2636
The liver is one of the most functionally important organs in the human body, responsible for many vital tasks. That is why his condition should be monitored. If discomfort, pain or other alarming signs occur, you should contact a specialist.
One of the most effective and informative ways to diagnose and examine organs is ultrasound (ultrasound). Both kidney ultrasound and liver ultrasound require special preparation on the part of the patient. This article will discuss exactly how to prepare for an ultrasound of the liver and kidneys.
An ultrasound examination of the liver allows a specialist to determine the structure of the liver tissue, the diameter of the hepatic arteries and vessels, the size and condition of the gallbladder tissue. Using ultrasound, you can analyze the deviation of these characteristics from the norm.
The healthy functioning of the liver often depends on the rest of the digestive system, so doctors recommend an ultrasound examination of the entire abdominal cavity. Timely diagnosis will help catch the disease at an early stage of development.
There are certain indications for which an ultrasound examination of the liver is prescribed:
- the results of general and biochemical blood and urine tests indicate liver pathology;
- long-term drug treatment;
- pronounced yellow tint to the skin, eye sclera and mucous membranes;
- abdominal tissue injuries;
- viral or chemical hepatitis;
- pain and swelling in the right hypochondrium;
- increase or decrease in the size of the organ and its segments;
- neoplasms (benign or malignant), the presence of which was detected during other diagnostic methods;
- the possible presence of a purulent neoplasm, as well as parasitic worms;
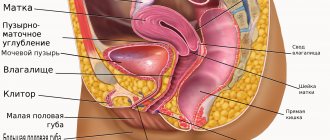
- gynecological examination;
- selection of hormonal contraception.
Blood and urine analysis
Drug treatment
Yellow skin tone
Viral hepatitis
Painful sensations
Gynecological examination
An ultrasound examination of the liver makes it possible to detect various hepatitis, cancerous tumors and metastases, cystic neoplasms, hemangiomas, cirrhotic changes in the liver tissues, cholelithiasis, fibrosis, and calcifications.
No less important is the examination of the kidneys, which are the main part of the urinary system of the human body. They are most susceptible to the development of cystic formations, polyps and stones, the presence of which can be detected through ultrasound.
There are a number of indications for which kidney ultrasound is prescribed:
- pain and discomfort in the lumbar region;
- unnatural color of urine;
- pain when urinating;
- swelling that lasts for a long time;
- deviations from normal values in urine analysis;
- inflammatory processes (cystitis, pyelonephritis);
- hypertension (examination of the arteries in the kidneys is necessary);
- trauma or pathology of the urinary system;
- pathologies of the genitourinary system;
- gout, diabetes.
How to prepare for a liver ultrasound?
72 hours before the start of the ultrasound examination, you need to eliminate from your diet those dishes and foods that can cause excessive gas formation. These include brown bread, fresh fruits and vegetables, carbonated drinks and dairy products, lentils, peas, and beans.
It is also necessary to adhere to a special diet, including the following dishes and products:
- wheat, millet, oatmeal, rice, buckwheat porridge with water;
- low-fat varieties of fish and meat that are steamed;
- hard varieties of low-fat cheese;
- boiled chicken eggs;
- fruits and vegetables cooked in the oven.
Food should be divided into several meals; overeating is strictly prohibited. The last meal should occur 5-6 hours before the ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity and liver. Ultrasound must be performed on an empty stomach. It is also recommended to drink at least one and a half liters of liquid (pure water or unsweetened tea).
For people suffering from diabetes, pregnant women and young children, a more gentle diet is suggested. Patients with diabetes are allowed to have a light breakfast before the test with barely sweet tea and two or three crackers. The baby can be fed on the day of the examination procedure, but the last meal should be taken 3-4 hours before the procedure, otherwise it will not be possible to conduct a high-quality liver ultrasound.
For older children, it is advisable to take a break of 4 hours between meals, and if the child has difficulty withstanding hunger, then you can give him some water. Pregnant women are also entitled to a gentle diet, but if she is able to withstand hunger, then it is better not to eat anything 2-3 hours before the ultrasound examination.
If the patient is obese, then additional recommendations and procedures are prescribed by a specialist. This often includes using a cleansing enema the day before the ultrasound (only if recommended by your doctor).
Before an ultrasound scan of the liver, you should consult with your doctor regarding the use of medications, both those that you take on an ongoing basis and those that are prescribed immediately before diagnosis. Most often these are medications that improve the digestive process and eliminate flatulence.
What to take for an ultrasound
Before you go for the test, there are a few things you need to prepare. Here is the list:
- A referral from a doctor with a suspected diagnosis.
- Towel.
- Paper napkins (to wipe the gel off the skin).
- Medical card.
- Results of previous studies (if any). This will allow the doctor to assess the dynamics.
It is better to dress in comfortable and convenient clothes that can be easily removed, providing access to the examination area.
Preparing for an ultrasound of the kidneys
As a rule, ultrasound is performed comprehensively, i.e. Instead of the kidneys, the remaining organs of the urinary system are considered. 72 hours before an ultrasound examination of the kidneys, it is necessary to eliminate fried, spicy, salty, fatty and sweet foods, beans, peas and cabbage, and carbonated drinks from the diet. All these products can increase the inflammatory process, if present, and also cause bloating.
Doctors recommend abstaining from food 8 hours before the diagnosis, and also taking activated charcoal an hour and a half after the last meal (it is necessary to take medications only as directed by a specialist). This will help rid the intestines of accumulated gases.
Immediately before the diagnosis, you should drink one or one and a half liters of still water or tea without sugar. Children under 2 years old need to drink 100 milliliters of liquid, children from 3 to 7 - 200 milliliters, from 8 to 11 - 300, and children over 12 - from 400 milliliters. You can give children compote or juice, but plain water is better. It is not recommended to urinate because a full bladder is required for a kidney ultrasound.
Methodology of the procedure
In order to get a complete picture of the condition of the gallbladder, it is better to do an ultrasound of all abdominal organs. After diagnosis, you should contact a gastroenterologist so that a specialist can decipher all the results and explain the condition of the organ.
Ultrasound of the gallbladder is of two types - simple and with determination of function .
- A simple ultrasound is done using an external probe through the anterior abdominal wall.
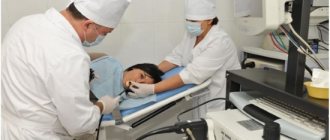
The patient undresses to the waist and lies down on the couch. Before starting the procedure, the doctor applies a special gel to the area of study to eliminate interference in the form of an air gap. Sometimes the patient may be asked to take a deep breath or hold his breath. This is necessary to obtain a more accurate result when the gallbladder is hidden by intestinal loops.
If the doctor asks the patient to stand up and bend forward a few times, you should not be surprised: in this way the doctor is trying to diagnose the presence of sand or stones in the organ.
- Ultrasound of the gallbladder with determination of function has other names - ultrasound diagnostics with a choleretic breakfast, dynamic echocholescintigraphy, ultrasound with a functional test or load.
This type of study allows you to determine the contractility of the gallbladder in real time.
The procedure consists of two stages. First, a simple ultrasound is performed. Afterwards, the patient needs to eat several foods to choose from:
- 250 ml of heavy cream, cottage cheese or sour cream with twenty-five percent fat content;
- several pieces of dark chocolate and banana;
- 2 raw or boiled chicken yolks;
- bread with butter;
- sorbitol solution.
Next, the procedure is carried out 3 times with intervals of 5, 10 and 15 minutes between each procedure.
If during the procedure the patient complains of pain, the doctor needs to record its intensity, nature and area of distribution.
Medicines and other procedures
To stimulate secretion function, before an ultrasound examination of the liver, the doctor may prescribe Mezim (Festal) , as well as enterosorbents (for example, Smecta, Polyphepan or Polysorb) . All of the listed medications can be used only after the recommendation of the attending physician, since the patient may have individual intolerance or other contraindications to these medications.
If a child has problems with the digestive system or flatulence, the doctor may prescribe Espusin, Kolikid and other similar medications. You should refrain from taking drugs such as No-spa, Aspirin, and acetylsalicylic acid.
Before an ultrasound examination, the intestines must be clean, so if you have problems with stool, you can take a laxative or use a suppository. If the intestines have not been cleansed within a few hours, then you can use a cleansing enema.
If the patient, before performing an ultrasound examination of the liver, underwent fibrogastroduodenoscopy, colonoscopy, gastrography or irrigoscopy, then the specialist must be informed about this, since an ultrasound examination after these diagnostic methods may show an incorrect or inaccurate result.
Indications
Ultrasound is not performed on every patient who comes to see a doctor. This procedure is prescribed if there are indications - complaints or symptoms indicating liver disease. The doctor recommends that the patient undergo an ultrasound when he discovers:
- change in blood test - increase in liver parameters;
- yellow discoloration of the skin, redness of the palms, vascular rash;
- enlarged liver upon palpation;
- darkening of urine or lightening of stools.
Indications for an ultrasound include a person’s complaints of pain in the right hypochondrium, vomiting bile, bitterness in the mouth, bleeding from the nose or gums. In these situations, the study is aimed at identifying the disease for the first time.
Liver ultrasound is regularly performed for people with chronic diseases:
- viral hepatitis;
- autoimmune hepatitis;
- fatty hepatosis;
- cirrhosis of the liver.
An ultrasound diagnostic method is necessary to monitor the dynamics of the disease and predict the outcome. Another useful examination method for such patients is elastography, or fibroscanning. The procedure determines the degree of degeneration of liver tissue into connective tissue.
The liver is indirectly examined by ultrasound in women during pregnancy. A frequent complication of the gestational period is acute fatty hepatosis. Therefore, when a woman undergoes a fetal ultrasound, liver damage is excluded. The examination is performed on newborns if a congenital infection or a developmental defect is suspected.
If necessary, along with conventional ultrasound, Doppler ultrasound of the liver is performed. This ultrasound method provides information about the condition of the blood vessels. Ultrasound is used not only for diagnostic purposes, but also during therapeutic procedures. For example, biopsies and surgical interventions are performed under ultrasound control.
A contrast study is done when it is necessary to distinguish a malignant tumor from a benign one. Cancerous tumors accumulate contrast agent and become clearly visible.
If a person independently decides to be examined, he needs to know the name of the doctor who performs an ultrasound of the liver and makes a conclusion. Liver diseases are dealt with by gastroenterologists, or more specialized specialists - hepatologists.
Diagnostic results
The results of liver ultrasound require interpretation by a specialist. When an ultrasound examination is performed, the size, surface and shape of the liver lobes and segments, as well as veins, arteries of the liver and kidneys, and bile ducts are examined. The data obtained during the study is compared with generally accepted medical standards.
The anteroposterior or sagittal size of the left lobe of the liver in an adult should not exceed 70 millimeters, the size of the right lobe - 125 millimeters. The normal size of the common bile duct is 60-80 millimeters, the diameter of the portal vein should not exceed 13 millimeters.
The edges of the liver cavity should be sharp and smooth in structure, the surface of the liver parenchyma should be free of dents, bumps and waves.
Kidney ultrasound can detect the presence of stones and tumors.
Normal liver parameters
The conclusion can be issued immediately or the next day. When decrypting, the data obtained is compared with the norms:
- thickness of the right and left parts – up to 14 and 8 cm;
- width and length of the organ - from 23 to 27 and 14-20 cm;
- transverse size – 20-22.5 cm;
- the lower angles of the left and right lobes are less than 45 and 75 degrees;
- the oblique vertical indicator of the right part of the organ is not more than 150 mm;
- craniocaudal parameter of the left lobe – does not exceed 100 mm;
- portal vein – 10-14, hepatic vein – 6-10, vena cava – 15-25 (in mm);
- main artery – 4-6 mm;
- bile ducts – 2-3 mm, common duct – 4-6 mm.
Normally, the boundaries of the organ should be clear, even, and the structure should be fine-grained, with many small point structures. The echo ability of the liver is slightly higher (or equal) to the response of the cortical substance of healthy kidneys. Sound conductivity is high, worsens only with diffuse abnormalities (for example, hepatosis, fatty lesions, fibrosis, etc.).
The thin veins of the liver are usually not visible on the image and can only be identified by the Valsalva maneuver. Also, normally the arteries and ducts of the organ are not visualized, but the inferior vein is clearly visible and its size fluctuates during entry and exhalation.
Read about liver examination using MRI here -
Features of ultrasound of the liver and kidneys
Usually an ultrasound examination is scheduled for the morning. Doctors believe that this is the most optimal time for diagnosis, since the patient does not yet have time to become very hungry, and if an ultrasound is performed after 14:00, the patient will have to fast (if this is not a pregnant woman or child). An ultrasound of the liver and kidneys is performed by a specialist with the necessary knowledge and extensive experience in the field of ultrasound.
A special diagnostic device is an echotomoscope. The procedure lasts no more than half an hour, unless additional examinations are required. An ultrasound is completely painless, but sometimes the patient may experience slight discomfort due to the pressure of the sensor.
No effort is expected on the part of the patient. Sometimes the doctor requires the person being examined to hold their breath or turn in a certain way to better view the organ. An auxiliary gel is also applied to the skin, which improves scanning of the abdominal cavity.
© 2019 — 2019, . All rights reserved.
Indications and contraindications for ultrasound
An ultrasound of the liver is done during clinical examination and in the postoperative period to monitor the dynamics of recovery. Other indications for ultrasound are:
- frequent pain in the epigastrium, between or near the ribs (especially on the right side);
- the skin and mucous membranes of the eyes become yellow;
- itching that occurs for an unknown reason;
- high concentration of bilirubin;
- excessive amylase activity;
- abdominal injuries;
- liver enlargement (primarily determined by palpation);
- cancer;
- metastases;
- suspicion of benign tumors;
- long-term use of medications toxic to the liver;
- alcohol abuse.
Ultrasound is also mandatory for pregnant women and children, especially when for some unknown reason their temperature rises, itching, pain in the ribs, or other negative symptoms appear. The examination is carried out at certain intervals in case of already detected liver pathologies.
Contraindications
These include only open wounds or damage to the skin where the sensor slipped. For example, purulent rashes, burns, eczema, etc. In this case, the pathological process can spread to healthy tissue.
However, these contraindications are relative and in case of emergency, the examination is still carried out. There are no other prohibitions for ultrasound.
Detection of pathologies and assessment of the development of liver diseases using ultrasound
A doctor may prescribe an ultrasound scan of the liver for preventive purposes, in order to identify any changes in the organ, as well as confirm hepatitis or another disease. If ultrasound results are performed in a timely manner and correctly interpreted, the doctor can prevent the possibility of developing cirrhosis, hepatitis or another disease by prescribing the necessary treatment. Ultrasound diagnostic results may indicate cirrhosis, acute hepatitis, chronic hepatitis, tumors, cysts, fatty degeneration, giardiasis.
If the doctor suspects the presence of hepatitis, then ultrasound diagnostics is only a complementary research method. To establish or confirm the presence of hepatitis, ultrasound alone will not be enough. But in the presence of hepatitis belonging to class C, an ultrasound examination will report the following changes: at the time of acute development of hepatitis on an ultrasound, the liver will appear enlarged, with increased density, as well as with changes in the tissue and a heterogeneous structure. In case of chronic hepatitis, the following changes will be noticeable on ultrasound: the organ is enlarged, with increased density, the vessels are not clearly shown, tissue changes are detected.
Using ultrasound, it is possible to visualize disorders and changes in the liver, indicating not only hepatitis, but also cirrhosis. Direct signs of the development of a disease such as cirrhosis are as follows:
- During the ultrasound procedure, changes in the size and structure of the organ are observed;
- The organ is characterized by increased density and fibrosis;
- When cirrhosis of the liver is diagnosed, the disease will be indicated by unclear outlines of the organ and its tissue;
- The lower edge is characterized by a rounded shape.
In order for the doctor to detect and evaluate the development of the disease, at the moment when liver cirrhosis is diagnosed, the patient must hold his breath for a short time after taking a deep breath. Thanks to this, the organ will lower slightly, which means it will be more open for inspection and detailed study.
Primary diagnosis of liver cirrhosis makes it possible to evaluate the obtained indicators and compare them with standard values. Based on these data, as well as the presence of irregularities and structural features of the organ, signs of cirrhosis are established.
Depending on the stage of the disease, the diagnosis of liver cirrhosis will show certain changes in the organ. The initial stage of cirrhosis is characterized by a slight enlargement of the organ and no changes in consistency. As the disease further develops, the size of the liver will differ greatly from the norm, and tubercles and small nodes will appear on its uneven surface. The last stages of the development of cirrhosis are characterized by a significant deviation in the size of the organ from the norm to a smaller extent.
Diagnosis of cirrhosis and hepatitis occurs not only by ultrasound photos. Hepatitis or the initial stage of cirrhosis may also be indicated by the results of blood and urine tests, for which the patient receives a referral during a doctor’s appointment.
Diet
Before an ultrasound examination of the liver gallbladder, you must adhere to a special diet that helps the body prepare. It will help in obtaining correct and reliable results. The diet should be light and balanced, not contain gas-forming foods, fatty or spicy foods. It is recommended to drink only purified water. You can eat until 7 pm. If you want to drink tea or coffee, you can only drink weak and sugar-free ones.
It is recommended to eat cereal porridges, beef and lean chicken meat, but only boiled meat; you can also eat low-fat cheese. Sweets of any type are contraindicated. Also, before examining the gallbladder, you should not drink juices, fish, or drink alcohol.
Decoding the results
During the examination, it is clear whether the size of the gallbladder and liver corresponds to age standards, whether the function is preserved or impaired.
Normal sizes vary depending on age, individual characteristics, body type, etc.
Ultrasound results of the gallbladder
Normal parameters of the gallbladder on ultrasound:
For the gallbladder, the normal options are as follows::
- length – from 7 to 12 cm;
- width – from 3 to 5 cm;
- wall thickness about 4 mm;
- transverse size from 3 to 3.5 cm;
- volume from 35 to 79 cm cube;
- the diameter of the common bile duct is from 6 to 8 cm;
The normal shape of the gallbladder is oval or pear-shaped.
In children, these parameters depend on age and physique.
Ultrasound results of the gallbladder for pathology
Acute cholecystitis:
- pain when exposed to the sensor (positive Murphy's sign);
- an increase in size with simultaneous uneven thickening of the walls;
- edema;
- changes in the lymphatic system;
- multiple partitions.
Chronic inflammation of the gallbladder:
- reduction of the organ due to wrinkling or scar processes;
- blurred contours;
- thickening or, conversely, thinning of the walls;
- change in shape;
- no changes in lymphoid tissue;
- pathological fixation of the bladder to nearby structures;
- heterogeneity of content.
Cholelithiasis:
- the presence of volumetric inclusions of a dense structure that give echo shadows;
- mobility of these formations (rarely the calculus is fused to the tissue, diagnosis is always made with a polyp or tumor neoplasm);
- uneven contours;
- organ deformation;
- violation of the patency of the ducts;
- reaction of surrounding tissues;
- sediment of bilirubin crystals, biliary sludge (stage preceding the formation of a calculus);
- thickening of the walls.
Ultrasound can detect small accumulations of salts indirectly, by expanding the diameter of the bile duct above the area affected by obstruction (blockage).
Establishing the mobility of formations requires performing research from different projections.
Choledocholithiasis on a sonogram is represented by an expansion of the common bile duct up to 7 mm and an expansion of the intrahepatic ducts, visualization of a calculus.
Tumor:
- : uneven contours of the organ;
- thickening of the walls;
- presence of a neoplasm.
Polyp:
pedunculated formation emanating from the wall. Differential diagnosis is carried out with malignant tumors.
Hydrocele of the gallbladder:
- enlarged organ;
- obstruction of the bile duct.
Ultrasound of the liver: interpretation
Normal liver findings on ultrasound:
During diagnosis, the doctor evaluates the following parameters:
- contour of the edges of the organ (clear and even);
- structure (homogeneous);
- width – from 23 to 27 cm;
- length – from 14 to 20 cm;
- cross-sectional dimensions – from 20 to 22 cm;
- the dimensions of the left lobe are from 6 to 8 cm;
- the dimensions of the right lobe are from 8 to 12 cm;
- diameter of the hepatic duct – from 3 to 5 mm;
- the diameter of the inferior vena cava is from 12 to 15 mm.
Visualization of all vessels is normal and good; the lower corner of the liver has a pointed shape. If there is a deviation from these indicators, either a dynamic study or an additional examination is indicated.
What pathology can be seen with liver ultrasound
The size, contours, boundaries, vascular architecture, position of the liver relative to the organs, the presence/absence of pathological formations and echogenicity are assessed. Changes in echogenicity can be diffuse or focal.
The picture of benign and malignant liver tumors is similar, so the diagnosis is made using cytological or histological examination . Fine-needle liver biopsy is performed under ultrasound guidance.
The likelihood of detecting a liver tumor depends on the size, location, qualifications of the doctor and the quality of the ultrasound machine.
Unfortunately, tumors smaller than 1 cm are diagnosed by liver ultrasound in 60–80% of cases. There are certain difficulties when performing examinations in overweight patients. To improve the quality of the study, Doppler is used, which shows the vessel feeding the tumor or tumor invasion.
According to indications, liver ultrasound is prescribed in combination with the administration of contrast agents.
Ultrasound of the liver helps in the diagnosis of cirrhosis: the diagnosis can be suspected by the presence of collateral veins, atrophy, enlarged spleen and ascites. The size of the organ in cirrhosis depends on the duration of the process: in the initial stage the liver is enlarged, with the death of functional units - hepatocytes and the proliferation of fibrous tissue, the liver decreases.
An ultrasound of the liver can confirm structural anomalies (additional lobes, absence of a lobe or part thereof), cysts, angiomyolipomas, adenomas, metastatic lesions, traumatic injuries.
Why the liver is enlarged on ultrasound cannot be answered unequivocally only by performing the study. There are many reasons:
- infectious lesion (infectious hepatitis);
- alcoholic damaging factor (cirrhosis, alcoholic hepatitis);
- cardiovascular failure;
- parasitic infestations;
- reactive increase in cholelithiasis;
- taking medications (drug-induced hepatitis), etc.
Relatively recently, diagnostic ultrasound elastography began to be used. The method is based on the different densities of healthy and diseased tissue.
Victoria Mishina, urologist, medical columnist
9, total, today
( 35 votes, average: 4.66 out of 5)
Testicular biopsy in men: indications, technique, explanation
Blood test for sugar: preparation, interpretation of results
Related Posts
How is ultrasound performed?
If the patient is concerned about the question of how an ultrasound of the liver will be done, specialists rush to reassure him that nothing terrible or painful will happen. The patient simply assumes a horizontal position, and the specialist, having applied conductive gel to the abdominal area, examines the desired area of the body with a special scanner. It is completely painless and does not cause any discomfort. There are no contraindications to this procedure, which indicates its complete safety even for small children and pregnant women.
During the procedure, the following parameters are assessed:
- Contours.
- Organ structure.
- Organ shape.
- Localization of pathology, disease or injury.
Methodology for performing the examination
Since the liver is a fairly large organ, the specialist scans the entire area of the right hypochondrium. These scans, along with the report, are sent to the attending physician, who will analyze them and evaluate the patient’s condition. The doctor will draw conclusions and make a diagnosis based on the interpretation of the ultrasound diagnostics of the liver, the clinical picture, the results of laboratory tests and the patient’s medical history.
Method of implementation
A sensor is used to determine the condition of the organ with further diagnostics. It is adjusted to the abdominal wall to make the ultrasound procedure easier. In order for the research to be carried out efficiently, it is necessary to free up space where the sensors will be installed. It is also necessary to get rid of the air that has formed between the body and the sensor so that there are no failures. In this case, the accuracy of the readings increases.
There are times when loops in the abdomen interfere with the correct diagnosis. You need to take a deep breath, or turn on your side. Ultrasound examination of internal organs is often necessary, since it is difficult to determine the extent and main nuances of the disease just by symptoms.
Preparing the gallbladder a week before the ultrasound
Preparing for an ultrasound is not difficult and takes a little time, but every day. Seven days before the test it is recommended:
- Stop drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Avoid eating fatty and spicy foods.
- Eliminate from your diet foods that contribute to the formation of gases in the intestines.
- Avoid carbonated drinks.
- Eliminate from the diet products containing flavors and dyes, stimulants and other chemical compounds.
It is advisable before the examination during this period to drink more purified water, eat fruits, vegetables, and cereals. This diet can also be followed after an ultrasound, since such a lifestyle will have a positive effect on the work and functioning of the liver and gallbladder.
Some subtleties
If the patient is prescribed medications that need to be taken hourly after meals, then the doctor must be informed about this. He will schedule a study at the earliest possible time or adjust the medications taken.
Treatment with other medications must be reported in any case. Some medications may affect the reliability of the results obtained. For example, an increase in liver size after taking medications for the heart and blood vessels.
Antispasmodics may affect the assessment of the functioning of the gallbladder and its ducts. Therefore, when preparing for a study, it is necessary to consult with your doctor in order to temporarily cancel them.
There are special conditions for patients with diabetes. They are allowed to eat a cracker and drink tea, because it is dangerous for them to remain hungry.
Preparing for an ultrasound of the liver does not cause any difficulties. Compliance with all recommendations will allow you to get the most reliable result. They should not be neglected, because the effectiveness of the treatment will depend on the correctness of the diagnosis.
In what cases is diagnostics prescribed?
A detailed liver examination is usually prescribed for elderly patients . The fact is that liver pathologies occur more often with age. After all, this organ is a natural filter of our body and the longer it functions, the more likely it is to malfunction. But even in young people there may be a need for an ultrasound examination of the liver.
The following symptoms are indications for this procedure:
- visible yellowness of the mucous membranes and skin;
- pale color of stool combined with brightly colored urine;
- pain in the abdomen or dull pain under the right rib;
- feeling of heaviness after eating.
An ultrasound of the liver is also indicated if:
- there are deviations from the norm in the results of laboratory tests;
- the patient has undergone radiation or chemotherapy;
- the patient took medications for a long time;
- the patient is prone to alcohol abuse, often smokes or uses drugs;
- the attending physician suspects the presence of neoplasms;
- there was an abdominal injury;
- correction of previously prescribed treatment is necessary;
- the patient has been diagnosed with helminthiasis, steatosis, cirrhosis, polycystic organ disease or hepatitis;
- preventive examination is necessary.
However, it is worth considering that the list of indications for liver examination can be significantly expanded and the procedure is carried out, first of all, at the discretion of the attending physician. The listed conditions are the most common reasons for prescribing an ultrasound of the liver. This will help make the correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Preparing the child
The differences in preparing a child and an adult for a liver ultrasound are insignificant. You also need a diet that excludes foods known to cause increased gas formation. A child prone to flatulence should take prescribed medications in advance. Constipation can be relieved with an enema or early use of mild laxatives. The only significant difference is that infants can have an ultrasound scan 3 hours before feeding, while children of preschool and primary school age should have their last meal 6-8 hours before the procedure. This, again, is associated with specific diagnostics - always on an empty stomach.
It is important to understand that early, timely diagnosis of liver disease, this most important internal organ, is already half the victory over the disease. The earlier a medical problem is diagnosed, the greater the chance of success. It is very important that ultrasound will allow you to track changes in the size and shape of the liver; in addition, with the help of ultrasound, you can detect many pathological changes in tissue density and their structure, identify stones, cysts, polyps and neoplasms. Normal liver ultrasound results indicate the patient’s good health and the absence of indications for surgical or drug treatment.
Ultrasound safety
Ultrasound is one of the safest and most painless types of examinations in medicine. To date, there is not a single proven fact of harm from this diagnostic procedure for humans. If necessary, it can be performed immediately after the birth of the child, including an ultrasound of the gallbladder, how to prepare for which is described above.
This procedure is prescribed even to pregnant women (at all stages), which also indicates a minimal risk of negative effects on the body. The study is informative and painless, which is important when diagnosing childhood diseases.
You can get the most objective results of the study only by knowing how to prepare for an ultrasound of the liver, gallbladder, pancreas and other abdominal organs. Simple rules will save the patient time and money that he could spend on a repeat procedure.
What does an ultrasound of the gallbladder show?
During ultrasound diagnosis of the gallbladder, the following diseases can be identified:
Acute and chronic cholecystitis . The presence of an inflammatory process is indicated by thickening of the walls of the organ, changes in its size, the presence of unclear contours, and increased blood flow.
Cholelithiasis . During an ultrasound of the gallbladder, the doctor detects stones that can move during a deep breath and a change in body position. Due to the impenetrability of stones, echo shadows appear. The walls of the organ are thickened and have an unclear outline. Biliary sludge (sediment) may be found inside the gallbladder. If stones are found in the area of the duct, the doctor may notice an expansion of its diameter just above the location of the stone.
Stones in the common bile duct . There is an expansion of the intrahepatic ducts and the presence of echo shadows in the bladder itself.
Dyskinesia of the gallbladder . Accompanied by a violation of the functionality of the organ; it may be detected by an inflection in the area of the neck, bottom or body. At the same time, the tone of the mucous walls is increased, and a characteristic thickening is noted.
Tumors, cysts . On ultrasound, the walls of the gallbladder are thickened; the diagnostician identifies formations whose size exceeds 7-10 mm. This is characterized by deformation and changes in the external contours of the organ.
Hydrocele of the gallbladder . The size of the organ is significantly increased. Using an ultrasound, a specialist determines blockage of the cystic duct, stones, and the presence of echoshadows.
Adenomyomatosis . With benign growth of the gallbladder wall, hyperplasia of the upper layers occurs, the cystic wall is thickened, its size can exceed 10 mm. Polyps are found in the form of round-shaped neoplasms. They can be malignant in nature, so when they are identified, additional diagnostic methods are required.
Congenital or acquired developmental anomalies . Ultrasound of the gallbladder is characterized by protrusion of the cystic walls; it is possible to identify an atypical localization of the organ and its kinks.
What needs to be done before the study?
Before the liver gallbladder examination, you are not allowed to eat or drink; you can eat lightly and eat dietary foods only if the examination is scheduled for the second half of the day. The night before, it is advisable to eat no later than 7 o'clock in the evening. Products should be light and satisfying. You will definitely need to empty your bowels naturally or with the help of special medications and means.
If a gallbladder examination is prescribed for a small child, then there is no need to give him medications, just adjust his food intake correctly. The child can drink water, but not in large quantities. Children over eight years of age need the same training as an adult. Medicines can also be given, but the dosage must be adjusted in accordance with the instructions of the attending physician.