From this article you will learn: what a heart attack is, what signs it manifests itself. First aid and treatment. How to prevent a recurrence.
Author of the article: Victoria Stoyanova, category 2 doctor, head of the laboratory at the diagnostic and treatment center (2015–2016).
Article publication date: 03/02/2017
Article updated date: 05/29/2019
A heart attack is the appearance of pain in the heart area, which is accompanied by additional unpleasant symptoms. This phrase serves as a common name for an acute form of coronary artery disease. The colloquial concept of “heart attack” roughly corresponds to the medical term “acute coronary syndrome” - a diagnosis that is given to the patient before a detailed diagnosis. After additional examination, the diagnosis is changed to unstable angina or myocardial infarction.
That is, a heart attack can be understood as either an intense attack of angina or a heart attack.
If it occurs, call an ambulance immediately. Depending on the severity of the condition, the patient may be hospitalized or receive medical care at home, and this will be enough. After a heart attack, you will need to see a cardiologist regularly.
Development mechanism
Regardless of the type of disease process, the essence is always approximately the same.
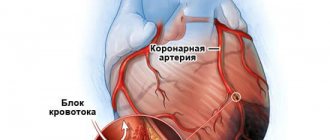
During the influence of one factor or another, there is a disruption of the normal blood supply to the myocardium through special arteries called coronary arteries.
The result is acute ischemia (oxygen starvation) of tissues. This phenomenon corresponds to an attack of angina pectoris, and if the degree of blood flow disturbance is great, to a heart attack.
During the episode, a slowdown or complete cessation of local hemodynamics and necrosis of cardiomyocytes (the actual units that make up the active muscular layer of the heart) are observed.
The process is accompanied by intense chest pain and other symptoms.
Without competent medical care, the contractility of the myocardium decreases, and blood output is insufficient.
The nutrition of the brain, organs and systems weakens. Hence additional manifestations, such as fainting and others.
The likelihood of death depends on the area of the lesion. The larger the lesion, the higher the risk of death.
A heart attack is an emergency condition accompanied by necrosis of cardiomyocytes and generalized symptoms and hemodynamic disturbances.
Recovery is carried out urgently, in a hospital or intensive care unit.
Hospital treatment
When a victim is admitted to the hospital, the following laboratory and instrumental examinations are prescribed to make an accurate diagnosis:
- blood test to detect the presence and concentration of cardiac enzymes;
- cardiogram (ECG);
- Ultrasound of the heart (EchoCG);
- cardiac catheterization using a contrast agent (if necessary);
- chest x-ray.
Analysis of the medical history and data obtained during a comprehensive examination of the patient’s cardiac status are the basis for choosing subsequent treatment measures.
The length of treatment in a hospital setting will depend on the patient’s age and the severity of the heart attack. On average, such patients stay in the hospital for at least two weeks.
Treatment and recovery after a heart attack will be especially long. During the first days, the patient is under the close attention of doctors in the intensive care unit or intensive care unit. As a rule, such patients are not transferred to the general cardiology department before three days.
In total, recovery after a heart attack requires at least two to three weeks, and after an attack of angina - up to one and a half to two weeks.
Patients are not recommended to stop rehabilitation therapy early and go home. When staying at home, the risk of possible complications and recurrent attacks increases significantly. The patient's condition requires monitoring of cardiac indicators using special equipment, which is impossible at home.
Drug therapy
After the incident, the patient is prescribed medications that are necessary to prevent a recurrent attack of angina or myocardial infarction.
Complex drug treatment and relapse prevention involves taking drugs from several drug groups at once:
- antiplatelet agents – prevent platelet aggregation (Aspirin Cardio, Acekor Cardio, Aspecard);
- beta-blockers - normalize heart rate and lower blood pressure (Sotahexal, Tenzol, Anaprilin, Blockarden);
- cardioprotectors (Prestarium, Mildronate);
- statins - medications that lower cholesterol levels (Liptonorm, Lipostat, Rozulip);
- diuretics - eliminate swelling, remove excess fluid (Aldactone, Veroshpiron, Indapamide).
Surgical intervention
In order to restore normal blood circulation in the heart muscle, various methods of surgical intervention can be used:
- coronary (balloon) angioplasty or stenting is a procedure, the principle of which is to insert a balloon catheter into a narrowed vessel. The operation does not eliminate the cause of ischemia, but relieves its consequences. To prevent the vessel from narrowing again, a stent is inserted into it - a device made of thin material that acts as a spacer that fixes the width of the vessel.
- coronary artery bypass grafting or bypass surgery of the heart vessels is an operation that allows you to restore blood flow in the arteries and large veins, bypassing blocked vessels. This is accomplished through an artificially created bypass path (shunt).
Classification
The main criterion is the nature of the pathological process. It has already been mentioned in passing that a heart attack is a simplified name for two phenomena.
Which ones:
Angina pectoris
Usually unstable form. Its essence lies in disruption of the normal nutrition of the heart muscle. But the volume of the lesion is not yet enough to cause extensive destruction of cardiac structures.
This form is characterized by constant, smooth or spasmodic progression without signs of improvement even with full therapy.
Recovery requires lifelong medication without any guarantees. Effective treatment is possible only at stages 1-2.
Heart attack
The second option is coronary insufficiency. Develops in response to critical narrowing or blockage of the arteries supplying the heart.
The essence is approximately the same - the death of muscle structures, only the volume of destroyed cells is greater. A heart attack occurs immediately, like an avalanche, in contrast to angina, when the development of the same condition may take more than one year, this is the main difference.
Treatment in intensive care, and then in the cardiology department. The prospects are vague. The prognosis depends on the quality of first aid and the area of involvement in the destructive process.
Common complications after a heart attack
This disorder is often accompanied by serious complications that can be life-threatening. These include:
- Arrhythmia is a heart rhythm disorder in which the heart begins to beat faster and faster and then stops (cardiac arrest);
- Cardiogenic shock is a condition in which the heart muscle is seriously damaged and ceases to supply sufficient blood to internal organs and tissues, which leads to disruption of many body functions;
- Heart rupture is the destruction of muscle tissue, walls or valves of the organ. Complications can occur soon after a heart attack and are one of the leading causes of death.
Many men can die suddenly from complications before they even get to the hospital, or within a month after a heart attack.
The prognosis often depends on the following factors:
- Age – the likelihood of severe complications increases with age;
- The severity of the disorder - how badly the heart muscle was damaged during the attack;
- How much time passed before medical assistance was received - treatment should be started as early as possible.
Causes
Factors in the development of an attack are divided into three groups.
- The first directly create the ground for the beginning of the state, being a kind of foundation.
- The latter increase the risk of developing a deviation.
- Still others act as triggers, trigger mechanisms for the onset of the phenomenon.
Etiological points
- Atherosclerosis. Almost the main process (up to 93% of cases) that causes the development of a heart attack (more precisely, coronary insufficiency in general).
Depending on the nature of the defect, two forms are distinguished.
Occlusion or blockage is considered a classic clinical case. The phenomenon consists of closing the lumen of the artery with a cholesterol plaque, or less often with a blood clot. May be partial or complete.
In the second case, vessel obstruction occurs, treatment is extremely difficult. The probability of death is almost 100%.
Another clinical option is stenosis or narrowing of the lumen of the coronary artery. The essence is the disruption of blood flow due to the difficult passage of liquid connective tissue through the vessels.
The result is ischemia (oxygen starvation) of tissues, and with stenosis of more than 70% of the lumen, the first symptoms of an attack occur.
Correction is carried out using surgical methods. Most often, there is a congenital or acquired anomaly of the great arteries.
- Vasculitis. Or an inflammatory disease of the walls of blood vessels (endothelium).
More often it is of an autoimmune nature, running parallel to other pathological processes (systemic lupus erythematosus or rheumatism).
Viral origin is also possible, but is much less common. The disease is always secondary and does not develop in isolation from other pathological processes.
Requires complex therapy. Without help, scarring of the artery occurs with a proportional narrowing of the lumen of the blood vessel. This is a difficult condition to treat. Prosthetic replacement of the affected area is required.
- Hypertonic disease.
Its essence is a stable increase in blood pressure. The danger comes from the second degree and beyond.
The first one proceeds relatively sluggishly, in addition, the tonometer readings are inconsistent, and there is no significant increase in the numbers. But this is the first alarm bell; it indicates the need for treatment.
Transformation and progression occur in a short period of time, sometimes a few months are enough. Recovery under the supervision of a cardiologist.
Excessive stress on the heart leads to chronic malnutrition. Sooner or later a heart attack will occur. Angina pectoris is possible, but not required.
- Diabetes. A systemic endocrine disease associated with insufficient insulin production or decreased tissue sensitivity to it.
Both options have a poor prognosis without treatment. And therapy does not provide a 100% guarantee of complete recovery.
The hallmark of the pathological process is generalized vascular damage, which is determined by stenosis, that is, narrowing.
Hence secondary atherosclerosis, including structures of the lower extremities, brain, coronary arteries.
- Other hormonal diseases. Hypercotricism occurs, that is, excessive synthesis of thyroid substances, excessive production of cortisol by the adrenal glands and other phenomena.
All of them turn out to be the culprits of vasoconstriction. Treatment is planned. Advanced forms are treated in a hospital under the supervision of a group of specialists, in order to avoid fatal consequences.
Risk factors
The second category of reasons or high-risk moments:
- Smoking. Patients who use tobacco have a 70% greater risk of heart attack than those who lead a healthy lifestyle. Research shows that not only experience plays a role, but also individual resistance to toxic agents, which is genetically determined. Therefore, the same time of tobacco consumption will cause different consequences in two different individuals. A drop of nicotine does not always kill, but the results are inevitable. No one will say when they will arise in a month, a year or more. You need to monitor the patient's condition.
- Alcohol consumption. Ethyl alcohol leads to general disturbances in blood vessels and blood pressure quite quickly. But again, individual resistance to ethanol plays a role, which is different for everyone.
- Obesity. It is not the increased weight itself that matters, but what lies behind it. In this case we are talking about a violation of lipid metabolism. Fats are distributed unevenly, and their normal deposition is deviated. The process is corrected with great difficulty; the main way to avoid adverse consequences is to change the very principle of nutrition (in other words, diet).
- Insufficient or excessive physical activity. In the first case, stagnant processes begin, myocardial contractility and vascular stenosis decrease. In another, there is a proliferation of cardiac tissues and compression of the coronary arteries. Both options are unfavorable. While the first is potentially curable, the second has negative prospects.
- Age 45+, male.
Trigger factors
- Stressful situation. Associated with the release of large amounts of cortisol and adrenaline, which provoke coronary artery stenosis. Depending on the extent of the narrowing, one of two types of heart attack is observed.
- Excessive physical activity. The required level of activity depends on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body and his fitness level. For some, it is enough to climb the stairs to the third floor to provoke an attack; for others, even a kilometer of jogging is not enough.
- Hypothermia. An exception.
The causes of a heart attack are both cardiac and non-cardiac. A group of factors plays a role; together they give rise to the pathological process. Eliminating the trigger or moment of risk is not enough. We need to fight all three categories.
Causes and risk group
The main prerequisites for a heart attack are the pathologies of the cardiovascular system, metabolic disorders and other chronic diseases that a person has:
- Hypertension and, as a consequence, hypertensive crisis.
- Coronary heart disease (CHD).
- Deviation in the functioning of the blood clotting system, a tendency to form blood clots (thrombophilia).
- Blockage of arteries and veins by blood clots (pulmonary embolism, coronary artery thrombosis).
- Chronic heart failure (CHF).
- Circulatory disorders caused by cholesterol and fatty deposits on the walls of large and medium-sized arteries (atherosclerosis).
- Diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation, caused by the lack of proper treatment for a long time.
- Various forms of atrial fibrillation, extrasystole.
- Dissecting aneurysm of the thoracic aorta.
Elderly people are at risk, this is due to age-related changes in the condition of the heart muscle and vascular elasticity. If we look at the incidence of heart attacks by gender, they disproportionately affect men. A person’s standard of living can also lead to a heart attack. Therefore, the risk group includes obese people and smokers.
In recent years, the age of angina attacks and heart attacks has decreased significantly. Heart attacks have become common in adults under 40 years of age. Moreover, in medical statistics there are even cases of heart attack at 25 years old and in 16-18 year old adolescents.
A heart attack at a young age can happen due to many factors:
- heredity;
- drug use;
- bleeding disorders;
- exposure to stress;
- emotional instability;
- atypical form of atherosclerosis.
An increased risk of developing angina attacks and pre-infarction is observed in pregnant women with chronic heart disease. This occurs due to a lack of oxygen and increased stress on the cardiovascular system during pregnancy caused by an increase in total blood volume.
Additional provocateurs are: bad habits, excess weight, insufficient physical activity or, conversely, excessive loads, stressful situations, age after 50 years.
Long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in high dosages can also provoke an attack.
Symptoms and first signs of a heart attack
The manifestations are specific, but there are no differences in symptoms between women and men. If you look closely, this gives reason to suspect an attack right away.
Approximate clinical picture:
- Chest pain of varying degrees of intensity is a typical symptom of a heart attack. Against the background of angina pectoris, it is of average strength, it burns and presses. It radiates to the left arm and shoulder blade. Lasts no more than 30 minutes. With a heart attack, the manifestation is much more active, occurs suddenly, and lasts for over half an hour. Attempts to independently distinguish between the two states are futile. Instead of dubious exercises, it is better to call an ambulance.
- Dyspnea. In complete peace. The patient is unable to draw in air to meet the need. Such symptoms are determined by impaired gas exchange.
- Feelings of anxiety, panic, fear. Corresponds to a neurotic state.
- Loss of consciousness. Up to several times in a row. An alarming sign indicating a weakening of brain nutrition.
- Cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle. Blue discoloration of the area around the mouth.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Arrhythmia type bradycardia (weakening of contraction frequency).
Signs of a heart attack develop almost instantly, and the duration of the episode is from 10 minutes to 30 with angina pectoris, and more against the background of an ongoing heart attack.
What to do during an attack
- If you have a heart attack during physical activity, gradually stop all your activities, sit down, calm down, try to move less, and don’t panic.
- If you have had similar conditions before, take the pills your doctor prescribed for pain relief (usually Nitroglycerin).
- If the medicine does not work within 3-5 minutes, call an ambulance (describe all your symptoms as fully as possible over the phone). While the doctors are on the road, take Aspirin. This is a very important part of first aid. Aspirin prevents the formation of blood clots and thins the blood, which facilitates blood circulation through the narrowed vessel. In this way, further death of the myocardium can be prevented. Even if it turns out in the end that you are not having a heart attack, but just an attack of angina, Aspirin will not harm.
- If you are very bothered by pain, you can take another Nitroglycerin tablet, but not earlier than 5 minutes after the first. Before doing this, it is advisable to measure the pressure. If it is lowered, you can no longer drink Nitroglycerin. If you are prone to low blood pressure, it is better not to take Nitroglycerin until the doctors arrive.
If your relative or friend shows signs of a heart attack, you need to act in a similar way. Sit the patient in a comfortable position, open the window if possible. Ask if he has had similar conditions before (it is advisable to inform him about whether this is the first or a repeated attack when calling an ambulance). Call a doctor. Give an Aspirin tablet.
How to recognize an emergency?
It’s not easy to do this without qualifications. A distinction is made between the main types of coronary insufficiency; it is also necessary to distinguish the described disease from intercostal neuralgia, perforated gastric ulcer, pneumonia and other phenomena.
What characterizes heart pain:
- Lack of response to breathing. Inhalation and exhalation do not affect the intensity of the syndrome. The same cannot be said about signs of non-cardiac discomfort.
- No changes when moving. If you stand up, sit down, lie down, the power of manifestation will be the same. This is the trait of heartache.
With intercostal neuralgia, the pain intensifies with inhalation and movement.
A perforated ulcer is defined by a sharp, cutting sensation in the abdomen and epigastric region. It is this nature of pain that makes it possible to distinguish the condition from others.
Pneumonia causes predominantly respiratory symptoms.
Diagnosis falls on the shoulders of doctors. There is no point in guessing on the coffee grounds. The brigade should be called. An attack can be recognized by the nature of the pain, its duration, and additional manifestations.
What are the symptoms in women and men?
Symptoms of an attack in men and women have slight differences.
Heart pathologies in the female body develop much later than in the male body.
The physiological characteristics of the female body are such that it has good natural protection during childbearing years. But with the onset of menopause, the chances of developing heart pathologies in men and women become equal.
Comparisons of symptoms between men and women
A physiological feature of the male body is that men suffer a heart attack more easily than women. The mortality rate for men from myocardial infarction is much lower than for women.
Women endure many of the symptoms of an attack without visible sensations, so it is especially important for women to diagnose disturbances in the functioning of the cardiac system in a timely manner. And start treating heart diseases on time.
Symptoms that are the same in men and women:
- Dyspnea. Shortness of breath is the most common sign of an attack. The patient feels a lack of inhaled air, both in a state of physical activity and at rest. The reason for this symptom is that the heart does not deliver enough oxygen to the internal vital organs. The symptom of shortness of breath is characteristic of myocardial infarction;
- The body produces increased levels of sweat and sweating continues for a long time. Constantly wet and sticky palms;
- Pain under the ribs, which is transmitted to the left side of the body: arm, neck on the left side and to the left side of the jaw.
Women do not always feel the symptoms of an approaching attack, especially chest pain. Sharp chest pain, like in men, develops quite rarely in women. Many signs are barely noticeable for women, so untimely treatment leads to death.
First aid
Before the doctors arrive, you only need to stabilize the patient’s condition at home. Not to cure it, but just to normalize the situation.
Approximate algorithm:
- Make the patient sit down and place a cushion of clothing or linen under his back. You cannot lie down, because normal gas exchange will be disrupted, pulmonary edema or other additional complications will occur.
- Open the window to ensure a flow of fresh air into the room.
- Give the patient a Nitroglycerin tablet to relieve pain. In case of a heart attack, the measure may be ineffective, but other drugs cannot be taken. The condition is unstable; any outside influence leads to a worsening of the situation.
- Loosen the collar, remove tight body jewelry.
If you lose consciousness, it is recommended to turn your head to the side so that the person does not choke on vomit during the reflexive release of the digestive tract.
Upon arrival, doctors should briefly describe the condition. Transportation to a cardiology hospital is indicated.
Effective measures can only be taken in a hospital. First aid for a heart attack consists of two things: calling an ambulance, stabilizing the condition of the injured person.
Causes
Typically, the root cause of a heart attack is the development of fatty plaques in the middle of the coronary vessels. If the plaque bursts, then the blood tries to be fixed
to eat it, thereby forming a blood clot. The latter blocks the path of blood flow and oxygen to the heart.
Causes of a blood clot:
- Strong physical activity;
- Sudden emotions affecting a person’s condition;
- Drinking alcohol and smoking;
- Taking drugs.
It is worth noting that these are quite common reasons. In eighty percent of cases, the nature of the occurrence of this pathological condition remains unclear.
Necessary examinations
Upon admission to the department, diagnostics are carried out urgently. Usually, results are not expected; urgent measures are indicated to bring basic vital signs back to normal. Then more careful work is needed.
Approximate list of events:
- Oral interview with the patient and collection of anamnesis. What matters is the number of attacks and how often they occur (if they have happened before).
- Measurement of blood pressure and heart rate.
- Daily monitoring. Registration of the same indicators within 24 hours using a Holter monitor. Can be carried out repeatedly to clarify conditions. The study answers the question about the dynamics of blood pressure and heart rate throughout the day, depending on circadian phenomena.
- Electrocardiography. Shows even slight arrhythmia. All functional deviations are clearly visible.
- Echocardiography. Demonstrates defects and the degree of destruction of cardiac tissues. This visual technique is essentially a version of ultrasound.
- General blood test, biochemical and hormone tests.
Prevention
In order to prevent a recurrent attack, you need to completely review your daily habits and change your lifestyle.
You must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Maintain a normal weight level, avoid fatty, salty foods, and stay hydrated. All foods and drinks that provoke an increase in blood pressure should be excluded from the diet. Fill your diet with healthy foods containing B vitamins. Be sure to consume foods high in potassium and magnesium.
- If you smoke, you should quit immediately. Nicotine not only increases blood pressure, but also increases cholesterol deposits.
- Do exercises, walk more often, and do not neglect therapeutic exercises. Elderly people should maintain their physical activity at the proper level. Physical education maintains vascular tone, stimulates blood circulation and will help you avoid an attack.
- Check your blood pressure twice a day, morning and evening, and take medications prescribed by your doctor. People who have survived a heart attack are prescribed medications for life that cause a decrease in blood viscosity and have an antithrombotic effect (for example, Cardiomagnyl).
- Visit a cardiologist every six months. Skipping routine checkups can also shorten your life.
- Perform relaxation exercises and breathing exercises. Find for yourself an effective way to relieve mental stress, since stress puts an increased load on the heart, which it may not be able to withstand.
Treatment
An approximate regimen of drug correction involves a long course of taking the following drugs:
- Angiagrangants. To thin the blood. Aspirin Cardio will do. This is a must-have pharmaceutical.
- Statins. In order to eliminate cholesterol plaques in the coronary arteries and more. Atoris as the main one. It is possible to use analogues at the discretion of the specialist.
- Beta blockers. Metoprolol, Anaprilin.
- Antihypertensives as needed. Reduce blood pressure.
- Nitroglycerin for pain relief. They are not taken constantly, but as part of relieving the discomfort.
- Diuretics. Regularly (several times a week) to remove excess fluid from the body.
- Cardioprotectors. Mildronate and the like.
- Potassium and magnesium preparations. In order to restore local metabolism.
Surgical treatment is indicated for vascular abnormalities, significant stenosis or advanced atherosclerosis.
The nature of the intervention is determined by a specialist. Most often, stenting or bypass surgery is performed.
The attack that has occurred imposes some restrictions on the patient’s life:
- You need to completely give up smoking and alcohol.
- You can't physically overload. Only walking and light exercise prescribed by a doctor.
- You should also adjust your diet. Fatty and fried foods are excluded; fortification of the menu is indicated. Salt no more than 7 grams per day.
An approximate list of products is indicated in treatment table No. 10. Based on the presented list, conclusions can be drawn. It is recommended to discuss any controversial issues with a nutritionist.
Risk factors for heart attack in men
Even young guys can fall into the risk zone, so you should approach this point with special attention.
- Age . The older the man, the higher the risk.
- Heredity . If one of the parents suffered from heart problems.
- Bad habits . Alcoholic drinks, alcohol, smoking - they are not even discussed, everything is obvious.
- High blood cholesterol levels . In combination with bad habits and stress, cholesterol leads to disruption of the heart.
- Diabetes . Diabetics often suffer from heart disease.
- Obesity and inactivity . The heart becomes overgrown with fat and it is more difficult for it to pump blood, the vessels lose their elasticity.
- Constant stress . Avoid situations and thoughts that make you nervous and constantly worry.
Treatment of myocardial infarction in men and preventive measures
After establishing the correct diagnosis, the doctor prescribes medication treatment. Nitroglycerin, isosorbitol, mononitrate eliminate heart pain, improve blood circulation, have a dilating effect on blood vessels and reduce the load on the heart.
Painkillers are suitable for localizing pain. To achieve quick results, narcotic analgesics are used. All patients are prescribed thrombolytic drugs, which increase blood flow to the heart and break down blood clots.
In order for blood clots to dissolve and the blood to become thinner, to avoid stress on the heart and to normalize biochemical processes, beta blockers are prescribed: Toprol, Inderal, which are started with a minimum dose, gradually increasing to normal. These are acetylsalicylic acid, Heparin, Warfarin. Statins, niacins, and fibrates lower cholesterol.
After a major heart attack, men may experience both acute and long-term consequences, and acute pain includes:
- Heart failure, when the left side of the heart is damaged by a heart attack. It contracts poorly due to the presence of a scar. As a result, the blood stagnates, its output decreases, and the internal organs are poorly supplied with blood.
- Pulmonary edema. Then the patient suffocates, coughs, lacks air, and shortness of breath appears.
- Arrhythmia arising in the left ventricle of the heart.
- Thrombosis. Blood clots travel throughout the body to the brain.
- Heart rupture occurs as a result of a large strain of blood on the heart muscle damaged by a heart attack.
Long-term consequences have less impact on the patient’s body, these are:
- cardiosclerosis, which appears due to poor blood circulation;
- left ventricular failure, which is manifested by cardiac asthma and circulatory disorders;
- arrhythmia, atrioventricular or sinoatrial block;
- pericarditis - inflammation of the serous membrane of the heart;
- cardiac aneurysm;
- post-infarction syndrome;
- thromboendocarditis;
- neurotrophic changes in the myocardium.
They need to visit a psychologist so that they can look into the future with optimism. The recovery period can last several months or can last several years.
A heart attack can be prevented. Patients who have had this disease need to change their attitude to life, forget about bad habits, and give up smoking and alcohol forever. Protect the nervous system from stress and depression.
It would not be a bad idea to engage in feasible sports, guided by the recommendations of a cardiologist. You cannot overload yourself with physical work; it is imperative to alternate it with rest. Sanatorium-resort holidays and treatment are shown.
13
It is very important to eat vegetables. They can be used to make stews and casseroles
White cabbage is not recommended for consumption.
14. Porridges (buckwheat, rolled oatmeal) are considered healthy. You can eat them almost every day. Cereals can also be added to soups.
1. Fats – lard, condensed milk, various creams.
2. Sweet confectionery - cakes, pastries, sweets, ice cream, etc.
3. Semi-finished products.
4. Pickled salted vegetables.
5. Sausages.
1. Avoid severe physical overload.
2. Eat right.
3. Have proper sleep and rest.
4. Avoid strong psycho-emotional stress and stress.
5. Give up bad habits.
6. Put moderate stress on the body and be physically active.
7. Consult a doctor promptly when the first signs of a heart attack appear.
8. Treat chronic diseases, as well as heart pathologies, in a timely manner.
9. Avoid sudden changes in blood pressure.
Statistics show that men aged 40-50 years are most susceptible to heart attacks, so people in this age category should be extremely attentive to their health.
Signs of a heart attack in men can be minimized in the early stages, through certain actions, completely getting rid of the symptoms of the disease. A well-designed diet, systematic feasible physical activity, adequate sleep, the absence of shocks and stress, and the absence of bad habits can prevent the development of a heart attack.
How to relieve a heart attack at home
If you have a heart attack at home, the first thing you should do is calm down. Then call an ambulance and open the windows to allow air to enter. Open the entrance doors for free entry of the medical team. After this, you should lie down on a hard surface, placing a high pillow at the head. Under no circumstances should you carry out any active actions.
The first aid kit should be in an accessible place.
It is advisable that it contains medications:
- cardiac;
- analgesics;
- sedative medications.
Causes contributing to the development of a heart attack
In most cases, a heart attack develops as a result of stress, against the background of existing cardiovascular diseases.
An interesting fact is that bitter people have a greater chance of having a heart attack or stroke, so be kind, gentlemen.
Reasons why a heart attack may occur:
- Lifestyle: cigarettes, hypertension, physical inactivity, high cholesterol and glucose levels, obesity (waist circumference in men should be less than 94 cm).
- Constant factors: male gender, age after 65 years, belonging to the Negroid race.
The cause of the development of damage to the heart muscle or stroke can be chronic kidney pathology. Damage to the glomeruli causes high blood pressure, which is very difficult to correct with medications.
Experts tend to identify the following causes of heart attack or stroke:
- Smoking. For doctors, this reason comes first; this is explained by the fact that when smoking, microtrauma of lung tissue occurs, followed by thrombus formation. The emboli break off, enter the bloodstream and reach the coronary arteries, where a blockage occurs. Once in small arteries, emboli provoke angina pectoris. The stenting procedure helps to widen the blood vessels.
- High calorie diet (cholesterol). As a consequence, the appearance of atherosclerotic plaques, which, in the same way as emboli, provoke a heart attack.
- Physical inactivity and, as a consequence, sagging muscle tissue of the body (“second heart”) and obesity.
Recently, myocardial infarction is increasingly being recorded in young people. If previously signs of a heart attack were usually diagnosed in men over 60 years of age, in recent decades the disease has been increasingly registered in men over 30 years of age.
According to statistics, men in the age group of 40–60 years are most vulnerable to heart attack. After 40 years and up to 60 years, the likelihood of a heart attack increases, then begins to decrease, and at 70 years of age, heart attacks are diagnosed much less frequently.
The reason is that with frequent attacks of angina, collateral vessels are formed, which are activated in case of circulatory disorders in the central arteries. In men over 50 years of age, the incidence of heart attack is the same as in women in this age group.
The most common causes of heart attack in men are atherosclerotic lesions of blood vessels. Often the pathological process develops in the presence of a genetic predisposition, kidney disease (with damage to the renal glomeruli), arterial hypertension, and endocrine disorders.
One of the main risk factors for the development of myocardial infarction is smoking, which leads to microtrauma of lung tissue, subsequent thrombus formation and blockage of the coronary arteries. The risk of developing myocardial infarction increases in the spring and autumn.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing a heart attack, much attention is paid to the patient’s complaints and clinical symptoms. Within 1.5 hours from the onset of a painful attack, motor excitation is observed, then lethargy sets in
Pallor of the skin, protruding sweat, blueness of the lips, fingertips, and coldness of the extremities are noticeable.
On the second day, a friction noise of the pericardial leaves may occur, which indicates the addition of aseptic pericarditis. Diagnostics is carried out using the following methods:
Laboratory methods
The most specific sign of cardiac muscle necrosis is an increase in the levels of troponins I and T. The troponin test helps diagnose the disease even before changes appear on the ECG.
Instrumental methods
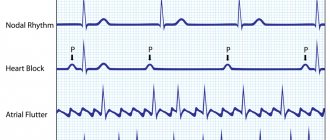
- That ST is several mm relative to the isoline, a Q wave appears (pathological), the R wave disappears, various conduction and rhythm disturbances are observed (blockades, arrhythmia, extrasystole). Depending on which leads there are changes, the localization of the infarction can be assumed.
- Echocardiography: ultrasound of the heart can identify affected areas of the myocardium, signs of ventricular dilatation, determine the presence of an aneurysm, assess the degree of contractility impairment and other indicators of cardiac activity.
- Chest X-ray: This is used to diagnose pulmonary edema, pneumonia, and other complications of myocardial infarction.
- Coronary angiography: necessary if surgical treatment of the disease is intended. This study allows you to determine which of the coronary arteries are affected.
First aid for heart pain
Here's how to act if a pain symptom appears in a person's heart:
- First of all, call an ambulance.
- It is recommended to take care of the supply of a sufficient amount of oxygen, calm the patient, make sure that he takes a position that is comfortable for him, and unbutton the buttons on his outerwear.
- Then (if there are symptoms specific to a heart attack), the patient should be given 0.25 g of aspirin and 0.5 mg of nitroglycerin.
Consequences
According to the time of occurrence, all complications are divided into:
- acute (0-3 days): ventricular arrhythmia, blockade of the sinus, atrioventricular node, cardiogenic shock;
- subacute (3-14 days): regurgitation of the mitral valve, rupture of the papillary muscle, ventricular wall, interventricular septum;
- delayed (more than 14 days): chronic pericarditis, arrhythmias, atrial fibrillation, left ventricular dysfunction, cardiac arrest.
All consequences of a heart attack can be fatal. The likelihood of developing complications depends on the patient’s health status, age, medical history, time, and quality of medical care.
Adversely affect the prognosis:
- left ventricular dysfunction;
- late medical care;
- the presence of other diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- elderly age;
- diabetes;
- specific changes in the cardiogram;
- high concentration of CRP factor;
- depression.
The probability of re-hospitalization is about 40%, death - 10-12% in the first year after a heart attack. Major MI is characterized by a higher in-hospital mortality rate, but the long-term prognosis is worse for small-focal MI.
It is known that the number of men who have suffered a heart attack is only increasing, and the age of victims is becoming younger. This is facilitated by lifestyle, stress, nutritional and environmental problems, and attitude towards one’s own health. These are all general factors, let's look at the disease itself to understand how to act.
A heart attack (myocardial infarction) is a medical emergency in which the blood supply to the heart is suddenly blocked. Most often it is caused by a blood clot. Lack of blood supply to the heart muscle can cause irreversible changes in it and lead to death.
Duration of pain
The fact of how long a man’s heart attack lasts also requires close attention. The main thing to remember is that such an attack does not cause immediate pain. If suddenly unpleasant and painful sensations appear suddenly, then this may be a sign of a completely different disorder. This does not mean that pain can be tolerated and forgotten about.
A heart attack lasts about 5 minutes, but there are cases where it lasts longer. Maximum duration is 30 minutes. The pain may be severe or not very strong, but if it is too long and does not go away, it indicates that a myocardial infarction is already occurring, so it is necessary to urgently show the patient to a doctor. The pain itself arises from the fact that the blood vessels narrow greatly and blood stops circulating through them. If the attack lasts more than 5 minutes, then the condition turns into a heart attack and requires the urgent attention of an observing specialist.
First aid algorithm for a heart attack
If symptoms of a heart attack occur, it is recommended to quickly provide first aid using the following algorithm:
- In the first minutes, call an ambulance.
- The patient should take a sitting or lying position, raising his head.
- Then the patient should take 0.25 grams of acetylsalicylic acid, the medication must first be chewed and then swallowed. After taking the medicine, you need to take 0.5 mg of Nitroglycerin sublingually, breaking the capsule in advance and allowing it to dissolve under the tongue.
- You should also take care to keep the patient calm and have enough oxygen (for example, open a window).
- If, 7 minutes after ingesting the drugs, the pain still does not go away, you should take a repeat dose of nitroglycerin.
- If 10 minutes after taking 2 doses of nitroglycerin the pain still does not disappear, you need to take the medication 3 times.
- If, after taking nitroglycerin, additional symptoms develop, which manifest themselves in the form of weakness, increased sweating, lack of air, pain in the head, then you need to stop taking this drug.
- If the victim takes cholesterol-lowering pills on a regular basis, it is advisable to have him take his daily dosage of the medication.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a heart attack in women most clearly manifest themselves during a heart attack.
This dangerous condition requires emergency help. Its mortality rate is very high. This attack is caused by an acute lack of oxygen in the heart. An attack develops against the background of blockage of a vessel by an atherosclerotic plaque or thrombus. Symptoms are most pronounced in the acute period.
Symptoms of a heart attack in women have a number of characteristic differences from the symptoms in men. Signs of a heart attack in women:
- a squeezing sensation appears in the heart area, pain begins to develop in the center of the chest, the intensity of pain can vary greatly, from weak, slightly noticeable, to severe;
- the pain can be reflected in other parts of the body, the arms, neck, back of the head, and sometimes the stomach begin to ache;
- one of the characteristic signs of an upcoming attack is shortness of breath;
- additional symptoms are possible: chills, nausea, cold sweat;
- constant feeling of fatigue, general weakness;
- numbness of fingers;
- lack of coordination;
- heartburn;
- dizziness.
To prevent a heart attack in women, you need to pay attention to the symptoms in a timely manner.
Many signs of a heart attack in women are different from those in men. For this reason, many women may ignore or misunderstand signs that indicate cardiovascular disease. Symptoms of a heart attack are the same in men and women:
- Shortness of breath, which may be accompanied by chest pain, but not always.
- Feeling of tightness in the chest or squeezing pain in the chest.
- Pain or pressure starting in the left side of the chest that radiates to the shoulder, arm, neck, and/or jaw.
- Sweating.
Keep in mind that many women don't experience chest pain when they're having a heart attack, but there are other signs—some literally subtle and some that appear alone or in combination with others—that may indicate that a heart attack is occurring. This could lead to a heart attack.
Among these symptoms:
- Abnormal heart rhythm
- Cough
- Dizziness
- Heart pain (burning)
- Indigestion
- Nausea
- Sudden, sharp fatigue, fatigue
- Vomit
- Weakness
The attack has gender characteristics. Men are characterized not only by earlier manifestations of pathology, but also by frequent susceptibility than women. In addition, pain syndrome is perceived differently by men and women, but the signs of a heart attack in men are essentially the same as for everyone:
- shortness of breath, manifested with a minimum of activity, even in a calm state;
- pain behind the sternum of a burning, pressing nature;
- dizziness to the point of loss of balance;
- cough;
- paleness of the skin to a gray tint;
- feeling of panic;
- nausea;
- cold profuse sweat;
- vomit.
In men
In a classic attack, the following often occur:
Initially, by identifying the symptoms of a heart attack in time, you can save a person’s life. The first step is to distinguish chest pain that occurs during a heart attack from pericardial pain, which can signal other disorders.
The following symptoms are determined by the following criteria:
Depending on which ventricle of the heart the pathology develops, the symptoms of the disease differ. If left ventricular failure leads to cardiac asthma - pulmonary edema, then right ventricular failure causes right ventricular infarction.
To prevent the development of left ventricular failure, you need to pay attention to the following symptoms:
Right ventricular failure has the following symptoms:
- Severe swelling appears. Initially, the abdominal cavity, hips, and lower back swell; sometimes swelling of the arms is noticeable. But the swelling mainly spreads below. Therefore, if a person has severe swelling in their legs, they should immediately consult a doctor.
- The liver enlarges, so the patient feels significant heaviness in the hypochondrium area.
- Possible accumulation of fluid in the pleural or abdominal cavities.
- Due to poor blood supply to the capillaries, a bluish tint of the skin appears (accrocyanosis).
- Appetite decreases. This is a consequence of congestive gastritis against the background of heart failure. Usually there is pain in the stomach and nausea, as a result of which the patient is unable to swallow medications.
- The veins of the neck are inflated, the pathology is especially noticeable when inhaling.
There are two types of heart failure: acute and chronic.
Primary right ventricular failure does not have pronounced symptoms. Secondary right ventricular failure is a consequence of many diseases and has a different etiology. This type of pathology causes acute heart failure.
The degree of pathology depends on the speed of development of the syndrome. Chronic heart failure in men is dangerous because it occurs latently over many years, and a man may not even be aware of this dangerous illness.
And usually the stronger sex tries not to attach importance to the first signs of illness and does not take them seriously.
The very first sign of incipient heart problems. Shortness of breath occurs when the heart is still slightly damaged, but can no longer pump enough blood.
Article on the topic
Swelling in the legs
These are signs of vascular disorders. Edema due to heart disease begins to appear in cases where the heart can no longer cope with the increased load and decompensation occurs.
Blue lips
In case of circulatory failure of the heart, a pale or bluish color of the lips is noted. If the lips are completely pale, anemia (anemia) should be excluded.
If you see an obese person in front of you, you are almost guaranteed to suspect cardiovascular disease. Extra pounds are a serious additional burden on the heart.
Bluish-red cheek color may be an indicator of mitral valve dysfunction.
Red bumpy nose
A red, bumpy nose streaked with blood vessels suggests hypertension.
Signs of conditions requiring emergency medical attention:
- superficial shortness of breath, in which the patient cannot take a full breath;
- extreme pallor or abnormally red complexion;
- weakly palpable but frequent pulse;
- suddenly clouded vision;
- the appearance of slurred speech;
- the patient’s inability to respond to speech addressed to him;
- loss of consciousness.
You should not ignore the feeling of discomfort in the chest, heaviness or pain behind the sternum, pain radiating to the arm, back, under the shoulder blade, throat, jaw, lack of air - these are symptoms of a heart attack.
What to prepare for the arrival of an ambulance doctor?
To make future work easier for emergency personnel, you should carefully prepare for their arrival:
- It is necessary to make a list of medications taken by the victim on a regular basis, and a list of those medications that he took when his complaints appeared.
- It is necessary to make a list of medications and/or substances to which the patient is allergic or intolerant.
- If there are results of previous diagnostics affecting the cardiovascular system, it is necessary to prepare them and show them to a specialist.
- You should collect documents and things required for the patient’s continued stay in the hospital.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation for heart attack
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation for myocardial infarction is resorted to only when signs of clinical death occur. Its main symptoms include:
- unconsciousness of the patient;
- absence of respiratory activity and jerky oscillations of arterial walls associated with cardiac cycles.
It is important to immediately call emergency help when the first clinical signs of death appear, if this has not been done before. Basic resuscitation includes:
- Indirect cardiac massage, which is performed at a speed of 100-120 compressions per 60 seconds, and at a depth of 5-6 cm.
- Also, if two people provide assistance, it is necessary to perform artificial ventilation, the ratio of compressions and breaths is 30 to 2.
- If it is not possible to perform artificial respiration, then it is necessary to continue performing cardiac massage without stopping.
Carrying out a mechanical ventilation procedure carries a risk of infection, therefore, in the absence of the necessary funds for its implementation, it is recommended to refrain from performing it.
Prevention of heart pain
There are also a number of rules that will help reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases, and in the future the appearance of heart pain.
- It is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, play sports, strengthen your body, and strengthen your immune system.
- You need to watch your diet and give preference to fresh vegetables and fruits. Avoid fast food, fatty and spicy foods.
- You need to monitor your weight. If your weight exceeds the norm, you need to exercise and watch your diet.
- If you have chronic diseases affecting the cardiovascular system, as well as endocrine diseases, you must regularly take medications prescribed/recommended by your doctor.
- If you have a genetic predisposition to heart pathologies, you should tell your doctor about it. It is important to undergo regularly scheduled diagnostic examinations.
- It is also recommended to get rid of bad habits, stop drinking and smoking.
To avoid unwanted consequences and complications after a heart attack, you need to recognize the symptoms of the disease in time and promptly seek professional help. According to statistics, many patients who experience a heart attack die within 60 minutes if they do not receive first aid.