In case of toxic poisoning, the liver often suffers, which is why liver hepatitis develops. This happens with acute or chronic penetration of toxic substances into the body. Symptoms are jaundice, pain in the right side, general weakness. Treatment consists of isolation from poison and regeneration of the cellular structure of the organ.
Causes
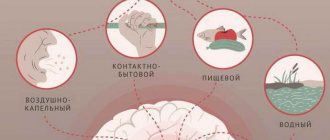
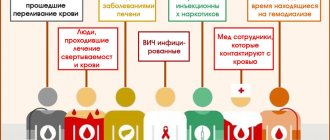
Toxic substances can enter the body through the respiratory tract (exogenous transmission route), skin, mucous membranes and gastrointestinal tract (alimentary route). Hepatitis is classified based on the nature of the toxic substance. The source of clinical manifestations can be:
Alcohol
- Alcohol. Ethyl alcohol leads to accelerated absorption of iron in the gastrointestinal tract. This is fraught with the occurrence of excessive accumulations of this microelement in the functional cells of the liver. Excessive amounts of the component lead to the formation of free radicals. The risk of alcoholic hepatitis increases when you drink alcohol on an empty stomach. Ethanol, when interacting with liver enzymes, turns into acetaldehyde. This compound is highly toxic. It provokes disruptions in metabolism, the replacement of functional tissue with fatty tissue. Hepatitis affects the entire body.
- Medicines. Uncontrolled use of drugs causes a deterioration in overall health. Therefore, self-medication is strictly prohibited in any case. The likelihood of developing hepatitis increases when using medications with antibacterial properties. Among them are nitrofurans, tetracyclines, and beta-lactam antibiotics. Toxic hepatitis occurs after intravenous administration, inhalation and parenteral administration.
- Poisons of synthetic and natural origin. The first category includes arsenic, phosphorus, and carbon tetrachloride. The second group contains poisonous mushrooms and herbs.
- Narcotic substances.
Medicines
The above factors have a negative effect on the parenchymal organ. Damaged hepatocytes undergo an inflammatory process that cannot be relieved without special medications. Massive death of functional cells leads to the development of acute liver failure.
Poisons directly affect the body. Other types of toxic substances negatively affect the functioning of the circulatory system. As a result, liver cells suffer from oxygen starvation, and subsequently they are destroyed.
Basic information
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver with an acute or chronic course. Pathology is provoked by viruses, bacteria, as well as toxic substances (alcohol, medicines, drugs).
The main feature of the disease is its latent course, that is, it is asymptomatic or manifests itself with unexpressed signs that can be confused with other diseases (for example, influenza).
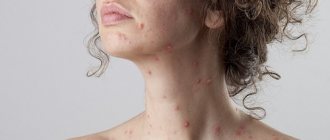
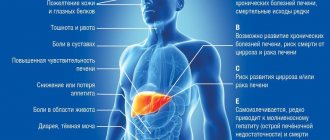
When the liver becomes inflamed, discomfort or pain appears on the right side under the ribs, appetite decreases or disappears, nausea, vomiting and headaches often occur. The person feels weak and the body temperature rises. In advanced cases, jaundice occurs (yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes).
In the absence of proper therapy, the risk of developing cirrhosis or liver cancer increases.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of an acute type of hepatitis includes the following manifestations:
Lethargy
- disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system;
- loss of orientation in space;
- spider veins and subcutaneous hemorrhages;
- change in the color of urine and feces, jaundice;
- overexcitation or lethargy;
- coma, hallucinations, dizziness;
- hormonal imbalance.
An enlargement of the spleen and liver, cytolysis of hepatocytes, and neutrophilic-type leukocytosis are also observed. The intensity of clinical symptoms depends on the type of toxic effect and the stage of the pathology. In the chronic form of hepatitis, there may be no signs. Manifestations are not specific.
Hepatitis is often diagnosed in pregnant women. In this case, severe liver failure develops gradually, so it is quite difficult to identify pathology at an early stage. The patient feels fine for a long period. People who are in her close circle can become infected. The list of possible complications includes:
- fetal death;
- cholestatic hepatitis, accompanied by disruptions in the blood clotting process;
- bleeding in the early postpartum period.
Bleeding
The development of the chronic form of toxic hepatitis begins with general malaise, increased fatigue and fever. Subsequently, the patient develops a mental disorder and pain syndrome. Disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system are a reason for an immediate visit to the attending physician. In the absence of medical care, the risk of irreversible consequences increases. These include liver necrosis, which is accompanied by coma and massive bleeding.
Types of jaundice
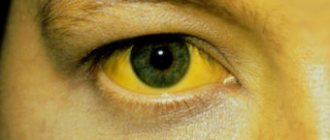
Yellowing of the skin most often indicates liver damage. However, viruses are not always to blame. The shade of the skin and the degree of damage to the mucous membranes can indirectly indicate the causes. Thus, with viral hepatitis, the skin color has a yellow tint with a slight orange tint, due to the destruction of liver cells. But jaundice with an olive, greenish tint more often occurs with inflammation of the liver due to stagnation of bile, if the outflow through the bile ducts is impaired. The most noticeable yellowness is on the sclera of the eyes, mucous membranes and palms. If such coloring appears, you should immediately consult a doctor for examination.
Statistics from the World Health Organization (WHO) indicate that more than 30% of the adult population of the Earth suffers from some kind of liver disease. In Russia, such diseases kill about 400,000 people every year. At the same time, the number of deaths from hepatitis, cirrhosis and hepatosis is constantly growing.
In this article we will talk about viral hepatitis, since they pose the greatest danger to future generations of residents of our country. Viral hepatitis is a collective name for acute and chronic liver diseases. The causes of hepatitis are different, which determines their wide distribution and variety of forms. Regardless of the etiology, signs of hepatitis always indicate the development of an inflammatory process in the human liver. For this reason, people often call the disease “jaundice” - the most characteristic symptom of hepatitis of all types.
Diagnostics
To find out the exact cause of the ailment, the patient must be fully examined. Diagnostics includes:
- examination of the patient;
- physical examination (auscultation, palpation, percussion);
- lab tests;
- hardware examination.
The doctor must take into account the presence (absence) of alcoholism, professional responsibilities, information from the medical history, and existing clinical symptoms. Among the most effective research methods are CBC, OAM, clinical examination of stool, and liver tests. The latter include protein fractions, ALT, total protein, and bilirubin. To determine the diagnosis, methods such as liver biopsy, ultrasound examination of internal organs, X-rays, scintigraphy, magnetic resonance and computed tomography are also necessary.
The indicators obtained after a coagulogram, enzyme immunoassay and biochemical analysis are of great importance. This is especially true for the level of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase and alkaline phosphatase. Clinical manifestations of toxic hepatitis are similar to those of other liver pathologies. It will take a certain period of time to differentiate and treat them. Hepatitis caused by intoxication of the body can be accompanied by autoimmune, viral, and parasitic changes in the parenchymal organ.
Development of viral hepatitis
Common to all viral hepatitis is the presence of an incubation period that lasts from the moment the pathogen enters the body until the first symptoms. This period will be the shortest in case of Botkin's disease (hepatitis A); on average, the clinic can appear within 2-3 weeks. For viral hepatitis B, the incubation period lasts up to six months, and only then its first signs may appear. For hepatitis C, incubation lasts up to 50 days, but the course of the infection itself can be hidden, without a single sign until the most severe liver damage.
Treatment
The drug therapy regimen is selected depending on the type of toxic substance, the form and stage of the toxic pathology. In the acute phase of hepatitis, all therapeutic procedures are carried out only in a hospital setting. The treatment course must include:
Gastric lavage
- Gastric lavage (natural, artificial).
- Blood purification (administration of electrolytes, consumption of milk and herbal decoctions, plasmapheresis).
- Introduction of antidotes.
- Drug treatment.
- Vitamin therapy.
- Diet.
Throughout the entire cycle, the patient must regularly undergo control clinical studies. With their help, the doctor evaluates the effectiveness of the treatment measures taken. If advanced hepatitis has caused irreversible changes, the patient undergoes a liver transplant.
When undergoing therapy against hepatitis, the patient must eat properly and observe semi-bed rest or bed rest. Thus, provoking factors are eliminated, liver functionality is increased and the functioning of the circulatory system is improved.
To reduce skin itching and relieve icteric symptoms, the doctor usually prescribes hepatoprotectors. You should take new medications only after consulting your doctor. The same applies to traditional methods of treatment. If symptoms of acute toxic hepatitis occur, you should quickly contact the clinic.
Hepatoprotectors
Effective remedies for hepatitis include medications such as:
Liv 52
- Liv 52 is a herbal preparation that is characterized by a wide spectrum of action. It neutralizes toxic compounds and increases the activity of vital enzymes. Its functions include stimulation of the production of components that block the influence of radicals. Thanks to this, harmful cholesterol and toxic substances are removed from the body.
- Essentiale forte is a medicine that includes phospholipids. The source of the main ingredient is soybeans. The drug stabilizes metabolism in the parenchymal organ, restores hepatocytes, and prevents the appearance of scars.
- Heptral - this drug for hepatitis is based on ademetionine. It is necessary for the synthesis of serotonin and the removal of toxins. The medication is characterized by choleretic and antidepressant properties. Alcoholic hepatitis is often treated with Heptral.
Diet
Table No. 5
A balanced diet (table No. 5) is a mandatory part of the drug regimen. Heavy meals can significantly complicate the condition of a patient suffering from chronic hepatitis. The diet will help relieve unpleasant symptoms and contribute to a faster recovery. The risk of negative consequences can be minimized through fractional meals. You need to be treated in accordance with your doctor's recommendations.
A proper diet is based on foods containing pectin and fiber. Industrial workers should drink milk regularly. You will also have to give up eggs, pork, smoked meats and baked goods. For hepatitis, the diet must include porridge, lean fish, bran and dried bread. Coffee and alcohol are replaced with healing infusions and compote. Portions for toxic hepatitis should be reduced. It is not recommended to mix animal and plant foods. This will complicate the process of digesting food.
Classification of hepatitis
Hepatitis A is the most common and least dangerous viral hepatitis. The incubation period of infection ranges from 7 days to 2 months. Infection occurs through eating low-quality food. In addition, acute hepatitis A is transmitted through direct contact with the belongings of a sick person and dirty hands. In most cases, the infection ends with spontaneous recovery, but sometimes patients are prescribed IVs, which reduce the intensity of the toxic effect on the liver.
Hepatitis B is transmitted through blood, during sexual intercourse, and by injection with unsterile syringes. This form is very dangerous because it causes severe liver damage and is accompanied by severe symptoms: fever, enlarged liver and spleen, nausea, vomiting, severe joint pain. Hepatitis B requires complex treatment in a hospital setting with the mandatory use of immune drugs, hormones, antibiotics and hepatoprotectors.
Hepatitis C is one of the most severe forms of the disease, often leading to cirrhosis, liver cancer and, as a consequence, the death of the patient. The most likely route of infection is through blood during transfusions, but hepatitis C can also be transmitted during sexual contact and from a sick mother to the fetus. The incidence in Russia and abroad is constantly growing, therefore, when diagnosed with hepatitis C, treatment and prevention require an integrated approach to solving the problem, careful monitoring of the condition of donor blood, and the dissemination of visual propaganda among the population. The danger of this form lies in the fact that hepatitis C is often combined with other forms of viral hepatitis, and, in addition, there is currently no effective vaccine that would reliably protect a healthy person from infection.
Hepatitis D was discovered and studied in 1977. Later, scientists proved that viral hepatitis delta is a type of hepatitis B, which appears as a result of the combination of the main strain of the virus and the delta agent.
Hepatitis E - signs of infection are similar to those of hepatitis A, but in severe cases, the disease affects not only the liver, but also the kidneys. The prognosis for treatment is almost always favorable. The exception is pregnant women in the third trimester, when the risk of losing a child approaches 100%. Prevention of hepatitis E is similar to the prevention measures taken against hepatitis A.
Prevention
To prevent the development of a toxic form of pathology, the patient must:
- Forget about harmful addictions.
- Follow your doctor's instructions.
- Avoid unprotected contact with industrial poisons and organic solvents.
- Get medical examinations regularly.
- Observe safety precautions when performing professional duties.
Milk thistle
Otherwise, the negative consequences caused by hepatitis will not keep you waiting. Therapy should be carried out under the supervision of a physician. It is strictly forbidden to select drugs and medicines used for hepatitis (celandine, chamomile, milk thistle, carrots, corn silk) on your own. Information about suitable treatment methods for chronic hepatitis should be obtained from a specialist, and not from forums on the Internet.
Preventive measures
To avoid getting hepatitis, you must follow these rules:
- Vaccinate at intervals of 6 to 10 years.
- Maintain personal hygiene.
- Consume only purified foods and water.
- Use condoms during sexual intercourse.
- Give up bad habits (alcohol, drugs).
- Take medications only as indicated.
- Avoid contact with chemicals.
As you can see, hepatitis is a dangerous disease that can lead to serious consequences, including death. When the first suspicious symptoms appear, you need to visit a doctor and conduct a thorough diagnosis. Timely treatment and compliance with all doctor’s recommendations guarantees a complete recovery.
Diet
During therapy, you need to avoid alcohol, fatty and fried foods, foods containing preservatives, flavors, flavor enhancers, and other chemical additives. You cannot drink carbonated drinks or strong black tea.
Currently reading: How to restore the liver: medical and traditional methods
Normalize your diet, don’t overeat, don’t starve. It is allowed to eat fermented milk products, cereals, vegetables, fruits, and berries. They prepare soup, porridge, minced meat products, fish, and scrambled eggs. Warm foods should be eaten, cold and hot foods are prohibited. Drink more mineral water, as well as decoctions of medicinal herbs. Helps restore the liver: rose hips, immortelle, celandine, wormwood, tansy, chamomile, mint, lemon balm, calendula. To speed up the flow of bile, it is recommended to consume 1 dessert spoon of vegetable oil in the morning on an empty stomach.
Acute and chronic hepatitis
The acute form of the disease is the most typical for all viral hepatitis. Patients experience: deterioration in health, severe intoxication of the body, impaired liver function, development of jaundice, increased amount of bilirubin and transaminase in the blood. With adequate and timely treatment, acute hepatitis ends in complete recovery of the patient.
If the disease lasts more than 6 months, the patient is diagnosed with chronic hepatitis. This form is accompanied by severe symptoms (asthenovegetative disorders, enlarged liver and spleen, metabolic disorders) and often leads to cirrhosis of the liver and the development of malignant tumors. A person’s life is at risk when chronic hepatitis, the symptoms of which indicate damage to vital organs, is aggravated by improper treatment, reduced immunity, and alcohol addiction.
Complications of hepatitis
Both acute and chronic hepatitis can lead to very serious consequences. Among them it is worth especially noting:
- inflammatory diseases of the biliary tract;
- hepatic coma (ends in death in 90% of cases);
- Liver cirrhosis – occurs in 20% of patients with viral hepatitis. Hepatitis B and its derivatives most often lead to cirrhosis;
- liver cancer;
- dilation of blood vessels and subsequent internal bleeding;
- accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity - ascites.
The greatest number of severe complications occurs with hepatitis C in the chronic stage of development. The problem is aggravated by the lack of effective treatments for this form, so if any unfavorable symptoms occur, a person should definitely consult a doctor. You should not neglect a visit to the clinic, because it is quite possible that timely prescribed treatment will save not only the health, but also the life of the patient.