Man lives in a world where a fifth of the world around us is oxygen. We are accustomed to the fact that it is necessary for life to such an extent that we do not even notice our own breathing until some problems arise with it. When we suddenly start to lack oxygen, we think about its importance. There may be several reasons for shortness of breath when walking and physical activity. Let's look at the most popular ones together to know exactly what it is and what you can expect from your own body.
Types and degrees of shortness of breath
Shortness of breath or dyspnea in medical terminology is a violation of the respiratory rhythm towards faster or slower. In medicine, there are three types of dyspnea:
- Inspiratory. Heavy breath. Difficulty in passing air through the upper parts of the lungs. A sign of inspiratory dyspnea is frequent inhalations when talking or speaking in public.
- Expiratory. Difficulty breathing. Narrowing or blockage of the lower parts of the lungs.
- Mixed. Both inhalation and exhalation are difficult. The respiratory surface of the lungs is reduced.
There are five degrees of severity of shortness of breath:
- 0 — shortness of breath appears with increased physical activity;
- 1 - difficulty breathing occurs after fast walking or climbing stairs;
- 2 — dyspnea begins due to minor exertion;
- 3 - a person needs rest even with minimal exertion;
- 4 - shortness of breath occurs at rest.
The fourth stage indicates the presence of a serious disease that requires careful examination.
Shortness of breath due to lung pathology
This symptom is observed in all diseases of the bronchi and lungs. Depending on the pathology, shortness of breath can occur acutely (pleurisy, pneumothorax) or bother the patient for many weeks, months and years (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD).
Shortness of breath in COPD is caused by a narrowing of the airways and the accumulation of viscous secretions in them. It is constant, expiratory in nature, and in the absence of adequate treatment becomes more and more pronounced. Often combined with a cough followed by sputum discharge.
In bronchial asthma, shortness of breath manifests itself in the form of sudden attacks of suffocation. It is expiratory in nature - a light short inhalation is followed by a noisy, difficult exhalation. When you inhale special medications that dilate the bronchi, breathing quickly normalizes. Choking attacks usually occur after contact with allergens - when inhaling them or eating them. In especially severe cases, the attack is not stopped by bronchomimetics - the patient’s condition progressively worsens, he loses consciousness. This is an extremely life-threatening condition that requires emergency medical attention.
Accompanies shortness of breath and acute infectious diseases - bronchitis and pneumonia. Its severity depends on the severity of the underlying disease and the extent of the process. In addition to shortness of breath, the patient is concerned about a number of other symptoms:
- increase in temperature from subfebrile to febrile numbers;
- weakness, lethargy, sweating and other symptoms of intoxication;
- nonproductive (dry) or productive (with sputum) cough;
- chest pain.
With timely treatment of bronchitis and pneumonia, their symptoms stop within a few days and recovery occurs. In severe cases of pneumonia, respiratory failure is accompanied by cardiac failure - shortness of breath increases significantly and some other characteristic symptoms appear.
Lung tumors in the early stages are asymptomatic. If a recently emerging tumor was not detected by chance (during preventive fluorography or as an accidental finding in the process of diagnosing non-pulmonary diseases), it gradually grows and, when it reaches a sufficiently large size, causes certain symptoms:
- at first mild, but gradually increasing constant shortness of breath;
- hacking cough with minimal sputum;
- hemoptysis;
- chest pain;
- weight loss, weakness, pallor of the patient.
Treatment of lung tumors may include surgery to remove the tumor, chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy, and other modern treatment methods.
The greatest threat to the patient's life is caused by shortness of breath conditions such as pulmonary embolism, or PE, local airway obstruction and toxic pulmonary edema.
PE is a condition in which one or more branches of the pulmonary artery are blocked by blood clots, as a result of which part of the lungs is excluded from the act of breathing. The clinical manifestations of this pathology depend on the volume of lung damage. It usually manifests itself as sudden shortness of breath, disturbing the patient during moderate or minor physical activity or even at rest, a feeling of suffocation, tightness and chest pain similar to that of angina pectoris, often with hemoptysis. The diagnosis is confirmed by corresponding changes in the ECG, chest x-ray, and angiopulmography.
Airway obstruction is also manifested by the symptom complex of suffocation. The shortness of breath is inspiratory in nature, breathing can be heard from a distance - noisy, stridorous. A frequent accompaniment of shortness of breath in this pathology is a painful cough, especially when changing body position. The diagnosis is made on the basis of spirometry, bronchoscopy, X-ray or tomographic examination.
Airway obstruction can result from:
- violation of the patency of the trachea or bronchi due to compression of this organ from the outside (aortic aneurysm, goiter);
- damage to the trachea or bronchi by a tumor (cancer, papillomas);
- entry (aspiration) of a foreign body;
- formation of cicatricial stenosis;
- chronic inflammation leading to destruction and fibrosis of the cartilage tissue of the trachea (in rheumatic diseases - systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, Wegener's granulomatosis).
Bronchodilator therapy for this pathology is ineffective. The main role in treatment belongs to adequate therapy of the underlying disease and mechanical restoration of airway patency.
Toxic pulmonary edema can occur against the background of an infectious disease accompanied by severe intoxication or due to exposure to toxic substances in the respiratory tract. At the first stage, this condition manifests itself only as gradually increasing shortness of breath and rapid breathing. After some time, shortness of breath gives way to painful suffocation, accompanied by bubbling breathing. The leading direction of treatment is detoxification.
Less commonly, the following lung diseases manifest themselves as shortness of breath:
- pneumothorax is an acute condition in which air penetrates the pleural cavity and lingers there, compressing the lung and preventing the act of breathing; occurs due to injury or infectious processes in the lungs; requires emergency surgery;
- pulmonary tuberculosis is a serious infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis; requires long-term specific treatment;
- actinomycosis of the lungs - a disease caused by fungi;
- emphysema is a disease in which the alveoli become stretched and lose their ability to carry out normal gas exchange; develops as an independent form or accompanies other chronic respiratory diseases;
- silicosis is a group of occupational lung diseases resulting from the deposition of dust particles in the lung tissue; recovery is impossible, the patient is prescribed supportive symptomatic therapy;
- scoliosis, defects of the thoracic vertebrae, ankylosing spondylitis - with these conditions, the shape of the chest is disrupted, which makes breathing difficult and causes shortness of breath.
Symptoms of dyspnea
Symptoms of shortness of breath may occur occasionally or be chronic. A severe attack of shortness of breath is characterized by such manifestations as changes in the frequency and depth of breathing, wheezing and whistling in the chest. Signs such as blue lips, severe pallor, and gasping for air are common.
If dyspnea is chronic, a person breathes heavily even in a lying position, so third-party muscles, such as the muscles of the neck, back and peritoneum, can be involved in the breathing process. The chronic form of shortness of breath is determined by the respiratory rate. If there are deviations in the respiratory rhythm, then this is a clear sign of pathology.
Associated symptoms:
- heartbeat;
- dizziness;
- low pressure;
- darkening of the eyes;
- panic attacks.
Which doctor should I contact?
The habit of sending patients to general practitioners – general practitioners – has become a standard cliché for budget medicine. This option will also work as an initial examination to determine the clinical specifics. But after collecting the necessary anamnestic information, it is better to visit a specialist:
Conclusion
Late-diagnosed diseases of the respiratory system tend to cause severe complications, including patient disability and death. Sometimes pathological changes in the body are asymptomatic. Therefore, even healthy people should not neglect annual medical examination and screening examination of the chest - fluorography.
Doctors often hear the complaint “Doctor, I have a cough and it’s hard to breathe,” especially in the cold season. In most cases, this turns out to be a harmless infection that can be treated with bed rest, plenty of warm drinks and rest, but it happens that the symptoms are caused by a much more serious disease.
In what cases can dyspnea occur?
Dyspnea manifests itself in a variety of situations: when walking, climbing stairs, heavy physical activity, having sex:
- Shortness of breath when walking and light running is most often associated with diseases of the cardiovascular system. More precisely, with the system of coronary vessels that supply oxygen to the myocardium. Other factors also influence the appearance of dyspnea: the presence of heart failure, thin vascular walls, and septal pathologies. All these symptoms are most often observed in older people.
- A person performs some amount of physical work every day. But if, even with minimal physical exertion, a lack of air appears, this indicates the presence of pathology. This pathology can occur for several reasons: disturbances in the functioning of the heart, chronic diseases of the lungs and bronchi. The result is a lack of oxygen and, as a result, shortness of breath.
- When climbing stairs, a healthy person does not experience much discomfort. Difficulty breathing when rising occurs in people suffering from pulmonary diseases: emphysema, pneumonia or ARVI. Cardiac pathologies also often cause shortness of breath when climbing stairs. With severe overload, dyspnea can cause pain in the chest area and even lead to loss of consciousness.
- Shortness of air on a frosty day often occurs in people suffering from anemia, diseases of the lungs and respiratory tract, and allergies to cold. Symptoms of shortness of breath in the cold also occur in people who are underweight. To prevent such situations from arising, when going out into the frosty air, you need to breathe only through your nose and not inhale too sharply.
- Choking at night most often occurs with advanced forms of heart failure or congestive processes in the heart muscle. If you have to sit or recline to fall asleep, you should consult a doctor immediately.
- Shortness of breath during sexual intercourse can occur for all of the above reasons. In addition, lack of air during sexual intercourse occurs in severe anemia, when iron in the blood is at a catastrophically low level.
When shortness of breath is normal: complex information is accessible
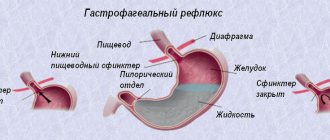
To begin with, it doesn’t hurt to understand primary anatomy if someone has taken a school anatomy course. Despite the fact that breathing seems to us something absolutely natural, simple and understandable, almost all systems of our body are involved in it. Blood, heart vessels, mouth, nasopharynx, bronchi and blood vessels, all of this is somehow involved in breathing.
The mechanism of the respiratory system: how shortness of breath occurs
By expanding the chest, we draw in another portion of air, which passes through the upper and lower respiratory tract, and then only enters the lungs.
There, oxygen is separated and enters the alveoli. It is there that the molecules of the gas we need so much are bound by the essential protein hemoglobin and attached to red blood cells (erythrocytes). Only after this, along with the blood, it spreads throughout the body. In the reverse order, hemoglobin “catches” harmful and toxic substances, and at the same time carbon dioxide, transporting it back to the lungs. As a result, we exhale all this unnecessary waste into the environment. But this is far from a complete cycle, because other organs also do quite serious work. For example, the heart pumps up pressure in the pulmonary circulation. The muscles of the diaphragm allow the lungs to contract and expand, releasing carbon dioxide and taking in air again. Control this complex mechanism that we simply do not notice, the respiratory center in the brain. It is so reliably designed that its operation generally ceases only after almost all other life support systems are turned off.
However, breathing does not always occur involuntarily. You can also control it consciously. The commands we give are sent through the spinal cord to the diaphragm, causing the chest to expand and contract again. When at least one of the elements of this complex “machine” is damaged, various breathing disorders, such as shortness of breath, may occur. The lack of oxygen is immediately felt by the lungs, then the heart and brain. Then the respiratory center gives a signal to increase the frequency of inhalations and exhalations in order to replenish the missing air reserves.
At its core, shortness of breath (dyspnea) is a violation of the frequency or depth of breathing. It would seem that there is nothing terrible, but the body perceives the lack of air very painfully. Moreover, there may be several reasons for a decrease in the level of oxygen in the blood, which most often causes symptoms of shortness of breath, both quite natural and truly dangerous.
Why shortness of breath shouldn't always be scary
After doing the exercises
Shortness of breath during exercise is quite normal. If muscles work actively, then oxygen consumption in them increases. At the same time, they literally “extract” it from the blood, causing breathing problems. Its rate increases significantly and natural shortness of breath may appear.
Emotional experience
If a person gets scared or feels anxious about something, the breathing process may also be disrupted. Any emotional experience is usually accompanied by the release of a portion of adrenaline into the blood. This hormone causes the diaphragm to work more actively, and the lungs to pump air through themselves faster.
Cough, runny nose or other similar problems
Viruses, bacteria and other microorganisms can cause severe coughing attacks. Nasal congestion is also far from conducive to proper normal breathing. As a result, despite our attempts to cough or blow our nose, the tree receives less oxygen than in its normal state. Therefore, the brain gives a signal to breathe even more often, more actively. If you are still moving towards everything, then the situation becomes seriously complicated, and severe shortness of breath may occur.
Anemia
With this disease, the body's absorption of iron, which is necessary for life, is impaired. Further, the logical chain is simple: the amount of hemoglobin also becomes reduced, but it is he who is responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the brain and other organs. If oxygen becomes very low, the body turns on its first defense mechanism - it begins to breathe more often.
Sedentary work
Few people pay attention to how they sit at the table. The majority does not control their posture at all, often resting their chin on their hands, tucking their legs under them, twisting and bending. This may cause some area of the lungs to simply “squeeze”, temporarily losing its functionality. Therefore, under any load, the brain immediately sends a signal to breathe more often. After all, the volume of air received is not enough for him. As a result, office workers who sit incorrectly for years become accustomed to their muscles so much that they no longer want to straighten at all. Then shortness of breath can become an eternal companion, but it cannot be said that it is too pleasant.
Obesity and overweight
If we talk about excess weight, everything immediately becomes extremely clear. The more difficult it is for you to move your muscles, which is very important with large fat deposits, the more oxygen they need. Since physical activity is considered almost the main cause of difficulty breathing, any movement of an obese person causes attacks of shortness of breath.
In addition, excess weight can be not only an external problem, but also a deeply internal one. Visceral fat can accumulate on internal organs. It envelops and also compresses the internal organs. These usually also include the heart and lungs.
Stuffiness, altitude and poor ventilation
Shortness of breath can occur not only for internal reasons, but also for external ones. For example, if there is a lack of oxygen in the environment, you will most likely experience unpleasant symptoms with the slightest activity. Such shortness of breath after physical activity is completely normal in a stuffy room, during the summer heat, high above sea level.
Causes of shortness of breath
However, not everything is as rosy as it might seem. The safe breathing problems we described above should not scare you. But when shortness of breath and sweating appear at the slightest physical exertion, for example, when walking at a leisurely pace, this may indicate serious problems in the body. Under no circumstances should this be ignored.
- High blood pressure.
- Pneumonia (pneumonia).
- Angina pectoris.
- Ruptured thoracic aneurysm.
- Asthma.
- Anaphylactic shock.
- Pneumothorax (mechanical damage to the lung).
- The presence of a foreign object in the respiratory tract.
- Hormonal imbalances, including thyroid dysfunction.
- Diabetes.
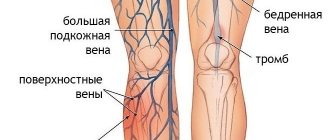
- Pulmonary embolism.
Under no circumstances should we ignore such problems. Shortness of breath for no reason may be the only sign of an asymptomatic heart attack. It is important not to miss the moment, to notice it in order to receive the necessary medical care on time.
Lack of air due to heart disease
The cause of cardiac dyspnea is diseases associated with circulatory disorders. Such pathologies include heart failure, mitral stenosis, and left atrial myxoma.
Symptoms of shortness of breath associated with cardiac pathologies are divided into two types: polypnea and orthopnea.
- Polypnea. In this state, a person breathes so often and deeply that there is a risk of hyperventilation. Polypnea is caused by excessive blood flow from the veins to the heart muscle. It appears most often in a horizontal position and during sleep.
- Orthopnea. This pathological condition forces a person to be in an upright position all the time. It is in this position that the patient feels an improvement in his condition.
Dyspnea can manifest itself sharply during myocardial infarction due to acute circulatory disorders. Other symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain, hoarse, heavy breathing, cold sweat, increased heart rate, and inability to raise the left arm.
Diagnostics
Expiratory shortness of breath is diagnosed during the initial examination of the patient, and additional studies are prescribed to determine the causes.
Laboratory research:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- study of blood gas composition;
- blood test for allergen;
- cytological examination of sputum.
Such tests will help identify inflammation and detect the presence of infection.
Instrumental diagnostics:
- An ECG is performed if there is suspicion of heart failure;
- X-ray examination will help determine the condition of the lungs and larynx;
- Bronchoscopy is prescribed to examine the condition of the bronchial mucosa.
Additionally, an ultrasound examination of the larynx may be prescribed, and if a foreign body is suspected, laryngoscopy is performed.
Central dyspnea
The central type is called dyspnea, which is a sign of pathological processes in the central nervous system (CNS). Such shortness of breath differs from all others in that it is not a symptom, but a cause of respiratory failure, leading to serious consequences.
The causes of shortness of breath can be different:
- Disturbances in breathing rhythm can be caused by disorders of brain function that occur due to head injury, stroke, inflammation and swelling. Chemical and drug poisoning can also contribute to lack of air.
- Bradypnea is rare breathing. Occurs due to drug poisoning or abnormalities in the central nervous system.
- Oligopnea is infrequent shallow breathing. May occur due to severe overheating.
- Tachypnea is rapid breathing. Often manifests itself in neuroses and malignant brain tumors.
- Hyperpnea is deep, rapid breathing. Occurs in people who are in a comatose state.
The causes of shortness of breath in children are the same as in adults: pulmonary and heart failure, problems with the bronchi, anemia.
Dyspnea in neurotic disorders
Complaints of shortness of breath of varying degrees are made by ¾ of patients of neurologists and psychiatrists. A feeling of lack of air, the inability to breathe deeply, often accompanied by anxiety, fear of death from suffocation, a feeling of a “blockage”, an obstruction in the chest that prevents a full breath - the complaints of patients are very diverse. Typically, such patients are excitable people who react sharply to stress, often with hypochondriacal tendencies. Psychogenic breathing disorders often appear against a background of anxiety and fear, depressed mood, or after experiencing nervous overexcitation. Even attacks of false asthma are possible - suddenly developing attacks of psychogenic shortness of breath. A clinical feature of psychogenic breathing features is its noise design - frequent sighs, groans, groans.
Neurologists and psychiatrists treat shortness of breath in neurotic and neurosis-like disorders.
Dyspnea in pregnant women
Young women during pregnancy may experience difficulty breathing in the third trimester of pregnancy. This happens due to the fact that the uterus, increasing in size, puts pressure on neighboring organs. Including the diaphragm. The degree of shortness of breath depends on how enlarged the uterus is. The larger the size of the fetus, the stronger the symptoms of lack of air.
A few weeks before the baby is born, shortness of breath usually goes away as the fetus descends into the pelvic area and the pressure on the diaphragm decreases.
If you are choking, what should you do?
If you suddenly feel like you can’t breathe, the first thing you need to do is:
- eliminate any physical activity;
- provide a person with peace;
- if we are talking about an asthmatic, immediately give him a respirator with medicine;
- when the patient has a history of pulmonary diseases, it is necessary to assume a sitting position.
If the reason that a person lacks air and complains “I’m suffocating” is a panic attack due to a vegetative-vascular disorder, then the best option for what to do would be to drink a mild sedative – hawthorn or valerian tincture. It should be noted that this reason (in the absence of other pathologies) is one of the most common, especially in women.
It is impossible to give any other recommendations within the framework of this article, since the reason that there is not enough air can be various pathological conditions that must be treated in a certain way. For obstructive conditions - bronchodilators, for ischemic conditions - nitroglycerin or other drugs prescribed by a doctor.
In situations where an attack of suffocation occurs spontaneously and manifests itself acutely, it is necessary to call an ambulance.
Psychogenic dyspnea
Psychogenic or neurological shortness of breath occurs due to frequent exposure to stressful situations. More than 60% of patients with neuropsychiatric disorders experience symptoms of difficulty breathing. Due to nervousness and strong excitement, a person begins to choke, feels dizzy and has an increased heart rate.
If psychogenic shortness of breath is not treated in time, it develops into neurotic asthma. And this is fraught with a deterioration in the patient’s condition, since it is difficult for the patient to distinguish the neurological nature of the attack from the physical one. If you have such a problem, you should contact a neurologist.
Shortness of breath due to pathology of the cardiovascular system
People suffering from heart disease report shortness of breath as one of their main complaints. In the early stages of the disease, shortness of breath is perceived by patients as a feeling of lack of air during physical activity, but over time this feeling is caused by less and less exercise; in advanced stages it does not leave the patient even at rest. In addition, advanced stages of heart disease are characterized by paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea - an attack of suffocation that develops at night, leading to the awakening of the patient. This condition is also known as cardiac asthma. It is caused by stagnation of fluid in the lungs.
Drug treatment
The most common causes of dyspnea and methods for their elimination:
- For bronchial asthma, Salbutamol is prescribed in tablets or inhalations are prescribed. The doctor may also prescribe Eufillin or Terbutaline intravenously.
- For heart failure, painkillers (mainly analgesics), diuretics, and nitroglycerin are prescribed.
- For unclear reasons for dyspnea, Lasix is prescribed.
- For psychogenic shortness of breath, it is recommended to do breathing exercises. Additionally, the doctor prescribes Diazepam intravenously.
- For obstructions, oxygen support and anxiolytics are prescribed.
Treatment of shortness of breath with pharmaceuticals
For pulmonary shortness of breath, treatment should begin with medications that reduce the load on the respiratory system.
Breathing exercises
Experts recommend, having passed the acute phase of the pathological process, move on to breathing exercises. Breathing should be accompanied by abdominal movements: when inhaling - forward, when exhaling - back.
- Lying or sitting, close your right nostril and breathe smoothly and steadily with your left. Repeat the manipulations, closing the left nostril.
- Sit on a high chair, straighten your back, take a deep breath through your nose. Exhale slowly through your slightly open mouth, pursing your lips or singing the sound “a-a-a.”
- Pull your shoulders back slightly and inhale. As you exhale, tilt your chin and slowly lower it towards your chest. Fix the position, holding your breath for a few seconds.
Simple exercises will help eliminate residual effects and activate the functions of the respiratory system.
Traditional methods
Treatment with folk remedies at home brings no less benefits than taking chemical medications. People know several proven recipes that help expand the bronchi and cure dyspnea:
- The following recipe will help you get rid of chronic shortness of breath. Grind 5 lemons and 5 heads of garlic in a blender. Add 500 ml honey and stir. Leave for a week in a closed container. Take 20 grams of the product (4 teaspoons) once a day for a month. In old age, the amount of lemons and garlic doubles.
- Onions baked in ash help fight dyspnea well. It can be consumed with sugar or honey.
- An infusion of motherwort can also relieve symptoms of suffocation. To prepare, you need to take 5-10 grams of dry product and pour 200 ml of boiling water. Leave for 15 minutes. Take a third of a glass three times a day after meals.
- Sesame oil helps relieve shortness of breath. At the onset of an attack, you need to drink a tablespoon of the drug. Consuming sesame oil every day reduces the risk of recurrent attacks.
- A good remedy for neurological causes of dyspnea is baths with chamomile. To do this, boil 500 g of dry grass in a saucepan and pour the broth into the bath. The duration of the procedure is no more than 10 minutes.
Formation mechanism
There are several theories about exactly how shortness of breath or dyspnea develops. The most objective assumption is that the brain incorrectly processes impulses coming from the respiratory muscles, which is why the felt muscle tension does not correspond to the intensity of inhalation or exhalation, and therefore a feeling of discomfort arises.
However, the mechanism under consideration only partially substantiates the physiological causes of shortness of breath, since the process of its formation is also influenced by other factors, for example, blood saturation with carbon dioxide, due to which chemoreceptors are activated, which respond to chemical stimuli and transmit the impulse to the control center.
Difficulty breathing, feeling as if there is not enough air or oxygen: first aid
If there is a person nearby who has an attack of lack of air, urgently open the windows, bring him and sit him by the window. Check to see if there were any injuries or anything getting inside. If possible, check for swelling. At the same time, call an ambulance and describe the situation over the phone; depending on the circumstances, doctors will adjust your actions.
If this is your relative or friend and this is not the first time the situation has arisen, you probably know that the patient has medications. Give medicine immediately to relieve symptoms.
The main means of combating is prevention
It is easier to prevent pathology than to treat it for a long time . To do this, it is necessary to carry out preventive measures. These rules do not require effort, but require constant adherence.
- Therapeutic exercises are effective not only during therapy, but also during the weakening of symptoms. Exercises help support and strengthen your back muscles. But when training, you always need to control the intensity of the exercises.
- A balanced diet also helps prevent the development of most diseases of the spine and other organs. Weight control is important. Therefore, it should not be allowed to increase excessively. If you have problems with this, you can contact a nutritionist. It will help you choose the right diet. First of all, exclude fried, smoked and too salty foods.
- They also pay attention to the choice of bed. The mattress should be quite dense and not very soft, the pillow should be of medium elasticity.
- Immunity plays an important role. To maintain its balanced functioning, it is necessary to take vitamins and immunomodulators.
- Walking in the fresh air will be useful at any stage of treatment and during remission. Walking areas should be located away from hazardous industries and roadways.
Osteochondrosis is a quite serious pathology. Changes occur not only in the spine but throughout the entire body. The blood vessels and respiratory organs are the first to be affected. What causes breathing difficulties. If you go to the hospital in a timely manner, all complications can be prevented. All unpleasant symptoms are eliminated after getting rid of the main pathological process.
Terminology
At the very beginning, you need to understand what shortness of breath is. So, first of all, it should be noted that this is a symptom that can accompany many diseases. However, to better understand the nature of shortness of breath, you need to consider its main signs:
- A person's breathing becomes more frequent.
- There is a feeling of suffocation, i.e. the person feels short of air.
- The depth of inhalation and exhalation changes. Breathing becomes noisier.
It is also worth saying that shortness of breath is always noticeable to people around you.
Tachypnea in children
With children the situation is somewhat different. In newborns, so-called transistor tachypnea sometimes occurs. More often, this condition occurs in those who were born as a result of a cesarean section or had an umbilical cord wrapped during intrauterine development. In this case, rapid, difficult breathing is observed, often with wheezing, and the skin becomes bluish due to lack of oxygen. No treatment is required. In a maximum of three days, the child will return to normal, since the traumatic factor has disappeared.
Another thing is children under 3-5 years old. In addition to diseases that are also typical for adults, they may begin to breathe partly for “childish” reasons. The main one is the entry of small objects into the respiratory system. If tachypnea began suddenly, you should immediately call an ambulance. The second, no less dangerous reason is epiglottitis, that is, inflammation of the epiglottis. Adults rarely get it, but it occurs quite often in children. In this case, you need to provide the baby with peace. Before the doctors arrive, you cannot change the position of his head and try to conduct an independent examination.
Origin of the disease
Almost all processes in the body occur with the participation of oxygen molecules. For example, thanks to the constant enrichment of gas, the following is carried out:
- airway patency, heating, humidification and air purification;
- proper functioning of the respiratory muscles;
- passive transport of oxygen molecules into the blood;
- transportation of blood to organs and tissues;
- maintaining the level of red blood cells in the blood;
- ensuring sufficient blood flow;
- proper functioning of the respiratory center.
If there is not enough oxygen to carry out any mechanism, a compensatory mechanism is activated. At the very beginning of a lack of air, a person is bothered by yawning, shortness of breath, rapid, difficult breathing and heartbeat, panic, and coughing at night. If compensatory mechanisms cannot meet the need for oxygen, the patient experiences suffocation and loss of consciousness, and the function of organs and tissues is impaired due to hypoxia.
Clinical signs
At the initial stage of the disease, no obvious symptoms are observed. But you should always pay attention to the slightest changes in breathing.
- One of the main points that indicates the presence of expiratory shortness of breath is the length of the exhalation. It increases, sometimes it can exceed twice the inhalation.
- Exhalation is accompanied by muscle tension.
- Intrathoracic pressure changes, protrusion and collapse of the spaces between the ribs occurs.
- As you exhale, the veins in your neck are visible.
In bronchial asthma, expiratory dyspnea is characterized by the presence of a box sound, which occurs due to the accumulation of excess air and limited movement of the diaphragm.
In addition, symptoms of dyspnea include:
- When exhaling there is a crunching sound or whistling sound.
- The person leans forward unnaturally.
- The patient often holds his throat or chest.
- The skin becomes paler.
- General weakness.
- Additional muscles are involved in the breathing process.
Rapid breathing: causes
Most often, tachypnea is a side symptom of “everyday”, conditionally non-dangerous diseases (such as influenza or acute respiratory infections). In this case, rapid breathing is accompanied by chills, runny nose, fever, and cough. However, tachypnea can also signal more severe illnesses. For example, about heart problems, the development of asthma, bronchial obstruction, tumors, the onset of acidosis in diabetics, pulmonary embolism. Therefore, rapid, difficult breathing that does not go away for a long time is a reason for an early visit to the clinic.
Help before the doctor arrives
If there is a person next to you who is suffering from expiratory shortness of breath, then you need to know how to help him. We hope that these tips will tell you what to do.
- Place the patient in a seat.
- Try to calm him down. It's no secret that stress, excitement, and anxiety lead to an increase in heart rate. In this regard, the consumption of oxygen and nutrients becomes greater, and the person’s condition worsens.
- Well ventilate the room where the patient is.
- Be sure to control air humidity. If it is dry, then put a pan of water on the fire. Do not cover it with a lid. There is another way to make the air in the room more humid - hanging wet towels and sheets.
People who often suffer from bronchial asthma must have an inhaler. You need to make sure that it is filled. Having alleviated the patient’s condition, immediately call an ambulance.
How does rapid breathing manifest itself?
For normal functioning of the body, an adult needs to inhale and exhale 18-20 times per minute. This is enough to provide oxygen to all organs and systems of the body.
The inhalation should be deep, continuous, and should not be accompanied by pain. With tachypnea, a person breathes quickly and shallowly. This describes the main symptom and cause of the phenomenon. The breathing rate increases when oxygen levels in the blood decrease and carbon dioxide levels increase. To restore normal saturation (oxygen saturation), the brain sends many signals through the respiratory center.
Patients often confuse tachypnea with shortness of breath. In the first case, the breath is shallow and sharp, and may be interrupted. With shortness of breath, both the frequency of respiratory movements and their depth increase. Rapid breathing of a pathological nature can turn into shortness of breath if the patient is not treated. The described symptom may be due to simple physiological reasons, or it may be provoked by a disease. Tachypnea during physical exercise, stress and training is considered normal.
In a healthy person, the frequency of inhalations increases in moments of stressful situations, anger or hysteria. Tachypnea caused by physical exertion or emotional shock does not require treatment. When the person is in a calm environment or rests, the symptom will disappear on its own. If breathing becomes frequent and intermittent without any exertion, at rest or sleep, you definitely need to be examined. The cause of this condition can be either a mild illness or a severe pathology.