If you experience abdominal pain, the first thing you suspect is a problem with the digestive system. The stomach plays an important role in this system; every person should know where this organ is located and how it hurts. Correct timely diagnosis of pain in the stomach helps to make an accurate diagnosis and begin immediate treatment of an important organ.
The stomach is responsible for the breakdown of essential substances such as proteins, carbohydrates, and also absorbs useful minerals and water. The hydrochloric acid of the stomach plays a special role, protecting it from microorganisms and breaking down food. The proper functioning of this organ ensures the health of the entire body, so you need to monitor it.
Abdominal organs and their functions
The peritoneum is a cavity with viscera, the walls of which are covered with a sulfur membrane, penetrated by muscles, fatty tissue and connective tissue formations. The mesothelium (sulfur membrane) produces a special lubricant that prevents the organs from rubbing against each other. This protects a person from discomfort and pain, provided that the organs are healthy.
The abdominal space contains the stomach, spleen, liver, pancreas, abdominal aorta, organs of the digestive tract and the human genitourinary system. All organs perform their functions, which are important for the functioning of the body. Since their main role is digestion, when talking about them in general they are usually called the gastrointestinal tract.
Important! The abdominals serve as a protective membrane for the entire internal organ system at the front. At the back, the protective function is performed by the bones: the pelvis and the spine.
The digestive system does the following:
- digests food;
- performs a protective and endocrine function;
- helps absorb nutrients;
- manages the process of hematopoiesis;
- eliminates toxins and poison entering the body.
The genitourinary system, in turn, performs reproductive and endocrine functions and removes metabolic products from the body.
A distinctive feature of the male and female composition of the abdominal cavity is only the genitals. All organs of the digestive system are identical and located in the same way. The only exception may be congenital pathology of internal organs.
Factors causing pain
An unhealthy lifestyle and indiscriminate eating also greatly affect the health of the entire digestive system. A person’s stomach hurts if food is taken on the go, if the food is of poor quality and unbalanced. The causes of pain and disturbances in the normal functioning of the digestive tract are as follows:
- fatty, spicy foods and smoked foods in the daily diet;
- eating hot food that burns the esophagus and stomach walls;
- insufficient chewing of food;
- poor quality of consumed products;
- stress and depression, as a result of a decrease in the amount of hydrochloric acid;
- long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that irritate the mucous membrane;
- taking chemicals;
- organ injury can lead to abdominal pain and hemorrhage.
Anatomical structure of the abdominal organs
The science of anatomy studies the structure and location of the internal organs in the human body. Thanks to it, people can find out the location of the insides and understand what hurts them.
Stomach
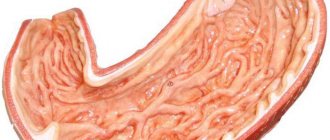
A cavity consisting of muscles that performs storage, mixing and digestion of food. In people with food addictions, the stomach is enlarged. Located between the esophagus and duodenum. Thanks to pulsating contractions, which is part of the motor activity of the organ, it removes chemicals, poisons and other harmful substances from the body. This ensures a protective (immune) function.
In the gastric pouch, proteins are broken down and water is absorbed. All incoming food products are mixed and passed into the intestines. The quality and speed of food digestion depends on the gender and age of the person, the presence or absence of diseases, capacity, and efficiency of the stomach.
The stomach is pear-shaped. Normally, its capacity does not exceed one liter. If you overeat or absorb a large amount of liquid, it increases to 4 liters. This changes its location. An overfilled organ can sink down to the level of the navel.
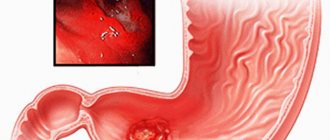
Stomach diseases can be very painful, so you need to be attentive to any unpleasant symptoms that arise in it.
Gallbladder
Serves as a cavity for the accumulation of bile excreted by the liver. Therefore, it is located next to her, in a special hole. Its structure consists of a body, bottom and neck. The walls of the organ include several membranes. These are sulfur, mucosa, muscle and submucosa.
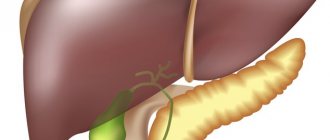
Liver
It is an important digestive gland for the functioning of the body. The weight of the organ in an adult often reaches one and a half kilograms. It is able to eliminate poisons and toxins. Participates in many metabolic processes. It deals with hematopoiesis in the unborn baby during the period of pregnancy by the mother, the absorption of glucose and cholesterol, and the maintenance of normal lipid levels.
The liver has an amazing ability to regenerate, but advanced diseases can seriously undermine a person's health.
Spleen
Parenchymal lymphoid organ located behind the stomach, under the diaphragm. This is the upper part of the peritoneum. It consists of the diaphragmatic and vesceral surfaces with an anterior and posterior pole. The organ is a capsule filled with red and white pulp inside. It protects the body from harmful microorganisms, creates blood flow in the unborn baby in the womb and in an adult. Has the ability to renew the membranes of red blood cells and platelets. It is the main source of lymphocyte production. Capable of capturing and purifying microbes.
Pancreas
An organ of the digestive system, second in size only to the liver. Its location is the retroperitoneal space, slightly behind the stomach. The weight reaches 100 grams, and the length is 20 centimeters. The structure of the organ looks like this:
The pancreas has the ability to produce a hormone called insulin. It regulates blood glucose levels. The main function of the organ is the production of gastric juice, without which food cannot be digested.
A person cannot live without the pancreas, so you should know which foods are most harmful to this organ.
Small intestine
There is no longer organ in the digestive system. It resembles a tangled tube. Connects the stomach and large intestine. For men it reaches seven meters, for women – 5 meters. The tube consists of two sections: the duodenum, as well as the ileum and jejunum. The structure of the first department is as follows:
The second two sections are called the mesenteric part of the organ. The jejunum is located at the top on the left side, the ileum at the bottom in the right region of the peritoneum.
Colon
The organ reaches one and a half meters in length. Connects the small intestine to the anus. Consists of several departments. Feces accumulate in the rectum, from where they are removed from the body through the anus.
What does not enter the digestive system
All other organs “living” in the peritoneal area belong to the genitourinary system. These are the kidneys, adrenal glands, bladder, and also the ureters, female and male genital organs.
The buds are shaped like beans. Located in the lumbar area. The right organ is comparatively smaller than the left. The paired organs perform the cleansing and secretory function of urine. Regulate chemical processes. The adrenal glands produce a number of hormones:
- norepinephrine;
- adrenalin;
- corticosteroids;
- androgens;
- cortisone and cortisol.
From the name you can understand the location of the glands in the body - above the kidneys. Organs help people adapt to different living conditions.
Important! Thanks to the adrenal glands, a person remains resilient in stressful situations, which protects the central nervous system from negative influences.
The appendix is a small organ of the peritoneum, an appendage of the cecum. Its diameter is no more than one centimeter and its length reaches twelve millimeters. Protects the gastrointestinal tract from the development of diseases.
Anatomical location and projection of the stomach on the stomach
According to the anatomical structure, the stomach can be divided into several parts:
- the confluence of the esophagus is the cardiac section;
- fundus department;
- a section that contains a large number of digestive cells - the body of the stomach;
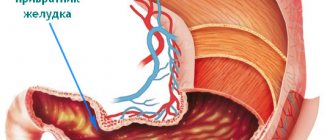
- The place where food is sent to the duodenum is the pyloric part.
It must be remembered that different parts of the stomach are projected differently onto the surface of the body. This is an important note that must be taken into account during the examination process:
- The human stomach is localized in the left hypochondrium, near the midline. That is, the location of the stomach occurs in such a way that a certain part of it is covered by the ribs.
- The cardiac section is located 2-3 cm to the left than the edge of the sternum is located - that is, approximately at the level of the xiphoid process.
- The fundus and body are located to the left, approximately 1-2 cm below the sternum itself.
- The pylorus is displaced to the right 2-3 cm from the midline of the abdomen and 2-3 cm below the sternum.
https://youtu.be/N_Izllc1UvA
How are the peritoneal organs checked for pathology?
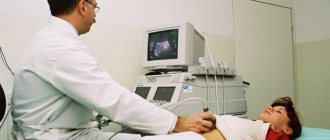
The main method for diagnosing the health of the abdominal organs is ultrasound. The study does not damage the structural units of tissues, therefore it is safe for the body. The procedure can be carried out repeatedly, if necessary. When eventration develops, methods of tapping (percussion), palpation and listening (auscultation) of the peritoneal organs are used. The correct location of the insides and the presence of foci of infection can be checked using MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) and CT (computed tomography).
Important! Diseases of the abdominal organs can threaten human life. Therefore, at the first symptoms, pain in the peritoneal areas, immediately seek help from medical professionals.
Condition of the glands
The secretory function of the stomach is provided by three types of glands, which contain the following types of cells:
- the main enzymes that secrete pepsinogen and other enzymes;
- lining (parietal) producing hydrochloric acid, which converts inactive pepsinogen into pepsin;
- cervical, produce protective mucus;
- accessory, also involved in the formation of mucus;
- endocrine, secrete hormonal substances (histamine, D somatostatin, serotonin, motilin and others), which are involved in the regulation of the release of enzymatic substances and hydrochloric acid.
Regulation of the formation of gastric juice is also carried out by the autonomic nervous system. The number of glands is about 40 million. With atrophy of the inner lining of the stomach, their number sharply decreases.
What diseases affect the abdominal cavity?
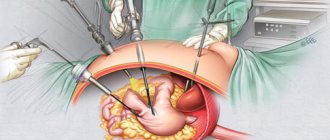
When a bacterial infection enters the body, appendicitis can develop. Treatment is carried out using a surgical method, that is, the appendix is removed. Organ prolapse is often diagnosed. The stomach usually goes down first. Therapy includes proper nutrition prescribed by a nutritionist, exercise therapy and wearing a special belt - a bandage.
If intestinal obstruction develops or adhesions appear, surgery is performed. If adhesions cause obstruction, they are removed, but only for health reasons. In such cases, relapses are possible. For frequent exacerbations of obstruction, doctors recommend a slag-free diet.
If you have inflammation of the stomach, it is not necessary to see a doctor if the symptoms go away within a couple of days. It is important to drink more fluids to avoid dehydration. If the patient does not feel better on the third day, it is necessary to go to the clinic. Doctors will prescribe the necessary tests and comprehensive treatment. In most cases these are medications.
The most common disease in the retroperitoneal space is hemorrhoids. Pathology brings a lot of unpleasant sensations. In cases of unbearable pain, doctors perform surgical treatment. If the progression of the disease is moderate, therapy is carried out with medications, lotions, compresses and baths using herbal preparations.
An abdominal hernia is a congenital or acquired disease, as a result of which the large or small intestine protrudes through an opening in the abdominal cavity. Occurs during pregnancy, obesity or heavy physical exertion due to constant pressure on a certain point in the peritoneum. Another reason is strong pressure on the lining of the internal organs. The pathology is treated through surgery.
Physiology [edit | edit code ]
The glands of the gastric mucosa secrete gastric juice containing the digestive enzymes pepsin, chymosin and lipase, as well as hydrochloric acid and other substances. Gastric juice breaks down proteins and partially fats, and has a bactericidal effect.
Due to the muscular layer, the stomach mixes food and gastric juice, forming chyme - a liquid pulp, which is removed in separate portions from the stomach through the pyloric canal. Depending on the consistency of the incoming food, it lingers in the stomach from 20 minutes (fruit juices, as well as vegetable juices and broths) to 6 hours (pork).
In addition, the stomach wall absorbs carbohydrates, ethanol, water and some salts.
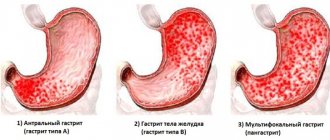
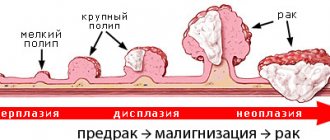
Gastric ulcer is a chronic disease caused by several causes, with the characteristic formation of ulcerative defects in various parts.