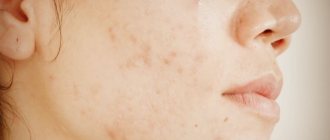
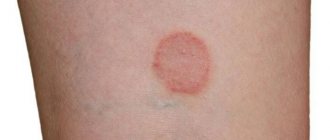
Types and localization of red rashes, associated symptoms
In adults, it is usually divided into 2 types:
- Primary. It appears on areas of healthy skin or on mucous membranes due to the development of pathological processes in the body.
- Secondary. It joins the primary one for certain reasons, for example, in the absence of proper therapy.
For quick elimination and diagnosis, rashes of a primary nature are considered the most favorable.
A red rash on the body of an adult varies according to the following characteristics:
- size;
- form;
- internal contents;
- coloration;
- grouping.
The main types of rashes include:
- Spot. It is characterized by a change in skin color or redness. It is provoked by syphilitic roseola, vitiligo, dermatitis.
- Bubble. It is formed in the thickness of the skin. The internal contents of the vesicle are hemorrhagic fluid. The size of the neoplasm is 2-6 mm. Typically, such a rash is provoked by eczema, herpes, dermatitis, and allergies.
- Blister. It is a swollen redness, the edges of which have smooth outlines. The blister can take regular or irregular shapes. The main causes include urticaria, insect bites, toxicoderma.
- Abscess. The internal contents of the neoplasm are pus. It is localized in the epidermis layer. Ulcers can be superficial and located in depth. They usually accompany pathologies such as acne, impetigo, furunculosis, and ulcerative pyoderma.
- Papule. The neoplasm is large in shape. It can reach 10 cm.
- Knot. It forms in any layer of the skin. Externally it manifests itself as a change in the epidermis with redness and thickening of the tissue. The size of the neoplasm is 1-10 mm. Nodules occur with psoriasis, papilloma, warts.
- Petechiae. A rash that occurs due to hemorrhages at the capillary level. A small amount of blood spreads under the skin, forming a spot with a diameter of no more than 2 mm. The rash does not cause pain or itching.
Classification
Skin rashes are divided into two types of rashes. Primary - appear on healthy skin or mucous membranes when a pathological process occurs in the body. Secondary - appear on the site of the primary ones in the absence of treatment. Primary rashes are easier to treat than secondary ones.
Rashes are distinguished by external signs:
A bladder is a cavity in the skin filled with serous-hemorrhagic or serous contents. Bubbles are divided into single- and multi-chamber.
Often they open with the formation of weeping erosions that do not leave marks on the skin after healing. Such rashes may indicate the following diseases: herpes, dyshidrosis, allergic dermatitis, eczema.
Pathological changes on the skin, characterized by rashes of varying localization and degree of damage, can be caused by several hundred different diseases.
Some of them are very dangerous and require careful diagnosis followed by adequate therapy.
All types of rash are divided into infectious and non-infectious:
- Infectious manifestations of the rash are characteristic of the development of rubella, scarlet fever, measles, chickenpox, typhus, herpes, lichen, meningococcemia, erythema, mononucleosis, urticaria.
- Non-infectious ones are formed due to allergic reactions, pathologies of the hematopoietic and vascular system, and problems with connective tissue.
- Diseases that primarily affect the skin or are limited in manifestation only to the skin. The rash is not a manifestation of other diseases, but affects only the skin.
Types of skin rashes are differentiated by shape, location on the body, color, and area of the rash.
There are two main groups:
- primary – spots, blisters, blisters, roseola, nodules;
- secondary – various types of dermatoses.
According to the location they are distinguished:
- skin rash on the abdomen;
- rash on the skin of the face;
- skin rash on the back;
- rash on the skin of the hands;
- rash on the skin of the body.
Causes of the rash
Infectious and fungal diseases can act as provocateurs. Often it acts as a response to an allergy or serves as a symptom of a disease of the internal organs.
Scabies
Scabies is a contagious skin disease that is caused by a tiny parasite, the scabies mite. The main signs of the pathology are itching and a red rash in the form of papules. Often secondary rashes with purulent contents appear when scratched.
Lichen
Ringworm is an infectious disease in which the skin is affected by a fungus. Pathology manifests itself in pigmentation of a certain area of the skin. A person complains of itching and flaking. The temperature may rise and the general condition may worsen. Ringworm can affect both a specific area of the skin and the entire body. The most severe form of pathology is eczema.
Fungal infection
Fungal infections manifest themselves in an erythematous-squamous and follicular-nodular form. The first type is characterized by damage to any area of the skin. The pathology is accompanied by intense itching. The rashes are group in nature. This form of the disease is characterized by a chronic course with exacerbations.
Red rash on the body
The course of the follicular nodular form is more severe. The pathology affects the deep layers of the epidermis in the area of the buttocks, lower legs, and forearms. The elements cover large areas of the skin over time. The disease is fraught with serious complications.
Herpes
Herpes is a skin disease of viral etiology. It is characterized by a rash in the form of blisters on the skin and mucous membrane. The bubbles are filled with transparent contents.
The disease is accompanied by:
- itching and burning of the skin;
- chills;
- asthenia.
Measles
Measles is an infectious disease.
It is accompanied by:
- red rashes on the body;
- increased temperature;
- conjunctivitis;
- cough;
- sore throat.
The virus enters through the mucous membrane of the mouth, nose and eyes. You can only get sick once in your life. After infection, the body develops immunity.
Rubella
Rubella is a pathology of viral etiology.
It is accompanied by:
- short rise in temperature;
- small rash;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Chickenpox
Chickenpox is a viral disease.
It is characterized by:
- increased temperature;
- inflammation of the mucous membranes;
- vomiting;
- headache;
- rash.
A red rash on the body of an adult is associated with the multiplication of the virus in the mucous membranes and skin. Due to the expansion of small capillaries, redness is provoked, then a papule is formed, representing an inflamed tubercle.
Subsequently, the upper layers of the skin begin to peel off, after which a vesicle is formed. A vesicle is a bubble with transparent contents. Sometimes it starts to fester. When the bubbles open, a weeping surface is formed. More often, the vesicles dry out and turn into crusts.
Scarlet fever
Scarlet fever is an infectious pathology that manifests itself in a tiny rash, intoxication and sore throat.
Most often children get it, but adults can also be infected. The causative agent is streptococcus. The first small rashes are localized in the neck and upper torso. The skin takes on a reddish tint and becomes rough. Within 2-3 days, the rash covers the entire body. It lasts up to 5 days. Then peeling occurs at the site of its formation.
Folliculitis
Folliculitis is a dermatological pathology in which inflammation affects the hair follicle. As a result, pus accumulates in it. The disease can affect the scalp and face. At the initial stage, the inflammation takes the form of a pink papule.
Often the skin around the growth becomes red. Then at this place the formation of an abscess - a pustule - occurs. Over time, the pustule breaks out and pus begins to ooze from it. It turns into erosion, which becomes crusty. Folliculitis is fraught with complications such as furunculosis. Pathology is provoked by viruses, fungi and bacteria.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is considered a chronic pathology of non-infectious nature. An indicator of the disease is pink-red rashes and skin peeling. Accompanied by intense itching.
Hives
Hives are a variant of rash. In most cases, its trigger is an allergy, but the infectious nature of the rash cannot be ruled out. Urticaria is not an independent disease. It acts as a symptom.
Usually manifests itself as a consequence:
- allergic shock;
- bronchial asthma;
- diabetes mellitus:
- immune system disorders.
Hives manifest as red blisters and spots that itch. The number of nodules depends on the severity of the pathological process. The rashes are characterized by changing location and inconstancy.
Prickly heat
Miliaria is a type of dermatitis. It is a consequence of skin irritation due to excessive sweating. In severe forms of miliaria, blisters with a diameter of 2 mm appear. They are filled with cloudy content and are distinguished by red borders that lack clarity.
The rashes do not merge. They are characterized by intense itching. Often the blisters are located under the breasts and in the inner thighs.
Allergic reaction
Rash of an allergic and infectious nature differs according to some indicators:
- With an allergic reaction, the temperature does not rise, while with an infectious lesion, its indicators increase.
- Allergic rashes are always accompanied by intense itching. In case of infection, this symptom may be absent.
- A red rash of an allergic nature on the body of adults appears in the shortest possible time and is localized at the site of contact with the allergen. Typically the rash is localized in the abdomen, chest, and folds of the arms and legs. With an infectious lesion, the rash forms in stages.
An allergic reaction on the skin signals a malfunction of the immune system. The rash can take the form of blisters, nodules, or dots. Only a specialist can make a correct diagnosis.
The following types of skin allergies exist:
- Drug allergy. Formed as a reaction to medications. Allergy manifests itself in the form of erythema, vasculitis, exanthema, dermatitis, and urticaria. Usually single neoplasms are formed. The rash disappears after taking medication.
- Atopic eczema is hereditary. It appears as pink papules that rise above the skin. New growths have unclear boundaries and a smooth surface. As the rashes merge, the skin begins to thicken and peel.
- Photodermatosis. This is a reaction to sunlight. The disease appears in the spring. It is characterized by the formation of nodes that can merge. As a result, the skin thickens, begins to itch and becomes crusty. Subsequently, the affected areas of the skin begin to become pigmented.
- Allergy to cold. Signs are observed when the body cools. Red blisters form on the skin and last for about 2 hours. They itch. A red rash forms on the face and hands. In some cases, blisters persist for a week. Usually the allergy disappears 3-5 years after its occurrence, but it is prone to recurrence.
- Insect allergy. It is a response to an insect bite. It is characterized by swelling, redness and itching. The rash may spread throughout the body. Lymph nodes may become inflamed.
- Food allergies. It includes urticaria, atopic dermatitis, erythema and a measles-like rash. The neoplasms do not rise above the skin and do not have a cavity. There is a change in the epidermis.
- Allergy to latex. It is provoked in individuals with atopic reactions. It is more often diagnosed in women over 30 years of age. Appears upon contact with latex products. The reaction is expressed in hyperemia of the skin. After 72 hours, the rash takes the form of blisters.
- Parasitic allergies can occur due to helminthic infestation. Ascaris, Trichinella spiralis, and Echinococcus can cause allergies. The clinical picture suggests the development of urticaria or Quincke's edema. Seals form at the site of reddish rashes. The skin begins to itch.
- Allergic vasculitis. It represents a reaction to infections, drugs, intoxication, endogenous allergens and nutritional disorders. The basis of vasculitis is the pathological reaction of blood vessels up to the main ones. Reddish nodules ranging in size from a pea to a walnut are formed. Neoplasms are localized on the legs and buttocks.
- Allergy to house dust mites. It is expressed in atopic dermatitis, which is characterized by a red rash and itching.
Simple contact dermatitis
A red rash on the body of an adult develops upon contact with stainless metal alloys. Contact dermatitis forms.
The pathology is characterized by:
- itching;
- swelling;
- redness of the skin.
Papules and blisters form, which burst and begin to weep.
Eczema
Eczema is accompanied by swelling and itching. Subsequently, a rash forms on the body. Combed skin becomes covered with tiny blisters filled with serous fluid.
Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic dermatosis.
It lies in defeat:
- hair follicles;
- sebaceous glands;
- skin capillaries.
The disease is characterized by the formation of persistent erythema and red nodules, which transform into ulcers. There is a significant thickening of the skin, which can provoke the development of cosmetic defects.
Furunculosis
Furunculosis has a purulent-necrotic nature. Dermatosis affects:
- hair follicles;
- sebaceous glands;
- capillaries.
The primary element is a red knot that forms in the hair follicle area. It is filled with pus and can reach the size of a walnut. The main cause of the pathology is the penetration of staphylococcus into the skin.
Pyoderma
Pyoderma is a purulent-inflammatory pathology of the skin, the provocateur of which is infection with staphylococcus or streptococcus.
Pathologies are inherent:
- rashes;
- inflammatory process in the epidermis;
- redness of the skin;
- itching feeling.
Increased proliferation of bacteria provokes extensive damage to the skin.
Athlete's inguinal
Inguinal athlete's foot is a fungal infection of the epidermis layer. It forms in large skin folds. It is characterized by pink spots that begin to peel off. The edges of the neoplasm are covered with vesicles and pustules. Most often, pathology forms in the groin area.
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus is a chronic pathology. The main manifestations are pink spots localized on the face (lupus butterfly). The disease is associated with a disorder of the immune system. Mostly middle-aged women are affected by the pathology.
Cancer
Skin cancer is characterized by the formation of a large red rash, which is aggravated by itching and pain. The appearance of new elements does not entail a change in the general condition of the patient, whereas in allergic and systemic pathologies it is observed.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Stevens-Johnson syndrome is a bullous dermatitis of allergic etiology. Pathology is characterized by the death of epidermal cells.
The disease affects:
- The mucous membrane of the oral cavity. Blisters form on it, causing pain and copious salivation.
- Urogenital tract. As a result, difficulty urinating occurs.
- Conjunctiva. A purulent form with souring of the eyelids is provoked.
Digestive system disorders
A red rash on the body of an adult with a disorder of the digestive system can have different causes:
- Bright red spots on the skin with gangrenous pyoderma belong to the group of neutrophilic dermatoses. The main reason is pathological processes in the intestines. The disease is characterized by the formation of red ulcers that hurt and degenerate into scars.
- Red pimples may indicate the presence of gallstones. Typically, the localization area for neoplasms is the temples. With pathologies of the small intestine, acne forms on the forehead. In complicated forms of the disease, the rash spreads throughout the body.
- Eczema or dermatitis is caused by pancreatitis. Eczema is characterized by a blistering rash and inflammation. Dermatitis rashes are accompanied by intense itching. The skin becomes dry.
Thyroid disorders
Violation of the functionality of the gastrointestinal tract provokes changes in skin morphology. A deficiency of beneficial bacteria causes dysfunction of the epidermis, which causes infection or inflammation. Thyrotoxicosis causes sweating and moisturizing of the skin. The palms and face become covered with a red rash.
Experts have proven the connection between autoimmune thyroiditis and chronic urticaria.
In the practice of clinicians, hypothyroidism causes such pathologies as:
- pemphigus;
- atopic dermatitis;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- thrombocytopenic purpura.
Diseases of the blood and blood vessels
Rashes due to pathologies of the blood or vascular system are provoked by a violation of the structure of the capillaries. Petechiae are formed - small red dots. Unlike hemorrhages, a rash due to blood pathologies does not change color when pressed.
Hematology is indicated by:
- pain in the joints;
- diarrhea;
- spread of the rash throughout the body.
Hemorrhagic rash is caused by the following pathologies:
- Werlhof's disease. With it, the smallest arteries are blocked by blood clots. The rash does not cause pain.
- Hemoblastosis. This is a cancerous tumor. The rash may look like red crusty balls, serous blisters, or bruising. All rashes are accompanied by intense itching.
- Hemophilia. It is characterized by the most dangerous rashes that form deep in the epidermis. They can spread to internal organs, joints and cause extensive bleeding. Hemophilia is mainly diagnosed in newborns and men.
- Diabetic angiopathy. When vascular permeability is impaired in diabetes, ulcers and erosions form.
Liver diseases
Skin rashes are among the early symptoms of liver pathologies. Cholestasis is characterized by localization of the rash in the area of the feet and palms. A rash in the form of red plaques looks like a burn. New growths are round in shape with clear boundaries. Gradually they transform into blisters, which burst and leave a red mark with a pronounced border and white src=»https://healthperfect.ru/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/krasnaya-syp-na-tele-13.jpg "class="aligncenter" width="700″ height="467″[/img]
With cirrhosis, the death of organ cells occurs, which provokes the covering of the entire body with red spots. Damage to the liver by parasites provokes rashes that resemble urticaria.
They are grouped in the lumbar and abdominal areas. Also, rashes with liver damage can manifest themselves in the form of pimples. They come with fatty and purulent contents. Papules often form. Typically, with liver pathologies, acne is localized on the face, neck and chest. Liver pathologies are characterized by a combination of rash and spider veins.
Nervous rash
Rash of nervous origin is a common occurrence. Violation of the emotional background provokes the development of diseases of internal organs and a malfunction of the immune system.
A nervous rash can take the form of:
- hives;
- eczema;
- scabies;
- psoriasis.
Bites
Urticarial rash is a response to an insect bite. It appears in the form of blisters that rise above the skin surface.
Blisters are different:
- density;
- itching;
- pink-red color.
Rash due to infectious diseases
Rashes in infectious diseases are often characterized by stages of appearance, first it appears in one place, then in another, also for each infection there are typical places for rashes, a specific shape and size, it is important to remember all the details and, when interviewing, report all this information to the doctor.
Below we look at rashes associated with various infectious diseases:
Rubella - in the initial period of the disease, a small rash appears on the face and neck, then within 2 to 6 hours the rash spreads throughout the body. Usually appears as round or oval redness ranging from 2 to 10 mm in size. Remains on the skin for up to 72 hours, then disappears without visible traces. If you find yourself with a similar rash, you need to consult and examine a doctor, since similar rashes are symptoms of many infectious diseases. We also recall that rubella poses a particular danger to pregnant women, since if the mother is ill, the infection can harm the fetus.
Measles – the disease measles usually manifests itself with catarrhal manifestations. The rash appears after 2-7 days. The primary places of protrusion are on the skin of the nose and behind the ears, then within 24 hours it spreads to the skin of the chest, face, then the arms and neck also become covered with rashes. After 72 hours, the rash also covers the legs; the rash is most often intense and confluent. After the active phase of the disease, the rash changes color and forms something like pigment spots.
Chicken pox - at the onset of the disease it manifests itself as red spots, then bubbles with a red ring and liquid inside appear, similar in appearance to dewdrops. After two days, the outer surface of the bubble collapses and becomes less elastic. Subsequently, the blisters become coarser, crust over and disappear within seven days without leaving any visible traces.
Scarlet fever - Rashes with scarlet fever appear 24 hours after infection, the areas of active manifestations are the back, groin, elbow and knee bends, and armpit skin. Then inflammation appears on the skin, sometimes there is a slight blue discoloration in the places where roseola forms. The face with scarlet fever is usually not affected by a rash.
| Chicken pox | Scarlet fever |
Causes of red rash during pregnancy, menopause
Rash during pregnancy is common. Neoplasms in the abdominal area can signal hormonal changes in the female body.
The rash may spread to the area:
- hands;
- backs;
- buttocks;
- hips;
- breasts
Another important cause of rashes is allergies. It can be provoked by:
- Food;
- cosmetical tools;
- cloth;
- plants;
- household chemicals;
- metal jewelry;
- medications.
Allergies usually cause blisters to form and burst. They often become further infected. Allergies are triggered by altered hormonal levels and can cause gestosis. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor in time.
During the summer, a pregnant woman may develop prickly heat. It is a consequence:
- increased sweating;
- wearing synthetic clothing;
- wearing a bandage;
- insufficient body hygiene.
Dermatosis often develops during pregnancy. Usually occurs in the last trimester with strong weight gain. The rash takes the form of red bumps. It does not pose a danger to the fetus and disappears after childbirth. The appearance of a small rash in a pregnant woman indicates the development of urticaria. It is an allergic reaction to food.
Menopause provokes a decrease in estrogen levels, which exacerbates the sensitivity of the skin. Often the skin begins to react to cosmetic products.
Hives may develop. Increasing testosterone levels enhances the function of the sebaceous glands. The sebaceous ducts and hair follicles become clogged more intensely than usual. Red pimples are formed, which are characterized by density and depth. As a rule, they are localized near the mouth, on the chin and neck.
ethnoscience
Depending on the nature of the tumors, treatment methods may vary. Until there is a final diagnosis, it is highly undesirable to use traditional medicine.
Thus, an ointment that can be used to cure scabies is strictly contraindicated for drying red moles.
However, there are some recipes that can help with non-dangerous diseases. A red spot on the face or limb with blisters around the edges may be lichen vesica.
In this case, traditional healers suggest using apple cider vinegar or viburnum juice as lotions. Carry out the procedure about 5 times a day for 10 minutes.
Purple spots in the throat are a clear sign of the disease. In this case, it is advisable to use beet juice with honey. For a glass of juice you will need 1 tbsp. l. flower honey. Gargle with the resulting liquid in the morning on an empty stomach and in the evening before bed.
A white tongue with scarlet dots is a sign of stomatitis. In this case, traditional medicine suggests the following: take a hair from the head, rub it over the areas of stomatitis, as if cutting them off, rinse your mouth with a decoction of sage and chamomile.
Medicinal plants have been used to treat skin diseases for thousands of years. Combining anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, hyposensitizing, and multivitamin activity, many of them can significantly improve the quality of treatment and life of patients.
Using folk remedies, you can cure, for example, scabies. In addition, they will help cope with dermatitis.
Scabies is caused by scabies mites and is accompanied by severe itching. The reasons for this may vary. For example, insect bites.
But these also include external medications (for example, streptocide or iodine). So with such a disease, it sometimes becomes impossible to use pharmaceutical products. Many people face a problem called acne. Unfortunately, this disease affects not only teenagers, but also people of other ages. Medicines to cure rashes do not always help, and sometimes also cause an allergic reaction - in addition to acne.
Therefore, folk remedies are often the way out. Traditional methods of treatment do not cause any harm and are often very effective in treating the disease. So, what can you use from natural pantries?
- Lingonberry juice is used externally for lichen and scabies.
- The juice of fresh knotweed grass is good for treating bleeding or old wounds, ulcers (you need to moisten a napkin with the juice and, after washing the wound with it, apply it to the site of damaged tissue).
- Oak bark decoction is used for washing and compresses for skin diseases, wounds, and burns.
- Grated carrots - applied to inflamed areas of the skin, burns, purulent wounds.
- Sea buckthorn oil - taken orally 2 milliliters per day and externally in the form of a 5% ointment made from sea buckthorn oil, cheilitis, eczema, and scaly lichen are quite successfully cured. Sea buckthorn oil also promotes rapid resorption of infiltrates, reduces erythema, swelling, pain and burning, stops peeling, promotes epithelization and the disappearance of itching.
- St. John's wort - it is suitable for the treatment of burns, various skin diseases and wound healing. Use St. John's wort oil (pour a tablespoon of flowers with a glass of vegetable oil, leave for 14 days).
- Cranberry juice - compresses made from it are used for lichen, dry eczema and other exudative skin processes.
- Lemon is a good remedy for all kinds of lichens and eczema. The course of treatment is as follows: on the first day, drink the juice of five lemons in several doses, on the second - from ten and so up to 25, adding five lemons every day. Then reduce the number of lemons until you reach five again. It is better to drink the juice through a straw so as not to spoil the tooth enamel; after drinking, you should rinse your mouth thoroughly.
- Strawberry leaves, roots and leaves, mint in the form of decoctions, linden leaves in a mixture have a calming effect on skin diseases, including various eczemas.
Pustular lesions are one of the most common groups of skin diseases. They are most often caused by bacteria, staphylococci and streptococci.
The disease is characterized by the appearance of rashes on the skin, predominantly pustular in nature. Some pyodermatitis is contagious to others and even becomes epidemic in schools or kindergartens.
As a rule, all patients with pyodermatitis have impaired carbohydrate metabolism. Therefore, when carrying out herbal medicine, patients are prescribed plants that have a hypoglycemic effect: ginseng or aralia roots, blueberry leaves, dandelion roots, horsetail herb, strawberry leaves, nettle herb.
To strengthen the body's resistance, patients are helped by tonic herbal remedies: aralia tincture, Chinese lemongrass, Eleutherococcus, ginseng. Tinctures are taken 30-40 drops in the morning and at lunch before meals.
Vegetable and fruit juices are also of great importance, especially the juice of potatoes, carrots, white cabbage, hawthorn, fireweed, and nettle. It is better to drink juices diluted with water in a 1:1 ratio.
In this case, traditional medicine recommends the following medicinal plants:
- A decoction of cocklebur herb is used for folliculitis. 10 grams of dry herb are poured with 200 milliliters of water, left for 1 hour, filtered. Used to wipe the skin.
- Fresh inner leaves of white cabbage mixed with egg yolk and chewed rye bread are applied to the lesions for pustular skin diseases.
- A decoction of willow bark (50 grams of bark per 500 milliliters of water, boil for 20 minutes) can be used for compresses.
- Plantain juice is used to treat boils and pyoderma, and a paste of mashed leaves is applied in the form of compresses.
- Resin from pine, fir and spruce is one of the best remedies for any pustular diseases. Apply as a bandage or lozenge to the affected area.
- Rose oil and Kazanlak rose are effective in the treatment of pyoderma, furunculosis and all pustular diseases. Used in the form of lotions or compresses, or internally.
With the frequent formation of acne and pustules on the face, the following folk remedies will help:
- Tincture of white lily petals: 10 grams of petals per 100 grams of vodka. Leave for 2 weeks and wipe your face before going to bed;
- Crushed seeds of coriander and orris (1:1) - they can be used as a powder in areas of rash on the face;
- Warm compresses from infusion of herbs and dill seeds;
- Adding some brewer's yeast to your daily meals.
Source: vashdermatolog.ru
What does it mean if a red rash on the body itches?
Itching itself is a marker of dysfunction of internal organs and systems.
The feeling of itching when a red rash appears on the human body can be provoked by:
- hives;
- scabies;
- deprived;
- heat rash;
- skin cancer;
- fungal infection
- digestive disorders;
- failure of the thyroid gland;
- chickenpox;
- scarlet fever;
- measles;
- rubella;
- herpes;
- folliculitis;
- pyoderma;
- eczema;
- rosacea.
Erythema
Erythema - large areas of hyperemic skin. Erythema occurs as a result of dilation of the blood vessels of the skin papillae and subpapillary choroid plexus. Within the erythematous fields there may be areas of skin with normal color. Such erythema with a diameter of up to 20 cm or more is characteristic of Lyme boreliosis.
Erythema in Lyme disease
When is it necessary to go to the clinic, which doctor?
Human skin is like litmus paper. It is an indicator of the functioning of internal organs and systems. A rash of any nature is an indicator of infection or internal pathology. In some cases, tumors form due to stress.
If the rash causes pain and does not resolve with over-the-counter medications within a week, you should consult a specialist. You should contact a dermatologist. If the rash appears in the genital area, then you should make an appointment with a urologist or gynecologist.
Types of rashes in adults
Experts identify different types of rash, the exact definition of which often determines the correct diagnosis:
Stains
They are located at skin level, without rising above the surface. Depending on the color, roseola (red or pale pink spots), hyperpigmented spots (nevi, liver spots - brown spots), depigmented spots (vitiligo-white spots) are distinguished.
Papule
A limited, slightly elevated formation with a flat or dome-shaped surface. Large papules are called plaques.
Blisters
Elements with a rough surface raised above the general level of the skin.
Bubbles
Formations on the surface of the skin filled with liquid contents (serous, bloody or purulent).
Ulcers and erosions
Areas of violation of the integrity of the skin, often covered with secretions of one kind or another.
Treatment
To eliminate rashes, it is necessary to determine the nature and cause of neoplasms. Self-medication is excluded. In case of an allergic rash, the allergen itself is eliminated first. For infectious rashes, drugs with antibacterial effects are prescribed. In case of skin rashes caused by pathology of internal organs, the root cause of the rash is also eliminated.
External medications
Rashes require quick elimination, since the skin acts as a barrier against the penetration of harmful bacteria from the environment. Dryness and acid-base imbalance develop with untimely treatment. Ointments can prevent complications and restore normal functionality of the skin.
| Hormonal ointments (Prednisolone, Flumethasone, Clioquinol) | Eliminate inflammation and allergic reactions. Do not use without a doctor's prescription. |
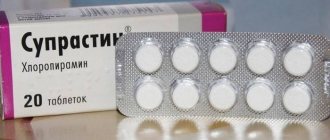
| Antihistamines (Zyrtec, Suprastin) | Reduce the number of tumors, eliminate itching and redness. |
| Combined products (Celestoderm B, Triderm, Flucinar) | Includes several components. For example, hormones, antifungal components and antibiotics. |
| Ointments with a healing effect (Belosalik, Lorinden, Akriderm GK) | Heal, soften and moisturize. Contains petroleum jelly, herbal extracts, glycerin, zinc, dexpanthenol. |
Internal preparations
Oral medications are also used.
| Antibiotics (Doxycycline, Erythromycin, Zinnat, Levomycetin, Tetracycline) | Eliminate purulent acne and inflammation. Prescribed in extreme cases. |
| Retinoids (Roaccutane, Retinol Palmitate, Isotretinoin, Adapalene) | Used for complicated rashes. Have side effects. Therapy is carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor. |
| Hormonal agents (Jess, Regulon, Yarina, Janine) | Prescribed for increased testosterone. |
| Preparations for cleansing the body (Bifiform, Linex, Lacto-filtrum, Polysorb) | Used for problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Removes toxic substances from the intestines and liver, improves skin morphology. |
| Dietary supplements and vitamins (Zincteral, Loma Lux Acnemol, Milgamma, Brewer's yeast) | Used in case of malfunction of the immune system and vitamin deficiency. |
| Antihistamines (Allertek, Zovirax) | Helps eliminate allergic reactions. |
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are also used to eliminate the rash.
Herbal tinctures for rubbing are widely used:
- Take 500 ml of boiling water and dissolve 1 tbsp in it. l. tinctures of pharmaceutical calendula. Leave the mixture for half an hour. Wipe the skin with the solution.
- Take 1 tbsp. l. sage Pour a glass of boiling water over the herb. Leave the mixture for 7 days. Wipe your face with it several times a day.
The following tinctures are recommended for oral administration:
- Take 3 tbsp. l. dry nettle. Grind it and pour 2 glasses of water. Boil for 5 minutes. Let it brew for 1 hour. Take 1/2 cup 3 times a day.
- Take 2 tsp. dry round-leaved sundew or English sundew. Pour 2 cups of boiling water over the herb and let it brew for 1 hour. Take 2 tbsp. l. 3 times a day. Drink in small sips.
- Take 10 g of cornflower flowers. Pour 300 ml of boiling water over the flowers. Leave the mixture for 2 hours. Drink 1/4 cup 3 times a day.
The following recipes are used to prepare masks:
- Dissolve salt in warm water. Add clay. Stir the water until it reaches a thick consistency. Apply the clay mixture to the affected areas for 20 minutes. The rash will dry out and disappear after a while.
- Take the dry string and grind it into powder. Brew with boiling water until a decoction is obtained. Leave for 20 minutes. Take white clay and mix with the infusion until a thick mass is obtained. Use the mask 3 times a week.
The following recipes are offered for preparing baths:
- Fill the bathtub with warm water to 20 cm. Add a little potassium permanganate to it until it gives a slight tint and a little salt. Dissolve the components completely. Lie in the bath for 20 minutes, then pat your body dry with a towel.
- Grind oat flakes in a coffee grinder. Add the resulting flour to the water bath and stir. Take a bath for 20 minutes.
The red rash can be eliminated quickly using folk remedies, but you should consult a dermatologist. Usually, tumors on the body in adults are eliminated in conjunction with the use of medications.
How to treat
After the disease is identified, it is determined how to treat its manifestations. Self-medication in this case is inappropriate. The treatment regimen in each case is individual. To eliminate skin diseases, oral medications, injections, or topical agents are used.
- The fungus is treated with Clotrimazole, Fluconazole, Nystatin or Ketoconazole.
- Antihistamines aimed at eliminating allergies include: Suprastin, Fenkarol, Clarotadine, Tavegil and Kestin.
- For skin diseases of viral origin, Acyclovir, Neovir, Ribavirin, Amiksin and Cycloferon are prescribed.
- Surgical treatments are available to treat the symptoms of the papilloma virus. These include the use of laser, cryotherapy, radio wave exposure and electrocoagulation.
- If there are problems with hormones, appropriate hormonal medications are prescribed.
- For nervous disorders, the use of Glycine, Afabazole, Novo-Passit, valerian and motherwort tincture is indicated.
Prevention
To prevent skin rashes, the following is recommended:
- Spend enough time organizing your daily routine and nutrition.
- Be sure to maintain hygiene.
- Be less nervous , in any case, try to direct your thoughts in a positive direction.
- If there are pets in the house , and an allergy to wool is noticed, then it is necessary, if possible, to limit contact with them and keep the apartment clean.
- In addition , if allergies occur when using cosmetics or consuming a certain type of product, they should be excluded. The same applies to household chemicals.
- In apartments and houses, it is recommended to do wet cleaning and ventilate rooms more often.
Leading dermatologists, based on the findings that manifestations such as skin rashes in people tend to increase, as evidenced by statistics, recommend that patients do not delay their visit to the hospital and, if such symptoms occur, immediately seek medical help.
This approach will make it possible to promptly stop any disease in the early stages of development, without waiting for complications and without pushing the disease deeper. In addition, experts advise not to neglect prevention methods and take care of your own health.
After all, any disease, including skin rashes, is always easier to prevent than to undergo long and grueling treatment.
Types of allergies
The appearance and characteristics of skin rashes depend on the type of allergic dermatosis. The rash can appear either on a separate area of the body, for example, an allergy on the legs, or be localized throughout the body.
That is why in medicine there are several main types of allergic reactions:
- Atopic dermatitis.
- Contact dermatitis.
- Hives.
- Eczema.
- Toxidermy.
- Neurodermatitis.
- Quincke's edema.
- Lyell's syndrome.
- Steven-Johnson syndrome.
What does a syphilitic rash look like?
If you want to understand what a syphilitic rash looks like, then you need to start with the stage at which the rash appears. Regardless of it, such a rash has similar symptoms:
- reddish spots may appear in the genital area, under the hairline; for women, localization is typical on the chest;
- spots disappear without intensive treatment after 2 weeks from the date of appearance;
- accompanied by fever and headaches.
In primary syphilis, the spots have a mild red pigmentation without itching or peeling. They do not cause any discomfort and do not require any treatment.
What does a syphilitic rash of the second stage look like? Localization occurs in the same places. But now the spots are more reminiscent of ulcers, blisters of a pale pink color, which over time acquire bluish and brown shades.
The third degree of syphilis has pronounced lumps of a rich brown color, which over time turn into purulent ulcers, after which serious scars remain.
It is worth considering that there may be spots of several stages of syphilis on the body. Therefore, it is impossible to say for sure what a syphilitic rash looks like in an advanced state, since the manifestations vary.
The mechanism of skin allergies
The main factor in the manifestation of allergic dermatosis is considered to be an allergen - a substance of molecular structure that is of protein origin.
It happens that allergens can be various elements that do not provoke an immune response when they penetrate the blood. Particles that are carried by antigenic determinants are called haptens. These elements can bind to tissue proteins. Haptens are found in medications and other chemicals.
If an allergen or irritant enters the human body, sensitization begins to develop, which subsequently leads to excessive sensitivity of histamine receptors. This action is explained by the formation of antibodies or the synthesis of sensitized leukocytes.
An allergic rash on the skin of an adult forms at the stage of pathophysiological development of the disease. At this time, mediators of the pathological process are able to affect normal skin cells, provoking an inflammatory process.
Itching
In most cases, skin allergies can be accompanied by itching of varying intensity. The main causes of itching are external and internal allergens.
The body begins to perceive such allergens as dangerous, which results in an allergic reaction in the form of itching. There are several main allergic skin diseases that can be accompanied by itching. These diseases are described below.
Here you will find in more detail the answer to the question of what to do when a spot on the skin itches due to an allergy.
What does an allergic rash look like?
Allergic reactions manifest themselves in different ways. And it is not at all necessary for a person to develop a rash. Skin irritation is just one sign of an allergy. What does an allergic rash look like? Very impressive: small, red, localized on the face, mucous membranes, hands and legs. It all depends on the immediate allergen.
All parents know what an allergic rash looks like in children. If it is caused by direct contact with an allergen, then the rash will be especially obvious at the points of contact. You need to be careful when choosing hygiene products for your baby and try them on small areas of the skin first. Often, young mothers make an irreparable mistake and treat the entire skin of the baby with oil or cream. In this case, the rash is especially obvious and can cause a rise in temperature. If the problem is a food allergen, then the rash usually appears on the face, small and red.
Steven-Johnson syndrome
Steven-Johnson syndrome is a form of exudative erythema multiforme, which is characterized by inflammation of the mucous membranes and skin.
This disease has a very severe course. Most often, Steven-Johnson syndrome affects people over 40 years of age, however, cases of the disease have also been recorded in young children. In the first stages, the disease affects the respiratory tract.
Symptoms of Steven-Johnson syndrome:
- Fever.
- General weakness.
- Cough.
- Headache.
- Joint and muscle pain.
- Vomit.
- Diarrhea.
- Rashes on the skin.
- Swelling of formations.
- The rash is red.
- Itching.
- Burning.
- Skin lesions bleed.
Causes of Steven-Johnson syndrome:
- Existing infectious diseases.
- Allergic reaction to medications.
- Malignant diseases (cancer).