are carried out:
- General examination and palpation of the abdomen;
- Fecal analysis (the structure, presence of blood, mucus, traces of parasites are studied);
- Blood test (the main indicators are the level of red blood cells, leukocytes and hemoglobin);
- X-ray of the intestines (prescribed only in controversial cases).
Since colitis is a very dangerous disease, especially for children under one year of age, treatment should take place exclusively in a hospital setting. For quick and effective rescue, complex therapy is prescribed, which includes the following measures:
Treatment requires calm and patience. During this period, you should not let your baby try new foods, so as not to cause an aggravation. Also, do not panic, if a child refuses food, it means that his damaged intestines are not yet ready.
For prevention purposes, doctors recommend eliminating all allergenic foods from the diet. Also, give each new food a try in small portions. Particular attention should be paid to the baby’s hygiene and behavior. For example, if your child puts everything in his mouth, then you need to ensure that all his toys and things that surround him are clean. You should not let your child play with keys, money, telephones and other things that are often found in public places.
Alternative medicine also has several methods in its arsenal. First of all, various decoctions based on honey and propolis are used to treat colitis. But these products can cause severe allergies. Therefore, doctors do not recommend resorting to such methods when treating children under one year of age. In such cases, you need to be careful in choosing a treatment method, because we are talking about the child’s health.
Colitis in children is a polyetiological disease of the colon, accompanied by inflammatory-dystrophic changes. Colitis in children occurs with abdominal pain, nausea, changes in the frequency and nature of stool, and malaise. Diagnosis of colitis in children includes scatological and bacteriological examination of feces, irrigography, rectosigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy, endoscopic biopsy of the intestinal mucosa. Treatment of colitis in children largely depends on its pathogenetic form and includes diet therapy, antibacterial and symptomatic therapy, herbal medicine, and restoration of normal intestinal microflora.
Features of treatment
Treatment of colitis involves taking medications and following a special diet. Young patients are prescribed antibiotics and medications with enzymes and probiotics. Analgesics are used to relieve pain. Infusions of chamomile and St. John's wort help to significantly alleviate the baby's condition.
READ ALSO: features of the treatment of gastritis in children
Treatment of diseases of an allergic nature is based on taking antihistamines. In exceptional cases, curing colitis requires surgery.
Prevention of childhood colitis
Pathogens of intestinal infections are transmitted through water, food, contact and household routes. Therefore, following the rules of personal hygiene is important! Mothers need to process food well, especially meat, because the causative agent of intestinal infection, salmonella, persists in it for up to 12 months. Salmonella does not change the taste, color or smell of food.
They die when boiled within a few minutes. It is also important to check the expiration date of a particular product (meat salads, confectionery products with protein cream). All the rules are very easy and elementary in action. Thanks to this, the disease is quite easy to prevent, the main thing is to watch what your child eats and drinks. Be healthy!
Prognosis and complications of intestinal pathology
With timely detection and treatment, full recovery from the disease is possible. Modern methods of therapy guarantee a favorable prognosis in more than 85% of cases of the disease.
If measures are not taken to cure colitis, complications such as disruption of the integrity of the intestinal wall, peritonitis, pathologies of the endocrine system, hypovitaminosis, paraproctitis, and intestinal abscesses may develop. Advanced types of the disease are often accompanied by cracks in the anus.
Loading…
Share with friends!
Colitis, what is it?
Colitis , an inflammatory-dystrophic disease of the inner (mucous) lining of the colon. Colitis is predisposed by a decrease in the body's overall resistance to the action of pathogenic factors, insufficient consumption of plant foods rich in fiber, dysbacteriosis, and inflammatory diseases of the anorectal zone (ascending infection).