General information about pathology
A tooth abscess is an inflammation of the pulp and periodontal tissues, characterized by the presence of a purulent sac located in the periodontium or ligamentous apparatus. That is, it is based at the tops of the tooth roots. May become chronic.
If left untreated, the infection affects the jaw bones, neck and facial muscles. Severe cases, especially without medical intervention, can lead to death due to intoxication. To minimize the consequences and speed up the recovery process, you should definitely consult a doctor. Later in the article we will tell you how to recognize the signs of an abscess and what to do next.
Important! Many patients confuse an abscess and a gumboil (the official name is “odontogenic periostitis”). These inflammations have similar symptoms and pose health risks, but the abscess affects deeper tissues.
What to remember:
- Do not open the inflamed area yourself, this can lead to unpredictable consequences (blood poisoning, penetration of pus into the walls of the vessel).
- An abscess is a purulent disease, so at the first suspicion you need to contact a surgeon to open the lesion.
- For preventive purposes and to avoid abscess after injections, as well as complications from diseases such as boils, carbuncles, follow the rules of personal hygiene, take vitamins (“Multi-tabs”, “Alphabet”).
- Drink Ribomunil, a powerful immunomodulator. It allows you to quickly strengthen the immune system.
- Do not delay treatment of infection, otherwise this will lead to metastatic (purulent) abscesses and inflammation of the lymph nodes.
The main causes of an abscess
The main factor in the occurrence of inflammation is pathogenic microorganisms that produce pus in the process of vital activity. Microbes are able to enter the tissues of the oral cavity through the teeth and gums, and through other organs - with the bloodstream.
Reasons that provoke the appearance of the disease:
- caries, microcracks and enamel chips: bacteria enter the pulp through the crown, and then go beyond the boundaries of the tooth,
- poor oral hygiene: the accumulation of bacterial plaque stones greatly increases the likelihood of inflammation in the gum pockets,
- diseases and injuries of the gums: gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease,
- poor-quality treatment and illiterate administration of anesthesia: untreated canals and non-compliance with antiseptic rules lead to tissue infection,
- chronic diseases of the ENT organs,
- viral and bacterial diseases of the body: ARVI, sinusitis, tonsillitis, etc. weaken the immune system. This also includes neoplasms and diabetes.
Causes
An abscess is the body's defense against infection. Our immunity creates a capsule that contains purulent inflammation in one place and does not allow it to spread further to healthy areas of the skin.
Causes of occurrence include:
- Violation of skin integrity (cuts, scratches, open fractures, burns).
- Previous infections (pneumonia, tuberculosis).
- Non-sterile medical instruments.
- Poor quality injection (shot).
- Chronic diseases (dermatitis, eczema, pharyngitis).
- Diabetes.
Symptoms of a tooth abscess
Experts distinguish several types of inflammation - acute, moderate and chronic. Their symptoms differ from each other only in the severity of their manifestation. The most pronounced form is an acute abscess, and the weakest symptoms are present in a chronic one.
The occurrence of the following symptoms should be an incentive to contact the clinic as soon as possible:
- the appearance of a purulent sac or ulcer above the tooth,
- swelling, hyperemia of the gums, hardening of soft tissues, facial asymmetry,
- reaction to cold and hot food, drinks,
- sharp or aching pain in the tooth,
- increased body temperature, poor health and headache,
- enlarged lymph nodes in the neck,
- bitter taste, unpleasant odor from the mouth.
Need to know! Gradually, the symptoms of the abscess become weaker, and the abscess can break through - the person will feel better. But this does not mean that the disease has passed. On the contrary, this is a signal of necrotic changes in the root tips (necrosis) and the risk of extensive spread of infection.
Kinds
Doctors distinguish several types of purulent inflammation (abscess). Depending on the location, they distinguish:
- Soft tissue infection. It is characterized by swelling, purulent inflammation and pain.
- Peritonsillar (near almond) appearance. This is an inflammation of the tissue that surrounds the palatine tonsils.
- Pulmonary. Nonspecific pneumonia.
- Post-injection. Limited soft tissue inflammation after injections.
- Brain infection. Accumulation of purulent fluid in the skull due to the development of infection (staphylococcus, streptococcus, toxoplasma, E. coli, anaerobic bacteria).
Wherever an abscess forms, it requires immediate treatment and surgery.
What are the types and forms of abscess?
In addition to classifying inflammation according to the severity of symptoms (discussed above), dentists distinguish types of abscess according to the site of occurrence - these are gingival, periodontal and periapical. Let's look at them in more detail.
Gingival type
The capsule with purulent contents is localized in the soft tissues of the gums. The inflammatory process does not affect the ligamentous apparatus and spongy substance of the jaw bone. The disease can begin abruptly - the site of a gingival abscess is accompanied by swelling, redness and a painful reaction. The help of a dental surgeon is required. And if the patient delays treatment, then purulent exudate begins to leak from the ulcer.
Periapical type
Sometimes a chip of an old filling or poor cleaning of the dental canals leads to infection in the pulp - where inflammation begins. Then the process flows into the deep tissues, and infection of the bone and surrounding soft tissues is possible. The patient may feel aching or sharp pain. This type is called a periapical abscess, that is, one that is localized near the apex of the tooth.
Periodontal type
The periodontal type is characterized by the appearance of a focus of inflammation deep in the tissues of the periodontal pocket. The initial stage of the process is sluggish, but over time the infection spreads to the roots of the tooth, causing necrosis of the apexes. The ligamentous apparatus weakens, therefore, the tooth begins to loosen. As inflammation grows, the patient experiences increased pain and swelling in the problem area.
Purulent contents leak from the periodontal pocket, which can infect neighboring teeth (if they are damaged) and also enter the gastrointestinal tract. The patient feels general malaise. The temperature rises and the head hurts. Unlike the previous one, inflammation begins from the gums and does not penetrate through the tooth.
Diagnosis of an abscess
Superficially located soft tissue abscesses do not cause diagnostic difficulties. With a deeper location, it may be necessary to perform an ultrasound and/or diagnostic puncture. The material obtained during puncture is sent for bacteriological examination, which allows identifying the causative agent of the disease and determining its sensitivity to antibiotics.
Oropharyngeal abscesses are identified during an otolaryngological examination.
Abscesses can occur as an independent disease, but more often they are a complication of some other pathology. For example, pneumonia can be complicated by a lung abscess, and purulent tonsillitis can be complicated by a peritonsillar abscess.
Diagnosis of abscesses of the brain, abdominal cavity, and lungs is much more difficult. In this case, an instrumental examination is carried out, which may include:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal and pelvic organs;
- magnetic resonance or computed tomography;
- radiography.
If the abscess is deep, an ultrasound and diagnostic puncture are performed.
In a general blood test, at any location of the abscess, signs characteristic of an acute inflammatory process are determined (increased number of leukocytes, shift of the leukocyte formula to the left, increase in ESR).
Diagnosis of the pathological process
In most cases, a specialist needs only a visual examination and medical history to make a diagnosis. After all, the main symptoms - abscess and swelling - are clearly expressed. However, to correctly assess the localization and volume of the inflammation, the degree of its spread through the soft tissues (especially with a long-term and indolent abscess), the dentist will need to study the results of X-ray diagnostics, cytology (assessment of the condition of the cells in the inflamed area), and a general blood test.
Important! Before visiting a doctor, you should not take aspirin or medications to relieve pain - this may lead to an incorrect diagnosis. Any heating of the sore spot is also prohibited - heat dilates blood vessels and there is a risk of spreading infection through the bloodstream.
Question answer
What complications does an abscess cause?
Untimely treatment can lead to complications such as lymphadenitis (inflammatory damage to the lymph nodes), blood poisoning, metastatic abscesses (most often occurring in the eye).
Can an abscess be treated without surgery?
No, an abscess is a purulent infectious disease. Therefore, surgical opening is necessary.
What to do in case of recurrent abscess?
Go through a full examination, take a general blood test, and, if necessary, culture (pus to the laboratory). Go to the hospital for repeated surgery.
How to distinguish an abscess from a tumor?
In appearance, an abscess resembles a tumor, and it can develop from a tumor. But its contents are purulent. The disease is accompanied by pain, fever, and general deterioration of the condition.
Why does purulent infection occur?
Decreased immunity, the occurrence of injuries, cuts, burns, unsterile medical instruments, poor-quality injection (injection) are the causes of an abscess. Leukocytes rush to places where pathogenic (disease-causing) microorganisms accumulate. Having fulfilled their protective functions, they die, forming a purulent capsule around harmful bacteria.
Treatment of the disease
The choice of treatment protocol is made after assessing the patient’s condition and determining the type of abscess. It is worth remembering that any inflammation in the oral cavity is a serious reason to refuse treatment at home and be sure to make an appointment with a dentist.
Therapeutic methods
The therapy is used for mild and moderate forms of inflammation. The dentist cleans the canals and pulp, and the purulent contents are removed through the tips of the roots. Then the filling material is installed and the tooth is covered with a crown. But this is not the end of the treatment. The doctor prescribes medications to reduce swelling and neutralize pathogens. Read on - we'll tell you about the most popular medications.
Surgical intervention
It happens that therapy does not bring the desired result due to the extent of the lesion. In this case, the surgeon will install a special drainage on the gum. This measure is necessary to remove all the pus. The tooth extraction procedure is used in cases of severe root necrosis and extensive pulp damage by infection.
With the gingival type of inflammation, the surgeon opens the abscess by making an incision in the mucous membrane and cleans the cavity. Drainage may again be installed for a few days.
An acute form of inflammation, accompanied by severe swelling, is a 100% case when the help of a surgeon is urgently required. After all, an abscess can break through not into the oral cavity, which is easy to clean, but inside the body. Thus, pus can travel to the carotid artery, trachea, or brain - infecting these vital organs. And if it enters the circulatory system, death due to sepsis is possible.
“Last year my cheek started to swell - I thought some midge had bitten me at the dacha. And the next day a hard lump appeared in this place, one side of the mouth also became swollen and red. I rinsed with baking soda all weekend, but it didn’t help. But the temperature jumped and it started to hurt. I made an appointment with the doctor. It turned out that I had an abscess and the tooth needed to be removed and everything cleaned out. The doctor said that a couple more days and I would have ended up in the hospital.”
Sergey P., review from the dental forum
Treatment
Regardless of the location of the infection, the affected area is opened. The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis (where you periodically come to the hospital for treatment and procedures). In severe cases (abscesses of internal organs, head, face), the patient is hospitalized in a hospital. The surgeon cleans the opened area of pus and treats the wound with an antiseptic (70% alcohol).
If the abscess affects internal organs, for example, the liver, lungs, then a puncture is performed. Pus is pumped out of the organ, and antibiotics are administered (“Cefazolin”, “Gentamicin”, “Kanamycin”).
Good to know! The extreme stage of surgical intervention for chronic abscesses is removal of the organ along with the abscess.
After the abscess is opened and cleared of pus, medication, increased nutrition, and blood transfusions (if necessary) are prescribed.
Antibiotics
To treat and speed up healing of the wound, use effective remedies - oral medications or injections, ointments. Pre-treat the wound, apply ointment and give an injection.
Treatment with antibiotics allows you to kill harmful (pathogenic) microorganisms and promotes rapid recovery of the body.
"Cefazolin" injections
Actively fights staphylococci and streptococci. Destroys them quickly. 1st generation antibiotic. Price at the pharmacy - 1.0 g. bottle 15 rubles.
Result: Kills staphylococcus and streptococcus bacteria, speeds up the healing process.
“Ampiox Sodium”
Antibacterial drug, active against gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. Price from 20 rubles.
Result: Kills bacteria resistant to penicillin (staphylococcus, streptococcus, enterococcus). Promotes speedy wound healing.
“Tetracycline Akos” ointment for external use
Biostatic antibiotic of the tetracycline group. It has a wide spectrum of action, fights gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria (staphylococci, streptococci). Price at the pharmacy from 25 rubles.
How to use: After pre-treating the wound (with 70% alcohol), apply the ointment to a gauze bandage and apply to the sore spot. Change the dressing every 12 hours. The course of treatment is 3 weeks.
Result: Accelerates the regeneration (healing) process, kills pathogens. After the first application you will feel relief (the pain will stop). The wound will gradually heal and the skin will recover.
After watching the video with Elena Malysheva, you will learn what you need to know about antibiotics if you had to take them. And what can they not be combined with?
Ointments for rapid wound healing
We have prepared a list of inexpensive, effective ointments that promote rapid regeneration (healing, restoration) of the skin after an abscess.
"Eplan"
It has an analgesic and wound healing agent. Not an antibiotic. Price at the pharmacy from 180 rubles.
How to use: Place a gauze bandage soaked in ointment on the damaged surface. Bandage it. Change the bandage once a day. Continue this procedure until complete recovery. The drug has no contraindications or side effects.
Result: Relieves swelling and itching, prevents infection, accelerates the process of healing and regeneration (restoration) of the skin.
Ointment “Ichthyol”
Anti-inflammatory and analgesic ointment. Has no side effects. The price in pharmacy chains is from 65 rubles.
How to use: Apply the ointment to a gauze bandage and apply to the sore area. Change the bandage 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 14 days.
Result: Relieves inflammation and soothes the wound. Promotes speedy recovery and healing.
Pharmacological solutions
Using solutions you can treat a wound after an abscess. The products can relieve inflammation and numb the wound.
Dimexide solution
Has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. Treats the wound well. The price in pharmacy chains is 39 rubles.
How to use: Treat the wound 2 - 3 times a day before applying the ointment.
Result: Allows relief from pain and inflammation, protects the wound from penetration of microorganisms (staphylococci, streptococci). Increases skin sensitivity to other medications.
“Dioxidin” (solution)
A powerful antiseptic that quickly kills streptococci and staphylococci. Price at the pharmacy - from 40 rubles.
Interesting to know! In Soviet medicine, the drug enjoyed great success. It was used in all purulent surgery hospitals. Doctors attributed the success of the drug “Dioxidin” to its high effectiveness in the fight against various microorganisms (gram-positive and gram-negative).
How to use: Treat the wound 2 - 3 times a day. Let the solution soak in, then apply antibacterial ointment (“Tetracycline”).
Result: Quickly destroys bacteria, has an antibacterial, anti-inflammatory effect. Promotes faster healing.
Drugs that relieve inflammation, pain and swelling
After going to the dentist, treatment does not end - because for a complete recovery it is necessary to get rid of pathogens. For this, the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics, and sometimes a complex. Usually, for inflammation in the oral cavity, metronidazole, amoxicillin, azithromycin and their analogs are taken.
To relieve swelling, antihistamines are prescribed - Suprastin, Loratadine, cetirizine-based drugs.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Ketorol, Ibuprofen, Nise - will help cope with pain.
For the first 12 hours, a cold compress is applied to the cheek. Rinses are often prescribed - with a solution of furatsilin or soda and salt.
Traditional methods
At home you can fight the disease (abscess). Traditional methods of treatment, used in combination with medical ones, allow wounds to heal faster after opening.
We have selected for you the most effective folk methods of treating purulent inflammation.
“Sodium chloride” (hypertonic salt solution)
Physiotherapeutic drug. To treat the wound, use a 0.9% solution, which can be prepared at home.
Ingredients:
- Medium ground table salt - 9 gr.
- Warm water - 1 liter.
How to prepare: Pour salt into warm water, stir until the crystals are completely dissolved. You should get a salty, cloudy liquid.
How to use: Treat the affected area with the solution 2 - 3 times a day before applying ointments. Use until complete recovery and healing of the wound.
Result: Draws in purulent fluids and also draws out pathogenic microbes (staphylococci, streptococci). Promotes speedy wound healing.
Aloe
A bactericidal plant that can destroy the causative agent of the disease (Staphylococcus aureus). To achieve maximum effect, use the plant correctly.
How to use: Wash the aloe leaf, cut it in half (along the leaf). Apply to the painful area. Secure with adhesive tape. To enhance the antibacterial effect, you can drop a drop of iodine onto the cut leaf. Change the sheet every 2 - 3 hours. Use until completely healed.
Result: Destroys bacteria, draws pus from the wound. Accelerates the process of skin regeneration (healing).
Horseradish root
One of the most powerful natural antibiotics. It is used to treat purulent wounds. Treat purulent wounds with horseradish tincture and make rinsing solutions.
Ingredients:
- Chopped horseradish root - 1 tbsp. spoon.
- Water - 200 ml.
How to prepare: Pour hot boiled water over the root. Leave in the thermos for no more than one hour.
How to use: Treat the wound 3 times during the day. Complete the procedure for 14 days until the wound is completely healed.
Result: Promotes rapid healing of the infected area, kills pathogenic microbes (staphylococcus, streptococcus).
Folk remedies for relieving inflammation
Traditional medicine, antibiotics and herbal medicine should in no way be used as an unauthorized remedy for the treatment of an abscess. And if the patient thinks: “here, my cheek is swollen, I probably have a flux, I’ll rinse with soda” - then such self-medication can lead to life-threatening conditions. The dentist will help you decide what to choose from traditional medicine and how often to do the procedures.
Popular rinses are decoction and infusion of sage, eucalyptus, chamomile, and propolis. Compresses and lotions made from aloe or gruel from raw potatoes help.
What is an abscess?
A skin abscess is an inflammatory phenomenon that affects human soft tissue and is accompanied by the formation of pus. An abscess after recently performed surgical procedures due to complications can occur quite often. This is an infection located in the cells of the epidermis, which first manifests itself in the form of redness. Over time, the affected area of the body hardens, and then the abscess softens, forming a capsule with purulent accumulations.
Important! Pus is a combination of leukocytes, protein and other cells whose functionality includes isolating infectious processes.
Abscess photo
The disease occurs equally often regardless of a person’s gender and age. For men, skin lesions are more common, localized in the head and neck areas, as well as on the extremities and perirectal area. In women, abscesses of the axillary, vulvovaginal and perirectal location are more common.
Types of abscesses
All diseases have several types of clinical manifestations. Abscess is no exception.
The disease is divided into the following types:
- Purulent inflammation of the lymph nodes. Usually occur in childhood, manifesting itself in the cervical lymph nodes. A similar problem occurs due to infection of the tonsils. This disease also accompanies tuberculosis of the lymph nodes.
- Suppuration of the mammary glands against the background of cracked nipples during breastfeeding.
- Abscesses of internal organs (kidneys, lung abscess, liver, etc.).
- Cold type. Purulent accumulations are concentrated in a separate limited area. In this case, no pronounced symptoms, such as fever, excessive redness of the skin or pain, are observed.
- Swelling abscesses are an accumulation of pus with no signs of acute inflammatory reactions. A similar phenomenon is observed in tuberculosis of the joints and bones.
- Periodontal abscess.
- Panaritiums, boils and carbuncles, boils - all this is also equated to abscesses.
- Subphrenic purulent accumulations of the peritoneum, concentrated under the diaphragm. Often accompanied by gas formation. The disease manifests itself due to complications after pancreatitis, appendicitis, as well as ulcerations of the gastrointestinal tract.
- A post-injection abscess occurs when the area where the injection was made becomes suppurated.
Abscess
An abscess is a serious problem that can create an imbalance in a person’s normal life and health. Therefore, if they occur, you must immediately contact a specialist.
Lung abscess
This abscess usually occurs after focal pneumonia. The development of an abscess is also possible after foreign bodies penetrate into the lung. Such an impact can cause blockage of the bronchus, resulting in an airless space and the development of an abscess.
A lung abscess often develops when the body’s immunity is reduced, in old age, or in childhood. Bacteria from any suppuration in the body can be transferred by blood to the lungs, which provokes the development of the disease.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a lung abscess may vary depending on the condition of the abscess. Before the abscess ruptures, the patient is in serious condition and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- accumulation of pus in the lungs;
- increased body temperature;
- increased sweating;
- no appetite;
- breathing is difficult.
After the abscess breaks through, the condition improves significantly and everything gradually returns to normal. However, until all the purulent sputum comes out of the lung, the patient is accompanied by a cough.
Throat abscess
A throat abscess can occur both from mechanical damage and as a result of various complications of throat diseases - for example, lacunar or follicular sore throat. This problem can also be caused by chronic inflammation of the nasal cavity, ears and throat.
Throat abscess, photo
This abscess is characterized by symptoms similar to a sore throat - the tonsils are swollen, breathing worsens, and a sore throat.
Specifics of inflammation after removal of figure eights
A wisdom tooth abscess most often appears as a result of improper removal of the figure eight. The reason for this is the surgeon’s insufficient qualifications or his careless attitude towards the operation. It is important to extract all roots and not introduce infection into soft or bone tissue. In most cases, antibacterial drugs are prescribed to prevent inflammation. Most often, patients are afraid of complications after extraction of impacted and dystopic wisdom teeth and strive to find an experienced dentist for this operation.
Possible complications
Undesirable consequences can develop even after treatment, which is why it is so important to strictly follow all instructions and prescriptions of the specialist. If you put off going to the doctor for too long, you may encounter serious complications:
- damage to the bone tissue of the jaw with the risk of further spread of infection throughout the body and the development of general intoxication of the body,
- pneumonia and other pathologies of the respiratory system,
- meningitis – develops against the background of a long course of the disease,
- formation of a fistula with constant discharge of pus, which is fraught with dangerous infectious complications,
- inflammation of the bone and brain, osteomyelitis in later stages.
This is what a fistula on the gum looks like.
Tooth loss occurs in advanced stages of pathology. As a result, the risk of facial deformity, sepsis, and serious systemic diseases increases.
Possible complications - what will happen if the pathology is not treated
Delay in treatment can cause serious complications, some of which can lead to disability or death. Among the main ones are tooth loss, phlegmon of the maxillofacial area, meningitis, pneumonia, sepsis, fistula in the oral cavity.
Purulent inflammation of a baby tooth is especially dangerous. Children do not always pay attention to mild pain in the mouth. Therefore, stomatitis and gingivitis at a young age are often diagnosed late. Therapy and surgical treatment of inflammation are often complicated by the little patient’s fear of pain - and, as a result, the inability to carefully carry out manipulations.
Parents should be attentive to their child's complaints of pain. After all, in order to form a correct bite, it is important to treat dental diseases in a timely manner.
Symptoms
It is worth noting that an abscess is a complex infectious disease. It occurs in an acute form, with severe pain and fever. It can occur anywhere on the human body. But purulent inflammations on the face and head are especially dangerous.
The infection can be recognized by its characteristic external symptoms:
- Redness of the affected area.
- Temperature rises to 39 - 40°C.
- Tumor.
- General weakness.
- Pain in the inflamed area.
- Decreased appetite.
The disease causes discomfort and acute pain to the patient. Therefore, immediate medical attention is required.
What is a boil
A furuncle is a purulent inflammation of the hair follicle.
The immediate cause of the development of the pathological process is staphylococcus - a conditionally pathogenic microorganism that is normally present on the surface of the skin, but under certain conditions penetrates its layers, causing inflammation.
Factors contributing to the development of a boil are:
- skin microtraumas;
- violations of personal hygiene rules;
- lack of vitamins in the body;
- diabetes;
- endocrine system disorders;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- chronic dermatological diseases;
- decrease in the body's defenses.
A boil in the groin and labia can occur not only due to poor hygiene and other aforementioned factors, but also due to wearing underwear made of synthetic fabrics or the wrong size (as a result of constant rubbing of the skin).
A furuncle in the armpit most often occurs in the fair sex after frequent hair removal and depilation in this area. The development of inflammation is promoted by the use of antiperspirants. Inflammation under the armpit in men is most often caused by increased sweating and neglect of personal hygiene.
The process of inflammation development is as follows: first, a cone-shaped nodule appears on the skin, around which there is redness and slight swelling; after 1-2 days, a rod forms at the top of the nodule - a purulent whitish-gray formation.
At this moment, it is strictly forbidden to open or remove the boil on your own - the released pus promotes the spread of the pathogen to neighboring tissues, in addition, the infection penetrates deeper through the open lesion, which can lead to more serious consequences, including blood poisoning.
The final stage of development is the breakthrough of the boil and the leakage of pus onto the surface of the skin. An ulcer forms at the site of the breakthrough, which heals over time.
Typical places for a boil to develop are: the skin of the neck, face, and groin area. The appearance of several boils in different places is called furunculosis .
Diagnostics
The doctor makes the final verdict after examining the patient and listening to complaints. Diagnosis of an acute abscess located on the surface is not difficult. Foci hidden in deep layers are more difficult to detect. To identify pathology, use:
- radiography;
- ultrasound;
- CT;
- MRI;
- general blood analysis;
- biochemical research.
The basis for establishing an accurate diagnosis are the results of tests and instrumental studies.
An abscess is...
In simple terms, an abscess is an abscess in the form of a local accumulation of pus enclosed in a capsule. The development of an abscess is caused by acute or chronic local infections, leading to tissue destruction at the site of the infectious lesion.
Purulent exudate (liquid) contains pathogenic microorganisms (causing diseases) that provoke an inflammatory reaction; products of tissue breakdown and metabolism of the pathogen, various protein fractions of the blood.
The development of abscesses manifests itself in acute and chronic clinical manifestations.
- In the acute course of the disease, a purulent process develops in the cavity of a single-layer tissue capsule. At the beginning of the process, it has the appearance of an inflammatory demarcation barrier, consisting of leukocytes - defenders of immune phagocytosis, striving from all corners of the body to the inflammatory focus. Over time, young granulation tissue with an extensive vascular network is formed.
- The clinic of the chronic course of an abscess is characterized by the presence of a two-layer capsule, consisting of an internal granulation layer and an external one, in the form of mature connective tissue, formed as a result of a protracted inflammatory reaction in the tissues.
Abscess prevention
To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to carefully monitor compliance with antiseptic rules during and after medical procedures, and promptly seek help from a medical institution if you suspect the development of purulent inflammation. If you have chronic infections, you should carefully follow the treatment plan prescribed by your doctor. Everyone should know what an abscess is and what an abscess looks like in order to promptly suspect that they have one and call a doctor.
Complications of an abscess
With adequate treatment, the outcome of the disease is favorable. Failure to promptly seek medical help or an incorrect diagnosis can lead to serious consequences . The severity of complications and the risk of their development is determined by the location of the abscess, the causative agent of the infection, and the state of the immune system. Brain damage always has a serious prognosis. About 10% of cases are fatal, while 50% of patients experience permanent disability. In addition, a purulent abscess can provoke:
- gangrene;
- infectious-toxic shock;
- complete or partial loss of functionality of the affected organ;
- sepsis;
- phlegmon;
- neuritis;
- purulent meningitis;
- peritonitis;
- pleural empyema.
Rapid maturation of abscess
To speed up the maturation of abscesses, folk experience recommends the following remedies:
- Onion patch. Take 2 parts of baked onion and 1 part of grated soap. Mix the ingredients well. Prepare a plaster from the mixture and apply it to the sore spot. Change the patch several times a day. Helps to quickly ripen and clear abscesses.
- Onion compress. Baked onions without adding soap are also a traditional remedy for speeding up the ripening of an abscess. The onion is cut in half, baked in a frying pan and applied to the sore spot for several hours, replacing the bandage with a new one.
- Aloe compress. Crush an aloe leaf (agave), put it on the sore spot and bandage it. Change the bandage after 7-8 hours. The compress helps the abscess ripen and draw out pus.
- Onion-milk compress. To speed up the maturation of abscesses, use onion pulp with milk. Compresses are made from the mixture.
- Beetroot compresses. When an abscess has just appeared, it is recommended to apply grated fresh beets to it. In this case, the abscess will either resolve or mature. You can also add a mixture of grated raw beets and sour cream.
- Alder compresses. Fresh leaves of sticky alder (or black) are applied to abscesses to accelerate ripening.
- Bread lotions. Apply a crumb of black bread or a crust of stale rye bread, soaked in hot milk, to the abscesses to speed up their maturation, change the lotions every 2-3 hours.
- Bean compresses. Make a paste or thick dough from bean flour and apply it to the abscesses for several hours to speed up their maturation.
Causes
The main reason for the development of an abscess is bacteria and viruses that penetrate the tissues and organs of the body. The most common pathogens of purulent lesions are streptococci and staphylococci. The ways in which bacteria spread are varied:
- Penetration of microorganisms through lesions on the skin. A small scratch or wound is enough for an abscess to develop. In this case, a simple subcutaneous abscess develops.
- The development of purulent inflammation as a complication of another pathology. A boil or small abscess on the skin under certain circumstances (for example, a large microbial load) can gradually transform into a lesion with pus or into phlegmon.
- Chronic infections and disruption of natural microflora. Sore throat or tonsillitis pose a risk of developing a disease such as purulent lung damage.
- Often, a purulent abscess appears after various types of medical procedures. This may be due to poor quality sterilization of instruments or medications, violation of the integrity of aseptic dressings, or the presence of infections among personnel.
Abscess stages
The pathological process is divided into two stages: development and breakthrough. In a situation where the purulent abscess is chronic, the second stage is absent. In this case, it is replaced by a stage of arbitrary change in the structure of the tissue. The duration of the first stage varies. A breakthrough of the abscess, or spontaneous release of exudate from the cavity, is accompanied by an improvement in the patient’s condition. Physiologically, this stage lasts several days. If the abscess does not break out on its own, the capsule is opened surgically .
Causes of abscess
The formation of a skin abscess occurs due to the penetration of pathogenic microbes into the tissue. This may be a consequence of injury, dirt getting on the skin, or intense friction. In males, development occurs when shaving the armpits and face, in women - from shaving the legs or epilation and intense friction during hygiene procedures in the genital area.
The disease can develop due to cysts and festering hematomas. It can also be caused by improper administration of subcutaneous and intradermal injections.
The risk of infection increases for the following local reasons:
- Excessive sweating;
- Overactivity of the sebaceous glands (usually caused by an increase in male hormones);
- Penetration under the skin of an object;
- Ingrown hairs.
Systemic causes provoke a weakening of the immune system:
- Long-term steroid therapy;
- Diabetes;
- Chemotherapy procedures;
- Hemodialysis in the treatment of chronic renal failure;
- HIV infection;
- Wrong diet;
- Crohn's disease;
- Hypothermia;
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis.
The main cause of an abscess is the flora present in the sebaceous and sweat glands, on the skin, particles of poisoning on the skin, in the air, and vaginal discharge. Usually it is Staphylococcus aureus. This is a very dangerous microorganism; it penetrates into the blood at high speed, and then into the organs, which is why abscesses form. Abscesses are also caused by Escherichia coli, streptococcus and the Proteus family. Most often, its development is provoked by streptococcus, staphylococcus and E. coli together.
Is it possible to cure an abscess without opening it?
Even the ancient Greek doctor Hippocrates liked to say: “where there is an abscess, there is an incision.” Since then, little has changed in the principles of abscess treatment.
Why does the abscess need to be opened? The human body is designed very wisely; it usually gets rid of everything unnecessary. If pus has accumulated somewhere, this indicates that natural mechanisms were ineffective. The body does not know how to remove it. In this case, the cavity with pus becomes like a time bomb. Pathogenic microbes can spread beyond the abscess, sometimes leading to severe complications, including sepsis.
The best solution in this situation is to release the pus through the incision. As a rule, after this, improvement occurs quickly and the healing process begins.
After opening the abscess, the surgeon may prescribe antibiotics, but not all patients need them.
Abscess treatment methods
When treating abscesses, the main technique is mechanical asepsis, based on centuries of experience of healers who followed the instructions of the ancient postulate - “if you find an abscess, remove the contents .”
And today, abscess therapy consists of surgically opening the purulent formation, removing the contents, draining and washing the capsular cavity. Abscesses are opened regardless of their location.
An autopsy is not performed only for cold and sinter formations formed during tuberculosis.
Surgical removal of ulcers located in internal organs is carried out using general anesthesia. Local anesthesia is used to remove superficial formations localized not deep from the surface of the skin in the soft tissue structure.
The operation is performed only at the stage of a fully formed capsule. At the infiltration stage, conservative therapy is indicated.
The operation includes: puncture of the abscess, a small incision of the capsule along the needle, removal of the contents, and after widening the incision, thorough cleaning of the cavity from necrotic masses. In severe cases, it is possible to remove the abscess along with part of the affected organ.
For further treatment, complex therapy is selected including antibacterial drugs, according to the sensitivity of the pathogen obtained during drainage and symptomatic therapy drugs.
Conservative treatment
You should not rely on self-medication. Any disease, including dermatological, requires timely assistance. By starting therapy at the initial stage of abscess development, you can prevent its breakthrough and also eliminate dangerous consequences.
At an early stage, cold treatment (compresses) is used, which promotes the resorption of the purulent mass. If this is ineffective and there are no negative changes (for example, an enlarged cavity or pronounced suppuration), heat compresses (a heating pad, etc.) are used.
In addition, the doctor prescribes antibacterial drugs, because in most cases abscesses and boils are caused by a bacterial infection. This may be systemic or local therapy. When an abscess is formed and there is extensive damage to the skin, opening and drainage of the cavity is required.
Prevention and prognosis
You can prevent the development of a purulent focus by following the rules of asepsis and antisepsis. Injections and wound treatment should be carried out by medical specialists in compliance with manipulation techniques. Injuries, wounds, damage should be examined in a timely manner and, if necessary, seek the help of a surgeon.
If the problem is stopped in a timely manner, the cause of the development of the pathology is determined and eliminated, after removal of the abscess, the prognosis for recovery is favorable. Advanced forms can cause quite serious complications, leading to intoxication, sepsis and even death.
Types of disease
An abscess is a fairly general concept; it is a process that develops in the event of infection of any tissues or organs. The infection can affect absolutely any organ of the human body. In this regard, abscesses can be classified based on their location.
One of the most famous types of abscess that develops in internal organs is appendicitis. In this case, the pathological process occurs in the blind appendix of the small intestine - the appendix. Naturally, the only way to treat purulent appendicitis is to remove it. Untimely surgical intervention can lead to rupture of the walls of the appendix and the release of purulent contents into the abdominal cavity. Subsequently, the process spreads to the peritoneum and peritonitis, an abscess of the abdominal cavity, develops quite quickly.
Another fairly common type of abscess is the well-known flux. The disease occurs as a consequence of untreated caries, when the infection gradually begins to penetrate into the deeper layers of the teeth, affecting first the dentin, then the pulp, and then the periodontium (periosteum of the tooth). It is also possible that a tooth abscess may occur as a result of trauma to the jaw or oral cavity.
People who often suffer from tonsillitis may develop a peritonsillar abscess, or phlegmonous tonsillitis, over time. In this case, the palatine tonsils are affected. Depending on the location of the infection, the process can be one- or two-sided. Often this condition is observed in chronic tonsillitis, when the infection constantly lives in the tissues of the tonsils, periodically causing exacerbations. Chronic tonsillitis is a disease most common in children, but it can also occur in adults.
The presence of an infectious focus in the oral cavity and in the pharynx can cause the development of a retropharyngeal abscess. Nearby organs can also become a source of infection, for example, with otitis media (inflammation of the middle ear), mastoiditis (inflammation of the temporal bone), etc. The occurrence of a retropharyngeal abscess is facilitated by a decrease in general and local immunity. The most dangerous complication of this disease can be swelling of the larynx and resulting suffocation.
One of the most serious conditions is a brain abscess. The cause of its development may be infectious processes in other organs and tissues of the body, purulent infections in nearby organs (purulent otitis or sinusitis), and traumatic brain injuries. In the first case, the infectious agent is carried through the bloodstream (metastatic abscess). In the second, there is an untreated advanced infectious process that spreads to the brain tissue. Trauma is the most common cause of brain abscess.
A brain abscess can affect any part of the brain.
There are two types of brain abscess: interstitial, when the abscess is limited by a connective tissue capsule, and parenchymal, when the capsule is absent and the accumulation of pus does not have clear boundaries. Parenchymal brain abscess is more difficult to treat and has a less favorable prognosis. If a brain abscess is suspected, treatment should be prompt. In emergency cases, the only possible treatment may be urgent surgery. During the development of purulent inflammation, the walls of the connective tissue capsule become thinner, which threatens its rupture and the outpouring of purulent contents into the tissues and ventricles of the brain. In this case, there is a high probability of death.
Another life-threatening type of abscess is a lung abscess. This condition can develop due to several reasons. A lung abscess can occur as a complication of purulent pneumonia (inflammation of the lung caused by pyogenic strains of staphylococci and streptococci), can be the result of aspiration pneumonia (pneumonia as a result of penetration of a foreign object into the lungs), can develop during the disintegration of a cancerous tumor, etc. The infection can also be brought in by blood from other inflammatory foci. In most cases, the disease is completely curable with timely diagnosis and proper treatment.
Purulent inflammation can also occur in the liver, resulting from inflammatory diseases of the digestive tract. There are two ways of infection of this organ: through the blood and through the ducts of the gallbladder. A liver abscess disrupts the normal functioning of this organ, which can have very serious consequences for the entire body. After all, the liver is our main chemical laboratory, where toxins entering the body are inactivated.
Kidney abscess may be a consequence of chronic pyelonephritis
The kidneys play an equally important role in removing toxic substances from the human body. However, this organ can also be affected by infection. In some cases, inflammation can also develop into an abscess. A kidney abscess can be a consequence of chronic pyelonephritis, occur when the urinary tract is blocked by calculi (stones), and can also be a complication of kidney surgery. In case of purulent inflammation of the kidney tissue, it is necessary to take timely measures in order to preserve the organ.
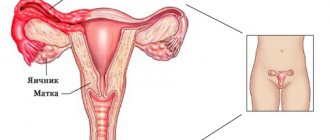
A consequence of inflammatory diseases of the genital organs in women can be an abscess of the Bartholin gland. This gland is located in the vestibule of the vagina, and its ducts exit in the area of the labia minora. It secretes a special secretion that acts as a lubricant during sexual intercourse. When an infection penetrates into the lumen of the opening duct, the contents of the gland first become infected - a false abscess. Over time, the condition can be aggravated by the development of a true abscess, which is characterized by severe pain in the external genital area, as well as the occurrence of swelling and hyperemia at the base of the labia majora.
Soft tissue abscesses are classified into a separate large group. We have already begun to talk about one of the manifestations of such an abscess above. These include boils, carbuncles, felons, erysipelas of the skin, etc. Purulent inflammation develops in the layers of the skin or in muscle tissue. As a rule, the occurrence of this process is preceded by injury or surgery, which was performed with insufficient adherence to the rules of asepsis. An abscess can also develop after an injection, in case of poor treatment of the injection field, damage to a vessel, etc. Since intramuscular injections are usually made into the gluteal muscle, in this case an abscess develops on the buttock.
Separately, we should talk about cold abscess. This condition is not characterized by hyperemia and a local increase in temperature in the area of inflammation. A cold abscess may not manifest itself at all. This pathology occurs as one of the complications of bone tuberculosis.