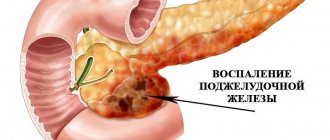
Pancreatitis is a disease that is not to be trifled with. But the condition becomes especially alarming when the acute stage of inflammation of the pancreas begins. During this period, usually effective medications do not help, and the pain is so unbearable that it can provoke loss of consciousness and shock. That is why treatment of pancreatitis in a hospital is the only reasonable option: only urgent hospitalization often saves the patient from disability or death. Sometimes they are limited to drug treatment, and complex cases require surgical intervention.
Indications for hospitalization
Inpatient treatment is necessary in two cases:
- if chronic pancreatitis has entered an exacerbation phase,
- when acute pancreatitis is diagnosed.
Both cases are equally dangerous, and the chronic form of the disease is also fatal. Therefore, it is required that the patient's condition be monitored by a doctor. Only in a hospital can the necessary tests be carried out to confirm the diagnosis of pancreatitis.
Characteristic symptoms are:
- Severe pain in the upper abdomen. They can be on the right, left or in the middle. Sometimes the pain radiates to the back. The slightest movement leads to a new attack. It becomes impossible to breathe and cough, so as not to provoke its intensification.
- Vomiting and nausea, with no relief.
- Tachycardia and weakness.
- Chills and fever up to 38°C.
- Reduced blood pressure.
- Diarrhea. Undigested food can be seen in the feces.
An attack of acute pancreatitis may require emergency surgery, as it often becomes a threat to the patient's life.
Nutrition and medications
After the patient has had an acute attack, he will have a difficult period of adaptation to a new life with significant changes, especially with regard to nutrition. To get used to a new way of life, medications alone will not be enough. The patient’s diet is also controlled, since this part of the therapy is no less important for pancreatitis.
It is recommended to avoid fried foods, fatty foods and certain types of meat. Products must be steamed or baked. From the liquid, you should give preference to rosehip decoction and compote (dried fruits). Dry cookies can replace cakes and cakes.
If diet therapy is disrupted, exacerbation of pancreatitis will return in a more severe form.
For pancreatitis, treatment is prescribed with the use of drugs of various types.
The acute period of pancreatitis lasts a little more than a month, but it will take about 12 months for the body to recover after this. Treatment in a hospital involves long-term medication use - the classic scheme.
- Drugs that relieve spasms (No-shpa, platifillin).
- Medicines that improve digestion (Mezim, Pancreatin, Festal).
- Agents that reduce acidity (Almagel).
- Complex of vitamins (A, B, E, D).
When the patient begins to recover, it is advisable for him to drink herbal decoctions. The healing plants from which the drink is produced quickly have a mild anti-inflammatory effect and normalize metabolism. Drug intolerance is also important, so a qualified doctor should carefully select medications.
How is acute pancreatitis treated in a hospital?
Treatment of such pancreatitis in hospital is the only option. In this case, it is impossible to take any action at home; painkillers cannot help.
To stop the acute form, in stationary conditions it is necessary to urgently solve several problems at once:
- reduce the activity of the pancreas,
- relieve pain syndrome,
- eliminate the factors that provoked the attack (ulcer, cholelithiasis, alcohol).
This set of measures can only be provided in a hospital.
Diagnostics
In the first days, an initial diagnosis is established, which should be confirmed when the patient’s condition improves - within 5 days. But the initial examination takes place in the hospital emergency room. There, body temperature and blood pressure are measured, the doctor determines the degree of swelling of the extremities, palpates the abdominal area and checks the sclera of the eye for yellowness if there is a suspicion of obstructive jaundice.
Other examinations:
- Clinical blood test - to confirm an increase in ESR and a decrease in the amount of proteins.
- Urinalysis - to detect alpha-amylase. Its high content is a symptom of acute and chronic forms of pancreatitis.
- Stool analysis - to evaluate the functioning of the pancreas. Oily sheen and undigested food in it clearly indicate this pathology.
- Using ultrasound, the exact localization of inflammation is determined.
Based on the results obtained, a diagnosis is made. The possibility of developing complications is assessed. If the patient's condition is moderate, he is sent to the intensive care unit. When there is a possibility of developing a coma, the hospital's intensive care unit is chosen.
Then comes the conclusion about the most effective type of therapy. There are two options - either drug treatment or surgery, but it is also combined with medication.
Drug treatment regimen
Fasting is the first measure necessary for vomiting and intense pain. In such conditions, even drinks are prohibited. Fluid is administered only intravenously. Dry fasting lasts 2-4 days, depending on the severity of the patient’s condition. Then for 3-6 days the patient is “put” on dishes with a liquid and semi-liquid consistency.
A thin catheter is inserted into the patient's stomach through the nasal passages to relieve it of aggressive acidic secretion. The pain syndrome disappears within a few hours. This procedure lasts from 1 to 3 days. To adjust the electrolyte and water balance, a sodium chloride solution is injected. For moderate symptoms, antacids (Sorbex, Almagel, Maalox, Phosphalugel) are prescribed to protect the gastric mucosa. But these medications are not recommended for nausea or vomiting.
Analgesics and novocaine blockades are prescribed intravenously or intramuscularly, and sometimes the use of narcotic drugs is allowed. Among antibiotics for intravenous infusion, Contrikal is used (3-4 times a day), once - Gabexat mesilate, 2 times a day - Gordox. Hypertension of the biliary tract is eliminated with the help of antispasmodics - No-shpa, Papaverine, Nitroglycerin. Taking complex vitamins is mandatory.
Indications for surgical treatment
It is not always possible to treat pancreatitis with medication, even in a hospital. Surgical treatment of the acute form is resorted to in the following cases:
- If severe intoxication and pain do not leave the patient two days after the start of drug treatment.
- When another symptom was added - loss of consciousness.
- A serious complication arose - obstructive jaundice. This is the deposition of bilirubin in the mucous membranes and skin due to blockage of the bile ducts of the liver.
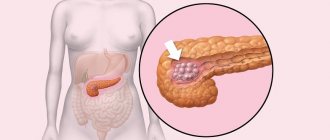
- The appearance of a neoplasm (cyst).
Surgery can be direct or indirect. Direct ones are performed in this way:
- cysts are drained,
- perform pancreatic resection,
- remove stones.
Indirect methods include operations on the gastrointestinal tract, biliary tract, neurotomy (nerve dissection). After surgery, the patient remains in the hospital for a maximum of a week, and the recovery stage takes one and a half to two months.
Anti-inflammatory
Anti-inflammatory drugs primarily include NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), used for mild pain and identified inflammatory process.
They inhibit the process of inflammation at the biochemical level and prevent the development of edema of the pancreas and the formation of foci of necrosis on it, thereby relieving the patient of the likelihood of complications.
For an adult body, it is permissible to use any of the above remedies, since the liver function of a mature person differs from that of a child, but preference should be given to Ibuprofen preparations, since it is tolerated much better by adults.
The most commonly prescribed medications are:
- "Diclofenac" - 100 mg;
- Meloxicam, Amelotex – 15 mg;
- “Paracetamol” – 500 mg;
- “Ketonal” – 150 mg;
- “Ibuprofen”, “Ibufen”, “Ibuklin” – 200 mg;
- "Analgin" - metamizole sodium, 500 mg.
Treatment of chronic pancreatitis
Typically, this type of disease can be successfully treated on an outpatient basis or at home. Only conservative treatment is used, to which a special diet is added. But there is an exception - the phases of exacerbation of the disease, when the remedies prescribed by the doctor are powerless. Treatment of chronic pancreatitis in the hospital is usually carried out with medication: it is treated in the same way as pancreatitis in the acute stage is treated.
Planned therapy is also carried out: all patients must go to the hospital twice a year. The entire course takes no more than 3.5 weeks. First of all, the body is cleansed of toxins and wastes; for this, the stomach is washed and enemas are given. The next stage is a three-day fast, during which the patient is under constant supervision. After examination, depending on the condition, sorbents, diuretics and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
Causes
- Gallbladder diseases.
- Drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Diseases of the stomach and intestines.
- Abdominal injuries.
- The presence of worms and the toxins they secrete.
- Incorrect treatment with medications.
- Overweight.
There are several types of pancreas problems.
- Reactive pancreatitis . The cause of this disease is considered to be a disorder of the gastrointestinal tract. During an exacerbation, intense pain appears under the left rib.
- Acute pancreatitis . Severe pain appears after certain factors: drinking alcoholic beverages the day before, spicy, fried or salty foods. And also after poisoning with preservatives or spoiled products. The patient's condition deteriorates very quickly. It is in this form that the symptoms of pancreatitis in a woman after 30 years of age are diagnosed. The pancreas must be treated for problems that are just beginning.
- Chronic pancreatitis . If a person repeatedly avoids treatment for pancreatitis, then gradually he leads his body to chronic manifestations of pancreatitis.
How long do they stay in the hospital with pancreatitis?
It is difficult to answer exactly the question of how many days the patient will spend in the hospital, because much depends on the form of pancreatitis in a particular patient. If the disease is discovered for the first time, and it manifests itself as an acute attack, then therapy will take from a week to 14 days; the acute attack usually disappears in 2-3 days. But for about six months the patient must take supporting medications - vitamins, choleretic drugs, hepatoprotectors, enzymes. A strict diet is also necessary, permanently.
First aid before the ambulance arrives
If there is a suspicion of an attack of pancreatitis, then you should not hesitate. Especially when the localization of the pain syndrome is in the hypochondrium - left or right. Unfortunately, ambulance teams do not always arrive quickly. But you need to understand that self-therapy while waiting for doctors is unacceptable. You should not take painkillers: analgesics and antispasmodics are prescribed only by a doctor. Even drinking is forbidden.
But you can alleviate the condition a little by doing the following:
- take a semi-sitting position;
- apply a cold or ice compress to the sore spot;
- ventilate the room.
All other actions are taboo. Only a doctor, having assessed the symptoms, is able to provide first aid, but the real war against pancreatitis will begin in the hospital.
At-risk groups
The disease affects all age groups and people of both sexes. However, chronic pancreatitis occurs more often in older people.
Conventionally, 9 risk groups can be distinguished, these are people:
- those suffering from alcohol addiction;
- those who eat haphazardly and often resort to fast food;
- taking a large number of medications;
- those suffering from nicotine addiction;
- having a history of gallstone disease;
- obese patients;
- patients with cardiovascular diseases;
- experiencing frequent stressful situations;
- those who have suffered a pancreatic injury or have recently suffered severe poisoning.
The disease causes anxiety, and constant pain in the left hypochondrium, lumbar and epigastric regions, as well as in the back between the shoulder blades keeps a person in constant irritation
What is the pancreas responsible for?
This organ performs the functions of producing enzymes directly involved in digestion. This means that any disruption of the gland leads to malfunctions of the entire digestive system. Exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis, treatment of which is not started in a timely manner, can cause the development of gastritis and ulcers. A perforated ulcer is mortally dangerous, in which surgical intervention is inevitable. Enzymes secreted by iron:
Amylase is responsible for breaking down large protein chains into simpler elements. If this enzyme is deficient, the intestines will be unable to absorb many nutrients.
Lipase breaks down fats into glycerol and fatty acids, thereby helping the intestines absorb them. A lack of substance in the human body reduces the ability of the digestive system to absorb vitamins A, D, E, which can lead to many problems.
Note. Without vitamin D, the absorption of calcium in the body is impossible. Lack of calcium makes bones brittle.
Nuclease takes part in the body's absorption of nuclear (nucleic) acids.
Trypsinogen is an auxiliary enzyme, without which amylase does not break down carbon compounds.
Prophospholipase breaks down phospholipids into simpler elements.
The pancreas plays a major role in digestion
Diagnostics
After determining the symptoms and etiology of the disease, the specialist doctor prescribes tests. Usually this:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- Analysis of urine;
- fecal biochemistry;
- saliva tests to determine amylase levels.
An accurate diagnosis may require additional abdominal tests, such as a CT scan, MRI, x-ray, ultrasound, or endoscopy.
Fact. Did you know that the symptoms of exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis in adults and children are the same?
Additional studies give specialists an idea of the extent of organ damage and the stage of development of the pathology, which is important for timely and effective treatment
Painkillers
A key link in the treatment of the described disease, since pain during an exacerbation is pronounced - the patient may lose consciousness or vomit due to the pain syndrome.
Medicines of different groups are prescribed as analgesics:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- traditional painkillers;
- narcotic painkillers.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-a77QDFFXWE{amp}amp;modestbranding=0{amp}amp;controls=1{amp}amp;rel=0{amp}amp;showinfo=1{amp }amp;enablejsapi=1{amp}amp;origin=
The active substance is selected by a specialist based on the severity of the patient’s condition and the severity of discomfort.
Frequently used means:
- “Diclofenac;
- "Meloxicam", "Amelotex";
- "Paracetamol";
- "Ketonal";
- “Ibuprofen”, “Ibufen”, “Ibuklin”;
- "Ketorol", "Ketanov";
- "Analgin."