Staphylococcus is the name of an insidious bacterium that is known to every person. With its help, a large number of infections and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are transmitted. Staphylococcal bacilli can cause a large number of diseases. Their manifestation is especially dangerous for infants, since their immunity has not yet fully developed. Staphylococcus aureus in infants has a number of special manifestations. Parents should know about them. Only in this case will it be possible to prevent the development of a serious illness.
Staphylococcus in newborns is a diagnosis that involves several separate infections. They are very dangerous to life and health, so if they are identified, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment. If you have the first signs, you should consult a pediatrician. The sooner parents begin treatment, the greater the likelihood of a positive result.
Causes of staphylococcus in infants
Staphylococcus aureus is a nosocomial infection, so a newborn baby can become infected with it almost during childbirth or immediately after birth.
- The baby can become infected from the mother, if she is a carrier of this bacterium, during the passage of the birth canal.
- A child can be infected through normal contact with a mother who is a carrier of staphylococcus.
- When breastfeeding, the infection enters the baby's body through mother's milk.
- When the mother does not observe personal hygiene, both in a medical facility and at home.
- Poor child care - they rarely and poorly wash the baby, they do not wash his hands, which he constantly puts in his mouth.
- In the event that the carrier of this infection is medical personnel who care for newborns.
- Medical workers do not properly clean their hands, soft equipment, instruments, and the room where the baby is located.
- With insufficient care, the baby can become infected through the umbilical wound, which must be properly handled with clean hands.
- The infection also spreads through airborne droplets, so people caring for the baby must be healthy.
How can you help?
S. aureus is a serious problem, and only a doctor can decide on the appropriateness of treatment and prescribe medications. Parents can only carefully follow the instructions and strengthen the baby’s health in every possible way.
It is absolutely unacceptable to self-medicate and give your child antibiotics without consulting a doctor. This will not bring relief, since S. aureus is not afraid of gentle doses and is rapidly developing resistance to drugs.
Treatment for S. aureus is usually carried out in a hospital setting, and refusing hospitalization is a very risky proposition.
Great attention must be paid to the general strengthening of the body and hardening. You also need to do your best to normalize the digestion process. Constipation is no less dangerous for a child than diarrhea. If there is chronic stool retention, the doctor may recommend an infusion of flax seeds, fennel fruits, chamomile and other mild remedies.
Oil mixtures such as Plantex or Baby Calm often bring good results. They contain various natural ingredients: anise, mint, dill, fennel oil, lactose. These drugs enhance intestinal peristalsis and normalize the movement of food mass through the gastrointestinal tract.
But even these remedies can be given to a child only after consultation with a specialist.
The abdominal muscles in young children have not yet strengthened, which often causes digestive problems and, in principle, may contribute to the development of S. aureus in the intestines. The faster a child can develop strong muscles, the better. Therefore, massage and gymnastics are necessary for children literally from the first days of life.
Every day the child should be placed on his tummy, massaged, and special exercises for the abdomen should be included in the gymnastics complex.
If a child receives breast milk, then in order to avoid constipation, the mother must exclude grapes, cabbage, blueberries, rice, and legumes from her menu. By the way, breastfed children are much less likely to suffer from staphylococcal infections than bottle-fed children. Mother's milk itself is a powerful medicine, and constant contact with the skin during feeding significantly accelerates the formation of healthy microflora in the baby's intestines.
If constipation is persistent, the doctor may prescribe cleansing enemas or glycerin suppositories. But these remedies are used only in really serious cases, so as not to interfere with the formation of normal intestinal function.
If the doctor prescribes antibiotics, they will have to be taken until the end of the course, despite the side effects. The doctor will definitely warn you what exactly you might encounter. If the undesirable effects are too severe, the therapy will be adjusted.
Liquidation usually takes 5-7 days. But the treatment does not end there, since now it is necessary to restore the normal intestinal microflora, which has also been greatly affected by the effects of the drugs. Recovery is well helped by various probiotics, mineral preparations and vitamin complexes.
Dear readers, if you decide to share this information with your friends on social networks, then you can do it much faster if you click on our convenient buttons that you see immediately below the text.
Did you like the article? Share with friends on social networks:
This blog is read and used by 6,939 adherents of a healthy lifestyle and uses its advice and recommendations, so their health is in order, their mood is good, and their work is going well. Read it too.
I agree to the newsletter and accept the privacy policy.
You may also be interested
What to feed a child with rotavirus infection - approximately...
Good day, dear readers of Alexey Shevchenko’s blog “Healthy image...
6 Read more
Music for kids – introducing children to music
Good day, dear friends of Alexey Shevchenko’s blog “Healthy Image...
6 Read more
Ketone bodies in a child’s urine - how dangerous they are
Greetings to all readers and guests of Alexey Shevchenko’s blog “Healthy Image...
8 Read more
How to increase breast milk lactation - a simple way...
Good day, dear readers of Alexey Shevchenko’s blog “Healthy image...
8 Read more
Where does the bacterium live and how is it transmitted?
Staphylococcus aureus is the causative agent of hundreds of infectious diseases. Here we have tonsillitis, appendicitis, pneumonia and cholecystitis, meningitis and cystitis. This bacterium is resistant to various antibiotics and is easily transmitted from person to person. In this case, the carrier of the infection may not even be aware of its presence in the body.
This microorganism lives on the skin and mucous membrane of humans and animals. It can be located both inside the body and on the surface - in the stomach, nose, genitals, armpits, etc.
There are different types of this bacterium:
- Staphylococcus epidermidis is widespread on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes.
- Saprophytic is localized in the area of the urinary system.
- Opportunistic usually causes minor inflammatory processes.
- Unconditionally pathogenic kills body cells.
This infection can be transmitted in a variety of ways. With blood, through the respiratory system, through the skin upon contact with objects and dirty hands. And in the event that there is contact with the mucous membrane, for example, with the help of contaminated food.
Habitat
It is important to know where the harmful bacteria comes from. In this case, it will be possible to put barriers in advance that will prevent her from infecting the baby. It can settle on the skin, face, throat, genitals and inside the intestines. In each individual case, Staphylococcus aureus has a number of special manifestations:
- If it is present, a rash appears on the skin. It may be red or form boils, purulent formations. Allergies spread due to infection. To combat staphylococcus on the skin, you need to use regular brilliant green. If cracks and wounds appear on the epidermis, the composition must be poured inside. In this case, it will be possible to prevent suppuration. The bacterium can even create small blood clots under the skin, which lead to an increase in formation over time. Additionally, it should be noted that the presence of staphylococcus in the mother can lead to the development of purulent mastitis.
- Every person has had a sore throat at least once in their life. It develops against the background of the presence of harmful bacteria in the nasopharynx. To prevent suppuration, it is necessary to pay attention in time to the active proliferation of staphylococcus. It can also form pus-filled lesions in the nose.
- The bacterium can also lead to the development of inflammation in the form of conjunctivitis in the eyes. In this case, barley is chronic and needs treatment.
- Klebsiella in the intestines poses a great danger to the baby's health. His immune system is not yet strong enough to kill large numbers of bacteria at once. The situation may worsen due to dysbacteriosis. In this case, an ideal environment is created for the growth and development of staphylococcus.
Choosing a course of treatment is a complex process. Parents are advised to pay attention to preventive measures. Additionally, it should be noted that staphylococcus from the pharynx or nose has access to the lungs. If the immune system is not functioning actively enough, the risk of developing pneumonia increases. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are used to treat it.
Risk group
Some people are particularly susceptible to contracting Staphylococcus aureus. When the body is weakened and in an unfavorable environment, infection is inevitable.
The risk group of people who most often become victims of Staphylococcus aureus includes:
- women in the postpartum period;
- infants with weakened immune systems who are often ill;
- premature babies;
- babies who often have to give injections, insert catheters, etc.
- adults and children after organ transplantation;
Staphylococcus is an opportunistic bacterium, which means the following: the infectious disease may not manifest itself, but the person will remain its carrier for a long time. At the same time infecting others. Usually, the carrier of the infection may not be aware that it exists in his body.
A baby may become ill due to infection with Staphylococcus aureus if, for any reason, immunity is reduced. Most often this happens if you follow simple rules of hygiene, eat stale food, or cook food poorly.
Immunity is also reduced when taking antibiotics, injuries, dysbacteriosis, hypothermia, etc. Therefore, you should not ignore even the slightest scratch, and always treat it with antiseptic agents. After all, Staphylococcus aureus infection manifests itself in many different diseases.
Signs of Klebsiella infection
Klebsiella blooms magnificently in a weakened child's body. When the level of lacto and bifidumbacteria in his intestines is sharply reduced, when it is weakened by previous infections or staphylococcus is already blooming in full growth, the associations with which are very typical for Klebsiella.
The clinical picture of Klebsiella enterocolitis differs from staphylococcal enterocolitis only in the color of the stool. In this case, the stool is often dark yellow-green, foaming. Gases are also released during stool. The child suffers from colic. And in the presence of gastritis, appetite decreases and vomiting occurs.
Symptoms of staph infection
Symptoms of staphylococcus can be completely different, because it all depends on where exactly the infection is localized in the child’s body. The degree of immune protection is also of great importance. In infants, this infection most often manifests itself in the nose, mouth, respiratory system and gastrointestinal tract.
If Staphylococcus aureus enters the baby's blood and the infection spreads throughout the body, sepsis occurs - a serious condition that can result in death. All these localizations clearly show the picture of infection, exactly how the infection entered the baby’s body.
In the nose
Through airborne droplets, Staphylococcus aureus infection can be carried into the respiratory system and begin to spread in the nose.
The following symptoms appear:
- Decreased appetite of the newborn;
- Weight loss, which follows from the first point;
- Rhinitis and nasal discharge;
Typically, this manifestation of infection is not dangerous, the temperature does not rise, and the baby’s general condition remains acceptable.
In the throat
Through the oral cavity, Staphylococcus aureus can penetrate into the baby's throat and be localized there. Symptoms may not be noticeable to parents. However, the baby will begin to cry more often, especially when swallowing, because he experiences a sore throat.
- Refusal to eat;
- Redness of the throat;
- Purulent plaque on the tonsils and palate;
- Temperature increase.
The infection can cause tonsillitis, laryngitis and even laryngotracheitis.
Such symptoms are not seriously dangerous to the baby's health. However, they must be dealt with, since the infection, together with breast milk, can penetrate further into other organs and affect, for example, the kidneys, causing complications.
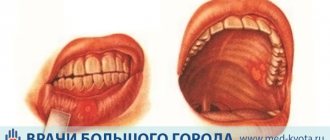
In the mouth
Once in the baby's mouth and settling in it, Staphylococcus aureus can cause stomatitis. It is accompanied by significant redness of the oral mucosa, the appearance of dark veins and ulcers.
This is a painful condition and can be very distressing for the child. Because it is unpleasant for the baby when food gets into his mouth. The child cries, eats less, weight decreases, and, accordingly, immunity decreases.
On the skin
Redness or small swelling in certain areas of the baby's skin may indicate inflammation caused by Staphylococcus aureus. The affected areas feel warmer to the touch than the surrounding tissue. Touching the inflamed skin causes pain in the baby.
Sometimes the skin is affected by pimples and small pustules, ulcers, boils and even necrosis. These formations can appear anywhere - both on the cheeks and on the buttocks, in the ear . They occur especially often under a diaper.
Staphylococcus aureus causes various skin diseases in infants - furunculosis and folliculitis, pyoderma and pemphigus. The main source of infection is non-compliance with hygiene standards.
In the intestines and stomach
The most common route of infection of infants with Staphylococcus aureus is food. Often this bacterium is detected during laboratory testing of a baby's stool. Normally, staphylococcus cannot be present there. If the test for staphylococcus is positive, then the child may develop gastroenteritis or gastritis.
The main signs of infection are as follows:
- Constant vomiting;
- Diarrhea – loose stools 6 times a day;
- Pale skin and various rashes - pemphigus, pustules and even boils;
The child experiences weakness and dizziness, which are accompanied by pain in the abdominal area. The newborn reacts to this by crying and refusing to eat.
Reviews
Nadezhda, 21 years old. My child developed three purulent formations on his face that looked like acne. A few days later their number increased. On the advice of the pediatrician, they began to treat them with Chlorophyte, since a large amount of Staphylococcus aureus was found. The treatment began to help and improved the condition of the skin. Fortunately, we had to do without antibiotics.
Zhanna, 26 years old. We were diagnosed with Staphylococcus aureus at two months. During this period, the child's stool was liquid, mixed with mucus, foam and blood. After passing the tests, we were prescribed Sextophage and Chlorophyllipt. After completing the course, I additionally needed to take beneficial bacteria. I had to take two courses with an interval of one month.
Diagnosis of the disease
If specialists suspect that a child has a staphylococcal infection, a special examination is prescribed. In addition to tests on the baby, breast milk will also be examined.
Materials are taken for analysis depending on what type of lesions occur during the course of the disease:
- In the case when the baby has a discharge from the nose and redness of the pharynx, mucus samples are taken for analysis.
- If there are lesions on the skin, then the pus is examined. A biopsy may be performed, where skin samples are taken for analysis.
- If diarrhea or vomiting occurs, stool is sent for examination.
- When signs of blood poisoning appear, a blood test is performed.
- If signs of pneumonia occur, a chest x-ray is taken.
- When it is necessary to take pictures of different parts of the body layer by layer, they resort to computed tomography.
- Magnetic resonance imaging will help identify foci of bacterial damage.
- During blood damage, a situation may arise when the body cannot cope, and fluid begins to accumulate around the heart. Then they resort to echocardiography to examine the exact size of the heart, its shape, and track how it works. This type of examination is carried out using sound waves.
- Sometimes the infection penetrates too deeply, so it may be necessary to find out whether the baby’s bones are affected by it. Therefore, they resort to osteoscinigraphy.
Today, diagnostic methods are so well developed that it is possible to establish a diagnosis very quickly and with complete accuracy. This will allow you to prescribe the correct treatment and eliminate the infection.
Diagnosis and treatment
Staphylococcus aureus is found in stool or nasopharyngeal swabs of infants. Also, when making a diagnosis, the doctor takes into account the complaints of the child’s parents and his general well-being. Treatment must be carried out in a hospital setting, and the baby and his mother must be placed in separate boxes, since this infection is contagious to other hospital patients.
Typically, treatment includes antibacterial drugs, which are prescribed in combination (several at once) to prevent the bacteria from developing resistance to them. It is advisable, before starting treatment, to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics - then it will be more effective. Treatment also involves the use of antistaphylococcal drugs and detoxification therapy. At the same time, treatment should be aimed at increasing the child’s immunity, for which the baby is prescribed vitamin complexes.
If Staphylococcus aureus is found in the intestines of a small patient, probiotic preparations, for example, Bifidumbacterin, should be included in the treatment.
Unfortunately, staphylococcus is difficult to treat, so treatment can be lengthy, and its results are assessed by repeated bacterial culture or taking stool for analysis.
What is the danger of staphylococcus for newborns?
Infants do not have the antibodies in their blood necessary to resist various infections. Therefore, immunity is practically absent; it is still developing. Staphylococcus aureus has the ability to penetrate tissue extremely quickly. The waste products of these bacteria are toxic and cause severe poisoning.
If the infection occurs during intrauterine development, this can lead to serious complications. The child may be stillborn, with various pathologies. The infection can cause a miscarriage. Moreover, treatment in such a situation is almost impossible.
There is no immunity to Staphylococcus aureus, so there is always a serious risk of another infection, even if the child has already been treated.
The main danger is that Staphylococcus aureus has now become resistant to antibiotics, especially from the penicillin series.
Disease prevention
Doctors note that staphylococcus is difficult to cure, so they advise taking preventive measures.
- Limit contact with sick people
- boost immunity (take vitamins),
- monitor the baby’s hygiene (wash hands, fruits and vegetables),
- carry out wet cleaning,
- drink water only from clean and proven sources,
- Before breastfeeding, rinse your nipples well,
- disinfect bottles and pacifiers,
- use only clean clothes.
Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium that is difficult to treat. You won’t be able to completely get rid of it, but you can prevent serious inflammation and consequences. The main thing is to follow the rules of prevention and go to the hospital at the first symptoms.
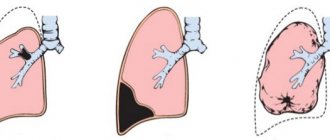
Staphylococcal pneumonia
This disease is extremely dangerous for newborns. It comes in two types – primary pneumonia and secondary. Primary pneumonia is diagnosed when infection occurs directly through airborne droplets.
Secondary pneumonia is a situation where the child first develops other symptoms, such as skin lesions. The body could not cope, and subsequently pneumonia occurred directly, which indicates a deeper penetration of the infection.
The disease is very severe, with high fever, shortness of breath, cyanosis, liver damage and cardiac dysfunction. In more severe cases, air and purulent cavities in the lungs are observed. With secondary pneumonia, there may be vomiting, diarrhea, and bloating.
In some cases, the disease is accompanied by purulent otitis media.
What are the causes of illness in a child?
Ways to spread staphylococcal infection:
- food;
- airborne;
- contact.
Newborn children become infected mainly through contact: during premature and/or difficult births. This also occurs through the hands of the mother or medical staff, unsterile medical instruments, underwear or household items.
Staphylococcus in children under one year of age can be caused by infection with mother's milk, if the mother has cracked nipples or breast mastitis. Feeding formulas can also be contaminated with staphylococcus.
The risk group includes newborns and infants because:
- have weak local antibacterial immunity of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory tract;
- do not secrete secretory immunoglobulin A, which is responsible for the body’s local immunity;
- their skin is very delicate and susceptible to external irritations;
- saliva does not have sufficient antibactericidal effect.
All this increases the risk of contracting a staphylococcal infection.
Staphylococcal sepsis
This disease occurs when bacteria and toxins enter the bloodstream directly from an existing lesion.
Most often, the disease begins in the second week of a child’s life. The baby is losing weight, the general condition is very poor, the skin takes on a gray, earthy tint. When the liver is damaged, the skin becomes icteric. The liver and spleen are enlarged. The child weakens very quickly and becomes apathetic. The temperature can be either normal or rise from time to time.
Vomiting, diarrhea, skin rash, swelling that quickly disappears. Bleeding may begin in the umbilical wound, nasopharynx, urinary tract, etc. The child may even vomit blood.
Convulsions and loss of consciousness may occur, including symptoms of meningitis. If the course of the disease is unfavorable, the heart works poorly, and purulent metastases appear in various organs. Purulent osteomyelitis, joint inflammation, lung abscess, peritonitis, meningitis and many other lesions also occur.
Diagnosis of staphylococcal sepsis is difficult for specialists, since poorly defined symptoms occur at the very beginning of the disease. The course of the disease subsequently develops rapidly. Therefore, it is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis at the very beginning of the development of the disease, so as not to waste precious time.
Diagnostics
If intestinal staphylococcus is suspected, the baby's stool is examined. Qualitative and quantitative analysis for sowing is carried out. To identify Staphylococcus aureus, the value of CFU (colony-forming units) in the feces of a newborn or infant is taken into account. For a child of the first year of life, the identified epidermal type of staphylococcus can be considered the norm, provided the child is in good health. There shouldn't be a golden type yet at this age.
To assess the general condition of the body and determine the exact course of complex treatment of Staphylococcus aureus to eradicate the pathogen in the intestines of infants, general blood and urine tests are prescribed. As a rule, there is an increase in the main indicators: leukocytes, erythrocytes (including their sedimentation rate) and hemoglobin.
If you suspect an infection, you should visit a pediatrician
In other forms of the disease (infection of mucous membranes or blood), blood (suspicion of sepsis) and snot (accompanied by signs of a cold) are examined. For any type of pathology, the mother's milk is additionally analyzed. If the test result is positive, the woman also undergoes treatment.
Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus in infants
Infection with Staphylococcus aureus is a very serious disease that can lead to the most unfavorable consequences. Therefore, parents of infants must take the situation responsibly.
For a specialist, this infection is a difficult, but completely solvable task. First, a diagnosis is made and the sensitivity of the identified infection to a particular antibiotic is determined.
Then the doctor prescribes treatment with various drugs - antibacterial, enzymatic, vitamins, immune stimulants, including probiotics. If the child’s condition is serious, hospitalization is urgently needed.
Drugs
Because the infection is resistant to many antibiotic drugs that can be used in the treatment of newborns. Therefore, a lot depends on how correctly the medicine is chosen. You need to prepare for the fact that your child will have to take pills and injections for a long time.
- Antibiotics that can eliminate infection are a group of cephalosporins and penicillins. For severe illnesses, such as pneumonia and meningitis, two different drugs are used at once.
- Preparations of biological origin that quickly boost immunity. These are anti-staphylococcal immunoglobulin and plasma. Staphylococcal bacteriophage and toxoid fight the infection directly.
- Since severe intoxication occurs during infection, intravenous drips are used to eliminate toxins - this is saline solution and glucose.
- The body loses a lot of strength during illness, it needs to be supported, so vitamins are required.
- Probiotics are bifidumbacterin, bificol is used if Staphylococcus aureus has infected the gastrointestinal tract.
In addition, in case of food infection, experts prescribe gastric lavage. If there is damage to the lungs, surgical intervention is possible.
Surgery
The unfavorable course of staphylococcal pneumonia in infants can cause pneumothorax, pleurisy, and purulent cavities in the lungs. This situation can be very difficult. The only way out is surgery, during which a puncture will be performed. This is necessary in order to remove accumulated air or pus from the pleura.
This procedure is used only according to diagnostic indications - chest x-ray. The decision on the need for surgical intervention is made by the patient's leading physician together with the surgeon.
ethnoscience
There are many effective traditional medicine recipes that help fight Staphylococcus aureus. They must be used along with pharmacological agents. They help boost the immune system well, which will contribute to a speedy recovery.
There is a herbal decoction of medicinal plants that can be used for infants:
- 3 parts fireweed;
- 2 parts chamomile;
- 1 part dill seeds;
- Oregano;
- Hop;
- Mint;
- Meadowsweet;
- Calamus root.
Pour boiling water over the mixture, boil for 10 minutes and leave. This decoction can be given to infants no more than 1 teaspoon per day.
To eliminate skin manifestations, use warm baths and lotions with apple cider vinegar. In this case, it is necessary to use only sterile materials and purified, boiled water. A solution for compresses is prepared at the rate of 2 tablespoons per glass of water. For bathing, a much lower concentration is needed.
Treatment
Therapy for infectious lesions of the gastrointestinal tract in children comes down to three main areas: combating infection, correcting water-electrolyte imbalances, and organizing therapeutic nutrition.
Treatment with antibiotics
Treatment with cephalosporins, macrolides, kanamycin is justified only in SEPTIC conditions and in premature infants with a high risk of infectious-toxic shock. The usual practice of infectious diseases departments to treat enterocolitis in children with intramuscular administration of cephalosporins can only be justified:
- job description
- lack of adequate funding
- reinsurance for doctors
In general, antibiotics knock out all the beneficial microflora in the intestines, and after a short lull, enterocolitis flares up with renewed vigor. But here the surviving staphylococcus is joined by hospital strains of Klebsiella, which is practically impossible not to “pick up” in the hospital.
As a result, during the first year of life, the child is repeatedly hospitalized or treated on an outpatient basis for severe forms of dysbiosis or recurrent gastroenterocolitis, and in return for the knocked out strains of bacteria, he calmly receives new types of staphylococci from the environment, but there is practically no one to compete with them in the “deserted” intestine.
At the same time, no covering with probiotics during antibiotic treatment will save the situation, but is only a waste of money, because:
- firstly, beneficial microbes are the first to die from the medicine
- secondly, they do not take root from preparations in the presence of a high microbial number of staphylococci or klebsiella
It is better to treat infants with bacteriophages
Staphylococcus aureus in children of the first year of life responds much better to treatment with bacteriophages. A bacteriophage is a virus that eats bacteria. Each bacterium has its own phage.
- A purified staphylococcal bacteriophage or an intestinal phage is used (a mixture against staphylococcus, shigella, salmonella, paratyphoid, enterococci).
- The course lasts from 7 to 14 days.
- Repeated courses are possible.
- The difficulty in use is that the drug is stored at 6 degrees (on the refrigerator door) and cannot be heated, but must be brought to room temperature by removing it from the refrigerator in advance.
Treatment of Klebsiella in feces is carried out with the bacteriophage Klebsiella pneumoniae or polyvalent purified. In case of association with staphylococcus, first a course of staphylococcal bacteriophage is carried out, and then Klebsiella is eliminated.
Nitrofurans
Enterofuril, Ersefuril, Stop-Diar in suspensions are approved for use in children from one month of age. Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella respond well to them; the drugs can be combined with treatment with bacteriophages. The course does not exceed 7 days. Klebsiella pneumonia can also be treated with furazolidone in children over one year of age.
Restoring water-salt balance
Restoring water-salt balance at home is difficult. If necessary, the child is supplemented between main feedings. During the first six hours, the child should receive fluids at the rate of 80-100 ml per kilogram of weight. Then they move on to maintenance doses of 100 ml per kg per day.
If vomiting continues, cerucal is administered intramuscularly. The liquid is given at the rate of one teaspoon per 5-10 minutes. In this case, solutions of rehydron or hydralazine and 5% glucose are administered in a ratio of 1 to 4. If such attempts are unsuccessful or if lethargy develops, decreased diuresis, or edema, the child is hospitalized for intravenous infusions.
Enterosorbents
In children's practice, microbes and toxins that collect microbes and toxins are represented by perhaps only Smecta, which should be used with sufficient caution, and then only with profuse diarrhea, since against its background there is a high risk of developing intestinal intussusceptions.
Immunostimulants
Of the immune stimulants, the best results for intestinal infections are shown by Kipferron, the course of which is about 5 days.
Probiotics
The turn of probiotics comes after intestinal sanitation, and these drugs are discussed in detail in the section treatment of dysbiosis and Linex analogues. In general, the course is at least a month.
Possible complications and consequences
No doctor can give an accurate forecast of the consequences of infection with Staphylococcus aureus. Since the spectrum of damage to various organs and systems of the body is very wide. However, if the infection is not eliminated in time and the baby’s condition becomes critical, then death is possible.
An infection of Staphylococcus aureus suffered by an infant may subsequently leave its unfavorable mark in the form of chronic diseases. In infancy, the foundations for the health of the body of the future adult are laid for life.
Complications can be different, depending on the location of the infection and its further spread in the body. These are otitis media, dysbacteriosis, damage to the nervous system due to meningitis, cardiovascular problems, diseases of the musculoskeletal system and much more.
The main reasons for the development of diseases
In newborns, the immune system is just beginning to form. Any bacteria can damage it, so sanitary conditions are maintained in the delivery room. In some cases, even after birth, the baby is left in quarantine. This is what you need to fight a large number of bacteria. However, Staphylococcus aureus may well exist in such conditions. It does not die even if all standards and rules of disinfection are observed.
The microorganism is very dangerous for premature and weak children. Their immunity cannot resist bacteria, so the risk of developing and spreading an infectious disease increases.
The causes of diseases lie in the penetration of bacteria through milk and the umbilical cord. They can also settle in the nose. Infection most often occurs through the mother. Additionally, it should be noted that if the baby’s body works correctly, then the likelihood of developing the disease is reduced to zero. However, this situation is not always typical for newborns. Even adult children can become infected with staphylococcus, for example, due to unwashed vegetables or fruits.
Children who are at increased risk of being harmed by Staphylococcus aureus:
- The baby was prescribed long-term antibiotics to treat the disease.
- Babies who were born prematurely and spent a long time in a pressure chamber. Artificial feeding immediately after birth can also play a negative role.
- The infection process can also be carried out through protective masks, catheters or tubes.
- The child's immunity suffers greatly due to diabetes.
- Direct infection with staphylococcus can occur from the mother or through her milk.
Staphylococcus aureus is always present in the intestines of infants. However, it begins to act negatively only if the intensity of the immune system decreases. Staphylococci are harmful microorganisms that can cause the development of serious illness.