- home
- Soft fabrics
Dropsy is a collective term that refers to various forms of fluid accumulation in the human body. This phenomenon can be observed in different tissues and organs - in serous cavities, in brain tissue, in fiber. The disease is characterized by a disruption in the balance between the circulation of blood components and tissue fluid.
Causes
Dropsy is a kind of symptom that indicates internal trouble in the body. Depending on where the swelling appears, the doctor will be able to determine which internal organ is malfunctioning.
The main causes of dropsy in adults and children:
- disorders of the central nervous system. In medicine, this condition has its own term – neuropathic dropsy. Edema is formed due to damage to the brain and spinal cord, neuralgic pain and damage to nerve trunks;
- various mechanical disorders that prevent lymph and blood from leaving the tissues;
- excessive secretion of fluid that enters the body cavities;
- changes in the composition of blood and lymph;
- heart defects;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- injuries to the external genitalia (a common cause of dropsy in boys and men).
Comprehensive diagnostics
To make a correct diagnosis, a comprehensive diagnosis is necessary, which includes the following activities:
- examination by a doctor, during which the tumor site is palpated;
- blood and urine tests;
- X-ray of the cavity in which the swelling has formed;
- Ultrasound to determine the volume of fluid in dropsy.
In order to clarify the diagnosis and distinguish (differentiate) dropsy from other diseases, a puncture is taken from the site of swelling. Next, the obtained samples are subjected to histological examination. Based on the information received, the attending physician will prescribe the necessary treatment.
Kinds
According to the location of edema in the human body, dropsy is distinguished into two types:
- General. The pathological process develops against the background of prolonged fasting, poor nutrition, chronic disorders of the kidneys, liver and circulatory organs.
- Local dropsy. This type is formed due to inflammation of certain cavities of the human body. The disease is the result of various disorders of the peripheral nervous system, as well as changes in the walls of blood vessels.
Types of local dropsy depending on its location:
Dropsy of the brain (hydrocephalus)
- inguinal;
- abdominal;
- chest;
- brain;
- knee;
- head;
- ophthalmic, etc.
Types of dropsy
The pathological process, which is called dropsy, is not a separate disease and usually these symptoms indicate the presence of disorders in the body. Most often, this disease affects tissues that have loose subcutaneous tissue. Edema develops due to the fact that fluid from the vessels seeps through the walls into nearby tissues, but it is either not absorbed back at all, or this process is very slow.
Forms of the disease:
- General. It is most often diagnosed in pathologies associated with the cardiovascular system, in which a general imbalance of water metabolism occurs (the most characteristic signs are swelling of the face and neck).
- Local dropsy. Failure occurs in one organ or in a specific area due to compression of large vessels.
Edema can be:
- Stagnant, when blood circulation in small vessels is disrupted, venous outflow worsens (phlebothrombosis, cirrhosis).
- Hypooncotic (with changes in the protein component of the blood).
- Membranogenic, which are formed due to disturbances in the vascular walls (hypoxia, poisoning, hyperthermia).
- Lymphatic, arising due to disruptions in the circulation of lymphatic fluid (lymph node hypoplasia).
Varieties of dropsy:
Brain (hydrocephalus). With this form of dropsy, cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the ventricles of the brain and under the meninges. This pathology is most often congenital, but in medicine there are cases where the disease is acquired during life. Children diagnosed with hydrocephalus suffer from metabolic disorders, neurological pathologies, and are almost always developmentally delayed. With this form of dropsy, the size of the skull circumference increases. A person is diagnosed with increased pressure inside the skull, which provokes vomiting and severe headaches.
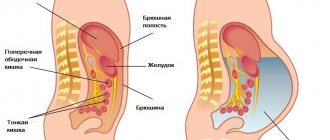
- Ascites. Fluids can accumulate in the peritoneum up to 30 liters. But most often its volume is up to 8 liters. The patient's abdomen enlarges, protrudes forward and descends. Peritonitis may occur due to an umbilical rupture. Rectal prolapse and swelling of the legs may also occur.
- Hydrocele of the testicle. Hydroceles can occur at birth or be acquired during life. The testicle swells and urination is impaired. Organ atrophy is possible.
- Dropsy of the joint. Hydrarthrosis develops when there is fluid in the ankle or knee. At the same time, the size of the joint increases, and swelling characteristic of the disease appears.
- Chest dropsy. This phenomenon often occurs against the background of ascites. In this case, fluid is retained in the pleural area. Most often this is a bilateral process, in which shortness of breath and skin cyanosis are observed.
- Dropsy during pregnancy. In this case, the body weight of the expectant mother increases due to the occurrence of obvious or hidden edema. Changes in the composition of urine and increased blood pressure are diagnosed.
Symptoms
The symptoms for all types of dropsy are almost the same. Adults tolerate this disease more easily. In children, it is necessary to carry out proper and timely treatment so that no complications arise in the future. It is necessary to know the first signs of dropsy in order to deliver a child or adult to a medical facility in a timely manner.
Main symptoms:
- the skin swells;
- at the location of the edema, the patient feels pain that is aching in nature;
- the skin over the swelling is shiny, dry and smooth;
- if you press with your finger at the location of the edema, the hole will not level out for a long time;
- strong thirst;
- feeling of heaviness;
- dyspnea;
- In men, testicular hydrocele will be accompanied by severe nagging pain. The patient notes that the scrotum is swollen;
- In a child with dropsy of the spermatic cord or testicle, the body temperature may rise to high levels.
Symptoms and signs of dropsy
The clinical picture of the disease depends on the cause of the pathology and the place of its formation. But despite this, the following general symptoms of dropsy are distinguished:
- swelling and pain at the location of the swelling;
- temperature increase;
- change in complexion (skin becomes greyish, shiny, cold, peeling often occurs);
- if you press on the skin at the site of swelling, the dent remains for a long time;
- there is an excessive need to drink;
- shortness of breath, weakness;
- movements may be limited (especially if there is dropsy in the arms and legs);
- pain (with hydrocele).
With acquired dropsy in adults, pain may be absent.
Since these are general clinical signs of pathology, each individual type of dropsy may have its own specific manifestations.
Ascites
The disease develops due to the accumulation of transudate in the abdominal cavity. The first symptoms of ascites development in a patient:
- dyspnea;
- feeling of heaviness;
- "frog belly"
Ascites most often develops with cirrhosis of the liver, intestinal diseases, and heart failure. This form must be treated only in a hospital setting.
Liver cirrhosis is one of the main causes of ascites (in 80% of cases). The first symptoms of ascites occur at the last stage of the disease - decompensation. With cirrhosis of the liver, the organ's reserves are almost completely depleted. Blood circulation is disrupted in the liver itself and in the abdominal cavity. Against the background of such changes, a large amount of fluid accumulates in the abdomen. Liver cirrhosis is an incurable disease, so ascites will appear periodically.
Symptoms of dropsy
The symptoms of dropsy are pronounced, the volume of the abdomen is greatly increased, the patient’s condition gradually becomes worse. In addition to swelling, other signs of dropsy can be identified:
- difficulty breathing in a lying position, cough, shortness of breath;
- pelvic pain due to abdominal enlargement;
- frequent urination (painless);
- dysfunction of defecation;
- drowsiness, weakness;
- frequent belching, heartburn;
- heart rhythm failure;
- hemorrhoids, protrusion of the navel.
Dropsy in cirrhosis and other chronic diseases is accompanied by abdominal pain. Due to the increased size of the abdomen, the patient experiences difficulty moving. Since blood circulation is impaired, the face, legs and arms become swollen.
Hydrocele in pregnant women
Hydrops of pregnancy most often develops in the second half of pregnancy. This is due to the fact that a lot of sodium accumulates in a woman’s body, which retains water in the tissues. The presence of pathology should be discussed if the weight of a pregnant woman has increased by more than 20 kg and her face, arms, legs and lower back are severely swollen. These symptoms indicate that this is already hydrops of pregnancy, which needs to be treated. The causes of its development can be kidney disease, endocrine disorders, liver disease, and hypertension. Treatment of dropsy must begin with treatment of the disease that provoked its development.
Dropsical edema does not have a negative effect on the unborn child. But treatment will be necessary, since dropsy can develop into a severe form of gestosis. The pregnant woman will be advised to reduce the amount of fluid she takes. Doctors often prescribe a course of vitamins. As a rule, dropsy in pregnancy goes away with this treatment. The first symptoms of recovery are increased diuresis and improved appetite.
What kind of disease is this?
Dropsy is swelling; the accumulation of transudate can occur in different organs or throughout the body, which determines the type of pathology. As a result of impaired outflow, the skin begins to swell. The contents of the edema are a clear liquid with a high protein content. Despite the fact that a person is 80% water, its stagnation is dangerous. The causes, symptoms and treatment of dropsy depend on its location. During the treatment process, regardless of the primary disease, it is recommended to eat foods low in protein and reduce water intake.
Congenital hydrocele
This disease occurs in newborn babies. The reason is pathologies of embryonic development. The immune form of hydrops in a newborn is more rare. The non-immune form develops with various viral infections, congenital syphilis, inflammation of the placenta, heart defects, and chromosomal abnormalities. But in many cases, specialists are unable to determine the reasons for the development of dropsy in newborns. This condition requires immediate treatment, as irreversible changes in the body may occur that are dangerous to the health and life of the child. Symptoms of the disease appear immediately after birth.
Complications
In most cases, if the patient consults a doctor in a timely manner, treatment of dropsy gives a favorable outcome. However, with large sizes of the hydrocele and prolonged compression of the organ, its dysfunction develops and it stops doing its job. An enlarging tumor leads to displacement and disruption of the internal organs adjacent to it, and a deterioration in the general condition of the patient.
The consequences of dropsy are varied and directly depend on which part of the human body is swollen. With abdominal dropsy, the fluid presses on the diaphragm and moves it upward. This leaves no room for the lungs to function normally, which leads to respiratory failure. Because of this, blood circulation worsens, disruptions in protein metabolism occur, which leads to various pathologies. If the cause of the disease is eliminated, the dropsy goes away. But this happens in rare cases.
Hydrocele without timely treatment can also lead to serious complications. If the amount of fluid in the scrotum increases pathologically, the pressure increases, blood circulation and lymph movement worsen. All this leads to testicular atrophy. Plus, the temperature of the affected area increases, which negatively affects sperm.
With hydrocephalus, mental retardation, emotional and mental disorders, and underdevelopment of the speech center are observed.
Hydrocele of the testicle
In medicine, this disease is called “hydrocele.” In boys, hydrocele can be congenital or acquired. In a newborn baby, dropsy is diagnosed only in 5–10% of cases. The cause of the pathology is intrauterine development disorders. The formation of testicles in boys occurs in the abdominal cavity. They then travel a long way and are placed in the scrotum. This process occurs gradually. As they descend into the scrotum, the testicles pull the abdominal membrane along with them. As a result, a tissue funnel is formed. It usually heals before birth, but in some babies this does not happen. Through this peculiar “path”, the liquid enters the scrotal tissue and edema develops. In this case, the pathology must be treated.
In the first months of life, boys do not show symptoms of hydrocele, since the child most often just lies down and little fluid enters the scrotum. Hydrocele of the testicle is detected at one or one and a half years, when the child begins to walk. Treatment for dropsy is only surgical. Such intervention is necessary to eliminate the risk of complications.
ethnoscience
Treatment of dropsy with traditional medicine is permissible in combination with basic therapy and after medical consultation. The following recipes are used in the fight against pathology:
- Black radish. Black radish juice with honey is considered effective in treatment. Initially, the daily dose of the medicine is 1/3 cup, after some time it is increased to 500 ml.
- Grape. Treatment consists of eating 10 fresh grapes in the morning, after which food intake should begin as late as possible.
- Nettle. Traditional healers recommend drinking tea from nettle roots. To prepare it you need 1 small spoon of raw materials per 250 ml of boiling water. The daily dose is 500 ml, drink 1 glass of tea in the morning and evening.
Hydrocele of the spermatic cord
Hydrocele of the spermatic cord is called funiculocele. The clinical picture of the disease is the same as with hydrocele, only fluid accumulates along the spermatic cord.
Funiculocele
The spermatic cord is a paired anatomical formation that is located between the internal inguinal ring and the testicle. Dropsy edema of this organ occurs in most cases due to injury. In the acute form of the disease, the child develops a high fever and severe pain in the scrotum area. The skin turns red and becomes swollen. If you palpate, you can feel an elastic, oval-shaped body that is not connected to the testicle. Treatment of dropsy in the presence of these symptoms must be carried out immediately.
In adult men and children, the causes of hydrocele of the spermatic cord differ significantly. Dropsy in newborns and children under three years of age is associated with the anatomical features of the body. The main reason for fluid entering the scrotum is the presence of a communicating canal. Often in the first year of life in boys, hydrocele of the spermatic cord goes away on its own. Surgical treatment of dropsy according to indications should only be carried out in a child over three years of age.
In men, hydrocele of the spermatic cord develops due to:
- injuries to the external genitalia (including the spermatic cord);
- tumors of the testicle and spermatic cord;
- inflammation of the scrotal organs;
- operations due to varicocele (dilation of the veins of the spermatic cord).
Treatment of dropsy
The disease occurs in an acute form and is treated with medication. The patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory and painkillers, cold and warm compresses, and wearing a suspensor (support bandage).
In the chronic course of the pathology, the following methods for removing fluid are used:
- Puncture. The liquid is extracted using a syringe. But this treatment for dropsy gives a temporary effect, and very soon the liquid accumulates again. Therefore, this method of treatment is used in cases where it is necessary to provide emergency assistance to a person, and also if after surgery the swelling continues to increase. Puncture treatment of dropsy is contraindicated in the acute stage of the pathological process, since in this case the likelihood of infection and the development of a purulent process increases.
- Injection. The fluid is removed by injecting the swelling with hydrocortisone and other drugs that cause scarring of the membrane.
- Surgery. Dropsy surgery is performed under anesthesia (general or local). Several punctures are made at the location of the liquid, and the liquid is pumped out through them. After this, the patient can have a drainage system installed that will suck out the resulting fluid.
Traditional treatment
Treatment of acute hydrocele includes the use of antibiotics and analgesics, cold and thermal procedures, and wearing a suspensor. The chronic form of testicular hydrocele is treated by puncture of accumulated fluid and administration of hydrocortisone. Most often, surgical intervention is used to avoid complications.
To treat dropsy in pregnant women, optimization of nutrition, restriction of liquid and table salt intake, fasting days, and drug treatment are used.
When treating hydrothorax and pneumothorax, the emphasis is on treating the underlying disease. If a patient is diagnosed with hydrocele of a joint, a puncture is performed to remove intra-articular fluid.
Treatment of ascites depends on the severity of the underlying disease that caused it. Usually the patient is prescribed diuretics, cardiac glycosides, oxygen therapy, and a salt-free diet is recommended. In difficult cases, surgery is used to remove fluid from the peritoneum.
Elimination of the manifestations of hydrocephalus can be either surgical or conservative.
To reduce intracranial pressure use:
- General strengthening procedures;
- Pine-salt baths;
- Drug treatment for dehydration, prevention of inflammation, desensitization;
- Relief of mental disorders.
Surgical treatment aimed at creating an artificial pathway for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles of the brain is more effective.
Auxiliary methods for the treatment of all types of dropsy can be scaling, hydrotherapy, compresses and wraps, and the use of traditional medicine recipes.
Regardless of the location of the swelling, patients should adhere to a vegetarian diet, and they should also give up not only water, but also tea, replacing it with lemon decoction with honey.
For complex treatment of the disease at home, you can use the following recipes:
- Pour 50 grams of finely chopped cyclamen roots into half a liter of alcohol and leave to infuse for two weeks. Shake regularly. Then filter and take 30 drops before meals.
- Pour 100 grams of horsetail with a liter of wine (red). Leave for three weeks, shake periodically. After which the mixture must be filtered and squeezed through cheesecloth. Take 50 grams before meals.
- If the swelling is very severe, and there are also problems with urination, the seeds of field bindweed will help. They are taken one tablespoon before meals.
- Red rowan juice mixed with natural honey is an excellent remedy for swelling.
- 50 grams of white lily (plant bulbs) are poured with a bottle of vodka. Infuse for 3 weeks, then filter and take a dessert spoon before meals.
We suggest you read: Causes of nervousness and irritability in men. Why do men experience increased nervous excitability? Traditional medicine treatment
Folk remedies and methods for treating dropsy can only be used as additional therapy. Therefore, all prescriptions must be agreed with your doctor before use.
Prevention of the development of pathology depends on the type and causes that can provoke swelling. To prevent dropsy during pregnancy, you need to eat right and undergo regular medical examinations.
Dropsy (swelling) of tissues is a dangerous condition that can be fatal. Therefore, at the first signs of illness, you must immediately contact a specialist to avoid possible complications.
• puncture – removal of fluid using a special needle and syringe. The puncture gives only a temporary positive effect. After some time, the liquid re-accumulates in the cavity. Therefore, the puncture method is used only if it is necessary to provide the patient with quick help or surgical treatment has been carried out, but the swelling continues to increase. Puncture is contraindicated in acute inflammation due to the high probability of infection of the hydrocele and the development of a purulent process.
• injection - removal of fluid with the introduction into the tumor of hydrokartisone and substances that cause scarring of the membrane, such as alcohol, carbolic acid, formalin.
• surgical intervention - surgery (laparocentosis) is performed under local or general anesthesia. Several small punctures are made in the area of the tumor, through which the liquid is sucked out, and the wounds are sutured. In this case, a small drain is inserted to suck out the resulting fluid.
Effective treatment of hydroceles without treatment of the underlying disease of which they are a symptom is impossible. Dropsy will form again, becoming chronic and causing a deterioration in the general condition of the patient.
Another excellent folk remedy is cucumber juice; its diuretic effect is enhanced in combination with other juices: carrot, apple, beetroot. No less popular is celery juice, which contains vitamins C, PP and group B. Drink it 30 minutes before meals, 100 ml per day.
Horseradish juice is recommended to be consumed in the form of a gruel, since it contains essential oils. A particularly strong diuretic effect is obtained by mixing 150 g of horseradish pulp and the juice of 2-3 lemons. It must be taken one teaspoon 2 times a day on an empty stomach.
Disease prevention
Hydrocephalus is characterized by the fact that cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in large quantities in the ventricular system of the brain.
This happens due to a disruption in the production or absorption of cerebrospinal fluid. This transparent liquid is formed by salts, proteins, and cells. With hydrocephalus (water on the brain), about 50 ml of cerebrospinal fluid may accumulate in a child. When adults become ill, this number approximately doubles. If a person is healthy, then the cerebrospinal fluid produced is absorbed in the required volume. Thus, the processes of absorption and generation are balanced. The volume of cerebrospinal fluid does not increase, remaining stable. In a healthy body, about 0.5 liters of cerebrospinal fluid are produced in the brain per day.
What causes dropsy?
- circulation disturbance;
- insufficient absorption (very slow);
- excess production of cerebrospinal fluid.
In order to prevent dropsy, pregnant women should eat properly, establish a work and rest schedule, prevent toxins from entering the body, strengthen the immune system to reduce the risk of infections, and undergo regular examinations.
In order to prevent organ dropsy, it is necessary to promptly treat all diseases that can provoke it, and be careful to prevent injuries to the scrotum and skull.
Treatment
For the treatment of hydrocele at home, many traditional medicine methods are offered. Some mothers say that they were able to cure the disease with sea salt or soda baths. However, there are no real positive reviews of such treatment, as well as reliable scientific studies that would allow the use of sodium chloride (table salt) for the treatment of testicular hydrocele.
Hydrocele should still be treated under the strict guidance of a urologist. In this case, the risk of complications of the disease will be minimized. It is important to note that in most cases, testicular hydrocele goes away on its own by the age of two years. In this case, the fluid completely resolves and the swelling goes away.
Typically, if symptoms do not subside by age two, doctors may recommend surgery. Before starting such therapy, urologists usually prescribe a course of medications. Usually medications are prescribed for 3-4 months. If during conservative treatment the symptoms have not decreased and there is no positive dynamics of the disease, then doctors recommend surgery.
Surgical operations can be divided into several categories:
Winkelmann method. In this case, a midline incision is made on the anterior surface of the scrotum. An aspiration syringe is used to remove all accumulated, excess serous fluid between all the membranes of the testicles. Then fixing sutures are made. For this purpose, absorbable biological suture material is used. There is no accumulation of fluid after such a procedure, since it easily penetrates into the underlying tissue. If the communication between the abdominal cavity and the scrotum is open, then at the same time a reconstructive operation is performed to remove it.
Bergman's method. It is usually performed for hydroceles of impressive size or severe severe swelling of the membranes of the testicles. In this case, surgeons excise the innermost membrane. A drain is placed to remove the remaining fluid, the wound is sutured and an antiseptic bandage is applied to the incision site. The drainage is subsequently removed. The wound heals quickly and only a small scar remains.
Lord's method. This surgical treatment option is most in demand among babies in the first months of life, as it is the most gentle among other urological interventions. Can also be used in older patients, but with minor swelling.
Ross method. In this case, the communication between the abdominal cavity and the scrotum is closed. This hole is sutured layer by layer, all serous fluid is aspirated. After which the wound is sutured and antiseptic bandages are applied. This surgical technique is mainly used in children of any age, as well as adults. The method is indicated for reported cases of hydrocele of the testicles.
The site provides reference information for informational purposes only. Diagnosis and treatment of diseases must be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. All drugs have contraindications. Consultation with a specialist is required!
Hydrocele (hydroxycele)
– a condition in which fluid accumulates around the testicle, in most cases it does not cause concern or danger, can go away on its own, in other cases it requires surgical treatment.
Hydrocele in facts and figures:
- About 10% of children are born with a hydrocele.
- This condition occurs in 1% of adolescent and adult men.
- Hydrocele of the testicle is most common between the ages of 15 and 30 years.
- Hydrocele is a purely male disease.
Prevention of ascites (dropsy)
To prevent abdominal dropsy (ascites), take an infusion of agave americana (leaf) and wormwood (herb) in the same proportion (30 g each): take 1 tsp. mix into a glass of boiling water, leave for 1 hour, filter. Take 1/4 cup 1 time per day 1 hour after meals.
For dropsy of the abdomen, a diet of three milk soups a day with fresh onions chopped into them (especially blue or purple) is recommended. The course of treatment is a week. It is through this time that intense healing occurs.
Main symptoms
Every mother with a little boy should know what a hydrocele looks like. Acquired forms of the disease can occur in children at almost any age after any traumatic injury to the scrotum. At the slightest suspicion of the development of testicular hydrocele, you should definitely show the baby to a pediatric andrologist. The doctor will be able to identify the disease at the earliest stages.
In most cases, with a mild course of the disease, symptoms that bring discomfort or pain to the baby do not develop. In newborns, the scrotum may be slightly enlarged or swollen. However, often this symptom goes unnoticed for a long time, since its manifestation is not too pronounced.
You should suspect testicular hydrocele in a baby if:
The scrotum is somewhat swollen and enlarged. In newborns, this sign is very difficult to identify. If the mother has any suspicions that the baby has some asymmetry or swelling of the scrotum, she should definitely show the child to a pediatrician or pediatric urologist.
Slight swelling. Typically, testicular hydrocele is unilateral. With slight asymmetry in the scrotum area, it can be assumed that there is swelling of the testicular membranes.
Severe mobility of the skin of the scrotum. Determined only by a urologist. The presence of serous fluid in the membranes helps improve the sliding of the skin over the surface of the testicles. It is one of the specific signs of hydrocele.
Unimpaired urination. Most urological inflammatory diseases are characterized by impaired urine outflow. The child may complain of some pain or even a burning sensation when urinating. This symptom is not typical for hydrocele of the testicles. Urination for babies with hydrocele does not cause pain or severe discomfort.
The appearance of symptoms of intoxication with testicular torsion or the development of other urological complications of the disease . Often occurs after traumatic injuries to the scrotum and infection with various viral or bacterial infections. In this case, the baby’s temperature rises, appetite and sleep are disturbed, and severe weakness increases. Immediate hospitalization of the child in a hospital is required.
In the chronic course of the disease - the development of an inguinal hernia. This form of the disease requires surgical treatment. In this case, testicular hydrocele is treated and the inguinal hernia is removed during surgery.
Dropsy in children
In children, blisters often appear on the fingers. The most common cause is heat rash, in which moisture, oil, and impurities accumulate in the folds of the skin. The pathology usually develops in premature infants, whose thermoregulation mechanisms are poorly adjusted. In most cases, the problem will resolve as the child grows, but at the same time it provokes discomfort and anxiety.
To avoid the development of this type of dropsy, it is recommended to wash the child more often and thoroughly dry all folds of the skin. In your daily routine, you need to use hygiene products designed for children and make sure there is no reaction to them. Clothing for newborns should be made from natural materials. Make sure your baby doesn't overheat.
What is dropsy
Dropsy itself implies an accumulation of water. The truth is not in the usual sense of the word, namely liquid. We are talking about transudate, which is released in abundance when there is a disruption in blood or lymph circulation. You need to understand that when transudate accumulates, no pathogenic processes occur. After all, the inflammatory process does not occur on its own, which means there are no bacteria. If there is already effusion due to pathogenic processes, then we are talking about exudate with a low level of protein.
Transudate can appear for various reasons. There are even problems with water-salt metabolism, which actively affect its excess.
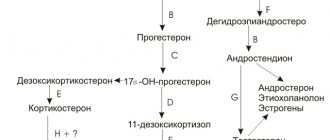
In fact, it may be: - hydrocele of the testicles is acquired or congenital, when an excess of fluid begins in the membrane. It happens that dropsy develops in men even of advanced age. - dropsy of pregnancy, accompanied by an abundance of symptoms other than edema. More often we are talking about late toxicosis - hemolytic dropsy in a newborn with active destruction of red blood cells - dropsy that forms on the ovaries in women - dropsy of the eye and lacrimal sac - dropsy of the heart, localized in the pericardium, is a fairly serious disease
There are several other types of dropsy.
The principle is the same. A seal with liquid filling is formed, which is absolutely painless and does not cause any particular concern.
Stages of the disease
In medicine, there are 3 stages of abdominal dropsy:
- Transitional. It is accompanied by an accumulation of ascitic fluid in the abdomen not exceeding 0.5 liters, so the person does not experience alarming unpleasant symptoms. It is impossible to determine the presence of the disease on your own at this stage. Diagnosis usually occurs accidentally during an ultrasound or MRI examination.
- Moderate. The amount of fluid reaches 4 liters, the person experiences shortness of breath, feels pain in the abdomen, which increases and sag noticeably. A doctor can diagnose it during a clinical examination using palpation of the abdomen.
- Tense. The accumulated liquid reaches 10 liters. The pressure in the abdominal cavity increases noticeably, and the functioning of the internal organs is disrupted. If you do not receive timely medical care, death is possible.
Attention! A special stage is also distinguished - refractory ascites. It is the most dangerous stage, as it is practically untreatable due to the large amount of fluid in the abdominal cavity. After its removal, it quickly arrives and ultimately the patient will die.
Dangerous complications
There are a number of diseases that cause abdominal dropsy; for this reason, if therapy is not started on time, you can get dangerous complications that turn into fatal diseases.
We recommend further reading: The main signs and methods of treating abdominal ascites
Depending on the volume of ascitic fluid collected in the abdomen, the following serious consequences can be identified:
- thrombosis;
- peritonitis;
- accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity;
- formation of an umbilical hernia;
- respiratory failure;
- occlusion of the intestinal tube;
- gastrophageal reflux disease.
To prevent serious complications, doctors immediately remove the accumulated fluid. The problem is most often solved surgically.
Diagnostic methods
A mandatory point before treating dropsy is a complete and detailed diagnosis of the body. Thanks to it, effective treatment methods will be selected to eliminate the cause of the disease. In addition to collecting tests, the patient must undergo:
- Ultrasound, which will help identify pathologies, accurately determine how much fluid has accumulated in the sac and accurately assess the structure of the scrotum;
- Diaphanoscopy using special beams will allow for a high-quality and quick examination of the scrotum. Determine whether there are any impurities, blood clots, or foreign bodies in the liquid.
If seals are detected, additional diagnostics must be performed to exclude the presence of malignant formations.
Consequences of the disease if surgery is not performed on time
Men are afraid of operations and prefer to come to doctors to have fluid pumped out at short intervals. But in fact, this is not the best option, since it is well known what complications the disease can cause in a chronic form. Let us list the consequences of inadequate or untimely treatment:
- Compression of the testicles, leading to impaired spermatogenesis;
- Development of infertility;
- Testicular atrophy, due to poor circulation;
- Decreased potency and pain during erection;
- The appearance of necrotic spots or death of internal tissues;
- A visual defect caused by an enlarged scrotum. Sometimes, even clothes cannot hide the pathology.
Remember a few tips to reduce your risk of getting dropsy. Protect the groin from direct blows and injuries, treat infectious and sexually transmitted diseases in a timely manner. It is also advisable not to overheat or overcool the scrotum area. Wear comfortable underwear that does not put pressure on your genitals.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the patient begins with an external examination and palpation of the abdominal part of the body. Certain diseases cause the following symptoms:
- bleeding with cirrhosis of the liver;
- with cardiac abnormalities, swelling of the ankle area appears;
- renal failure provokes swelling of the subcutaneous tissue.
To confirm the diagnosis, doctors prescribe special examinations:
- local ultrasound diagnostics of organs;
- computer and magnetic resonance imaging;
- laparoscopy;
- laboratory research and analysis of the biological composition of the liquid.
In addition, liver enzymes are carefully studied from samples taken of accumulated fluid in the peritoneum.
Sometimes additional examinations are required to distinguish ascites from other diseases.
In such cases, the following is prescribed:
- cytopathology;
- paracentesis;
- Dopplerography;
- radiography.
The appearance of abdominal exudate can tell a lot about the disease. So, with cirrhosis of the liver, the liquid becomes straw-colored, and in the presence of generalized edema, it becomes milky.
Purulent processes cause a cloudy purulent color. With new growths, the color changes from transparent to milky.
Diagnosis of dropsy
Dropsy is diagnosed upon examination.
Usually, whether it is dropsy of the testicle in men or dropsy of the eye, it is better, in addition to the examination, to prescribe a comprehensive examination: - examination by a specialized doctor - puncture of fluid from the dropsy to clarify whether there is an inflammatory process or not - urine analysis to clarify the presence of protein and kidney problems - a blood test with clarification of the number of leukocytes, which allows us to confirm the non-inflammatory course of the disease - ultrasound of dropsy to understand that there is only liquid inside the capsule and that’s all. dropsy in children
If cancer is suspected, the doctor is also obliged to give a referral for a tomography or computer examination of the patient’s body.
This will help to accurately determine the root cause and eliminate the consequence.
How many testicles does the disease affect?
In adult men, in most cases, dropsy affects one testicle.
Most often the left testicle is affected, but sometimes severe swelling occurs in the right testicle.
In very rare cases, the disease affects two testicles. According to statistics, the disease is diagnosed in men over 40 years of age.
The disease can have an acute or chronic form. The acute form is characterized by the formation of tumors, the presence of an inflammatory process and the development of infections in the genitourinary system.
The chronic form occurs either due to improper treatment or failure to consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Painful sensations are most often observed in the right testicle, since most often all inflammatory processes occur on the right side, where the appendages are located.
Therefore, with dropsy, in most cases, only one testicle, which is located on the right side, enlarges.
Most often, the trigger for the disease is epididymitis, which affects the right side of the genitourinary system. Next, we will show you what dropsy looks like; the photos will help you understand whether you have this disease or not.
How to get rid of itching?
Most often, irritation causes unpleasant sensations, such as severe itching. Discomfort can be constant or occurs during periods of exacerbation. No matter how much the blisters itch, you should not scratch them. This way you risk getting an infection, which will only worsen the condition.
To make you feel better, take a warm, but not hot, bath. Do not use aggressive hygiene products. Choose soap with low hardness and gentle composition. Opt for clothes made from natural materials that will not squeeze the skin.
If you work with chemical substances, then use mandatory protective equipment. Ithiol ointment and aloe juice will help reduce irritation. However, do not self-medicate. You risk worsening the condition. It is necessary to identify the cause of the skin defect in order to get rid of it.
Symptoms of ascites
Clinically, dropsy does not appear immediately. This usually takes several months, which significantly complicates timely diagnosis. Because patients think that they have only gained a few extra pounds.
Signs of abdominal dropsy may include:
- Abdominal pain.
- Intestinal dysfunction, development of flatulence, possible constipation or, conversely, diarrhea.
- Frequent attacks of heartburn and belching.
- With liver pathology, symptoms are expressed in a feeling of bitterness and a metallic taste in the mouth, yellowness.
- Swelling in the legs.
- Lymph nodes enlarge.
- Kidney swelling, difficulty urinating.
- Shortness of breath and heavy breathing.
As fluid accumulates, the abdomen increases in size and resembles a ball. Stretch marks may form and veins may dilate. If the fluid pinches the liver walls of blood vessels, the person develops jaundice.
What is a water callus?
It is not difficult to treat callus. The healing process consists of treating the inflamed area with antibacterial agents and protecting it from damage with a patch. If you properly care for the damaged area, there will be no unsightly trace of dropsy left.
Doctors do not recommend piercing a water callus that appears on the foot. Because of this, an infection can get into the dropsy and infection can occur. But what to do if the callus bursts and fluid flows from it?
- Wash the damaged area with warm water and soap. Disinfection. Applying antibacterial ointment or cream. After the procedures, you should apply cotton wool and secure it with a band-aid.
- It is allowed to apply lemon peel to the heel and fix it with a bandage. After several dressings, the callous formation will dry out; it is removed with pumice.
- You can apply figs to the dropsy, secure with a bandage and leave overnight. First, steam your feet in hot water (preferably with the addition of soda). Then wipe them dry.
- Mixing fish oil and aloe juice is suitable. Soak a cotton swab in the resulting mixture and apply it to the callus for several hours.
The best effect of treatment is observed at the initial stage of callus formation.
To eliminate the causes of swelling of the legs, both conservative and surgical treatment methods are used.
Basic conservative treatment methods:
- Treatment with medications;
- Compression treatment;
- Physiotherapy.
Drug treatment is the main method of treating dropsy of the legs. Medicines eliminate the cause of the disease, act on the mechanism of edema, and have a symptomatic effect.
Pharmacological groups of drugs for the treatment of dropsy:
- Antibiotics – eliminate pathogenic microflora;
- Antiseptics – neutralize the effect of pathogenic bacteria;
- Antiparasitic drugs – used for filariasis;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs – eliminate swelling, pain, reduce the intensity of inflammation;
- Anticoagulants – reduce blood clotting;
- Fibrinolytics – destroy blood clots;
- Diuretics – remove excess fluid from the body through the kidneys;
- Cardiac glycosides – stimulate the work of the heart muscle;
- ACE inhibitors – lower blood pressure;
- Angioprotectors – increase the resistance of blood vessels to damage;
- Hepatoprotectors – strengthen the walls of liver cells;
- Detoxifying agents – remove toxins from the body;
- Sclerosing agents – regenerate pathologically dilated veins.
Physiotherapeutic methods are used to treat and prevent edema, reduce inflammation, restore lymphatic drainage, and immunostimulate:
- Electrophoresis;
- UHF therapy;
- Magnetotherapy,
- Massotherapy,
- Radon and iodine-bromine baths,
- Oxygen therapy.
To reduce the negative manifestations of dropsy, wear compression hosiery (socks, stockings, tights), and bandage the legs with an elastic bandage. This treatment method creates uniform pressure on the vessels of the lower extremities and does not allow fluid to move back into the tissue from the vessels.
If conservative methods are ineffective, surgical treatment of diseases that provoke edema is used:
- Installation of a pacemaker, replacement of artificial vessels, heart transplantation in the treatment of heart failure;
- Sclerosis and removal of superficial veins for varicose veins;
- Removal of leg vein blood clots;
- Removal of liver cysts and tumors;
- Treatment of fractures and wounds resulting from trauma;
- Joint puncture for arthritis.
In many cases, a combination of conservative and surgical methods is used to treat dropsy of the legs.
Author of the article: Alekseeva Maria Yurievna | General practitioner
About the doctor: From 2010 to 2019. practicing physician at the therapeutic hospital of the central medical unit No. 21, the city of Elektrostal. Since 2019 he has been working at diagnostic center No. 3.
Other doctors
‹
Delicious and very healthy salad “Metelka” - the best recipes
Onions and garlic provide 80% protection against colon cancer
›
Causes of dropsy
Depending on the type of dropsy, it can be congenital or acquired during life. With the first option everything is clear.
Here the problem needs to be looked for during pregnancy. There were already obvious disruptions in metabolic processes, infection of the mother with serious diseases or preconditions due to chronic processes in the mother’s body.
Acquired dropsy of various kinds can appear after injuries, metabolic problems, obesity, problems with the outflow of lymphatic fluid, oncological processes, impaired water-salt balance, kidney disease.
Prevention
The main preventive measures are avoiding alcohol, maintaining a proper and balanced diet, and playing sports. But the most important thing is timely treatment of any disease, as well as regular routine medical examinations.
Author: Nasrullaev Murad
Candidate of Medical Sciences, mammologist-oncologist, surgeon
Data on dropsy are often found in the literature. But few people really understand what we are talking about at all. After all, dropsy can occur in different parts of the body and organs. It’s worth talking in more detail here.
What tests are needed?
Before starting treatment for the disease, the patient must undergo the following tests:
- a general blood test will show the level of hemoglobin, will help determine whether there are inflammatory processes in the body, and will identify any disturbances in the blood supply system;
- a blood test for RW will allow you to determine the patient’s blood group;
- a biochemical blood test will allow you to evaluate the functioning of internal organs and reveal whether there are any pathological disorders in the body;
- A general urine test will reveal the presence of various diseases, but first of all it will show how the kidneys and genitourinary system work;
- An ECG will reveal any dysfunctions in the cardiovascular system;
- visit a therapist for a general examination of the body;
- Lastly, they visit the urologist with all the collected data. He makes a diagnosis and prescribes appropriate treatment. If necessary, he gives a referral to the clinic for surgery.
Why is it not recommended to pierce blisters?
Piercing reduces pain and promotes rapid healing of the wound. So why do doctors recommend refraining from piercing and treating dropsy with other means? The fact is that a punctured bladder is an “open gate” for germs, and moreover, it requires careful care.
Infection of the puncture site
A staphylococcal infection can enter the body through an open wound, causing inflammation and suppuration. Small blisters can be cured with antiseptic drugs in 2-3 days without compromising the integrity of the film. The main thing is to protect the dropsy from possible damage.
Puncture of the bladder is allowed only if absolutely necessary, for example, if it is located in a place where there is a risk of damage. Or when it is very large. This procedure must be carried out under sterile conditions; it is better to consult a doctor.
You cannot puncture the callus, as it is connected to blood vessels. The infection will enter the blood through the wound and circulate throughout all organs. Such formations can only be removed through surgery.
Consequences
The risk of developing serious complications with hydrocele is quite high. Like any urological disease, testicular hydrocele can occur quite safely, or it can cause serious complications. The scrotum is very tense due to the presence of a large amount of fluid between the membranes. Any traumatic injury or exposure to a provoking factor can lead to adverse complications.
Most often, children may experience various torsions or compression of the testicles due to a large amount of serous fluid. The addition of a secondary bacterial infection provokes infection in the scrotum and the development of inflammation. In this case, the skin in the groin area turns red, becomes hot to the touch, and the pain increases. If the inflammation has spread to the urinary organs, there may be a disturbance in the outflow of urine or a burning sensation when urinating.
In the long-term period of the disease, if treatment is not carried out in a timely manner or the course of the disease is insufficiently monitored, male infertility may occur in men who suffered from hydrocele in childhood. Such situations require consultation with an andrologist and drawing up a treatment plan that will help restore fertile function.