Pregnancy and hepatitis C are a combination that frightens all expectant mothers without exception. Often this diagnosis is made when a woman is already pregnant and not planning a child. Diagnosis is carried out through standard screening for infectious processes. It includes HIV infection, hepatitis C, B.
The interaction of chronic hepatitis C and pregnancy leads to various negative consequences. The disease can provoke premature birth, the birth of a child with a deficiency of body weight. There are equal risks of infecting the baby during natural childbirth or caesarean section.
Let's consider the danger of chronic pathology for mother and child, clinical signs during exacerbation, diagnosis and treatment features for a pregnant woman.
General information
The disease is caused by a virus that penetrates the human blood. The pathogen affects the liver due to the increased sensitivity of hepatocytes to infections. Harmful microorganisms, after penetrating an organ, may not have an active effect for a long time. This period is latent, there are no symptoms of pathology.
There are several genotypes of the virus that causes hepatitis C during pregnancy. They differ in the nature of the course and possible complications. The disease occurs in a chronic form. It is extremely difficult to detect pathology in the early stages due to the lack of pronounced symptoms.
Basic symptoms and diagnostic procedures
Hepatitis in pregnant women, forms B and C, can occur with virtually no symptoms and this is where their insidiousness lies. A woman often learns that a virus is present in her body from test results. In some cases, the pathology manifests itself with the following symptoms:
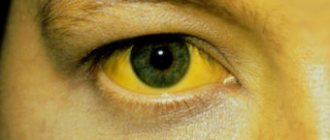
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes.
- Dull aching pain in the right side.
- General intoxication, accompanied by headache, fever, vomiting, nausea.
- Decrease in working capacity, rapid fatigue.
- Itching sensation and loss of consciousness.
Laboratory tests (blood biochemistry) can detect the presence of the virus in the body. Based on these data, ultrasound diagnostics are prescribed, as well as a test for specific markers. Instrumental examination techniques are extremely limited for pregnant women, so the doctor can only rely on the results of general studies.
Features of the flow
Chronic hepatitis C during pregnancy occurs in the same way as in other categories of patients. The disease presents with a mild clinical picture. Women often make the mistake of mistaking the symptoms of liver pathology for side effects that occur during pregnancy.
It is important to know! Transmission occurs parenterally - by the entry of viral microorganisms into the blood. The risk of contact and household infection cannot be excluded. A woman can become pregnant after infection, or, on the contrary, acquire an infection during pregnancy.
Possible methods of transmission of the hepatitis pathogen:
- Through transfusion of infected blood.
- Use of non-sterile medical instruments.
- Unprotected sexual intercourse.
- Repeated use of syringes and needles.
- Contact with the semen of an infected man.
The incubation period ranges from 14 days to six months. The duration depends on numerous factors, the main one among which is the number and degree of activity of pathogenic microorganisms. In the vast majority of cases, early signs appear 8-10 weeks after infection.
Symptoms of the disease:
- Muscle weakness.
- High fatigue, decreased performance.
- Manifestations of dyspepsia (bitterness in the mouth, heartburn, belching).
- Nausea with vomiting.
- Discomfort, less often pain in the right hypochondrium.
- Itchy skin.
- Rashes.
- Hepatomegaly.
- Joint pain.
- Darkening of urine.
- Colorlessness of stool.
Many of these symptoms are similar to signs of toxicosis that women suffer from. Because of this, it is extremely difficult to detect the disease in a timely manner. The occurrence of such manifestations is a direct indication for a diagnostic examination.
To identify pathology, a blood test is performed to detect viral antibodies. The screening test is performed three times during the entire pregnancy period. At the same time, the presence of pathogenic RNA in the samples is determined by PCR. This method allows you to accurately determine the type of hepatitis and its genotype.
There are common cases in which the test result is positive, but the woman is not infected. To exclude a false diagnosis, tests are performed several times. An unreliable response is provoked by concomitant disorders occurring in the body, autoimmune processes, and the use of certain medications. Also, a false positive result occurs due to errors by laboratory technicians when preparing samples for testing.
The presence of the disease does not affect the ability to conceive a baby. Therefore, a woman’s pregnancy with hepatitis C often occurs unplanned. In such cases, a decision must be made to terminate. The possibility of abortion is considered if there is an increased likelihood of negative consequences for the child.
Treatment
Almost all medications aimed at restoring liver function are teratogenic for the fetus, therefore, if laboratory tests show that the liver is functioning stably and the patient feels well, treatment is interrupted while the child is pregnant.
But there are situations (5% of cases) when the regenerative reserves of the liver are not preserved. Then severe pain occurs in the hypochondrium on the right, cholestasis develops, and the pregnant woman’s condition rapidly deteriorates.
The infectious disease specialist selects the safest antiviral drugs for her. Traditional "Ribavirin" and "Interferon", which are most often used in the treatment of hepatitis C, are not recommended for pregnant women - they have an adverse effect on the fetus. They are replaced with medications whose active ingredient is ursodeoxycholic acid.
It is important for a woman to listen to medical recommendations and, if necessary, take medications. If she refuses to use them for fear of harming the fetus, the disease will progress, which will have an extremely negative impact on her health and the health of the baby.
The expectant mother should not prescribe any medications for herself.
Risk to the fetus
Previously, it was believed that hepatitis C and pregnancy are incompatible due to the high likelihood of having children with disorders. The main complication of the pathology is intrauterine infection. However, this phenomenon is observed rarely - in 6% of cases.
Viral microorganisms are able to pass through placental tissue. Therefore, the pathogen can be transmitted to the child from the mother vertically. During the neonatal period, these babies are more likely to develop jaundice, but the risk of serious complications is small.
The development of severe abnormalities or other significant abnormalities is considered rare. In most cases, this occurs against the background of concomitant complications of pregnancy and hepatitis C in the mother. Aggravating factors include late fading, the presence of bad habits, chronic diseases, especially HIV.
After birth, the child must be regularly examined for symptoms of liver damage. If these are not detected in the first 12 months, the baby is considered healthy. The presence of infection is indicated by the presence of antibodies to the hepatitis virus in children aged one and a half years.
general information
Viral hepatitis is a fairly large group of diseases, the main etiological factor (cause of occurrence) of which is various hepatotropic viruses with multiple transmission mechanisms.
Viral hepatitis manifests itself primarily as liver damage and disruption of its normal functioning in the form of intoxication, dyspeptic syndromes, hepatomegaly - enlarged liver - and jaundice - yellow color of the skin and mucous membranes.
The group of viral hepatitis, which are the most common and studied today, includes hepatitis A and B, hepatitis C, hepatitis D and E. The list of new “candidates” being discussed for the role of causative agents of hepatitis includes viruses F, G, SEN V, TTV. A rather serious problem these days is the existence of mixed hepatitis - an association of several viruses.
Therapeutic measures
The simultaneous course of pregnancy and hepatitis C in the mother excludes the possibility of taking medications. Drugs such as Ribavirin or Sofosbuvir should not be taken by women who are pregnant. Moreover, this restriction applies for all periods. This is explained by the fact that medications significantly enhance the protective reactions occurring in the body. Because of this, the fetus may be affected by immune agents, leading to miscarriage.
During the therapy period, intense physical activity is strictly prohibited. Do not expose the body to cold or toxic substances, including alcohol. It is necessary to exclude the possibility of overwork.
Safe medications can be used for treatment. These include drugs from the group of hepatoprotectors (Essentiale, Karsil, Hofitol). However, the main method of therapy is diet.
The expectant mother must eat well in order to fully provide her own body and fetus with the necessary substances. It is recommended to eat food 6-8 times a day in small portions. Any foods that overload the liver are excluded from the diet. These include fatty meat and fish, canned food, smoked, fried, confectionery, and sausages.
Attention! Self-treatment is prohibited, as this can harm the unborn child. The use of alternative remedies and pharmaceutical medications whose safety has not been proven through clinical trials is not recommended.
How does infection occur?
Group B hepatitis is transmitted from an infected person through blood.
The most common ways of transmitting the virus are:
- Blood transfusion. Due to the fact that this method has a high probability of infection with hepatitis B (up to 2% of donors are carriers of the disease), before the infusion procedure, the blood is checked for the presence of the virus.
- Using non-sterile needles, manicure accessories and other things on which blood could remain (even in dried form). Sharing the same syringe needle by several people is the most common method of infection among drug addicts.
- Sexual contact. Every year this route of infection becomes more common.
- From mother to child. Infection can occur both in utero and during the passage of the birth canal. The likelihood of infection is especially high if an active virus or an acute form of it is detected in the mother.
It is not always possible to reliably find out exactly how the infection occurred - in approximately 40% of cases the method of infection remains unknown.
Childbirth with hepatitis C
Women diagnosed with a viral disease give birth in a special department. It is intended directly for the infected. The difference from a regular maternity hospital is the observance of anti-epidemiological measures.
Infected women can give birth naturally. To reduce the risk of negative consequences of hepatitis C during pregnancy for the child, a caesarean section is recommended. This method reduces the likelihood of transmission of the virus to the newborn.
Children born to sick mothers are observed by infectious disease specialists. On the first day of life, they are vaccinated against hepatitis groups A and B. It is possible to determine whether a child is infected only after 1-1.5 years, with repeated tests.
Diagnostics
Among the activities that are carried out to detect the virus:
- Blood analysis. Thanks to this, you can find out how much a woman’s immunity copes with hepatitis C.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The most informative method. Allows you to detect the number of copies of the virus in a woman’s blood, which indicates its activity.
- Biochemistry of blood. Determination of the efficiency of the affected organ.
- Ultrasound. The structure of the liver and the degree of change in its tissues are assessed.
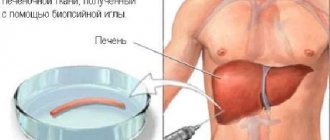
- Biopsy. A small fragment of liver tissue is carefully examined under a microscope to understand the level of severity of pathological processes.
During pregnancy, a false-positive blood test for hepatitis C is common. Therefore, after receiving the results, women are advised to donate blood again to eliminate the possibility of an error.
Prevention
It is impossible to completely eliminate the risk of infection. A vaccine capable of producing immunity against hepatitis C has not been developed. However, there is a significant risk of illness, including in pregnant women.
Preventive measures include:
- Avoiding contact with possible sources of infection.
- Competent planning and management of pregnancy.
- Compliance with hygiene standards.
- Regular diagnostic examination.
- Compliance with doctor's recommendations.
- Protected sexual intercourse.
Hepatitis C is a common disease in pregnant women. The pathology has a mild clinical picture, which is why it is often diagnosed untimely. The greatest danger to the fetus is intrauterine infection. Therapy excludes the possibility of taking antiviral medications, so the disease is treated with diet and auxiliary medications.
False positive result
A positive result can be shown if you are a carrier. Interestingly, with repeated studies, the results may differ radically. This is due to the use of different diagnostic kits. A false positive result can be caused by the following reasons:
- tumor processes;
- autoimmune reactions;
- infectious diseases;
- taking immunosuppressants;
- low quality of diagnostics;
- improper preparation of biological material - venous blood;
- accidental sample substitution;
- laboratory technician's mistake.