Causes of the disease
Hernia in children most often develops as a result of congenital disorders. For example, a baby is born with an incorrect position of the stomach relative to the thoracic region. In such a situation, the problem can be solved exclusively surgically.
In adults, the development of axial (hiatal) or other hiatal hernia occurs under the influence of the following factors:
- weakening of the tissues of the digestive organs that occurs with age;
- pathologies that are associated with congenital defects of the ligamentous apparatus;
- inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases of the esophagus;
- damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive system;
- increased intra-abdominal pressure observed over a long period of time.
The cause of increased blood pressure may be the following:
- heavy physical activity;
- lifting weights;
- frequent vomiting;
- constant constipation;
- increased gas formation;
- excess body weight;
- neoplasms of the abdominal organs.
Hiatal hernia is rare and is mainly observed in older people, but can occur in young people and even children.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing hiatal hernias, instrumental visualization methods play a leading role:
- esophagogastroscopy;
- intraesophageal and intragastric pH-metry;
- esophagomanometry;
- impedancemetry;
- X-ray of the esophagus, stomach and chest organs.
Strangulated hiatal hernia on radiography
Endoscopic examination allows us to identify reliable signs of a hiatal hernia: enlargement of the esophageal opening, upward displacement of the esophagogastric line and changes in the mucous membranes of the esophagus and stomach, characteristic of chronic esophagitis and gastritis. Esophagogastroscopy is often combined with pH measurement; if severe ulcerations and erosions are detected, selection of a biopsy specimen is also indicated in order to exclude oncopathology and precancerous conditions.
On x-rays, signs of axial hernias are clearly visible: high location of the esophagus, protrusion of the cardia above the diaphragm, disappearance of the subphrenic part of the esophagus. When a contrast agent is administered, there is a retention of suspension in the hernia area.
To assess the condition of the upper and lower esophageal sphincters and esophageal motility, esophagomanometry is performed - a functional study using a water-perfusion catheter equipped with a registration sensor. Pressure indicators in the contracted state and at rest make it possible to judge the strength, amplitude, speed and duration of contractions of the sphincters and smooth muscles of the esophageal walls.
Impedansometry allows you to get an idea of the acid-forming, motor-motor and evacuation functions of the stomach, based on the indicators of electrostatic resistance between the electrodes of the esophageal probe. Impedance measurement is considered the most reliable way to recognize gastroesophageal reflux with simultaneous assessment of its type - depending on the pH value, acidic, alkaline or weakly acidic reflux is distinguished.
We suggest you read: Crunching in joints, causes, treatment with folk remedies
In case of severe anemic syndrome, a stool test for occult blood is additionally performed. To exclude cardiovascular pathology in the presence of cardiological complaints, it may be necessary to consult a cardiologist and conduct gastrocardiomonitoring - combined daily monitoring of stomach acidity and Holter ECG.
The main diagnostic methods for identifying a diaphragmatic hernia are a laboratory blood test to detect anemia, as well as an instrumental examination, which includes:
- X-ray of the abdominal organs;
- fibrogastroscopy;
- manometry;
- acidity level measurement;
- biopsy.
Radiography is a mandatory method for diagnosing the disease. The study allows us to identify the fact of a change in the position of the stomach, as well as the nature of damage to the esophageal opening of the diaphragm. Thanks to x-rays, the form of the pathology is determined - the presence or absence of an enveloping hernial sac.
Fibrogastroscopy - swallowing on an empty stomach a medical probe with an optical camera installed at the end. An internal examination of the stomach reveals deformations, damage to the mucous membrane, dysfunction of the esophagus, duodenum, and vascular bleeding. Manometry is necessary to measure pressure in the abdominal cavity, the increase in which is caused by anatomical changes in the esophageal opening of the diaphragm.
Typically, hernias are first detected during X-ray of the OGK, X-ray of the esophagus and stomach, or during an endoscopic examination (esophagoscopy, gastroscopy). X-ray signs of pathology are the high location of the esophageal sphincter, the location of the cardia above the diaphragm, the absence of the subphrenic part of the esophagus, the expansion of the diameter of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm, the retention of barium suspension in the hernia, etc.
CT scan of the abdominal organs. Hiatal hernia. Prolapse of perigastric tissue into the chest cavity through the dilated esophageal opening
During endoscopy, as a rule, a displacement of the esophageal-gastric line above the diaphragm, signs of esophagitis and gastritis, erosion and ulcers of the mucous membrane are determined. To exclude tumors of the esophagus, an endoscopic biopsy of the mucous membrane and a morphological examination of the biopsy specimen are performed. In order to recognize latent bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract, feces are examined for occult blood.
A special place in the diagnosis of hiatal hernia is given to esophageal manometry, which allows assessing the condition of the sphincters (pharyngeal-esophageal and cardiac), the motor function of the esophagus at various levels (duration, amplitude and nature of contractions - spastic or peristaltic), as well as monitoring the effectiveness of conservative therapy. To study the gastrointestinal tract environment, impedance measurements, gastrocardiomonitoring, intraesophageal and intragastric pH measurements are performed.
https://youtu.be/_5p2sunxlhg
Degrees of development
A diaphragmatic hiatal hernia occurs in several degrees, which differ from each other in how much volume of the stomach or esophagus penetrates into the chest cavity.
Doctors distinguish 4 stages of hiatal hernia:
- Esophageal. This is the first degree, in which the abdominal part of the esophagus, cardia, enters the thoracic region. These organs are located at the diaphragmatic level, and the stomach is adjacent to the diaphragm itself.
- Cardiac. This is the second stage, also characterized by penetration of the abdominal part of the esophagus into the chest cavity. The only difference is that the stomach enters slightly into the esophageal region of the diaphragm.
- Cardiofundal. This is the third degree, in which the abdominal esophagus, cardia and part of the stomach are located above the diaphragm.
- Gigantic. This is the fourth, most pronounced stage, which is characterized by the elevation of all gastric parts above the diaphragmatic region.
Knowing what this is, grade 1, 2, 3 and 4 hiatal hernia, the doctor can determine how severe the disease is and what treatment tactics to choose to achieve the desired effect.
Symptoms of a hiatus hernia
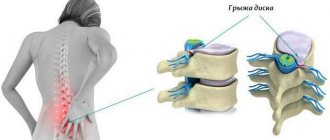
This disease is also called hiatal hernia and is characterized by a pathology such as a change in the location of some organs or their parts, moving from the abdominal cavity to the chest through the diaphragmatic opening.
In this case, the organs involved may retain or lose their mobility. When only a small part of the organs moves from the peritoneum into the chest cavity, then the prognosis can be considered the most favorable compared to complete movement of the organs.
But in this case, the signs of the disease may go unnoticed, and treatment will not be started in a timely manner, which can lead to complications.
As noted above, at the very beginning the pathology is not expressed by particularly obvious symptoms, but later patients may complain of such unpleasant sensations as:
- dull or burning pain behind the sternum that appears after eating or moving;
- bloating, flatulence, hiccups, belching, heartburn;
- pathology in the form of gastroesophageal reflux, during which the reverse movement of food into the esophagus from the stomach occurs;
- difficulty swallowing food.
In the future, if treatment is not started, the hernia may pinch the blood vessels through which the internal organs are nourished, or these organs themselves. Due to the fact that blood flow is disrupted, tissue necrosis occurs.
The process of infringement can occur gradually or be sudden. The latter can occur due to excessive physical activity, eating large amounts of food, laughter, etc., while the patient experiences acute pain, increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, and severe sweating.
These symptoms are characteristic of a serious condition and are indications for calling an ambulance for hospitalization.
If the hernia is small, there are usually no symptoms. However, there are also cases when you may notice nausea and vomiting.
In more serious situations, the canals leading from the stomach to the esophagus become blocked. This can lead to serious consequences.
For example, a complication expressed by reflux esophagitis will occur. This term refers to a disease that leads to the release of stomach acid into the esophagus.
Reflux esophagitis is very easy to detect. With it, gag reflexes are not caused by nausea, but occur as a result of contraction of the stomach.
Classification of pathology
The disease varies not only in severity, but also in type. Scientists divided them based on anatomical features. The following types of pathology exist:
- axial hiatal hernia: characterized by the fact that it is able to freely penetrate into the thoracic region through a gap in the esophagus, and then also return back without hindrance. This often happens in patients when they suddenly change their body position;
- irreducible hiatal hernia: characterized by the fact that part of the stomach gets stuck in the hernial orifice and is unable to move forward or backward;
- paraesophageal hernia: with it, the esophagus and cardia are observed to be in their places, and part of the stomach goes into the thoracic esophagus.
There are also cases when a person develops two types of the disease at once, then a diagnosis is made - a mixed type of hiatal hernia.
Esophageal hernia - symptoms and signs, diagnosis, treatment and nutrition
This hernia is most often treated conservatively. Since a violation of the anatomical relationship of the stomach and esophagus leads to the reflux of gastric contents into the esophageal lumen, this disease is always accompanied by inflammation of the esophageal walls.
(if the table is not completely visible, scroll to the right)
A gastric hernia (abbreviated as GH) is a type of hiatal hernia in which the stomach penetrates completely or partially into the chest cavity.
This pathology is often asymptomatic and becomes an incidental finding during examination for another reason. In the classic case, a hernia causes heartburn, belching, burning in the chest and difficulty swallowing, which worsen the person’s well-being.
In 95% of cases, hernia is effectively treated with conservative methods: with the help of a special diet and medications, the manifestations of a hernia can be reduced to nothing. The need for surgery arises only in complicated hernias. Surgical treatment also has good results: there are almost no relapses of the disease after the intervention.
If a gastric hernia is detected, is treatment with folk remedies a real help to the body or a waste of time and effort? In order for everything to fall into place, it is necessary to understand the issue in more detail.
A gastric hernia is a condition that occurs in the esophagus and is characterized by enlargement of the esophagus in the diaphragm and enlargement of the ligaments that support the stomach and esophagus.
As a result of this, the upper part of the stomach penetrates into the chest cavity, and its activity is disrupted in the lower esophageal sphincter. This process in medicine is called a gastric hernia.
The most common signs of the disease include:
- Heartburn and constant belching, which causes pain.
- There is a burning sensation in the chest.
- After eating food, severe pain is felt in the stomach.
- Pain is felt when lying down and bending over.
- In some cases, pain and burning of the tongue appears.
- Long lasting hiccups.
- Heart pain.
How to detect a hernia yourself:
- If a hernia appears in an infant, you will be able to see a characteristic protrusion. Monitor the child’s behavior: if the baby cries when sneezing and when straining, the swelling increases and disappears in a horizontal position (the hernia penetrates back into place), then most likely this is a hernia. You should consult a doctor immediately.
- In an adult, the swelling disappears when lying down. When pressing on the formed lump, pain is felt in the groin. When the hernia is self-reduced, the pain disappears.
- The larger the hernia grows, the higher the risk of intestinal obstruction. In this case, you should be alerted to symptoms such as bloody discharge in the stool and an increase in body temperature to high levels. In this case, do not hesitate and contact a doctor immediately, as this is a serious threat not only to health, but also to life.
The disease can be treated with traditional methods, but you should still visit a doctor first, as there are cases when surgical intervention may be necessary. Indications for surgery may include large hernias or those that provoke the formation of ulcers.
Also, a lot depends on the stage of the disease, so do not let the disease get worse, go to the doctor as early as possible. The longer you leave a hernia untreated, the larger it will grow. After the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes medication, you can begin traditional therapy.
But your doctor must know about your home treatment and approve it.
Factors that predispose to the development of a hernia can be general or local. Local factors for hernia development:
- Congenital anomalies of the development of the abdominal wall, where already from birth there is an opening through which part of the stomach penetrates into the chest cavity.
- Expansion of the passage in the abdominal wall.
- Thinning and loss of elasticity of tissues due to aging of the body or congenital abnormalities in the structure of connective tissue.
- Wounds or injuries in this area, including post-operative ones.
- High intra-abdominal pressure.
Common causes of a hernia in the stomach:
- Age and gender of the sick person.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Anatomical features.
- Ascites, in which intra-abdominal pressure increases.
- Excess body weight.
- Carrying a child.
Some diseases can also contribute to the formation of a hernia, in which the following symptoms are observed:
- Long-term constipation.
- Lung diseases accompanied by severe cough.
- Narrowing of the urethra.
- Prostatitis.
First of all, you need to limit yourself in food intake. There should be a small amount for one serving. Develop a menu for yourself, increase the frequency of meals, while reducing portions.
During treatment you will have to avoid or minimize fried, fatty, salty foods, coffee and alcohol.
The medications prescribed by the doctor are mainly aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease. These are belching, constipation and heartburn. Therapeutic measures are in many ways similar to the treatment of reflux esophagitis.
But this therapy, including diet and medication, will bring temporary relief. As soon as the patient stops treating the disease, all symptoms return. Therefore, in some cases, surgery is performed. The essence of the operation is to give the stomach its normal anatomical position.
Indications for gastric surgery may include:
- Lack of effect from drug treatment.
- If the hernia has caused complications, for example, in the form of an ulcer, erosion, esophagitis, anemia or bleeding.
- Large size hernia.
- Dysplasia of the mucous membrane.
Following simple rules will help you quickly get rid of the symptoms of a hernia and help in treatment:
- The sore spot should be washed with cold water and vinegar.
- To relieve pain, put ice on the hernia site.
- Apply an oak bark compress; leave for 30 minutes.
- Before you begin treatment for a gastric hernia, eliminate the cause of its occurrence; it could be overeating, bad habits, etc.
- Don't forget about meal frequency and small portions. At night you should avoid eating altogether.
- Refusal of unhealthy foods and carbonated drinks.
- Eat in a way that prevents constipation and flatulence.
- After eating, try to walk at a slow pace.
- Don’t forget about gymnastics; all physical exercises should be done without tension.
Remember that the disease should not be neglected, since in severe cases surgery cannot be avoided; all therapeutic measures, both traditional and folk, lose their effectiveness after cessation of therapy.
A hernia is a pathological formation characterized by protrusion or displacement of organs and their parts from their usual locations into other cavities, outward.
Several conditions are necessary for the formation of a hernia:
- The presence of a hollow organ;
- The cavity into which the displacement occurs;
- The dividing line between the normal and pathological location of the organ.
All these conditions are also suitable for the stomach.
The stomach is a hollow organ of the digestive tract. Any of its walls or sections can shift under the influence of certain factors; the diaphragm serves as the boundary. It divides the human body into two parts: thoracic and abdominal.
The diaphragm has an esophageal opening; normally the esophagus and blood vessels pass through it. With pathological changes, the stomach can protrude into it; the thoracic part of the body serves as the cavity.
A gastric hernia is a change in the position of an organ or its parts relative to the diaphragm. Normally, the stomach is completely immersed in the abdominal cavity, its parts do not penetrate into the overlying sections.
When a hernia occurs, the wall protrudes into the chest cavity through the esophageal opening. The most dangerous condition is the complete displacement of the stomach into the chest.
The phenomenon occurs when the retaining muscles of the diaphragm are stretched and weakened, with a persistent and prolonged increase in intra-abdominal pressure.
The hernia consists of the hernial orifice, the hernial sac and the hernial contents. The hernial orifice is represented by the esophageal opening of the diaphragm.
The hernial sac consists of layers of the gastric wall and layers of the diaphragm itself, and the hernial contents are the wall that has changed its anatomical location.
For the development of the disease, several conditions must form: increased intra-abdominal pressure, incompetence of the diaphragm, its ligaments and muscular apparatus, diseases of the stomach and esophagus. Most often, the disease occurs in older people, mostly in men.
Doctors identify a number of causes and conditions that contribute to the development of the disease.
The older a person gets, the weaker his muscular system becomes. This applies not only to the musculoskeletal system, but also to internal organs.
The diaphragm muscles stretch, wear out, and become less elastic. This affects the change in the anatomical location of the organs adjacent to the diaphragm, and a hernia occurs.
Prolonged increase in intra-abdominal pressure.
There is some difference in pressure between the chest and abdominal cavities. Due to it, the respiratory act and other physiological processes occur. When abdominal pressure predominates over thoracic pressure, organs are pushed into a cavity with less pressure.
Chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, pulmonary apparatus, cardiovascular system.
Doctors include obstructive pulmonary disease, heart failure, cirrhosis of the liver, stomach ulcers, and cancer.
Strong physical activity.
As a result, atrophy of the diaphragm, its movement, and increased pressure in the subdiaphragmatic zone can occur.
Pregnancy in the third trimester:
- It is complicated in women who had diseases of the stomach, esophagus, lungs or heart before pregnancy.
- Congenital anomalies of the esophagus, stomach, diaphragm.
- Excess body weight.
People who are overweight very often encounter hernial protrusions:
- Injury in the abdominal or thoracic area.
- Abdominal or thoracic surgical interventions.
- Connective tissue diseases: scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus and others.
- Chronic constipation.
- Frequent overeating.
Only an experienced specialist can give a complete, detailed diagnosis based on characteristic symptoms when prescribing laboratory and instrumental research methods.
If you detect certain signs, you should not diagnose yourself; it is better to consult a doctor.
Clinical picture
With a hiatal hernia, symptoms may not appear for a long time. Therefore, doctors often discover the disease completely by accident when conducting an examination for another pathology.
It is also possible to display some basic signs that are characteristic not only of a hernia, but also of other disorders of the digestive system. Therefore, very often people simply do not pay attention to them.
Among these symptoms of a diaphragmatic hernia, heartburn can be identified primarily. This is a common symptom and varies in severity; patients complain of a strong burning sensation behind the chest. This phenomenon is mainly observed in the following cases:
- after eating;
- when the body is in a supine position;
- when bending down;
- during physical activity.
The occurrence of heartburn should be a serious reason to consult a doctor and check the state of the gastrointestinal tract, as it is an early sign of malfunctions in the functioning of the digestive organs.
In addition to burning, a hiatal hernia has the following clinical manifestations:
- pain in the chest and epigastric area, resulting from pressure from the protruding part. In its advanced form, the pain can be severe, but it can be difficult to distinguish from angina attacks or cardiac infarction;
- belching, which causes a bitter or acidic taste in the mouth;
- a violation of the swallowing process, in which the patient has difficulty swallowing food. A disorder often occurs when a person is in a hurry when eating or drinking;
- hiccups;
- gagging.
Patients with hiatal hernia also experience cardiac symptoms, for example:
- pain in the heart area;
- increased heart rate;
- dyspnea;
- coughing attacks;
- cyanosis of the skin after eating.
Having identified the symptoms of a hiatal hernia, treatment cannot be carried out independently. It is important to consult a specialist and undergo an examination. Self-therapy can aggravate the course of the disease and provoke complications against its background.
Conservative treatment
The purpose of drug therapy in the treatment of a hernia is to eliminate unpleasant symptomatic manifestations associated with the progression of the disease, reflux of gastric contents through the esophagus into the oral cavity.
https://youtu.be/W8jxPKaqido
When carrying out drug correction, symptomatic signs of pathology are eliminated:
- burning sensation along the esophagus;
- pressing, widespread and bursting pain inside the chest;
- bad breath;
- disturbance in the contractile robot of heart contractions.
The groups of drugs used as medicinal correction of the disease are as follows:
- Anthracite drugs. Such medications can neutralize the effect of the acidic contents of the stomach cavity.
Preparations of this group not only have extremely high enzymatic properties, but they also envelop the gastric mucosa, forming a kind of barrier as protection from mechanical stress.
- Drugs that can inhibit the production of stomach acid.
Today, folk remedies are considered the most accessible and widespread method of treatment. Herbal preparations are used as treatment. Their use helps eliminate unpleasant symptoms and normalize the normal functioning of the digestive canal.
Treatments that can be used include baking soda, chamomile, mint tea, lemon juice, lactic acid products, ginger and apple infused vinegar.
Traditional medicine is based on the use of medicinal herbal preparations, which can be bought at a pharmacy or collected independently in ecologically clean regions.
The use of traditional medicine must be reported to the attending physician to avoid unpleasant consequences.
To achieve the desired result, the attending physician selects a technique that suggests how to cure a hiatal hernia without surgery individually for each patient.
In medical practice, the following approaches to the treatment of hiatal hernia are used:
- Drug therapy.
- Physiotherapy.
- Breathing exercises.
- Dieting.
An important aspect of conservative treatment is giving up bad habits and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Sometimes traditional treatment methods are used as auxiliary therapy.
Diagnostic methods
To identify a hiatal hernia, the patient first undergoes a medical examination, then he is sent for the following diagnostic methods:
- X-ray examination. A good examination method that allows you to see the relief of the surfaces of the internal digestive organs. To carry it out, you need to take a contrast agent, which improves visualization. X-ray images show the displacement of organs and the degree of development of the pathology.
- Fibroesophagogastroscopy. Helps in examining the mucous membrane of the digestive tract for peptic ulcers, erosions, scars and other damage.
- Ultrasonography. Using this method, doctors detect various defects of the diaphragm and displacement of organs.
- CT scan. An effective diagnostic method that allows you to accurately determine the volume of the defect, the contents of the hernia, as well as assess the blood flow in the affected area and the stage of development of the disease.
Based on the examination results, treatment tactics for hiatal hernia are prescribed.
Special breathing exercises
Another way to treat a hernia without surgery is to regularly perform special breathing exercises and movements – breathing exercises.
Many doctors believe in this method of treating hiatal hernia without surgery and recommend performing gymnastic breathing exercises with the patient.
MORE ABOUT: Pain in the wrist of the right and left hand: what to do, causes and treatment
Gymnastics using breathing exercises is carried out in the morning, mainly on an empty stomach. To begin with, patients need to take a position lying on their side.
After taking the position, a deep breath is taken, the stomach should be tense, after a deep breath, a deep exhalation is made, relaxing the abdominal press.
The exercise must be performed several times a day for 10 minutes.
When the body is positioned horizontally, bends in different directions; when bending the body, inhale, and when extending, exhale. This exercise can be repeated either on your knees or on your feet. A similar procedure can be performed while lying on your back.
Breathing exercise is indicated for all patients with a hiatus hernia. Simple exercises help strengthen the muscles of the diaphragm, narrowing the opening to the esophagus:
- Lying on your side, take a deep breath, strongly protruding your stomach. As you exhale, relax. After some time, the exercise becomes more difficult. After each protrusion of the abdomen, the patient needs to retract his stomach as much as possible and hold his breath, then relax.
- Sitting on a chair, take a short rhythmic breath, hold your breath, then inhale the air again, fixate again, after a few seconds slowly exhale, completely relaxing the abdominal muscles.
- Standing with your feet shoulder-width apart, inhale, turn your body to the left, and exhale to return to the starting position. Repeat the turn in the other direction.
Regular exercise will provide the desired result within a few months. Most patients report improvement.
Methods of therapy
To get rid of hiatal hernia, treatment is prescribed conservative or surgical, depending on the degree of development of the pathology.
Changing your diet and giving up bad habits
All patients diagnosed with a diaphragmatic hernia must adhere to the following healthy eating rules:
- eat in fractional ways, that is, often, but in small portions;
- do not eat food 2-3 hours before bedtime;
- do not lie down for an hour after eating;
- include more fresh fruits, vegetables, lean soups, cereals, fish and lean meat in your diet;
- exclude fried, smoked, sweet, spicy foods from the menu;
- reduce salt intake to a minimum.
Doctors also advise patients to drink a tablespoon of vegetable oil before eating.
In addition to diet, patients are advised to completely give up bad habits, namely quit smoking and drinking alcohol.
Drug therapy
For hiatal hernia, treatment without surgery is possible only in the early stages - 1-2 degrees of pathology. The purpose of using drugs is to eliminate the clinical symptoms of the disease.
To get rid of the symptoms of a hiatal hernia, the following remedies are used:
- antacids, which are designed to neutralize hydrochloric acid found in gastric juice;
- antihistamines or proton pump inhibitors, which help reduce the amount of hydrochloric acid produced;
- prokinetics, which tidy up the condition of the mucous membrane of the digestive organs, improve their motility, eliminate pain and nausea.
In addition, patients with gastric hernia are prescribed B vitamins, which help accelerate the recovery of gastrointestinal tissue.
https://youtu.be/cOJaUp6XQpQ
Exercises
Physical exercises are recommended for axial (hiatal) hiatal hernia. For patients with this type of pathology, exercise for the respiratory system and general muscle strengthening is important.
Doctors recommend the following complex:
- Sit on the floor, place your hands in the area under your ribs, bend your legs at the knees. While exhaling, bend forward, and while inhaling, press on the hypochondrium. Each time it is important to press harder, deeper.
- Stand up straight, keep your arms along your body, inhale and lean forward, sliding your hands along your thighs, then exhale and return to the original position.
- Stand up straight, raise your arms above your head, while inhaling, perform circular movements with your arms in one direction, then the other, and while exhaling, take IP.
- Get on your knees, keep your back straight, bend to the side as you inhale, and take IP as you exhale. After this, repeat the exercise in the other direction.
- Take a lying position on your back, place your hands on your stomach, inhale deeply, raising the peritoneum, and lower it as you exhale.
Rules for performing exercises for those who have a hiatal hernia:
- It is important to do gymnastics exclusively on an empty stomach;
- it is imperative to control your breathing;
- Do not lean forward too sharply;
- choose loose clothing for classes;
- Do not exercise if you experience heartburn, pain or other unpleasant sensations.
Heavy physical activity during hernia disease is strictly prohibited.
Traditional methods
When fighting a hiatal hernia, the use of alternative medicine is allowed, but only as an addition to the main treatment regimen.
For pathology, take a decoction based on the shoe. To prepare, pour a teaspoon of herbs into a glass of boiling water and let it brew for a couple of hours. The resulting drink is filtered and consumed a quarter glass three times a day.
To eliminate signs of a hiatal hernia, they also drink gooseberry infusion. It is prepared like this: a tablespoon of the dried plant is poured with half a liter of hot water and left to infuse for 2 hours. Take home medicine 4 times a day, 120 ml.
Before using traditional medicine, you should definitely consult a specialist.
Surgical intervention
At stages 3-4, the hernia is treated with surgery. At these stages of pathology development, medications no longer give a positive result; the defect in the esophagus is too large. Surgical intervention is also indicated for complications of the hiatal hernia in the stomach area.
Fundoplication is now more often performed using the Nissen method. It reduces the opening of the diaphragm using interrupted sutures, thereby saving the patient from acid from the stomach entering the esophagus, as well as from protrusion of organs into the thoracic region.
An operation is performed to remove a hiatal or other hiatal hernia using an open or endoscopic method. The last option is the most preferable, since it is less traumatic, does not require long rehabilitation, and minimizes the risk of complications and relapse of the disease.
Recipes for decoctions and tinctures from medicinal plants
Chamomile and calendula
You need to take dried chamomile and calendula flowers, pour 1 teaspoon of hot boiled water in a volume of 200 ml, and put on fire until it boils. Next, you need to infuse the prepared decoction for about 1 hour.
It should be stored at room temperature. The decoction should be used 1 teaspoon 2-3 times a day.
Liquorice root
To prepare a decoction of licorice, you need the roots of the plant, which differ by type. 2 tablespoons of ground roots are poured with boiling water in a volume of 500 ml. The decoction should be infused for 8 hours, taken 3 times a day, 1 tsp.
Dill seeds
To prepare a tincture of dill seeds, you need to take 1 teaspoon of the plant seed and add 1 glass of water. The broth must be boiled for 5 minutes. It must be used after it has cooled, no more than 3 times a day.
slippery elm
To prepare the decoction, you need to take 1 teaspoon of the plant and add 250 ml of water. Boil the broth for 3 minutes. Then you need to let it brew for about 1 hour. The decoction is used 1 glass per day.
Black Walnut
To prepare the tincture, use about 80-100 unripe nuts. Before cooking, they must be cleaned and filled with water for a period of about 1 month. The water should be changed several times a day. After soaking, the nuts should be covered with slaked lime, then soaked again for several days.
After soaking, boil for 20 minutes, then change the water and boil for 10 minutes. Next, you need to remove the nuts themselves from the broth, and continue to cook the syrup. 2 kg of sugar is added to the syrup. Cook until boiling.
To prepare the tincture, use about 80-100 unripe nuts. Before cooking, they must be cleaned and filled with water for a period of about 1 month. The water should be changed several times a day. After soaking, the nuts should be covered with slaked lime, then soaked again for several days.
After soaking, boil for 20 minutes, then change the water and boil for 10 minutes. Next, you need to remove the nuts themselves from the broth, and continue to cook the syrup. 2 kg of sugar is added to the syrup. Cook until boiling.
Rehabilitation after surgery
After surgical treatment of hiatal hernia, the body needs some time to recover. Immediately after the operation, the patient is sent to the ward, a tube is installed in the stomach, with the help of which its contents are removed.
Patients whose hiatal hernia has been removed are strictly prohibited from eating and drinking on the first day.
On the second day, saline solutions or glucose are continued to be administered through the installed probe. These funds help to activate the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
The patient is still prohibited from eating and drinking, but is already allowed to sit, stand up, and move around the room a little.
On the third day after surgery to remove an axial or other hiatal hernia, the patient can drink water, but in small quantities and only in a sitting position. The tube is removed from the stomach.
From the fourth day, patients begin to eat little by little. Preference is given to liquid and soft dishes, for example, soups, minced meat, grated vegetables and fruits.
After discharge from the hospital, doctors advise following the principles of dietary nutrition, not drinking alcoholic beverages, and not engaging in heavy physical activity.
Physiotherapy
Physical exercises are carried out to strengthen the ligamentous apparatus and muscle fibers of the diaphragm. The workout should be done on an empty stomach or a few minutes before eating.
To consolidate the result, you need to use several techniques:
- The initial position is lying on your back. The shoulder girdle should be placed on the pillow, the hands should be placed along a conventional line drawn through the center of the abdomen, and a deep breath should be taken.
When exhaling, the fingers located on the stomach must be inserted as deep as possible into the stomach, while the fingers move the stomach down into the abdominal cavity - this exercise should be repeated no more than 6 times in 1 approach;
- The initial position is sitting on a chair or any other surface.
To carry out this exercise, you need to relax as much as possible, the hand should be located under the costal arches, preferably on the right, the remaining fingers are located along the line of the abdomen, and when exhaling, the fingers are drawn into the abdominal cavity.
The exercise is very effective, as the pressure is completely directed downwards and maximum mobility of the distal parts of the digestive canal is ensured. Exercises must be repeated no more than 6 times.
According to experts, physical therapy is a very effective method of treating hiatus hernia without surgery.
Treatment of a hiatal hernia without surgery includes physical therapy aimed at strengthening the connective tissue of the diaphragm and restoring muscle tone. At the initial stages, gymnastics is carried out using simple exercises, the load increases gradually. The treatment complex includes the following exercises:
- The patient needs to lie on his back, place his fingers on the midline of the abdomen under the ribs. As you inhale, press your fingers on your stomach, trying to gently move it down and slightly to the left. The exercise is repeated 3-5 times.
- In the same position, alternately roll first to the left, then to the right side. Breathing is smooth and rhythmic.
- Get on your knees, inhale air, slowly tilt your body to the left, exhaling to return to the starting position. Repeat the movement in the opposite direction.
- Lying down, raise your bent knees and use your fingers to lightly press on the abdomen and chest area. In this position, take 10 slow breaths in and out.
- In the same starting position, arms along the body, resting on the feet, slowly raise the pelvis above the floor, tensing the muscles of the abs and buttocks. As you exhale, return to the starting position.
Complications
If you do not promptly treat a diaphragmatic hernia, negative consequences may occur.
- organ infringement. In most cases, the stomach is exposed to this phenomenon, which is why there is a risk of developing a purulent inflammatory process and even death. Patients experience abdominal pain, vomiting, hiccups, and heartburn. Injury is treated with urgent surgical intervention;
- erosion, ulcers on the surface of the digestive organs. When the stomach and esophagus remain in the hernial sac for a long time, the work of these internal organs is disrupted, the sphincter becomes weak, acidic contents enter the esophagus, resulting in the formation of defects in the intestinal mucosa;
- bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract. Often this complication occurs latently and develops as a result of ulcers and erosions. If there is hemorrhage, the patient may experience vomiting with blood.
Such consequences of the disease require immediate medical attention.
Gastric hernia - causes, symptoms, treatment without surgery, folk remedies and diet
An increase in intra-abdominal pressure can provoke mechanical damage to the esophagus. All this is accompanied by intestinal obstruction and chronic constipation. These conditions can be corrected with proper nutrition. Diet for a hiatal hernia is a very important component of conservative treatment.
Meals should be fractional. It is best to eat small meals throughout the day. Last dose 3 hours before bedtime.
Products should not irritate the walls of the esophagus and cause heartburn. It is prohibited to eat very hot and, conversely, too cold food. Foods that cause stomach upsets and bloating are excluded from the diet.
Prohibited products include:
- Fatty meat, lard;
- Bakery;
- Soy products;
- Legumes;
- Spicy, salty, smoked;
- Citrus fruits, sour apples, cabbage, raw beets;
- Coarse porridge;
- Nuts and seeds;
- Black bread;
- Seasonings, spices;
- Chocolate;
- Carbonated drinks;
For hiatal hernia, the following are recommended:
- Dairy products;
- Vegetable soups;
- Boiled fish;
- Light porridges;
- Lean meat;
- Fresh vegetables and fruits (pears, peaches, bananas).
A therapeutic diet and following a diet have a positive effect on the well-being and condition of the patient. The risk of developing complications dangerous to health is significantly reduced.
Esophageal hernia: symptoms and causes of the disease, treatment methods
Diseases of the digestive system affect from 30 to 55% of the population of developed countries. Most people know firsthand what gastritis and colitis are. But we do not often encounter such a disease as a hiatal hernia, the symptoms and causes of which will be discussed below.
A natural interest immediately arises - what is it, and why is the pathology dangerous? A diaphragmatic, otherwise hiatal, hernia is formed when the cardiac part of the esophagus or the fundus of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragmatic ring. A distinction is made between sliding (axial) and fixed formations; in addition, the pathology is classified according to the stage of development.
Treatment is selected based on the complexity of the process and the risk of complications. What does such a diagnosis mean for a person, how does his life change and what are the consequences?
To clearly answer what a hiatal hernia is, you should remember human anatomy. The esophageal tube is a hollow organ 25–30 cm long; when connected to the stomach, it passes through a special opening in the diaphragmatic bridge, which divides it into the thoracic and abdominal sections.
The diaphragm is essentially a muscular transverse partition that participates in the act of breathing due to the pressure difference created in the intra-abdominal space.
The esophageal tube, large blood vessels and nerve trunks run through the opening of the diaphragm.
When the ring is overstretched and weakened, the following protrudes into the chest cavity: the lower part of the esophagus along with the sphincter, the fundus of the stomach, and other organs. The occurrence of such a protrusion is called a hernia.
The disease is classified in ICD 10 as K 44.0 - patent hernia and K 44.9 - hernia with obstructed patency. The next question is how to treat the emerging pathology depends on the severity of the disease, which means that correct diagnosis plays an important role.
What causes hiatal hernia and is there effective prevention of the disease? Often the pathology has a hereditary predisposition.
In other cases, the development of the disease is caused by:
- Weakness of the diaphragmatic ligaments, thinning of the fatty and connective tissue layer under the diaphragm. Observed: in untrained adults who lead a sedentary lifestyle, as age-related changes.
- Prolonged or sudden increase in intra-abdominal pressure. Occurs during pregnancy, persistent cough due to obstruction, chronic constipation, and heavy lifting.
- The cause of a hiatal hernia is surgical intervention for pathologies of the upper digestive tract.
- Injuries to the chest and abdomen.
In childhood, the causes of the development of the disease lie in abnormalities of intrauterine formation. Then the symptoms appear in the first months of the child’s life, and surgical treatment methods are used to eliminate the problem.
Symptoms and signs of a hiatal hernia, as well as the intensity of manifestations, are determined by the size of the formation. At the initial stages, the clinical picture of the disease is completely absent or manifests itself sporadically in the form of reflux.
As a rule, the symptoms of a hiatal hernia are attributed to other pathologies of the digestive tract or associated with dietary errors:
- The main symptom of the pathology is heartburn. It appears immediately after eating food, when lying down for a long time, after physical activity with bending over. Frequent attacks of heartburn cause the development of esophagitis - inflammation of the esophageal mucosa.
- Pain localized in the retrosternal or epigastric region is another characteristic symptom. In some cases, it is impossible to clearly determine where the pain is, since the sensations are of a girdling nature.
- Air belching and a feeling of fullness in the hypochondrium are recorded in 70% of cases.
- Dysphagia is a disorder of the act of swallowing, heaviness and the presence of a “coma” in the esophagus - this is a consequence of a violation of the patency of the esophageal tube and a food bolus getting stuck in the place of compression of the organs.
More rare symptoms include: nonproductive cough, obsessive hiccups, hoarseness, shortness of breath.
Not all of the listed symptoms are observed in one person. With a fixed hiatal hernia, the prevailing symptom is pain. The pain may occur in the chest area, in the epigastric region, or radiate to the lower back, under the scapula, or into the intercostal area. Nature of pain:
- aching;
- spastic;
- cutting.
Sometimes such sensations are confused with an attack of angina.
A sliding hernia has its own characteristic symptom - heartburn, and the accompanying esophageal disease. In the initial stage, such attacks are easily eliminated with antacids. Subsequently, dysphagia and difficulty passing liquid and semi-solid food occurs.
What is dangerous about a hiatal hernia is its complications:
- strangulation - compression of the hernial sac by the diaphragmatic ring, which stops the blood supply and leads to tissue necrosis;
- development of the inflammatory process in surrounding tissues.
Also, a hiatal hernia is dangerous due to the gradual formation of respiratory and heart failure.
Classification
Hiatal hernias are divided into types according to the type of formation, the following are distinguished:
- Axial (wandering) - this sliding formation is represented by 90% of the total number of requests. They are characterized by free penetration of the cardiac portion of the esophagus and the upper parts of the stomach into the diaphragmatic ring and the chest cavity. When the position of the body changes, the organs return just as easily.
- A fixed hernia (paraesophageal) is distinguished by static localization and exit of the upper parts of the stomach into the supradiaphragmatic region. It is this type that often causes complications in the form of pinching.
- Mixed.
Based on the degree of expansion of the diaphragmatic ring and the volume of the hernial sac, pathology is distinguished:
- 1st degree - the cardiac sphincter of the esophagus and the body of the stomach are adjacent to the diaphragm, and only the abdominal section of the esophageal tube is compressed in the ring.
- Grade 2 – both the lower sphincter and the apex of the stomach penetrate the esophageal opening of the diaphragm.
- Grade 3 – complete entry of the stomach into the supradiaphragmatic zone, sometimes part of the small intestine also penetrates there.
Diagnostics
To understand how to diagnose a disease and which examination method to choose, the doctor begins by interviewing the patient. Symptoms of the disease are often blurred; people treat other organs for a long time and to no avail. Standard examination methods make it possible to identify the disease itself, accompanying pathologies, and determine the degree of development of the disease:
- Radiography using radiation-contrasting barium sulfate. Gives an idea of the state of the digestive tract along its entire length, determines the presence of a hernial sac and its location.
- Ultrasound allows you to assess the level of development of pathology. Determines the degree of involvement of neighboring organs, the size and type of hernial formation.
- FGDS - endoscopic diagnostics allows you to visually assess the situation, determine what the esophageal mucosa looks like, and how much the organ has suffered from compression.
In addition, the diagnosis of a hernia includes laboratory tests, biochemical tests and an analysis of the acidity of gastric juice.
Treatment methods
There are two directions in the fight against hiatal hernia: surgery or medical treatment. The choice depends on the severity of the pathology. Conservative therapy is justified for small lesions and mild symptoms. In other situations, surgical intervention is used:
- Nissen fundoplication is the formation of a “cuff” around the esophageal sphincter in the upper third of the stomach, lowering the organs into the abdominal cavity and suturing the diaphragmatic ring.
- Surgical intervention according to Belsey is used for grade 3 hernial pathology, when there is a large hernial ligament. It is performed through an open thoracic approach; fixing sutures are applied to stabilize the position of the esophagus and stomach relative to the diaphragm.
- Laparoscopy is a low-traumatic method, in which access is carried out through punctures in the abdominal wall.