Kinds
Classification by type of wounding object and method of injury.
- Stabbed - inflicted with a piercing weapon, such as a needle or bayonet. They are distinguished by significant depth and damage to nerves, blood vessels, and organs. In the first hours the symptoms are poorly expressed.
- Cut - formed from the impact of a sharp object: a knife, a piece of glass. They heal well because a minimal number of cells are destroyed.
- Chopped - applied with a sharp, heavy weapon such as an ax or saber. The skin is significantly torn, which complicates treatment and promotes rapid infection.
- Torn - occurs when a sharp weapon (for example, a saw) slides along the surface of the body. They are characterized by uneven edges, necrosis of tissue fibers and prolonged healing.
- Bruised - appear from the impact of a wide, heavy weapon (car accidents, blows, etc.). Characterized by uneven edges and a large amount of dead tissue.
- Bitten – inflicted by domestic and wild animals. They have various forms. They become contaminated with saliva when bitten, which can lead to rabies infection.
- Crushed - occurs when pressed by a massive hard object (for example, a concrete block). They are characterized by a huge area of injury and require urgent hospitalization.
- Gunshot - formed as a result of being hit by a bullet or shrapnel. Characterized by significant organ damage.
In addition, all wounds are divided according to the following criteria:
- area of injury – small and large zone;
- anatomical features - soft tissue injuries or nerve rupture, fracture of bones and joints;
- shape – patchwork, linear, star-shaped, perforated;
- circumstances of application - accidental, operational, combat;
- placement to body cavities – penetrating and non-penetrating;
- additional negative factors - infected, bacterially contaminated, radioactively contaminated, poisoned.
Causes
The most common cause is domestic trauma. Less commonly, injuries occur as a result of criminal incidents, accidents, car accidents, falls from a height, sports, and failure to comply with safety regulations at the enterprise.
Stab wound
The wound is characterized by an entrance hole, a wound channel, and an exit hole. The entrance is characterized by edges and ends, with a depression passing into the walls of the wound canal. The outlet, like the inlet, has edges and ends.
Description of the stab wound:
- depth exceeds its length;
- has sharp ends and smooth edges;
- during diagnosis, the main incision is noted - from the introduction of a piercing-cutting instrument into the tissue, and the secondary one - from the movement of the blade in the body.
The constructive properties of the instrument make it possible to evaluate stab injuries by the number of structural elements involved in the formation of the wound. The complexity of the forensic medical examination, as well as the amount of information obtained, depends on their number and diversity.
Differences between wounds in surgery and traumatology:
- Based on the depth of penetration, wounds are divided into through and blind;
- according to the peculiarities of formation - with possible damage to internal organs;
- by the presence of local complications - with massive bleeding, partial prolapse of organs.
Features and methods of treatment
The surgical treatment method is one of the key ones. With his help:
- parts of the projectile and foreign objects are removed from the wound;
- vessels, tendons, soft tissues are sutured;
- necrotic foci are excised;
- the integrity of damaged internal organs is restored;
- the condition of the bones is normalized: small fragments are removed, and large ones are compared with each other.
The operation is indicated for damage to internal organs, as a result of which part of the non-viable tissue or the entire organ is excised.
Gunshot wounds can be treated surgically
Suturing is appropriate only when the edges of the wound are torn, uneven and diverge from each other by 3-5 cm. Single sutures are applied, under which drainage must be installed.
Drainage of the wound channel is necessary so that at the initial stage of regeneration (inflammatory process), exudate does not accumulate in the tissues, but is freely removed outside. This will reduce the likelihood of developing a purulent-inflammatory process.
Drug therapy is prescribed in the following order:
- Antishock therapy drugs contain high concentrations of hormones that can be used to control the functioning of the entire body.
- Antibiotic therapy - allows you to neutralize the activity of pathogenic microorganisms that have entered the blood along with the projectile through the wound surface.
- Complex analgesics - help reduce pain. Both non-narcotic drugs and opioids that block the formation of pain in the cerebral cortex can be used. The latter are used in extremely severe cases.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs – help reduce pain, swelling and fever. Prescribed mainly in the second half of treatment.
- Wound healing drugs, antiseptics - are used to treat and speed up wound healing.
A gunshot wound is treated with antiseptic solutions, reducing the number of pathogenic microorganisms. When sutures are applied, they are removed no later than on the 6th day, which will allow the regeneration process to take place in full.
In most cases, a bandage is applied to the wound, under which ointments and creams with antibacterial, wound-healing and anti-inflammatory effects are applied (Levomekol, Panthenol, Vishnevsky ointment). Dressings are changed at least twice a day, using only sterile bandages.
Signs
Signs of a stab wound:
- inlet;
- wound channel;
- outlet.
Peculiarities:
- shape: arched, spindle-shaped, angular, slit-shaped;
- edges: smooth, with slight subsidence;
- shape of ends: angular, sharply rounded, p-, m-, g-shaped;
- wound channel: slit-like, with even smooth walls, with protruding subcutaneous tissue, the depth does not necessarily correspond to the length of the instrument, it changes under the pressure of the organs and with changes in body position.
Burn
Any weeping wound or burn is accompanied by bacterial infection. Dampness occurs when the immune system is unable to cope with inflammation.
Treatment of weeping burns consists of systematic dressings, taking antiseptics and wound-healing drugs.
They are able to ensure fluid outflow, tissue regeneration, and prevent the development of inflammatory processes
Step-by-step therapy for weeping injuries:
- Antiseptic treatment. These include Miramistin, Furacilin.
- An hygroscopic dressing is used, which is changed every 2-3 hours.
- When changing the dressing material, the damage is treated with an antiseptic. Then the antibacterial drug Betadine is applied. It can dry out the skin.
- If pain is present, painkillers (tablets, aerosols, injections) are used.
- For purulent injuries, ointment compositions Levomekol and Levosin are applied under the bandage.
After eliminating inflammation, you need to use a burn patch. At the stage of recovery and scarring of the skin, Solcoseryl ointment is applied under the bandage, at least 4–6 times a day. Vitamins A, C, and E are taken in combination with the main therapy.
Output damage
Damage of this nature is possible with through and through stab wounds. The outlet hole follows the shape of the inlet hole, its edges are smooth, without sedimentation, the drying border is not expressed or expressed to a relatively small extent.
The actions of the handle, limiter, and bit are not tracked. The ends of the exit damage relative to the butt part of the blade are rounded or U-, M-shaped; opposite ends are sharp. The length of the outlet hole is less than the inlet hole. The number of affected hairs on the inlet side exceeds the amount on the outlet side.
Folk recipes
Together with pharmaceuticals, traditional medicine, which is prepared at home, is used to treat weeping injuries:
- Potato juice. Fresh potatoes are grated using a grater. The juice is squeezed out. A sterile napkin is moistened in the liquid, applied to the wound, and bandaged. The compress is applied before bedtime. The medicine draws out bacterial exudate.
- Onion. Vegetable (1 large head) is grated. The gruel is laid out on a gauze cloth and applied to the damage (20 - 30 minutes), 4 -5 times a day. The drug reduces swelling and cleans the surface.
- St. John's wort oil. The leaf and inflorescence (100 grams) of St. John's wort are finely chopped, and the golden mustache (50 grams) is added. The mixture is poured with olive oil (250 ml). The container with the medicine is covered with paper and infused for 15–20 days in a warm place. The product is filtered and stored in the refrigerator. The napkin is moistened with the medicine and applied to the wound 2 – 3 times a day.
Folk remedies are used after consultation with your doctor.
Damage to skin tissue
The origin of stab wounds is a blow with a knife or other similar instrument. Their formation involves: the blade, the bevel of the back of the knife, the sharp end, and when the tool is fully inserted into the body, the heel of the blade. The smaller the angle of action of the blade to the surface, the more clearly noticeable is the effect of the bevel of the butt. The wound on the skin follows the shape of an angle with an apex corresponding to the area where the tip is inserted. The lines creating the sides of the angle are located according to the movement of the blade and the bevel of the butt.
Formation phases:
- in the phase of blade penetration, tissue tension and compression occurs under the influence of the tip, and then, with the removal of the tool, they are cut under the tip and ruptured;
- cutting tissue along the line of movement of the blade from the side of the sharp edge and simultaneous pushing of tissue with a rupture upon contact with the butt;
- when removing the blade, the clarity of the cutting action is minimal if the extraction trajectory follows the immersion area of the wounding weapon;
- the length of the wound created corresponds as much as possible to the width of the blade in the area of immersion;
- when removing the instrument of damage with emphasis on the blade, its cutting action is more pronounced with the formation of an additional cut;
- the direction of the additional cut merges with the main one, if there was no rotation around the longitudinal axis and the victim’s body was static - the length of the wound differs from the width of the blade at the mark of its insertion;
- in the presence of a rotational movement with the removal of the blade and a change in the position of the victim, the main and secondary cuts do not coincide.
Treatment
When providing assistance, the doctor first determines the strength and danger of bleeding, as well as the degree of damage. After the bleeding has stopped, measures are taken to protect the wound site from the penetration of harmful bacteria.
Minor cuts and punctures are treated with antiseptics, followed by a bandage. The injured area is cleaned with cotton wool and alcohol and lubricated with iodine, after which gauze is applied.
Treatment of very deep and extensive wounds is considered more difficult. In addition to cleaning and treatment, the problem is diagnosed, foreign bodies are removed, and dead tissue is excised.
All injuries are accompanied by pain of varying intensity that must be eliminated. If the patient is in shock, he is first taken out of this state and only then surgery begins. At the end of the operation, the patient is administered antitetanus serum.
You should carefully monitor the progress of healing, and if complications arise (swelling, redness, appearance of pus), immediately make an appointment with a surgeon.
Muscles and organs
In relation to skeletal muscle, the shape of a stab wound depends on the trajectory of the injury relative to the muscle fibers. Wounds, the length of which is parallel to the bundles of muscle tissue, are distinguished by their slit-like shape.
If the location is transverse or oblique, the wound is spindle-shaped, oval when the muscles contracted. Based on the relief of damage to internal organs, one can determine the nature and mechanism of action of the damaging weapon. The dense consistency of the fabrics allows you to evaluate the peculiarities of the movement of the butt, its width, and the volume of the end part of the blade. Heart, liver, kidneys - will show damage with the greatest degree of accuracy.
The predominance of the depth of a stab wound over its length is an unfavorable factor for its healing. External or internal bleeding may occur.
Typically, a stab wound to the chest involves the heart and aorta, not just the lung. During a murder, there are many scattered wounds of this type on the body. Shallow wounds are not fatal, but death occurs due to large loss of blood.
Victims of a stab wound to the abdominal cavity often experience injuries to the kidneys, liver, spleen, and intestines. The difficulty of diagnosing these organs is that victims have injuries to the chest, head, lose consciousness, experience severe shock or are intoxicated.
Healing process
If the injury oozes and does not heal for a long time, there is a possibility of a secondary infection. As a result, a wet surface is formed.
The immune system tries to fight inflammation on its own, and the production of excess blood plasma increases.
On the foot
Damage to the skin on the leg with the release of fluid occurs as a result of injuries, varicose or erysipelas, thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, and diabetes.
The main goal of treatment is to create a systematic outflow of fluid. When purulent fluid accumulates, inflammation spreads to nearby tissues.
In a hospital setting:
- Treatment with antibacterial solutions (Dioxidin);
- For painful symptoms, painkillers are used (lidocaine spray, Xylocaine);
- To cleanse necrotic masses, trypsin powder is used (a napkin is moistened with the drug and applied to the affected area).
For shallow, weeping injuries on the legs, therapy is carried out at home. Salicylic or Ichthyol ointment is used.
Streptocide (tablets or powder) is used as an antiseptic. Before applying ointment compositions, the skin is treated with hydrogen peroxide.
Reasons for long delays
Weeping wounds that do not heal for a long time indicate the presence of pathology in the body and the addition of an infection.
Why skin abrasions do not heal:
- Improper treatment of wound surfaces.
- Diabetes. When the disease occurs, the limbs swell, blood circulation is impaired, and the activity of the immune system decreases. Skin cells lack nutrition.
- Age criteria. The immune system of older people is weakened. The body is unable to fight inflammatory processes on its own, and regeneration slows down.
- Lack of vitamins in the body. The wound does not heal with vitamin deficiency.
Cell regeneration slows down in people diagnosed with cancer, obesity, exhaustion, HIV.
Liquid oozing
The fluid that oozes from the wound is lymph. Its release is a normal, natural phenomenon. It removes salt impurities, proteins, toxins, and water from tissue structures. Then it returns them to the circulatory system.
If the ichor is not released abundantly, there is no cause for concern. Carry out the prescribed course of treatment.
The abundant flow of lymph from the wound surface is affected by:
- Poor quality leather processing;
- Polluted ecology;
- Alcohol and nicotine;
- The presence of vascular and dermatological pathologies;
- Excessive physical activity.
If there is an abundance of fluid secreted, you should consult a doctor.
First aid
If injured, first aid will prevent complications and consequences and save the life of the victim. But medical care in the case of a cut and stab wound should be provided taking into account the classification of the injury and combined with further actions.
Help steps:
- treat injuries and abrasions with an antiseptic, especially if infected;
- avoid touching the wound with your hands to prevent re-infection;
- You cannot independently remove foreign bodies that have penetrated into the tissue - this is dangerous due to the risk of infection;
- apply a sterile bandage to the wound, providing complete rest to the wounded area;
- take the victim to a medical center for a professional examination;
- first aid must be performed within the first minutes after injury, otherwise there is a high risk of death.
Rules for applying a bandage:
- position yourself on the side of the injured area of the victim;
- When applying a bandage, place the damaged area on the roller;
- cut and remove clothing from the victim;
- start bandaging from the periphery and strengthening moves.
In case of damage with loss of internal organs, they must not be placed back. The injury site should be covered with a clean bandage and reported to medical personnel. In case of excessive blood loss, a pressure bandage is applied before the patient arrives at the medical facility.
Possible complications
In the case where a gunshot wound affects vital organs (heart, lungs, brain), the chances of survival are directly proportional to the speed of providing qualified medical care. The following complications may also occur:
- Development of disability - with damage to internal organs, the musculoskeletal system or the brain, in which a person is not able to fully think, move and live independently in society.
- Impaired mobility of damaged areas of the body, decreased sensitivity, scars and cicatrices will always remind a person of what happened.
- Failure in the functioning of internal organs, which dictates the need for the rest of your life to limit yourself in food, sports and other little things.
During the wound healing process, an infectious process may occur, which slows down the regeneration of damaged tissues. This requires the prescription of complex antibiotics, and in some cases, blood transfusions to prevent the development of sepsis.
Application of a tourniquet
Harnesses can be made from available materials: towels, scarves, belts.
Instructions for using the tourniquet:
- apply a tourniquet above the level of damage at a distance of 7 cm;
- the injured limb must be elevated;
- You must first place a cloth on the injured area;
- pulling the tourniquet until the bleeding stops;
- A piece of paper should be placed under the tourniquet indicating the time of clamping of the vessels;
- The tourniquet can be worn for up to two hours in the warm season and up to an hour in the cold season;
- take care of the nutrition of the limbs with intact vessels;
- loosen the tourniquet briefly, renewing its pressure.
Contour bandages-corsets, “chain mail”, and other cotton-gauze forms are in demand. First aid is provided as quickly as possible and without panic. In a restless state, there is a risk of causing more harm. While waiting for the arrival of paramedics, you need to observe the breathing and heartbeat of the victim with a readiness to carry out resuscitation when it stops - artificial respiration, massage.
Rules for treating wounds
Treatment of wounds
There are general rules for treating wounds:
- This process is carried out only with clean hands.
- The victim is positioned in such a way that there is no pressure on the damaged part of the body and maximum peace is maintained.
- The wound surface should be immediately covered with a clean cloth, gauze bandage or bandage to prevent the entry of germs and dirt. The bleeding should be stopped as quickly as possible.
- The surface of the wound or abrasions is washed with water. If there is no clean water in camping conditions, you need to filter and disinfect water from the nearest body of water using available means.
- The edges of the wound are treated with any antiseptic. If it is applied to the wound surface itself, it can damage the tissue and, in some cases, cause necrosis.
- Do not use oil or alcohol antiseptics to treat abrasions in the mouth, nose, or eyes. For this, a weak aqueous antiseptic solution is used.
If tissue damage is not treated and the bleeding of a deep wound is not stopped after two hours, there is a possibility of tetanus, sepsis, cardiac dysfunction, dizziness, and loss of consciousness. If your health has sharply deteriorated within a day (the temperature has risen sharply, chills have begun, confusion has begun, muscle aches and weakness have appeared), there is a high probability that an infection has entered the bloodstream and it may become infected, which is very difficult to treat.
How to treat an injured leg
What to treat and how to do it, the doctor knows best. During the examination, the surgeon determines the characteristics of the injury and symptoms. When a leg is injured, the following symptoms may be pronounced:
- Sharp pain.
- Heavy bleeding.
- Tissue defect
- Leg functions are impaired.
An open wound on the leg, in some cases, can also cause shock, traumatic toxicosis and infections. After a certain period of time after the injury, the area will recover, but the speed of healing will depend on the circumstances under which the injury occurred.
In order to quickly and without complications heal open wounds on the leg that were caused by a sharp object, you should take this process seriously.
Key points that influence the healing process:
- Competent first aid for injuries.
- Followed rules during the first surgical treatment.
- Daily and methodical execution of all assignments.
Why are wounds and wounds dangerous?
Almost all types of wounds are dangerous to human life and health. First of all, this is due to the penetration of pathogenic microflora into their cavity. Even with a low level of infection in the wound, microorganisms can multiply, since it contains a nutrient medium - completely or partially dead tissue. It is the development of infection in the wound cavity that poses the main threat to human health.
Cut, chopped and puncture wounds are at the lowest risk of developing a secondary infection, since destruction and necrosis of tissue in them occurs in areas with which the object that caused the injury was in direct contact. In addition, with these types of injuries, blood flows freely from the wound cavity, which contributes to its spontaneous cleansing. Puncture wounds become infected less frequently for other reasons: as a rule, their edges are closed quite tightly, which means that the wound does not gape and infection cannot freely penetrate into its cavity from the outside.
The greatest danger regarding the development of infection is posed by lacerations, crushed wounds, gunshot wounds and bite wounds. Due to the large area of damage characteristic of them, as well as the fact that the tissues in their cavity are practically non-viable, the risk of developing anaerobic and other infections is very high. Numerous blind pockets filled with fragments of muscle tissue and blood clots can become an excellent breeding ground for bacteria that have entered them. This can cause suppuration to form even outside the wound and lead to sepsis. Lacerated wounds accompanied by tearing off a flap of skin (so-called scalped wounds) are considered one of the longest to heal, however, due to the shallow depth of the lesion, the risk of developing infection in them is somewhat reduced.
First aid to the victim
The main task is to correctly assess the condition of the victim, the nature of the injury received, a thorough examination for additional damage and take urgent measures. Assessment of the victim’s condition depends on the amount of blood lost and the degree of pain shock received. Necessary measures include immediate stopping of bleeding and prevention of possible. Since first aid measures usually have to be provided to people who have little knowledge in this area, it is necessary to treat this matter with all responsibility. But in any case, if the victim’s condition is serious, it is necessary to call emergency help.
In case of a deep wound and heavy bleeding, a tourniquet is applied to the limb above the site of injury. The tourniquet should not be applied for more than an hour and a half; every forty minutes it must be loosened slightly.
After this, you should disinfect the wound by first rinsing it with clean warm water. Hands must be perfectly sterile; it is better to treat them with alcohol or potassium permanganate. Only after these manipulations is the tissue processed. This can be done using hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate, medical alcohol or vodka.
Head wounds
Help should begin with treating wounds and abrasions. In this case, it is advisable to exclude such material as cotton wool, since in the future it will be problematic to remove particles remaining on the surface.
If the wound is on the scalp, before treating it, it is necessary to trim the hair so that the injured area is accessible. The areas around the affected area are smeared with iodine or a solution of brilliant green.
In case of severe bleeding, a gauze pad is made and a pressure bandage is applied on top. This area should not be opened or disturbed until the bleeding stops. For pain and swelling, you can relieve the condition with ice or a heating pad with cold water.
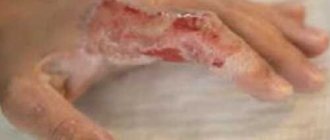
Open purulent wound
Wounds containing purulent exudate are formed as a result of a violation of the integrity of the skin. The lumen is filled with purulent contents, and inflammation is noted at the edges. The causes of the pathology are infection of a clean wound or breakthrough of an abscess.
Therapy is carried out:
- Antibacterial drugs;
- Detoxification measures (toxins are removed from the body);
- Medicines that stimulate the immune system.
The goal of treatment when a purulent focus forms is to clean the open wound, reduce inflammation, and eliminate pathogenic bacteria.
To accelerate the process of skin regeneration, the following is prescribed:
- Vishnevsky ointment;
- Synthomycin liniment;
- Tetracycline ointment composition.
Medicines are applied to a bandage. Use once a day, preferably before bedtime. To eliminate pus from large wounds, drainage is installed.
Consequences
In some cases, such injuries can lead to quite serious consequences:
- The likelihood of bleeding, which may result in anemia.
- In some situations, the integrity of vital organs may be compromised.
- A state of shock leading to organ dysfunction.
- Development of infection.
Most often, this category of injuries does not pose any particular danger. And when a person begins to treat an open wound right away, the healing process goes much faster. However, there are situations in which the simplest home methods do not help.
Symptoms and types of open wounds
The symptoms of injury depend primarily on the type of injury. Small scratches that barely touch the mucous area do not cause concern to people; they heal quickly without the help of specialists, often without even leaving a trace of themselves after some time. But there are types of wounds that require increased attention.
Signs of injury are:
- presence of bleeding;
- pain;
- mechanical type of damage to the skin layer;
- lack of proper functioning of the limbs;
- defects in skin layers.
Wounds are divided into cut, puncture and laceration injuries. Wounds that will be caused by surgery will be called surgical injuries. Each has characteristic signs that will help you choose the method of treatment and therapy.
An incised wound is characterized by smooth edges. Just like with other open wounds, bleeding is observed when cutting. It can be severe or moderate depending on the location of the injury.
A lacerated wound is marked by jagged edges. For a puncture wound, the depth rather than the width of the wound is more important, since this type is obtained with an awl, rod or other long object with a sharp edge.
The degree of injury is determined by the depth and width of the wound, as well as the presence of damage not only to the skin. Often muscles, tendons or important internal organs are affected.
Despite the fact that at first glance the wound seems harmless, the victim may experience severe blood loss, or an infection may enter the wound, which will complicate the treatment procedure. Therefore, first of all, measures should be taken to reduce the risk of complications.
Symptoms of festering wounds
The main local signs of a purulent process are the presence of exudate of different colors in the wound, pain, local increase in temperature, redness and swelling around the wound. When infected, a large amount of toxins enters the body, which leads to the appearance of signs of intoxication at a later phase of the development of the disease.
Signs of a purulent process:
- increased sweating;
- loss of appetite, nausea;
- weakness, fever;
- migraine, fever;
- pain in the affected area is of a pressing or bursting nature;
- sometimes a rash appears on healthy areas of the skin that are located near the source of inflammation.
The presence of a purulent and inflammatory process helps to identify a clinical blood test - the ESR increases, the leukocyte formula shifts to the left.
Excessive sweating may indicate wound suppuration
Rehabilitation period
from an incised wound within 7-10 days . If there were no complications, then there are no special recommendations in the rehabilitation period. Main:
- protect the site of injury (scar) from excessive pressure and rubbing with clothing, otherwise there is a risk of hypertrophy of this scar (it will degenerate into a keloid);
- adhere to a rational diet high in water, protein, and vitamins;
- If, after discharge from the hospital, you are advised to dress a wound, then do not neglect the rules for changing the dressings.
If there were complications in the form of damage to the nerve trunks, the rehabilitation period may take up to several months .
The function of the limb below the wound will not be restored immediately; it will be necessary to develop the muscles using special exercises.
Photo 2. To restore the fingers and wrist, you can use special balls for the development of motor skills. Source: Flickr (Sophie Saller)
Some diseases (diabetes mellitus, immunodeficiency) cause long and problematic healing of any type of wound. In diabetics, wounds are prone to suppuration. For such patients, treatment and rehabilitation tactics are selected individually, in combination with treatment of the underlying disease.
Creams and ointments for treating wounds at home
If the damage is minor and there is no large cavity, then such open wounds can be treated at home using various ointments. What experts recommend using:
Salicylic ointment. This product belongs to the antibacterial category. First you need to treat the wound with hydrogen peroxide, then apply Salicylic ointment directly to the wound and cover everything with a sterile bandage. Ichthyol ointment can be used in the same way.- Streptocide. This remedy is used only for superficial damage. If you have Streptocide tablets in your medicine cabinet, you need to crush them and cover the wound. Many people use special medical glue BF for superficial wounds, but this is wrong - treatment with this drug is a mandatory procedure.
- Balm Rescuer. When it is applied to a wound, a thin film is formed, so doctors remind you that before using this balm, you must wash the open wound with hydrogen peroxide.
- Solcoseryl. It is available in the form of an ointment - it is applied to a dry open wound, and in the form of a jelly - used in the treatment of weeping open wounds.
- Heparin ointment, Troxevasin ointment, Dolobene gel. Used in the presence of a bruise or extensive hematoma at the site of an open wound. Applied directly to the skin, it quickly relieves swelling and hyperemic areas.
- Cream Eplan. It is made on the basis of polyethylene glycols and has antibacterial and disinfectant properties. The use of this product significantly reduces the risk of infection of open wounds.
Puncture wound of the foot with a nail treatment
Puncture wounds of the foot. Diagnosis and treatment
Glass, metal or other foreign bodies
usually clearly visible on radiographs. Based on this, the authors believe that radiographic examination should be performed for any puncture wound. The most common bacterial pathogens of wound infections are staphylococcus and streptococcus.
For staphylococcal infection
An abscess usually forms with characteristic creamy or yellow contents. Penicillin-resistant patients can be given erythromycin or clindamycin. A streptococcal infection is characterized by soreness and redness of the skin.
Osteomyelitis
after puncture wounds of the foot can be caused by the entry of Pseudomonas aeruginosa into the wound, it is described below. After a long stay of a foreign body in a puncture wound of the foot, cases of the formation of epidermal cysts have been observed.
Johaanson
described 11 patients with osteomyelitis with puncture wounds of various etiologies, and Houston et al. examined 2583 patients admitted to the emergency department with puncture wounds of various locations, and found that 10% of them later suffered an infectious process. In an observation by Fitzgerald et al. 132 of 774 children examined with puncture wounds had panniculitis (cellulitis), and 16 had osteomyelitis.
For clinical picture
It is characteristic that a patient who stepped on a nail 2-3 weeks before admission, correctly treated and with visible improvement, later begins to experience increased pain at the injection site without signs of a general disease. Local swelling, redness and soreness are noted at the injection site. Some patients may not have a febrile state, while others have a low-grade fever, a slightly elevated ESR with a leukocyte count not exceeding the norm. Radiographs show the picture of osteomyelitis.
Key points in the approach to the treatment of puncture wounds of the foot
:
1. All puncture wounds suspected of having a foreign body require x-ray examination.
2. When washing puncture wounds, iodoform should be used instead of hexachlorophene, which has a bacteriostatic effect.
3. If indicated, tetanus prophylaxis should be administered.
4. If the wound is deep and the doctor suspects that its bottom is bone, or it communicates with the joint cavity, or, perhaps, there is a foreign body left there, a revision of the wound or excision of the wound canal is indicated.
5. Heavily contaminated wounds should not be covered.
6. If there is a deep wound, you should take the discharge for culture and, according to indications, prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics.
7. For puncture wounds, immobilization of the limb, its elevated position and careful observation are recommended to avoid the development of an infectious process.
We welcome your questions and feedback:
Please send materials for posting and wishes to [email protected]
By sending material for posting you agree that all rights to it belong to you
When quoting any information, backlink to MedUniver.com
- required
To obtain the coordinates of the authors of articles, please contact the site administration
All information provided is subject to mandatory consultation with your attending physician.
The administration reserves the right to delete any information provided by the user
Features of cuts
Most often, cut wounds can be obtained at work or at home; more severe cases are criminal incidents. Based on the clinical history, the final diagnosis is made. Treatment of such wounds falls on the shoulders of traumatologists, specialists to whom patients are delivered every day, including those with bodily incisions.
From the moment of injury until several days later, pain occurs, which over time develops into aching. The intensity of pain from an injury depends on the following factors:
- the number of nerve elements in the cut area;
- the neuropsychic state of the victim and his further reaction to what happened;
- speed and duration of injury;
- the nature of the weapon that left the cut.
In the latter case, if the knife is incredibly sharp, the cut is thin. Consequently, there are significantly fewer damaged nerve cells than when injured by a blunt object. The most disgusting wound is considered to be a cut made with a dull knife, the blade of which has already undergone oxidation and further corrosion.
The severity of bleeding also depends on the object used to inflict the wound, as well as on the area of skin affected by the blade. It is worth remembering that cuts on arterial veins can cost a person’s life if delayed. With timely intervention, healing can be accelerated through adequate treatment.
What is a wound definition
Everyone has probably encountered various injuries and knows what they look like. Let's first figure out what wounds are from a medical point of view. We will look at types of wounds a little later. First of all, this concept implies mechanical damage to the skin and mucous membranes and adjacent soft tissues, nerves, muscles, tendons, blood vessels, ligaments, and bones.
The main sign of injury is the presence of separation of the edges of the skin and muscles, that is, gaping, bleeding and pain. Multiple or single injuries can cause shock due to blood loss and severe pain, as well as lead to infection by a variety of microbes that can harm the entire body.
First aid for a lacerated lip
When treating a lip laceration, the first step is to stop the bleeding. This can be done by applying a tight bandage that will compress the wound site. Doctors recommend applying an antiseptic bandage; in the future, it will help avoid any complications in the form of inflammatory processes, suppuration and other adverse consequences. If the severity of the pain syndrome is very pronounced, then the doctor may prescribe the patient a complex of drugs that can produce an analgesic effect.
If you need to stop the bleeding process, the doctor prescribes drugs that stop the bleeding, for example, “Vikasol” or “Ditsinon”. If the wound is large, with heavy bleeding, then in order to replenish the blood volume and take preventive measures to avoid a state of shock, you need to use infusion therapy methods along with the introduction of intravenous drip special solutions of helovusin or venofundin. They are able to compensate for the lost liquid part of the blood. In order to carry out the first surgical treatment and suturing a large wound, the patient must be sent to the inpatient department, where the bleeding process will be stopped and the development of shock will be prevented.
Very often, when there is a minor injury to the lips, the victim does not need hospitalization, and after he has had the wound surgically treated, subsequent treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis.
Preventive measures
To protect yourself from lacerations, you need to follow safety precautions when working with construction tools. If your work involves factory equipment (lathes, milling machines), then following safety precautions and wearing personal protective equipment is especially important.
In everyday life, avoid potentially dangerous objects (sharp hooks, heavy objects that can fall from the top shelf, etc.), keep them away from children.
Violation of the integrity of the skin and mucous membranes, which is formed under the action of a rupture when the skin’s ability to tension stops - this is called a laceration.
Such a lesion occurs with damage to muscles, blood vessels, nerve fibers and is accompanied by bleeding. The boundaries of the wound are uneven, sometimes significant skin detachment and scalping are noticeable. In this case, only surgical treatment is used, but in any situation it is clearly necessary to provide first aid as soon as possible.
Pathological features of a cut wound
A wound is created by sliding and pressing a sharp blade onto the skin.
Rounded areas of the body receive linear-arc-shaped cuts. In the case when the affected area for some reason was folded, it is quite natural that the resulting wound will be zigzag or tooth-shaped. If the depth of the wound has reached the bone, the initial direction changes in 90% of cases. Moreover, the closer the skin is to the corners of the wound, the more it narrows, while its widest part can be almost half its length. Therefore, such wounds have another name - spindle-shaped. Most of the incisions do not penetrate deeper than the skin and its subcutaneous tissue. But the wound from a strong knife blow, causing a cut under the influence of force, is caused by damage to anatomical formations. Particularly dangerous are wounds with damage to blood vessels (in this case, intense external bleeding is observed, the likelihood of increased blood loss, as well as the development of hypovolemic shock), nerves (which leads to impaired sensitivity; temporary or partial paralysis is also possible) and internal organs (results in internal bleeding and a high probability of developing post-traumatic shock, in addition, complications are possible, for example, resulting peritonitis when the abdominal organs are damaged). When injured by a blade, the integrity of bone and cartilage tissue is not compromised. However, there is always room for exceptions.
During a suicide attempt, a cut wound appears on the victim's forearm. A less popular cut option is the area on the inside of the elbow.
If there is a suspicion of damage to the nerve endings, the patient's sensitivity is checked. To establish a more accurate diagnosis, you should go to a neurologist or neurosurgeon, proceeding further according to the situation. The most popular method of finding out various types of data about a particular wound and the affected area is electromyography. Chest X-ray, ultrasound, MRI and other studies are prescribed when the wound affects the abdominal cavity and chest area.
Primary treatment in the treatment of open wounds
Before the victim seeks professional medical help, he must thoroughly wash the wound with antiseptic agents - this will ensure complete disinfection of the open wound. To minimize the risk of wound infection during treatment, hydrogen peroxide, furatsilin, a solution of potassium permanganate or chlorhexidine should be used. The skin around the wound is treated with brilliant green or iodine - this will prevent the spread of infection and inflammation. After the described treatment, a sterile bandage is applied on top of the open wound.
The speed of its healing depends on how correctly the initial cleaning of the open wound was carried out. If a patient comes to the surgeon with punctured, cut, lacerated open wounds, then he must undergo specific surgical treatment. Such deep cleaning of the wound from dead tissue and cells will speed up the healing process.
As part of the initial treatment of an open wound, the surgeon removes foreign bodies, blood clots, and excises uneven edges and crushed tissue. Only after this the doctor will apply sutures, which will bring the edges of the open wound closer together, but if the gaping wound is too extensive, then the sutures are applied a little later, when the edges begin to recover and the wound begins to heal. Be sure to apply a sterile bandage to the site of injury after such treatment.
Please note: in most cases, a patient with an open wound is given anti-tetanus serum, and if the wound was caused by an animal bite, a rabies vaccine.
The entire described process of treating an open wound reduces the risk of infection and the development of complications (sepsis, gangrene, suppuration), and accelerates the healing process. If the treatment was carried out on the first day after receiving the injury, then no complications or serious consequences are expected.
Bites and poisonous wounds
Experts call large-scale and deep tissue damage the main feature of bites. They are also distinguished by a high degree of contamination of the wound surface with biological products unusual for humans: saliva or poisons. As a result, they are very often complicated by putrefactive processes and acute infection of adjacent tissues or the entire body. Poisoned wounds caused by reptiles, arthropods and many insects are often accompanied by the following symptoms: intense and prolonged pain, swelling and discoloration of the skin, the appearance of blisters on the skin at the site of the bite, as well as deterioration in the general condition of the victim.