Pseudotumoral pancreatitis: causes, symptoms and treatment features
Provoking factors in the development of this disease are pathologies of the hepato-biliary system (for example, cholelithiasis) and long-term alcohol intake. Much less often - taking medications and other somatic diseases. Most often, pseudotumorous pancreatitis is a consequence of a chronic inflammatory process in the pancreas tissues and much less often (about 10% of cases) it is detected after acute inflammation.
The development of symptoms against the background of cholelithiasis is more often recorded in women. However, not only it can become a provoking factor; malformations of the biliary system, diseases of the bile duct or papilla of Vater are also of great importance. In these cases, inflammation develops due to the constant reflux of bile into the pancreatic duct.
One of the ways of developing pseudotumorous pancreatitis can be lymphogenous damage to pancreas tissue (usually the area of the head of the gland), when the inflammatory process spreads from the gallbladder through the lymphatic network of nodes and vessels.
In more rare cases, the pseudotumor form of chronic pancreatitis can occur due to long-term use of estrogens, acetaminophen and other drugs, or be hereditary. Moreover, with hereditary etiology, the disease actively progresses, the likelihood of malignancy (malignancy) increases and glandular insufficiency rapidly increases.
With the described disease, an enlargement of the pancreas occurs, which is associated with the occurrence of cysts (chronic pseudotumor pancreatitis, pancreatic cyst), the development of lipomatosis and autoimmune lesions.
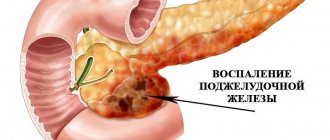
The inflammatory process, as a rule, affects the head of the pancreas - the exit site of the main pancreatic duct. As a result of this, the latter narrows, and the pancreatic juice stagnates in the organ. As a result, the duct becomes overfilled and the pressure in it increases. The enzymes contained in the juice begin to digest pancreatic tissue, which causes the occurrence of severe pain, which is often accompanied by the pseudotumor form of pancreatitis.
Let us understand in detail what pseudotumorous type of pancreatitis is and why the disease begins. The described disease does not occur without cause, but becomes a consequence of a number of pathologies, which include:
- Chronic form of pancreatitis.
- Gallbladder diseases.
- Some infectious diseases.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Mechanical injuries of the pancreas.
- Tumors and cysts on the pancreas.
In most cases, the development of the disease is caused by the lack of treatment for chronic pancreatitis, non-compliance with the prescribed diet and, in particular, bad habits - smoking and alcohol. A hereditary factor appears.
It is believed that middle-aged men who drink alcohol in large quantities are at risk.
Pseudotumorous pancreatitis is one of the forms of long-term pancreatitis with a chronic course. This disease affects men more often than women.
The name of the pathology comes from the ancient Greek words “pancreas” - pancreas, “itis” - inflammation and “tumor” - tumor.
That is, it can be literally translated as follows: inflammation of the pancreas, simulating a tumor process.
Signs of pancreatitis appear suddenly and after the first critical period, it is important to begin treatment rather than allow it to progress to the chronic stage and accompanying deterioration.
The chronic stage of pancreatitis tends to transform into a different clinical and morphological type over a long period of time. The complication develops over five to ten years from the beginning of the protracted stage.
This type of disease is called chronic pseudotumor pancreatitis. In fact, this is the same inflammatory process in the pancreas, only the symptoms become more progressive and exacerbations last longer, the manifestations of the disease are more difficult to stop.
Symptoms of pseudotumorous pancreatitis
The clinical manifestations of this disease resemble the course of acute pancreatitis and cancer. As the disease develops, symptoms of pseudotumor pancreatitis will appear, such as:
- pronounced pain syndrome, which is girdling in nature. For this reason, pain often spreads to the back, as well as in the left and right hypochondrium. A characteristic sign is that there is an increase in pain after drinking alcoholic beverages and eating food;
- manifestations of obstructive jaundice, which include the acquisition of a yellowish tint by the skin and mucous membranes, darkening of urine and discoloration of stool. In severe cases of the disease, skin itching is observed;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- weight loss;
- increased gas formation;
- disruption of the defecation process - expressed in alternating constipation and diarrhea. The stool has an unpleasant, foul odor;
- increase in abdominal volume.
In addition, such a disease causes an increase in the volume of the pancreas, in particular its head, which can be easily detected by a specialist during an examination. Under the influence of inflammatory processes and other unfavorable factors, a narrowing of the main duct of the affected organ occurs, which entails a violation of the outflow of pancreatic juice.
In severe cases, there is a complete blockage of the duct, against which enzymes begin to accumulate. For this reason, the pancreatic cavity becomes overfilled, causing the development of autoimmune processes in it, in which the body produces antibodies against its own cells.
If one or more symptoms appear, you should seek help from a gastroenterologist as soon as possible. The first thing the specialist will do is study the medical history and thoroughly examine the patient. This will make it possible to identify factors in the formation of the disease, as well as the presence and first time of onset of symptoms.
If pseudotumor pancreatitis is suspected, laboratory tests such as:
- a general and biochemical study of the blood will show some signs of the disease. For example, a slight change in its composition, impaired glucose tolerance. In addition, a study is carried out for the presence of tumor markers, which makes it possible to confirm or exclude the presence of pancreatic cancer;
- general urine examination;
- microscopic examination of feces.
But instrumental examinations of the patient have the greatest diagnostic value, which include:
- Ultrasound of the affected organ - this is necessary to detect an increase in the volume of the pancreas and characteristic changes in the bile ducts;
- CT and MRI - allow you to get a more detailed image of the affected organ. It is carried out to exclude a slow-growing cancerous tumor;
- ERCP – to visualize the main pancreatic duct;
- angiography of gland vessels.
The obtained test results will make it possible not only to make the correct diagnosis, but also to differentiate pseudotumor pancreatitis from pancreatic cancer.
The first step in diagnosing pseudotumor type is collecting anamnesis and objective examination of the patient. The doctor, as written above, can detect signs of obstructive jaundice, organ enlargement and pain in certain places upon palpation.
Development mechanism
According to ICD 10, the disease has code K86.1. It usually occurs in a chronic form. The disease is an inflammation of the pancreas, due to which partial fibrosis occurs and the tissue of the organ grows. The growth occurs unevenly, affecting a certain area, which is why the pathology is similar to the appearance of neoplasia.
The pseudotumorous form of chronic pancreatitis begins to develop with increased production of enzymes. This causes the formation of edema, and self-digestion of gland tissue is also observed. Because of this, cells die and necrosis of individual parts of the organ occurs.
To prevent infection of the body with cell decay products, the active formation of connective tissue begins, which protects the damaged areas. As a result, pseudocysts are formed. Their number increases as the disease progresses, which leads to the appearance of edema.
Over time, pseudocysts become covered with lime, which causes hardening of the pancreas and a pathological increase in its size. This protects the body from infection, but at the same time, the hypertrophied pancreas puts pressure on neighboring organs.
Particularly affected are:
- duodenum;
- bile ducts;
- splenic, portal veins.
These changes affect the patient’s well-being even more, which leads to complications.
Since chronic pseudotumorous pancreatitis begins with disturbances in the production of enzymes, it is necessary to find out what causes them.
The following may cause this deviation:
- gallbladder diseases;
- alcohol abuse;
- improper treatment of chronic pancreatitis or lack of therapy;
- pancreas injuries;
- infectious diseases;
- autoimmune disorders.
The listed problems can not only provoke the development of the disease, but also contribute to its active progression.
Clinical manifestations
The clinical picture of the disease is similar to the signs of pancreatic cancer, which greatly complicates differential diagnosis. Most often it is indicated by symptoms such as:
- severe pain syndromes of a shingles nature in the area of the left hypochondrium;
- dyspeptic disorders, when frequent constipation is replaced by causeless diarrhea;
- disturbances in food digestion;
- the appearance of nausea and vomiting, especially after eating;
- causeless weight loss.
During an objective examination, the doctor is alarmed by such physiological factors as:
- pallor and yellowness of the skin;
- pain in the epigastric region upon palpation;
- enlarged head of the pancreas (easily palpable);
- sagging and dry skin as a result of sudden weight loss.
Against the background of these signs, patients also complain of weakness, fatigue, disturbances in sleep and emotional state.
The symptoms of this form of pancreatitis are associated with compression of the biliary tract, endocrine insufficiency and lack of pancreatic enzymes, which are involved in digestion. In addition, among the clinical manifestations there are symptoms of tumors and severe pain. The initial stage of the pseudotumor form may be asymptomatic.
But most often patients present with the following signs of the disease:
- obstructive jaundice;
- girdle pain that occurs after eating spicy or fatty foods, any alcohol or overeating;
- undigested food in stool;
- nausea followed by vomiting, which brings relief;
- “fatty” feces (steatorrhea);
- diarrhea alternating with constipation;
- decreased glucose tolerance;
- causeless weight loss;
- on palpation – compacted head of the pancreas;
- enlargement of the gland.
Obstructive jaundice
In the mechanism of development of this symptom, the leading role is played by the enlarged head of the gland, compressing the common bile duct (bile duct). As a result, the bile formed in the liver cannot enter the duodenum, which is why the pressure in the duct increases, and the bile gradually penetrates into the bloodstream.
The main complaints with obstructive jaundice are: discolored stool, severe itching, darkening of urine and yellowing of the sclera and skin.
Pseudotumorous pancreatitis: symptoms and treatment
Elimination of the disease in most cases occurs using conservative methods, the basis of which is drug treatment of pseudotumor pancreatitis. In most cases, patients are prescribed:
- enzyme preparations – for the correction of exocrine and intrasecretory insufficiency of the affected organ;
- the use of antacids, which are aimed at compensating for the lack of bicarbonates;
- anticholinergics;
- antispasmodics - to reduce pain;
- antibacterial substances.
To relieve swelling of the pancreas and increased secretion of enzymes, regional radiation therapy and local hypothermia are used. Often patients are prescribed dietary table No. 5.
If the head of the pancreas is enlarged and obstructive jaundice is pronounced, endoscopic papillosphincterotomy is performed.
The prognosis of pseudotumor pancreatitis in cases of timely treatment is relatively favorable, since the disease is characterized by infrequent periods of exacerbation and sluggish progression. Endocrine insufficiency quite rarely causes nephropathy and angiopathy.
There are no specific preventive measures for this disease. People just need to lead a healthy lifestyle, stop taking certain medications, and promptly treat diseases that can cause this disease. For patients with a similar diagnosis, compliance with such recommendations will prolong the period of remission.
It includes:
- General tests of blood, urine, feces. With pseudotumor syndrome, the level of leukocytes and ESR in the blood increases. The urine contains large amounts of bilirubin and alpha-amylase in the absence of urobilin. Stool analysis can detect problems in the digestive system.
- Ultrasound. An abdominal ultrasound shows an enlarged pancreas. Also, such a study helps to study the condition of the pancreatic ducts.
- Blood chemistry. The presence of a pseudotumorous form of pancreatitis is indicated by an increased content of trypsin, lipase, sialic acids, and bilirubin in the blood.
- Radiography.
- CT (MRI). Thanks to these methods, it is possible to assess the condition of the organ and determine the likelihood of developing carcinomas.
- Study of the pancreatic ducts using endoscopy.
- Histological examination. It is necessary to distinguish this form of pancreatitis from pancreatic cancer.
If necessary, the doctor may prescribe additional procedures: enzyme blood test, cerulein test, cholecystography.
Echogram of chronic calcific pancreatitis: a) virsungolithiasis; b) dilated Wirsungian duct
To eliminate pseudotumor pancreatitis, a complex effect is required, which includes different methods:
- Medicinal influence. Conservative treatment is not considered effective for this pathology. The use of medications does not have the necessary effect, especially at an advanced stage of the disease. It should be used at the initial stage of pseudotumor pancreatitis (if the disease was diagnosed early). Drug treatment also helps slow down the rate of progression of the pathology. It is most often used to prepare for surgery. Medicines reduce symptoms, improve well-being, making it easier for the body to endure surgery. For this pathology, medications should be prescribed by a specialist based on the characteristics of the clinical picture. Painkillers and agents that help normalize the activity of the pancreas are often used.
- Surgical intervention. This route is the main one in treatment. During the operation, overgrown tissue is excised, which reduces pressure on adjacent organs. It is imperative to conduct an immediate histological examination of these tissues and, if cancer cells are detected, remove damaged areas of the pancreas. If no cancer cells are found, the largest cystic formations should be removed and the head of the pancreas should be truncated. This will reduce pressure on the pancreatic ducts. Surgery is the most effective method of treatment, since improvements occur almost immediately after surgery. It is very important to fix them with the help of drug therapy and folk remedies.
- Use of folk remedies. Traditional methods of treatment are often used, although it is impossible to achieve results only with their help. But when combined with other therapeutic methods, they are very useful. Among the most popular folk remedies are decoctions of medicinal plants. They help normalize the activity of the pancreas, relieve pain, cleanse the body, and reduce inflammation.
- Diet therapy. Diet allows you to slow down the rate of development of the disease. By eliminating harmful foods from the diet, it is possible to reduce the burden on the gastrointestinal tract. Also, a balanced diet allows you to replenish the supply of essential microelements, strengthening the body. During exacerbations of pathology, fasting is sometimes indicated, which cleanses of toxins. After surgery, diet therapy helps speed up recovery.
Diagnostics
The disease requires differentiation from other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and cancer. When examining a patient, instrumental diagnostic methods and laboratory analysis are used. A diagnosis can only be made based on the results of a complete examination of the patient.
Ultrasound
The ultrasound diagnostic method is used to assess the enlargement of a part of the gland and the degree of compression of the pancreatic ducts. The study reveals all contour irregularities and pathological changes in the density of organ tissue. If the data obtained is ambiguous, the patient is referred for MRI diagnostics.
Analyzes
Laboratory testing of urine allows us to establish the absence of urobilin in it against the background of increased levels of bilirubin and alpha-amylase. Stool analysis can confirm problems with the digestive system.
Studying the patient's blood helps to identify a large number of leukocytes, lipase, bilirubin, and trypsin.
To exclude a malignant neoplasm in the gland area, a biopsy of organ tissue is used. In pseudotumor pancreatitis, there are no atypical cells in the biological material.
How to find out whether a patient has pseudotumor pancreatitis or cancer
The described diagnosis implies that all complaints and clinical manifestations of the disease were taken into account and other diseases were excluded, not only the pancreas (for example, cancer), but also neighboring organs that have similar symptoms. For this, the following are required:
- Consultation with a gastroenterologist.
- Collection of medical history and complaints (previous pancreatitis, cholelithiasis, taking medications, complaints of pain in the right hypochondrium and epigastric region, and others).
- Examination of the patient with palpation (possible compaction and soreness in the pancreas area).
- Blood tests. This form of pancreatitis is characterized by a slight increase in the levels of trypsin, amylase and lipase, and impaired glucose tolerance.
- Determination of levels of tumor markers and pancreatic polypeptide (to exclude cancer). With an increase in the amount of cancer embryonic antigen, CA 125, CA 19-9, pancreatic polypeptide, the diagnosis of a tumor is confirmed, and with a decrease in the above-described substances, a conclusion is drawn about the presence of an inflammatory process, which confirms the diagnosis of “pseudotumorous pancreatitis”.
- Ultrasound of pancreas (presence of hypertrophy, changes in the structure of ducts and gland tissue, absence/presence of calcifications).
- CT or MRI (to exclude malignant neoplasms).
- ERCP. Method for visualizing changes in the pancreatic duct.
- Selective celiacography (determination of the state of pancreatic vessels).
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosing PTP begins with identifying the signs of the disease based on the patient’s complaints. Afterwards, more in-depth studies are prescribed.
Laboratory tests can determine the following factors:
- blood test - the state of ESR and leukocytes, the presence of bilirubin, various enzymes and acids;
- urinalysis - the presence of bilirubin, urobilin and amylase;
- scatology - the quality of food digestion and the presence of fats.
Instrumental studies:
- CT;
- Ultrasound of the digestive system;
- radiograph;
- endoscopic echolocation;
- gastroscopy of the gallbladder and biliary tract;
- intravenous cholangiography - injection of contrast fluid into the pancreatic veins to study the patency of the ducts, the presence of stones and neoplasms;
- radionuclide cholecystography - the introduction of contrast agents for subsequent x-rays of the organ, allows you to obtain a clear image of the pancreas in the image;
- histology is the study of living tissue obtained from a patient for the presence of oncology.
Important information: Symptoms of exacerbation of pancreatitis
Therapy
It includes:
- Drug therapy.
- Diet therapy.
- Endoscopy.
- Surgical intervention.
- Traditional medicine recipes.
Pseudotumorous pancreatitis, the treatment of which during periods of exacerbation is carried out in gastoenterology, is characterized by an undulating course (that is, alternating remissions and exacerbations).
Therapy for this pathology involves prescribing a gentle diet (table No. 5). Frequent meals are allowed (five to six times a day), but in small portions. Cooking methods: boiling and baking, rarely stewing. Fatty, fried foods, scrambled eggs, strong tea, coffee are prohibited, and the amount of meat (especially pork) and milk is strictly limited.
The main direction of therapy is etiotropic treatment, that is, the elimination of provoking factors (alcohol intake, medications) and the reasons that caused this condition. For example, in case of cholelithiasis - cholecystectomy, and so on.
Drug treatment should be aimed at correcting intra- and exocrine gland insufficiency. For this purpose, enzyme preparations are prescribed: “Pancreatin” in combination with “Solizim” or “Lipase”. To reduce steatorrhea, antacids and calcium supplements are used.
To reduce dyskinesia, anticholinergics are prescribed. To relieve severe pain, antispasmodics or Atropine are used. Mebeverine or Gimecromon are used as an effective antispasmodic for the sphincter of Oddi. During the period of exacerbation, treatment includes antibacterial drugs.
In addition to the treatment methods described above, endoscopic operations (for example, papillosphincterotomy) aimed at decompressing the ductal system are often performed for pseudotumor pancreatitis. Such interventions are especially effective for prepalillary strictures, papillostenosis, enlargement of the head of the pancreas, accompanied by obstructive jaundice and compression of the common bile duct.
Etiology
Pseudotumorous pancreatitis always develops against the background of untimely treated acute pancreatitis. However, provoking factors for its occurrence may be:
- long-term abuse of nicotine and alcohol;
- poor diet, for example, frequent overeating;
- a person has gallstone disease;
- a wide range of diseases of the liver and bile ducts, in particular congenital structural anomalies;
- long-term use of certain medications.
In addition, there is a lot of controversy in medicine about hereditary predisposition.
Prevention and prognosis
The chronic form of pancreatitis does not always degenerate into pseudotumor. Following six simple preventive rules will help you avoid this stage.
- When the first signs of pancreatic disease appear, consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment plan.
- Alcohol consumption and smoking are kept to a minimum.
- Strict adherence to the diet and nutrition regimen prescribed by the gastroenterologist is mandatory.
- Taking medications that regulate the production of enzymes is carried out in accordance with the doctor’s prescriptions.
- Regular preventive examinations are mandatory.
- In consultation with the attending physician, it is allowed to additionally use traditional methods of treatment.
If the diagnosis of “pseudotumorous pancreatitis” has already been made, do not despair. Strict adherence to medical recommendations will most likely allow you to achieve stable remission and avoid serious consequences.
In order to prevent the development of pseudotumor pancreatitis, it is advisable:
- renounce bad habits;
- change your diet;
- engage in feasible sports and lead an active life;
- promptly treat all foci of chronic infection (sinusitis, caries, otitis media);
- undergo preventive medical examinations.
With proper and timely treatment of pseudotumor pancreatitis, the prognosis is favorable. The patient can lead a normal life, provided he pays attention to prevention.
Preventive measures:
- Quitting bad habits (alcohol abuse, smoking).
- Take only medications prescribed by a doctor.
- Timely treatment of infectious diseases and disorders of the gallbladder.
- Proper nutrition.
Compliance with these recommendations will help avoid relapses of the disease and the development of complications. If you ignore the rules, the disease may worsen again.
In addition, you can join it:
- vein thrombosis;
- diabetes;
- peritonitis;
- jaundice;
- formation of new cysts;
- degeneration of cysts into a malignant tumor.
Pseudotumorous pancreatitis is a dangerous pathology fraught with the threat of developing cancer. Therefore, it is important to detect it in a timely manner and begin treatment.
Preventive measures for the diagnosis of “pseudotumoral pancreatitis” come down, first of all, to abstaining from drinking alcoholic beverages. Adequate and timely treatment of diseases that can provoke this pathology is also very important. Careful, specialist-supervised use of potentially dangerous drugs will also help to avoid pathology.