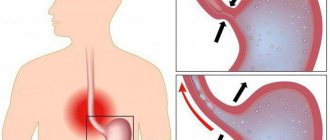
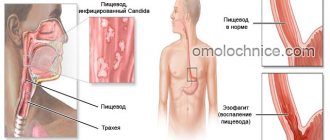
Esophageal diverticula are a pathological process that is characterized by deformation of the esophageal wall and protrusion of all its layers in the form of a pouch towards the mediastinum. In the medical literature, esophageal diverticulum also has another name - esophageal diverticulum. In gastroenterology, this particular localization of saccular protrusion accounts for about forty percent of cases. Most often, the pathology is diagnosed in males who have crossed the fifty-year mark. But it is also worth noting that usually such individuals have one or more predisposing factors - gastric ulcer, cholecystitis and others. ICD 10 code – acquired type K22.5, esophageal diverticulum – Q39.6.
- Etiology
- Varieties
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
Diverticula of the esophagus in humans are manifested by characteristic symptoms - the appearance of a putrid odor from the mouth, the feeling that there is a lump in the throat, dysphagia, hypersalivation, etc. It is important, when the first alarming signs appear, to immediately contact a qualified doctor for diagnostics, during which he will be able to confirm or deny the presence of the disease, establish the reasons for its progression, and also prescribe competent treatment. In difficult situations, the patient is prescribed surgery - the esophageal diverticula are excised or everted into the lumen of the esophagus. If proper treatment of esophageal diverticulum is not carried out in a timely manner, dangerous complications may develop - necrosis, inflammation of the sac, its rupture, etc.
Esophageal diverticulum: what is it?
Esophageal diverticula, the classification of which is discussed below, appear in men and women of different age categories. A true protrusion contains all layers of the organ, a false protrusion passes through a wall defect and is formed by the mucosa.
ICD-10 code – esophageal diverticulum acquired (K22.5), congenital (Q39.6).
The wall defect itself is not dangerous to human health. Unpleasant consequences occur with concomitant diseases of the esophagus and other digestive organs. A diverticulum can be accompanied by inflammation of the mucous membrane, reflux, bleeding and ulcerative lesions of the esophageal tube. Esophageal diverticulum is also dangerous for people with a predisposition to cancer. There is a risk of the protrusion transforming into a cancerous tumor.
The development mechanism is associated with the following factors:
- congenital weakness of the muscles of a separate part of the wall of the esophagus;
- deviation of esophageal peristalsis;
- spastic contractions of the organ;
- the presence of adhesions of the esophagus to the lymph nodes.
results
The results of the study showed that performing diverticulectomy using the videoendoscopic transillumination method significantly reduces the time of surgical intervention. Thus, in the main group, where this technique was used, the average duration of the operation was 47±12 minutes, while in the comparison group (classical diverticulectomy) it was 68±14 minutes. Another difference is the cosmetic appearance of the postoperative scar. In patients of the main group it was almost 2 times shorter than in patients in the comparison group. In the comparison group, there was 1 intraoperative complication - opening of the lumen of the esophagus during isolation of a Zenker diverticulum, which was sutured with interrupted sutures in the transverse direction. No intraoperative complications were observed in the patients of the main group. Long-term results of surgical treatment of pharyngoesophageal diverticula were monitored over a period of 1 to 3 years. Of the 39 operated patients, only 1 of them (the comparison group) had a relapse of the disease.
Causes
Factors in the development of the disease have different origins. Congenital diverticulum appears as a result of impaired development of the muscle layer during the period of intrauterine formation.
A secondary or acquired defect has the following causes:
- chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract;
- high intrauterine pressure;
- ulcerative lesions of the stomach;
- gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- injury close to the epigastric region;
- connection of an organ with lymph nodes.
conclusions
1. The main method of treatment for pharyngoesophageal diverticula is the classical surgical method.
2. Diverticulectomy performed using the videoendoscopic transillumination method has advantages over classical diverticulectomy: safety, shorter duration, better cosmetic effect.
3. In order to prevent relapse of the disease, excision of the diverticulum must be supplemented with extramucosal esophagomyotomy (cricopharyngeal myotomy).
Types of disease
Esophageal diverticula are classified depending on the etiology, the number of layers of the esophagus involved, location and mechanism of development.
Depending on the source, a distinction is made between congenital and acquired protrusion. In the first case, the wall defect appears in the womb or all conditions favorable for its appearance are formed. Acquired protrusion occurs in children and adults due to the influence of unfavorable factors. Depending on the development mechanism:
- Traction . Diverticula appear when the organ is regularly stretched.
- Pulsating . They arise under the influence of external factors.
Depending on location:
- pharyngoesophageal or Zenker's ;
- supradiaphragmatic (epiphrenal);
- subdiaphragmatic;
- midesophageal.
How to prevent disease
There is no specific prevention of the disease. To avoid its development, you should adhere to the general norms recommended for the digestive system. And at the first symptoms of the disease, contact a gastroenterologist for diagnosis and treatment.
The development of esophageal diverticulum causes a lot of unpleasant symptoms, significantly worsening a person’s quality of life. It’s easy to prevent its occurrence; just stick to a healthy lifestyle.
Esophageal diverticulum makes itself felt in females and males.
Basically, the disease manifests itself when a person passes the age of fifty. The disease is accompanied by symptomatic manifestations.
The site provides reference information. Adequate diagnosis and treatment of the disease is possible under the supervision of a conscientious doctor. Any medications have contraindications. Consultation with a specialist is required, as well as detailed study of the instructions! Here you can make an appointment with a doctor.
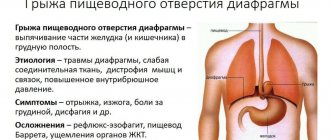
Diverticular disease of the esophagus is a local protrusion of the esophageal wall, which communicates with the lumen of the designated organ. Its central symptoms will be a feeling of a lump in the throat, a constant desire to cough.
There is an unpleasant odor from the oral cavity, and the voice timbre also undergoes modifications. There is a diverse classification of diverticular disease of the esophagus, which is based on different criteria.
According to their origin, diverticula are:
- Congenital, which is a defect formed in the early phases of a child’s development.
- Acquired, which appear during life.
Considering the relationship of the mucous membrane to the formation of a diverticulum, 2 types are distinguished:
- False, which are formed due to the involvement of only the mucous membrane in the process.
- True, they are formed as a result of the formation of hollow mucous sacs and other membranes of the organ wall.
Depending on the preferred location of diverticula, several types are distinguished:
- Tsenkerovsky;
- Located above and below the diaphragm;
- Middle esophageal.
There are 2 types of diverticular disease, which are based on the mechanisms of formation. A pulsation diverticulum makes itself felt as a result of exposure to external irritants. Traction - mediated by systematic stretching of the esophageal wall.
Complications
The danger of the defect lies in the progression of the disease under the influence of concomitant abnormalities. In patients with diverticula, the formation of polyps and multiple adhesions may begin. When the esophagus becomes inflamed, there is a risk of ulcers and perforation, which then leads to hemorrhage into the lumen of the organ. There is a possibility of transformation of the diverticulum into a malignant neoplasm. The defect can lead to an abscess and pneumonia.
Self-medication attempts at home often lead to such complications. This disease can be identified in a timely manner and high-quality drug treatment can be carried out with a favorable prognosis, but not everyone seeks help.
If you ignore the need for examination and treatment, there is a high risk of one or more complications. Thus, an initially safe defect moves into the category of deadly conditions.
Therapeutic measures
If small diverticula have been diagnosed and complications do not progress, then conservative methods of therapy are preferred. It is important to follow a gentle diet - the incoming food should not irritate the esophageal mucosa. After eating, it is recommended to carry out simple measures that will help empty the formed cavity - drink a lot of water, strain, rinse the cavity with a weak antiseptic solution. It is worth noting that the use of folk remedies for therapy is not recommended. The only exceptions are cases when the attending physician himself prescribed to take this or that drug.
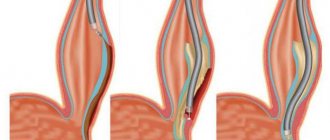
The operation is prescribed for severe pathology, when severe pain occurs in the esophagus, there is no way to eat normally, etc. It is important to carry out the intervention in a timely manner to eliminate the risk of complications. The most common operation performed is to excise the diverticulum. Next, plastic surgery is performed using a pleural flap. For small diverticula, a slightly different type of operation is indicated - intussusception of neoplasms. In this case, the surgeon reduces the diverticula into the esophagus. Both operations are performed under general anesthesia. During the postoperative period, the person is in the hospital under the supervision of doctors. If after the operation the patient feels unwell and his temperature rises, this indicates the development of complications. Measures are taken immediately to eliminate them.
The prognosis of the disease is favorable (if you seek help in a timely manner).
Esophageal diverticulum: symptoms
A slight protrusion of the wall of the esophagus of a congenital or acquired nature does not give any symptoms. The person does not feel discomfort and does not have difficulty swallowing. Zenker's diverticulum already has specific manifestations, regardless of size. It is this that often becomes complicated and requires surgical treatment.
Zenker's diverticula have the following symptoms:
- difficulty swallowing;
- pain as food passes through the esophagus;
- belching with a sour smell;
- reverse reflux of food from the esophagus.
Characteristic symptoms are observed when a person assumes a horizontal position. There is a feeling of a foreign body in the throat, soreness and burning. There may be bouts of severe coughing without sputum, and less often blood is discharged.
The patient is worried about nausea and vomiting. Salivation increases, and general signs of malaise appear. The symptoms of diverticulum are complemented by deterioration of health, high body temperature and dyspeptic symptoms in the form of constipation and bloating.
While eating food, signs of choking, dizziness, and skin flushing may appear. In severe cases, the person loses consciousness. Relief occurs after vomiting.
A large protrusion gives the following symptoms:
- severe chest pain;
- cough at night and in the evening;
- reflux of undigested food into the oral cavity.
Recommended dietary intake
For successful treatment, you need to follow a proper diet.
Basically, dietary nutrition for the formation of esophageal diverticulum is similar to diet number one, which is intended for gastric or duodenal ulcers.
During the diet for diverticular disease of the esophagus, you can consume the following list of products:
- Dried wheat bread and flour products;
- Dishes made from beef, lean lamb, rabbit, chicken breast, turkey, steamed or boiled;
- Fish - cod, pollock, heh, carp, pike, pike perch and other low-fat species;
- Kefir, cottage cheese, natural yogurt, fermented baked milk, cottage cheese dishes;
- Semolina, buckwheat, rice;
- Potatoes, carrots, beets, cauliflower, it is advisable to serve them boiled or steamed;
- Berries and fruits, mousses, jelly, compotes, jelly based on them.
Excluded from the diet:
- Carbonated water, coffee drinks;
- Fresh bread, sweets and confectionery;
- Smoked meats, pickles, canned products;
- Hot and spicy food;
- Wheat, barley and corn grits, pearl barley.
Meals 5 times a day, each meal should be accompanied by a sufficient amount of clean water.
In order to improve the passage of food before starting to eat, you need to drink a teaspoon of any oil, be it olive, vegetable, flaxseed, sesame. To prevent food bolus from getting into the diverticulum cavity, you should chew food thoroughly and eat in small portions.
Diagnostics
Zenker's diverticulum is detected by a doctor upon palpation. A rounded soft formation is felt, which decreases when pressed. Confirmation of the diagnosis is carried out using instrumental research methods. Before the main diagnosis, the doctor collects anamnesis by asking about lifestyle, existing risk factors and previous diseases.
Hardware examination for esophageal diverticula:
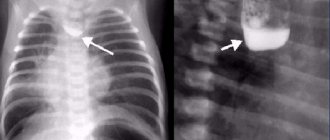
- Contrast radiography . The presence of one or more protrusions is confirmed, their location and size are determined. The presence of polyps, fistula, and cancer is excluded or confirmed.
- CT scan . Appointed to study large defects.
- Esophagoscopy . The defect cavity is examined, areas of bleeding and ulcerative lesions are determined. During the examination, a portion of the tissue is removed for further study.
- Esophageal manometry . The functional ability of the esophagus is studied.
A false diverticulum (intrawall pseudodiverticulum) can be detected by X-ray with contrast, the substance penetrates into the mouths of the glands. In this case, barium accumulates in the lower part of the organ.
When the patient is worried about angina pectoris, an additional ECG and EchoCG . Some diseases of the cardiovascular system produce similar symptoms as diverticula. Differential diagnosis is carried out with an atrium cyst, angina pectoris, hernia of the atrial fissure, structures and oncology.
Epiphrenal type of pathology
Epiphrenic diverticulum is located in the lower third of the esophagus on the right side of the wall. In its formation it has the principle of a pulsion mechanism. This is due to an anatomical shift in the designated area of the esophagus to the right side and an increase in internal pressure on the right side during the movement of the food bolus.
Congenital underdevelopment of the esophageal wall is formed in this part of the organ, hence the pathological condition manifests itself.
Epiphrenic diverticulum is solitary.
As usual, it does not reveal itself in any way, so it can be detected using x-rays.
https://feedmed.ru/bolezni/sistemy-pishhevarenija/divertikul-pishhevoda.html
The central symptomatic manifestations in the case of epiphrenic protrusion will be a feeling of dull pain in the chest, regurgitation of eaten food, aerophagia, stagnation of food in the area of the xiphoid process, sharp pain in the epigastric area.
In the vast majority of cases, this type of diverticula is characterized by a slow change in size, and its outcome is not associated with the occurrence of serious problems. Complications may include relapse of pneumonia, bronchial asthma, pleurisy, pulmonary abscess.
If the inflammatory process of the diverticulum develops, this can give rise to bleeding and perforation of the esophagus.
Esophageal diverticulum: treatment
Small bulges that do not cause discomfort or impair swallowing function do not require treatment. Therapy is required when there is reflux esophagitis and the esophageal mucosa is constantly irritated by acidic contents. Surgical removal is required when the diverticulum reaches enormous sizes, dysphagia appears, and there is a risk of a malignant tumor.
Treatment of esophageal diverticulum with folk remedies is acceptable in cases where there is heartburn; some recipes will help get rid of the unpleasant symptom. For diverticulum of the cervical esophagus, diet and medication are indicated. Complex treatment of esophageal diverticulum includes:
- medications to relieve inflammation and pain;
- following a diet, excluding solid and hot foods;
- elimination of concomitant gastrointestinal diseases;
- physiotherapeutic procedures to maintain the condition of the mucous membrane;
- avoidance of smoking and alcohol;
- restorative therapy;
- surgical removal if the diverticulum is large.
Symptoms of esophageal diverticulum manifest themselves differently, so each patient is prescribed separate medications.
Drug therapy
Medicines should be taken to reduce the harmful effects of gastric juice on the walls of the esophagus. When the diverticulum is accompanied by erosion, proton pump inhibitors and the drug Omeprazole . Therapy is supplemented with the drug Pantoprazole and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
If the symptoms are mild, the patient is prescribed antacid drugs and prokinetics . For moderate severity, medications are supplemented with a strict diet and painkillers. When there is severe inflammation, several drugs are prescribed simultaneously in combination; these can be PP inhibitors , prokinetics and antispasmodics .
When heartburn occurs, antacid medications are prescribed, which begin to act within half an hour after administration. Rennie , Almagel , Gestal , Maalox , Phosphalugel will help cope with this symptom .
To neutralize hydrochloric acid and prevent irritation of the esophageal mucosa, alginates are prescribed. Representatives are the drug Gaviscon and sodium alginate.
Alginates are the safest medications prescribed for the treatment and prevention of reflux in diverticula. Women can take them during pregnancy, but only with the permission of a doctor.
Prokinetics will help reduce the time of contact of the esophageal mucosa with acid. This drug is Domperidone , Metoclopramide . They relieve the feeling of heaviness and burning behind the sternum. When a diverticulum is accompanied by a peptic ulcer, the drug De-Dol is prescribed. Depending on the general condition of the digestive system, the doctor may prescribe enveloping and restorative agents.
Diet
An important component of treatment for diverticula is diet. It is necessary to follow certain nutritional rules to maintain the health of the walls of the esophagus and reduce symptoms. It is important to exclude foods that increase the secretion of gastric juice, burn and irritate the esophagus.
Prohibited products include:
- hot spices;
- highly carbonated sweet water;
- seeds and tomatoes;
- citrus;
- sour fruit juices;
- strong tea and coffee.
With diverticula, it is not so important what to eat, but how to do it. Food should be well chopped and at normal temperature. You need to chew thoroughly and swallow in small portions. The recommended food temperature should not exceed 60 degrees.
Prevention and prognosis for the patient
The disease can be prevented by adhering to the following recommendations:
- chew food well;
- exclude too cold or hot dishes;
- eat food slowly, in a sitting position;
- avoid snacking on the go;
- promptly treat diseases of the digestive system;
- avoid injury to the esophagus;
- follow the advice of a nutritionist.
If the disease is detected early, the prognosis for recovery is favorable. Severe forms of pathology and its complications develop in the absence of treatment and failure to maintain a healthy lifestyle and diet.