595
Hepatitis C (HCV) is one of the most complex, dangerous and intractable diseases that exist. 2% of the world's population suffers from this liver disease. Just recently, 5 years ago, there was no treatment for hepatitis - the virus, entering the human body, was a mortal danger.
Now, approximately half of the patients are not cured and die within 8–10 years. This high mortality rate occurs due to complications. These are cirrhosis and other diseases that produce irreversible effects in the digestive system.
Knowledge about the possibilities of infection, symptoms, and the incubation period of hepatitis C will help you be more careful about your health and protect you from the danger of infection.
Methods of infection with hepatitis C
The main source of the virus is people who are infected or have been sick for a long period of time. Those who have just “caught” the virus do not yet see symptoms or pathological changes. And therefore they don’t know that they are infected.
Only a blood test can show whether the hepatitis virus is present in the body.
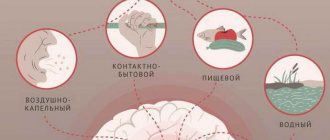
HCV cannot be transmitted through household objects, hugs, a friendly handshake, or through the air during communication. It is transmitted exclusively through the blood. Therefore, patients with hepatitis should not be pushed away, avoided, considered outcasts for fear of becoming infected, since this is impossible at the everyday level. The patient can live as before: go to work, go to school, communicate with whomever he wants, live at home with his family.
Most often, hepatitis is contracted by drug addicts who, when injecting a narcotic substance into the blood, do not observe basic hygiene rules, using one syringe for everyone. You can become infected with the bacteria in places where the same tools are used and insufficient attention is paid to sterilization: in beauty salons during manicure and piercing services.
The same applies to medical institutions where common instruments are used to perform operations when transfusing the blood of a sick person to a healthy one. In all these cases, the problem is the negligence of specialists who are not responsible enough for personal responsibilities and do not promptly disinfect each instrument used.
Even in developed countries there is a considerable risk of contracting hepatitis. It remains very large, for example, during a routine visit to the dentist's office.
There are private beauty salons where they do not particularly monitor compliance with sanitary standards, where all hygiene rules are grossly violated. The risk of becoming infected through intimate relationships is unlikely (only 4%) and is only possible through unprotected sex if one of the partners is sick.
Promiscuous sex life, frequent changes of partners, lack of protection during sex can increase this percentage of danger.
In rare cases, the embryo can become infected from the mother. This occurs during the birth process, when the mother's blood enters the baby's body. During pregnancy itself, the disease cannot be transmitted through the placenta. But during childbirth it is impossible to control or prevent the infection process.
Important! The hepatitis virus poses a serious danger because its incubation period is very long: it is not possible to immediately identify the problem and begin timely treatment.
Cause of the disease
Hepatitis A virus is one of a whole group of viruses that can cause hepatitis. Today, seven varieties are known: A, B, C, D, E, F, G. The source of infection is a person with viral hepatitis A, from whose body the virus is excreted in feces and urine. The sick person can infect the people around him.
Isolation of the virus is observed already 5 days before the onset of jaundice and continues for approximately 5 days already in the icteric period. The virus is released most intensively at the end of the incubation period, when there are no manifestations of the disease yet, and the infectiousness of humans increases. During the period of jaundice, the patient is less infectious. Billions of viruses are released with the patient's secretions, but only about 10 are enough to infect another person.
Of particular danger are patients with the anicteric form who do not isolate themselves and spread the infection.
Hepatitis A is a disease with a fecal-oral transmission mechanism. You can become infected by consuming water or food products contaminated with the hepatitis A virus. Viruses can be introduced into food products through the dirty hands of the sick person or the person in contact with him or her, if they do not follow basic hygiene rules.
Infection through water occurs when drinking water is poorly treated or when dirty water gets into the mouth when swimming in water bodies. The hepatitis A virus remains viable for several months not only in fresh water, but also in salt water.
A contact and household route of infection through any common item is also possible:
- dishes;
- towel;
- bed sheets;
- dirty hands.
Family outbreaks with diseases of several people indicate ignorance of hygiene rules in the family. Some scientists believe that hepatitis A virus can be transmitted through airborne droplets and sexual contact.
There have been cases of infection through donor blood taken from him during the incubation period.
Viral hepatitis A occurs mainly in childhood, since children do not always adhere to the rules of hygiene and are in closer contact with each other. Mostly children from 1 to 15 years old are affected. Babies up to one year old are protected by maternal antibodies, so they practically do not get sick.
Risk group
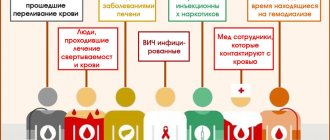
The hepatitis C virus affects the population from 18 to 46 years old. This is the age of greatest risk, when there is a danger of getting difficult-to-treat liver disease. In extremely rare cases, the disease affects children and the elderly. People who can become infected with hepatitis are:
- They become addicted to drugs by using disposable syringes several times;
- Often undergo hemodialysis;
- Regularly visit dubious beauty salons and medical institutions to undergo procedures involving the use of reusable instruments;
- Forced to agree to a blood transfusion in order to restore their health;
- They work in hospitals, clinics and deal with the blood of patients.
Treatment
Hepatitis therapy is aimed at destroying the virus, alleviating the patient’s condition, eliminating intoxication and liver damage.
The method of treatment directly depends on the stage of the pathology and the patient’s condition. First of all, the patient is prescribed a strict diet. The patient should not eat fatty, spicy or salty foods. Therapy for the chronic form consists of the use of antiviral medications of the group of alpha interferons and nucleosides (lamivudine, adefovir). Treatment generally lasts from 6 months to several years. In addition, for hepatitis B, hepatoprotectors and drugs that strengthen the immune system are used. But in the chronic form of the disease, complete healing occurs very rarely.
But they cannot be donors, and are forced to constantly take medications.
Hepatitis B is a complex disease. You should not self-medicate; unreliable and dubious methods can lead to fatal consequences. There is no easy or very quick treatment for hepatitis B. Only a doctor can correctly diagnose and prescribe the right medications.
We recommend reading:
Before talking about the incubation period, it is worth recalling that hepatitis (whatever form it may be) is an infectious disease that, to one degree or another, affects healthy liver cells, contributes to their massive destruction and is not subject to final recovery. The disease manifests itself in different ways, and the intensity of the pathological process depends not only on the prevailing form of diagnosis, but also on the individual characteristics of the body (hypersensitivity or the presence of chronic diseases).
Symptoms of hepatitis C
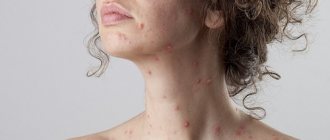
At the very beginning of the incubation period, VSH does not manifest itself in any way and is asymptomatic. It is often diagnosed accidentally during an examination or tests for the treatment of other diseases. In the first few weeks, symptoms cannot be detected. And yellowing of the skin appears only in the most severe stages of the disease.
Usually the patient feels a decrease in general tone, reluctance to move, and fatigue for no reason. His fatigue increases even after minimal exertion. Appetite decreases, and sleep becomes restless, or insomnia appears. If hepatitis C is characterized by an acute form in a person, then the patient may complain that the joints sometimes hurt, as well as malfunctions of the digestive system.
These symptoms often indicate the presence of other diseases that appear outwardly in the same way. Therefore, if a person does not even think that he may have the hepatitis C virus, he will not associate the appearance of weakness or temporary intestinal upset with this dangerous disease.
Due to the fact that timely diagnosis is almost impossible, hepatitis develops and can become chronic. It progresses over a long time, sometimes lasting 15 years. During this period, the patient may observe:
- Darkening of urine;
- Slight yellowness of the skin;
- Body itching;
- Frequent muscle pain, like fever.
What is hepatitis A
The fact that hepatitis A is an infectious disease was proven in 1883 by Sergei Botkin. Before this, hepatitis A was considered non-contagious. Among hepatitis, Botkin's disease is considered one of the safest: it very rarely causes death and does not become chronic.
Hepatitis A is caused by a virus that, penetrating into the body through the fecal-oral route, settles on the mucous membranes and through them enters the blood. Further development of the disease manifests itself in the form of general toxic and dyspeptic phenomena.
Transmission factors for hepatitis A are most often water, food, dirty hands, and personal items. Sometimes parenteral methods of infection are possible, as well as through sperm and menstrual blood.
Despite vaccination, this disease has not been completely eradicated. The hepatitis A virus is very resistant: boiling kills it only after 5 minutes; at a temperature of 1800C, the infection dies within an hour.
Complications
If, after identifying hepatitis C, you do not treat it with high-quality drugs and do not fight it, then very soon the disease may develop complications.
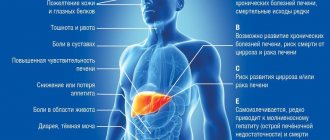
Cirrhosis will occur, from which it is virtually impossible to cure. In extreme cases, liver cancer, often inoperable. And if a severe form of hepatitis occurs, the following signs are observed:
- Swollen, distended abdomen;
- Unnaturally red color of palms;
- Problems with memory and concentration, inability to remember new information and retain it in consciousness for a long time;
- Pain in the right side in the liver area;
- Muscle contraction that occurs involuntarily (it cannot be controlled, similar to cramps);
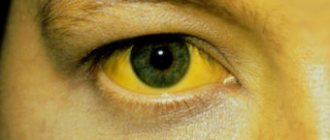
- Strong yellowness, which appears not only on the skin, but also on the whites of the eyes;
- Serious digestive disorders;
- Internal bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, which can be detected by analyzing stool and vomit.
Chronic hepatitis B
Patients with chronic hepatitis B are registered in all countries of the world. Their number on Earth is more than 400 million people (1/3 of the total population). The frequency of transition from acute to chronic hepatitis B varies. On average, this figure is 5 - 10%. In newborns this figure is 90%, in children aged 1 - 5 years - 40%.
An early sign of chronicity is, along with the determination of HBV DNA in the blood serum, the persistence of the surface (Australian) antigen HBsAg for more than 10 - 12 weeks. The diagnosis of chronic viral hepatitis B is established no earlier than 6 months from the onset of the disease. It should be clarified that 30 - 40% of patients with chronic hepatitis in the past did not tolerate the manifest form of acute hepatitis.
The spectrum of manifestations of chronic hepatitis and its course options are varied - from asymptomatic to progressive. The disease ultimately leads to the development of fibrosis, cirrhosis and primary liver cancer.
Most patients have no symptoms of chronic hepatitis B. In some cases, weakness, increased fatigue, muscle and joint pain are noted, signs and symptoms appear indicating liver damage: heaviness and pain in the right hypochondrium, jaundice, signs of the development of hemorrhagic syndrome (petechiae, “liver palms”, spider veins, multiple hemorrhages, etc.). Extrahepatic manifestations include signs of periarteritis nodosa, aplastic anemia, papular acrodermatitis, and glomerulonephritis.
There are 4 stages (phases) of chronic hepatitis B:
- Immunotolerant stage.
- Stage of HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B.
- Stage of HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B.
- Stage of inactive carriage of HBV.
Rice. 10. Ascites in liver cirrhosis. Multiple hemorrhages are visible on the skin, as a sign of dysfunction of the organ.
Immunotolerant stage of the course
The immunotolerant stage of the course occurs during perinatal transmission of the virus. Up to 85% of children born to infected children suffer from this form of hepatitis B. The immune system reacts poorly to the infection, as a result of which viruses actively multiply. The nuclear antigen HBeAg and a high level of viral load are detected in the blood serum. ALT is recorded within normal limits. A liver biopsy shows that inflammation and fibrosis in the organ are absent or minimally expressed. This stage lasts a long time - many years and even decades.
HBeAg-positive phase of chronic hepatitis B
The HBeAg-positive phase is characterized by the presence of an inflammatory process in the liver and immune-mediated destruction (lysis) of hepatocytes, which is confirmed by histological examination of biopsy material. The immune system begins to actively respond to the infection. In the blood serum, the concentration of HBV DNA decreases, the level of ALT and AST increases, and the nuclear antigen HBeAg is detected over a number of years. But then, as a result of mutations, strains of viruses that do not produce the HBeAg antigen begin to predominate. This is how HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis turns into HBeAg-negative. Long-term chronic infection leads to the formation of liver fibrosis.
HBeAg-negative phase of chronic hepatitis B
The transition of chronic hepatitis to the HBeAg-negative stage indicates the progression of the disease and a worsening long-term prognosis. This form of the disease is extremely widespread throughout the world, is more often recorded in males aged 35-46 years, and is prone to constant progression, with rare remissions. Inflammation of the liver is necrotic in nature, resulting in fibrosis and cirrhosis of the organ. The goal of treating patients is active antiviral therapy, which is necessary to slow the progression of hepatitis.
HBV inactive carrier stage
This stage of the disease develops after the development of antibodies to the nuclear antigen HBeAg and is characterized by a significant decrease in the viral load, normalization of biochemical parameters and resolution of the inflammatory process in the liver. The stage of inactive HBV carriage can last quite a long time. Subsequently, about 10 - 20% of patients return to HBeAg-positive status. Some patients develop HBeAg-negative status.
Rice. 11. Jaundice with cirrhosis of the liver.
Sources
- https://InfoPechen.ru/gepatity/drugoe/inkubatsionnyj-period-virusnyh-gepatitov-avs-red.html
- https://privivku.ru/infekcionnaye-zabolevaniya/gepatit-b.html
- https://venerologia03.ru/gepatit/inkubatsionnyj-period-gepatita-c.html
- https://microbak.ru/infekcionnaye-zabolevaniya/virusnyj-gepatit-b/simptomy-gepatita-ba.html
Hepatitis C incubation period
The incubation period of hepatitis C is a period of time that begins at the moment of infection and lasts until the initial symptoms are detected. The incubation period reveals how the body reacts to the penetration of infection, whether the bacteria manifests itself in any way or not.
The incubation period of this disease can vary in length. It can be short and covers only 14 days. And sometimes it reaches 30 weeks. Therefore, from the time of infection, a person can live for about a year without suspecting the presence of the virus in the body.
Hepatitis C in its incubation period is very similar to hepatitis B, which also does not show its existence for a very long time. The average number of days of the WASH incubation period is 59.
During the incubation period, the virus rapidly increases in size, spreads and progresses in every possible way. It multiplies and its numbers grow. After spreading, it penetrates into the liver and begins its pathological effect there.
In the active stage, the virus produces destructive processes in liver cells, making the tissues inoperative and unable to perform their direct functions and responsibilities. At first, liver cells fight and counteract the viral bodies. But from constant struggle the organ is weakened, its protective properties are reduced. The destructive process leads to a number of clinical changes.
45% of cases of hepatitis are expressed in a fairly acute form. And then the incubation period will last no longer than 20 days.
Then symptoms appear immediately. The acute form quickly makes it possible to identify the pathology and diagnose it at a very early stage, when it has not yet reached dangerous proportions. If you start intensive therapy right away, the person will become completely healthy in a couple of months.
In the other 55% of cases, the incubation period is slow and long. At this time, the disease takes on a “long-lasting” form, called chronic, and its symptoms are not clearly visible. A person becomes a passive carrier of the disease without knowing it. Meanwhile, the virus produces invisible destructive processes in his liver.
Diagnostic procedures
When the first symptoms of hepatitis appear, significant changes occur in the blood. To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis of the disease - this measure will allow you to start treatment on time and prevent the development of complications.
If you are suspected of being infected with hepatitis A, the following tests are prescribed:
- coagulogram (shows blood clotting);
- PCR method (a high-precision method of molecular genetic research that allows you to identify various diseases);
- enzyme immunoassay ELISA (for the presence of antibodies to pathogenic agents);
- General blood test, biochemical.
To diagnose hepatitis B and C, you first need to take a biochemical blood test. Levels of liver enzymes AST and ALT are indicators of inflammatory activity and viral development. The concentration of bilirubin in the blood (bile pigment, the main component of bile) allows us to assess the functioning of the liver - in case of pathologies of the organ tissue, part of the produced bile enters the blood, causing an excess of bilirubin.
There are rapid tests to determine these diseases; they are done within a few minutes, but they are not highly accurate, so they are only suitable for initial diagnosis. If the result of this test is positive, more detailed examinations are prescribed - ELISA, PCR. The coagulogram, which evaluates blood clotting, worsens in hepatitis due to a decrease in the level of prothrombin. Sometimes, to determine the extent of organ damage, tissue is taken for examination (liver biopsy is performed).
Instrumental methods for diagnosing hepatitis include:
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs. Allows you to determine the size and shape of the liver, determine surface changes, stage of disease development and severity.
- Fibroelastography is a modern non-surgical method for diagnosing liver diseases. Helps to identify structural features of organ tissue, see pathologies, and assess the level of damage. In terms of accuracy, the method is close to a biopsy, but is much less traumatic.
Such research methods are non-invasive, and therefore can be used in recognizing the disease in both adults and children.
Being viral in nature, the incubation period of hepatitis A is characterized as short-term and is approximately 1 month. Affecting the full functioning of the liver, the disease becomes one of the common forms of hepatitis, referred to as Botkin's disease. Remaining virulent for a long period, the virus is found on household objects, water and food.
Prevention of hepatitis C
Since it is not easy to detect hepatitis C right away, and therapy takes a long time, requires a lot of money and is painful, it is better to follow preventive and hygienic standards that will protect against infection.
- Use only your own hygiene items - toothbrush, razors. After use, blood often remains on them, and if a person is infected with a virus, this is a direct path to infection;
- Go only to those beauty salons that have earned a good reputation;
- Visit those medical institutions for surgical procedures that take seriously the issue of disinfection of working instruments and devices;
- In sexual life, prefer only protected sex.
It is important to monitor your health. If you have any symptoms of hepatitis, you should immediately see a doctor and donate blood to an immunologist. Taking simple preventive measures will eliminate possible risks and protect you from health problems.
© 2020 – 2020, . All rights reserved.
Is a person contagious during the incubation period?
The contagiousness of the pathology directly depends on the incubation period of hepatitis C. The risk that a sick person poses to others directly correlates with viral load indicators. In other words, the higher the concentration of RNA in the blood serum, the greater the likelihood of infection.
Experts agree that during the incubation period, hepatitis C is practically not contagious. The level of HCV in the blood is minimal not only for the occurrence of any clinical symptoms, but even for laboratory detection.
But during the first weeks after infection, the patient is at risk for:
- HIV-infected;
- people undergoing chemotherapy, treatment with cytostatics (these medications have a pronounced immunosuppressive effect);
- people who have had organ transplants and are taking immunosuppressants;
- people with concomitant liver damage (alcoholic and other types of viral hepatitis, cirrhosis, cancer);
- malignant lesions of the hematopoietic system;
- newborns;
- pregnant women.
Everyone who belongs to the listed categories needs to pay special attention to preventive measures. Casual sexual contact should be avoided, otherwise condoms must be used. If a person prefers to use the services of cosmetologists, it is necessary to choose salons and clinics where instruments are processed in a dry heat or autoclave and disposable craft bags are opened in front of the visitor.
To carry out any medical procedures, it is necessary to correctly select a clinic. Doctors recommend personally making sure that the doctor uses disposable or properly sterilized instruments.
Viral hepatitis C (HCV) is one of the most dangerous viral diseases in the modern world. The methods of infection, the incubation period of hepatitis C, the symptoms and complications of this disease have their own specifics, which every person should know. This will allow him to understand the seriousness of the disease and protect himself from possible infection.
Is the patient contagious during the incubation period?
The risk of infection for a healthy person directly depends on the level of HCV RNA (this parameter is called viral load). The higher this indicator, the greater the risk of infection upon contact. During the incubation period, viremia is low, so the likelihood of “catching” hepatitis C for an uninfected person is low.
However, the danger remains for:
- HIV-infected;
- undergoing chemotherapy;
- taking cytostatics and other drugs that significantly reduce immunity;
- patients with malignant lesions of the bone marrow and lymphatic system;
- people suffering from liver diseases, regardless of their etiology;
- have already had hepatitis C or are suffering from HBV infection;
- patients with systemic severe infections (for example, tuberculosis).
Throughout the latent course of the disease, the infected person is unaware of the risk he poses to family members and relatives, which increases the risk of infection. An unfavorable prognosis is also typical for HCV transmission either in utero or during childbirth.
The baby’s body is not able to cope with the viral load, which is fraught with irreversible damage to the liver in the first place and internal organs in general.
| Instrumental examinations | The structure of the liver remains unchanged, noticeable changes begin 8–11 years after infection in the absence of previous liver diseases |