February 4, 2020
In the 21st century, stomach cancer began to lose ground in incidence, but only in developed countries. Since the 1970s, the cohort of cured patients in the United States has doubled - every third person with a neoplasm can be confident of a healthy future.
Just like a hundred years ago, the main method of salvation from stomach cancer is surgery, but modern oncology is inclined towards reducing the volume of tissue removed while maximizing the functionality of the entire gastrointestinal tract.
Treatment methods for stomach cancer
Most methods of surgical treatment of malignant processes of the stomach were developed at the end of the 19th and the first half of the 20th century; later the interventions were modified and complicated to combined operations with removal of the entire stomach and adjacent organs. The expansion of the scope of intervention was facilitated by advances in anesthesiology and improvement of postoperative recovery of patients.
In the last quarter of the twentieth century, postoperative mortality reached 25%, today it is no more than 1–2%. Meanwhile, the complication of operations did not affect the overall life expectancy of patients, who, as a rule, died from metastases.
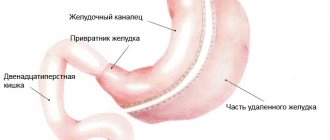
Today, oncologists have many modifications of standard operations in their arsenal, from endoscopic resection - removal of the mucous membrane in early stomach cancer to resection of part and the entire organ - gastrectomy, in combination with removal of the spleen, resection of the pancreas and large-scale reconstructions of the intestine to restore the physiological movement of food.
The results of the classic incision and laparoscopic approach are absolutely equivalent, but after laparoscopy recovery is faster. Initially inoperable cancer can often be operated on at the second stage after two to three months of neoadjuvant chemotherapy, preventing possible metastasis and relapse of the disease with a subsequent six-month course of adjuvant chemotherapy.
If the operation is technically impossible due to the involvement of the most important anatomical structures of the abdominal cavity in the cancer conglomerate, there is an alternative in the form of local radiation therapy with cyclic drug antitumor treatment.
The choice of treatment tactics is determined by the spread of cancer in the stomach and neighboring anatomical areas, the level of damage to the lymphatic collectors, the degree of aggressiveness of cancer cells and the initial condition of the patient.
In addition to the individual characteristics of the cancer patient, the talent of the oncologist surgeon, the clinical experience of the operating team and the professionalism of the rehabilitation team contribute to the success of treatment.
What allows one to suspect the development of an oncological process?
Diagnosis of stomach cancer begins with an assessment of the patient’s complaints, study of his medical history and family history, and an initial examination. The disease can be suspected already at the initial appointment, especially if the patient has been diagnosed with other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which can act as a factor in the development of oncology, and also if the symptoms begin to differ from those of a chronic disease.
A malignant tumor of the gastric mucosa is manifested by lack of appetite, weakness, weight loss, pain in the xiphoid process, nausea and vomiting, impaired swallowing, flatulence, and gastric bleeding. But at the early stage of the disease, clinical symptoms rarely appear; gastric carcinoma is most often suspected when the tumor grows into the submucosal layer.
At a late stage of oncology, the patient’s appearance changes (the face becomes sallow in color, the sclera turns slightly yellow, the skin is dry, the look is dull, there is no subcutaneous tissue). These symptoms are not specific and can appear in various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, so the diagnosis can only be confirmed after obtaining the results of a biopsy.
However, if you have this clinic, you need to urgently consult a doctor so that you can detect stomach cancer in the early stages.
During palpation of the stomach, the doctor can detect a neoplasm, of course, if it is already large enough (more than 2 cm). If the tumor is still small and the tissue separation is insignificant, then it will not be possible to feel it. Palpation should be carried out several times: when the patient is standing, lying on his back, and also in a position on the left and right side.
It is impossible to palpate a tumor on the posterior wall of the stomach, or if it is located deep in the hypochondrium, or due to abdominal obesity. If a tumor is palpable, this does not always indicate the impossibility of its surgical removal.
After a preliminary examination of the patient, laboratory and instrumental tests are prescribed, which will allow an accurate diagnosis to be made. Difficulties in differential diagnosis appear only if the tumor grows in the submucosal layer.
Treatment of gastric cancer with metastases
Almost every second patient with a newly diagnosed gastric tumor has distant metastases, which excludes radical surgery for any size of the primary tumor. However, such life-threatening complications of cancer as bleeding due to tumor decay, rupture of a thinned gastric wall, circular closure of the outlet tract are absolute indications for palliative surgery, often in the form of a full resection or gastrectomy.
The only possible treatment in the metastatic stage is chemotherapy; in the absence of further cancer progression, it is limited to 6–8 courses. After completing the first block of drug treatment, stop there until signs of progression appear. A disease that is insensitive to the initially chosen regimen is the basis for changing the combination of cytostatics. In recent years, courses of cytostatics have been supplemented with targeted drugs that improve the overall outcome of therapy. Most often, in almost 40% of stage 4, there is metastatic dissemination throughout the abdominal cavity with the production of ascitic fluid.
In order to identify hidden foci of cancer in the abdominal cavity, all patients undergo diagnostic laparoscopy before surgery. Unfortunately, the results of standard drug treatment for the ascitic form of the disease are not very encouraging.
Metastasis to the ovaries is typical for gastric carcinoma; often this is the only metastatic focus. If the primary tumor is operable, they try to simultaneously perform a radical operation on the stomach and remove the affected appendages. In most cases, the life expectancy of such patients does not differ from the population of initially operable patients.
Stage 4 cancer: how do they die?
Final stage oncology is an irreversible cancerous lesion of the body, in which atypical and uncontrolled proliferation of cellular components occurs, as well as their mutation. This process is accompanied by the formation of many metastases, which damage all the most important organs. Often, the progression of a cancer lesion to stage 4 is not accompanied by any special abnormalities. Because of this, the disease is diagnosed too late.
All therapeutic measures in this case are aimed only at suppressing symptoms and improving the quality and length of life of patients diagnosed with stage 4 cancer. How do such patients die? The answer to this question is contained in the description of the stages of further progression of the disease.
Food refusal and cachexia
First of all, the daily ration is reduced. As cancer cachexia and muscle weakness develop, the patient's need for food and fluids decreases. Refusal to eat is the first signal that the terminal stage of cancer is approaching. As a rule, at the dying stage, the patient wants to be in the circle of relatives. Even if the cancer patient is in a coma, doctors advise being present with the dying person, because... There is evidence that a person will still hear loved ones.
Predagonia and agony
This phase is characterized by impaired functionality of the central nervous system, suppression of physical and emotional activity, pallor of the skin, and decreased blood pressure. This condition, in the presence of honey. help may last a long time. Agony is, by and large, the final phase of death. During agony, there is an imbalance of vital functions, due to which tissue components are unevenly supplied with oxygen. Oxygen deficiency causes cessation of breathing and blood flow, which is the main cause of death; agony can last about 3 hours.
Deviations in the intensity and completeness of breathing
The preagonia stage is accompanied by a decrease in respiratory rate and amplitude. This is due to inhibition of metabolic processes and a decrease in oxygen demand. The appearance of noise when inhaling and exhaling is a sign that there is fluid inside the lungs. In such situations, it is easier for the patient to breathe by turning him over to one side. The picture of a patient dying is described by the respiratory rate with so-called apnea intervals. To alleviate suffering, experts may suggest using an oxygen cushion, which will ensure the supply of oxygen. People caring for a dying cancer patient should systematically wet their lips and mouth with water.
Clinical death
Clinical death is no longer the answer to the question: how do they die with stage 4 cancer? , because During this phase, the functionality of the body is inhibited and therefore the patient can already be considered dead. This death is characterized by the occurrence of minimal metabolic processes within cellular components. With other pathologies, the described condition is correctable (if measures are taken within 6-8 minutes), however, with oncology, the transition to full-fledged death is inevitable.
Treatment of stomach cancer reviews
A 59-year-old patient ended up in the Medicine 24/7 clinic, as he himself said, “in a completely desperate situation” - in a state oncology institution he was denied surgery and recommended to “look for a clinic abroad.” The far from optimistic parting words did not plunge the man into depression; on the contrary, on the advice of friends, he immediately went to the clinic on Avtozavodskaya.
The examination confirmed that the operation at the first stage is impossible due to the spread of the process to the neurovascular bundles, the pancreas and with metastases to the lymph nodes. I had to endure 9 weeks of not very pleasant treatment with cytostatics, but subsequent examination showed that it was very successful.
The patient's stomach was completely removed, but the chosen reconstruction technique made it possible to minimize the likelihood of serious consequences in the form of dumping syndrome. One and a half months after the intervention, preventive chemotherapy began. After two years, the patient feels well and continues to work in his specialty.
Etiology
The causes of gastric cancer have not been reliably elucidated, but it is known that carcinomas among members of the same family are 20% more common. Also, this disease is more often registered among people with the first blood group, which indicates the possibility of a genetic etiology. In addition, deficiency of ascorbic acid and poor nutrition play a certain role in the development of stomach cancer, when a person often abuses smoked, fried, spicy and salty foods or eats canned foods that contain nitrates. Risk factors that increase the risk of developing stomach cancer include the following:
- contact with asbestos or nickel;
- primary and secondary immune deficiency;
- pernicious anemia, in which cancerous tumors in the stomach are found 20% more often;
- alcoholism and smoking;
- viral lesions, especially infection with the Epstein-Barr virus;
- cyanocobalamin deficiency.
Also worth mentioning are precancerous diseases of the stomach, which can develop into cancerous lesions. These include chronic atrophic gastritis, chronic ulcers, adenomatous polyps (if their size is more than 2 cm, the frequency of degeneration into a cancerous structure is about 40%). In addition, infection with a specific bacterium – Helicobacter Pylori – is of etiological significance.
Stomach cancer traditional methods of treatment
The effectiveness of traditional medicine in the treatment of cancer in general and gastric carcinoma in particular is confirmed only by popular rumors; in reality, there has not been a single case of curing a malignant process with a decoction or infusion of herbs.
Neither alone nor in collections, not a single plant is capable of killing a cancer cell. The tumor actively resists the pressure of cytotoxic chemotherapy; it is naive to believe that it will recede under the influence of collecting medicinal herbs and bee products.
It is sad and criminal that in addition to the infusion of chamomile or thyme, which is harmless for tumors, all kinds of healers and on Internet sites offer regular use of tinctures of poisonous plants aconite and hemlock, which cause chronic poisoning. An infusion of celandine and St. John's wort guarantees a burn to the gastric mucosa, which definitely will not improve the health of an oncology patient.
Any means of traditional medicine distract from special treatment, give false hope and always lead to a “broken trough” of life. An oncological disease does not give the patient extra time; weeks and months spent on illusory therapy with folk remedies are sure to result in forever lost therapeutic opportunities.
Forms of cancer
There are two forms:
- Early ones, which in turn are divided into two more types:
- the first type is intraepithelial cancer (carcinoma in situ), that is, cancer cells spread only in the mucous epithelium, the tumor size is less than 3 mm,
- the second type - the tumor grows into the submucosal layer and muscular plate of the mucous membrane.
- Late (progressive) - the neoplasm grows along the surface layer of the muscularis propria, throughout the entire thickness of the muscularis propria, or throughout all layers of the organ wall. This form of cancer tends to spread to nearby organs and metastasize.
Possibility of recovery and mortality statistics
On average, the life expectancy of men with stomach cancer is reduced by 12 years. For women, this figure is 15 years. According to Russian statistics, the survival rate of patients is as follows:
- At the first stage, as a rule, it is possible to detect pathology in about 10-20% of patients. And in most cases, 60-80% of them survive within 5 years.
- At the second and third stages, damage to regional lymph nodes occurs. And this sign, as a rule, is detected in 30% of patients, among whom about 15-45% survive for 5 years
- At the fourth stage, metastases are already present in neighboring organs, so at this stage the pathology is much easier to detect, and it is detected in half of the patients. Within 5 years, only 5-7% of them survive
There are plenty of clinics where stage 4 stomach cancer is treated in Russia. But still, experts advise receiving a course of treatment in Israel or Germany. Their methods are newer and more effective.
In the process of researching this disease, new methods are being created for better treatment of this disease and methods for detecting it at various stages.