How do vaccinations affect disease incidence? In some countries, thanks to universal immunization, many diseases have been eliminated forever, and the likelihood of contracting seasonal infections has decreased by several tens of percent. Then, perhaps, the time has come to exclude vaccinations from being mandatory?
Is the tetanus vaccination necessary and when is it given to adults? Why are such injections dangerous and how long does the next vaccine last? Do vaccinations really help protect a person from the disease and how often do they have to be done?
Composition and mechanism of action of tetanus vaccines
The composition of tetanus vaccinations depends on the manufacturer and type of drug.
For example, there are many combination vaccines that protect against tetanus and a number of other diseases. Polyvalent vaccinations have approximately the following composition:
- tetanus toxoid;
- aluminum hydroxide as an adsorbent;
- merthiolate (preservative).
The mechanism of action of tetanus vaccines is based on the fact that after penetration into the body, the antigenic material stimulates the production of antibodies, which for a long time can fight the causative agent of a dangerous infectious pathology.
Contraindications to vaccination
Any vaccination has some contraindications, most often associated with reduced immunity or temporary illness. Contraindications to tetanus vaccination are:
- problems with the immune system;
- diabetes;
- exacerbation of neurological diseases;
- allergic reaction to the components of the vaccine;
- colds (after recovery, you need to wait at least three weeks to get vaccinated);
- acute course of any disease, especially if accompanied by a rise in body temperature.
It is not recommended to vaccinate at any stage of pregnancy, especially in the second half. In extreme situations, a decision may be made to carry out preventive vaccination in the first trimester.
After vaccination, immunoglobulins must be administered.
Adults with a registered contraindication to ADS and AS are administered human tetanus immunoglobulin (TTE) or purified equine tetanus serum (PES) in emergency situations. The serum is injected subcutaneously, and the IPS is injected into the gluteal muscle.
Emergency situations of vaccination include: surgery, injuries, burns, cuts. Vaccination is mandatory after animal bites, as well as for long-term non-healing purulent wounds and ulcers. In all these cases, unscheduled administration of an anti-tetanus drug is carried out.
Why does tetanus vaccination cause complications? Errors in vaccine production lead to infection and intoxication of the body. The entry of live bacteria into the drug can lead to serious consequences and even death. The effect of vaccination on the body is most often manifested by the following consequences: rash on the body, indigestion, runny nose, pharyngitis, bronchitis, and rarely there may be convulsions.
Is it necessary to get a prophylactic tetanus injection?
Tetanus vaccination is included in the National Immunization Calendar of the Russian Federation. Therefore, it is necessary to install it. According to the approved schedule, children are vaccinated with a drug that simultaneously protects against diphtheria, tetanus and whooping cough - DPT. Immunization can also be carried out with the ADS vaccine, which does not contain the pertussis component.
The antigenic material provides protection against tetanus only temporarily. Therefore, revaccination of children and adults is periodically carried out. Although vaccination is mandatory, any person has the right to write a refusal to receive it. Some are given a medical exemption due to health reasons.
Incorrect administration of the drug
It often happens that after a tetanus shot your arm or shoulder hurts because the nurse who administered the tetanus shot administered the drug incorrectly. If most of it gets under the skin, it will cause inflammation, which will be accompanied not only by pain, but also by redness, and a subcutaneous thickening may be noticeable. To avoid such a mistake, most often the tetanus vaccine is given into muscle tissue.
© shutterstock
Features of symptoms
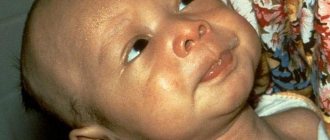
Pain after a tetanus vaccination, and it can be localized not only at the site of the vaccination itself, but also nearby. Sometimes the entire limb can hurt - this is a consequence of the inflammatory process. In this case, the site of the tetanus shot will swell and may become red and swollen - this reaction also indicates inflammation. Possible increase in body temperature.
Treatment methods
Most often, if the tetanus vaccine was administered incorrectly and most of the anti-tetanus drug gets into the subcutaneous fat layer, this causes quite strong and vivid side symptoms, often frightening patients.
Pain, swelling, redness, fever - all this is a natural reaction to a mistake. In addition, such a tetanus vaccination will last longer, since the components of the drug will be absorbed and absorbed into the blood more slowly than with a correctly administered tetanus vaccination.
However, treatment is not required in this case either - the inflammation, as well as the accompanying redness, swelling and pain, will subside on its own as soon as the components of the tetanus shot are completely absorbed by the body.
Doctors advise that in case of severe pain, take appropriate painkillers or use ointments that neutralize the sensation of pain.
In addition, doctors note that the increase in body temperature after a tetanus vaccination can be either weak or quite noticeable, but in most cases it is not associated with the immune system’s response to the components of the tetanus vaccination, but is caused only by the entry of a foreign substance into the blood. Therefore, doctors advise in such cases not to neglect taking antipyretic drugs.
In what cases is it necessary to get vaccinated?
Regular tetanus vaccination helps maintain strong immunity against this disease.
Vaccinations are given to children and adults.
But prevention is especially important for children: undeveloped immunity, a high probability of injury, and frequent contact with dust and sand put the child at risk.
It is imperative to administer tetanus serum in the following cases:
- animal bite;
- injury resulting in disruption of the integrity of the mucous membranes or skin;
- burn;
- performing surgery in out-of-hospital conditions.
It is advisable to get vaccinated as quickly as possible: within the first five hours after injury.
How to apply a compress to the injection site
If side effects appear after a tetanus shot at the injection site, you can apply a compress with anti-inflammatory ointment. Most often, Vishnevsky or ichthyol ointment is used for these purposes, which is applied to gauze and applied for 3 hours once a day. It is better to undergo a course of treatment - within one to two weeks the pain will go away without a trace.
You can use a different composition:
- In 2 tbsp. alcohol (vodka) dissolve 1 tablet. aspirin.
- Apply the composition to gauze.
- Apply heavy cream or sunflower oil to the injection site so as not to burn the skin.
- Apply an alcohol compress to the injection site and cover the top with film.
- Secure the compress with a bandage and leave it overnight.
- The course is 2-3 procedures, after which the pain and lump will go away. In extreme cases, you can repeat the compress until the lump is completely resolved.
What will happen if you don't do it
If you do not get a tetanus vaccination, a person's risk of developing this disease increases.
According to statistical authorities, the majority of cases of infection with Clostridium tetani bacteria occur in individuals who ignored immunization.
The pathogen is not transmitted from one person to another.
Bacteria penetrate through spores and begin to release toxins, which provoke spasms in the muscles of the neck and lower jaw.
Characteristic symptoms of tetanus:
- difficulty in swallowing;
- spasm in the abdominal area;
- numbness of the neck;
- trismus of the muscles of the neck, lower jaw.
Sometimes hyperthermia, tachycardia, and hypertension are observed. Tetanus can cause the following complications:
- pneumonia;
- embolism;
- fractures;
- convulsions;
- laryngospasm.
The danger of tetanus is that medicine does not yet have effective drugs to combat it. In pediatrics, there have been cases where a child suffered a bone fracture due to seizures. With this course of pathology, death can occur 3-4 hours after the onset of involuntary muscle contraction.
In children, infection is fatal in 95% of cases. Mortality among adults is 16-80%. Unvaccinated people develop severe complications. The risk of infection with Clostridium tetani bacteria increases after natural disasters.
What to do if the injection site hurts after a tetanus shot
If you belong to the category of people who experience severe pain after vaccination, keep in mind that this is a normal reaction that you just need to wait it out. At the same time, carefully monitor the injection site. Some allergic reactions - for example, hives - can develop several days after the injection. In this case, you will have to consult a doctor to relieve the painful condition.
Also, make sure that swelling does not develop; if this occurs, you should also go to the doctor on duty. Swelling is not a normal reaction, but rather a manifestation of an allergy. The swelling may be localized to the injection site or may spread to the arm or even the neck.
Pain may occur when the vaccine enters the subcutaneous layer. Aluminum hydroxide causes local inflammation, which will gradually subside only after the drug is completely absorbed into the blood. To speed up the absorption of the medication, you can use absorbable ointments Troxevasin, Aescusan, and to reduce pain - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Diclofenac, Nimesil, etc.
To get through unpleasant days, take painkillers, make compresses or use absorbable ointments. In most cases, symptoms disappear within three days, sometimes they can last up to five. In rare cases, soreness at the injection site may persist for several weeks.
Where do adults and children receive tetanus vaccinations?
If the vaccine is used incorrectly, it will harm the body.
Therefore, you need to understand how and where to give the injection. Antigenic material is introduced into those areas of the body that have a well-developed muscle layer, where the skin is thin and there is little fatty tissue.
For children, the optimal injection site is the lateral thigh. For adults, the injection is given intradermally in the back area under the shoulder blade or in the deltoid muscle of the shoulder.
It is strictly forbidden to administer a tetanus vaccine into the buttock, where the subcutaneous fat layer is visible. The effectiveness of the vaccine depends on where the injection is given.
Why does a tetanus injection hurt?
The tetanus shot site may be sore for several reasons.
- One of the components of the tetanus vaccine is aluminum hydroxide, which causes unpleasant pain. Tetanus toxoid does not cause pain, but in order for it to form lasting immunity it must be absorbed into the bloodstream long and slowly. Aluminum hydroxide retains the toxoid for a long time at the injection site, causing swelling, redness, and hardening.
- If a person is vaccinated with the complex DPT vaccine, then the cause of pain may be the drug against whooping cough. It contains live, immobilized bacteria that cause whooping cough, which can cause such a reaction from the human body.
- Incorrect administration of the drug may cause discomfort. If the vaccine is placed in the subcutaneous fat layer (for example, in the buttock), then a strong lump appears that hurts.
All unpleasant symptoms disappear as the components of the vaccine are absorbed into the blood. If the pain does not subside, purulent discharge appears, and the compaction exceeds 9 cm in size, you need to consult a specialist.
Names of tetanus vaccines
Today, the pharmaceutical industry offers a number of multivalent and combination vaccines that protect against tetanus. The drugs differ in composition, manufacturer, list of adverse reactions and contraindications, and tolerability. Imported and domestic vaccines are available for sale.
Names of Russian popular tetanus vaccinations:
- DPT. This is a complex pertussis-diphtheria-tetanus adsorbed vaccine. Suitable for use by children up to one year old.
- ADS. Contains diphtheria and tetanus toxoids.
- ADS-M. This is an analogue of ADS. Differs in lower concentration of antigenic material.
- AC. Protects only against tetanus. It is used when a person has intolerance to DTP or ADS.
- Bubo-M. This is a vaccine against hepatitis B, diphtheria and tetanus.
Foreign vaccines containing tetanus toxoid:
- Tritranix (Belgium).
- Infanrix (Belgium).
- Triaceluwax (Germany).
- D.T. Coq (France).
- D.T. Vax (France).
- Imovax D.T. Adult (France).
- Tetrakok (France).
For emergency prevention of the disease, the following vaccines are used:
- PSHI – human tetanus immunoglobulin.
- PSS is purified concentrated horse serum against tetanus.
The appropriate vaccination is selected by the doctor individually based on the patient’s health status, age and body weight.
What not to do
You should not visit shops or other crowded places immediately after the injection. It is better not to leave the medical facility for half an hour so that doctors can provide emergency assistance in case of an allergic reaction.
After the procedure, it is important to follow the following rules.
- Abstain from alcohol for at least three days.
- Do not visit baths, saunas and steam rooms, avoid baths using oils and salts.
- Eliminate sports from your schedule, it is especially important not to resort to strength training (from 3 to 5 days).
- If your overall health allows, you can take leisurely walks in the fresh air. This also applies to children with whom you can walk, focusing on the child’s condition.
- Despite the popular belief that the injection cannot be categorically wet, a light shower is quite acceptable, but without rubbing the injection site with a washcloth.
- Eliminate fatty foods from your daily diet for several days, replacing them with light diet foods and plenty of warm drinks.
Possible complications of vaccination
If there are no serious contraindications for vaccination, then tetanus vaccination does not lead to serious complications, but if they exist, getting vaccinated is simply dangerous. Sometimes the reasons for not getting vaccinated are so serious that you can’t get vaccinated under any circumstances. Absolute contraindications are:
- severe allergy to vaccine components;
- immunodeficiency.
Relative contraindications only delay the procedure, these include:
- acute respiratory or infectious disease accompanied by elevated temperature;
- exacerbation of chronic pathologies;
- recovery period after suffering a serious illness;
- recovery period after courses of radiation and chemotherapy;
- premature infants with insufficient body weight are not vaccinated until their condition normalizes;
- pregnancy and lactation period.
Sometimes it happens that the patient has contraindications. This could be, for example, a nonspecific allergy or mild malaise. Such conditions do not lead to an increased risk of complications, but, nevertheless, the pediatrician gives medical advice. This leaves the child defenseless against a dangerous infection. The approach to deciding on admission to the procedure should be flexible. For example, if a patient had an acute reaction to DPT, the vaccine may be replaced with a less reactive DPT.
It is important to understand that a prolonged manifestation of a negative reaction to the vaccine indicates the development of complications:
- the temperature rises above 39 °C. This may be a sign of developing inflammation;
- signs of laryngitis, bronchitis and pharyngitis appear;
- pain lasts longer than 5-7 days;
- the redness has a large area (more than 8 cm), and the diameter of the bump exceeds 5 cm.
Vaccination in adults can cause seizures, heart failure, arthritis, confusion and brain problems, and anaphylactic shock. Such reactions are very rare, since we are talking about revaccination, and all possible negative manifestations in a particular person are already known. More often, complications occur in children, so parents should monitor the behavior and well-being of the child after the injection.
When to see a doctor
Although complications from tetanus vaccination are extremely rare, death is still reported in 4% of cases. Therefore, if symptoms deviate from the norm, you should seek medical help. If a person who has received a tetanus shot complains of severe headaches, a high fever, extensive swelling and redness at the injection site, convulsions and confusion, we can already assume the development of complications. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor, since severe reactions, firstly, can lead to unpredictable consequences at the present time, and secondly, are a reason to avoid tetanus vaccinations in the future.
Vaccination scheme
Tetanus vaccination is carried out according to routine immunization. Vaccinations begin from infancy. The schedule largely depends on the drug used.
The routine ADS vaccination schedule for children is given below:
- first vaccination – at 3 months;
- the second - at 4-5 months;
- third - in six months;
- fourth - at 1.5 years;
- fifth - at 7 years old;
- sixth - at 14 years old.
Further revaccination is carried out every 10 years. A single dose for children and adults is 0.5 ml.
It is important to get vaccinated on time to minimize the chance of infection with Clostridium tetani bacteria.
Complications after the vaccine
Serious complications are extremely rare. Statistics show that only about 4% of such complications result in the death of an adult.
After the medicine dissolves and begins to interact with all body systems, the following complications may appear:
- Tissue necrosis at the injection site.
- Fever. In this case, doctors take urgent measures to normalize the patient’s condition.
- Arthritis.
- Complications on the digestive organs. Severe diarrhea, pain in the abdomen in the form of cramps. If diarrhea persists for too long, there is a risk of dehydration.
- Malfunctions of the cardiovascular system, for example, an attack of angina, which in particularly severe situations can develop into a myocardial infarction. Increased heart rate may occur.
- Skin rashes similar to hives, which are accompanied by severe itching.
- Severe swelling in the grafting area. The armpit area swells greatly, which brings a lot of discomfort to the patient.
- Convulsive seizures. This condition in a patient usually lasts for a fairly short period of time.
- A disorder of brain activity that can cause loss of consciousness.
- Severe allergic reaction (sometimes anaphylactic shock).
It should be noted that all of these complications are a contraindication for continuing the course of tetanus vaccination. After such manifestations, the doctor examines the patient individually and decides how to treat.
Most often, severe complications after a tetanus vaccine appear when the scheduled vaccination schedule is not followed and the quality and storage of the drug is violated.
What not to do after vaccination
To avoid the development of post-vaccination complications and adverse reactions, you need to know and adhere to a number of restrictions after vaccination. The physician informs about all prohibitions before or after immunization.
Not recommended after vaccination:
- bathe;
- visit the bathhouse, sauna;
- sunbathe;
- eat exotic fruits, chocolate and other highly allergenic foods;
- drinking alcohol;
- walk in crowded places;
- rub the injection area, treat it with lotions, ointments or creams, and cover it with a band-aid;
- eat heavy food;
- contact with a person sick with a viral or infectious disease.
How to relieve pain after grafting under the shoulder blade
As a rule, vaccination is carried out in the femoral part of the leg, shoulder or under the shoulder blade. The latter option is most often performed by adults. If your tetanus shot hurts under your shoulder blade, it may be due to improper administration of the medication. This happens if the needle does not get into the muscle tissue, where the drug is absorbed better, but under the skin. The second common reason that the tetanus vaccination site under the shoulder blade hurts is a violation of the rules of behavior after vaccination. Pain can be relieved with medications and compresses.
Taking painkillers
Pain at the vaccination site in adults occurs extremely rarely; the vast majority tolerate immunization without side effects. If the injection area begins to hurt, non-aspirin painkillers will help reduce the heat and discomfort, for example:
- Tylenol;
- Acetaminophen;
- Ibuprofen.
How to apply a compress to the injection site
If the tetanus shot under the shoulder blade hurts and a lump has formed, you can use multi-component ointments. They have an anti-inflammatory, absorbable effect. Vishnevsky's preparation is often used, which is applied to a bandage and a compress is applied for 3 hours, once a day. It will take 1-2 weeks for the symptom to subside. Another version of this procedure can be used:
- Take a piece of bandage cloth.
- Dilute 1 aspirin tablet in 2 tablespoons of alcohol.
- Apply the liquid to the bandage.
- Rub the injection site with a rich cream to avoid burns from the compress.
- Apply a compress to the injection site and wrap it with cling film overnight.
- After 2-3 repetitions of the procedure, the pain and lump under the shoulder blade should go away.
Dangerous side effects and consequences
DTP is considered one of the most reactogenic vaccinations. A third of immunized people experience adverse reactions. The likelihood of post-vaccination complications is increased by the following factors: non-compliance with the rules of preparation and manipulation, ignoring the doctor’s recommendations, using a low-quality drug, hypersensitivity of the body.
After vaccination, you may experience fever, lethargy, headache, drowsiness, loss of appetite, redness and swelling of the injection area, and the formation of a lump . These are acceptable reactions indicating the beginning of the formation of specific immunity. The condition returns to normal without treatment after a few days.
Side effects of the vaccine include:
- severe pain in the injection area;
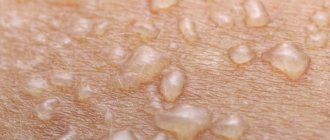
- allergies (urticaria, anaphylaxis, angioedema, rashes);
- inflammation of the injection site;
- heat;
- seizures;
- arthritis;
- loss of consciousness;
- tachycardia;
- disorders of the stomach and intestines.
To prevent the development of dangerous complications of vaccination, it is worth staying in the clinic for at least half an hour after the injection.
Allergic reaction
In some cases, you may develop an allergy to the tetanus shot. Severe forms of allergies, such as angioedema or anaphylactic shock, appear immediately at the time of vaccine administration or immediately after. This is why doctors recommend sitting in the hallway for 20 minutes after vaccination. If these reactions develop, seek immediate medical attention. If you find it difficult to breathe during the vaccine administration, notify your healthcare provider immediately.
Dermatological reactions - rash, hives, itching can develop later at home. If the rash lasts for a long time, you should also consult a doctor. Be sure to report this reaction to your body the next time you get vaccinated.
Can a vaccinated person get sick?
None of the vaccinations provides 100% protection. The tetanus vaccine is quite effective: its effectiveness is 95%. Even if a person gets sick, the pathology will pass without complications. Persistent immunity after vaccination lasts about five years. Then the body’s defenses begin to gradually fade away. Therefore, it is recommended to revaccinate every ten years. Even if a person gets tetanus, he will not develop lifelong immunity to this disease. Therefore, everyone should be vaccinated on time.
Vaccine components
The first reason why a tetanus shot hurts is because of its composition. The fact is that the tetanus strain administered to a person is a weak virus of a dangerous disease that does not threaten health, but activates the body’s defense systems and allows one to develop immunity to the disease - this is a certain mixture of medications.
© shutterstock
The tetanus vaccine contains, in particular, a toxoid - it is thanks to it that our immune system learns to fight a dangerous enemy. However, the toxoid substance itself is very unstable - it is quite quickly absorbed into the blood and neutralized by the body’s defense systems. To achieve the desired effect - hardening the immune system - the substance must act for a longer time.
That is why the doctors who developed the tetanus vaccine added another substance to its composition - aluminum hydroxide. It is more stable than toxoid and is absorbed much more slowly - usually taking from one to three days. However, it is aluminum hydroxide that causes the tetanus shot to hurt for some time .
So, if you're wondering if it's normal for your tetanus shot to hurt, the answer is yes, it's completely natural and as it should be.
Features of symptoms
Pain felt at the injection site after a tetanus shot. They may not go away within one to three days. They may also be accompanied by redness and thickening of the skin at the site where the tetanus shot was given.
Treatment methods
These symptoms and pain that accompany a tetanus shot are considered normal, natural, and expected. They are associated with the characteristics of the drug’s composition and its effect. Therefore, no additional treatment is required. However, doctors say that the site of the tetanus shot can be quite painful, especially in people with sensitive skin, hypersensitivity to one or more components of the drug, and also with a low pain threshold.
That is why doctors have prepared several recommendations on how to reduce pain after a tetanus vaccination. To do this, you can use the following medications for pain.
Pills:
- Tylenol.
- Acetaminophen.
- Ibuprofen.
Ointments:
- Troxevasin.
- Heparin.
As indicated in the medical record
All vaccinations given are recorded in the medical record. This document notes the name of the drug used. For example, the complex adsorbed pertussis-diphtheria-tetanus vaccine is designated by the abbreviation DPT. In addition to the name of the vaccination, the administered dose of antigenic material, the manufacturer, the date of the manipulation, series and number are indicated.
The reaction of the vaccinated person to the vaccine must also be described.
Negative manifestations after the vaccine
The human body often reacts painfully to various vaccines. There is nothing wrong with this, since this is a protective reaction of the body and only indicates that it is strong and healthy. After vaccination, a person may experience the following reactions:
- The injection site became thicker, turned red and slightly swollen. Pressing the seal causes severe pain.
- The tetanus vaccine is given under the shoulder blade. A painful lump appears in this place. To reduce pain, doctors recommend that the patient apply a clean bandage lubricated with levomekol to the lump. Sometimes a simple hypoallergenic adhesive bandage can help. Doctors may also prescribe suprastin.
- The general condition of an adult is either sleepy and lethargic, or hyperactive.
- Slight fever and headache. In this case, you should not take any medications, as the discomfort will go away on its own.
All these negative phenomena are short-lived and pass after a short period of time, without causing any harm to an adult healthy body.
Price and where to do it
Immunoprophylaxis against tetanus is mandatory.
The state is concerned about citizens and provides vaccinations free of charge. The vaccination is carried out at a local clinic or hospital. The drugs DPT, ADS, AS, and DPT-M are usually used here. In private medical centers the service is paid. But here you can immunize with another vaccine: for example, Infanrix, Tetrakok, Imovax D.T. Adultery.
On average, the procedure costs from 500 to 3200 rubles. It all depends on the vaccination used and the level of the institution.
Before vaccination, an examination is required to exclude contraindications . In local clinics, diagnostics are performed free of charge. In private centers, you will have to pay a certain amount of money for tests and consultations with specialists. A doctor's visit to your home to examine the patient before immunization is also paid additionally.
What should you pay attention to?
After receiving a tetanus vaccination, serious side effects may occur that indicate the development of complications:
- In a state of shock, urinary retention may occur.
- Intestinal upset, constant vomiting.
- Severe cough, which is paroxysmal in nature.
- Excessive salivation and runny nose.
- Loss of appetite. The patient may not want to eat for several days, which can cause decreased immunity and weakness of the body.
- Menstrual cycle disorders in women.
- Asthmatic attacks. They usually appear a few hours after vaccination. Asthma may develop 2-3 weeks after the tetanus injection.
It should be noted that such side effects are easily overcome, but require mandatory and constant monitoring by a doctor. At the slightest sign of the symptoms described above, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Feedback on effectiveness
Since tetanus vaccination is mandatory and is carried out periodically throughout life, there are many reviews about it on forums on the Internet. Most patients speak positively about this vaccine, noting normal tolerability and effectiveness. But there are those whom the vaccine has harmed, causing adverse reactions. Most often, complications that arise are a consequence of non-compliance with the rules of preparation, technology and algorithm for introducing antigenic material, or ignoring the doctor’s recommendations.
Doctors advocate vaccination against tetanus. Experts especially insist on immunizing children and weakened individuals. Doctors warn that not getting vaccinated increases the risk of contracting Clostridium tetani and can be fatal.
Reviews about the effectiveness and tolerability of tetanus vaccine:
- Svetlana. My husband, my child and I are regularly vaccinated against tetanus. My sister suffered from this disease. I am well aware of all the consequences of infection with tetanus bacteria. So I stick to my immunization schedule. My family and I tolerate prophylaxis well. After vaccination, the temperature stays up to 37.5 for a couple of days. But this is a natural reaction of the body. Therefore, I advise you not to be afraid of vaccination and trust your doctor.
- Vitaly. My son had side effects from DPT: fever, diarrhea. The pediatrician recommended further prophylaxis with DTP-M. But my wife and I have not yet decided on further immunization. I have never been vaccinated against tetanus for health reasons and still have not gotten sick. Therefore, I am sure that my child will also not become infected without vaccination.
- Alexander. I am a pediatrician and have been working in a local clinic for over 15 years. Tetanus is a very serious disease. Therefore, everyone who has no contraindications should be vaccinated against it. The drug DTP is usually used. Although this vaccine is considered reactogenic, in my practice only a few patients experienced side effects, and the complications were reversible.
Thus, the tetanus vaccine creates reliable protection against the pathology caused by the bacteria Clostridium tetani. Immunization is carried out from infancy. Usually the drug DTP is used. The vaccine may cause side effects. But with proper preparation and implementation of the procedure, the risk of complications is minimized.
What side effects might there be?
Side effects may develop after receiving a tetanus shot. The following manifestations are considered normal:
- slight swelling, inflammation of the place where the injection was given (but not more than 7–8 cm);
- headache of varying intensity;
- Body temperature after tetanus vaccination normally does not exceed 38.3 degrees;
- drowsiness, loss of appetite, decreased performance;
- changes in the functioning of the digestive system (may cause upset stool, dysbacteriosis, flatulence, nausea, increased salivation);
- increased heart rate.
A tumor develops after vaccination as a result of part of the drug getting under the skin. In this case, the components are absorbed into the blood even more slowly, causing pain and discomfort.
All these symptoms are not dangerous, and they go away on their own within two days. If your body temperature rises to 39–40 degrees, nausea and vomiting, convulsions, cough appear, heart rhythm is disturbed, or other unpleasant and dangerous symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
The consequences should not be a reason to refuse vaccination. This is only a reaction to toxoids, and they are not pathological. These temporary changes in the body should be tolerated for a couple of days. But the body will be reliably protected from infection.
Where is the vaccine given?
Where is the vaccine given? It all depends on the age of the patient. Choosing the right injection site affects whether the patient will feel pain after the injection and how long the site will ache.
The ideal place for grafting is a place with a small amount of fatty tissue and with maximum amounts of muscle mass. This is all explained by the fact that when the tetanus vaccine gets into the fat layer (gluteus muscle), absorption into the blood takes longer, and patients feel discomfort and pain.
For children under 1 year and 5 months, the vaccine is administered into the front or side of the thigh. For older children and adults, the vaccine is administered under the shoulder blade or in the deltoid muscle area.
The location for vaccination is determined only by the doctor; he will evaluate the muscle and fat condition, and choose the most suitable place for vaccination.
Contraindications to tetanus vaccination
There are situations when tetanus vaccination should never be carried out. This can cause serious complications in both children and adults.
The tetanus vaccine cannot be given in the following cases:
- There are severe allergies to many medications.
- A history of an allergic reaction to tetanus vaccine.
- The presence of an infectious disease in an acute form, as well as a chronic disease during an exacerbation.
- Immunity problems. People with reduced immunity should avoid this procedure. After a thorough examination, doctors prescribe another drug to the patient.
- Pregnancy. In this case, vaccination can be carried out only for the purpose of emergency preventive measures. Most often, the expectant mother is prescribed immunoglobulin.
Taking simple precautions will help you stay healthy.
What is tetanus?
First you need to figure out what tetanus is and why it is so dangerous. This is an infectious disease in which human nervous tissue is affected as a result of exposure to a very strong toxin of the pathogen. The patient develops intoxication and severe convulsions, from which he may die.
Most often, children of preschool age, from three to seven years old, become ill with tetanus infection. At this age, they are the most mobile, disobedient and restless, so the risk of receiving various wounds with their further infection by the tetanus pathogen is very high. But in general, all age groups are susceptible to tetanus.
Tetanus was, is and will be. We rarely encounter it because vaccination protects us. But in poor countries in Africa, Asia and Latin America, where vaccinations are not very good, tetanus claims lives every year. However, every day there are more and more opponents of childhood vaccination among our parents. Therefore, it is possible that cases of children contracting this terrible infection in our country will no longer be so rare.
Side effects
Immediately after the vaccination is given, the body's reaction to it should be observed. The norm is:
- Swelling of the place where the injection was given, pain and compaction;
- Slightly elevated temperature;
- Drowsiness or, on the contrary, increased activity;
- Headache.
All these side effects indicate that the body has tolerated the vaccine adequately and you just need to survive the incubation period.
By the way, it is impossible to acquire the tetanus virus after vaccination and there is no point in being afraid of it at all. Other side effects and actions may be much more dangerous.
So, if side effects such as too high a temperature, the urge to vomit, increased salivation and runny nose, heart rhythm disturbances, cough, intestinal upset and loss of appetite appear, you need to visit a doctor not only necessarily, but as quickly as possible!
Complicated side effects after the incubation period are rare. These include:
- Body temperature is too high;
- Swelling at the vaccination site;
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- Arthritis;
- Pharyngitis and bronchitis;
- Convulsions;
- Brain dysfunction and loss of consciousness.
It is extremely rare (3-4%) that such complications can lead to death, so it is important to monitor for complications and call a doctor immediately.
WE ADVISE YOU TO READ:
Imported DPT vaccine, advantages, disadvantages, cost
Previous article
When is DTP done - how and when do they vaccinate babies?
Next article
A normal reaction to a tetanus vaccine in children
If a child has been vaccinated with DPT, the following reactions of the body can be expected:
- Increase in body temperature. It happens up to three days. Some children tolerate the vaccine without hyperthermia, which is also a normal variant.
- Redness and thickening at the injection site. The skin reaction sometimes lasts up to 5 days.
- General malaise. Expressed in lack of appetite, increased drowsiness, increased anxiety. Goes away on its own within a week after immunization.
If a child’s body temperature rises, there is a headache and general malaise, then it is necessary to use antipyretic drugs. It is better to give medications based on paracetamol or ibuprofen in an age-appropriate dosage.
Timing of administration after injury
It is important to give your child a tetanus injection as soon as possible. Doctors recommend not to wait longer than 5 days. You should immediately seek medical help after soft tissue damage and inform the hospital staff that the child has not previously been vaccinated against an infectious disease.
The incubation period of the disease does not exceed two weeks. The bacterium quickly spreads in the body and affects vital systems. Therefore, it is much more dangerous to wait and hope for a miracle than to give a baby a tetanus injection after an injury.
Emergency vaccination
Emergency vaccination is a set of measures aimed at administering a tetanus vaccine to a person as quickly as possible to prevent infection.
This event is carried out if there is no information about the date of the patient’s last vaccination (when he does not remember this or is unable to inform the doctor about it because he is unconscious), in the following cases:
- frostbite or burns with damage to the skin;
- stab, cut, chopped, gunshot and any other wounds;
- bite of a wild or domestic animal;
- suppuration of wounds;
- before surgery.
How to behave correctly after vaccination
Vaccination is not only painful, but also responsible. A person’s behavior after the administration of any drug largely determines his further well-being. And when children are vaccinated, the responsibility falls on their parents.
What can and cannot be done after a tetanus shot?
- Try not to visit active crowded places. There is no need to take your child to the playground with other children, to the store, or to child development centers; among them there may be patients with ARVI. Immunity weakened by vaccination picks up infections more quickly.
- The introduction of a new substance into the body is always accompanied by a high risk. It is difficult to predict how the immune and other body systems will behave. Therefore, at least 30 minutes after immunization, you need to be in the field of view of health workers so that they can react in a timely manner if a child develops anaphylactic shock to the vaccine.
- Is it possible to get a tetanus shot wet? There are no restrictions on water procedures. You just need to remember a few key points: on the day of vaccination, you do not need to leave the baby in the bathroom for a long time (the child does not need unnecessary emotional shock); you cannot swim for several days in natural reservoirs (there you can sometimes become infected with other infections); Do not rub the injection site with a sponge. After vaccination, it is better to use a shower rather than a bath.
- It is important to consult with your doctor about the possible consequences and how best to avoid them or how to deal with them more quickly. For example, if after a tetanus shot the injection site hurts, some people just need to drink a sedative; this may just be a reaction of the nervous system to the emotional situation. In other cases, such a reaction goes away on its own after a day.
How is the vaccination done?
Tetanus vaccination is given at regular intervals. They are done more often in children than in adults. The fact is that immunity in children develops over a long period of time, so the risk of infection with various diseases increases significantly.
To ensure that the baby can easily endure this procedure, the doctor must conduct an examination. If signs of colds and other pathologies are observed, then medical advice is given. If there are no health abnormalities, parents receive recommendations for caring for their child after vaccination and are sent to the vaccination office.
Vaccination rules and vaccination schedule
The first tetanus vaccine is prescribed to a child at 3 months. Then it is repeated twice (after 45 days), namely at 4, 5 and 6 months. Usually, the DPT vaccine is used so as not to give the baby several injections separately (see also: how are the second and third DTP tolerated?).
READ ALSO: What are the side effects of DTP vaccination in infants?
This frequency is necessary for the proper formation of immunity to infection. It should be understood that no vaccination will protect a child from possible infection 100%, but it will help to survive the disease in a mild form and without complications.
READ ALSO: What can be the complications after vaccination with measles, rubella, mumps?
Revaccination is carried out three times:
- 1.5 years;
- 6–7 years;
- 14–15 years old.
Revaccination is mandatory before entering school, then in adolescence and at 18 years of age, after which it is repeated every 10 years. There are also a number of emergency cases when a tetanus vaccination is given as soon as possible:
- animal bites;
- open wounds due to injuries and frostbite;
- gangrene, ulcers that do not go away for a long time;
- before performing surgical operations (if there is no information about the availability of tetanus vaccinations).
To exclude the development of side effects after vaccination, parents are advised to start giving their child antihistamines in advance (2-3 days). A runny nose, cough and other signs of illness are a reason to postpone the vaccination until complete recovery.
Where is the vaccine given?
The tetanus shot is always given into a muscle, in places where there is no large amount of subcutaneous fatty tissue and the skin is quite thin.
For a child under 3 years of age, toxoid is injected into the lateral thigh, for adolescents and adults - into the shoulder or subscapular region.
Before the procedure, you should check the ampoule - it should have the appropriate markings. The presence of sediment and flakes at the bottom is not allowed.
How to behave after vaccination and is it possible to wet the injection site?
After vaccination, a person can lead a normal life, but babies sometimes experience undesirable effects. To prevent this, you must adhere to certain recommendations.
When your baby is given the injection, make sure that the body reacts normally to the toxoid. It is better to stay in the clinic for an hour - if allergies or other complications arise, doctors will promptly help you.
Is it possible to get a tetanus shot wet? The answer is yes. The child is allowed to wash; the injection site can be wetted, but not rubbed with a sponge or hand. It is also prohibited to swim in open water, as there is a risk of contracting an infection.
You cannot visit the bathhouse/sauna; you should refrain from walking in the fresh air and in places with large crowds of people for 2-3 days. Active physical activity is also undesirable.
Doctors advise immediately upon returning home to give the baby an antipyretic and continue taking antihistamines. All medications are prescribed for preventive purposes; medications should be dosed according to age. It is also recommended to drink plenty of fluids for 1-2 days.
How long does it last?
The tetanus vaccine does not have a permanent effect, so it must be repeated periodically to be effective. It is better to consult a doctor for how long its effect lasts. He will look at the timing of the toxoid administration and tell you the expected date of the next vaccination. The vaccine is given to adults for 10 years, but it is less effective in children.
READ IN DETAIL: What vaccination is given once every 10 years?
Contraindications
This vaccine, like any other, has its contraindications for use. It is worth noting that almost all contraindications are temporary, but not always.
So, you cannot get a tetanus vaccine if your body has an allergic reaction to any of the components of the vaccine. Also, if during the previous administration of the vaccine the patient developed anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema, or rash, repeated administration of the drug is contraindicated.
During pregnancy, the decision to administer the vaccine should be made by the mother, taking into account the fact that in the first and second trimesters, the effect of the active components of the drug on the fetus may cause the development of any abnormalities or otherwise have a negative impact on it. Therefore, we still recommend postponing revaccination to a later date.
However, immediately before giving birth, the woman in labor is vaccinated with a low-dose vaccine to prevent the baby from becoming infected when passing through the birth canal.
Also, vaccination is not carried out during lactation due to its negative impact on the child.
The presence of chronic and other diseases is also a reason for temporarily postponing DTP vaccination.
These contraindications are dictated by the safety of the child and minimizing the consequences after vaccination.
Do children need a tetanus vaccine?
In the modern world, for some reason, many parents refuse to vaccinate their child. This is absolutely not allowed!
The causative agent of the disease normally lives in the intestines of every person and animals, then, together with feces, enters the natural environment (earth, aquatic environment, etc.). When an injury occurs, the integrity of the skin is damaged, the infection penetrates inside and begins to actively reproduce.
Antibiotics have a detrimental effect on pathogenic microorganisms, but the toxins that are released during their life processes often cause death. Moreover, the pathology in this case lasts from 3 hours to 1 day, after which death occurs.
There is no effective cure for the disease, but tetanus vaccination can avoid disastrous consequences. Every year, in 70% of cases of infection, the patient dies, especially for children. There is no need to risk the health and life of your child; you should definitely get vaccinated when required.
The importance of tetanus vaccination
A distinctive feature of tetanus is that it is not the bacterium itself that disrupts the functioning of the central nervous system, but the toxin that it produces.
The second distinctive feature is that the development of the disease is almost asymptomatic, which does not allow timely initiation of drug treatment.
And the third is a very short incubation period and rapid development of the disease, which can kill a person within two weeks.
Failure to immunize the body in time can lead to dire consequences.
For children and adolescents, tetanus vaccination is a mandatory scheduled procedure, according to the vaccination schedule.
An adult, from the age of 18, independently determines for himself the need for immunization of the body.
Over the past five years, not a single case of infection of a child has been recorded in Russia. While adults still face this terrible disease and more than a third of cases are fatal.
Importance of vaccination
To understand how necessary the immunization process is, you need to consider several facts:
- Tetanus infection belongs to the group of zooanthroponoses. Its causative agent is present in the intestines of humans and animals. With feces, the infection penetrates into water and soil. Due to this, the risk of infection when the skin is damaged significantly increases;
The causative agent of the fatal pathology is a gram-positive rod. Under favorable conditions, it undergoes transformation outside living organisms and turns into spores. Tetanus bacilli tolerate low and high temperatures painlessly. In the soil they can continue to live for a hundred years;- After an illness, lifelong immunity cannot be formed. There is a risk of re-infection;
- the pathology is characterized by increased mortality. 96 percent of infected children die. Among adults, the mortality rate reaches 80 percent.
Tetanus is an extremely dangerous disease that is difficult to treat . Vaccination is intended to prevent its development. It is extremely important to carry out this procedure strictly according to schedule. Every person is at risk.
Previous
For adults, can pregnant women be vaccinated against tick-borne encephalitis?
Next
AdultsVaccination of education workers: which vaccinations are required, list, consequences of refusal
Tetanus vaccination and pregnancy
Routine vaccination of women of childbearing age has become the most important step in the fight against neonatal tetanus (this form of tetanus is characterized by 100% mortality). Therefore, when planning pregnancy, it is recommended to revaccinate against tetanus if more than five years have passed since the completion of the full course of scheduled vaccinations.
Ideally, a tetanus vaccination should be completed a month or more before a planned pregnancy. However, a tetanus injection can also be performed during pregnancy, for medical reasons. The advisability of routine administration of the vaccine is considered individually, after balancing the expected benefits and possible risks.
Also, according to indications (contaminated puncture wounds, infected burns, frostbite, etc.), pregnant women are given emergency tetanus prophylaxis.
At what age is the tetanus vaccine given?
The causative agent of the disease is an aerobic bacterium. Its spores are common in the soil, especially in warm regions with a humid climate. But they can exist in the intestines of humans or animals.
It is very easy to become infected; just cut the skin (for example, with a nail or glass). Once in the wound, the spores grow into bacteria, which release poison - tetanus exotoxin. This substance causes damage (spasm) to the motor cells of the central nervous system.
To protect a child from a terrible disease, anti-tetanus vaccination is provided in the first months of life. This is precisely the time when the baby is especially vulnerable to infection. The very first immunization against tetanus occurs at 3 months of age. Usually the procedure is carried out with polyvaccines, which protect the baby from other diseases.
Traditionally used:
- ADS . Includes (in addition to 20 units of tetanus toxoid) also an anti-diphtheria component;
- ADS-m . This is a lighter version of ADS, since the vaccination dose contains only 10 units of tetanus toxoid;
- DPT . Added anti-pertussis component.
If immunization is carried out with the DTP vaccine, then you should know that this is the most “heavy” drug for a small organism. It is noted that on average, a third of vaccinated children are diagnosed with post-vaccination reactions, but not to every vaccination.
DPT vaccine
They manifest themselves as a slight increase in temperature or mild malaise. Normally, these unpleasant symptoms develop no more than 3 days and last 2-4 days, no longer. Other types of tetanus vaccines are less reactogenic, so post-vaccination manifestations are rare here, and vaccination is generally easily tolerated.
Any vaccine has a number of contraindications. This means that the immunization procedure should be carried out only after the baby has ruled out an allergy to the antitetanus drug and in the absence of any infections at the time of vaccination.
The child must be healthy - this is important! If in doubt, discuss an alternative vaccination schedule with your pediatrician.
When should you get a tetanus vaccine?
There are clearly regulated standards for vaccination. First of all, they determine at what age vaccinations should begin. In general, the following scheme is used:
- 3 months from birth.
- 4.5 months.
- 6 months.
- 1.5 years.
- 6-7 years.
- 14-15 years old.
Entering the human body through wounds, including cracks in the skin, the tetanus bacillus produces one of the strongest nerve poisons - a toxin.
Many people believe that vaccination is carried out only for children, but this is a big mistake. After such a regimen, immunity lasts for about 10 years, while the danger of contracting tetanus does not go away. To maintain protection, the vaccination is repeated every 10 years.
At the same time, if there is no longer immunity from tetanus, it is never too late to start building it. Adults and children over 5 years of age are vaccinated according to the following schedule:
- When contacting.
- In 45 days.
- In 6-9 months.
But it’s better not to risk your health and complete the full course of immunization as early as possible. This is especially true for children, who are injured more often and suffer from tetanus much worse.