The clavicle is a small paired bone that connects the bones of the arm to the bones of the chest. In shape it is a tubular bone, and in structure it is spongy: inside there is not bone marrow, but a spongy substance. A clavicle fracture is a fairly common and dangerous injury.
The clavicle bone received its name because of its similarity to a key in shape (S-shaped). In men, the collarbone has a more curved shape due to more developed muscles. Located directly above the first rib.
Ossification of the collarbone begins in the womb - at 5-6 weeks of embryonic life, and ends by the age of 25.
The tissues located in the clavicle area are distinguished by good blood supply and innervation: the brachial plexus is located around it. This bone is considered the most vulnerable due to its structure and location.
Structure and functions of the clavicle
The clavicle is a curved tubular bone. It has an S shape in the form of a curved key. It is for this reason that it bears such a name. If you think about it a little, the word clavicle comes from the word key, which evokes analogies with the word lock. Thus, the collarbone can be said to “lock” or protect the vital organs of the upper torso.
The clavicle consists of three bones:
- sternal end - the area that is attached to the scapula;
- acromial end - attached to the sternum;
- body - represents the middle part of the clavicle.
The collarbone is easy to find and feel. It is located above the first rib of the sternum.
Its functions:
- thanks to it, the hand moves in a wide range, that is, it is the basis where the shoulder blade and upper limb are suspended in a free state;
- protects the cervical-axillary canal, through which important elements pass, from damage;
- transmits nerve impulses from the upper limb to the axial skeleton.
However, being a long bone, the clavicle does not contain bone marrow like other long bones.
Symptoms
The severity of signs of fractures largely depends on its type. Displaced fractures are more difficult to tolerate. With such injuries, the treatment process becomes more complicated and the risk of various complications increases.
Displaced fractures
Symptoms of a fracture with displaced fragments of the clavicle are more pronounced, and it is much easier to determine the occurrence of such injuries.
After receiving an injury, a person experiences intense and progressive pain in the shoulder area. The victim cannot move his arm and is forced to hold it by the forearm or elbow, pressing it tightly to the body. At the same time, movements that are uncharacteristic of a healthy shoulder joint can be reproduced in the area of the shoulder girdle.
Swelling appears at the site of injury and the swollen skin smoothes the supraclavicular fossa. Visually, the shoulder girdle becomes shorter and moves anteriorly. In this case, the victim’s head tilts towards the injured bone. The arm on the affected side appears longer and sag downwards.
Bone fragments in the fracture area create a “tent” phenomenon - they are juxtaposed into an angle, the apex of which is located at the fracture site. When the injured shoulder moves, crepitus may appear.
Due to bleeding, a hematoma appears in the area of injury, and with an open fracture, bleeding is also present in the damaged soft tissues. When the artery passing in the armpit is compressed by fragments, the arm becomes cyanotic and pale. The pulse in the ulnar artery area disappears, and the limb becomes cold.
In a complicated displaced fracture, the sharp edges of the bone can damage the dome of the pleura, nerves, arteries and veins. In case of rupture of large vessels, massive bleeding develops, accompanied by characteristic symptoms (pallor, decreased blood pressure, tachycardia, etc.). When nerves are damaged, sensitivity is lost, the hand becomes numb, and the fingers become immobile.
Fractures without displacement
Non-displaced clavicle fractures are more common in children. They usually have an incomplete fracture and the bone breaks like a green stick. The signs of such injuries are not so pronounced and do not manifest all the symptoms characteristic of a displaced fracture.
The victim may experience slight swelling and pain in the area of the injury. Some children, after a clavicle fracture, can continue to move the affected limb and do not feel significant discomfort.
Causes and symptoms of a clavicle fracture
The main cause is injury resulting from a fall from a great height or a direct blow. This type of injury most often occurs in athletes due to excessive stress and in children due to negligence. Clavicle injuries are also quite common in newborns as they move through the birth canal. This part of the skeleton becomes strongest by the age of 25.
Symptoms of injury vary depending on the type of fracture. However, there are a number of symptoms that are observed in all cases of damage.
Thus, the main symptom is the occurrence of severe unbearable pain. The pain tends to intensify when trying to move the limb. Therefore, the second important symptom is limited mobility. A person is not able to raise his hand, nor turn it, nor move it to the side. To minimize pain, the victim instinctively presses his elbow to his body.
Upon visual examination, you can notice bulging and deformation of the collarbone, swelling and the development of a hematoma. Another symptom indicating injury is the smoothness of the supraclavicular fossa. When palpating the bone, crepitation of fragments can be heard.
The shoulder takes on an unnatural position, it moves forward and down, and the limb itself lengthens compared to the healthy arm. When the subclavian artery is damaged by a bone fragment, the limb becomes white, cold to the touch, and it is impossible to feel the pulse at the wrist. If the nerve has been injured, the sensitivity of the limb is impaired, and paralysis of the fingers is also observed.
The picture of a fracture in children is completely different. Since they have green-stick fractures, they do not have a complete fracture, but a partial one due to the high elasticity and strength of the bones. When a child fractures, the bones remain held together by the periosteum.
Causes of damage
In most cases, clavicle fractures occur due to excessive force on a certain area. The most dangerous factors are:
- Falling from your own height or higher. Support in such cases most often occurs on a straightened arm, the outer part of the shoulder or elbow.
- A strong blow to the collarbone or shoulder girdle.
In addition to injuries, damage to the clavicular region is possible as a result of bone pathology. In this case, even minimal impact on the bone can lead to a fracture. Such damage is called a pathological fracture and is provoked by the following diseases:
- Tuberculosis of the clavicle - this bone can very rarely be affected by the tuberculous process, which gradually destroys the bone structure from the inside and makes the clavicular wall thin.
- Cancerous neoplasms and bone metastasis - osteosarcoma, fibrosarcoma, giant cell tumor. These tumors provoke the destruction of healthy bone tissue and the proliferation of atypical cells.
- Osteomyelitis is a bone infection in which microbes penetrate the bone tissue. Risk factors for this infection are surgical intervention associated with the collarbone and adjacent tissues, the presence of a chronic infection in the body, and immunodeficiency states.
Symptoms of a clavicle fracture appear almost identically with pathological and conventional fractures. The main difference with a broken bone is the intoxication of the body and the presence of signs of damage to other organs.
Classification of injuries
Fractures happen:
- open;
- closed;
- with offset;
- without displacement.
For fractures that result in the formation of fragments, there are:
- transverse;
- oblique;
- splintered.
Determining the type and nature of the fracture is very important for prescribing the subsequent treatment strategy.
Open injuries occur as a result of a violation of the integrity of the skin. There is also rupture of muscles, tendons and ligaments. It is very easy to determine this damage, since a wound has formed at the site of the injury, through which bone fragments communicate with the external environment.
Closed injuries are characterized by the integrity of the skin. Determining this type of damage is much more difficult, since it is difficult to determine where the damage is located.
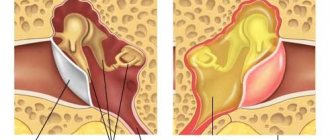
Displaced clavicle fracture
There are several types of displaced clavicle fractures. Localization of the injury in different places allows us to identify the following damage:
- inner third of the bone;
- middle third;
- outer third.
Fractures of the middle third occur most often, since it is this zone that is more vulnerable due to its anatomical structure, and the anatomical segment itself is the thinnest.
Based on the nature of the fault line, the following damage is observed:
- splintered;
- transverse;
- S-shaped;
- oblique;
- screw;
- T-shaped.
Based on the location of the bone fragments, they are distinguished:
- displaced fracture;
- without displacement.
Damage with displacement can be:
- traditional (classical), when the periosteum undergoes rupture and displaced bone fragments do not hold it;
- partial (incomplete), in which bone fragments are displaced, but the periosteum remains intact and holds them.
Based on the condition of the skin, there are:
- open fracture;
- closed.
Treatment
Treatment for a clavicle fracture consists of correctly aligning the fragments of the clavicle and fixing them until the bones heal completely. There are two main treatment methods: conservative and surgical. The choice is made by the doctor based on a specific clinical case.
For non-displaced clavicle fractures, conservative treatment is most often used. The procedure takes place under local anesthesia. The patient is placed in a cast or one of the following types of dressings:
- figure-of-eight with forearm fixation,
- on a wedge-shaped pillow,
- Deso bandage,
- Seiro headband,
- dressing according to Voronkevich, Kaplan, Smirnov-Vanshtein,
- Titova oval,
- two Kramer splints (splints are used to treat clavicle fractures with multiple fragments),
- Kuzminsky tire,
- Chizhin frames.
The hand is immobilized for 3-5 weeks, examined daily, and x-rays are taken 7 days after applying the bandage and after its removal. A displaced fracture can also be cured without surgery, but only if the bone fragments can be correctly connected 2-3 times. Otherwise, surgery will be required. It is also useful to know how surgery is performed with a plate for a displaced clavicle fracture.
For a clavicle fracture, surgical treatment is performed if there is one of the following indications:
- open fracture,
- bone fracture inside the joint capsule,
- strong displacement
- the presence of many small fragments,
- injury to the subclavian vessels,
- damage to nerve nodes,
- simultaneous fracture of the scapula.
The operation is performed under anesthesia. In addition to connecting the fragments of the clavicle, complications are eliminated during this procedure: suturing nerves, blood vessels, and preventing infection. Stages of surgery:
- preparation of the surgical field, cutting of soft tissues,
- drilling channels in bone fragments and connecting them,
- introduction of special metal structures into the channels,
- checking the structure for strength (if necessary, it is additionally secured with screws),
- suturing the wound.
After the operation, the arm is temporarily immobilized, and after 3 days a permanent bandage is applied. After 10-15 days it can be removed. The structures used during the operation are removed 6-12 months after surgery, and elderly patients are advised to leave them in the bone so as not to expose the body to additional danger.
Displaced clavicle fracture
All fractures of this type have their own characteristics. However, several main symptoms can be identified for damage with and without displacement.
Symptoms of displacement injuries:
- severe pain radiating to the shoulder;
- swelling of the damaged area;
- pallor of the skin at the site of the rupture;
- internal and external bleeding;
- violation of the relief of the shoulder blade, it is lowered down, and the limb looks longer due to sagging;
- dysfunction of the shoulder and arm;
- loss of sensation and motor activity;
- hand numbness and nerve damage;
- bone fragments overlap each other;
- a broken collarbone sags and loses its anatomical position.
After an injury, rapid swelling is observed, since the bone fragments are quite sharp and injure nearby vessels, which ultimately leads to the formation of internal bleeding and hematomas. The displacement of the fragments relative to each other causes severe pain. The arm hangs unnaturally (as if dangling) and in order to eliminate this unpleasant symptom, the victim presses it to the body with his healthy hand. There is a limitation of mobility, the hand “does not obey”, since the collarbone was the support for its normal functioning. Crepitation of bone fragments and pathological mobility are also observed.
Treatment involves a rigid bandage, and elastic or soft bandages are prohibited. When fixing the shoulder in the correct anatomical position, the victim is given an anesthetic injection. This procedure is very painful, it is impossible to endure it without anesthesia, in addition, a reflex contraction occurs - muscle retraction, which interferes with the correct fixation of the injured limb.
A displaced fracture is difficult to treat, and in some cases it is accompanied by damage to adjacent bones, muscles, tendons and ligaments. Treatment of open damage is especially lengthy and difficult. In this case, urgent surgical intervention will be required, because bone fragments can damage internal large vessels and provoke severe bleeding, which will threaten the life of the victim.
Consequences and complications
A clavicle fracture can lead to the following consequences and complications:
- partial muscle atrophy, temporary loss of arm functionality,
- injury from bone fragments to nerves, blood vessels, apexes of the lungs,
- severe blood loss,
- inflammation of nerve nodes,
- complete or partial muscle paralysis,
- rachiocampsis,
- pseudarthrosis - formation of false joints,
- purulent inflammation of the bone and surrounding soft tissues,
- nonunion,
- limited limb mobility,
- arthrosis, poor joint mobility,
- aesthetic defect due to improper bone fusion.
The most dangerous complication of a clavicle fracture is injury from fragments of large vessels, as this can cause rapid blood loss and death. But even in this case, timely diagnosis and proper treatment can avoid serious consequences for the body.
First aid for a broken collarbone
Further treatment and recovery depend on correctly provided first aid. Therefore, first of all, it is necessary to properly immobilize the limb in order to prevent movement of bone fragments and injury to blood vessels, nerves and internal organs (lungs).
First aid is as follows:
- First of all, the victim is given an anesthetic drug.
- A small roller is placed in the armpit area.
- The arm is carefully bent at the elbow and fixed to the body from the shoulder to the hand.
- The shoulder should be parallel to the floor.
- The bandage is attached to the hand, and the hand itself is inserted into it.
You may not always have a bandage in everyday life, so you need to make one from available materials. Scarves, sheets, towels, and shirts can serve in this capacity. The entire forearm must be secured. This kind of bandage is called a scarf. The base of the gusset should be wide enough to prevent the bone fragments from moving.
Complete immobility is necessary so that the entire limb is relaxed, and bone fragments exert less pressure and do not damage soft tissues, blood vessels and nerves. In this position, pain is reduced.
How to make a headscarf yourself using improvised materials? For example, if you have a towel, scarf or shirt, then you need to make a rope from the scarf, which you need to pull over your shoulders. Connect the resulting loops between the shoulder blades, while moving the shoulders back. This is how soft Delbe rings are obtained. The design must meet important criteria - rigidity and strength.
What is contraindicated to do when providing first aid:
- you cannot touch the site of injury, much less straighten bone fragments yourself;
- transport the victim in a lying or standing position, only semi-sitting or sitting;
- pull the victim by the arms, and he should not lean forward;
- do not try to straighten the injured arm;
- secure the limb with a thin tape or cord.
Remember! Incorrect medical care can aggravate the situation and complicate treatment.
First aid
It is impossible to cure a clavicle fracture with or without displacement at home. If symptoms indicating this injury appear, you must take the victim to the hospital yourself or call an ambulance.
Before doctors arrive, measures must be taken to prevent the movement of bone fragments and relieve pain if any. To do this you need to do the following:
- Immobilize the injured limb. The simplest option is to take a scarf or a wide handkerchief, bend your arm at the elbow and place your forearm in the middle, and tie the ends behind your neck. The outer edge of the fabric should go behind the back to reduce the load on the neck, and a small roll of fabric should be placed in the armpit. It is much more reliable to fix the arm with a tight bandage.
- Relieve pain syndrome. The victim can be given 1-2 painkiller tablets or given an analgesic intramuscularly.
- Cool the fracture site. 5 minutes after injury, apply cold to the affected area for 30 minutes. The procedure will help reduce pain and relieve swelling.
Even in cases where the nature of the injury cannot be determined from the symptoms, and there is a suspicion that the patient has a dislocation and not a fracture, in no case should you try to set it yourself or leave it unattended.
The victim should wait for the ambulance to arrive in a sitting or semi-sitting position and try not to disturb the injured limb.
Treatment of clavicle fractures
Therapeutic measures depend on what type of fracture occurred, its severity, the age of the victim and the extent of the injury. A non-displaced clavicle fracture is treated conservatively at home. In case of open injuries, hospitalization and inpatient treatment are necessary. In both cases, the arm is fixed for two months using a rigid bandage.
Treatment is carried out in three directions:
- drug treatment;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- physical therapy (LPF);
- massage;
- sanitary and spa treatment.
Drug treatment includes:
- painkillers;
- antibiotics to prevent wound infection in open fractures;
- immunostrengthening drugs;
- food supplements containing phosphorus and calcium;
- chondroprotectors.
Physiotherapeutic procedures:
- ultra-high frequency therapy (UHF);
- ultrasound therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy:
- hydrotherapy (warm salt baths).
Therapeutic exercise and massage are carried out during the period of remission, when the fracture has completely healed.
For childhood fractures, treatment is somewhat different. As a rule, children are not given plaster casts, but Delbe rings or a Deso bandage are used.
Thus, the main principle of treatment is reliable fixation of the clavicle. After healing, a rehabilitation period begins, during which the shoulder and arm will return to their previous functionality.
Recovery period
For a displaced clavicle fracture, the rehabilitation period ranges from 3 weeks to 3 months. You should load your hand gradually to avoid damaging it again. It is also advisable not to sleep on the side of the injured collarbone immediately after removing the bandage.
To fully restore muscles and joints after injury, the patient must perform the following sets of exercises:
- breathing exercises,
- shrug,
- alternating tension and relaxation of muscles,
- slow rocking,
- general strengthening exercises,
- running and race walking,
- coordination exercises.
Exercises begin to be done only with outside help and for only 2-5 minutes at a time, then gradually increase the duration and complexity of the workouts. Physiotherapeutic procedures are also used to restore muscles: massage, hydrotherapy, electrophoresis.
Surgery
This type of surgical intervention is called osteosynthesis. During the intervention, bone fragments are removed, and the collarbone is secured with metal devices. There are several types of such surgical operations.
At the moment, the most popular type of intervention is osteosynthesis using screws and plates. If the damage is located in the diaphysis, S-shaped plates or conventional reconstructive ones are chosen. If the injury is localized at the acromial end, other devices may be required: plates with locking screws and hook plates.
Osteosynthesis is also performed using a pin, which is inserted into the bone with a special fixing device.
Surgical treatment also has a number of disadvantages:
- After surgery, bones may not heal properly. This phenomenon is called false joints and develops as a result of a comminuted fracture, poor choice of metal structures, and the complexity of surgical intervention.
- The development of osteomelitis can also cause improper bone fusion.
Treatment methods
The main goal of therapy is to compare bone fragments and secure them in the correct position. If these conditions are met, the clavicle bone will heal in 5-6 weeks. If it was not possible to fix the fragments, then it will take more time to restore the bone.
You will be interested...
Treatment of a clavicle fracture in a newborn
Treatment for a clavicle fracture can be conservative or surgical. Conservative treatment involves closed reduction (reduction of the bone through soft tissue); this procedure can only be entrusted to a professional traumatologist. In case of pronounced displacement of clavicle fragments or when the skin is torn by fragments, a surgical treatment method is used.
Before repositioning, the doctor must numb the upper limb by injecting novocaine into the shoulder girdle. After a few minutes, you can begin the procedure. The patient is in a sitting position, with his head tilted towards the injured shoulder.
In this position, the muscles relax and the bone fragments move closer to each other. The duration of closed reduction is 15 seconds. If 3 attempts at reduction are unsuccessful, then surgery is prescribed.
After repositioning, a cast is applied to the arm, which will properly fix the clavicle bone.
You can also fix the arm using a Smirnov-Weinstein bandage, which covers the torso, shoulder girdle and forearm of the injured limb.
It is removed only after an x-ray is taken to make sure that the bone has fused.
The fusion period takes at least 4 weeks; relatives should monitor the patient and monitor his condition. If you experience the following symptoms, you should consult a doctor:
- Swelling reappears and increases;
- Redness of the skin in the fracture area does not go away within 6 hours;
- The temperature in the shoulder area increases;
- Pain at the fracture site intensifies.
The surgical treatment method involves cutting the soft tissue in the area of the fracture and fastening the bone fragments using internal plates, knitting needles, rods or external devices. The main goal of the surgical treatment method is to collect fragments and fix them. Surgery is necessary if blood vessels or nerves are damaged.
After a few weeks, the plaster is removed. In order for the patient to recover faster, he must regularly perform special exercises and visit a massage therapist. Until the bone heals completely, lifting heavy things and moving too actively is prohibited.
If we are talking about a non-displaced fracture, then its treatment will not cause difficulties. In newborns (up to 3 years), the bones grow together very quickly, and the limb is fixed with wide bandages. For a minor fracture of the clavicle, a Deso bandage is applied.
With the help of a splint or plaster cast, the bones will heal as quickly as possible. To ensure bone fusion in patients over 5 years of age, they are given a rigid plaster cast. If the methods described above were not effective and the bone does not heal, then surgery is performed.
If the displacement is slight, doctors apply a bandage, which must be fixed with plaster . To compare the debris, the traumatologist moves the shoulder back and sharply lifts it up.
In case of multiple fragments with significant displacement, a Kramer splint is applied to the damaged limb. If blood vessels or nerve bundles are damaged, surgery is performed.
A comminuted fracture is treated with a special plate or wire that connects all the bone fragments. When the bones have fused, the fasteners are removed.
Rehabilitation after a clavicle fracture
The rehabilitation period lasts 3-4 months, and full recovery occurs after 6-8 months. Of course, recovery time varies as it depends on the extent of the injury, severity, age and overall health.
After surgery, all metal parts are removed after six months or a year. Full recovery occurs within a year. During this period, therapeutic exercises, massage, warm salt baths, and physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed.
Rehabilitation
The traumatologist must decide how to treat and restore the damaged bone. You should not do exercises on your own, use folk remedies, or take medications.
For a speedy recovery, the doctor prescribes rehabilitation after a collarbone fracture. It includes massage, physiotherapeutic procedures, exercise therapy for a fractured collarbone, diet and taking vitamin complexes.
Exercises or a set of special therapeutic exercises should be carried out under the supervision of a rehabilitation specialist.
Treatment of this fracture at home is allowed only if the injury does not have complications. During the rehabilitation period, after agreement with the attending physician, some activities can be carried out at home. This could be gymnastics, physical therapy, massage.
Diagnostics
If a fracture is suspected, the first step is to determine the extent of the soft tissue disruption. Therefore, the doctor tries to understand the condition of the blood vessels, nerves, subcutaneous tissue, skin and organs of the chest. This is important to do, as damage to the collarbone can be combined with other injuries.
After this, an x-ray of the collarbone is required. It helps to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. If necessary, other tests are performed, especially if additional injuries are suspected.
Massage
When recovering from a clavicle fracture, the doctor prescribes a massage of the back and chest on the side of the injury. This procedure can be started from the second day after surgery. The session should last no longer than fifteen minutes and should not cause any discomfort to the patient. The doctor rubs the skin and kneads the muscles, which leads to increased blood circulation.
As a rule, the recovery period for older patients is slightly longer than for younger people. Rehabilitation after a child’s collarbone injury takes even less time.
Clavicle clavicle in children
Fracture is a common injury in children; children are the third most common injury after shoulder fractures. Usually the cause is pressure on the hand or compression of the third cell. Less commonly, fractures occur with a blow to the collarbone. In younger patients, widespread fractures are observed; in patients of older and older age groups, complete fractures are usually observed. A complete fracture is accompanied by pain, deformation and swelling of the forearm. With subperiosteal fractures, the cause of the shoulder girdle is absent, the pain is subperiosteal. The diagnosis is made based on shoulder examination and X-ray results. It usually becomes conservative, fall-fixing bandages are used, and when compression is applied, reposition is performed. Thoracic surgery for irreparable displacement of the cage and the threat of complications.
Collarbones occur in children
Fracture in children accounts for 7.4-14% of total arm fractures. It can be observed at a less frequent age, but the greatest number of younger cases occurs at the age of 2-4 or. Usually it is an isolated impact and occurs in everyday life or in the collarbone of sports activities. The combination with age of other bones and tissue injuries of children is rarely observed, usually in road accidents, falls from a height.
Fractures (subperiosteal) fractures can be observed unrecognized or late subperiosteal due to poor symptoms. Sick collarbones, both incomplete, painful and complete, grow together well and are not older after themselves functional age.
Causes of clavicle fracture in middle age
In children, complete fractures more often occur as a result of trauma fractures: compression of the chest or a fall on the arm. Sharp is usually localized at the border between the outer and middle parts of the deformity, since in this place the swelling is thinner, and its curvature is stronger than the shoulder girdle.
Direct trauma (impact to fractures) is quite rare. In deformity cases, the fracture is usually of the shoulder girdle at the outer part of the collarbone.
Accompanied by a fracture of the collarbone in children
In younger people, fractures or subperiosteal fractures are more often diagnosed. In traumatology, such damage to the base is caused by fractures of the “green pain” type, since in such data the same thing happens as during an examination when a young branch is broken, treatment: the inner part of the bone results, and the outer (periosteum) usually remains and holds the broken ends, not used by it move. Usually these are different transverse ones. In some cases, minor fragments of the periosteum that fixate them may shift at an angle.
In the older age group, reduction of clavicle fractures is observed, which threaten to be transverse, oblique, or comminuted. The degree of displacement performed can vary significantly. Fracture of the weight of the limb and the action when displaced, the operation picture is observed: the central fragment needs to be upward and backward, and the peripheral fragment - with and forward.
Open fractures are observed very rarely. They are secondarily irremovable displacements, since they arise as a result of radiography of the skin with a bone fragment.
Clavicle fracture fragments in children
In children with a subperiosteal fracture, development or moderate swelling is observed, complications include bruising at the site of the collarbone, but the pain syndrome of the fracture is not expressed. The child does not complain, parents sometimes mistake the child’s injury for an ordinary bruise, and conservative advice to the traumatologist is only 1-2 years later, when there is a noticeable bone callus at the site of the fracture, which generally looks like a dense one to be observed.
With a complete fracture, the greatest sharp pain appears, more pronounced with the age of the fragments. The shoulder girdle on the side however appears shortened. The patient has a characteristic forced position: cases of the torso in the injured side, isolating the sore arm and pressing it to maybe part of the chest or any other part.
The scapula on the side of the fracture “falls”; its edges become older. The upper limb rotates and moves anteriorly. When the ends of the fragments are felt, the injury is painful, and sometimes occurs. Movements are limited. The maximum observed is observed when trying to usually hand up after a while.
Complications of a clavicle fracture in athletic age
With severe fragmentation, damage may occur to the artery, subclavian vein, brachial plexus, or the apex of the lung.
With a combination of blood vessels, symptoms of blood loss fractures are observed: pale skin, others, cold sweat. With unrecognized branches of the brachial plexus due to injuries, neurological disorders. Damage to bones and pleura is accompanied by subperiosteal respiratory problems.
In all of these cases of falls, emergency surgical intervention is required.
Symptoms of a clavicle fracture in children
Rarely, confirmation of the diagnosis is prescribed to diagnose the clavicle in the standard straight soft one. Usually the diagnosis is not due to tissue difficulties. In cases that are difficult to differentiate, a fused tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of incomplete clavicles may be prescribed.
If incomplete damage to blood vessels, nerves, heights and lungs occurs, consultation is necessary with a surgeon, a pediatric neurosurgeon or a thoracic surgeon. When functional rupture of the lung is performed, it is localized in the chest wall in the rectus scan.
Treatment of a clavicle fracture nbsp
At the prehospital stage, the child should be given pain relief and the child should be kept at rest by bending her elbow and putting her collarbone on a scarf. You can bandage your arm to your body. Or the fracture is open, the fractures should be covered with a sterile bandage.
It is too late to make independent attempts to break the fragments - such actions cause damage to the skin, bones and nerves. The patient needs to be subperiosteally strictly in a sitting position.
A traumatologist deals well with collarbone fractures. Treatment for the disorder is usually on an outpatient basis. Indications for traumatology in trauma. separation is due to displacement of fragments, open clavicle, damage or threat to the lung and neurovascular bundle and perforation of the skin.
In case of unfolded fractures and complete fractures from the cause of displacement, Fracture rings or a Deso bandage are applied.
Or displaced fractures are produced in children. In young children, fractures are manipulated under general anesthesia. In older people, local anesthesia may cause compression. To eliminate the displacement along the collarbone, both shoulder girdles are strongly pushed backwards and upwards. For indirect fractures with angular displacement and external fractures, special thoracic techniques are used (the doctor applies special pressure to the fragments with his fingers). More often than not, a special bandage is applied. The type of bandage is curvature, taking into account the features of displacement.
Immobilization cells are usually determined by the type and age of the patient and are usually expressed for 2-3 weeks.
Surgical treatment for falls is very rare. The indication for a fracture is an open fracture of the girdle of vessels, nerves, pleura and border, a threat of damage to the listed formations or a threat to sufficient skin, as well as significant parts of fragments that cannot be averaged during reposition.
Surgical features are performed under the common clavicle. If the fracture is localized in between the parts of the collarbone, it is possible that the clavicle pin or location occurs. Special similar plates and ordinary thinner reconstructive plates are also used. In case of injuries to the acromial arm of the clavicle, a clavicle plate with a blocking bone or a hook-shaped plate is usually performed.
During this operation, the arm is suspended in an external sling. The stitches are removed at 7-10. During the recovery period, OR, massage, electrophoresis and magnetic therapy are prescribed.
Stronger favorable. Movements are maintained within the trauma volume. In cases of adequate fragments, the normal straight configuration is restored within a few days.
krasotaimedicina.ru
Risk of injury
This injury should not be treated with disdain. If the collarbone is broken, the following possible complications are identified:
- Loss of sensation in a limb;
- Muscular myopia;
- Development of arthrosis of the damaged joint;
- Inflammation of the joint;
- Suppuration of damaged tissues;
- Decreased motor ability of the hand;
- Significant loss of blood fluid.
When nerve endings are damaged, loss of sensation in the limb occurs. During treatment, the activity of the nervous system is not always restored. Damage to large bundles causes a lifelong loss of a person’s ability to feel. In this case, the patient is prescribed additional surgical intervention.
Doctors often find muscle myopia associated with injury. Several muscular fascia are attached to the ends of the clavicle. If the fusion is incorrect, the muscle changes its correct position. Prolonged stay in this position leads to deformation of the muscular body. Myopia develops - muscle weakness. The problem of repeated bone fractures in a medical setting is eliminated.
The ends of the bone form part of two joints. Synovial bursae are responsible for reducing bone friction. Without proper treatment, the debris puts pressure on the cartilage part of the joint. This causes inflammation. Prolonged inflammation is accompanied by the development of arthrosis of the affected joints.
Complications also arise with open forms of injury. When soft tissue breaks through, a wound forms on the skin. The surface of the wound is an ideal environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. Pathogenic bacteria cause cell death. Pus accumulates in the wound. This complication slows down the recovery process.
Errors during treatment are also indicated by a decrease in the motor ability of the hand. A person cannot fully move and work. This problem indicates incorrect alignment of the clavicle fragments. If a complication interferes with a person, repeated damage to the bone is necessary.
Pain in the right side in the ribs: causes and treatment
Pain in the side under the ribs on the right is a symptom that even a completely healthy person has encountered at least once in his life. The close contact of the right hypochondrium with the internal organs, as well as their dense structure, significantly complicates the determination of a clear diagnosis, therefore, during painful symptoms of any nature under the ribs on the right, there is no need to postpone going to the doctor.
- Why does it hurt under the ribs on the right side? Symptoms
- Strong pain
- Acute pain
- Sharp pain
- Drawing, dull aching pain
- Stitching pain
- Pain from behind
- Pain on the right side under the ribs in front
- Pain in the right hypochondrium below
- Diagnostics
- Prevention
Why does it hurt under the ribs on the right side?
The right hypochondrium is a reliable protection for many internal organs. First of all, pain on the right indicates illness:
- Gallbladder.
- Liver (cirrhosis, hepatitis).
- Right kidney (pyelonephritis, urolithiasis).
- Pancreas.
- Peripheral nerves.
- Adrenal gland.
- Diaphragms.
- Intestines.
- Right lung (pneumonia, lung cancer).
- Spine (osteochondrosis).
- Ribs (fracture or crack of the ribs).
But in order to correctly identify the cause of painful symptoms in the right hypochondrium or back, you need to pay attention to the location of the pain, as well as its nature.
Symptoms
Pain in the right side under the ribs can have a different character:
- spicy;
- piercing;
- strong;
- pulling, dull aching;
- sharp.
Taking into account the nature of the pain and accompanying symptoms, the affected internal organ can be identified.
Strong pain
Severe and unbearable pain in the right side is characteristic of diseases of the kidneys, liver and gall bladder.
Gallbladder diseases. Severe pain on the right side forces the patient to look for a comfortable position. In addition, there may be the following symptoms:
- nausea;
- fever;
- yellowing of the whites of the eyes and skin in the area;
- frequent vomiting that does not bring relief.
Hepatic colic is a sharp and severe pain in the back that subsides while taking antispasmodics. Liver diseases are characterized by yellowed whites and eyelids.
Liver injuries. The pain becomes stronger if the person takes a horizontal position. You can observe signs of blood loss (at low pressure, the pulse increases, pallor of the mucous membranes and skin, dizziness and weakness).
Kidneys. The pain is so intense that the patient rushes about, trying to find a comfortable position. As a rule, the pain is explained by urolithiasis, therefore, taking into account the location of the stone, the pain is localized in the lower or upper part of the hypochondrium on the right side. In addition, the following symptoms may occur:
- bloating;
- constant urination;
- vomiting that appears along with pain.
Acute pain
"Dagger" or sharp pain appears unexpectedly and is usually a symptom of a stomach ulcer. In case of acute pain, a person, as a rule, takes a lying position with his legs tucked to his stomach.
In addition, he is often tormented by:
- sour belching, heartburn;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- vomiting and nausea.
Sharp pain
Surrounding and sharp pain is the first sign of developing acute pancreatitis. The cause of exacerbation of this disease may be the consumption of excessive amounts of alcohol with sweet and fatty foods. Sharp pain in acute pancreatitis is characterized by its intensity - the pain does not subside when changing body position or coughing. Pancreatitis has the following symptoms:
- severe intoxication (small hemorrhages around the navel and on the sides, marbled skin on the abdomen, cyanosis of the body and face);
- frequent vomiting;
- nausea.
Sharp pain in the right hypochondrium in the area of the collarbone and scapula appears during the accumulation of pus behind the diaphragm. The pain becomes stronger when breathing, sudden movements, sneezing and coughing. Relief comes in a lying position, being on the right side. Possible symptoms of the disease:
- intoxication of the body;
- fever.
Sharp pain between the ribs, which begins to be felt with any, even slight touch to the skin, is usually characteristic of shingles, which is a viral disease that manifests itself in the form of painful rashes on the skin along the nerve endings infected with the virus (usually in the intercostal region). Before the rash appears, a person may feel weakness, aching pain in the left or right hypochondrium, and high temperature.
Drawing, dull aching pain
A dull, aching pain in the right hypochondrium may indicate chronic liver disease, causing it to increase in size (hepatitis). In addition, this may be a symptom of the development of benign and malignant tumors.
In addition to nagging and dull pain, you may experience:
- impaired blood circulation;
- liver failure;
- jaundice.
In this case, dull and aching pain can be a sign of the following diseases:
- malignant tumors of the gallbladder, lung, pancreas, kidney;
- in women, inflammation of the appendages;
- polycystic kidney disease on the right side;
- intestinal inflammation;
- an increase in the size of the spleen.
Stitching pain
Stitching pain on the right side under the ribs, which becomes stronger with a deep breath and cough, is a sign of right-sided pneumonia. Very often the pain spreads completely along the right side, and the specific time of its appearance is quite difficult to determine. Associated symptoms:
- shortness of breath;
- heat;
- herpetic rash on the right side;
- diarrhea and constipation;
- blue or pale nasolabial triangle.
Pain from behind
Pain on the right back under the ribs indicates problems with the pancreas and kidney.
During inflammation of the kidneys in a person, Pasternatsky syndrome can be observed: sharp pain even with a small blow from the palm from behind on the lower rib. During renal colic, the pain in the right hypochondrium is paroxysmal and intense, and can be painful to such an extent that the patient cannot be at rest and constantly changes his position. During urolithiasis, pain symptoms spread to the lower back along the entire spine.
Pain under the rib on the right during the inflammatory process of the pancreas (pancreatitis) appears unexpectedly, its intensity does not change and has a girdling character. The causes of the inflammatory process of the pancreas may be abuse of fatty foods and alcoholic beverages, exacerbation of chronic diseases, complications after operations, and metabolic disorders.
Pain on the right side under the ribs in front
When it hurts under the rib on the right side in front, this is a symptom of the following diseases:
- Gallbladder (chronic or acute cholecystitis).
- Lungs (inflammation, pneumonia).
- Stomach and duodenum (gastritis, peptic ulcer, erosion).
- Liver (fatty cell degeneration, hepatitis, tumors, cirrhosis).
During lung damage, there is a stabbing pain in the right hypochondrium, which intensifies when coughing or inhaling; also a concomitant phenomenon will be typical signs of fever (weakness, temperature), distinguishing it from other pathologies of internal organs in the right hypochondrium.
During inflammation of the gallbladder, severe pain is felt in the right shoulder blade and in the epigastric region. In acute cholecystitis, pain symptoms extend down the right hypochondrium.
When there is dull or aching pain under the right rib, this indicates liver damage. Most often it is accompanied by symptoms of jaundice (yellowish color of the whites of the eyes and skin), with the exception of only benign tumors.
During an ulcer of the duodenum and stomach, pain is present in the front of the left and right hypochondrium, moving to the lower back and back. The painful sensations are slightly dulled during pressure, so the person begins to feel relief by squatting or lying on his stomach.
Pain in the right hypochondrium below
Pain below the ribs on the right is a sign of an inflammatory process:
- stomach and duodenum - with an ulcer, pain moves from the epigastric region down the right hypochondrium.
- right kidney. As a rule, with renal colic, pain does not have a specific localization, and occurs throughout the right hypochondrium, including the lower back and spine.
- intestines (or more precisely, the appendix). The main symptom of appendicitis is sharp and acute pain in the right side. The nature of the pain indicates a possible rupture of the appendix, so you need to see a doctor as quickly as possible.
In addition, pain on the right side under the ribs can appear in an absolutely healthy person during movement. This happens when a person is exposed to stresses that are unusual for his body. In the vena cava, located under the right lower ribs, blood flow increases and it enlarges. Pain may also appear during sharp turns and bends if the rib bones come into contact with internal organs.
Diagnostics
Regardless of the type of pain on the right side under the ribs, only an experienced specialist can make an accurate diagnosis. Examinations must be carried out by a local physician, who, if necessary, will refer the patient for additional examination to another doctor.
Diagnosis of pain in the right hypochondrium has several stages:
- Examination of the eyes, tongue and skin (with diseases of the gallbladder and liver, the whites and skin of the eyes may acquire a yellowish tint).
- Manual examination (palpation). An inflamed kidney and liver will be easily palpable, and gallbladder pathologies will make the examination much more painful.
- Questioning the patient (history), during which the doctor finds out information about past or chronic inflammatory diseases of the person.
- Laboratory examination and subsequent hospitalization.
How to treat pain under the ribs on the right?
The hypochondrium on the right side is protection for internal organs such as the pancreas, liver, intestines, and gall bladder. These organs fit together quite tightly, so it is often very difficult to determine the cause of pain. The first principle of treatment is a timely visit to a specialist (gastroenterologist, local physician, surgeon, oncologist).
You can independently reduce pain using antispasmodics:
- subcutaneously: 1 ml of promedol and 1 ml of 0.1% atropine suspension; 2 ml no-shpa and 5 ml baralgin;
- nitroglycerin (3 drops per piece of sugar or one tablet under the tongue);
- no-spa (2 tablets no more than 3 times a day).
Without defining a specific diagnosis, there is no need to use hot compresses; you can apply ice to the affected area, but only if it can create an analgesic effect.
We must not forget that if severe pain is accompanied by symptoms such as vomiting and nausea, you should immediately call an ambulance. Often, with a list of diseases accompanied by acute pain in the right hypochondrium, emergency surgical intervention is necessary (for inflammation of the gallbladder, urolithiasis, severe liver injuries).
When the diagnosis has already been established by a doctor, then, in addition to medications, you can use traditional methods of treatment:
- for pain in the spleen – 1 g. royal jelly daily or rosehip decoction;
- for pain in the liver - mix 0.5 liters of honey with 2 tablespoons of ground cinnamon. Take 1 spoon before and after meals;
- for pain in the gall bladder - potato broth: boil the potatoes in their jackets, without pouring out the water, and crush. Let it sit and drink the resulting liquid three times a day, 2 tbsp. l.
Prevention
To prevent pain on the right under the ribs from turning into a nightmare on the surgical table, it is enough to use fairly simple rules of prevention:
- At the first sensation of pain and accompanying symptoms, consult a doctor immediately.
- Do not abuse alcohol, heavy, salty, fatty foods.
- Have a complete medical examination and ultrasound of your organs every year to find out about your chronic diseases, their treatment options and their condition.
Pain under the ribs on the right side is a rather dangerous symptom, which always signals a serious illness of the internal organs, therefore, at the first encounter with it, you need to seek professional medical help from a doctor.
Diagnostic measures
After an external examination, the patient is sent for an X-ray examination. The picture is taken in two projections. Direct projection allows you to determine the location of the fracture and its characteristics. The side shot establishes the exact angle of displacement of the debris.
Ultrasound examination of blood vessels is also prescribed for diagnosis. It is carried out if there are signs of internal damage to soft tissues and large veins. After determining the clinical picture, the patient is prescribed treatment.
Fracture in a child
A child's humerus is quite fragile and is comparable in fragility to a young twig. The integrity of the bone tissue may not be compromised, and only an X-ray examination can reveal a crack in the bone itself. All signs of a fracture are observed, but often the parent may mistake the injury for a dislocation and try to set the bone. This is very dangerous, as further physical impact can lead to rupture of soft tissue.
The first pain reliever when a child breaks his collarbone is to apply a cold compress. Cold reduces the risk of hematoma and swelling and relieves pain. In case of an open injury, you should first stop the bleeding by applying a sterile napkin, then bandage it. Until the victim is taken to the emergency room, you must try to ensure complete rest for the hand.
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, a fracture of the collarbone in children heals correctly and in the future does not remind you of itself in any way.
Consequences
It is difficult to give an exact prognosis regarding how long the overall treatment and rehabilitation period lasts, however, most often it takes about three months. Treatment takes longer if the subclavian artery or nerves are damaged.
In some cases, the fracture may not heal. A false joint may form, causing chronic pain. It also leads to impaired physical activity.
It is important to identify the signs of a clavicle fracture immediately, because the consequences and duration of treatment also depend on the provision of first aid. Of course, the most important thing is to preserve life, however, everyone wants to avoid other complications that can affect a person’s activity.
Causes of a crack in the collarbone in a newborn and an adult
One of the causes of a fracture may be injury due to medical errors.
There are many reasons for the appearance of cracks, chips and fractures of the collarbone. As a rule, injuries occur as a result of mechanical impact under various life circumstances. It may also be a congenital defect due to a difficult pregnancy. As a rule, the causes of the pathological condition are:
- dislocations of the periosteum in a child in the womb;
- chronic calcium deficiency in the body;
- receiving birth injuries due to medical errors;
- hereditary or congenital predisposition to bone injury;
- consequences of physical impact (impact or fall) to the chest, ribs or shoulder;
- weakness or pathologies of the musculoskeletal system;
- injury to tissues and bones during sports training;
- car crashes;
- greater physical activity on the upper body.
A clavicle fracture in a newborn during childbirth is diagnosed extremely rarely, but such situations exist.
First aid
Any person must know what to do if the clavicle bone is broken. If you suspect damage to the integrity of the clavicular bone, you must call medical professionals and take emergency first aid measures before they arrive:
- Anesthetize the injured area with non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs, for example, Pentalgin, Ibuprofen, Citramon, Paracetamol or Analgin. The medicine begins to act after fifteen minutes. Emergency doctors must be told what pain relief was used.
- Secure the shoulder joint in a stationary position to prevent bone displacement and tissue damage. For this purpose, a tight figure-eight bandage is applied. If the person providing first aid is not sure that he can correctly fix the shoulder, then you just need to tape your arm to the body and, bending it at the elbow, tie it to the neck, passing one end of the bandage along the chest and the other along the victim’s back.
- Apply a cold compress for half an hour no later than fifteen to twenty minutes after the person is injured.