In all cases, stage 4 pancreatic cancer cannot be treated. During this period, the loss of specific functions of the organ occurs, the tumor grows, grows into nearby systems, and forms metastases. In this case, the patient feels pain in the abdomen, dyspeptic symptoms and severe exhaustion of the body appear. Features of the clinical picture also depend on the localization of subsidiary neoplasms in other organs.
Since the pancreas is responsible for the production of insulin, when this organ is affected by cancer, glucose tolerance is impaired and symptoms of diabetes mellitus develop.
What is stage 4 pancreatic cancer?
The diagnosis of “stage 4 cancer” is made when the changed cells penetrate the blood and lymph flow, and the tumor spreads throughout the body. The severe phase of the disease occurs mainly at the age of 60 years and older. Statistics show that mortality from pancreatic cancer ranks 4th among all cancers; men over 50 years of age are more likely to suffer.
Before this phase, the pathology is not diagnosed for several reasons:
- The topography of the pancreas makes it inaccessible to palpation during a routine objective examination (it is located retroperitoneally).
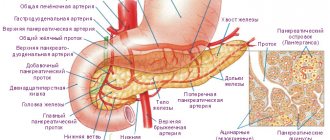
- Due to the complex anatomical structure of iron, it plays a dual role: exocrine (digestive) and endocrine (hormonal).
The parenchyma of the pancreas consists of delicate glandular tissue, which is easily destroyed under the influence of external and internal unfavorable factors. The dead cells of the organ are not restored, and it gradually loses its functions. The initial stages of cancer development are either asymptomatic, or a patient with existing pancreatitis and diabetes mellitus may not pay attention to the change in his condition, considering it a manifestation of the underlying disease. They most often come to the doctor at the last stage of cancer, when the condition is serious and there are many complaints due to the impaired functioning of several organs.
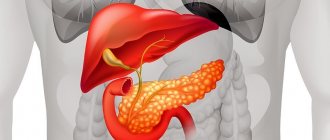
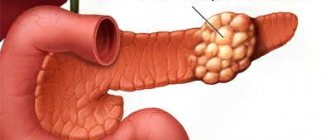
Most often, the location of a severe tumor is the head of the pancreas.
Symptoms
Clinical manifestations of stage 4 cancer are nonspecific. The main signs of the disease are:
- constant and intense abdominal pain;
- weight loss;
- weakness;
- decreased performance;
- low-grade fever;
- increase in abdominal volume;
- heaviness in the hypochondrium on the right or left;
- formation of soft subcutaneous nodules;
- soreness in the veins;
- yellowness of the skin;
- skin itching;
- darkening of urine;
- lightening of stool;
- nausea;
- vomit.
Features of stage 4 cancer
A feature of stage 4 pancreatic cancer is the serious condition of the patient with a detailed clinical picture. There are symptoms of pathology of the digestive system and manifestations from other organs involved in the malignant process. At this stage, multiple metastases:
- occupy nearby organs: stomach, liver, intestines, spleen;
- spread to distant bones, brain, lungs.
Cancer of the head of the pancreas always affects the liver. This is explained by topography and anatomical structure: the organ is located close to the gland, the common bile duct passes through the head of the pancreas and in most cases connects with the Wirsung canal into one common ampulla, flowing into the lumen of the small intestine through the papilla of Vater. With metastasis to the liver, the prognosis sharply worsens: the tumor quickly affects its entire parenchyma.
When the bile ducts are involved, obstructive jaundice develops. This occurs at the last stage of the disease, when there is an active process of growth and metastasis.
Enlarged lymph nodes are characteristic: they are painful, loose, and those that are accessible are easily palpated.
Due to the proximity of the intestine (the pancreas directly borders both the small and large intestines), its obstruction develops.
Metastases invade the peritoneum, spread to the spleen tissue, causing rapid development of liver failure with ascites (the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity, sometimes up to 20 liters) and splenomegaly. Severe intoxication occurs, leading to a sharp disruption of the condition.
Risk factors and probable causes of pathology
The causes of malignant lesions of the pancreas are still unknown, so scientists offer reliably identified risk factors studied on a large number of patients.
The greatest attention is paid to:
- Tobacco smoking - the risk is proportional to the “experience” and intensity. A cancerous tumor in the pancreas develops in 2% of smokers (in the lungs - in 10%). When smoking, the risk of developing cancer doubles; this cause dominates in every fourth patient.
- Nutritional characteristics - an opinion is expressed about an increased incidence of people who consume a lot of animal products, coffee and have a lack of plant fiber, vegetables, and fruits. However, it is not considered sufficiently substantiated.
- Obesity and type II diabetes mellitus are the most likely factors for the development of adenocarcinoma. The risk increases by 60% compared to people without diabetes and persists for at least 10 years. The most dangerous age is considered to be over 50.
- Chronic pancreatitis – increases the risk of adenocarcinoma by 20 times, regardless of the form of inflammation. Patients who have suffered from pancreatitis for more than five years are most susceptible. The occurrence of malignant growth is explained by the proliferation of epithelium in the ducts and acini of the gland with a simultaneous disruption of the process of restoring the structure of the organ.
- Hereditary pancreatitis occupies a special place; it increases the likelihood of malignant degeneration by 50 times. Although it occurs in 2% of patients. The cause is associated with mutations in the PRSS1 gene. In 40% of patients with a hereditary form of chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic adenocarcinoma develops. The addition of other listed factors significantly reduces the age of the sick. In pathogenesis, the main role is played by impaired inactivation of the trypsinogen enzyme, for which the altered gene is responsible. This leads to “self-digestion” of the acini cells.
- Infections – a connection has been established with previous viral hepatitis and Helicobacter. Microorganisms are important not only as a cause of stomach and liver cancer, but also in the pathology of the pancreas.
- Experts consider the carcinogenic effects of chemicals containing naphthylamine, benzidine, benzopyrene, asbestos, and acetylaminofluorene in industries associated with pesticides to be an important complicating factor.
Asbestos is widely used in the production of slate; builders are constantly in contact with it
Gastrectomy and cholecystectomy (removal of the stomach and gallbladder) operations have not yet been recognized as confirmed risk factors. But they continue to study.
Reasons for the transition of a tumor to a late stage
The main reason for the development of stage 4 cancer is late diagnosis. The disease is determined in the inoperable phase, which is explained by the latent period in its course: several weeks or even months pass from the onset of the first minor to severe manifestations. Because of this progression in the early stages, pancreatic cancer is called a silent killer.
As indicated, late detection is associated with the absence of symptoms, their inconsistency in the initial stages, or the patient’s inattention to his health: manifestations of the disease can be missed if a person suffers from diabetes, chronic pancreatitis with frequent exacerbations, gastritis, colitis or other pathology of the digestive system . Late contact with a specialist leads to the fact that only symptomatic therapy is prescribed due to the inability to influence the widespread process.
Definition
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma is a tumor disease that originates from the mucous cells of the gland of the same name or its ducts through which pancreatic juice is excreted. This disease is one of the most dangerous types of cancer that can affect the digestive tract. It is found in nine out of ten people with suspected neoplastic process in the pancreas.
Its rapid development, rare diagnosis in the early stages and fairly widespread distribution make it the cause of high mortality among older men. In the international clinical classification, which is used by all doctors in the world, pancreatic adenocarcinoma is listed under code C 25.
Adenocarcinoma of the pancreatic body
Typically, such an adenoma is quite large in size - more than ten centimeters. Morphologically, it is a soft, nodular accumulation of cells with irregular outlines.
How long do you live with stage 4 pancreatic cancer?
No specialist can say exactly how long a patient will live. Each patient with the last stage of pancreatic cancer lives for different periods of time and may die from complications. What matters is the level of spread of metastases and their number. If the liver is involved, death occurs within a few months. Intoxication and its severity also play a role.
The average life expectancy is 4−6 months. Inoperable patients live about 6 months. Only 5% of patients can survive more than a year after intensive treatment.
Acting:
- old age and male gender;
- intensity of intoxication;
- complex of anticancer therapy;
- quality of patient care.
The more severe the pathology, the faster it spreads.
1-2% of patients manage to live up to 5 years with stage 4 pancreatic cancer. If you agree to medical manipulations, the probability of prolonging life increases by 3−5%. Most patients die refusing the proposed treatment, and for those who decide to use chemotherapy for stage 4 pancreatic cancer, life is prolonged from 1 to 3 months. This is due to poor tumor growth control.
Types of cancer
In modern medicine, it is common to use several classification schemes that identify pancreatic cancer and also predict how long a person with this disease can live. Based on the type of structure of cancer cells, the following forms of pathology are distinguished:
- Ductal adenocarcinoma;
- Cystadenocarcinoma;
- Mucinous carcinoma;
- Squamous cell form of cancer pathology.
Each histological type determines which cancer treatment will be most relevant, the main methods of pain relief, and also allows one to predict the possible growth rate of the tumor conglomerate. Taking into account the primary localization of the malignant neoplasm, the following categories are distinguished:
- Tumor of the tail organ;
- Cancer of the head of the pancreas;
- Cancer of the body of the gland.
In the early stages, any type of pathology does not manifest itself in any way. Only grade 3–4 cancer gives a very “colorful” clinical picture, which will differ depending on the histological affiliation and location of the disease.
Signs and symptoms of stage four
The main clinical sign of stage 4 pancreatic cancer is pain. It can be constant, but intensifies at night due to frequent intense attacks or with sudden movements and bending of the body.
In 100% of cases, significant weight loss occurs due to impaired pancreatic secretion and decreased appetite. Since pancreatic cells undergo changes during cancer, they lose their functions and multiply intensively. As a result of their uncontrolled division, the tumor grows rapidly and increases in size. Even tissue that has not undergone cancerous changes is compressed by the growing tumor and ceases to function. Pancreatic juice ceases to be produced in the required quantities, incoming proteins, fats and carbohydrates are not broken down into simple components and are not absorbed. With a normal amount of food eaten, a person loses weight sharply. Due to severe intoxication with the decay products of the tumor and its foci, appetite also decreases, an aversion to various types of foods and dishes appears, and dyspeptic disorders - nausea, vomiting, diarrhea - dehydrate the body and contribute to even greater weight loss. The general condition sharply worsens, progressive general weakness, exhaustion, and sleep disturbance appear.
In 80% of patients, when the bile ducts are compressed by a growing tumor, obstructive jaundice develops - bile stops being released into the duodenum. The skin, mucous membranes, and sclera become yellow with a greenish tint. This is accompanied by painful itching, which intensifies at night. Multiple traces of excoriation (scratching) appear on the skin, which can become inflamed. There is no fever, a large painless gallbladder is detected by palpation (Courvoisier syndrome).
A feature of the last stage of cancer is multiple enlargement of regional and distant lymph nodes. In some of them, secondary tumor foci are found.
Pancreatitis and diabetes mellitus also occur, which further worsens the condition.
Early symptoms
The symptomatic picture of the disease is mild, blurred, which is often the reason for late detection of the disease.
In the initial stage, pancreatic cancer is curable if the patient contacts at the first minor signs of poor health. An early symptom is discomfort or mild abdominal pain without clear localization. In the future, it may bother the epigastrium, umbilical region and right hypochondrium. This is due to the location of the tumor in the head of the pancreas. If a malignant formation develops in the tail or body, unpleasant sensations may appear in the left hypochondrium, radiate to the back, or take on a girdling character.
Discomfort or pain increases after eating fried, fatty foods and alcohol. Smoking, smoked, salty foods, carbonated drinks, strong tea and coffee can also provoke their appearance.
In addition to unpleasant sensations, the following appear:
- nausea;
- unstable stool - constipation or diarrhea, especially after errors in diet;
- decreased appetite;
- damage to the esophagus - due to esophagitis, a burning sensation may appear behind the sternum;
- dysphagia - an unpleasant sensation in the chest and difficulty swallowing when the esophagus is damaged (there is a direct relationship between the degree of dysphagia and the stage of cancer);
- gradual weight loss;
- manifestations of asthenic syndrome - increasing unmotivated weakness not associated with physical activity or mental work, sleep disturbance, feeling of constant fatigue;
- dry mouth, thirst, polyuria with beginning endocrine dysfunction.
This condition can last for months, gradually worsening. But with timely consultation with a doctor at an early stage, the tumor can be cured.
Late signs
Late signs are a very poor condition of the patient with a predominant manifestation of the clinical picture of impaired functions of the affected organs (in addition to the pancreas itself). All symptoms that were not noticed by the patient at an early stage of the disease have extreme degrees of severity:
- Abdominal pain is constant, with intense attacks that occur at night and when changing body position, bending, or moving. Its localization may vary depending on the location of the tumor, its size and extent;
- uncontrolled weight loss, up to cachexia;
- jaundice due to compression of the common bile duct (common bile duct);
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea;
- signs of severe intoxication - severe weakness, poor sleep, lack of appetite, aversion to food;
- enlargement of lymph nodes with changes in their structure. Sometimes the leg may swell when regional lymph nodes are involved;
- secondary diabetes mellitus, especially when the tumor is localized in the caudal part of the pancreas, where the bulk of the islets of Langerhans that produce hormones are located, thirst, polyuria, and constant dry mouth (hyperglycemia) appear.
Sometimes pancreatic cancer provokes increased production of insulin, which is accompanied by tremors of the limbs, general weakness, even loss of consciousness (hypoglycemia).
Signs of tumor metastasis
In addition to the parenchyma of the pancreas itself, the following are affected:
- The lymph nodes;
- nearby and distant organs due to cancer cells entering the blood, lymph, peritoneum and spreading throughout the body.
Organs in direct contact with the pancreas: duodenum, stomach, liver, intestines, spleen. Distant: lungs, kidneys, brain, bones.
If the respiratory system is affected, cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, and hemoptysis may occur.
When the kidneys are involved in the pathological process, difficulty urinating and changes in the urine appear.
If metastases have reached the brain, a variety of neurological symptoms may be observed depending on the area of the lesion:
- excruciating headaches;
- dizziness;
- impaired coordination of movements, voice, and clarity of speech;
- loss of consciousness;
- mood swings.
All this indicates the presence of metastases in the brain.
Clinical picture
Symptoms in such patients can be quite varied and depend on the location of the adenoma, its size and stage.
As for the frequency of occurrence, clinical statistics provide the following data:
Localization in the head – 70%
Diffuse damage – 20-35%
Like most paraneoplastic processes, the initial stages of adenocarcinoma are asymptomatic. A tumor cell has arisen, it is actively dividing, there are no metastases yet, so there is no serious impact on the body yet. The growth rate is determined by factors such as age, gender, immune reactivity, and metabolic rate.
Epigastric pain is a serious signal for examination
After the size of the adenocarcinoma has reached the point that the tumor is capable of growing into the surrounding tissues, symptoms such as pain in different places of the abdomen appear, which can be constant or occur against the background of various human conditions. Portal hypertension also develops, causing fluid to accumulate in the free abdominal cavity.
Due to impaired digestive function, anemic syndrome, decreased performance and severe weight loss to anorexia may develop. When pancreatic carcinoma is localized in the head, signs of compression of the duodenum or extrahepatic bile ducts appear. The patient may become jaundiced due to obstruction of bile flow, itching will appear and the body temperature will increase.
Ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas will manifest itself a little earlier. It can be suspected based on the occurrence of intense pain in the epigastrium, which is girdling in nature. Attacks are most often associated with eating. This is explained by the reflex secretion of pancreatic juice in response to irritation of the gastric mucosa by lumps of food. Violation of the outflow of juice will lead to damage to the fiber of the gland by proteolytic enzymes, resulting in pain.
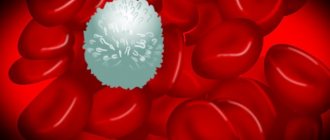
Normally, cancer cells are constantly destroyed by the immune system; the picture shows a paraneoplastic cell that is destroyed by leukocytes
Dyspeptic syndrome will be manifested by frequent bloating, alternating constipation and diarrhea, belching, and vomiting. Following the growth of the tumor, the pain will increase, as well as the yellowness of the skin.
Stage 4 pancreatic cancer is difficult to treat and is characterized by distant metastatic foci. Even radical surgery does not cure patients and restore organ functions.
The human pancreas is located in the abdominal cavity next to the stomach. It produces hormones and produces pancreatic juice, which is involved in the breakdown of nutrients. This organ is formed by a head, body and tail.
Late stage diagnosis
Due to the asymptomatic development of the tumor in the initial stages, pancreatic cancers are detected already in the final stages. Since the pancreas cannot be palpated during an objective examination due to its retroperitoneal location, the diagnosis is made taking into account:
- patient complaints;
- life history (it is found out whether there were any cases of cancer in close relatives) and illness;
- laboratory and functional examination methods.
Basic laboratory methods:
- general clinical blood tests (inflammation, anemia are detected) and urine;
- biochemical (diastase, bilirubin, transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, total protein and fractions);
- tumor markers (cancer antigens to pancreatic tissues are detected);
- stool analysis (coprogram).
Functional examination methods for detecting stage 4 pancreatic cancer:
- Ultrasound of internal organs: ultrasound is used to detect the presence, location and size of a tumor. It has a good review from doctors of all specialties who use it for diagnosis. This is the screening method that is used first. It is informative, convenient because it does not require special training, safe, fast and takes little time.
- CT, MRI - allow you to carry out layer-by-layer scanning of any organ and obtain an accurate three-dimensional image. MRI is a preferable method due to the lack of radiation exposure: it is based on the use of a magnetic field, it is possible to detect a tumor as small as 2 cm, enlarged lymph nodes and metastases. If the patient has contraindications, a CT scan is prescribed.
- Laparoscopy with biopsy for histological and cytological analysis is necessary to confirm the malignancy of the tumor and clarify the type of cancer. At stage 4, it is rarely performed; other, less traumatic methods (percutaneous) are used to take a biopsy.
Carrying out diagnostics
To recognize the course of adenocarcinoma, the following types of studies are carried out:
- ultrasonic;
- tomography;
- blood chemistry;
- angiography;
- laparoscopy.
An ultrasound will determine the presence of a tumor, its size and location. The doctor can also examine nearby structures and detect secondary foci of inflammation in them if they reach a large size.
Tomography is the most informative examination method, without which it is impossible to make a correct diagnosis. This research method accurately shows the localization of the tumor, the degree of its germination into organs, the exact size and the presence of metastases.
When conducting a biochemical analysis, the degree of decompensation of the “pancreas” is assessed. Adenocarcinoma is always accompanied by severe disruption in the functioning of anatomical structures. However, it is worth noting that it performs a very important function, so oncologists prescribe a replacement type of therapy after receiving accurate examination results.
Angiography is a technique aimed at accurately examining the walls of blood vessels, which is used to detect the blood supply to the tumor. Laparoscopy refers to a surgical procedure intended for diagnosis and treatment, which makes it possible to assess the general condition of the affected organ.
The diagnosis of cancer is established only after a biopsy followed by histological examination.
Treatment methods for breast cancer at stage 4
In the late period, the tumor grows and becomes enormous in size, so the disease cannot be cured. You can only alleviate the condition and prolong life, since metastases in this phase of the disease cover other organs. Goal of treatment:
- reduce the size of education;
- stop its further spread.
To achieve the desired result, complex treatment is carried out:
- palliative surgery;
- chemotherapy;
- radial;
- targeted;
- symptomatic.
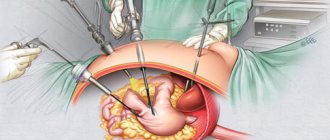
To reduce the tumor, part of the pancreas and affected organs are removed (Whipple operation). Thanks to surgical interventions, the patency of the intestines and common bile duct compressed by the neoplasm is restored.
Chemotherapy reduces the aggression of cancer cells. This is one of the effective methods: it stops or slows down tumor growth and metastasis to other organs. Cytostatic drugs are used that are unsafe for humans: they contain poisons and toxins. This technique allows the patient to live for several more months after the course.
Radiation therapy destroys the structural protein of cancer cells, causing the tumor to shrink. Exposure to highly active X-ray radiation causes the death of aggressive cells, which provides slight stabilization of the tumor.
Radiological therapy with the CyberKnife device is increasingly being used.
Narcotic analgesics are prescribed for pain relief. Symptomatic treatment for digestive dysfunction is also used.
Targeted therapy is a new technology that affects the tumor at the molecular level. It is prescribed to seriously ill patients in the absence of effect from other treatment methods. The idea is that the drug blocks the molecule responsible for the development of cancer cells. As a result, metastases completely disappear. The difference between this method is that the drugs used do not affect healthy tissue. Drugs used: Rituximab, Avastin, Imatinib.
Possible treatment
For patients with pancreatic cancer, stage 4 cancer leaves no chance for a long life, but with the right approach to therapy and your health, you can significantly increase the years of life by stopping the development of pathology. Without taking measures to stop the spread process, the life prognosis is approximately 2 years.
What to do if stage 4 pancreatic cancer develops to prolong the patient’s life? The main problem is that surgical intervention will not bring positive results, since excision of damaged tissue is impossible due to their large number. The survival prognosis for this pathology is about 12% of the total number of patients, while the rest end their life journey within 2 years of this degree of oncology.
For treatment, radiation and chemotherapy are applied to the body. This makes it possible to temporarily stop the development of pathological and oncological processes in the human body. True, these methods do not always provide or be beneficial, because a weakened immune system is sometimes unable to tolerate these activities. After carrying out additional calculations and diagnostic measures, the doctor decides whether to carry out the necessary procedures or not. Sometimes, if metastases at stages 3 and 4 have not yet damaged the patient’s internal organs, a surgical operation will be performed. The operation is called Whipple. How is this surgery performed?
chemotherapy
The operation is performed to remove the head of the pancreas and dry out the tissues damaged by metastases. Can such an operation increase the patient's chances of life expectancy? It all depends on the quality of these manipulations and the body’s ability to withstand the heavy load on the operating table. There is a high probability that the operation will be the last for a person.
If the operation was successful, then a critical condition can now occur during rehabilitation. After these steps, the patient is given chemotherapy, which makes it possible to completely destroy cancer cells, which will prevent them from starting to re-spread in the human body.
Will folk remedies help defeat a tumor?
A favorable prognosis is possible with early consultation with a specialist. According to statistics, 10% of patients come to the doctor when the tumor is still within the pancreas. It is for this group of patients that the prognosis becomes most favorable. In later stages, survival rates drop sharply.
It is not recommended to self-medicate and use traditional methods without consulting a specialist. Even if these are medicinal plants, any recipe from them must be agreed upon with an experienced herbalist after a preliminary consultation with an oncologist. Folk remedies, when properly prescribed and used, can only temporarily alleviate the condition, but cannot defeat the tumor.
Recently, the miraculous properties of the drug ASD-2 (Dorogov’s antiseptic stimulant of the second fraction) have often been mentioned. The annotation states that the medicine is a powerful adaptogen and has a radioprotective effect, eliminates pain and slows down the further development of the tumor. The author of the drug prescribed the drug to fight cancer in severe cases. It was stipulated that a mandatory condition for use is the supervision of a specialist. It is strictly not recommended to prescribe and use it on your own, since there are negative reviews about the use of the drug due to the deterioration of the general condition. Therefore, it is impossible to talk about its effectiveness and the fact that it really cures cancer.
The soda treatment method was developed by Professor I.P. Neumyvakin. He recommends taking sodium bicarbonate daily on an empty stomach according to a specific schedule. According to the patients themselves, with proper treatment it is possible to recover even from the fourth stage of cancer. But there are no statistics or evidence-based medicine studies that would confirm the effectiveness of such treatment.
Carrying out the operation
Surgical treatment is the main measure against neoplasms. It allows you to completely eliminate the tumor by removing the lesion. Surgery is almost always performed at all stages of cancer. The only contraindications are the large size of the tumor and its ingrowth into nearby organs. At stage four, the cancer is considered inoperable.
The surgical method is selected separately by a specialist after diagnosis. To eliminate the formation, resection and gastrectomy are used. If complete or partial removal of the affected organ is impossible, then auxiliary techniques are used. These include laser therapy and stenting.
During the operation, there is still a possibility of serious complications. These include abscesses and anastomotic leaks. During the rehabilitation period, bleeding may occur, pyloric stenosis and relapse may occur.
Pain relief for the patient
In the later stages of the disease, the main symptom is severe pain. Symptomatic treatment is the use of analgesics.
Initially, they try drugs from the NSAID group: Ketanov, Ibuprofen, Naproxen. If there is no effect, opiates are prescribed (Tramadol, Promedol). Their main side effect is addiction, which is why you have to increase the dose.
In the terminal stage, powerful narcotic drugs (Prosidol, Fentanyl) are used. If the patient is at home, the injections are given by a health care worker, since the drugs belong to the group of strictly controlled narcotic drugs.
Diagnostic methods
The disease can last for a long time under the diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis. It is very difficult to detect the initial stage. The following methods are used:
- general blood and urine analysis - indigestion leads to mixed type anemia (B12-deficiency + iron deficiency), if an infection is added to the blood, leukocytosis appears with a shift of the formula to the left;
- study of biochemical blood tests for the content of residual nitrogen, protein fractions, glucose, bilirubin, enzymes (alkaline phosphatase, amylase and transaminase);
- tumor markers and antigens DuPan, CA19-9, TAG72, Spanl, CA125;
- ultrasonography;
- the patency of the ducts of the gallbladder and pancreas is checked endoscopically (retrograde cholangopancreatography);
- X-ray duodenoscopy is performed using a contrast agent;
- computed tomography is also best used with contrast;
- histological examination and biopsy.
How to prolong the life of a terminally ill patient?
The patient’s life during this period depends on his mental and psychological mood. Without it, therapy will not give good results. A psychotherapist is needed to maintain a normal mental state.
Care and proper nutrition play an important role in prolonging life. This will prevent the condition from getting worse. Frequent small meals are recommended. The food is served in a ground, mushy form. The food temperature should be comfortably warm—hot and cold foods are excluded. Food is boiled, stewed, steamed, baked. With this method of preparation, beneficial properties are preserved and adverse effects on the pancreas are eliminated.
Fried, spicy, salted, smoked and pickled foods are completely excluded from the diet. Alcohol, strong coffee, tea, chocolate, sweets and spices are prohibited.
How much will it cost to treat a cancer patient at stage 4?
The chances of recovery for patients with stage 4 cancer are extremely low, so not all medical institutions are ready to treat such patients. But after therapy carried out in oncology clinics in Moscow and abroad, the life of patients is extended to five years in 15% of cases.
In Russia
The cost of cancer treatment depends on several important factors. Therefore, even an experienced doctor is unlikely to be able to accurately name the cost of treatment right away. The level of the clinic, the qualifications of doctors, and the available equipment play a role. Surgery with hospitalization and further therapy, which requires staying in the hospital for some time, accounts for the majority of the costs. But the doctor determines the need for the amount of treatment in each case individually, taking into account examination data, the stage of the disease and the severity of the patient’s condition.
In specialized clinics in Moscow (European Clinic and Blokhin Oncology Center) for patients with stage 4 cancer, special techniques have been developed and continue to be studied that increase survival to 10−15%.
Moscow oncologists have introduced and successfully use stereotactic radiation therapy using the modern CyberKnife device. This method successfully treats pancreatic cancer with metastases.
Principles of disease treatment
A stage 4 cancerous tumor on the pancreas cannot be removed. This is due to the fact that atypical cells are found not only in the endocrine organ, but also in many others. However, in some cases, even stage 2 or 3 malignancy is inoperable. This is primarily affected by its localization. Moreover, the pancreas is located deep and closely intertwined with large blood vessels and nerve trunks.
Treatment is aimed at suppressing the uncontrolled growth of cancer cells. This will stop the progression of the disease and reduce the severity of clinical manifestations. For this purpose, chemotherapy is actively used: it is the fourth stage of cancer that is treated with this method, when it is no longer possible to remove the tumor surgically.
Complex treatment of the disease includes symptomatic therapy. Its main goal is to eliminate the prevailing symptoms. This will improve the patient’s well-being, because at the terminal stage of the disease he no longer lives, but simply survives. For this purpose, detoxification therapy and analgesics are used.
It is possible to carry out surgical interventions to restore the patency of the intestines, bile ducts, etc. However, the removal of the pancreas is not performed, since the degree of damage to the body by cancer cells is so great that there will be no effect from this.