From this article you will learn: why a rapid heartbeat (or heart rate - abbreviated heart rate) can occur, and whether it is dangerous. How is it treated, and is it always required?
Author of the article: Victoria Stoyanova, category 2 doctor, head of the laboratory at the diagnostic and treatment center (2015–2016).
Article publication date: December 24, 2016
Article updated date: 05/25/2019
A pulse rate of 90 beats per minute (in adults) is considered rapid. In newborns, heart rate should not exceed 150 beats per minute. In children under 10–12 years old – up to 120–130. In teenagers - up to 110 beats per minute.
The causes of heart palpitations can be different, and they are not always associated with heart disease. In some cases, a high heart rate may be normal and nothing needs to be done - but in most cases treatment is still required.
In itself, a rapid pulse is not an independent disease, but a symptom of other disorders in the body. They are treated by doctors such as a cardiologist, arrhythmologist, cardiac surgeon, endocrinologist, nutritionist, sports doctor, neurologist, and psychotherapist.
If you have an increased heart rate, consult your doctor first.
Heart rate detection
When is a high heart rate normal?
Normally, the heartbeat increases for the following reasons:
- exercise stress;
- waking up after sleep;
- change in body position (when you suddenly stand up);
- strong emotions (both negative and positive);
- eating (if you have eaten heavily, your heart rate may increase).
Usually such a rapid heartbeat is not even felt. Or you may notice it, but it will not be accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms (discomfort, chest pain, a feeling of your heart “jumping out” of your chest, severe shortness of breath, etc.)
In this case, you don't need to do anything. This condition is not dangerous unless you have heart disease.
The heart beats faster in childhood and adolescence. If you notice that your baby's pulse is faster than yours, this is normal. If nothing bothers the child himself, you can rest assured.
The so-called idiopathic tachycardia also occurs. A condition where a high heart rate is associated with the individual characteristics of the body. Typically, in this case, the heart rate deviates from the norm by 10–15 beats per minute. In this case, there is no reason that provokes a rapid pulse, and no health problems. In this case, you also don’t need to do anything, no treatment is needed.
High heart rate due to poor lifestyle
Tachycardia can be provoked by:
- smoking;
- unhealthy diet (large amounts of fatty, fried, spicy, fast food, lack of fish products);
- emotional or physical stress (stress at work or school, excessive sports activity);
- lack of sleep;
- drinking large amounts of coffee or energy drinks.
In this case, contact a cardiologist and undergo an examination to determine whether you have any diseases of the heart or other organs. If doctors have not identified any pathologies, in order to normalize the heart rate, it is necessary to eliminate the reasons that caused its increase.
To adjust your diet, you will need to consult a nutritionist. To draw up a further physical activity plan, athletes will need a sports doctor. If you suffer from constant stress and sleep problems, consult a psychotherapist.
If an incorrect lifestyle provokes any diseases, treatment of the underlying pathology that caused the tachycardia will be needed.
Increased heart rate caused by illness
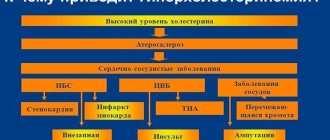
Tachycardia is a sign of many diseases of the cardiovascular system:
- chronic cardiac ischemia (it, in turn, is provoked by pathologies of the coronary vessels, for example, atherosclerosis or thrombosis);
- heart defects (stenosis of the mitral and other valves, patent ductus arteriosus, myocardial conduction disorders, atrioventricular block);
- myocarditis (inflammatory process in the heart);
- previous myocardial infarction;
- WPW syndrome (the presence of a bundle of Kent - an abnormal conduction pathway between the atrium and ventricle).
In this case, the rapid heartbeat is paroxysmal in nature. This is the so-called paroxysmal tachycardia. It is accompanied by other unpleasant manifestations. A life-threatening type of arrhythmia, ventricular fibrillation, may occur.
Often the pulse may increase due to disorders of the nervous system:
- neurocirculatory dystonia,
- vegetative-vascular dystonia.
These diseases are difficult to diagnose because they are accompanied by many symptoms similar to other diseases.
Also, high heart rate can be a symptom of diseases of the endocrine system:
- hyperthyroidism;
- very rarely - hypothyroidism.
In this case, the pulse is constantly frequent, not in the form of attacks. Complications include atrial flutter or fibrillation.
Set heart rate rate
The pulse is assessed using several indicators. Frequency is the number of times the heart beats per minute. When a person sits or lies, the indicators may change. Therefore, during the measurement process you should be in one position. Increased heart rate may be observed towards the end of the day. If the tapping is 10 units higher in the evening or in the morning, this is a variant of the norm.
Heart rate is also taken into account - this is the period of time between beats. If it is different, it means that the patient is developing an arrhythmia.
People of different ages have different heart rates. It is considered normal for children if the heart beats rapidly.
In newborns, it can reach 170 beats per minute, and this is not considered a deviation.
Over the years, the norms decrease. Therefore, in adults, the heart rate should be between 60-80 beats per minute. Exceeding the norm is called tachycardia, and lower levels are called bradycardia. In some situations, being rejected should not be a concern.
When there is a constant increase in heart rate, it is necessary to undergo examination and treatment.
Symptoms that accompany rapid heartbeat
Other manifestations depend on what disease caused the rapid pulse. To understand which doctor to contact and what to do, familiarize yourself with the manifestations of diseases, one of the symptoms of which is tachycardia.
Paroxysmal tachycardia with heart defects
It has clear time boundaries, meaning you can remember exactly when the attack started and when it ended. It can occur either spontaneously at rest or as a result of provoking factors (stress, physical activity, taking substances that affect the cardiovascular system).
An attack of rapid heartbeat (up to 220 beats per minute) is accompanied by:
- dizziness;
- sometimes - fainting;
- tinnitus;
- a feeling of constriction in the chest and “jumping” of the heart out of the chest;
- sometimes - nausea and sweating.
During paroxysm, ventricular flutter or fibrillation may develop. A prolonged attack can cause cardiogenic shock and cardiac arrest.
If you have experienced a paroxysm of tachycardia at least once, contact an arrhythmologist who will prescribe an additional examination and then treatment (will depend on the specific cause, in most cases it is surgical).
Tachycardia due to disorders of nervous regulation
An increase in heart rate is observed with VSD and NCD (neurocirculatory dystonia).
Tachycardia with VSD is persistent (up to 140 beats per minute), the heart reacts poorly to physical activity. Sometimes it is so bad that the patient cannot perform daily activities (walk for a long time, climb stairs, etc.)
With NCD, the increased heart rate can be either constant or paroxysmal.
Manifestations of VSD, except tachycardia:
- frequent dizziness and tinnitus;
- weakness and fatigue;
- sweating;
- intolerance to stuffiness;
- anxiety and suspiciousness;
- drowsiness;
- sudden mood changes;
- temperature changes;
- panic attacks and obsessive states are possible.
With pronounced psychological symptoms, the disease can be difficult to distinguish from neuroses or psychoses.
Manifestations of neurocirculatory dystonia:
- chilliness of feet and hands;
- cold hands and feet, pale skin;
- fatigue, weakness;
- headaches and dizziness;
- low or high blood pressure.
Treatment of these diseases is symptomatic. It is carried out by a neurologist and a cardiologist.
Symptoms of neurocirculatory dystonia
Rapid heartbeat due to endocrine disorders
Tachycardia is always accompanied by hyperthyroidism - excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. With this pathology, the heartbeat is constantly increased, heart rate reaches 120 beats per minute, even at rest. The pulse does not slow down even during sleep.
The disease can be identified by the following symptoms:
- enlarged thyroid gland;
- large difference between upper and lower pressure;
- stomach ache;
- increased appetite, despite this – weight loss;
- sweating;
- irritability, fatigue;
- menstrual irregularities in girls, enlarged mammary glands and decreased potency in boys;
- liver enlargement (reversible);
- high blood sugar.
If you notice these symptoms, contact your endocrinologist.
Very rarely, persistent tachycardia can be a sign of hypothyroidism, but usually with this disease the heartbeat, on the contrary, slows down
Click on photo to enlarge
What causes heart rate to jump in childhood?
A child's pulse beats faster than an adult's heart. And the younger the child, the faster the heart beats.
Causes of increased heart rate in children:
- Joyful excitement;
- A moment of stress or fear;
- Reaction to weather changes;
- Increased physical and sports activity;
- Heart diseases;
- Non-heart diseases.
If tachycardia is caused by a super load on the child’s body, then it goes away on its own. You just have to relax and unwind.
But tachycardia can also be a consequence of serious heart pathology: cardiac arrhythmia, myocarditis, even heart failure.
Diagnostics
To identify the cause of tachycardia, doctors examine the heart, internal organs, blood, thyroid gland, and nervous system.
If you notice an increased heart rate, which is accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms, consult a doctor (first of all, a cardiologist, he can then refer you to other specialists).
To determine the cause of an increase in heart rate, you need to do:
- ECG;
- Holter examination;
- Echo CG (ultrasound of the heart);
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland;
- Ultrasound of the liver;
- general blood test, for cholesterol and glucose, for infections;
- Analysis of urine.
After studying the results of all tests, the doctor will prescribe treatment, depending on the identified disease. For endocrine or nervous diseases, you will have to take medications, and for heart defects, surgery is most often performed.
After getting rid of the underlying disease, the heartbeat returns to normal.
External and internal factors leading to increased heart rate
These factors include:
- insomnia or too restless sleep;
- use of antidepressants that stimulate the nervous system;
- use of psychoactive drugs such as narcotics or aphrodisiacs;
- stimulants used;
- drinking large doses of coffee, strong tea or energy drinks;
- constant stressful situations;
- frequent overwork;
- drinking alcohol in large doses;
- use of potent medications in larger quantities and for a long time;
- excess body weight;
- high blood pressure;
- elderly age;
- the presence of illnesses such as influenza or ARVI.
It should be noted that during illnesses in which body temperature rises, the pulse and heart rate always increases. With each increase in temperature, the pulse becomes higher by an average of 10 beats.
How to treat tachycardia in various diseases
Palpitations can be cured completely by getting rid of its cause.
Elimination of heart diseases
The causes and treatment of rapid heartbeat are closely related: depending on the disease, increased heartbeat is treated with different methods (conservatively or surgically).
Drug treatment
| Disease | Drugs for treatment |
| Cardiac ischemia caused by atherosclerosis or thrombosis | Statins, antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants, nitrates, beta-blockers |
| Myocarditis | Immunomodulators, antiviral, antifungal or antibacterial drugs, depending on the pathogen |
| Post-infarction period | Supportive medications (glycosides, B vitamins, magnesium, potassium) |
For heart defects, surgical intervention is most often required, since medications do not eliminate the cause of the disease.
Surgical treatment of heart defects
| Disease | Operation |
| Mitral valve stenosis | Mitral commissurotomy |
| Patent ductus arteriosus | Occluder installation |
| WPW syndrome | Radiofrequency ablation |
| Atrioventricular block, myocardial conduction disorders | Installation of a pacemaker or cardioverter-defibrillator |
| Atherosclerosis or thrombosis of the coronary arteries | Coronary artery bypass grafting |
What to do in case of paroxysm (attack-like tachycardia)?
If an attack of tachycardia occurs for the first time, call an ambulance immediately.
After the paroxysm is relieved, the doctor will inform you about what to do if it occurs again.
As soon as you feel the onset of an attack, perform vagal tests, in which you stimulate the vagus nerve:
- press on closed eyes;
- massage the carotid sinus (located under the lower jaw);
- press on the root of the tongue;
- hold your breath and wash with cold water;
Before using vagal maneuvers, consult your doctor to learn the correct technique.
The doctor also prescribes antiarrhythmic drugs to relieve an attack of tachycardia. Often this is Verapamil. However, it is contraindicated for WPW syndrome and some other diseases. For WPW syndrome, ATP is used intravenously.
Use antiarrhythmic drugs only as prescribed by your doctor. Their incorrect use is life-threatening.
Treatment of VSD and NCD
Treatment of these diseases is symptomatic. Doctors prescribe medications to relieve the symptoms that most bother the patient.
If tachycardia is severe, beta-blockers are prescribed (for example, Anaprilin).
If rapid heartbeat occurs due to increased anxiety, anxiolytics (Phenazepam, Valium, Seduxen) or antidepressants with an anti-anxiety effect (Paxil, Amitriptyline) are prescribed.
The following procedures also apply:
- massage,
- pine baths,
- electrophoresis.
Electrophoresis apparatus
Therapy for hyperthyroidism
For hyperthyroidism, doctors recommend thyreostatic drugs that reduce the production of thyroid hormones (for example, Mercazolil).
For the symptomatic treatment of tachycardia, beta-blockers (Obzidan) are prescribed.
Also, to eliminate hyperthyroidism, and with it tachycardia, follow the following diet:
- eat more dairy and fermented milk products, vegetables, fruits;
- give up tea, coffee, cocoa, spices and chocolate.
Possible complications
To avoid irreversible consequences, everyone should know the dangers of a high heart rate. Regardless of the cause of the increased heart rate, the presence of high rates can provoke:
- the formation of blood clots in the heart cavity, which is dangerous for the development of a stroke;
- cardiac ventricular failure;
- arrhythmic shock;
- syncope;
- sudden death due to cardiac arrest.
All diseases are quite serious. Therefore, at the first symptoms, you should not talk about what to do with a high pulse and haphazardly swallow pills, but get examined immediately. This way you can prevent severe pathological diseases.
Folk remedies for palpitations
They help well if the cause of tachycardia is VSD.
| Hawthorn | Take 15 g of berries, pour a glass of boiling water, leave for 2 hours, drink 1-2 tablespoons 3 times a day before meals. |
| Herbal collection | Take 40 g of crushed valerian root, 40 g of hawthorn, 20 g of lily of the valley flowers, 30 g of mint, 30 g of fennel. Pour a liter of boiling water. Take a glass a day, dividing it into 3 doses. |
| Sand immortelle | Take 15 g of medicinal plant, pour a glass of boiling water, leave for an hour. Take 1/3 cup 3 times a day. |
Before drinking decoctions, get diagnosed, since many herbs are contraindicated for heart defects.
In general, the prognosis for tachycardia is favorable. You can completely get rid of palpitations by following the recommendations for treating the underlying disease.
Treatment
If a person is diagnosed with a high pulse, everyone needs to know what to do in such a situation. The patient should be placed on the bed, tight clothing should be removed, and the patient should be allowed to calm down. Among the medications that are usually found in every first aid kit, Corvalol, Motherwort tincture, and Valocordin are suitable; they will help you calm down and lower your pulse. You can place a cold compress on the patient's forehead and call an emergency ambulance. Upon admission to a medical institution, a thorough diagnosis of the pathology will be carried out, aimed at identifying its causes, after which the necessary treatment will be prescribed.
Tachycardia in mild forms is well relieved by valerian tablets. Quite often, doctors prescribe another herbal remedy that, in addition to valerian root, also contains lemon balm and mint - “Persen”. These drugs have a good sedative effect, easily relieve psycho-emotional stress, and help get rid of feelings of anxiety and irritability.
In more complex cases with persistent tachycardia, it is recommended to take synthetic drugs that help lower the heart rate. These include:
- "Diazepam" ("Relanium"). It has anticonvulsant, muscle relaxant and powerful sedative effects. Effectively relieves anxiety caused by stress and also reduces heart rate.
- "Phenobarbital". A powerful sleeping pill, when prescribed in small doses, helps relieve anxiety attacks that provoke increased heart palpitations.
If tachycardia develops against the background of low blood pressure, medications are selected with extreme caution. Many drugs designed to lower heart rate also lower blood pressure, which can have very serious consequences.
It is also necessary to choose medications carefully if a pregnant woman’s pulse is elevated. During this period, according to indications, herbal preparations, as well as tablets containing magnesium, may be allowed. It is also acceptable to use some folk recipes at home. In very severe cases, a doctor may prescribe Verapamil.
Did you like the article? Save it!
Still have questions? Ask them in the comments! Cardiologist Mariam Harutyunyan will answer them.
Ivan Grekhov
Graduated from the Ural State Medical University with a degree in General Medicine. General practitioner
How to relieve the condition at home?
If the cause of a high heart rate is not another medical condition, the goal of treatment is to reduce the heart rate. Special maneuvers can help with cardiac tachycardia.
Vagal maneuver
The vagal maneuver is the first choice among options for what to do with tachycardia (low pressure, normal, high) to stop episodes of rapid heart rate. By stimulating the 10th cranial nerve, called the vagus nerve, the speed of electrical impulses in the heart can be reduced, thereby slowing the heartbeat. However, this method of getting rid of tachycardia is effective in only 1 out of 3 patients.
Valsalva maneuver
The next way to treat tachycardia is the Valsalva maneuver. It involves closing your nose and mouth and trying to exhale. At the same time, you should tense your gluteal muscles as if you were on the toilet. The same effect can be achieved by immersing your face in a bowl of cold water or placing an ice pack on your face.
Symptoms
A condition in which there is a rapid heartbeat and normal blood pressure is characterized by:
- a feeling of a sinking heart, which is then replaced by strong and frequent tremors with pulsation in the phalanges of the fingers and in the temporal region.
- weakness, wobbly legs, heat throughout the body;
- dizziness to the point of fainting with ringing in the ears.
Panic attacks cause a lot of stress for a person and cause a feeling of fear, but they do not pose a threat to life.
If measures are not taken, the condition gradually worsens. Observed:
- increased sweating;
- cold and clammy hands and feet;
- feeling of anxiety, fear, panic;
- decreased appetite;
- chest pain.
Timely measures taken to eliminate increased heart rate will relieve unpleasant symptoms and normalize the condition. Drugs for tachycardia with normal blood pressure will help eliminate the onset of negative consequences, such as impaired blood supply to the brain, congestion in the lungs, cardiac asthma, and stroke.
Causes of tachycardia in women
The pathological form of rapid heartbeat can be provoked by a wide variety of reasons. The most common of them are considered to be:
- Significant physical activity.
- Natural changes in hormonal levels during puberty, pregnancy or menopause.
- State of stress, frequent nervous shocks.
- Drinking tonic drinks.
- Infectious diseases.
- Drug intoxication.
- Some thyroid diseases.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Anemia, hypotension, heart pathologies.
Causes of tachycardia
What pills should I take?
Only a specialist can recommend specific medications. The listed groups of drugs are sold by prescription.
Table 4. Blood pressure is normal, but pulse is high - what to take in this case
| Group of drugs | Information | Indications |
| Membrane stabilizing | Slow down the conduction of impulses leading to heart contractions. Suitable for cases where blood pressure is low but pulse is high | Unspecified heart rhythm disturbances, tachycardia, atrial fibrillation and flutter, etc. |
| Calcium channel blockers | They slow down the penetration of calcium ions, promote vasodilation, etc. You can take these tablets for high heart rate, but they can lead to a decrease in blood pressure. | Pain in the heart area, tachycardia, atrial fibrillation and flutter, etc. |
| Beta blockers | Block beta adrenergic receptors. Reduces the strength and frequency of contractions of the heart muscle, reduces its conductivity | Arrhythmia of various etiologies, hypertension, prevention of heart attack, etc. |
General recommendations
To prevent rapid heartbeat, it is necessary to take preventive measures, for example:
- avoid stressful situations;
- do not overexert yourself psycho-emotionally;
- do not burden the body with excessive physical activity;
- Healthy food;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- do not drink a lot of coffee and strong tea.
In addition, it is necessary to undergo annual preventive examinations with a doctor. Self-medication in such pathological processes is excluded, since there is a high risk of severe complications. If you feel unwell, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Originally posted 2018-03-09 15:14:14.