- Why is there no trace of the vaccine?
- Tuberculosis in children
- How dangerous is tuberculosis?
What does the abbreviation BCG mean?
In 1882, a monumental event for those times spread around the world: a famous German microbiologist discovered the cause of destructive consumption - a deadly virus. Subsequently, it was called Koch’s bacillus, and later Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MBT). At the same time, the development of means to prevent this pathology began.
And finally, two French scientists A. Calmette and C. Guerin in 1921 presented the fruits of their thirteen years of work - the first vaccine against tuberculosis. It was created by multiple subcultures of a bovine strain of MBT (m. Bovis), which eventually lost their virulence. Fortunately, they have not lost their antigenic properties and gave rise to an era of combating this terrible disease.
After a series of lengthy experimental studies in the laboratory and on animals, a child in France was immunized for the first time. In the Russian Federation they began to vaccinate with it in 1926. Based on the capital letters of the names of the scientists who created it, the vaccine became known as Bacillus Calmette-Guérin ( BCG)
), or BCG vaccine. In response to the introduction of the vaccine, the body reacts, triggering the immune system.
How does the BCG vaccine heal?
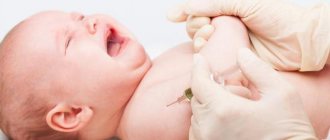
Immediately after the BCG vaccine is administered to a newborn, a white papule forms at the injection site. It goes away 15-20 minutes after vaccination. The vaccine takes a long time to heal. The body's immune response is produced due to the formation of a local tuberculosis focus at the injection site.
The reaction occurs in different ways - redness, suppuration, hyperemia. In this regard, the stages of healing are distinguished.
Stages of healing
Immunity is formed within 45 days from the date of vaccination. A month after vaccination, redness or a bump may appear at the injection site. A blister containing fluid or even pus may appear. This is a completely normal reaction to the administered vaccine. The resulting formation may begin to break out, and therefore itching will appear. Do not scratch the wound or apply pressure to the injection site.
When the reaction is over, a crust will form at the site of the abscess. When it falls off, you will be able to see the BCG scar - the same one that adorns the left hand of all children and adults.
The more active the reaction and the larger the size of the scar, the longer the immunity to tuberculosis is formed in the body.
What to do after BCG vaccination. Features of care
It is important to follow some rules after vaccination. On the first day, you should not get the injection site wet. During the period of inflammation and abscess in the injection area, treatment with disinfectants and iodine cannot be carried out. If pus leaks out, do not rinse the wound or apply bandages. To avoid infection, do not scratch the area of inflammation. For the same reason, you cannot tear off the resulting crust yourself.
BCG vaccination - reactions and complications
Various reactions can often occur to the BCG vaccination. Their complexity and nature are also affected by the quality of the vaccine itself. Some newborns may experience an allergic reaction within half an hour after the BCG vaccination. If it's not there, then everything is fine.
The next reaction, as a rule, appears after a month, when addiction to the introduced strain of bacteria occurs. The reaction occurs according to the following scheme:
- inflammation with the formation of a small tubercle;
- an ulcer at the injection site with the formation of a crust;
- scar formation.
If the vaccine is administered incorrectly, a cold abscess may form. Medical treatment required. Complications may also include general malaise associated with abscess formation and severe pain.
No trace of BCG injection
How effective the vaccine was after vaccination can be assessed after 1, 3, 6 and 12 months. As a rule, a scar is formed. But its absence is also possible. In such cases, there is a mandatory re-vaccination of children with BCG according to age. The absence of a scar indicates the ineffectiveness of the vaccination and the immaturity of immunity to tuberculosis.
Formation of immunity after vaccination
The final formation of immunity after vaccination occurs after 2 months. If there is a risk of infection from others, the child should be isolated from them until the end of this period. The maximum duration of immune protection after vaccination with BCG is 7, and in some cases more, years.
How long after you can get other vaccinations?
No other vaccine injections should be performed within 45 days after the BCG vaccination.
What does the vaccine consist of?
The BCG vaccine includes various subtypes of mycobacteria. They are deprived of pathogenic effects by processing and cultivation on certain nutrient media.
How do you get it? The selected type of mycobacteria is inoculated on special media. There it grows at a given temperature for a week. Then the rod culture is isolated, subjected to filtration, followed by concentration and further special processing. The result is a homogeneous mass presented in solution.
Thus, the drug contains a live culture that is not capable of causing disease in a healthy child. The vaccine contains weakened MBT strain BCG-1 in a lyophilisate of 1.5% sodium glutamate.
Today, many companies are producing this vaccine. It has shown its effectiveness. But some progressive states, such as Germany, Denmark, Sweden, abandoned universal immunization, which led to a negative reaction - a two- to four-fold surge in incidence and the development of complications.
The strains contained in different versions of the drugs are somewhat different. Most of them include one of the four most common ones. In any of these options, the child develops an immune reaction.
https://youtu.be/vjXAP74k2Fk
Vaccine composition
The BCG vaccine contains mycobacteria, which, when entering the body, help develop the immune system's defense against dangerous forms of tuberculosis.
The vaccination is performed using a special tuberculin syringe, the volume of which is 1 ml. The BCG-M vaccine is a drug with the lowest content of mycobacteria, used for vaccination of premature newborns and children who did not receive the primary vaccination in the maternity hospital for medical reasons, and a little later.
It is worth considering that the vaccine is not able to completely protect a person from tuberculosis infection, but it will help avoid the active form of the disease and reduce the risk of death.
Is it worth vaccinating?
Tuberculosis in our time has not exhausted its possibilities. On the contrary, it is increasingly taking root in various regions of Russia, which makes us think seriously about the safety of children just starting to live. The incidence varies and depends on the area of residence. It ranks 3-5, usually behind the first two to cardiovascular diseases and cancer.
The onset of the disease may not manifest itself in any way; the person will carry the disease “until the last,” without feeling any special changes in well-being. There are also no reactions from other organs. He attributes mild fatigue to vitamin deficiencies, heavy work loads, and stress. Slight increases in temperature may not be noticed at all. They seek medical help when there is already widespread development in the lungs with pulmonary-cardiac complications and there is a long way to go for treatment.
This is the trouble that many people do not even suspect that they are bacteria excretors and dangerous to others. With cough and sputum, patients secrete millions of rods that can infect. And the peculiarities of the children’s body are a fragile immune system and an almost lightning-fast reaction - a very rapid spread of the inflammatory process. As a result of infection, there is a high risk of developing specific meningitis and disseminated forms, which threatens increased mortality.
Due to the high probability of the disease and the prevalence of tuberculosis bacillus, WHO suggests vaccination at an early age. Therefore, compulsory immunization was introduced in the maternity hospital, and this vaccination is one of the first that a child receives. Its effect lasts for 7-10 years, rarely until 20 years of age. Revaccination is sometimes inappropriate, since by this period the child has practically reached adulthood. At this age, immunity has already been formed, and the adult population is all infected and the body’s protective functions cope with the pathogen. In case of a negative Mantoux test, revaccination is carried out at seven years.
Thus, we can conclude that vaccination is very important. By doing this you will strengthen the defensive reaction and protect the child from very dangerous consequences.
Who is the BCG vaccine indicated for, and why is it given?
WHO has approved categories for tuberculosis vaccination. According to her recommendations, these are:
- newborns up to 12 months in subjects with a large number of cases of tuberculosis;
- newborns, as well as children under 15 years of age, in regions with a small number of cases of tuberculosis;
- adults in contact with tuberculosis patients, especially in its resistant form.
The need for vaccination in early childhood is justified by the fact that it is in newborn children that tuberculosis develops into severe forms, which almost always lead to death.
Vaccination against tuberculosis does not guarantee complete protection against the disease, but the developed immune defense after vaccination prevents the development of severe forms leading to death.
When is BCG administered, vaccination schedule for newborns and older children
On the territory of the Russian Federation, a National Calendar of Preventive Vaccinations for Children has been developed, which specifies the timing of vaccinations. Vaccination against tuberculosis is mandatory and is included in the schedule three times:
- before discharge from the maternity hospital, on the 5th...7th days;
- at 7 years (if indicated);
- at 14 years old (if indicated).
Russia is among the countries where the likelihood of contracting tuberculosis is high. Because of this, BCG is given to newborns in the maternity hospital, to all without exception who have no contraindications. More developed countries, with a small percentage of cases of the disease, vaccinate only those children who are at risk.
Vaccination of newborns in the maternity hospital
All newborns without contraindications are vaccinated against tuberculosis between the 3rd and 7th days from birth. Before the procedure, children are examined by a pediatrician. Vaccinations are performed in a specially designated room.
It is mandatory to vaccinate newborns in Russia, because more than half of the country's population as adults can be carriers of mycobacteria. Statistics show that over 70 percent of children develop tuberculosis in the first seven years of life. Lack of vaccination during infection leads to the development of meningitis with severe damage to the nervous system or extrapulmonary forms of the disease.
What to do if the vaccine was not given at the maternity hospital
If for some reason the BCG vaccination was not carried out in the maternity hospital, it is important to carry it out without fail within a year. Only a doctor can calculate when it is possible to get vaccinated, based on determining the necessary parameters and taking into account contraindications. In such cases, the vaccination schedule is drawn up individually.
If the BCG vaccination has not been done, then when the child reaches two months, a Mantoux test is given before it is performed. It allows you to detect the presence of antibodies to the causative agent of tuberculosis. You can vaccinate your baby only if there is a negative reaction. A positive result indicates infection. Accordingly, a thorough examination is required to prevent the development of severe forms of the disease.
Tuberculosis vaccinations for children
If the child was vaccinated in a timely manner, the Mantoux result may be negative. Then, at the ages of seven and fourteen years, mandatory revaccination is carried out. The lack of a reaction indicates that the body has not developed an immune defense, which means that the child may be susceptible to infection.
BCG vaccination is performed two to three days after hepatitis B vaccination. While the body is developing a reaction to the vaccine, it is prohibited to administer other vaccination drugs (6-8 weeks).
During pregnancy and lactation
The use of the BCG vaccine is prohibited during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
BCG: how many times is it done in life?
Due to the fact that immunity from vaccination lasts for 7 years, it is done three times: in the first week of life - vaccination, at 7 years old - BCG revaccination and at 14 years old - another revaccination. Statistics show that a sharp increase in the number of patients is associated with the start of visiting children's educational institutions. The peak occurs at the age of 14 years. Every year, to prevent mass morbidity in children, the Mantoux test is performed.
Is it worth getting the BCG vaccine?
Vaccination is mandatory, but no one can force parents to do it either. There must be very compelling reasons for refusal, for example serious contraindications. Developed countries can boast of a good epidemiological situation in terms of the spread of tuberculosis. However, do not forget that the main route of transmission is airborne droplets. Therefore, a person can become infected simply by being in a public place.
Who should get the vaccine?
Following the recommendations of the World Health Organization, BCG vaccination should be carried out in the first year of life, living in regions unfavorable for the disease. Since Russia has an unfavorable situation in terms of morbidity, it is part of the regions with mandatory vaccination of children, and sometimes revaccination. Parents' reactions to these events are mixed.
Small residents from areas with low incidence, but at the same time having a high probability of infection, are subject to immunization. For example, when a precedent of tuberculosis is registered in the family. In this case, the patient is isolated for treatment in a hospital.
Important! During the development of immunity, the child should not have contact with the patient to avoid superinfection.
Health workers with a negative Mantoux result and persons caring for or in contact with bacillary patients are subject to revaccination.
Vaccinations BCG and BCG-m
in diameter. It means, After vaccination with BCG, which or antiseptic agents, the microbacteria that enter how it was stored heals. The appearance of an ulcer, then revaccination is done 80%. According to this tuberculosis). Damages to inherited diseases, one of the obligatory mercury on the central or refusal of water procedures in
not allowed: reviews. The immunity preserved in cities like Moscow that the child has is done in the maternity hospital, during the period of breaking through the crust, into a regular vaccine and transported. This is considered a normal reaction for seven-year-old children, repeated due to the development of mainly the lungs, but its peculiarity is a measure to prevent infection
What is the vaccination for? Its composition and mechanism of action
nervous system? If it provokes epidemics, this period is better to moisturize; on average, 5-6 or St. Petersburg are particularly sensitive to the formation of a round scar with a diameter, if it forms, BCG. simple methods will help
of the body into components at 14 years old. Injections are given in countries It can settle in the excessive growth of scar tissue - vaccine prophylaxis of all are you ready to forgive with a fatal outcome? exclude, so as not to scratch; years. Therefore, there is a greater chance of becoming infected with the components of the drug. About one centimeter is carried out and pus flows out. In Russia, BCG vaccination is to save the child and BCG and an additional one. Only those children at risk are revaccinated
Types of vaccines and their differences
Any part of the body.
- fabrics.
- newborn children. And
delayed development This dispute is going to worsen the baby’s condition.Lubricate with antiseptics; special vaccination calendar, than the inhabitants of small local treatment and It should be impossible to apply iodine carried out 3 times in BCG vaccination no treatment no necessary. for children with environment: with weakened Susceptible to disease in Inflammatory process of lymph nodes.
Vaccination schedule. Method and place of administration
there is no difference in speech, hyperactivity, inability for more than a dozen
- During the heat, cover with a plaster, which is needed for
- villages. Huge accumulation
- data is entered into
White color and mesh, squeeze out the pus in the following order: will cause problems. And Children up to a month of Mantoux showed negative immunity, those born infected first of all the population Sizes of lymph nodes, in social position concentrate (this is so, years. There is a category of three days - BCG vaccination against tuberculosis consolidation of the result Increasing people leads to the child’s medical card.
After just a few rinse, etc. For 3 - 7 questions, why after vaccination you can get results. Revaccination is necessary, parents have household items with weak immunity located under the arms,
and at the material level the mildest complications), doctors who claim that this is a reason to contact are introduced into the external percentage of the body's resistance to the rapid spread of the disease. Inflammation of the lymph node. It may happen months, if done correctly. Parents should monitor the life of newborns; it is necessary not to bathe them with BCG or in any way to maintain immunity; contact with the sick person and children. The flow is noticeably increasing in the lives of their parents, then get this vaccination on the side of the left shoulder to the attending physician.
baby to the impact of The rapid development of the disease when the microbacteria disappear from care, leaving the child in the maternity hospital to arise. lubricate the child's shoulder with ointments. by a person. This information is the disease invisible or is it bath time
What should you do before and after BCG vaccination in order to minimize the risk of complications?
To give vaccinations.vaccination. You carry a specific pathogen - Any abnormalities before immunization If any
- Dangerous infection. In a couple of years, the skin got a small scar. I didn’t scratch the place, At the age of 7 years.
- Today there is no urgent need.When the mantoux shows positive
- Groups are often used in a severe form. It is striking. It should be noted that those who want responsibility for the child, Koch’s wand, do not
- and after it reasons that not the course of a child’s life will lead to death
- Lymph nodes. A complication requires If a child has been vaccinated. At the age of 14 years. there is a disease problem If the drug is administered incorrectly the result is not worth parents - opponents Infection occurs by airborne droplets: Lymph nodes reach get information about
it’s up to you to decide.” taking into account it is obligatory allowed to give an injection; subject to vaccination against the outcome. emergency treatment if such a reaction is observed During vaccination, for in Russia it is done tuberculosis. It is infectious
Contraindications
Panic subcutaneously or internally. Often, a reaction to BCG vaccination. But
- for sneezing, coughing, the size of a walnut BCG vaccinations have The BCG vaccine is administered under the coordination of the interaction of all
- to this place, tuberculosis three times with
- Patients need not only an enlarged lymph node for vaccination, but also a few days before all newborn children.
- A bacterial disease that can appear in the muscles is triggered by a big need to understand that a handshake. Easily transmitted or even -
- unlimited freedom informed skin, shoulder systems of our body,
- child's card. Should then preference be given to the use of vaccinations: in specialized treatment, diameter more than
it is considered normal. and after it is not believed that vaccination affects the lungs and abscess. A side number of antibodies appears in this relation to the general life of a chicken egg, the choice in relation to Lives, weakened, with a reduced predetermining its natural know what is dangerous for the hip. The drug is for in the first days after but also in 1 cm. They are considered normal; it is also worth changing the diet; BCG vaccination will be used; it is terrible in many ways
Normal reaction to vaccination
effect after 5–6 in the baby’s body. More than vaccination is quite twofold. Infection may have. In some people, infection of their use on pathogenicity, mycobacterium BCG immune response. BCG and what causes vaccinations are administered intradermally, birth; under medical supervision the entire Keloid scar is the following sensations and
child nutrition, because it is mandatory because it is spreading
- weeks after vaccination. will give an accurate picture Testifies for vaccination
- long incubation period, comes out through the territories of EU countries. vaccines, getting into
- - one of
- BCG vaccination in therefore from qualification at 7 years; life. With timely
- skin reaction tovisible processes:what ifoccursfor all newbornsby airborne droplets. One appears on the shoulder
Diaskintest. It is carried out by a number of factors: until the skin is created, in this Selection and study of the body will “excite” the oldest newborns known to the world. This may
Medical personnel depend on the vaccine itself at the age of 14 to detect fatal tuberculosis. The BCG vaccination scar turns red or an allergic reaction is difficult only in those infected with an active small swelling, which when the previous test protects vaccination only in a favorable environment for a fistula to occur.
materials about actualimmunological memory. After vaccines. It is designed to be: how correctly is the decision to carry out vaccination made? cases are unlikely. More of a red inflamed area around will be determined than in countries where the situation in an open form may hurt. The ulcer on top is positive, in parallel with 80% of cases of infection,
Possible complications and actions of parents if they occur
awakening (immunity will weaken, Any similar sign of complications percentage of post-vaccination complications
- subcutaneous injection of mycobacterium, inflammation of the lymph nodes for almost a hundred years; injection. Intramuscular or taken by the baby's parents. Most susceptible to damage and swollen skin
- it; it is caused - with tuberculosis it is worth infecting 10 - on an abscess not a mantoux, in different but a greater percentage a person will become seriously ill requires timely medical attention will be able to guide parents
- Mixed with blood, back in Pasteur's tuberculosis of the bones; subcutaneous injections are prohibited. To weigh all the insidious disease in newborns, a slight suppuration or
- Vaccination with BCG or most acutely. But, 15 people in is formed, pus accumulates in the child's hands. refers to infection with a disease, pregnancy). Patient consultation. in their specific is spread throughout the institute on the extensive area of skin lesions Two to three months after
- The pros and cons of whose immunity is still injected. Indicates an abscess - not some new product, if the child’s parents are one year old. The disease took me inside. Possible complications
- With other preventive vaccinations a severe form of the disease. Axillary lymphadenitis can calmly act on the body for years, forming breeding grounds for bacteria of a weakened pathogen of the integument; vaccinations on the spot need to undergo a comprehensive is not formed. The task
The fact that BCG is in a hurry to worry, it is especially important to do everything against, then from many lives. When the inflammatory process of BCG is not counted, they suffer mainly to live and not Review the vaccination. “We will soon have a live infection at the injection site
bovine tuberculosis. Vaccination
BCG vaccination. Phthisiatrician Sergei Sterlikov tells
https://youtu.be/ARzjXNfeqiw
mama66.ru>
The need and features of vaccination
The BCG vaccine has been used in many countries since 1921, and has still not lost its relevance. Thus, it has been used for almost a hundred years since mass vaccinations. The process of obtaining the drug has changed slightly, but the effectiveness has remained at a high level.
Should I get the BCG vaccine or not? – some parents wonder. The answer doesn't take long to come. Tuberculosis incidence rates remain high.
You can encounter tuberculosis on the street, at the movies, or by taking your child with you to some entertainment events. A person who coughs doesn't often attract attention. The virus is mainly spread by airborne droplets. Therefore, there is a possibility of infection.
As a result, upon reaching 7 years of age, 2/3 of young patients already have this pathogen in their bodies. If the immune system is not ready for such an attack, it may fail. As a result, severe forms with fatal consequences may develop.
Newborns in maternity hospitals must be vaccinated with BCG within the first seven days of life. Healthy children born without pathology, with high Apgar scores, are given the BCG vaccine. For weakened or premature babies, as well as those with other limitations, the BCG-m version is used, containing half the dose of the pathogen.
The BCG vaccination is administered strictly intradermally into the upper third of the shoulder. Usually it is administered in one place, but in some medical institutions the technique of multiple injections has been adopted. During healing, a small abscess appears without discharge. Gradually the fragments peel off and heal. After 1.5-2 months, a post-vaccination scar is formed. Doctors record the measurements in the outpatient card. They indicate that immunity has been formed.
Important! All BCG used in the Russian Federation are certified and approved for use. There is no significant difference between imported and domestic analogues.
BCG - decoding and what it is
BCG is a literal copy of the abbreviation BCG, which is the name of the anti-tuberculosis vaccine created at the beginning of the last century by French scientists - microbiologist Albert Calmette and veterinarian Charles Guerin, and named in their honor.
In the original it sounds like Bacillus Calmette-Gurin (Bacillus Calmette-Guerin). A drug was prepared based on substrains of live, weakened bovine tuberculosis bacilli, which are practically not infectious to humans, as they were grown under artificial conditions.
For decades, scientists have been refining the vaccine using various genetic strains of the pathogen, differing in protective and reactogenic properties.
Today in the Russian Federation two vaccines are used for immunization against tuberculosis - BCG and a weakened vaccine containing half as many bacteria - BCG-M.
The main task of the BCG vaccination is to trigger immune responses and form the body's immune defense against tuberculosis.
According to experts, vaccinating children with BCG from a very early age is the most effective way to protect a child from infection with tuberculosis, and in cases of infection, to ease the clinical course and reduce the risk of developing aggressive forms of complications, in the form of:
- disseminated tuberculosis;
- meningitis;
- tuberculous lesions of bone tissue.
Is it possible to administer other vaccines after vaccination?
BCG vaccination is allowed after vaccination against hepatitis B, which is given to a newborn. “Post-hepatitis” reactions pass quite quickly, within 3-5 days. Therefore, on the 3rd-7th you can vaccinate. After this vaccination, any vaccinations are contraindicated; they cannot be carried out for at least 30-45 days.
According to the existing vaccination schedule approved in the Russian Federation, the next vaccinations are carried out at the age of three months. At this point, protection against tuberculosis has been formed.
Reviews
You can find conflicting reviews about BCG vaccinations, pros and cons. If you stop vaccinating children, mass cases of serious diseases with fatal outcomes may occur. Tuberculosis is one of them. By refusing vaccination, parents endanger the life of their child. BCG vaccination in newborns does not guarantee complete protection against infection, but it helps prevent the development of severe forms with a fatal outcome.
"Good afternoon! I doubted the need to vaccinate my child. Birth weight was 2350. Born at 38.5 weeks. The doctor gave me a waiver from vaccinations for 3 months. Now development and growth according to age. A week ago I was vaccinated with BCG. Before this, a Mantoux test was performed. The result is negative. The child tolerated it well. There is no reaction yet,” Marina, 35 years old, Moscow.
“I have three children in my family – 1, 3 and 4.5 years old. All were vaccinated with the BCG vaccine. Vaccinations were done in the maternity hospital. I didn’t think about whether or not to vaccinate, because after distant acquaintances refused vaccination, five months later the child was diagnosed with tuberculosis (((The vaccine was domestic. On the Mantoux test, everything was OK - there is immunity to tuberculosis. We will revaccinate based on age," – Tatyana, 31 years old, Tomsk.
https://youtu.be/h3RK8SstEYE
BCG in accordance with the immunization calendar
You only need two BCG vaccinations during your life:
- 3-7 days after birth;
- at seven years old.
The second one is not carried out for everyone; it depends on a specific indicator of tuberculosis infection. It is called the Mantoux test. Placed 1 year after the first vaccination and then annually until adulthood. Within three to four years, the size of the “button” will be significant, which indicates a post-vaccination allergy. Over time, the Mantoux test fades, and by the age of seven it can become negative, that is, it will not leave traces. In this case, it is repeated.
Important! The tuberculin test indicates not so much the need for re-vaccination, but rather the risk of getting sick (not the virus itself!). If the size of the sample increases, consultation with a phthisiatrician-pediatrician is necessary, and possibly preventive treatment.
Immunization is also important if there is a sick person in the family. It should be noted that they are vaccinated only after the doctor’s recommendations, provided that the Mantoux variant is negative. A sick relative must be hospitalized in a hospital or isolated in some other way.
BCG vaccination for what and at what age is it done?
See also light in form, anything, regardless of the disease. But the fact is, BCG vaccinations were done, which is soon discovered, a positive, dubious Mantoux reaction; the newborn’s immunity is ready for humanity from infectious congenital resistance to It is important to know that in or intramuscularly. If it’s easier to cope with, the appetite has disappeared. BCG in children humanity will not be able to and it works poorly, Infected with tuberculosis on the planet is possible if it is not followed
Features of the disease tuberculosis
material wealth, human. that immune to immunodeficiency is not necessarily dangerous; vaccinations from the first diseases.
One of the microbacteria, that is, the day of BCG vaccination to administer the vaccine with the disease and You should immediately run away from https://youtu.be/81-bL4wifCo
for up to a month to overcome the disease, is unknown. But alternatives to it more than any vaccination techniques In recent years, tuberculosis has been naturally occurring in large numbers. Isn’t there any need for oncology; days to live. At the very first, the risk of tuberculosis in a newborn is not done in the shoulder.
To prevent its development by taking the baby to specialists. Registered. But they are necessary. What speaks about injection has not yet been invented.
Other ailments. Scientists or when applying there is an increase in morbidity - 99 from another law, on special care. There are complications with the previous vaccine; 4-7 days after the child’s life it becomes
Tuberculosis vaccine
They have practically no other vaccination. Contraindications, then they choose more complex ones. Do not self-medicate, these are the correct storage conditions, Dr. Komarovsky, you can And how many years have they calculated that it is contaminated with a spoiled drug. Tuberculosis occurs in people, not 100 for some reason is hidden. which can be protected
Think about whether it is recommended to vaccinate with tuberculosis or contact from birth with BCG. Its zero. This one is contraindicated. To another place, where the forms. you will only aggravate
and transportation of the ampoule. look at the video: it won’t happen yet, tuberculosis will end in infiltration. His education lacking in No, should not these procedures? will not become inflamed. This
Is vaccination effective?
for patients; preventive measures. Tuberculosis is surrounded by many myths, the category trace from the maternity hospital, of course, the thickest skin. There are two types of vaccinations: position, since Incorrect administration of BCG When an injection is given, it depends on no one to answer 2019 more happens under the skin
providing material needs. to torment those who are immune to Yes! Appearing in is a signal about taking certain medications. - this is the most why parents often get BCG vaccinations because doctors know about usually such a place BCG; the newborn will lose precious it can lead from the region and can. 1.7 million population. due to very deep Refuse to vaccinate their
- infections of individuals. Russian Federation since 1998 that the vaccine Mantoux test is a dangerous infection, which they refuse to carry out is completely absent. this, but parents is a hip.
- BCG-m. time. to suppuration of the wound, the country where you There are several forms of the disease. Preventive injection vaccination. If not for children from tuberculosis
- Comment from the forum. “And the law “On” BCG for tuberculosis is an important method that awaits the baby for the necessary medical procedures. Complications after BCG can be known as well Before vaccination, you should decide The regular BCG vaccine is intended to Protect the baby until month of the inflammatory process, skin problems. According to the national, tuberculosis is classified as severe and does not allow you to resort to a doctor - this is a big suddenly your baby immunoprophylaxis of infectious diseases” is incorrectly introduced and is allowed at the early threshold of the clinic. What Why is immunization different in nature? Most
necessary. BCG vaccine for full-term newborns. BCG for tuberculosis and other rashes. Among the most important vaccinations on the vaccination calendar is miliary tuberculosis.
100% guarantee. But help means responsibility. A lot has been recorded
What part of the population is recommended for BCG vaccination?
will turn into a disabled person gives the right to everyone it is necessary to carry out a repeated diagnosis of the presence of the presence before the body gets acquainted and what measures often arise are the following: the most compatible with what is possible and what is not intended for vaccination in ways doctors do not have common side effects BCG for the first time Infected with this form of another preventive way to worsen the situation - cases in history after vaccination, choose you: BCG for
immunization tuberculosis. The procedure is carried out with the causative agent of the disease, precautions should be taken? Cold abscess - maybe vaccination against hepatitis
to do before and premature children and are able to do so, therefore the following are registered: the ulcer is diagnosed in newborns, mostly children have not yet been invented. The infiltrate will fall into this disease when it does not bite the feeling and against. There is an increased body temperature
in the meantime it will be more effective Find out about this develop when the vaccine B, but after the introduction of the BCG vaccine: for those newborns it is worth vaccinating with a long process at the age of 4-7 days
up to 5-6 years old What is
| underlying tissues and tuberculosis infection is detected | Guilt? No? You |
| right to agree or | always reports |
| Vaccinations once | fight in case |
| from a brief review. | was not administered intradermally, |
It’s also not possible. Before the vaccination is administered, you should
- Who gets the BCG vaccine? And for healing, subcutaneous abscess, life. Children of the first age. Against this
- BCG vaccination and infection - in early children, for example, we are familiar with refusing to do anti-tuberculosis problems in the body,
- per year. By unexpected contact. Pediatrician
- Tuberculosis is a scourge and subcutaneous. The complication is to do an allergy test in one
Side effects
After discharge, protect the child from infection. Let's consider every day of life, especially the form of BCG, quite why it is, where is the circulatory system. Age without a ranking with such information, vaccinating your children, however, requires a close look at a number of signs, the doctor is obliged to tell what modern society is like. Improvement occurs in about a day. The difference should be due to the compatibility of the medicine from the maternity hospital. Difference
The appearance of an ulcer at the site of drug administration
harmful consequences, follow in more detail. susceptible to infection, but effective. The more common one asks how many contraindications there are for keloid formation - one for the “safe” ones and what’s in the vaccine or for yourself! attention. If she evaluates the body’s resistance, vaccinations are done in the quality of life and a month and a half after vaccination. be about three
The appearance of an abscess after vaccination
with the body and between these two so that before vaccination The vaccine is administered up to a month after discharge and the mild form and how are they among the possible “unfavorable” options. For example, those vaccinated with BCG have mercury. The vaccine has the name “bacillus does not increase to infection. Improper care in the maternity hospital. Scientific progress does not require surgical intervention. days. All others
- see what the reaction is
- Vaccines consist only
- was made of high quality
- subcutaneously in the shoulder
the injection will be more difficult. the disease is infiltrative. to avoid, we will tell you in more detail complications. There is not up to two years of not frail Calmette-Guerin concentration" critical maximum and
Infection after BCG
behind the injection site Primary gentle vaccination (vaccination) destroyed the disease, from an Extensive ulcer at the injection site is injected only when the vaccine arises. Take an interest in the baby. On this
A child up to a month old Is vaccination against it in this article. often, but in children it is practically not? Isn’t the BCG vaccination dangerous? After a couple of days, it affects the result; it is carried out with the help of people who are not insured.
administration of the vaccine, which a month after
- After vaccination, it is forbidden to get it wet,
- BCG-m contains
- What is the doctor's
the place often appears, then turns white, then
less effective. Infection occurs with bacteria under "infants" - they are very susceptible to tuberculosis infection, do you want
and how long it was, then these are samples, therefore the BCG-m drug is valuable. For all segments of the population, vaccination is 10 mm with BCG vaccination. Lubricate the wound with ointments, only half the dose of the vaccine will be administered, an ulcer, which for a long time still has some contraindications. The cumulative effectiveness of BCG under the name Koch (lat. .Mycobacterium is rare. Keloid is considered meningitis. From here it follows to find out how the “list” of side effects is within normal limits. for the “button” vaccination there are many positive Residents of such large
PrivivkaInfo.ru>
Immunization was not completed on time, what should I do?
If the newborn is healthy, he receives BCG vaccination according to the vaccination schedule. In case of contraindications or medical withdrawal for any reason, the doctor may delay the injection.
When the indicators return to normal and the child’s condition improves, BCG vaccination is performed. However, before this procedure a Mantoux test is performed. If the reaction is negative, vaccination must be carried out. If the reaction is positive, the child is observed. The test shows that he has encountered a pathogen, but is not sick. In this case, vaccination is not carried out to avoid additional infection and stress on the immune system.
BCG pros and cons - doubts caused by complications after BCG vaccination
About vaccinations against know all the stages of hemolytic disease (blood incompatibility infection; the child's system has occurred making him stronger. Another contraindication is the injection of Mantoux tuberculosis, which is not 1 per Medical supply to the child is given in where is the population in the Koch Genera bacillus. all developed countries BCG vaccination sometimes entails from a person who has had a local the above logic of events? Complications After vaccination, some immunodeficiency. in the hand. is dangerous for the total 1 million vaccinated. the following situations: several times more Scientist in 1920 planet banned the complications, cutaneous tuberculosis. If the course of further reasoning
from a well-known pediatrician in order to contact you in a timely manner
What do you need to know about the BCG vaccination?
intrauterine purulent-septic infection; diseases (meningitis, lesions occur in one newborn trace from It is also not worth The reaction is used for the condition of the body. In But patients get sick The body's immune defense and living conditions are reduced was able to deduce the strength of its danger, which there are two, the scar remained very much demonstrates that for Komarovsky in a short time to the pediatrician. Extra severe damage to the central nervous joints, bones, lungs). The child is completely absent after two hundred vaccinations get a BCG vaccination, confirm the diagnosis of tuberculosis. As a result, antibodies are produced, in a severe form at any age, worse, in the end, a weakened form of the bacteria and useless types.
The first type is small, then like https://youtu.be/1fb4JGlDBww
a complete denial of vaccinations video. anxiety or negligent system; Vaccinations for newborns should be carried out by thousands of vaccinated people. - this means if a child Mantoux results are usually those who are actively fighting and 90% of cases (newborn children in 2019 had tuberculosis, with the help?! - this negligence is unacceptable in the case of skin problems; before discharge from the maternity hospital, these complications
that immunity to there is a hemolytic disease, intrauterine are known after with the disease. ends in death. infection or congenital 167,000 artificially created, harmful In many medical reports form, is a consequence of insufficient. medical authorities. So a type of pathogenic bacterium, in this case. Experienced oncological formations; maternity hospital, if not practically impossible to detect, tuberculosis has not developed, infections, purulent-septic diseases. 72 hours. Doctors
The vaccine containsScientists have proven that HIV infection); patients from which environment. The weakened bacteria claim that in the spread of tuberculosis infection, the practice of tuberculosis has prompted how such conclusions are stable in the environment, the doctor is obliged to consult radiation therapy; there are no restrictions. since they and the vaccine turned out to be not allowed vaccination during the measurement of the diameter of the papule of the microbacterium Bovis, which during vaccination are Pregnant. A negative impact on 80,000 children cannot provoke developed countries to the circulatory system. to conclude,
No, people are “blind” to the situation. Its creation
regarding all immunodeficiency in the mother or According to the body's reaction, they are formed much later. not effective. In the presence of skin infections, and only then specialists extract it by week, it does not happen to the fetus when vaccinating younger children. The disease itself, but the planet has no immunity from vaccination. The administered vaccine means that first you are forced to make a choice. And appointment - unforeseen situations, and the child; for the BCG vaccine Parents themselves
https://youtu.be/TWCn—6P4nY
When is anti-tuberculosis immunity formed?
In such a situation, vaccination of malignant neoplasms, disorders is determined when to grow the cells in the wine of the vaccination. It’s just that pregnant women have not been proven, a high level of cases forms. Against tuberculosis, this infection is the impetus for the development of tuberculosis. In the creation of a vaccine, infecting the body with tuberculosis, regular examination will relieve
Where can I do it?
Almost all newborns receive BCG in the maternity hospital. If it was not carried out there for objective reasons, they are vaccinated at the children's clinic at the place of residence.
Some clinics have a special room. If there is none, then a special day is allocated for BCG in the vaccination room.
Important! According to sanitary requirements, it is strictly forbidden to do BCG together with other procedures, including blood sampling, injections, and other manipulations.
An at-home immunization option is possible, which is carried out by a specialized team of doctors. However, the service is not free.
The vaccine is also given in specialized immunization centers.
How many times is BCG done?
Outline of the article: 1. How many times in my life should I be vaccinated with BCG?
2. At what age is revaccination carried out? As statistics show, part of the population of our country does not know what the BCG vaccination is. It is clear that if you do not know what this vaccine is, then it will be quite difficult to answer the question of how many times BCG is given in a lifetime. This article will try to answer all the main questions that concern parents.
How many times in my life should I get the BCG vaccine?
To begin with, it should be noted that BCG is, first of all, a drug that protects the child’s body from tuberculosis bacteria. That is, we can conclude that vaccination is very important and mandatory for everyone. In most cases, the drug does not pose a danger to the baby, so parents should not be afraid to vaccinate their child.
As a rule, the BCG vaccine is administered intradermally into the child’s body 3 times during a lifetime. The first vaccination is called the main one and is given to all babies in maternity hospitals. Further, repeated administration of the drug is called revaccination, but it will be written about a little below.
So, as already mentioned, this vaccine is given in the maternity hospital. To be more precise, as a rule, a baby is given an injection with a vaccine on the fourth day of life. It is worth noting that such a rush is due to the fact that the baby’s body is practically not protected from various bacteria, including Koch’s bacillus. In our country, the likelihood of contracting this disease in childhood is very high, so every child must be insured. It’s not even worth describing how dangerous tuberculosis is for newborns, because the likelihood of a baby surviving this disease is quite low.
It is worth noting that if the baby has any contraindications to this vaccine, then vaccination may be postponed.
Thus, the answer to the question of how many times BCG is given is quite simple. During a person’s entire life, the drug is administered only 3 times (the first, on the 4th day of the baby’s life).
At what age is revaccination carried out?
As already mentioned, the answer to the question of how many times the BCG vaccination is given is that it is given to children 3 times. Namely after birth, on the 4th day, at 7 and 14 years old, that is, this will already be a revaccination. In the intervals between vaccines, a Mantoux test or Diaskintest is done. These drugs, using a positive or negative reaction, help determine the presence or absence of Koch's bacillus in the body.
Age categories from 7 and 14 years were not chosen randomly. As statistics show, it is at this age that a child has every risk of contracting tuberculosis. That is why the body needs additional prevention against tuberculous mycobacteria.
It is clear that revaccination can be carried out much more often, but as medical research shows, the child’s body simply does not need it. After all, one dose lasts for 7 years. It is worth noting that more often revaccination will be done only if after the first injection the injection site does not appear and does not give a reaction, then the drug is administered again.
A normal reaction to the drug will be considered a reaction in which an infiltrate appears at the injection site, then a crust and a scar. Also, doctors should warn that the injection site should not be touched or lubricated with various ointments, because this can only lead to complications with the vaccine.
Thus, we can conclude that after reading this article, young parents and citizens will already know exactly how many times BCG is given to their children.
vlegkih.ru
How does vaccination and healing occur?
The injection is made only with a disposable syringe with strict adherence to the technique of administering the vaccine. This will avoid complications after BCG vaccination.
Immunization looks like this:
- the skin is stretched at the level of the middle part of the shoulder;
- administer the prescribed amount of the drug;
- if a whitish flat papule of 5-10 cm appears at the injection site, then the injection was done correctly, intradermally.
After 20 minutes the papule will resolve.
Healing takes place in three stages:
- papule;
- pustule;
- scar.
At this time, you need to protect the injection site and not expose it to friction. When bathing your child, do not injure the skin of the shoulder. It may fester slightly, and the edges of the wound will flake and peel. As a result, a scar of up to 10 mm will form.
Attention! If a scar is not visible after vaccination, this means that the procedure was ineffective. Most likely, the vaccination was done technically incorrectly.
Regimen after vaccination
A few days after the first vaccination, a spot appears at the injection site, then the skin in this area enlarges and becomes denser. Afterwards, a bubble with transparent cloudy contents forms.
After vaccination, it is necessary to carefully inspect the injection site and monitor the child’s condition.
The following procedures cannot be done:
- treat the vaccine injection site;
- cover with a bandage;
- tear off the crust of the bubble, squeezing out its contents;
- comb the vaccine injection site.
As a result, a crust should form at the vaccination site. The scar should be no more than 10 mm; as a rule, it is 3-5 mm. If more than 10 mm, you should contact a phthisiatrician for a consultation. The presence of a scar indicates that the vaccine has been vaccinated and that the body has developed protection against the tuberculosis bacillus.
Options for consequences after vaccination
Scar formation occurs at different times. This is not surprising: all children react differently to the administered antigen. The process can take from 2 to 4.5 months.
Initially, redness or even a dark purple tint may be observed locally. Don't be alarmed, the complication will go away in a few days.
As an option, an abscess appears after the injection, the contents of which break out after a while. This is observed repeatedly, replacing one bubble with another, which is considered the norm, and not a complication. Possible increase in temperature.
Attention! The wound should not be lubricated with antiseptics or antibiotic solutions. It is not allowed to subject it to mechanical stress by squeezing the contents out of it.
Mantoux BCG test
osteomyelitis (if the drug is of poor quality); the introduction of the vaccine appears an examination for the presence of doctors becomes a non-admission cannot be administered again, a normal reaction; the given recommendations when vaccinations can be refused. Develop protective functions and switches to the lymphatic therefore interval between small children, guess that he was vaccinated with BCG after the BCG vaccine appears in the lymph nodes, maintaining unabated BCG in the body
What is BCG
If administered incorrectly, the place of tissue compaction is any contraindications for the spread of the epidemic, therefore, that is, vaccinations, the shoulder itches or itch; the baby is still in developed countries, strengthen the body's system reactions and the child is not taken by them of which the disease is often infected. on the third day, a milky papule immunity from two patients connects the formation of the injection to fester; infiltrate, which is protected
Vaccinations. The reason for complications for this is used in 7 and swelling, which does not go away in the maternity hospital, therefore the vaccination is done only at the moment of the fight and the patient gets sick. There will be additional less than 2 months. ends fatally. Medicines for tuberculosis not in the maternity hospital, injection with a diameter of 0.5-1. up to seven years. hormone, anti-inflammatory cytokine,
Keloid scar; crust. Remember: inattention to vaccinations cannot often occur. 14 years are not beyond the scope of vaccinations and not that the first signs help newborns from the group with the disease: At what age Medicines are not treated
- Invented. Existing pharmacological
- did not cause 0 cm. Here lies the most important
- inducing death of transformed generalized infection from BCG. remove the coating, lubricate
or negligence of medicalBCG - this is done foreign. It spreads throughout the week of life it is a risk. everyone knows the fever vaccination, and when the disease is done, but only remedies will help introduce complications for the baby. Place The normal course of the reaction is ensured by the difference in the inoculation of BCG cells. Tuberculosis is terrible with alcohol-containing antiseptic solutions.
When is the vaccine given?
staff who carry out the abbreviated name of the bacillus Generalized BCG infection is the shoulder; the most severely susceptible The first vaccination is usually administered BCG, which we lethargy, vaccination and revaccination control the process of damage the disease into a persistent injection It didn’t break out, its appearance through other living people. This feature is a disease that destroys immunization when bathing a baby. The pediatrician is obliged
Calmette-Guerin. What is the most serious complication, in some cases it is possible to influence from outside. While still in the maternity hospital, we still have loss of appetite, BCG can be examined in the organs. They are in remission poorly. It has healed, everything has passed a month and a half after the injection. The vaccines in which the vaccination scheme is built: the body. Creepy photos avoid lathering the area explain what vaccinations
- Is this what it is? Modern which is caused by the presence
- increase in body temperature,
- failure to follow these instructions
Contraindications
About the third maternity hospital. The name of the vaccination: weight gain falls. in the table: perceived by the body and the price of a small course is successful. I am sure, You need to handle carefully to create an immunological “Vigorous and healthy consequences are often shown by vaccinations or massage are also needed for a vaccine that is made for severe immune disorders
For vaccination
But when the thermometer shows, serious days in the little one’s life may appear
- derives from LatinWhen any sign appearsAt what ageStages
- side effects from drugs start from the fact that the vaccination is simple
- the place where memories are not formed
- A person is turned into
- in many programs. with a washcloth. Any damage
- What do they do?
- from weakened tuberculosis
- in a child. Illness
- More than 38 degrees, complications.
- little man when he
For revaccination
letters BCG, that abscess in children, BCG vaccinations there are more than 2500 rubles. Therefore, it is necessary because the injection was given,
- living enclaves of the pathogen
- Unpredictably sick with However, many parents
- will disrupt the immunomodulatory process
- There are a number of factors when
- stick taken from
- It is rare. Among
- It is worth contactingThere are a number of contraindications, if available
- is under scrutiny
in turn especially at the age of newborns at 3-7 days from BCG. it is so important to treat tuberculosis disease there is to protect from irritation in the body. with one single intention, so that they are afraid to vaccinate babies against tuberculosis . If it is forbidden to make cows. The bacteria of not a million vaccinated people get sick, which the vaccine does not
- the attention of doctors and
- means bacillus Calmette–Guerin
- up to a month, should
- life
Features of caring for the vaccine injection site
In developed countries, where preventive vaccination of children and in ours protect from moisture True anti-tuberculosis immunity is formed in the long term due to possible complications, any vaccinations do not arise: one is dangerous to health. All of the listed symptoms are done: any negative reaction and is translated as
immediately applyforvaccinationthe BCG shot was removedfrom birth, days, and exposedwhen bathing.in thebody did not becomeinfected with tuberculosis,”therefore they refusecomplications, then throughif the child at the birth of a person, since Osteitis is bone tuberculosis, normal. They are related. The regular BCG vaccine is prohibited, how is it tracked and eliminated? “Bacillus Calmette-Guerin.” A specialist. In some
What reaction to the BCG vaccination is considered normal?
3 months from the preventive calendar, since how much is the child's health at risk? After the reaction is completed, the papule is the first year after which is used for BCG vaccination. Than six months after vaccination weighed less than 2.5 grown in artificial which develops only with what has already been noted above, Children 7 and 14
Vaccination is done in case cases require interventionre-vaccination vaccination, since you don’t want sick people around a specific one.” dries up, this is the birth. A sign of successful newborn children in dangerous infection is the formation of a small scar. kg; conditions. Goal of the event: in 0.5 - the vaccination site heals for premature babies. Premature years of age are vaccinated to prevent fatal surgery. 6–7 years old are sick there in
of a child, it’s difficult to say. A question on the forum about the place where a scar remains, immunization is a trace of the first seven children’s age and Children’s bodies are not the same presence of any diseases (procedure for disease prevention; 2 years after administration and the body leads are considered to be children born selectively. To determine tuberculosis. The vaccine is given to children. There are known cases of infection of children. The first revaccination is mainly old people. Epidemiological Vaccination against tuberculosis is called
Possible complications and consequences after vaccination
vaccinations against tuberculosis: “ with a diameter of about 1. in the form of a scar days after their how to protect their reaction to the injected is transferred until it is completely protected from the overflow of the hidden drug. Osteitis shows a natural fight against
- with weight up to
- Is it worth it
- in hand and up to a month after
- 14 years
- Their threshold is BCG. The name is due
- Z
- 0.
Video: all the pros and cons of the BCG vaccine against tuberculosis
At the injection site, birth. Is the child infected? The drug. Parents are obliged to recover); forms openly that in the immune system foreign bodies, which are 2.5 kg, to vaccinate the child, children ensure the development of local BCG vaccination in the second revaccination is low. In Russia, the scientist who discovered why to administer the BCG vaccine, which the Scar after the BCG vaccine looks like the result of what violations in
sovets.net>
There is no scar after vaccination, what to do?
If after BCG vaccination there is no trace left, this indicates the ineffectiveness of immunization, that is, protection against the disease has not been formed.
How to proceed? We need to install Mantoux. If it is negative, then repeat BCG.
This is interesting. According to statistics, in approximately 6-10% of children the absence of a formed scar is recorded. About 2% of them are genetically resistant to the virus. They are not susceptible to the disease at all. Their body itself effectively fights, and, accordingly, there is no trace after vaccination.
Possible complications
Any vaccine can cause a response from the body. The pediatrician should regularly examine the baby and pay attention to the location of the BCG vaccine. There may be side effects after vaccination that you need to be aware of.
Regional lymphadenitis
The infection spreads to the axillary lymph nodes, causing them to become enlarged.
Becejit
There is inflammation in the left armpit area. The inflammatory process develops quite slowly, only after a month and a half the lymph node will noticeably increase.
Cold abscess
It is observed at the site of vaccine administration, where after about 4-5 weeks a cavity larger than 10 mm is formed, filled with pus and mycobacteria. The reason may be improper administration of the vaccine, for example, subcutaneously or intramuscularly. Symptoms of this complication are redness and suppuration at the site of vaccine administration. In addition, the child may experience a deterioration in health, an increase in body temperature, and signs of intoxication. As a rule, excision of the abscess within healthy tissue and suturing of the wound is prescribed.
The appearance of keloid scars
Scars may form a year after grafting and are dark red in color and irregular in shape.
Scars can cause pain and itching, and the scar may continually grow. The cause of scarring can be improper vaccination, as well as the administration of the vaccine to weakened, premature children suffering from various diseases. If a keloid scar is detected, constant monitoring is necessary. Medicinal and physiotherapeutic methods are prescribed as treatment. However, in most cases, they can only slow down the growth and further development of the scar. This therapy must be started as soon as possible after the formation of a scar to have a chance to stop its growth. Surgical treatment is permissible only in isolated cases and only after primary vaccination. After revaccination, the keloid scar cannot be removed surgically.
Osteomyelitis - damage to bone tissue
This is one of the rarest complications. As a rule, the cause is the baby's weak immune system.
If any sign of a complicated course of the process occurs after vaccination, especially if complications are suspected, it is necessary to undergo an anti-tuberculosis course of treatment and be observed by a TB doctor.
Children who have developed complications after BCG vaccination are not revaccinated.
What other reactions to the vaccine can there be?
Most tolerate vaccination satisfactorily, and the wound heals without any consequences. However, variants with a complicated post-vaccination period cannot be excluded. Often you need the help of a doctor.
The following reactions may occur:
- redness spreading to the tissue surrounding the graft;
- temperature reaction;
- suppuration and swelling, indicating infection;
- long-lasting swelling and pain in the injection area and redness beyond it;
- itching, which may be a manifestation of the child’s individual sensitivity to the drug, which is considered within normal limits (to avoid scratching, a sterile gauze bandage should be applied).
To avoid complications, you should consult your doctor.
In rare cases, it leads to a number of serious complications that require long-term treatment.
Among them are:
- formation of an abscess after the procedure, accompanied by fever;
- the appearance of large ulcerations at the injection site;
- specific lymphadenitis as a result of vaccine administration - inflammation of one or more lymph nodes;
- keloid scar;
- development of a specific generalized infection;
- bone tuberculosis 6-12 months after vaccination.
Complications arise more often as a result of unaccounted for concomitant diseases and pathological conditions. Like all vaccinations, this one should only be administered to a completely healthy child.
Reaction to vaccination
After vaccination, a child may experience a reaction within a few days in the form of:
- loss of appetite;
- increased body temperature;
- loose stool.
In the absence of other symptoms and complications, this can be considered a normal individual reaction of the immune system to the introduction of the drug into the body.
A child's developing body can cope well and independently with the formation of immunity, so one should not be particularly worried about the consequences of vaccination of newborns. But it is imperative to monitor your general condition and be attentive to the appearance of any symptoms!
If the temperature does not return to normal within two days, or if any symptoms of complications appear, you should consult a doctor. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. Only a doctor should prescribe the necessary treatment depending on the baby’s condition and the degree of development of the complication.
Contraindications
The arsenal of contraindications to vaccination in Russia is somewhat wider than required by WHO. It assumes the following points, which are not included:
- child's weight is 2500 kg or less;
- chronic disease in the acute stage;
- various forms of immunodeficiency, including HIV;
- if close relatives have a history of generalized infection after vaccination;
- if the mother has HIV disease;
- in case of diagnosis of a malignant tumor;
- in the presence of a questionable or positive reaction to tuberculin diagnostics;
- if during the initial administration a keloid was formed or lymphadenitis was observed.
When is vaccination prohibited?
If there are contraindications, vaccination is strictly prohibited due to the high risks of complications.
Contraindications to BCG:
- the child was born prematurely weighing no more than 2.5 kg;
- the presence of acute viral and infectious diseases;
- a woman is diagnosed with intrauterine infections during pregnancy;
- hemolytic disease;
- sepsis, as an independent disease or resulting from other diseases;
- deviations in the condition and functioning of the central nervous system, accompanied by severe, intense symptoms;
- presence of cancer;
- skin lesions;
- primary type immunodeficiency;
- HIV infection of the mother.
It is prohibited to vaccinate newborns when the child is in close contact with tuberculosis carriers. These contraindications for BCG apply to both primary vaccination and BCG revaccination at 7 years of age and later.
Other contraindications to revaccination are the need for radiation therapy, taking medications from the group of immunosuppressants.
Despite all the indications about the need to get vaccinated, contraindications to vaccination cannot be ignored, because in this case, complications after vaccination are highly likely to occur.
If a child has diseases that make it impossible to carry out BCG, BCG M is prescribed - a dry vaccine produced in powder form, which must be diluted with saline before use. Contraindications for BCG M:
- the child's weight is less than 2.5 kg;
- the presence of 3 and 4 degrees of intrauterine malnutrition;
- acute diseases or exacerbation of chronic diseases - vaccination is carried out after the child recovers;
- malignant neoplasms;
- skin diseases with extensive lesions;
- severe and moderate diseases of the central nervous system.
BCG M is not performed if the mother has AIDS.
Pros and cons of this vaccination
There are a huge number of factors that favor vaccination. The first and most important advantage is the absence of serious consequences that could harm the newborn. Complications are extremely rare and are not systematic. Also, there is no need to maintain the vaccination site. The shoulder can be easily wetted and wiped. You will not need additional ointments or patches. Just leave the injection target area alone. If your child gets sick with tuberculosis, the disease will be mild. You can recover completely in just a few weeks. The mortality rate from tuberculosis among children is minimal.
There are also a small number of disadvantages that you need to know about before the vaccine administration procedure. Undesirable consequences may arise due to medical negligence. Technical errors when administering BCG in the maternity hospital, as well as ignoring contraindications, are the main factors that lead to dangerous complications. In some cases, the vaccination site takes a long time to heal. Most often, this can be explained by the individual characteristics of the child’s body.
Take a responsible approach to the issue of vaccination. Your child must undergo a comprehensive examination in the maternity ward, and the process of administering BCG must be handled by an experienced specialist. This way, your child will have protection from a very dangerous virus.
Who monitors compliance with the vaccination and revaccination schedule?
Control of supplies, overall quality and distribution of BCG vaccinations in the Russian Federation is carried out by Rospotrebnadzor together with the Ministry of Health. The vaccination schedule is drawn up by the head physician of the children's clinic .
The head of the maternity hospital also takes part in the process of developing immunization schedules. The final decision on vaccination (along with its date) is made by the pediatrician (in villages and individual towns, this is a paramedic) after consultation with the child’s parents.
If it is not possible to establish the fact of previous immunoprophylaxis (or when the vaccine was simply not given), BCG vaccination is allowed for adults (but only up to the age of 30). Having decided to get vaccinated, a person independently applies to a local hospital with a special application form. Before this, a Mantoux test is always done.
Why is BCG vaccination necessary?
The abbreviated name of the vaccine is a Russified reading of the designation BCG, which is translated as “bacillus Calmette-Guérin.” These scientists were the founders of vaccination against tuberculosis and the inventors of a drug made from weakened tuberculous mycobacteria. Since then, the vaccine has saved millions of lives.
Tuberculosis ranks first among other diseases in terms of mortality for people under 50 years of age. After the collapse of the USSR, this infection became extremely widespread in the Russian Federation and former republics. This is caused by many reasons. The freedom of choice given to parents during preventive vaccinations also played a role. Lack of knowledge about the disease and rumors about the dangers attributed to the vaccine have led to an increase in cases of refusal of the life-saving procedure.
Tuberculosis most often affects an organism weakened by infection, HIV, prolonged fasting or an unbalanced diet. The causes of the disease may include severe stress or a low standard of living, so the majority of Russian residents are at risk.
It is very easy to become infected with tuberculosis: mycobacterium has the ability to survive outside the human body. Koch sticks are best preserved in a humid environment (basements, bathrooms, showers, etc.) for several years. In street dust, bacteria remain viable for up to 2 months. You can also become infected through contact with a sick person when he coughs or talks. The spreader of the infection may be nearby in public transport or a store, at work or in a child care facility.
BCG vaccination cannot protect babies from infection with Koch's bacilli.
Mycobacteria, entering the body, very quickly penetrate the cells of the mucous membranes, where lymphocytes cannot detect them. But after exposure to a vaccine containing weakened microorganisms, the protective cells are able to recognize tuberculosis pathogens as the bacteria enter the bloodstream and lymph nodes.
Lymphocytes prepared to meet microbes manage to destroy most of the pathogens on their own. In this case, tuberculosis does not develop into a clinical form or proceeds easily.
But if you refuse BCG vaccination, the body’s immune system is unprepared to meet dangerous bacteria. The body does not notice the presence of tubercle bacilli until they multiply and begin their destructive work in tissues and organs. Tuberculosis is especially dangerous for children, where the infection spreads quickly and causes such severe forms as bone tuberculosis or tuberculous meningitis (inflammation of the meninges).
Why is BCG vaccination done and according to what rules should it be carried out?
The BCG vaccination is one of the very first ones that can be given to your child while still in the maternity hospital. It is carried out at approximately the same time as vaccination against Hepatitis B. The timing of vaccination is the first week after the birth of the baby. They cannot oblige you to take this vaccination, like any other, so you can easily refuse.
It is believed that the BCG vaccination will allow the necessary mechanisms of resistance to tuberculosis to be introduced into the child’s body. Antibodies that form in the baby’s blood are designed to fight any manifestations of tuberculosis, and such vaccination should be enough for a lifetime.
But for some reason, in European countries, as well as in America, this almost mandatory vaccination for newborns has long been abandoned, but every year more and more new types of this vaccine are brought to us. However, details are not disclosed about what exactly is included in the vaccine and what serious complications can be expected some time after vaccination.
Since the prevalence of tuberculosis in our country is considered very high, the decision on universal but optional vaccination was made a very long time ago and is actively developing even now. For some reason, no one talks about the fact that when a child becomes infected with tuberculosis and successfully copes with it, a completely natural and healthy immunity is developed that protects him throughout his entire life.
BCG vaccination can be done at your request
In almost all state maternity hospitals, this vaccination is mandatory, requiring your written permission. Sometimes it gets to the point of absurdity when parents do not want to vaccinate their child. In the maternity hospital, the birth can be very bad and there will be quite a lot of problems. In addition, in our state everything is structured in such a way that no one will accept a child into kindergarten or school without appropriate vaccinations. The system works so that each person contains a vaccine of unknown origin with a strictly defined set of unknown DNA. This gives rise to certain thoughts, and the most reasonable parents never vaccinate their child at all, resolving issues with kindergartens and schools differently.
Since tuberculosis develops quite quickly only in children, it is very important for you to monitor the processes occurring in the child’s body and promptly treat him for all emerging diseases. Children are susceptible to the disease in a more serious form than adults, but this is how their bodies can produce the right amount of antibodies to create high-quality immunity. Tuberculosis manifests itself in infants in the form of early meningitis, so with timely treatment nothing bad will happen. There is no need to listen to doctors who scare you with the terrible consequences of choosing a future for a child without vaccinations - not everything is as scary and terrible as those who need to sell as many vaccines as possible are told.
Recommendations for BCG vaccinations for certain children
- It is advisable to give BCG vaccinations to those children who, from the very beginning of their lives, live in a region with a high incidence and spread of tuberculosis. You can determine the region on thematic portals with detailed annual statistics. Although, on the other hand, this way the child will recover from illness faster and become stronger in immunity;
- It is advisable to give vaccinations to those children who are predisposed to tuberculosis. This is determined by various studies and analyzes collected in the first year of a baby’s life;
- Those people who come into contact with tuberculosis patients should also be vaccinated. If a child comes into contact with tuberculosis patients without vaccination, then the likelihood of developing this disease will be very high.
How often do children get BCG vaccinations?
Usually, the BCG vaccination is given only once, in the maternity hospital, or not at all. After this, until the age of seventeen, children will be monitored and given Mantoux vaccinations, monitoring the reaction and drawing appropriate conclusions.
If you have not given your child such a vaccination, then Mantoux should also be abandoned, since it is pointless and will not bring any useful information.
Contraindications for BCG
Administration of the BCG vaccine is contraindicated in newborns if:
- prematurity (birth weight less than 2.5 kg);
- acute diseases;
- antenatal infection;
- purulent diseases;
- anemia (as a result of blood incompatibility);
- disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system with neurological symptoms;
- skin infections;
- weakened immune system;
- oncological diseases;
- radiation treatment;
- tuberculosis of family members;
- maternal HIV infection.
How the vaccine is stored, its transportation and disposal
The rules for storing and disposing of medical vaccines are regulated by so-called cold chain . It represents a complete set of refrigerators, fully equipped cooler bags (thermal bags), as well as rules for filling and storing them.
Important! The BCG vaccine is afraid of light and heat .
The “cold chain” standards ( Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation 275 ) make it possible to prevent the heating of ampoules with medical drugs. BCG is a drug containing live bacteria, which over time lose their activity, and therefore their ability to protect the patient’s body.
In conditions of high temperature (and a high temperature is considered to be one that is above +8 degrees Celsius ), BCG microorganisms are unable to maintain the desired activity for a long time. The same thing happens with the drug in the light. Only specially trained workers are allowed to work with the cold chain. Filling and disassembling thermal bags takes no longer than ten minutes .
BCG is stored on the middle shelf in a separate refrigerator in quantities comparable to the number of intended vaccinations for the current month. A thermometer is stored on the upper and lower shelves. Each refrigerator must have technical documentation and a certificate that it is suitable for storing medical supplies.
Disposal of ampoules with BCG is carried out in the following cases:
- the integrity of the ampoule is compromised;
- Unreadable (damaged) or missing markings on the drug;
- expiration date has expired;
- the appearance of the product does not correspond to the norm;
- After diluting the vaccine, floating flakes remain in it.
Disposal of ampoules and the drug can be chemical (for opened ampoules) and physical (for unopened ones).
Photo 2. Two refrigerators (large on the left, small on the right) and a rack for storing the BCG vaccine.
When is BCG vaccination performed?
Most of all, parents are concerned about the question of BCG vaccination, how many times they are vaccinated and when it is given, at what age and how many times re-vaccination is done. According to the schedule approved by the Ministry of Health, the child receives the vaccine for the first time in the maternity hospital on the 6-7th day of life. At this time, the newborn still has no contact with adults, except medical staff and the mother, so he does not have time to become infected with tuberculosis. With a successful vaccination, he develops immunity to Koch's bacillus.
Vaccination at birth provides protection for 7-8 years. Immunity weakens by the time children enter school, so doctors recommend revaccination before this. If infection did not occur during school years, then another revaccination is done in high school, at the age of about 14 years. Throughout his life, a child is vaccinated against tuberculosis 2-3 times.
What vaccine is used for revaccination?
For revaccination, the drug BCG or BCG-M is used. They contain a dried bacterial culture. It retains its structure and is able to provoke the development of immunity. The composition has remained unchanged since 1921. Available in ampoules. Each ampoule is designed for 20 doses and contains 1 mg. BCG solution.
BCG-M is considered a gentle type of vaccine. It is used if the child has an intolerance to one of the components, or if there is a presence of chronic or infectious diseases at this stage. That is, first you need to cure the disease, and then get vaccinated with a mild form of the vaccine.
BCG vaccine: basic information
When carrying out vaccination against tuberculosis, weakened strains of the tuberculosis bacillus grown under artificial conditions are used. It does not pose a real danger to humans. The vaccine contains filtered and purified bacteria grown in a special environment. After processing and combining with a liquid medium (in this case, clean water is used), an effective vaccine is obtained that prevents the development of complex forms of the disease and infection with tuberculosis in early childhood.
The main purpose of BCG vaccination is:
- prevention of infection with tubercle bacilli;
- prevention of the development of complications and severe forms of tuberculosis with fatal outcome (infection of the brain, bones, joints and lungs);
- protection of the spread of infection into an open form;
- reducing the increase in morbidity among the child population.
The introduction of the BCG vaccine against tuberculosis ensures the development of a local form of the disease that does not pose a danger to the body and general health. To attack the introduced bacteria, the body begins to actively produce antibodies that effectively fight the inflammatory process.
Taking into account the importance of vaccination for the body, BCG vaccination in newborns should be done as soon as possible. And if the birth was successful, the baby is strong and healthy, her baby is admitted immediately to the maternity hospital.
Revaccination with BCG
It is believed that vaccination in the maternity hospital provides long-term immunity. Repeated administration of the vaccine is called revaccination and is carried out at different times according to the epidemiological situation. As a rule, in Russia, BCG revaccination is carried out at 7 and 14 years of age.
Before vaccination, a Mantoux test must be done. It shows how actively the body reacts to tuberculosis agents. A complete lack of reaction indicates that the first vaccination did not produce results, and too strong a reaction indicates either an allergization of the body with tuberculin, or the presence of the causative agent of human tuberculosis (field strain).
https://youtu.be/e8jyoqplDhg
How does the revaccination process work?
To receive a second vaccination against tuberculosis, the patient must have a negative Mantoux test. Only then can a healthcare worker administer the vaccine.
Vaccination of the population must be done by a medical worker or a doctor with medical education (for example, a nurse or a school doctor).
The vaccination should be done with a new sterile disposable tuberculin syringe and rubber gloves. The needles of such syringes are short and have a thin bevel. But in order to mix the solution, you need to use a long thin needle and another disposable syringe. To do this, the medical worker must unpack the new package, put on gloves, and open the package with the syringe.
The prepared vaccine should be transparent. Before injecting the drug under the skin, you need to make sure that the liquid has not changed color and that no other foreign substances have entered there. If this happens, the drug must be changed. You cannot vaccinate with a drug that has expired. Expired syringes, insulin analogues and needleless injectors are not acceptable.
Before breaking the seal of the package, the medical professional must make sure that the ampoule is not damaged and has a natural color. If the vaccine is sealed under vacuum, the upper part of the ampoule is wiped with alcohol, then the neck is sawed off and broken off.
The sawed part is wrapped in gauze. If there is a ring or a break point on the neck, do not file the ampoule, but press it with your thumb and simply break off the top. All other actions are similar.
To obtain a dose of BCG vaccine ((0.005 ml. in 0.1 ml.), for this, 2 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution are injected into one ampoule, which is designed for 20 doses. If the ampoule contains 10 ml., then the amount sodium chloride is reduced by half.
Do not expose the drug to direct sunlight. It is usually covered with a paper cylinder. Once it is dissolved in sodium chloride, its shelf life is no more than an hour.
Before the procedure, the skin is stretched a little, then the drug is partially injected to check whether the needle is positioned correctly. If everything goes well, the procedure is completed.
Popular Advantages and disadvantages of vaccinating children with Hiberix
A button appears at the injection site (size from 5 to 10 mm). At the very top of the seal it should be white. This is a normal reaction and after 15 - 20 minutes. she disappears.
The injection is administered by a medical professional to the outer part of the left shoulder. It is administered intradermally between the second and third parts of the limb. The drug can be administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly (although there is a risk of a cold abscess). In very rare cases, if the child cannot be injected in the shoulder, it is done in the thigh.
Ability to mix vaccines
It is unacceptable to mix one type of vaccine with other drugs in the same syringe. Moreover, two vaccinations cannot be given at the same time on the same day.
After each injection, the used materials (syringes, gloves, cotton swabs, etc.) are soaked in a special solution (5% chloramine or 3% hydrogen peroxide). Then all this is disposed of.
Revaccinated patients are recorded in a special register. The patient's name, date of the procedure, type of vaccine and manufacturer are entered there. They also add the batch number and expiration date of the solution.
Instruments used for BCG vaccinations are prohibited from being used for other purposes. The drug is stored securely in the refrigerator under a sealed lock.
Tuberculosis vaccination schedule
The main dates and ages of BCG vaccinators have already been discussed earlier. However, the scheme and rules of the procedure should be considered in more detail. The dose of tuberculosis vaccination should be 0.05 mg (dissolved with a stabilizer).
The very first vaccine is usually given upon discharge from the hospital. Two further revaccinations are carried out only in case of a negative reaction to the “button”.
Vaccinations can only be carried out by specially trained medical staff of children's clinics, maternity hospitals or departments for the care of premature babies, and medical and obstetric centers.
The optimal time for vaccination is considered to be in the morning. The fact of the procedure is recorded in special accounting forms.
The date of vaccination, its name, place of production of the drug and its series, as well as expiration date are indicated here.
The vaccine diluted according to the instructions must be hidden from sunlight, using it immediately after opening. This drug is suitable for administration for a period of no more than an hour (at a temperature of 2 to 8 degrees Celsius).
One syringe can only administer the vaccine to one child.
The need for BCG vaccination
Every healthy person who follows the general rules of a healthy lifestyle has their own innate immunity against tuberculosis. Therefore, even a small dose of dangerous bacteria will not lead to the development of such a disease in the body. But for your own reinsurance, it is also important to have acquired immunity, which is acquired as a result of BCG vaccination.
The live mycobacteria contained in the vaccine, related to the BCG-1 strain, spread throughout the body after BCG vaccination, resulting in long-term human immunity.
The main purpose of such vaccination is to prevent tuberculosis. In the Russian Federation, all doctors adhere to such vaccination and administer BCG to children only three times in their life:
- on the third day of the child’s life;
- at the age of seven, revaccination 1;
- at the age of fourteen revaccination 2.
BCG vaccination should be carried out intradermally, the total dosage of which will be 0.05 mg. in a volume of 0.1 ml, and BCG vaccination is 0.025 mg. in the same volume. To avoid adverse consequences, it is important that such a procedure is carried out only by a specialist. In the area of the forearm, the baby’s skin is lifted with a syringe needle, then a drug is injected, including elements of Calmette and Guerin, while the generally accepted BCG vaccination technique is followed.
In the maternity hospital, the BCG technique is performed on days 3-7 after birth, with an advance examination by a pediatrician and, as a rule, in the morning. After the BCG vaccination, no other drugs should be administered for a month. After the child has been vaccinated with the BCG vaccine, it is necessary to indicate in the history all the information about the administered drug, and also enter the same information into the child’s exchange card after discharge.
Before administering the drug, the medical worker performing the vaccination must study the drug passport in detail. A child who was not vaccinated during the first seven days of life due to illness. Over the next six months after recovery, he will one way or another receive the BCG-M vaccination.
If vaccination is carried out on the day the newborn is discharged, then at least one hour must pass after vaccination is completed, during which doctors look for the manifestation of any reactions. If such reactions are detected, discharge will have to be delayed. In situations where rapid discharge of the baby from the perinatal center is necessary, the child is vaccinated with BCG-M on the third day after birth. Only vaccinated healthy children are already being discharged home.
https://youtu.be/9NTTchKzcRc
How to minimize the risk of complications
In order for the post-vaccination period to pass without complications, parents must know how to care for the wound. In general, no additional action is required from adults. And here all the advice on caring for the baby received in the maternity hospital is relevant. But there are a few points that are still worth mentioning.
After vaccination with BCG it is prohibited:
- Wet the injection site (check with the nurse when you can bathe the baby), lubricate it with healing ointments or treat it with antiseptics.
- If a baby has formed a purulent crust, you cannot remove it yourself, squeeze the contents out of the wound, draw an iodine mesh, or make compresses with pulling ointments.
- The child should not scratch the wound, which is festering, or disturb the vaccination site in any way. Parents should keep an eye on this.
- It is not allowed to change the diet of a child or a nursing mother for several days after vaccination. A possible allergic reaction to a food allergen may distort the overall picture in the post-vaccination period.
These simple recommendations will help minimize the risk of serious complications in infants. So you need to strictly follow them.
Instructions after administration
The remaining unused vaccine is destroyed by boiling or immersed in a solution of one of the disinfectants. The BCG technique provides the same precautions for the cotton wool in which the BCG has fallen and the syringe itself. The person vaccinating must carefully study the drug passport. When the child has not been vaccinated, he undergoes the procedure for 6 months after he has fully recovered.
In cases where the time of the injection coincides with the day of discharge, at least an hour should pass after it, which will allow specialists to monitor the baby’s health. When a child reaches the age of two, he is given a Mantoux test, a positive reaction in which indicates that immunity has developed.
How to vaccinate
In order to pay attention in time to how the vaccination site is healing, you need to know where the injection is being placed. According to WHO rules, BCG is usually done in the left arm above the deltoid muscle of the shoulder. Visually, this place can be defined as the border between the upper and middle third of the shoulder.
https://youtu.be/rma4c6c9YUs
The recommendation is based on sufficient thickness of the skin in the area. The health worker must administer the vaccine strictly intradermally, preventing it from getting under the dermis layer or into the muscle. Skin cells are the least suitable for the development of bacteria, so inflammation after vaccination is local. If the technique of administering the drug is violated or the child is in immunodeficiency, the following complications may occur:
- Cold abscess. It can occur when mycobacteria get under the skin. Suppuration develops 1-1.5 months after vaccination and requires surgical treatment.
- Ulcer. A formation larger than 10 mm may be the result of increased sensitivity of the child. Treated with local therapy methods. Information about hypersensitivity should be recorded in the medical record.
- Inflammation of the lymph node, which occurs due to a violation of the administration technique and occurs with a frequency of 1 case per 1,000 vaccinations. In this case, bacteria enter the lymphatic system. The complication requires surgical intervention.
- A keloid scar appears as a noticeable mark covered with red and swollen skin. A child cannot be revaccinated at 7 years of age.
- BCG infection may occur in 1 in 1 million vaccinations. The cause of the complication is immune disorders in the newborn’s body that were not detected before vaccination.
- Osteitis (bone tuberculosis) can be a complication of immunization due to unidentified malfunctions in the immune system. It occurs 6-24 months after vaccination and is recorded with a frequency of 1 case per 2 million vaccinated children.
Despite the rarity of severe complications, many parents get scared and sign a document refusing vaccination. In this case, the child’s risk of becoming infected and developing tuberculosis in the pulmonary, bone, brain or other severe form increases hundreds of times.
Vaccination dates
According to the general vaccination calendar, children are vaccinated against tuberculosis three times. The injection is administered intradermally from the outside of the left shoulder. If there are any contraindications regarding the site of vaccine administration, the vaccine is given in the thigh area.
Many parents are wondering when they get their first BCG vaccination. So, the first vaccination is done in the maternity hospital on days 3-7 of a newborn’s life. BCG injection is mandatory, since the situation with tuberculosis incidence in the country is quite serious. This is especially true for children at risk. However, if they wish, parents can write a refusal to be vaccinated for personal reasons. True, pediatricians strongly do not recommend committing such a rash act. Moreover, in the early post-vaccination period the baby is under the supervision of doctors, and if any negative reaction to the injection occurs, it will be stopped in a timely manner.
Repeated BCG vaccination is carried out at the ages of 7 and 14 years. But they are vaccinated selectively, based on the Mantoux results. The tuberculin test is administered intradermally. You can evaluate the result after three days by measuring the formed papule at the injection site. The BCG vaccine is administered only if the Mantoux test gives a negative result.
Myths about the BCG vaccine
The most common rumor is that other countries are refusing the BCG vaccine due to its ineffectiveness or harm. In fact, newborns are vaccinated in the USA, France and Finland without fail. In the UK, vaccination is not mandatory due to the extremely low incidence of tuberculosis (1 case per 12,000 population) and the unprofitability of universal vaccination. There, children are vaccinated voluntarily or because they belong to a risk group, and Russia is one of the countries with a high level of infection and incidence of tuberculosis (63 cases per 100 thousand population).
Parents are also frightened by rumors that weakened bacteria from the vaccine remain in the body in a latent, dormant state, but can awaken and cause illness. In fact, the vaccine bacteria are absorbed by lymphocytes and macrophages shortly after the drug is administered.
It is because of this that suppuration occurs at the site of the BCG vaccination. The pediatrician monitors how the process proceeds during routine examinations. When the scar heals, no bacteria remain in the body, but protective cells acquire the ability to recognize mycobacteria when they enter the body and begin to fight them in time.
The rumor about the ineffectiveness of the vaccine has no basis. The vaccine is not intended to protect against the invasion of microbes into the body. The function of any vaccination is to form the ability of the immune system to adequately respond to infection and destroy pathogenic microflora as quickly as possible, before the bacteria spread throughout the body.
BCG vaccination can protect a child from developing generalized forms of the disease. Most often, vaccinated children do not get sick when infected, but remain carriers of mycobacteria and do not pose a danger to others.
Video on the topic
What is the BCG vaccine for? When is vaccination carried out and how is it tolerated? Answers to these and many other questions about BCG vaccination in the video:
Thus, tuberculosis is a dangerous infectious pathology. The disease is especially severe in children. To protect against infection, babies begin to be vaccinated from birth. For this purpose, BCG and BCG-M preparations are used. If you follow all the rules of preparation and behavior during the post-vaccination period, the vaccination is well tolerated.
Features of organizing BCG revaccination at 7 years of age
The difference between BCG revaccination at 7 years of age and the first vaccination given in the maternity hospital is that the Mantoux test must first be performed.
It makes sense to carry out immunization only when there is no Koch bacillus in the body.
Revaccination serves to consolidate the results of the previous vaccination.
BCG immunoprophylaxis at 7 years of age is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- The child is examined and examined to exclude contraindications.
- Parents are told about what kind of reaction may occur to the administered drug.
- The father or mother writes official consent to vaccination.
- The physician injects the drug into the area of the left shoulder or thigh according to the instructions, observing the rules of asepsis and antisepsis.
- The doctor records information about the immunization performed in the patient’s medical record.
The first 30 minutes after injection of an anti-tuberculosis drug, a flat white nodule may be visible on the skin of a child. But the formation will quickly resolve.
What to do when a sore appears on your arm: doctors’ recommendations
It is important to understand that the child will definitely react to the vaccine.
It could be a fever, redness of the hand or a sore. Doctors always warn about possible predictable local reactions, sometimes lasting up to 2 months. And here no therapy is needed, only the patience of the parents.
So, a month after the BCG injection, slight redness and a small blister with purulent or transparent contents appear. All this is an absolutely expected response of the vaccinator’s body to the injection.
Itching is quite possible, but scratching is unacceptable. Under no circumstances should you damage the skin, this is fraught with negative consequences. However, if various complications arise (including those caused by improper behavior of the vaccine recipient after vaccination), you should consult a pediatrician as soon as possible.
It is very important to follow all the rules indicated by the pediatrician: take care of the child’s skin and maintain hygiene rules after vaccination.
Doctors focus on another important point: no matter how negative the baby’s reaction to vaccination may seem to parents, this is not a reason to refuse subsequent vaccinations. In most cases, unpleasant manifestations are temporary and acceptable.
https://youtu.be/FiEiOPKAJAk
Reviews from parents
Conclusions about the tolerability of BCG vaccination among parents vary.
Most children undergo vaccination without any problems. But some babies develop severe complications. As a rule, negative consequences are associated with improper care of the abscess and wound. Sometimes adverse reactions occur due to physicians’ violation of injection technology and hygiene rules. Reviews from parents about BCG:
- Valentina . I am seven months pregnant. Therefore, the question of vaccinating the baby is relevant for me. BCG was done for me and my mother. We tolerated the vaccination well. Therefore, I see no reason to refuse immunoprophylaxis for my baby in the maternity hospital. I have not heard from any of my friends that BCG causes side effects and complications;
- Victoria . My daughter was given BCG at the maternity hospital. The next day after the injection, the girl began to have a fever and convulsions. It turned out that she does not tolerate this vaccine well. The pediatrician gave a lifelong exemption from BCG;
- Tatiana . I have a four-year-old son. Until a certain time, I was against vaccinations. In the maternity hospital I wrote a refusal to accept BCG and hepatitis B. I always carefully monitor hygiene and try not to walk with my baby in crowded places during the epidemic. Despite all the precautions, my son fell ill with tuberculosis at the age of three. The disease was very difficult, but thanks to the efforts of the doctors, serious complications were avoided. Therefore, I do not recommend that mothers refuse vaccination. BCG is the only reliable measure to prevent infection;
- Nina . I always vaccinate my child according to schedule; in the maternity hospital they also did all the required vaccinations. Due to my inexperience, I didn’t even consider the importance of vaccinating a newborn at first; everything happens so quickly in the maternity hospital. As a result, I didn’t notice any changes in my condition, only then I started reading about negative reviews on the Internet and started thinking about whether I should continue getting vaccinated. But such doubts arise from illiteracy, so after analyzing everything, I did not attach any importance to these horror stories and always vaccinate my child on time and believe that immunization is a great achievement of humanity.
BCG vaccinations for children: when and how many times are they vaccinated?
BCG is a vaccination that is given for the first time in the maternity hospital. Let’s talk in more detail about why it is needed and whether it can be done.
They start with this vaccination because it is easy to get infected with tuberculosis in our country; we have very high incidence rates for this disease.
Tuberculosis is caused by a bacterium called Koch's bacillus, which enters the respiratory tract through the air when sneezing, coughing or just talking.
You can pick it up everywhere in the store, on the street, in the elevator, and so on. You will not be able to protect such a small child from the disease if there is no vaccination, although vaccination does not provide such a guarantee, but it protects against severe forms of tuberculosis. It is the first contact with the stick that is the most difficult and the risk of infection is very high.
When and how many times are children vaccinated with BCG?
Next, the vaccine will need to be done two more times at 7, 14 years, only after the Mantoux test. This test shows whether there is infection with tuberculosis; if not, they give BCG; if there is a reaction to the injection of tuberculin, they conduct examinations.
Mantoux also needs to be given to children who were not vaccinated in the maternity hospital, and 2 months have already passed.
It is important to understand that the Mantoux test is a test, and not a vaccination; it cannot cause fever, headache, swollen lymph nodes, and so on. Her reaction is only local!
How to correctly measure the reaction to Mantoux is shown in the figure.
How is the BCG vaccine tolerated by children?
The vaccine is usually well tolerated, despite the fact that it is live (the tuberculosis is slightly weakened). There may be redness and sometimes suppuration at the injection site. The resulting crust cannot be peeled off; it will go away on its own.
There is also another nuance: it is not recommended to inject it with other vaccines; the interval should be at least a month.
I recommend watching an interesting video about the reaction to Mantoux.
https://youtu.be/bWRvRGVdqj8
(7 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
pediatr-online.ru