Intestinal dyskinesia is a functional disorder of the intestine, which is based on a violation of its motor-evacuation function. A functional intestinal disorder is said to occur when examination does not reveal genetic, morphological and metabolic changes that would explain the existing symptoms.
The development of dyskinesia is based on a lack of coordination between different types of intestinal movements (peristaltic, pendular, segmental and antiperistaltic). These movements ensure the mixing of food and its movement, as well as the formation of feces in the final sections of the large intestine.
Causes of dyskinesia
All the causes of colon disease have not yet been fully identified. Doctors agree that the factors contributing to the occurrence of dyskinesia are:
- Disorders associated with changes in psychological state. Psychosomatic disorders contribute to the occurrence of primary dyskinesias. Prolonged stress, neurotic conditions, the predominance of a negative background in life, conflicts within a person’s personality become triggers for the further development of the disease.
- Poor nutrition. Overconsumption of fast food and high-calorie foods leads to nutritional imbalance. Plant fiber does not enter the body in the required amount.
- Passive lifestyle. When consuming a large number of calories, they do not find a way out and become ballast in a person’s life.
- Lack of ability to digest some components of familiar foods. An organ that does not have the ability to develop the correct reaction to the arrival of any type of food constantly leads to malfunctions in its functioning.
- The presence of various infections in the body. The consequences of intestinal infections become especially unpleasant.
- Heredity. If one of the parents has an anomaly of the digestive system, then there is a high probability of it being detected in children.
- Imbalance in the functioning of the endocrine system organs. Excessive production or lack of hormones has a negative effect on the digestive organs. The food consumed is not sufficiently processed with enzymes due to their small quantity. Or a person has the opposite effect when too many agents are produced. Nutrients do not enter the systems in the required quantities.
- Women who have problems with reproductive function are susceptible to the development of intestinal dysfunctions.
- Uncontrolled use of medications that have a negative effect on colon motility, leading to pathological conditions.
- Children with hormonal disorders, increased nervous activity and hypovitaminosis are at greater risk of being diagnosed with colon dyskinesia.
- Problems localized in the plane of endocrinology, incorrect balance of hormones, distorted activity of the autonomic and nervous systems lead to the development of dyskinesia.
Types of dyskinesia
The manifestation of colon dyskinesia is conventionally divided into hypertonic and hypotonic types, with a primary and secondary stage of the course. In the first case, the pathology develops as an independent disease, the consequence of which is a disorder of intestinal motor activity. This form of dyskinesia occurs due to stress and unbalanced nutrition. The secondary form of dyskinesia develops against the background of other diseases of the digestive system (gastritis, pathologies of the biliary tract, pancreatitis). This variety does not have clearly defined symptoms, so it is quite difficult to distinguish it from other diseases.
Hypertensive (aka spastic)
Dyskinesia of the large intestine, which occurs according to the hypertensive type, is characterized by increased tone and spasms of the rectum. Incomplete emptying of the sigmoid colon is also observed. As a result, the process of digestion of food is disrupted, diarrhea occurs, accompanied by cramping pain in the lower abdomen and cramps.
After emptying, the pain disappears and relief comes. This type of intestinal disease is associated with infection and poor diet.
The main danger of spastic dyskinesia is a decrease in sphincter tone during constipation, since stool is passed in large volumes, expanding areas of the intestine. Subsequently, this phenomenon will cause fecal incontinence.
Hypotonic (atonic) dyskinesia
With the atonic type of pathology, a weakening of intestinal motility is observed, a person experiences chronic constipation, flatulence, a feeling of intestinal distension appears, and cramps occur in the abdomen, accompanied by dull pain. The pain syndrome extends to the entire abdominal cavity, so it is difficult to determine its localization.
Symptoms of the disease
The symptoms are extensive. The main manifestations are:
- Pain in the abdominal area. The strength and nature of painful manifestations become different. Increased pain is noted after eating cooked foods. Stress and a negative atmosphere increase the sensation of pain. Their strength is growing. Some relief is possible upon completion of the act of defecation and the release of accumulated gases. The pain subsides at night, but returns when you get up in the morning.
- Nauseous urge, unpleasant belching, bloating and heaviness.
- Increased gas formation. There is a peak in activity in the evening hours. Accompanied by loud sounds.
- Defecation disorder. The main signs of manifestations are constant constipation. The patient observes mucus impurities in the stool. The act of defecation itself is accompanied by difficulties. The patient feels like he needs to defecate again. A peculiarity of fecal masses during the disease is the fragmentation of feces. They become similar to goat or sheep feces. Diarrhea, which replaces constipation, can occur up to three times a day. Mucus becomes noticeable when there is a sharp increase in the load on the individual’s nervous system.
- Nervous system disorders and imbalances in human mental health. Increased anxiety, sad mood, turning into signs of depression accompany problems in the large intestine. The nature of the dysfunctions is rather psychosomatic in nature. When the organs are fully functioning, the patient complains to the doctor about painful sensations in them.
Difficulty defecating leads to increased levels of toxins in the body. Manifests itself in dizziness and lack of appetite. The consequence is the appearance of unusual allergic reactions and weakness. The result is reduced human performance and an impact on the entire life activity of the individual.
Colon dyskinesia is divided into primary and secondary. In case of dysfunction, one of the clinical signs predominates:
- intestinal disorders. Alternating stool dysfunction, expressed in diarrhea and constipation;
- severe pain syndrome;
- dominance of neurotic manifestations.
The origin of dyskinesia may be:
- neurogenic. Occurs in the presence of organic matter in the damage to the nervous system or pronounced distance;
- psychogenic. The starting point is considered to be signs of depression, neurosis, manifestations of asthenic syndrome;
- hormonal. Dysfunction in the activity of the endocrine system creates conditions for improper functioning of the digestive organs. This group includes a violation of the production of sex hormones;
- toxic. The root cause is long-term abuse of alcoholic beverages and alcohol-containing products. This includes the toxic effects of paint fumes in industries, lead poisoning;
- medicinal. Uncontrolled use of medications that promote the release of feces or have a binding effect leads to the development of problems with the digestive organs;
- nutritional. The impetus for dyskinesia is an incorrectly selected diet or uncontrolled eating;
- hypodynamic. It becomes a complication upon completion of surgery of the abdominal organs or a background in the diagnosis of asthenic manifestations, hypokinesia;
- becomes the result of impaired metabolism, allergies and intolerance to certain types of foods. Patients complain of pain of varying intensity;
- abnormalities in the development of the digestive organ.
Reasons for development
Key factors in the development of the disease include:
- Weak physical activity. Excessive time spent on the computer and TV, sedentary lifestyle.
- Improper eating behavior. Unbalanced diet, eating on the run, without drinking the proper amount of water, overeating, abuse of fatty foods, hasty absorption of food.
- Vegetovascular dystonia (VSD). Disruption of the autonomic nervous system due to complications during pregnancy and childbirth (intrauterine infections, birth injuries, long or rapid labor), diseases of the endocrine system, traumatic brain injuries, conflicts in the family.
- Inflammatory processes in the abdominal and pelvic organs.
- Genetic predisposition.
Gastroenterologists distinguish 4 types of dyskinesia:
- esophageal dyskinesia;
- gastric dyskinesia;
- biliary dyskinesia;
- intestinal dyskinesia.
Diagnostics
To obtain an accurate diagnosis, the complaints presented are not enough. Dyskinesia of the large intestine can be confused with related diseases that have similar clinical symptoms. The research consists of several stages. To begin with, exclude the possibility of pathology. To confirm assumptions, laboratory and instrumental studies are used. The laboratory performs blood and stool analysis, coprogram and microflora detection.
The second category of methods includes irrigoscopy, colonoscopy and other endoscopic examinations, and biopsy. The biopsy is examined to exclude cancer cells in the organ. Hypertonicity and impaired peristalsis do not necessarily indicate the presence of a malignant neoplasm.
Esophageal dyskinesia
Esophageal dyskinesia is a violation of its motor function. It is characterized by several forms:
- Atony. Characterized by decreased tone of the walls of the esophagus.
- Esophagospasm. Involuntary spasms of the esophageal muscles.
- Sphincter dysfunction. Constant ejection of food together with gastric juice back into the esophagus (lower sphincter disorder), or difficulty swallowing (upper sphincter disorder).
Signs
The main symptom of this type of disease is dysphagia - a feeling of a “lump in the throat” when eating, when the swallowing process causes difficulty. The following symptoms are also observed:
- Acute pain behind the sternum. They arise in response to experienced stress, but also occur in a calm state. Sometimes accompanied by sweating, chills, and fever.
- Regurition (regurgitation). Involuntary regurgitation of stomach contents for no apparent reason. More often occurs when bending forward and in a lying position. For an infant, this is considered a normal physiological phenomenon.
- Swallowing disorder. For example, swallowing liquid is difficult, but solid food passes through the esophagus easily.
Diagnostics
The main informative diagnostic method for this type of dyskinesia is fluoroscopy. Stool analysis, esophageal manometry, esophagoscopy and endoscopic examination are also used.
Treatment
A gastroenterologist prescribes drug therapy, which includes calcium channel blockers, anticholinergics, nitrates, and sedatives are also widely used. If dyskinesia is a concomitant disease, then treatment is determined by eliminating the main disease. Surgical intervention is indicated in cases of severe forms of the disease and the ineffectiveness of the conservative method.
Doctors advise trying not to take body positions that provoke regurgitation, reducing physical activity, and avoiding stressful conditions. It is recommended to sleep with the head of the head elevated. Avoid foods that are too cold/hot, spicy, fatty foods, sour-tasting juices, and coarse fiber. Take food little by little and in fractions of 4 - 6 rubles. per day, give preference to boiled and grated food.
Treatment
To rid a person of an illness, the doctor must take into account many factors. Based on the tests received and the patient’s complaints, he will correctly determine the type of dyskinesia. Then, during therapy, the causes of the disease will be eliminated.
The treatment method must be comprehensive and consist of:
- Use of medications.
- Changes in diet and habitual activities in life.
- Physiotherapy.
- Psychotherapy.
- Therapeutic physical exercises.
Drug treatment is designed to normalize peristalsis and metabolism in order to correct the situation with going to the toilet. It is possible to prescribe sedatives and psychotropic drugs.
Oxygen-containing and pine water procedures as a method of physiotherapy are recommended simultaneously with acupuncture and paraffin baths. In addition, massages, cleansing enemas, and intestinal lavage with a liquid with a high content of mineral derivatives are prescribed. After meals, it is recommended to drink mineral water. Low or high mineral content varies depending on the type of intestinal dyskinesia. Treatment of colon dyskinesia is aimed at stimulating organ motility. Every day you can eat bran and foods containing lactic acid bacteria.
It is possible to treat the disease with traditional medicine only after consulting a doctor. Some substances can cause not only allergies, but also negatively affect the digestive system. Traditional methods are designed to alleviate symptoms, but not eradicate the root cause. With continued use, the patient may notice a decrease in pain.
When getting rid of inflammatory diseases in the large intestine, you must adhere to a diet. You should avoid fatty, fried and smoked foods. Temporarily stop consuming foods that have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane.
Foods rich in essential oils are excluded from the diet. Mushrooms are a difficult food to digest. It is prohibited to use them.
After the main methods of therapy, preventive measures are important that can improve the functioning of the digestive system. The main factor is changing your diet, giving up bad habits and increasing your time in active activities.
The information" on our website is provided by qualified doctors and is for informational purposes only. Don't self-medicate! Be sure to consult a specialist!
Author: Rumyantsev V. G. Experience 34 years.
Gastroenterologist, professor, doctor of medical sciences. Prescribes diagnostics and carries out treatment. Expert of the group for the study of inflammatory diseases. Author of more than 300 scientific papers.
In gastroenterology, the term intestinal dyskinesia defines a symptomatic complex of disorders of the digestive organ that occurs as a result of a violation of its motor and functional activity. Most often, intestinal dysfunction occurs in the colon, representing the so-called irritable bowel syndrome with a predominance of functional constipation. According to statistics from the World Health Organization, colon dyskinesia is diagnosed in every third inhabitant of the planet, with a predominance of frequency in women of childbearing age.
Diagnosis and treatment
Colon dyskinesia can be detected by differential diagnosis, that is, the gradual exclusion of diseases with similar symptoms. What studies does a gastroenterologist recommend for a patient:
- laboratory tests of stool, urine and blood to determine the location of the inflammatory focus;
- coprogram for identifying intestinal dysbiosis;
- sigmoidoscopy to assess the condition of the colon;
- colonoscopy to determine the type of dyskinesia;
- irrigoscopy to detect damaged areas of the colon.
If these methods are insufficiently informative, instrumental studies are carried out: ultrasound, MRI, computed tomography of the intestine.
When choosing a therapeutic tactic, the gastroenterologist takes into account all factors: the type of disease and its immediate cause, symptoms. Diet for dyskinesia is one of the most important stages in the treatment of adults and children, comparable in importance to taking pharmacological drugs.
Advice: “In some cases, it is enough to adjust your diet to get rid of constipation and flatulence forever. At the initial stage of therapy, strict restriction of certain foods is required, and then gradually the list of permitted foods expands.”
Diet
A decrease in the functional activity of the intestines is always complicated by symptoms of flatulence, so you should exclude from the diet foods the consumption of which provokes excessive gas formation and triggers the processes of putrefaction and fermentation. The diet for intestinal dyskinesia is based on the absence of the following products in the daily menu:
- legumes - lentils, beans, peas;
- whole milk (especially if you are lactose intolerant);
- potatoes, white cabbage, raw onions;
- fatty meats and fish;
- rich broths;
- fresh white bread, various types of black bread;
- alcoholic drinks;
- baked goods made from puff pastry and butter dough;
- strong coffee and tea;
- chocolates, confectionery with custard and butter cream.
Gastroenterologists recommend that patients eat fractionally (6-7 times a day), but in small portions. During treatment, you should drink about 2 liters of clean still water daily, but only before or after meals. If you drink drinks during meals, the concentration of gastric juice will decrease, which will affect the quality of digestion. What can you eat if you have dyskinesia?
- clear broths;
- seafood, lean fish and meat;
- fermented milk products: cottage cheese, soft cheese, kefir, fermented baked milk, Varenets;
- puree soups;
- juices from fresh fruits and vegetables;
- dried white bread;
- infusion of rose hips;
- cereal porridge;
- hard cookies.
At the initial stage of treatment, it is necessary to exclude from the daily menu products containing essential oils: spicy fresh herbs, radishes, radishes.
Types and causes of intestinal dyskinesia
Dysfunction of the colon (according to ICD10 - K59.8.1) is divided into several classification characteristics:
- Hypomotor dyskinesia of the large intestine is a functional disorder of the muscle layer, leading to constant relaxation and contraction, resulting in difficulties in the movement and evacuation of feces.
- Spastic dyskinesia of the large intestine is caused by constant tension of the organ of the digestive system, leading to disruption of its peristalsis.
- The hypertensive form of large intestinal dyskinesia is characterized by increased hypertonicity, leading to the development and progression of persistent constipation and painful sensations (colic).
- Hypotonic or atonic dyskinesia of the colon is a sharp weakening and disruption of wave-like contractions in the intestinal walls, accompanied by constipation, dull bursting pain in the abdomen and a feeling of heaviness.
In gastroenterology, primary and secondary forms of intestinal dyskinesia are determined. The probable cause of primary dyskinesia of the colon, according to medical experts, is considered to be a psychogenic factor - intrapersonal conflict, negative emotions, mental or nervous diseases. Among other probable cause-and-effect factors in the formation of symptomatic disorders of the intestinal system, excessive consumption of low-fiber foods is considered, that is, those food components that are not digested by the digestive enzymes of the human body, but are processed by the intestinal microflora. In addition, the causes of intestinal dyskinesia may be due to the occurrence of an acute infection in the colon. Along with the primary disorder of the large intestine, a cause-and-effect relationship can be provided by secondary factors in the occurrence of dyskinesia:
- chronic gastritis;
- cholecystitis;
- peptic ulcer;
- diabetes;
- disorders of the pancreas and/or endocrine system.
Slow transit of intestinal contents through the large intestine may be due to myopathy and neuropathy of various origins.
Description of dyskinesia
Bowel dyskinesia is a functional disorder. During the development of pathology, there are no lesions, but the organ cannot cope with its work.
Intestinal dyskinesia is a violation of patency, as a result of which the removal of feces is difficult
Irritable bowel syndrome is the second name for the pathology. A disease is understood as a set of disorders that occur due to the following failures:
- changes in the tone of intestinal muscle tissue;
- motor impairment.
The pathology is characteristic of the large intestine and its parts:
- transverse;
- blind;
- ascending colon;
- descending colon;
- sigmoid.
In some cases, dyskinesia affects the duodenum.
Dyskinesia may develop in one part of the large intestine
Pathology affects the functioning of other organs involved in digestion:
- liver;
- spleen;
- stomach;
- gallbladder;
- esophagus.
Irritable bowel syndrome - video
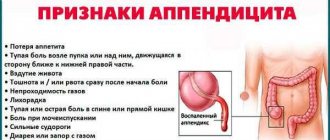
Symptoms of intestinal disorder
Intestinal dyskinesia provides the patient with various discomfort sensations, including pain symptoms, which vary in intensity. Acute, dull, aching or cutting pain in the abdomen can bother a person from several minutes to several hours until he receives qualified medical care. The localization of pain with dyskinesia of the colon affects almost the entire abdominal cavity, and the painful sensations do not subside until gas is released or a complete bowel movement occurs. The pain intensity subsides for a while during sleep and resumes after waking up. All these factors of impaired intestinal motility cause emotional overload and stressful situations in a person. Also, the emerging spastic colitis or irritable bowel syndrome with dyskinesia, leading to stagnation of feces, can provoke an allergic reaction or general intoxication of the body.
Regardless of the type of food consumed, the main symptoms are rumbling and bloating with dyskinesia of the large intestine, as well as bowel dysfunction.
General symptomatic characteristic signs, regardless of the degree of neglect and type of intestinal disorder, are as follows:
- constipation;
- nausea and frequent persistent vomiting;
- unmotivated increase in body temperature;
- weight loss or gain, regardless of a person’s appetite;
- increased gas formation and flatulence;
- changes in the general blood test, for example, an increase in ESR, leukocytosis;
- pain in the abdominal cavity without local localization, which goes away after defecation;
- dizziness and general weakness of the body.
Intestinal dyskinesia in a child
This pathological condition is found more often in children than in adults. It is characterized by alternating diarrhea and constipation. In the hypertensive form, the child experiences severe pain that cannot be eliminated with large doses of antispasmodics. Warming up the abdominal area helps relieve the condition. The following signs may suggest irritable bowel syndrome: decreased appetite, increased fatigue, pale skin. Complications of this disease can include muscular dystrophy, exhaustion, and anemia. An important part of treatment is adherence to the principles of proper nutrition.
A diet for intestinal dyskinesia helps restore organ functions and normalize metabolism. Fiber-rich foods are added to the menu: fresh vegetables and fruits, cereals, bran. Nutrition should provide the body's needs for nutrients, vitamins and minerals. The diet should include foods that stimulate intestinal motility and excretion of feces. During exacerbation of intestinal dyskinesia, you should not eat food that contributes to the processes of fermentation and putrefaction.
All foods must be steamed, boiled or baked. You should avoid fried, fatty and smoked foods. Prohibited products are baked goods, rice, oatmeal, radishes, garlic, and onions. When preparing dishes, you should not add spices. It is necessary to exclude pork, lamb, and fatty fish from the diet. Avoid eating chocolate, blueberries and pasta. Coffee, whole milk, cocoa and alcohol are on the list of prohibited foods.
During the period of exacerbation of intestinal dyskinesia, it is recommended to eat lean meat, crumbly cereals, lean fish, and offal. Soups, fruit and vegetable salads are healthy. Vegetable oil, butter and hard-boiled eggs are allowed for consumption. White cabbage, carrots, cucumbers, and beets can be used to prepare dishes. Getting rid of the signs of irritable bowel syndrome is impossible without restoring the microflora. Prebiotics and fermented milk products help with this: kefir, cottage cheese, fermented baked milk. However, they are not recommended for use in cases of hypotonic dyskinesia.
Sugar, honey, jam, and ice cream are allowed in small quantities. Dried fruits, bananas and plums, which contain organic acids that enhance intestinal motility, help get rid of fecal stagnation. For constipation, you need to drink cold mineral water, and for diarrhea, warm clean water. In addition to following a special diet, the doctor may recommend introducing moderate physical activity into your daily routine: walking, swimming, gymnastics. Timely treatment allows you to get rid of unpleasant symptoms and avoid the development of complications.
Differential diagnosis
Patients with dyskinesia of the large intestine present complaints with strictly specific syndromes of digestive system disorders. However, it is necessary to clearly differentiate symptomatic signs from other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract that occur with similar clinical indicators:
- nonspecific ulcerative or post-infectious colitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- intestinal polyposis;
- colon cancer or tuberculosis;
- diverticulitis and so on.
The required scope of laboratory instrumental diagnostics includes:
- blood chemistry;
- scatology;
- analysis of stool for worm eggs and dysbacteriosis;
- bacteriological examination of stool;
- lactose tolerance testing.
In addition, the attending physician will conduct an ultrasound scan of the abdominal cavity and a study of the speed of colonic transit, a colonoscopy with a biopsy of the mucous contents of the colon, and a survey X-ray examination - irrigography, when the intestinal tube of the digestive system is examined.
If necessary, other medical specialists are involved in the diagnostic examination - gynecologist, psychiatrist, neurologist, endocrinologist, and so on.
Types of pathology
Based on the mechanism of development of the disease, dyskinesia is distinguished:
- primary - refers to independent pathologies;
- secondary - various factors lead to its formation - taking medications or the development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The following subtypes are distinguished: hepatogenic;
- medicinal;
- allergic;
- gastrogenic;
- pancreatogenic.
The pathology is extremely insidious; in some cases it is difficult to establish the type of intestinal dyskinesia.
Based on the nature of violations, the following types are distinguished:
- Spastic dyskinesia, or hyperkinetic (hypermotor / hypertonic). As a result of increased tone and contractions, intestinal colic occurs.
- Atonic, or hypokinetic (hypomotor / hypotonic). A decrease in intestinal motility leads to dilation of the pelvic veins and stagnation in the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. The pressure in the peritoneal area increases. The muscle fibers do not relax, and frequent muscle spasms occur.
Treatment and diet for intestinal dyskinesia
The widespread prevalence of the disease leads to the fact that most patients, following generally known information, self-medicate, increasing plant dietary fiber and the amount of fluid in their diet. Such therapeutic and preventive measures do not cause harm and are welcomed by official medicine. However, in most cases, trying to get a quick result, patients with severe intestinal dyskinesia use laxatives or daily cleansing enemas, while ignoring visits to a medical facility.
A critical disadvantage of pharmaceutical laxatives is the rapid addiction to them, as well as a gradual increase in the dose of the drug, which ensures degeneration of the receptor functions of the colon.
You should know that frequent use and increased dosage of a laxative cause osmotic pressure in the intestinal lumen and bloating, and the systematic use of cleansing enemas results in a loss of visceral sensitivity and defecation reflex in the colon.
The treatment program for symptomatic colon disorder includes basic therapy based on dietary recommendations and medication. For large intestinal dyskinesia, the patient is prescribed a special diet that excludes the consumption of foods that cause excessive gas formation:
- caffeine;
- lactose;
- vinegar;
- black and red pepper;
- pickled and smoked products.
The predominant products in the diet remain vegetables and fruits with an increased fiber content, which contribute to the softening of feces and their high-quality transit through the intestinal tract. Sufficient amounts of fiber can be obtained from the following foods:
- carrot;
- white and cauliflower;
- beet;
- pumpkin;
- corn;
- avocado;
- flax seeds;
- banana;
- apple;
- pear;
- dried apricots;
- raisins, etc.
However, given the fact that the main clinical syndrome is abdominal pain, the primary task of medical workers is to eliminate pain through the use of pharmacological drugs. All efforts of the gastroenterologist should be aimed at reducing visceral sensitivity and normalizing intestinal motor functions. Among the most effective means of drug treatment are the following drugs:
- Cerucal® is a prescription drug in the form of a solution for intramuscular and intravenous administration from the German manufacturer AWD.pharma GmbH & Co.KG. The drug helps to increase the tone of the intestines and stomach, accelerates emptying, stimulates peristalsis and reduces hyperacid stasis. Contraindications: hypersensitivity to the active substance – metoclopramide, first trimester of pregnancy, children under 5 years of age.
The course of treatment and dosage of these pharmaceutical combinations is determined by the attending physician.
Treatment tips
As additional therapeutic measures, it is recommended to carry out:
- Physiotherapy. It includes:
- performing massage;
- enemas;
- intestinal lavage with mineral waters;
- acupuncture;
- carrying out paraffin applications.
- Taking carbon dioxide baths.
- Carrying out electrophoresis with novocaine and calcium.
In addition, it is very important to maintain proper nutrition when treating hypomotor dyskinesia. This diet includes:
- Quitting drinking alcohol and smoking.
- Avoidance of use:
- fatty foods;
- fried;
- acute;
- meat broths;
- spices and sauces;
- flour products;
- sweets;
- lard;
- canned food;
- vegetables that contain coarse fiber;
- coffee;
- garlic
- Minimize consumption of beans, mushrooms, hard cheese and potatoes.
- Replace eating white bread with rye bread.
- Eat porridge cooked in water every day.
- Drink at least two liters of water daily, not counting liquids from soups and juices.
- Drink rosehip decoction.
- Eat small portions.
- Switch to fractional meals.
- Consume vegetable oil regularly.
Important! Overeating should be avoided to prevent intestinal overload. The last meal should be no later than three hours before bedtime.
- Food should be steamed, baked or boiled.
- The menu should include fresh vegetables and herbs every day.
- Every day it is advisable to eat stewed zucchini, lean meat, fish and fruits.
Traditional medicine for intestinal dyskinesia
Along with official drug treatment, you can use proven methods of traditional medicine:
- Freshly squeezed potato or cabbage juice will improve the motility of the gastrointestinal tract and ensure high-quality transit of feces from the large intestine.
- Green tea with honey will have a relaxing effect.
- Watermelon rinds will help improve intestinal peristalsis.
Any actions to use folk remedies for the treatment of intestinal dyskinesia should be agreed with the treating medical consultant.
Features of therapeutic therapy
Treatment of hypomotor dyskinesia is carried out comprehensively depending on the severity of the patient’s condition, its symptoms, age and concomitant diseases.
Drug treatment involves taking the following groups of drugs:
- Taking medications to normalize stool.
- Taking sedatives.
- Prescription of antispasmodics (No-spa).
- Taking painkillers (Paracetmol).
- Prescription of intestinal medications (Motilium, Cerucal).
- Taking medications that improve the process of bowel movement (Duflac, Reguklax).
- Prescription of choleretic drugs (Festal, Allochol).
- Taking enzymes.
- Taking vitamin B and potassium.
Important! The use of laxatives during treatment is contraindicated.
You can also use herbal products:
- hay leaves;
- buckthorn bark;
- rhubarb.
Forecast and prevention of intestinal disorders
In general, the prognosis for symptomatic intestinal disorder is favorable, provided clinical recommendations are followed. The course of the disease will not develop complications in the form of intestinal obstruction, formation of fistulas, perforations or strictures if all the prescriptions of the attending physician are carried out by the patient in good faith. Among the preventative measures, the following must be observed:
- Monitor your own weight and nutrition.
- To live an active lifestyle.
- Avoid nervous and mental stress.
- Comply with the sanitary and hygienic rules of the hostel.
- See a doctor promptly.
When performing intestinal prophylaxis, do not forget to teach children to do this.
Dyskinesia is a pathology associated with disturbances in the motor activity of the affected organ. For example, dyskinesia of the colon of the hypotonic type suggests the absence of organic damage to this organ, however, the colon is no longer able to function normally. Due to the widespread prevalence of this unpleasant disease, interest in the disease and methods of its treatment has recently increased.
Gastric dyskinesia
A rather rare disease, it occurs mainly among newborn boys in the first months of life and is manifested by pain in the abdominal area. At the same time, it can be difficult to determine the location of the pain, since it usually has a blurred character. Often painful sensations have nothing to do with eating or nervous shock.
Symptoms
The following manifestations are typical for this type of dyskinesia:
- Heartburn. Unpleasant sensations, a burning sensation in the pit of the stomach or in the throat due to the release of acidic contents into the esophagus.
- Belching. Reflex expulsion of gases from the stomach through the oral cavity with the accompanying smell of rotten eggs.
- Vomit. Sudden expulsion of stomach contents through the mouth. The vomit is greenish in color.
- Pneumatosis. Increased concentration of gases in the stomach, characterized by distension in the abdomen and constant loud belching.
- Breathing disorder. As a result of excessive concentration of gases, the enlarged stomach props up the diaphragm, causing breathing problems and chest pain.
- Feeling of squeezing in the abdomen.
Diagnostics
Electrogastrography is considered the main method for diagnosing gastric dyskinesia. An equally informative method is fluoroscopy. Gastroscopy and esophagogastroduodenoscopy are also used.
Treatment
Treatment of this type of dyskinesia, as a rule, occurs in laboratory conditions, but for the purpose of advanced diagnostics (in case of severe pain), a gastroenterologist may refer for hospitalization. The main condition for recovery is nutritional adjustments - the child should adhere to the regime, observe the size of portions and frequency of meals.
Medicines
Sedative, neurotropic and psychotropic drugs are prescribed. Treatment of disorders of motor functions of the stomach occurs with the help of M-anticholinergics; caffeine, Proserin (for atony), and Eufillin are prescribed. Since gastric dyskinesia is often accompanied by a disorder of its secretory function, replacement therapy is prescribed - the child takes natural gastric juice, pancreatic enzyme preparations, and Acidin-pepsin.
Procedures
Physiotherapy is highly effective in this type of pathology: mud applications, electrophoresis, warming procedures, diathermy, ozokerite therapy and paraffin treatment. When determining the method of treatment, the doctor relies on the type of contractile activity disorder and the clinical picture of the disease.
General understanding of colon dyskinesia
This disease has another name - irritable bowel syndrome, spastic colitis. The basis of the pathology is disturbances in the tone and motor activity of the intestinal tract. Colon dyskinesia can lead to disruption of other gastrointestinal organs. For example, dysfunction of the esophagus, stomach and other parts may occur.
Every third inhabitant of our planet has to deal with a similar pathology. Representatives of the fair sex especially often suffer from it.
Etiology
The causes of intestinal dyskinesia are not fully understood, but most often diarrhea or chronic constipation occurs as a result of neurological disorders. It is not surprising that the disease is diagnosed mainly in the fair sex, who are less resistant to stress compared to men. Dyskinesia of neurogenic origin is a difficult to diagnose pathology and requires a special approach to treatment.
Factors that provoke a decrease in motor skills also include:
- lack of foods high in fiber in the diet;
- abuse of fatty, fried, high-calorie foods;
- decreased motor activity;
- predisposition to the development of allergic reactions;
- bacterial and viral intestinal infections;
- diseases of the endocrine system - hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus, adrenal insufficiency;
- genetic predisposition to colon dyskinesia;
- course treatment with pharmacological antibacterial drugs, anticholinergics, anesthetics;
- emotional instability.
Intestinal dyskinesia in children develops as a result of a deficiency of vitamins in the body, increased nervous excitability and disruption of the production of hormones by the endocrine glands. It is extremely rare that the cause of intestinal dyskinesia is the penetration of helminths into it.
Causes of colon dyskinesia
Among the main reasons that can provoke dyskinesia of the colon are the following:
- Psycho-emotional stress. Psychosomatic disorders are the main reason provoking the development of dyskinesia of this unpleasant disease. The motor activity of this organ is negatively affected by stress, anxiety, neuroses, and internal conflicts.
- Poor nutrition. The disease can develop due to the excessive presence in the diet of high-calorie foods and refined products that do not contain plant fiber.
- Weak physical activity, lifestyle features (sedentary activity);
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Intolerance to certain foods;
- Infectious disorders of various types;
- Disruptions in endocrine processes;
- Gynecological diseases that can provoke intestinal dysfunction in women;
- Excessive enthusiasm for medications that can have a detrimental effect on the motility of the colon;
Despite such an impressive list of reasons, the primary role belongs to hormonal imbalances that affect the state of intestinal motility.
What causes intestinal dyskinesia?
The reasons why this disease develops are not fully understood. The mechanism of formation of functional disorders has not been determined. It is believed that the development of intestinal dyskinesia is promoted by: unhealthy diet, stress, intestinal infections, endocrine pathologies, gynecological diseases, food poisoning. The main cause of dyskinesia is considered to be a disruption in the production of hormones responsible for the functioning of the digestive system. IBS often develops against the background of dysmenorrhea, obesity, and diabetes mellitus.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of dyskinesia are very diverse. There are several basic ones by which pathology is recognized.
- The appearance of pain in the abdominal area. Moreover, they can be paroxysmal, constant, cutting or dull in nature. They are usually localized in the navel area. After eating, during stress or emotional turmoil, pain may intensify. The pain usually goes away after the passage of gas or defecation. A characteristic feature of this pathology is that the pain completely disappears at night and returns in the morning.
- Flatulence. The appearance of this symptom is typical in the evening or before defecation. It is possible that pain and rumbling in the abdominal area may occur.
- Problems with stool. As a rule, constipation alternates with short bouts of diarrhea. It happens that mucus comes out along with the feces.
- There is a feeling that the stomach is swollen, bursting, and heaviness appears. Nausea and belching of air may occur.
- Psychoneurotic disorders. You can learn about them by manifestations of depression, anxiety, and nervousness.
Symptoms and manifestations of hypomotor dyskinesia
Most often, this disease manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- Insomnia.
- Obesity.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Mental disorders (development of depression, nervousness, frequent anxiety)
- The appearance of pain in the area of the heart or spine, even when they are completely healthy.
- Mucous discharge during defecation.
- Flatulence.
- Belching.
- Feeling of heaviness in the stomach.
- Feeling of fullness in the abdomen.
- Abnormal stool (diarrhea, diarrhea, constipation).
- Bloating.
- Frequent nausea.
- Cutting pain in the abdomen, which can be of varying intensity. Also, the pain can be cramping and paroxysmal. Sometimes they can get worse after eating or stress.
Dyskinesia is also characterized by the absence of pain at night and its appearance immediately after waking up.
Types of dyskinesia
There are two types of dyskinesia, each of which has its own characteristics.
- Hypertensive dyskinesia of the colon involves the presence of increased hypertonicity and spastic contractions of the intestine. The result is the appearance of colic and constipation, which progresses. Cramping pain appears, localized mainly in the inferolateral and lower abdomen. Typically, this type of disease develops in those who suffer from foodborne illnesses or eat foods that are incompatible.
During the examination, abdominal bloating may be noted, the patient’s mouth smells unpleasant, and a white coating appears on the tongue.
If we are talking about the hypertensive type of pathology, the development of fecal incontinence is possible.
- Hypotonic dyskinesia is characterized by the fact that the patient suffers from weakened peristalsis and intestinal tone. The result is not long in coming and is manifested by constipation, pain, bloating, and heaviness.
Most often, the patient has problems determining the exact location of the pain.
As a result of a reduced level of peristalsis, metabolic processes in the body slow down, resulting in excess weight gain. In this case, defecation occurs rarely, the volume of feces is small, but a lot of gases are released. During bowel movements, the intestines are not completely emptied. Stagnant feces can lead to intoxication of the body.
Intestinal motility may weaken if a strict diet has been followed, as well as due to low physical activity or excessively sparing nutrition.
Important! Hypomotor dyskinesia of the colon can provoke such a dangerous complication as intestinal obstruction, requiring immediate surgical intervention.
In very rare cases, a mixed type of dyskinesia occurs.
Pathology in pregnant women
Intestinal motility disorders often occur in pregnant women. Heavy loads due to the characteristics of this period affect the general condition of the patient. The digestive function also suffers, which has to adapt to new conditions.
According to statistics, about 70% of pregnant women experience dyskinesia.
The hormone progesterone is of great importance. It affects the development of the fetus, but at the same time, the tone of the intestinal muscle tissue decreases, resulting in impaired peristalsis and problems with bowel movements. A sedentary lifestyle makes the situation worse.
Symptoms during pregnancy do not differ from typical signs of dyskinesia: pain, problems with bowel movements and a feeling of heaviness in the stomach. However, these signs can frighten a woman, which will affect her psychological state, which is especially undesirable with an increased risk of miscarriage.
When selecting medications and other agents, the degree of their impact on fetal development is taken into account.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosing dyskinesia is not an easy process. Based solely on the patient’s stories, it is very difficult to draw conclusions regarding the nature of the disease, because many deviations in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract have similar symptoms. Diagnostic measures involve more than one stage in order to exclude the possibility of other types of pathologies. In this case, one cannot do without laboratory and instrumental research methods.
From the laboratory, a blood test is required, and stool is examined for hidden blood and dysbacteriosis. A scatological analysis will also have to be done.
Instrumental diagnostic methods are widely used. Irrigoscopy, fibrocolonoscopy, and endoscopic tests are performed, during which the doctor takes a tissue biopsy. This is necessary to exclude tumor formations of malignant etiology, which X-ray signs will help to draw a conclusion about.
Typically, in patients experiencing dyskinesia, tumors are not detected, but weakened peristalsis or intestinal hypertonicity and dysbiosis are detected.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of dyskinesia is a complex and multi-stage process. The child undergoes the following tests:
examination and palpation of the internal organs of the gastrointestinal tract;
- internal examination of the intestine using an endoscope;
- taking stool for analysis;
- irrigoscopy and biopsy (to clarify the form and severity of the disease);
- collection and analysis of medical history (questioning parents to determine the child’s diet and daily routine).
During diagnosis, the doctor carefully examines the symptoms. It is important for him to consistently exclude the development of concomitant diseases in order to accurately determine the cause and make a diagnosis.
Treatment of intestinal dyskinesia with medications
When giving preference to one or another method of treating pathology, it is necessary to take into account a number of important factors. Namely:
- type of dyskinesia;
- main symptoms;
- reasons that provoked the development of the disease.
Treatment of dyskinesia should be comprehensive and include not only conservative drug therapy, but also adjustments to diet and lifestyle, physiotherapeutic procedures, psychotherapy, and therapeutic exercises.
Treatment with medications consists of taking medications prescribed by the doctor, designed to normalize stools and regulate intestinal activity. In addition, patients should simultaneously take psychotropic and sedatives.
If we consider a physiotherapeutic technique, we can highlight acupuncture, paraffin baths, and enjoy oxygen and pine baths. In addition to these procedures, patients receive massage.
Patients facing this unpleasant disease are recommended to drink mineral water. Moreover, if the patient is confirmed to have a hypotonic type of pathology, then he should take highly mineralized water. The hypertonic type involves medicinal water with a low degree of mineralization. Water should be consumed an hour before meals, always warm and without gases.
In addition, patients are recommended to engage in therapeutic exercises containing relaxation exercises. You can improve your well-being through hydrotherapy procedures, warm radon and carbon dioxide baths.
Drugs prescribed for hypotonic dyskinesia should be aimed at having an enhancing effect on peristalsis and motor functions of the intestinal tract. Your doctor may prescribe laxative medications to increase the volume of your stool and make it easier for you to empty your bowels.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic measures include taking oxygen and pine baths. Acupuncture and paraffin treatment are effective. Along with these procedures, therapeutic massages and an enema with mineral water are widely used. The patient is recommended to drink mineral waters throughout the day. It is worth considering that in case of hypertonic dyskinesia of the large intestine it is recommended to drink water with a low degree of mineralization, in case of hypotonic dyskinesia - with a high degree.
Diet food
For a speedy recovery, the patient is recommended to follow a diet that includes vitamins, essential trace elements and minerals. The daily diet should include foods that stimulate the motor activity of the characteristic organ. Foods that contribute to excess gas formation should be avoided.
If you have dyskinesia, you should stick to proper nutrition.
Following the principles of a balanced diet will help get rid of the discomfort caused by dyskinesia and improve the quality of life. Any dish needs to be steamed or boiled. It is advisable not to grind the products too much. To restore normal motor function, the menu should include fresh fruits and vegetables that do not linger in the intestines.
Different types of digestive disorders require an individual approach to diet. For patients with hypotonic dyskinesia, the menu should include foods rich in fiber. But food containing essential oils (onion, parsley, dill) should be excluded from the diet.
It is allowed to eat lean meats. Products containing live bifidobacteria are useful. To make bowel movements regular, it is recommended to eat cold food.
In the case of hypertensive dyskinesia of the large intestine, the approach to diet is somewhat different. People need to consume more vegetable oils, exclude bread, fatty meat and fish, and strong tea or coffee from their diet. You should avoid foods rich in fiber, as they increase the contractile activity of the characteristic organ, causing pain.
Physical activity
In combination with dietary nutrition for dyskinesia, it is recommended to engage in physical therapy. It helps improve the patient's health and well-being. But before starting physical exercises, it is necessary to consult a doctor conducting treatment. He will tell you what you should focus on first. If you perform physical activity incorrectly, you can harm the body and worsen the condition.
If you have dyskinesia, you should do physical therapy
Treatment of dyskinesia with traditional methods
To eliminate an unpleasant pathology, you can also use folk remedies, but only after the approval of the treating doctor has been obtained.
- Irritable bowel syndrome can be eliminated by drinking a glass of cabbage or potato juice every morning.
- A medicinal decoction will help normalize intestinal activity and eliminate constipation. To prepare it, you need to prepare a decoction based on lingonberry berries, rhubarb, buckthorn, hay leaves and Alexandria leaves.
- A decoction based on raisins, dried apricots, and boiled beetroot salad are excellent laxatives.
- Compresses made with vinegar are designed to relieve pain in the abdominal area. 100 ml of this product is diluted in 3 liters of water. A piece of gauze is soaked in the prepared composition, which is then applied to the problem area for 1.5 hours.
- With the help of a sedative infusion of herbs, you can get rid of intestinal hypertonicity. To prepare it, you need to take equal quantities of sage, mint, motherwort and yarrow leaves, St. John's wort flowers and oak bark. 2 tablespoons of this herbal mixture are poured with 200 grams of boiled water. The decoction should steep for 2 hours. Strain the finished drug. Drink a third of a glass in the morning, lunch and evening for 7 days.
Nutrition for intestinal dysfunction
The basis of therapy for any intestinal problems in children is a balanced diet. It is useless to try to treat dyskinesia with medications alone, because without following a special nutrition program it is impossible to achieve a positive result. When forming a diet for a sick child, factors such as the quality of food and cooking methods must be taken into account.
It is important to follow the following recommendations:
In addition to drug treatment for intestinal problems, you need to focus on proper nutrition
Drug treatment
After the diagnosis, the doctor decides to prescribe drug therapy. Usually, children with dyskinesia are given enzymatic agents, vitamins, sedatives and choleretic drugs. If a child complains that his stomach hurts a lot , parents can give him some of the antispasmodics (No-shpa, Papaverine) in a dosage appropriate for his age. It is not recommended to give other medications to children on their own.
Gymnastics
A special set of exercises helps improve intestinal motility of a sick child. For atonic type dyskinesia, therapeutic exercises are aimed at strengthening the abdominal muscles. The complex includes walking and breathing warm-up - the emphasis is on mastering diaphragmatic breathing techniques. Imitation of cycling and exercises to change body position help well with intestinal atony.
In spastic forms of the disease, the emphasis of the therapeutic gymnastics complex is on relieving spasms. Therefore, all exercises are performed at a slow pace with limited range of motion. A specialist from the exercise therapy department should draw up a training program and select exercises that are appropriate for the age of the sick child.
Traditional methods of treatment
Medicinal herbs are widely used to treat dyskinesia in children. The natural medicine is completely harmless to the child’s body and quickly normalizes intestinal activity. From herbs you can prepare decoctions, infusions, and medicinal teas. The list of useful herbs includes:
- chamomile,
- senna,
- mint leaves,
- oak bark,
- valerian root,
- buckthorn bark and other natural ingredients.
Any traditional recipe must be agreed with your doctor. The specialist will advise which composition is most suitable for the sick child.
It is worth remembering that different ingredients are used for spastic and atonic forms. The dosage and regimen for taking medicinal formulations should also be determined by a medical professional.
But if the main symptom of dyskinesia suddenly manifests itself at home - spastic colic, parents can do the following:
Chamomile, familiar to everyone, can relieve a child of intestinal problems. The main thing is to know how to prepare the decoction
Prevention of dyskinesia
The main rule to avoid dyskinesia is to monitor your daily diet. Nutrition should be thoughtful and balanced. You will have to give up harmful addictions completely.
Any traumatic manifestations must be discussed with a psychotherapist.
Important! You should not prescribe treatment for yourself. Only a specialist is able to establish an accurate diagnosis and determine the correct therapy.
Colonic dyskinesia is a disease that does not pose a direct threat to life, but is unpleasant and slowly undermines a person’s vitality. Knowing how to treat an unpleasant illness, it will be possible to eliminate the pathology in a timely manner, thereby increasing the quality of life.
Work experience more than 7 years.
Professional skills: diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and biliary system.
>
Prevention measures
The goal of prevention is to prevent the development of pathologies and complications. You must adhere to the following recommendations:
- lead a healthy lifestyle: give up addictions and play sports;
- organize proper nutrition;
- strengthen the immune system;
- rest properly;
- normalize metabolism;
- avoid stressful situations.
Intestinal dyskinesia is dangerous due to its complications, therefore, if specific symptoms occur, it is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible and undergo a course of treatment.
Features of dyskinesia during pregnancy
Intestinal dyskinesia occurs in almost every pregnant woman. This is due to both psychological factors and the effects of progesterone, which weakens the tone of the intestinal wall. In addition, the body and its enzyme systems have to adapt to new conditions and increased stress.
Pathology in pregnant women is most often manifested by constipation, heaviness in the stomach and pain. With a severe course of this disease, there may be a risk of miscarriage, since the spastically contracting intestines will irritate the uterus, and the urge to defecate and straining will increase pressure on the fetus. Therefore, at the first symptoms of the disease, you should consult a doctor.
The difficulty of therapy in pregnant women is that many drugs are contraindicated during this period. Among the methods that can improve well-being are:
- drinking at least 1.5 liters of fluid per day;
- a glass of water in the morning on an empty stomach;
- moderate physical activity;
- proper and regular nutrition;
- wearing a bandage.
A pregnant woman should strive to regulate her bowel movements and, if possible, have bowel movements at the same time.
Classification
The classification is based on the Bristol stool scale, which indicates the fact that the longer it takes for stool to pass through the intestines, the denser the stool becomes. However, the gastroenterologist should pay close attention to the patient’s complaints, because diarrhea and constipation often mean a change not in stool consistency, but in the frequency of bowel movements. There are four main clinical forms of intestinal dyskinesia:
- With constipation
. More than a quarter of all bowel movements involve the passage of dense, fragmented stool; less than a quarter have diarrhea. - With diarrhea
. More than a quarter of cases of defecation are with loose stools, less than a quarter are with dense stools. - Mixed
. Both hard and loose stools occur in more than 25% of cases). - Unclassifiable
. Changes in stool consistency are not sufficient to verify any of the above forms of the disease.
There is also a division of the disease according to symptoms: with a predominance of intestinal symptoms, pain, and flatulence. According to etiology, post-infectious dyskinesia associated with the consumption of certain foods or stress is distinguished.
How to treat correctly
Treatment of gastric dyskinesia in an infant begins with adjusting the level of enzymes that contribute to the functioning of the digestive system. For this purpose, medications are prescribed that contain protein elements. For children over five years old, it is important to add infusions based on medicinal herbs to their diet. The most effective plants are St. John's wort, bittersweet, and tansy.
To normalize intestinal motility, the child is prescribed Metoclopromide . If acute abdominal pain causes discomfort to your baby, you need to take No-shpu or Drotaverine. These are two drugs that have the same effect. Drotaverine is an analogue of No-shpa. Medicines belong to the group of myotropic antispasmodics.
Action of No-shpa
The active component is drotaverine hydrochloride, which is included in the drug in an amount of 40 mg. The product is produced in the form of yellow tablets or solution for injection. The action of the drug is aimed at instantly eliminating spasms in the body. No-spa helps to dilate blood vessels and reduce muscle tone in internal organs.
The components contained in the composition do not affect the child’s central nervous system. Young children are not given No-shpa in tablet form, but are administered intramuscularly. The dosage is set individually, depending on age. The drug is not prescribed to children under six years of age.
Drotaverine for children
Drotaverine contains drotaverine hydrochloride in an amount of 40 mg. The drug helps children eliminate spasms in the smooth muscles of the intestines and internal organs. This occurs by reducing muscle tone and reducing the supply of calcium ions.
Drotaverine is an effective and efficient drug that has virtually no contraindications for use. The drug, like No-shpa, is not prescribed to children under six years of age. Dosage and method of application are prescribed individually.
It is strictly forbidden to buy antispasmodics for children on your own. If intestinal colic does not manifest itself intensely, you can try applying a warm compress to the stomach. Treatment is recommended using a rubber heating pad filled with hot water.
Traditional medicine
Treatment of children with traditional medicine is recommended only after consultation with a pediatrician. This therapy is most effective when combined with medications. Traditional medicine recipes:
- To improve the functioning of intestinal motility, the child is given a tincture based on valerian roots, chamomile flowers and mint leaves. The medicine is easy to prepare at home. You can buy plants at the pharmacy. To make an infusion, you need to take valerian root, chamomile flowers and mint leaves one tablespoon each. The dry mixture is poured with two glasses of boiling water. Infusion time is 20-25 minutes. You need to strain the broth and give the child 100 ml 3 times a day before meals.
- Recipe for the second decoction: take a tablespoon of oak bark, sage, St. John's wort and motherwort. Pour everything over with two glasses of boiling water. You need to drink 100 ml 4 times a day. This medicine will help quickly eliminate the negative symptoms of dyskinesia.
All traditional medicine can be used if the child does not have an allergic reaction to medicinal herbs. You need to take the decoction at regular intervals.
Causes
Constant consumption of dry food is a provocateur for the development of the disease.
Common provocateurs for the development of gastric dyskinesia are nutritional factors, such as:
- disruptions in eating patterns and nutritional quality;
- constant consumption of dry food;
- hasty consumption of food, which disrupts the process of its complete processing by gastric juice;
- excessive predominance of carbohydrates;
- deficiencies in vitamins, minerals, proteins or other important microelements;
- abuse of peppery and fatty foods.
Motor impairment may be associated with exogenous factors:
- toxic effects of chemicals, alcohol, tobacco, drugs;
- a sharp increase in ambient temperature, burns.
Internal provocateurs for the development of pathology include:
- food allergies, most often to dairy products, fish, eggs;
- various pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (cholecystitis, enteritis, viral hepatitis);
- cardiovascular disorders (myocardial infarction, hypertensive blood pressure disorders);
- autoimmune condition (rheumatism);
- pathologies of the nervous system (the result of chronic stress, stroke, encephalitis);
- diseases of the kidneys, endocrine glands, lungs, if the problem lies in the improper production of enzymes and gastrointestinal hormones.
In children, dyskinesia is often caused by helminths.
What is therapy?
If dyskinesia in an infant is indicated by symptoms characteristic of this pathology, then the doctor begins treatment by eliminating the main causes. First of all, the balance of food enzymes is corrected. For this purpose, the child is prescribed special medications that can compensate for enzyme deficiency. Drug treatment is aimed at relieving pain and other symptoms that negatively affect the general condition of the child.
When treating older children, the therapeutic complex is based on creating an adequate nutritional regimen for a particular child. In this case, a dietary diet implies adherence to a strict meal schedule. Often the treatment complex is supplemented by physiotherapeutic procedures and therapeutic exercises. When developing a treatment program, doctors attach great importance to organizing the child’s active leisure time and sleep patterns.
Diet
For any form of the disease, be it dyskinesia of the stomach, intestines, biliary tract or other organs, you must follow the following diet:
- food intake is carried out fractionally (in small portions), overeating should be avoided;
- you need to eat 5-6 times during the day;
- Spicy, smoked, fatty foods, foods with spices, etc. are not recommended;
- alcoholic beverages are prohibited;
- You should limit your consumption of foods high in fiber (vegetables, berries and fruits, bread, cereals and pasta, legumes and nuts).
To restore normal function and balance, it is recommended to follow a more restrictive diet for two weeks, consuming food only in chopped or pureed form (minced meat); dilute fruit juices with water, and exclude vegetable juices from the menu; add chopped greens.
Species categories
The disease, depending on the impairment of motor functions, has two main types.
Hypotonic dyskinesia
The pathological process, which occurs in a hypotonic type (atonic), causes a significant weakening of the tone of the colon and its peristalsis. This, in turn, provokes stool retention and the following symptoms:
- aching dull pain without specific localization;
- heaviness and feeling of fullness in the intestines;
- significant weight gain caused by a slow metabolic process;
- rare bowel movements and excretion of feces in small quantities leads to increased gas formation, intoxication and the development of allergic reactions.
Hypomotor dyskinesia contributes to the development of hemorrhoids and dilation of veins in the pelvis. The disease, which occurs in a hypomotor type, often leads to intestinal obstruction.
Hypertensive appearance
Pathology developing according to the hypertensive type (spastic) is characterized by increased tone and spastic contractions of the colon. They provoke:
- Intestinal colic and prolonged constipation.
- Paroxysmal pain, localized in the lower abdomen and lower lateral zones. The pain goes away after defecation.
- Excretion of feces in large quantities becomes a prerequisite for an increase in the volume of the colon, which subsequently becomes the cause of involuntary bowel movements.
Spastic dyskinesia is accompanied by other characteristic symptoms:
- bloating, flatulence;
- pungent odor from the mouth;
- formation of fecal stones;
- the appearance of a white coating on the surface of the tongue.
In most cases, the disease “starts” after poisoning and infectious diseases, accompanied by severe intoxication.
Features of dyskinesia in children
The etiology of the disease in childhood almost always has a neurogenic basis.
The disease is more complex than in adults . Children have a harder time with changes in bowel movements from diarrhea to constipation and vice versa.
The most noticeable symptom of illness in a child is acute pain. It is sometimes difficult to eliminate it even with strong painkillers.
In most cases (excluding severe diarrhea and intoxication), it is possible to save a child from suffering by adjusting the diet.
Clinical picture
Intestinal dyskinesia occurs in humans regardless of age, but children most often suffer from the disease. The disease can occur in the following forms:
- Hypomotor dyskinesia is accompanied by constant constipation.
- Hypermotor dyskinesia is caused by the rapid pushing of stomach contents into the intestines, all of which is accompanied by diarrhea and pain.
In a 9-year-old child, intestinal dyskinesia may indicate another hidden disease, for example, pathology is often a consequence of chronic pancreatitis. The fact is that a lack of bile impairs the processing of fatty foods; as a result, the child will not only have liquid stool, but it will also be possible to see mucus impurities in it.
Recognizing the disease is sometimes difficult, because it has similar symptoms to other pathologies of the stomach and intestines.
Intestinal dyskinesia and its symptoms in children
Nervous overexcitation and disorders are a direct indication for the disease in children, since then spasms occur in the intestines due to disturbances in the conduction of nerve impulses. The hypermotor form at the time of diagnosis by doctors is defined as the more common irritable bowel disease. After this, they begin to treat IBS, and accordingly there are no positive results. Complications begin. For a child, the main symptom is constipation, which is not typical at their age, and spasms. Fatigue, weight loss, lethargy.
Types of functional disorders of the stomach
The condition can be triggered by changes in the volume of the stomach, vertical or horizontal position of the organ. Due to this, pathology is usually divided into primary organ prolapse, which develops in utero, and secondary, which occurs after a certain mechanical pressure, for example during pregnancy and after it. In case of a secondary disorder, the patient may exhibit symptoms such as acute atony, paresis of the corresponding muscles, while the gastric walls begin to contract and stretch with a reflex. This phenomenon occurs during myocardial infarction, inflammation in the abdominal cavity, pneumonia, after surgery and various injuries.
Dyskinesia also develops secondarily with pneumatosis of the digestive tract, which occurs as a result of gas formation associated with the waste products of many bacteria. Thus, the contractility of the organ walls is impaired. There are types of disease - hypertensive dyskinesia, characterized by too active contraction of the walls, hypotonic - with slow contraction, and atonic, when any motor functions are absent.
Based on clinical symptoms, nosology is divided into pain, dyspeptic and mixed. Depending on the etiological factor, the disorder can be exogenous, that is, as a result of exposure to external factors, and endogenous, in the presence of internal changes. Depending on the course of the disease, there are options:
- Development of cardiospasm, manifested by impaired swallowing function and chest pain.
- Spasms of the pyloric part of the stomach, due to which the evacuation function does not work properly. It manifests itself as a feeling of discomfort in the epigastric region and belching with an unpleasant sour odor.
- Tetanic spasms are convulsive contractions that bring acute painful sensations to its owner.
- After surgery, decreased muscle tone of the organ, systematic overeating, and flatulence, an expansion of the organ cavity occurs, which leads to disruption of peristaltic function.
- With rapid absorption of food, large volumes of air are swallowed.
Diagnostic criteria for the disease
The main task of diagnosis is to exclude organic changes in the stomach in the presence of clinical symptoms. A gastroenterologist, based on patient complaints and the nature of the pain, assumes the development of hypertonic or hypotonic dyskinesia, identifies the cause and helps in selecting the correct diet, work and rest, and prescribes treatment. The doctor conducts an examination, palpates the abdomen, and the patient experiences pain and discomfort.
With deep palpation, in the absence of peristalsis, an expansion of the size of the organ is detected. Hypotonic and hypertensive dyskinesia is detected by electrogastrography. The method is based on the occurrence of electrical potential when contractile activity of muscle fibers occurs. If there are changes, the electrogastrogram will show a different result of the examination over a certain time.
The most accurate method is fluoroscopy of the stomach using contrast agents, such as barium suspension. Thanks to the method, it is possible to distinguish hypotonic dyskinesia from hypertensive or complete atony. The study shows the development of gastroesophageal reflux (return of a bolus of food from the stomach into the esophagus), a change in the topical location of the stomach, and spasm of a certain part of the organ.
The gastroscopy method helps to see changes in the mucous membrane, manifested by thickening of the folds. During the examination, attention is paid to the occurrence of a spasm when a small amount of air is introduced. A small amount of the latter can provoke spasms during dyskinesia. When performing EGDFS, biological material is necessarily taken for histological examination (biopsy). The result will show the absence of changes at the cellular level, which will confirm the diagnosis.
Symptoms
The main clinical manifestation of the pathology is a change in the consistency and shape of stool. Feces may look like:
- separate and solid fragments;
- formed but fragmented feces;
- formed feces having a heterogeneous consistency;
- serpentine “sausage” shape with a smooth and soft surface;
- soft fragments with smooth edges;
- unstable fragments with uneven edges;
- watery stool.
Hypomotor type dyskinesia has the following symptoms:
- dull painful spasms in the abdominal area that are not clearly localized;
- absence of stool passage for 3 or more days;
- feeling of fullness and heaviness in the abdomen;
- increased gas formation;
- overcrowding and insufficient bowel movements;
- signs of intoxication of the body;
- nausea, rarely leading to vomiting;
- weight gain;
- development of allergic reactions to fermented milk products and cereals.
Hypermotor or spastic dyskinesia has the following symptoms:
- progressive and persistent violation of the act of bowel movement, which is expressed by alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- intestinal colic;
- cramping pain localized on the sides of the lower sections of the anterior wall of the peritoneum;
- bloating;
- bad breath;
- the appearance of a white, yellowish or grayish coating on the tongue;
- flatulence;
- formation of fecal stones;
- rumbling in the stomach.
Symptoms of intestinal dyskinesia of a non-gastroenterological nature:
- constant feeling of anxiety;
- fatigue and weakness;
- tendency to depression or apathy;
- frequent mood changes;
- sleep disorders.
In children, the clinical picture of the disease has some peculiarities. Intestinal dyskinesia is expressed by the following symptoms:
- severe pain in the abdominal area;
- frequent regurgitation in infants;
- lethargy and weakness;
- emotional instability;
- apathetic state;
- poor appetite;
- pale skin;
- gradual loss of body weight;
- anemia;
- dehydration;
- convulsive seizures.
Why does intestinal dyskinesia appear?
Most pediatric doctors say that digestive problems in a young child are most often directly related to poor nutrition. When a child does not eat enough fiber, a disease called colon dyskinesia gradually begins to develop. In children, the main cause of this disease is infection of this digestive organ. Parents are obliged to promptly respond to the initial symptoms and consult a specialist, otherwise, in the end, one disease can lead to serious complications.
The whole essence of the disease is that the contents of the stomach are quickly pushed into the intestines and specific pain and diarrhea appear. There are cases when, on the contrary, the baby may suffer from constant constipation. An accurate diagnosis can be made by a professional doctor who will carry out the necessary diagnostics and determine the cause of the disease.
How to diagnose?
Only a gastroenterologist can make a correct diagnosis, who will identify the causes of the pathology, establish the nature of changes in motility and prescribe additional, clarifying diagnostic procedures. Among them are:
- Inspection and palpation. When palpated, abdominal pain is determined. If atony is present, percussion reveals the expansion of the organ.
- Electrogastrography. The procedure is used to determine electrical potentials during muscle contraction of a diseased organ. With dyskinesia, strong variability of results is determined.
- X-ray. The method allows you to determine spasm or hypotonic syndrome, pylorospasm or cardiospasm, peristaltic dysfunction, gastroesophageal reflux disease, prolapse.
- Gastroscopy. The technique is based on visual inspection of the upper organs of the digestive tract (from the esophagus to the duodenum) using a flexible probe equipped with a camera. Examination reveals thickening of the folds of the gastric mucosa.
- Biopsy. The procedure is carried out together with gastroscopy using a probe to collect tissue from suspicious areas, which will subsequently be examined in the laboratory for organic disorders.
Main manifestations
Common symptoms for all types of intestinal dyskinesia are:
- Pain syndrome. The pain can be sharp, aching, stabbing, or dull. They intensify when eating and are localized mainly in the umbilical region. Unpleasant sensations disappear after defecation, passing gas and at night.
- Nausea, bloating, feeling of fullness in the intestines, belching.
- Flatulence. It occurs in the evening and is accompanied by rumbling.
- Weight gain.
- Incomplete emptying of the colon after defecation.
- Abnormal stool. Most often it manifests itself as constipation, which can be followed by diarrhea. At the same time, mucus is abundantly released along with feces.
- Neurological disorders (mental). Expressed in drowsiness, loss of appetite, anxiety, decreased performance.
With duodenal dyskinesia, vomiting occurs with an admixture of bile and mucus; painful sensations are localized in the right hypochondrium and are most pronounced in the evening.
Symptoms of spastic and atonic dyskinesia - table
| Spastic dyskinesia | Hypotonic dyskinesia |
|
|
Physiotherapy for the treatment of dyskinesia
Physiotherapeutic methods have a positive effect in the treatment of gastric dyskinesia, helping to relieve spasms and pain.
Main events:
- electrophoresis in the stomach area with novocaine helps relieve pain;
- mud applications;
- warming procedures (ozokerite, paraffin therapy, etc.);
- diathermy - hardware warming and stimulation of blood circulation using high-frequency alternating current, which promotes tissue restoration;
- baths based on mineral water;
- UHF and microwave.
During the therapy period, doctors advise patients to avoid all negative factors that can cause a worsening of the condition. These include, first of all, violations in the dietary menu and nervous tension. It is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right and avoid any stressful situations.
Causes and risk factors
The main cause of intestinal dyskinesia is considered to be acute or chronic stress. Persons with a neurotic character, a tendency to somatization, increased anxiety, and emotionally unstable individuals are more susceptible to pathology.
Risk factors include:
- genetic predisposition;
- acute infectious intestinal diseases (in particular, those caused by Campylobacter and Shigella);
- endocrine disorders;
- pathologies of the central and peripheral nervous system (neoplasms and spinal cord injuries, syringomyelia, parkinsonism);
- diseases of the urogenital tract;
- poor nutrition (including eating too quickly, irregular meals, eating excessively spicy, fatty, hot foods);
- excessive mental stress;
- overweight;
- individual intolerance to certain foods;
- irrational use of medications (especially antibacterial, diuretic, psychotropic drugs);
- bad habits.
Folk remedies for intestinal dyskinesia
Harmless treatment of spastic and atonic colitis is carried out using folk remedies. Mint leaves, chamomile flowers, and valerian roots contribute to the restoration of normal peristalsis of the tract. The components take 1 tsp. each, pour a glass of boiling water over the phyto mixture and leave covered for 20 minutes. The napar is filtered and given to the child 3 times. 100 ml per day half an hour before meals.
Another remedy is obtained from sage and yarrow herbs, oak bark, St. John's wort flowers, and motherwort raw materials. The amount of each ingredient is 2 tbsp. l. The collection is doused with a glass of boiling water and allowed to brew for a couple of hours. Then the drug is filtered and the child is given 4 rubles. per day, measuring 100 ml of drink each time.
- Organize bowel movements in a timely manner if your baby suffers from constipation. Difficulties with the excretion of feces entail not only dyskinesia - their danger lies in general intoxication of the body, loss of appetite and decreased performance. Improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract contributes to stagnation and rotting of food masses, which can subsequently cause the child to develop allergies.
- If dyskinesia causes a frequent urge to defecate, give your baby a decoction of chamomile and calendula flowers, thick jelly or a hard-boiled egg. Specific treatment for intestinal disorder will be prescribed by your pediatrician.
- To relieve spastic colic, use compresses. Apply a bandage soaked in vinegar solution to the intestinal area. The ratio of acidic product and water is ½ cup to 3 liters. If you have the opportunity to give your child a pine bath, be sure to take advantage of it. Treat yourself with paraffin applications.
Prevention of intestinal dyskinesia for children is to create a favorable atmosphere in the family, avoid stress, and eat high-quality foods without dyes, preservatives and flavoring additives. If you have constipation, it is important to limit your intake of rice in your diet.
Pathological changes in the digestive tract in children begin as a result of poor nutrition. More often, violations are recorded in children whose diet is not rich in fiber. Against the background of infectious intestinal diseases, primary intestinal dyskinesia occurs in children, the symptoms and treatment of which we will consider in more detail. The secondary form of the disease is caused by a disease of any organ of the peritoneum. Intestinal dyskinesia in children, symptoms and timely treatment will help get rid of the disease.
Possible complications
Among the negative consequences of the disease are:
- bowel prolapse, which can only be treated surgically;
- intestinal obstruction;
- intoxication;
- cholelithiasis;
- diseases of the liver, pancreas;
- gastritis, damage to the mucous membrane.
It is possible to avoid serious consequences with careful attention to health and timely seeking medical help. Self-medication only leads to a protracted course of the disease and complications.
Features of the disease in children
Pathology is often diagnosed at a young age.
Parents need to pay attention to the characteristic signs of the disease:
- constant alternation of periods of diarrhea and constipation;
- pronounced gas formation, bloating;
- frequent regurgitation;
- decreased appetite;
- pale skin;
- weight loss;
- anemia;
- dysbiosis.
Treatment should only be prescribed by a qualified specialist. To slightly reduce discomfort, you can offer your child:
- a warm heating pad on your tummy;
- cranberry jelly (for diarrhea).
In addition, it is important to establish proper and regular nutrition, teach the child to follow a daily routine and review physical activity.
Dyskinesia can occur even in children
General manifestations
Dyspeptic symptoms: nausea, loss of appetite, feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, belching of air. Neurotic disorders. Symptoms of intestinal dyskinesia disrupt a person’s usual way of life, leading to increased irritability and emotional lability. In severe cases, depressive changes develop, sleep is disturbed, and a person’s performance decreases. A person focuses on his problem, trying to find signs of a malignant neoplasm in the symptoms.
Dysbacteriosis. Existing changes in intestinal function lead to the growth of pathogenic microflora in the intestine and the development of inflammatory changes and the addition of infections. All clinical manifestations of intestinal dyskinesia can be divided into three groups. The first includes signs related directly to this organ, the second category includes symptoms characteristic of other organs of the digestive system, and the third includes non-gastroenterological expressions.
Intestinal signs include: pain in the abdominal area - pain with an organic disorder will never be expressed at night. The pain syndrome can be dull, aching, dagger-like and periodic in nature, and the patient will not always be able to indicate the location of the pain syndrome. Often, the intensification of pain is associated with food consumption, and its easing is associated with the act of bowel movement; increased gas formation - very often increases in the evening, after dinner; chronic constipation; profuse diarrhea is a characteristic symptom of dyskinesia of the hypertensive type.
Most often it occurs after breakfast. It is noteworthy that patients complain of a feeling of fullness in the intestines. Pathological impurities of blood and pus are not typical for such a disease, but at the same time, the presence of mucus is noted quite often.
The second group of clinical signs includes:
- increase in abdominal size;
- release of unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- coated tongue with a white or yellowish-white tint;
- feeling of abdominal distension;
- nausea and belching;
- the appearance of a characteristic rumbling sound.
General symptoms of intestinal dyskinesia: gaining excess body weight, despite poor appetite; the appearance of allergic reactions - occurs due to incomplete bowel emptying and stagnation of feces; increased anxiety; headaches and dizziness; development of nervousness and depression; pain in the spine; feeling of lack of air; internal trembling.
Infants and young children, in addition to the above symptoms, may experience the following signs: pale skin; refusal to eat; slight increase in temperature; decreased physical activity; general malaise.
Due to the fact that all of the above manifestations are not specific and are characteristic of a large number of other gastrointestinal pathologies, it is not possible to independently diagnose and cure the disease.
Characteristics of the disease
The main function of the stomach is to accept food from the esophagus, digest it and push the resulting mass further into the intestines. Therefore, disruption of its work is expressed in a slowdown in the passage of food during contraction of smooth muscles. Typically, the stomach muscles make wave-like movements directed from top to bottom.
And with gastric dyskinesia (lat. dyskinesia; gaster), the food entering it moves in the opposite direction. As a result of improper functioning of the organ, the patient experiences unpleasant sensations: nausea, belching and vomiting.
At this time, the bile produced by the liver, after passing through the gallbladder, during contraction with the correct reflexes of the ducts, enters the stomach through a special passage - the sphincter. Here it is mixed with the contents (food, etc.) so that after digestion it enters the intestines. A violation of this sequence occurs when the sphincter contracts incorrectly. This is possible with diseases of the bile ducts, liver or dyskinesia: bile accumulates in the stomach and, when released back, enters the esophagus and oral cavity. The result is a feeling of bitterness in the mouth (heartburn).
Most often, the diagnosis of Dyskinesia is made in children and young people, as well as in patients with functional and organic diseases of the central nervous system.