What is afraid of Staphylococcus aureus, which has settled in the throat and nose of a person, should be understood in order to effectively combat it. This bacterium is the reason why a person begins to suffer from sore throat, laryngitis and pharyngitis. A strong immune system, as well as timely seeking help, play a significant role in the prevention of the disease. To treat diseases caused by staphylococcus, a whole range of different drugs are taken.
Staphylococcus. Symptoms, causes, types, tests and treatment of staphylococcal infection
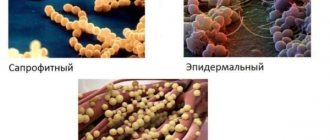
Staphylococci are non-flagellate, non-spore-forming, lilac-stained Gram-stained spherical bacteria. Under strong magnification, it can be seen that microorganisms are arranged in pairs, in the form of chains, or connected to each other in the likeness of bunches of grapes.
Microbes are not afraid of drying and do not die under the influence of antimicrobial and saline solutions. Staphylococci are aerobic microorganisms - they do not need oxygen to survive. Staphylococcus aureus lives mainly on humans. The microbe settles in the pharynx, less often in the vagina, under the arms, in the perineum and very rarely in the intestines. Staphylococcus aureus can be found in the vagina of 10% of women.
During regulation, bacteria multiply rapidly, which can cause toxic shock syndrome. In the case of Staphylococcus aureus, bacterial carriage can be permanent or temporary - it depends on the stability of the bacterial culture and the activity of the microbial flora competing with it. There are especially many carriers of staphylococci among health workers, people who take drugs, and people with dentures, including dental ones, since these categories of the population are often exposed to microtraumas that violate the integrity of the skin.
There is a staphylococcal vaccination, which is produced in 1 ml ampoules. This is a complex of soluble heat-stable antigens obtained from bacterial microbial cells. The vaccine provokes the formation of antimicrobial antistaphylococcal immunity.
It can be used to vaccinate children from 6 months of age. In addition, there is a staphylo-protean-pseudomonas aeruginosa adsorbed liquid vaccine. It contains staphylococcal antitoxin, cytoplasmic antigen of staphylococcus, antitoxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, polyvalent proteus antigen.
It is used to prevent purulent-septic exacerbations in patients from 18 to 60 years old. It is administered subcutaneously to patients with isolated injuries and closed fractures, as well as during planned operations. As a rule, when staphylococcus gets on an area of skin, it takes root and, with good immunity, does not provoke any diseases; a person can simply be its carrier.
But do not forget that you cannot fight staphylococcus with antibiotics on your own. There are only a few main types of staphylococcus; they are considered the most dangerous to humans.
In parallel, there are subspecies - strains that differ from one another in various properties. This explains the ability of staphylococci to take on all sorts of forms.
The main types include:. Doctors have long known the factors that contribute to the development of staphylococcal infections in the human body. Such factors include weakened immunity, the presence of chronic diseases, and the adverse effects of a polluted environment. The immune system plays a key role here. It is simply impossible for staphylococci to penetrate and reproduce in a healthy, strong body.
On the contrary, with a weakened immune system, the proliferation of these bacteria becomes very likely. These factors negatively affect the entire body, creating good soil for various diseases. To protect yourself from the disease, you should adhere to a scheme that normalizes immunity and metabolism. Mechanisms that protect the body:. Thus, both staphylococcus and streptococcus bacteria develop due to a number of unfavorable factors, including:.
Staphylococcus can cause conjunctivitis, stye and other inflammatory eye diseases. Staphylococcus aureus is known as one of the pathogenic microorganisms that are resistant to many antimicrobial agents.
Modern medicine offers a wide range of antibiotics for Staphylococcus aureus in adults. This microorganism can live almost everywhere, for example, in a person’s home, on furniture, on walls, and plumbing fixtures. This is the so-called domestic staphylococcus. Outside the home, you can become infected with it through airborne droplets by communicating with its carrier. The most stable and dangerous type of pathogenic bacteria lives in hospitals; newborn children and young mothers become infected very easily due to weakened immunity.
In the case described above, treatment of Staphylococcus aureus with antibiotics will most likely be contraindicated. Hospital-acquired staphylococcus can cause more than a hundred different diseases.
Its easy victims are people with weakened immune systems. The list of diseases can be continued almost endlessly. In order to find out for sure whether Staphylococcus aureus is the cause of the disease, the specialist will prescribe tests to the patient based on which he will select the correct treatment and antimicrobial agents that can defeat it. In most cases of illness, the doctor prescribes antibiotics against Staphylococcus aureus.
Almost any doctor can treat the disease, for example, a therapist, ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, surgeon, infectious disease specialist. Treatment of pathogenic bacteria comes down to several methods. One of them is taking antimicrobial agents or antibiotics. The specialist does not immediately prescribe the above drugs in all cases, since treatment with them must be justified. These medications are usually prescribed for severe forms of the disease.
The most modern method of treating staphylococcal infections is considered to be immunostimulation, since it is believed that weakened immunity contributes to the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. The patient is prescribed injections of drugs that stimulate the immune system of the human body. In some cases, the fight against bacteria is carried out by normalizing metabolism in the body. The sick person is prescribed a special diet.
The doctor develops a special diet based on tests and physical data of the patient. The most gentle method of combating pathogenic microorganisms is the intake of vitamins and biologically active food supplements. The point of this method is to help the immune system cope with the disease by replenishing it with missing elements. Antibiotics have opened up great opportunities for medicine in the fight against almost any infection. But, even highly qualified specialists in certain cases may have a question about what antibiotic to treat Staphylococcus aureus.
The thing is that this bacterium is capable of adapting to the effects of a particular drug, so to speak, developing its own immunity against it. All elements of the human body are able to exchange information with each other on how to resist this or that type of antibiotic.
In order to select the right drug, the doctor must find out what antibiotics the patient took not so long ago, if he has any other diseases, find out the type of staphylococcal infection, whether the patient is allergic to medications, and whether the patient is currently taking any other medications. some medicine.
The main fight against bacteria involves taking antibiotics. On the question of which antibiotics are effective against Staphylococcus aureus, most experts agree that they belong to the group of cephalosporins. Local antimicrobial agents are used for skin diseases, these can be: Bactroban, Bonderm, Supirocin. But you should understand that they alone cannot help the body cope with the disease. If you have symptoms indicating the presence of Staphylococcus aureus in the body, you must see a doctor and, having passed all the necessary tests, strictly follow the prescribed treatment regimen, since stopping taking antibiotics at the slightest improvement in well-being can provoke a new outbreak of the disease.
The dosage of the drug is prescribed individually by the treating doctor. You cannot interrupt treatment on your own, as bacteria develop resistance to the antibiotic. Any unauthorized actions with medications lead to dysbiosis or disruption of the liver and kidneys.
As a rule, the minimum course of therapy is a week. In more complex cases, the period varies from day to day. During therapy, you need to adhere to a certain diet, since some foods can weaken or, on the contrary, enhance the effect of the drug.
For example, the consumption of milk, sweets, juices, yoghurts, buns, and alcohol is not allowed. The drug should not be taken with soda or coffee-containing drinks. A product with a wide spectrum of action. Has antibacterial, bacteriostatic, bactericidal properties.
It is used for rhinitis, inflammation of the skin and tissue, carbuncle, furuncle, abscess, folliculitis, impetigo, thermal burns, injuries. Almost all types of staphylococcus are sensitive to it, including aureus and saprophytic. Mupirocin ointment is applied to the affected areas of the skin, the duration of treatment is prescribed by the doctor.
For nasal diseases, the drug is administered into the nasal passages. Antibiotic with a broad spectrum of action. It was most active in the fight against Staphylococcus aureus. Indications for the use of this ointment are:. The drug is intended for external use only. Apply the ointment to damaged areas of the skin. From the first days of treatment, the skin condition should improve; if on the third day of use no positive effect is visible, the treatment should be reviewed and adjusted.
Bacterial culture studies help determine the number of microorganisms, the properties and sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics, and also identify the cause of the disease. Having understood the diagnosis, you can proceed directly to treatment. Diagnosis of Staphylococcus aureus in the intestines is based on two methods, which are preceded by a mandatory oral questioning of the patient and taking blood for a general clinical analysis. An antibiogram helps to finally decide how to treat Staphylococcus aureus in the intestines - a method that reveals the resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to antibiotics.
Now that you know how and how to treat a staphylococcal infection, it is equally important to determine how to properly treat bacterial diseases. In fact, antibacterial treatment methods are not difficult to implement and require compliance with a number of rules. Without ignoring the rules listed above, you can cure yourself or a loved one of a staphylococcal infection in the shortest possible time from 1 to 3 weeks.
Do not forget that the appearance of any complications in the course of the disease requires immediate contact to the clinic to organize the most competent therapy. In general, choosing antibiotics for a staphylococcal infection is not so difficult and not problematic for any person.
The main thing in making a choice is to know the nuances of a particular case and use the material presented above. We hope the article provided answers to your questions.
Diagnostics
To obtain material for diagnosing Staphylococcus aureus, it is necessary to take a smear from the pharynx (throat), nasal mucosa, skin or other surfaces (depending on the disease). Some preparation is required before taking a smear.
Preparation for taking a smear is as follows:
- Avoid using mouth rinses. At least a few days before the test, you cannot use various sprays and solutions for gargling, nasal sprays and ointments containing antibacterial agents and antibiotics, as their use can contribute to a false negative result (tests will not detect staphylococcus, even if it is present on the mucous membranes).
- Refusal to brush your teeth before the examination. In the morning before taking the test for the study, you should not eat, drink, or brush your teeth, as this may lead to an incorrect result.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytadvertiseru
The main methods for diagnosing Staphylococcus aureus are:
- Microscopic method. The study of preparations stained using the Gram method is used more often for the preliminary diagnosis of infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Microscopy reveals pathogenic cocci (spherical bacteria) in the smear, located singly, in pairs or in clusters. Staphylococcus has a positive Gram stain (blue color), it is immobile, with a characteristic regular spherical shape.
- Culture method. In most cases, in order to accurately establish the pathogenicity of detected staphylococci, it is necessary to isolate these bacteria in pure culture by inoculating the test material on nutrient media. At the same time, there are a large number of nutrient media for cultivating pathogenic staphylococci, since they are unpretentious to nutrient media and are well cultivated even on simple media. The optimum temperature for the growth of staphylococci is 30 – 37ºС.
- Antibioticogram is a method that allows you to determine the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics. In order to determine the sensitivity of a microorganism to a specific antibiotic, the microbe is inoculated on a solid nutrient medium, then special disks soaked with an antibiotic are placed on the surface of the medium. The essence of the method is that an antibiotic that is effective against a given microbe suppresses its growth. The results of the antibiogram are of great importance for prescribing the correct treatment.
Before identifying the disease, the attending physician conducts a full examination of the patient, including a detailed medical history. Further differential methods for diagnosing Staphylococcus aureus are carried out similarly to streptococcal lesions.
Common detection methods include:
- Sowing of biological material. It makes it possible to accurately identify the main causative agent of the pathology and, if possible, determine an antibiotic drug that can eliminate it.
- Latex agglutination. A method for identifying specific pathogenic strains that multiply inside the human body.
- Standard test for coagulase activity in vitro. If after 4 hours the result is negative, repeat testing is prescribed.
- General tests of urine, feces and blood. Allows you to determine the level of erythrocyte sedimentation rate, leukocytosis, as well as protein and the total number of leukocytes in the blood.
In the development of diseases affecting the skin, the Widal agglutination reaction test is used, thanks to which the total level of antibodies can be determined.
Also, to prescribe the correct treatment method, a special test for the presence of conjunctivitis is often performed, a smear of which is taken from the lower eyelid.
Staphylococcus aureus in the nasopharynx symptoms in adults treatment
This bacterium belongs to gram-positive microorganisms, which means that with the assistance of special tones it will change color in a specific way. This bacterium is pathogenic. The golden microbe, also known as staphylococcus, appears on the mucous membrane or skin of a person, and it begins to provoke many diseases. The patient exhibits severe intoxication of the body, and disturbances of internal organs occur. The staphylococcus bacterium, which has entered an organ and developed purulent tissue breakdown there, has a high probability of further spread through the blood to other organs.
When a patient develops boils or pustules, the purulent contents are also sent for analysis. The skin around the boils is treated with an antiseptic and the crust is removed.
Immunomodulators
In addition to the use of vitamin-mineral complexes, the use of special immunomodulators will be effective, which will allow the patient’s immune system to be restored as soon as possible
The most popular include:
- Autohemotransfusion is the introduction of the patient’s own blood into the muscle. The method is the most effective in treating and eliminating complications of furunculosis.
- Introduction of special antitoxic serum or plasma against staphylococcus.
- Immunostimulants based on plant origin. They allow you to normalize internal metabolism, providing a calming and stress-resistant effect on a person. The most popular preparations of this type are tinctures of ginseng, echinacea and lemongrass. Also, immunostimulants can always be found in tablet form.
- Synthetic immunomodulators and peniciplins with a pronounced effect on the immune system.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=https:accounts.google.comServiceLogin
A positive prognosis for treatment largely depends on the location of infection, the degree of the disease and the correctly chosen method of treating staphylococcal infection.
With minor lesions of the mucous membranes and skin, the prognosis is almost always positive, completely excluding possible relapses. The spread of infection to internal organs in most cases ends in death.
- What's the difference between steamed rice and regular rice: which is healthier, possible harm
Tags: golden, win, staphylococcus
- Related Posts
- Mackerel benefits and harm to the body
- What do you drink cognac with?
- Red caviar kbju 100
« Previous entry
Acne from staphylococcus
Staphylococcus lat. Staphylococcus is a non-motile, spherical bacterium belonging to the Staphylococcus family Staphylococcaceae. Staphylococcus belongs to the group of positive, immobile, anaerobic, opportunistic microorganisms for the human body. The type of metabolism is oxidative and enzymatic. They do not form spores or capsules. The diameter of a staphylococcus cell is 0.2 microns, depending on the strain of the species. The most common colors are purple, gold, yellow, and white. Some staphylococci are capable of synthesizing characteristic pigments.
Staphylococcus in the intestines symptoms in adults treatment
Having Staphylococcus aureus in the throat is normal for most people. If immunity is at a good level, then this bacterium can peacefully coexist with other microorganisms in the mouth and throat. However, when the level of protective forces is weakened, Staphylococcus aureus gives rise to an inflammatory process with suppuration and other severe symptoms. Moreover, staphylococcus can cause inflammation in the throat in both adults and children.
Staphylococcus aureus is a spherical, non-motile and aerobic airborne bacterium, Gram-stained positive, which causes various diseases in children and, less commonly, in adults.
How dangerous is the bacterium?
The main danger of Staphylococcus aureus is that the bacterium quickly develops immunity to antibacterial drugs. The most resistant are those that live in medical institutions; they are called methicillin resistant because they do not respond to antibiotics of the penicillin group, cephalosporins and Amoxicillin.
What diseases can Staphylococcus aureus cause:
Author:
Mironova Elena
Didn't understand the article or need help? Ask a question now and get an answer.
auto RU
- staphyloderma - purulent boils, pimples, barley appear on the skin, which absolutely cannot be squeezed out;
- intoxication with waste products of staphylococcus, purulent processes in various internal organs;
- staphylococcal pneumonia is a dangerous pathology; if the bacteria penetrates the lungs, death is possible;
- staphylococcal tonsillitis, without proper treatment an abscess and phlegmon develop;
- panaritium - inflammation of the cushion near the nail, staphylococcus penetrates into wounds and scratches;
- sepsis, coma, death;
- purulent mastitis - staphylococcus penetrates from the skin into the mammary gland.
When internal organs are affected by staphylococcus, cystitis, pyelonephritis develops, the temperature rises, pain in the lower back or lower abdomen, and weakness appear.
In women, Staphylococcus aureus can cause toxic-septic shock when using hygienic tampons during menstruation.
Diet for Staphylococcus aureus
Although treatment with antibiotics is the most effective in the fight against pathogens, this does not mean that if staphylococcus is detected, you should immediately resort to the help of these drugs. Sometimes in such situations it is enough just to carry out local sanitation of the skin, respiratory tract, ENT and other organs. It makes sense to use these drugs in the presence of diseases that threaten human life. This may include:. Antibiotics for staphylococcus can also be prescribed for chronic inflammation of the nasopharynx, rhinitis, sore throat. Before deciding on treatment tactics, it is imperative to do a culture to identify the pathogen and its sensitivity to drugs.
Hormonal treatment
The danger of drugs containing hormones lies in their inability to eliminate the cause of inflammation - the pathogenic bacteria. Goyucocorticoids (medicines derived from corticosteroid hormones) help prevent the development of any inflammation. The disadvantage of this treatment is that these remedies only eliminate the symptoms of the disease, but not the cause. Hormone-based ointments: prednisolone, triamcinolone, etc. interrupt the body’s natural response to infection, which stops the proliferation of leukocytes, and with it a number of unpleasant symptoms (abscesses, fever, pain).
Hormone therapy is possible only in combination with other drugs that can eliminate staphylococcus. In their pure form, such drugs only relieve symptoms, preventing the development of antibodies, which leaves the body defenseless against the disease. It is acceptable to use ointments containing glucocorticoids in combination with antibiotics. Taking hormones internally in the presence of a bacterial infection is strictly prohibited.
Staphylococcus aureus treatment with antibiotics
Staphylococci surround us everywhere and everywhere. There are 50 species of this microorganism. The most dangerous strain is Staphylococcus aureus. Let's look at the signs of ear inflammation caused by staphylococcus. Let's find out what other pathogen causes skin damage in the area of the auricle. Let's find out how to treat such different diseases. The most common manifestations of staphylococcus are carbuncles, styes, and boils. The cause of the development of staphylococcal inflammation of the skin is damage to the epidermis through which the pathogen enters the body. The infection penetrates into the outer part of the hearing organ from unwashed hands.
However, the bacterium never causes skin infections. A starvation diet and fluid replenishment is the best way to cope with food poisoning of any nature in adults and children.
How do staphylococci affect human health?
The human body has a hard time suffering from staphylococcal infection due to the fact that these bacteria, in the course of their life activity, actively produce various toxins that are dangerous to health:
- Membrane-damaging toxins.
These substances bind to receptors located on the cell membrane and form a channel-pore passing through the membrane. Through the formed channel, ions and molecules rush into the cell. The cell swells and ruptures. These toxins include hemolysins, which destroy red blood cells.
- Exfoliative toxins.
These substances are the cause of scarlet fever rash, pemphigus in newborns, etc.
- An exotoxin that causes toxic shock syndrome (TSS).
Under its influence, fever, a drop in blood pressure, kidney damage develop, rashes are observed on the skin, lymphocytopenia (a decrease in the level of lymphocytes in the blood), etc.
- True leukocidin.
This substance is similar in principle to hemolysins, but it destroys leukocytes rather than red blood cells.
Staphylococcus also produces a number of enzymes designed to penetrate a foreign body and protect the bacterium itself. These enzymes can also have pathogenic effects.
Both exotoxins and individual components of bacterial cells have the ability to cause an allergic reaction. It is staphylococci that most often lead to the development of skin allergies (dermatitis) and respiratory allergies, such as bronchial asthma.
It should also be mentioned the special factors (proteins) that staphylococcus produces to slow down the processes of phagocytosis. Phagocytosis itself is intended to destroy foreign organisms and diseased or destroyed cells. By inhibiting this vital process, staphylococci prevent the body from getting rid of them. And even more than that, these factors affect the functioning of T and B lymphocytes, reducing the effectiveness of the body's immune response and undermining human health.
Staphylococcus aureus: causes, symptoms and treatment
VIDEO ON THE TOPIC: Intestinal dysbiosis - true or false.
Treatment of dysbiosis. Even despite the rapid development of medical science, the number of cases of people contracting staphylococcal infections is not decreasing. This name very accurately characterizes the color of this microbe, or rather its golden-yellow hue. That is why, by its external appearance, Staphylococcus aureus becomes easily recognizable among all human microflora. Through the lens of a microscope you can easily see, when examining staphylococcus, forms that are very reminiscent of a bunch of grapes.
Staphylococcus is a non-motile bacteria that develops on human mucous membranes and skin. There are 3 dangerous types of this infection, which include Staphylococcus epidermidis.
Preparations for prevention
Some people have this peculiarity: they have more Staphylococcus aureus on their mucous membrane or skin than they need, or the mechanism restraining their reproduction is broken, so the question: “how to get rid of Staphylococcus aureus” is always relevant for them. In this case, you should regularly undergo preventive therapy, which will help “invigorate” the immune system and make it more effective in fighting the bacteria.
Staphylococcal toxoids
Anatoxins are preparations containing the endotoxin of Staphylococcus aureus, produced during reproduction in the patient’s body. It is because of them that a person feels severe weakness, his temperature rises, intoxication develops and the functioning of many internal organs, for example, the heart and lungs, is disrupted.
The administration of small doses of purified staphylococcal toxoid may lead to a short-term deterioration in health, but after this the immune system will produce its own antibodies to effectively combat the microorganism in the future.
People who are undergoing major surgery with a long recovery period should undergo a course of staphylococcal toxoids. They start it 2-3 months before the procedure, injections are made every 25-30 days, the last one should be 4-5 days before surgery.
Bacterial lysates
To increase local immunity on the mucous membranes of the mouth, nose and pharynx, a person can use bacterial lysates - medications containing specially selected types of staphylococci, and sometimes bacilli, which, when contacted with the mucous membrane, will cause an active immune reaction.
Is it possible to cure a disease with their help? The answer is clear: no, because against the background of a staphylococcal infection, the immune system is too weakened to fight additional microorganisms.
Effective bacterial lysates include the following drugs:
- bronchomunal;
- IRS-19;
- imudon;
- polyoxidonium.
The drugs are produced in the form of sprays, lozenges and aerosols. The dosage form of the drug is chosen depending on the place where it is necessary to increase immune resistance. Only a doctor can tell for sure whether a patient needs to use bacterial lysates after bacterial culture of a smear from the mucous membranes, so you should not use these medications yourself for “prevention.”
How to treat staphylococcus? 12 best drugs for the treatment of staphylococcus
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria are one of the most aggressive microorganisms to humans. The usual habitat for this type of bacteria is the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx; staphylococcus is less common in the gastrointestinal tract. Facts about the bacterium:. The first reasons for the appearance of Staphylococcus aureus in the intestines is the consumption of food products that have been kept for a long time in rooms with a temperature regime that does not correspond to their storage conditions. In rare cases, infection with Staphylococcus aureus can occur while swimming in bodies of water with stagnant water. In adults, symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus in the intestines appear within the first hours after infection, which is due to its short incubation period. Clinical manifestations:.
How can you get infected?
There are many different methods of infection, thanks to which any type of staphylococcus can enter the human body and not manifest itself until favorable flora is formed.
The most common routes of infection:
- Airborne. A person's constant presence in places with significant crowds of people significantly increases the risk of infection, which is especially typical during the season of respiratory diseases. In this case, it is not necessary to have physical contact with a sick person - it is enough to be in the same room.
- Airborne dust. Staphylococci and other pathological bacteria can infect humans through household or street dust, which contain a sufficient number of microscopic particles - from flower pollen to animal fur.
- Contact and household. In this case, infection occurs through the use of shared personal hygiene items, utensils or wearable clothing. The risk of household contact infection increases if there are cuts or injuries on a person’s skin.
- Medical. Staphylococcus enters the human body through general contact with contaminated medical instruments or surgical interventions.
- Nutritional or fecal-oral. Characterized by eating food with unwashed hands or failure to comply with personal hygiene standards.
When infected, the bacterium begins to actively multiply and produce toxic substances that negatively affect the health and general condition of a person, which leads to the occurrence of various diseases. Primary sites of infection most often include the skin, respiratory tract or gastrointestinal tract. Infection of other organs, including joints and bones, is a secondary process caused by various diseases.
Secondary reasons for development:
- taking antibiotics or hormone therapy;
- the presence of stressful situations and failure to comply with a proper sleep schedule;
- improper nutritional standards;
- hypo- or vitamin deficiency;
- infectious diseases;
- dysbacteriosis;
- lack of personal hygiene standards.
The level of negative impact depends on the immune system and the bacterial strain. So, the stronger the immunity, the fewer complications and consequences bacterial structures can cause. There are many different methods of infection, thanks to which any type of staphylococcus can enter the human body and not manifest itself until favorable flora is formed.
Staphylococcus aureus in the nose: causes and treatment. Therapy methods
Staphylococcus is a group of infectious diseases that differ in their clinical picture and are distinguished by purulent-inflammatory foci and intoxication of the body. The causative agents of the disease are:. There is no special diet for staphylococcus, but you should adhere to the principles of nutrition for infectious diseases. Since in acute forms of staphylococcus the body is intoxicated by the waste products of pathogens, individual organ functions may change, the body’s energy metabolism is disrupted, the level of energy expenditure increases, protein metabolism increases, protein breakdown occurs, water-salt metabolism loss of mineral salts and fluids, and the level of vitamins in the body decreases.
Use of vitamin and mineral preparations
Staphylococcal bacteriophages are actively used during prevention or complex therapy aimed at eliminating staphylococcus. Phages are bacterial viruses that effectively eliminate strains of many varieties of cocci. At the moment, this is the best alternative to antibiotic drugs, which often have many similar phenomena.
In case of complications or severe cases, specialized bacteriophages are used together with antibiotics, which allows for maximum effectiveness in treating the disease. Their use is also possible when treating fresh wounds or growths.
In all other cases, phages are the safest drug for treatment and prevention. The standard course of therapy is from 1 week to a month.
One of the possible reasons for a decrease in the level of immunity and further relapses of the disease is the lack of useful microelements and vitamins in the human body. Based on this, the use of vitamin and mineral preparations has an effective effect on a favorable outcome of the disease.
Experts recommend paying special attention to the use of such vitamins and bioactive supplements during off-season periods of vitamin deficiency.