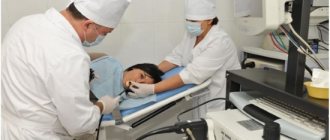
Sore throat after gastroscopy is a common complaint among people who have undergone the procedure. FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy) or gastroscopy is a procedure for examining the stomach and esophagus (gastrointestinal tract). Send for analysis if gastritis, duodenitis, tumors and bleeding in the duodenum, peptic ulcer, gallbladder disease, hepatitis are suspected. The procedure is considered unpleasant, patients are afraid to undergo it, including due to painful sensations for a number of days after the procedure. In particular, a sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and severe pain in the stomach.
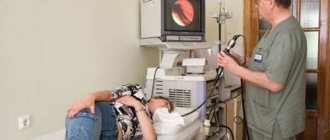
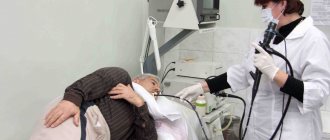
A referral for an FGDS is prescribed by the attending physician. The basis is the symptoms of the above diseases. To carry out the procedure, the patient lies on his left side. A special mouthpiece is clamped in the teeth, through which the doctor carefully inserts the gastroscope. The device is a tube made of elastic material. At the tip there is a camera and a device for collecting samples for biopsy. Using a camera, researchers monitor the state of a person's gastrointestinal tract on a monitor in real time.
The procedure itself is unpleasant and can cause severe pain for the patient. The analysis lasts 10-15 minutes. During the procedure, the patient feels nausea, and the gag reflex is triggered due to irritation of the receptors in the throat. To minimize pain, the patient’s throat is pre-treated with a spray containing lidocaine solution. It is recommended to lie still and breathe deeply, reducing the gag reflex. Failure to follow the rules doubles the duration of the procedure. Accordingly, the risk of unpleasant pain after endoscopy increases.
In modern conditions, with the latest technology, the FGDS procedure is the least painful; local or complete anesthesia is used at the patient’s request.
The process of conducting FGDS
The entire procedure takes approximately 10 minutes. Only if it is necessary to take material for a biopsy, more time is required.
The procedure is as follows:
- The patient lies on his side.
- The healthcare provider treats the throat with a numbing drug to reduce sensitivity (for example, lidocaine).
- A mouthpiece is placed in the patient's mouth and a probe is inserted through it.
- An endoscopist examines the condition of the stomach based on information transmitted by the camera to the screen.
Features of the FGDS procedure
Gastroscopy is done using a medical instrument called an endoscope, which is a fiber-optic hose with a tip. There are two types of endoscope:
- ocular endoscope;
- video endoscope.
Using a videoscope, the image of the stomach cavity is displayed on the monitor, making the diagnosis more accurate and detailed.
To eliminate discomfort during the procedure, the throat and root of the tongue are treated with lidocaine - there will be no pain. If allergies are present, lidocaine is replaced with falimint. The patient is placed on his left side, with a towel placed under the face to collect saliva.
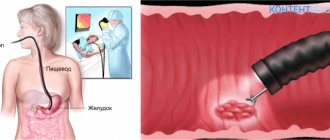
A mouthpiece is then placed in the mouth, which the patient must hold with his teeth. A hose is inserted through the mouthpiece and directed into the stomach. It is the movement of the hose along the esophagus that is considered the most painful and unpleasant moment.
Next, a procedure for examining the stomach cavity occurs, during which the doctor moves the tip in different directions. When performing a biopsy, a piece of tissue is taken from the walls of the stomach. Removing the tube from the stomach is painless and quick.
Possible complications
With this method of research, the root part of the tongue is affected. This causes a gag reflex. Sometimes after the procedure your stomach or throat may hurt. Experts consider such manifestations to be a completely normal reaction of the body to the insertion of a probe.
But what to do if the throat pain does not subside for several days? In this case, you should consult an otolaryngologist.
Equipment for FGDS can damage some internal organs:
- walls of the esophagus;
- the inner lining of the stomach;
- surface of the upper intestine.
Among the most common complications after the FGDS procedure:
- mechanical injury to organ walls;
- pneumonia;
- perforation of the wall of the stomach or esophagus;
- laryngotracheitis, as a result of mechanical injury;
- During the procedure, the rhythm of heart contractions is disrupted.
If the procedure was carried out in violation of sanitary standards, then pathogenic infections may enter the intestines.
If a patient develops a gag reflex during FGDS, stomach contents may enter the lungs, which can cause pneumonia.
See also
How and with what to treat a sore throat quickly at home
Read
Contraindications to gastroscopy
There are certain contraindications for which gastroscopy cannot be performed. But, if a person’s life is at risk, this procedure can be carried out even in the presence of severe bleeding. We indicate contraindications to performing planned gastroscopy:
- hypertensive crisis;
- respiratory failure (severe);
- stroke, acute cerebrovascular accident;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- cardiovascular failure;
- aneurysm of the aorta, carotid sinuses, heart;
- rehabilitation after myocardial infarction, stroke;
- myocardial infarction;
- mental disorder (its serious forms).
Usually, if a patient has such contraindications to gastroscopy, a specialist assesses the feasibility of diagnosis. It calculates the likelihood of various negative consequences occurring.
Is it possible to do FGDS if your throat hurts?
Before FGDS, some patients ask whether the procedure can be performed if they have a sore throat or there are signs of a cold. A significant contraindication for this procedure is nasal congestion and runny nose, as this will negatively affect the respiratory process. With such symptoms, it is better to postpone FGDS to a later time or use vasoconstrictor drops. Their use will ensure breathing through the nose.
You should definitely refuse to examine the stomach with a probe in case of pharyngitis, laryngitis, or tracheitis. These diseases are characterized by inflammation of the throat mucosa. The pharynx at this time has increased sensitivity to irritating factors. Touching it with a fiberscope can aggravate the inflammatory reaction, and sometimes cause a spasm that impairs breathing.
FGDS for cough and runny nose
Is it possible to do FGDS for a cold, if the throat does not hurt, but there is a cough? When coughing, especially dry and paroxysmal, inserting an endoscope is quite problematic. With colds, the upper respiratory tract is usually swollen. The insertion of an endoscopic probe can cause spasm of the airways, which will lead to the development of acute respiratory failure.
Another problem with diagnostics during a cold is a runny nose.
Since breathing during gastroscopy can only be done through the nose, if nasal breathing is difficult as a result of a runny nose, the procedure is impossible. In this case, diagnosis should be postponed until recovery. If rhinitis occurs in a chronic form, the nasal cavity should be prepared before performing an FGDS. How to do this correctly?
- It is necessary to clear the nasal passages of mucus and crusts. To do this, it is recommended to rinse your nose with a solution of sea salt. You can buy it in a pharmacy in ready-made form (Aquamaris, Aqualor, Rinomaris and others) or prepare a solution yourself by diluting sea salt in warm water. If you don't have sea salt, you can use regular table salt.
- After rinsing, it is necessary to remove the remaining contents of the nasal passages by blowing your nose or using an aspirator.
- Then vasoconstrictor drops based on Naphazoline, Oxymetazoline or Xylometazoline should be dripped into the nasal passages. The drug will cause vasoconstriction and relieve swelling. As a result, nasal breathing will be restored.
- If the swelling of the mucous membrane is severe, then on the eve of the study, antihistamines for internal use may be prescribed.
After nasal breathing has been restored, gastroscopy can be safely performed.
Ways to relieve pain
If pain occurs after an FGDS study, gastroenterologists advise waiting for a while, since in most cases they go away without any intervention. If you have a sore throat, it is recommended to gargle frequently (about every hour). But if such recommendations do not help, and the pain bothers you for a long time, then you need to consult a doctor.
It is recommended to treat the throat with gargles. The following agents and preparations can be used as an antiseptic:
- Aqueous solution of Furacilin.
- A solution of soda, salt and iodine in warm water. For 1 glass of water, 2-3 drops of iodine and 0.5 tsp. soda and salt.
- Pharmacy spray Chlorophyllipt. In addition to relieving pain, it stops the inflammatory process.
- Inhalipt is used to eliminate pain.
- A mixture of milk and honey (1 teaspoon of honey per 250 ml of warm milk).
- Chamomile decoction.
- Pain relievers with the addition of zinc gluconate.
In these ways, you can speed up the healing process of the throat after examining the stomach using FGDS. If your throat hurts after gastroscopy, bee honey helps heal minor injuries on the throat. It can be consumed as usual without dissolving in water. Also good results come from tea with the addition of milk and natural honey.
Pharmacy products
The drug Kameton has a good effect. It eliminates pain when swallowing and has not only an analgesic effect, but also an anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect. The unpleasant sensation in the throat is relieved by the menthol included in it.
See also
What to do to avoid getting sick if your throat starts to hurt at home
Read
A popular remedy is Orasept. The pain goes away within a few minutes after irrigating the mouth. This drug also relieves the inflammatory process.
It is recommended to purchase the drug TeraFlu Lar at the pharmacy. It contains lidocaine, which has an anesthetic effect. For some time it helps relieve pain.
In addition to sprays, tablets intended for resorption are used to quickly eliminate the unpleasant consequences of FGDS. Both adults and children can use Grammidin Neo lozenges with anesthetic.
Chlorhexidine rinse is used as follows. First, rinse your throat with regular warm water. Then pour 1 tbsp into the oral cavity. l. the drug and rinse for 30 seconds. It is not advisable to eat or drink water for 1 hour after rinsing. Rinse with Chlorhexidine 3 times a day.
How to behave after gastroscopy
Negative consequences after FGDS are a rare phenomenon. This diagnostic procedure has been worked out to the smallest detail, so even novice specialists do not make fatal mistakes that could lead to life-threatening consequences for the patient. Doctors are allowed to perform gastroscopy on “living patients” only after completing a special training course and passing an exam.
No matter how strange it may sound, the main danger of gastroscopy is the patient’s inappropriate behavior during the examination. Gastroenterologists and endoscopists note that those most susceptible to violating behavioral recommendations are those who, before diagnosis, are very worried about whether it is harmful to do an FGDS of the stomach. As a result of anxiety, they may forget how to breathe properly and resist, which increases the likelihood of injury.
Important! Diagnostic and therapeutic gastroscopy, during which the doctor and patient follow a set of standard rules, does not cause harm to health. This method is approved for use even in infants, which indicates the absolute safety of FGDS.
Theoretically, damage to the esophagus and stomach as a result of FGDS is not excluded, especially if the subject is not mentally prepared to undergo such a procedure. Real statistics show that the occurrence of such consequences due to gastroscopy occurs in extremely rare cases - less than 1%.
In what cases is there a risk of damage to the stomach or esophagus:
- there is a mental illness or nervous disorder that does not allow you to control your behavior;
- there is a strong curvature of the thoracic spine, due to which the esophagus is curved;
- varicose veins of the esophagus were diagnosed.
Such diseases are absolute contraindications to FGDS, and the doctor must make sure before conducting the examination that the patient does not suffer from them. Fulfilling this condition reduces the likelihood of injury to a minimum.
Important! If the esophagus hurts after gastroscopy, this does not mean that damage to health has occurred.
It is almost impossible to become infected with various types of infections during gastroscopy, although such concerns arise in many people who are indicated for FGDS. Experts say that it is impossible to become infected through a hose inserted into the digestive tract or instruments used to take a biopsy, since clinics follow strict aseptic rules. Equipment and tools are treated with special agents that destroy bacteria, viruses and protozoan microorganisms.
Despite compliance with sanitary standards in the endoscopist's office, the risk of infection is still present, but its degree depends on the person being examined. If he has an infection of the throat, mouth or larynx, which the doctor was not warned about, the pathological process may spread or worsen.
Note! The likelihood of contracting infections during gastroscopy is increased in patients with HIV, since they have virtually no immunity.
Asphyxia or respiratory arrest during gastroscopy is unlikely, since the doctor constantly assesses the condition of the patient and can interrupt the procedure if serious problems arise. Experts note that breathing during FGDS is possible without any difficulty if you inhale and exhale only through the nose. This technique will help relieve nausea and calm you down.
Important! Preference should be given to thoroughly pureed soups with vegetable or low-fat chicken broth, pureed boiled vegetables, fresh fermented milk drinks and herbal tea.
It is important for 1-3 days after FGDS to carefully listen to the sensations in the stomach and intestines, periodically measure the temperature and generally pay attention to your well-being. Do not immediately take on hard work, attend sports training or perform active movements. It is necessary to give the body time to recover after gastroscopy for at least one day, and only then return to the usual rhythm of life.
Cause of sore throat after FGDS
Gastroenterologists have to listen to complaints of pain from almost all patients who have had their stomach examined using a tube. This occurs primarily due to mechanical trauma to the walls of the pharynx during the advancement of the probe. Also, due to the gag reflex, bile is released into the throat, which leads to irritation of the walls. Usually, unpleasant pain goes away 1–2 days after the procedure.
To reduce the level of unfavorable condition of the throat walls after FGDS, it is not recommended to eat hot foods, as well as spicy and sour foods, which can create an additional irritating effect.
Description of the gastroscope
Home » Gastroscopy » Why can the stomach hurt after FGDS - and what to do?
FGDS is a procedure that causes concern for many people due to the discomfort it causes. But in the vast majority of cases, everything goes away without the slightest consequences. However, there are exceptions, which is why sometimes patients complain that their stomach hurts after FGDS. Let’s figure out what can trigger this problem – and whether you should be wary of such symptoms.
The essence of the procedure
The term “biopsy” came to medicine from the Greek language. It is formed from two words: “life” and “appearance”.
The method is based on taking a tiny piece of tissue from the patient and carefully examining its cellular composition at high magnification. Biopsy differs in the method of collecting material and in the accuracy class.
In some cases, the material may be needed for histological examination. This means that the structure of the tissues of the sample taken will be studied.
In others - for cytological analysis. This means that the structure, reproduction and condition of the cells of the sample taken will be studied.
A classic biopsy, which has a second name - exploratory. This procedure is performed in the early stages of the disease, when the location of the tumor cannot yet be detected visually.
Open biopsy, when material for research is taken during surgery. This may be the entire tumor or any part of it.
A targeted biopsy, which can be performed when a tumor is detected, when the doctor can take material directly from the tumor at the border with healthy tissue. A targeted biopsy is performed using an endoscope, under ultrasound supervision, under X-ray control or stereotactic method.
Preparation for the procedure
Doctors recommend preparing in advance for the FGDS examination procedure. This reduces possible unforeseen situations. First of all, such a patient needs to prepare himself psycho-emotionally.
Also, before going for an examination, you should avoid fatty, hot or spicy foods. This may make the procedure difficult.
The last meal before the examination should be no earlier than 8–10 hours. The menu should consist only of light foods. It is also forbidden to drink water. A few sips can be taken no later than 3 hours before FGDS.
A patient who is prescribed a course of medications is recommended to consult with his doctor about temporarily stopping their use. As a rule, taking medications complicates this procedure, so it is better if you do not take them the day before the procedure. Drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking is not advisable.
When is the procedure unacceptable?
Sometimes pain may occur due to the fact that contraindications to this procedure were not observed, so it is necessary to familiarize yourself with their list in advance. The main contraindications are as follows:
- Severe obesity or emaciation of the patient.
- Acute infectious diseases, primarily ENT organs (pharyngitis, tonsillitis or tonsillitis).
- Hemophilia.
- Mental illness in the acute stage.
- Heart problems (stroke, heart attack, heart failure, etc.).
Of course, not all of these contraindications are directly related to the fact that the stomach may hurt, but, firstly, all these contraindications increase the risk of incorrect procedure and harm to the body, and, secondly, the pain can be localized in other areas, but give exactly in the stomach.
Symptoms of manifestations
Mild moderate pain and discomfort when swallowing are normal and require monitoring throughout the day. Usually the unpleasant consequences end there. The addition of complications entails the appearance of the following symptoms:
- swelling of the mouth, throat;
- burning in the larynx, nasopharynx;
- soreness;
- irritating cough.
With neurological disorders, the patient suffers from nausea, headaches, vomiting, spasms of the esophagus when eating any food or even water, and difficulty swallowing. The addition of infections often leads to an increase in body temperature. Dangerous symptoms are:
- hemoptysis:
- deterioration of health;
- reverse reflux of food from the stomach into the esophagus (due to disruption of smooth muscles);
- loss of appetite;
- blood pressure surges;
- acute unbearable pain in the stomach, esophagus.
Acute unbearable pain in the stomach is a possible symptom after FGDS.
If necessary, an X-ray with a contrast agent is required to assess pathological changes in the organs of the gastrointestinal tract.