Metabolic syndrome is a complex of a number of metabolic disorders that are risk factors for the development of multiple cardiovascular and hormonal diseases. Otherwise known as insulin resistance syndrome. Diagnosed by: taking a detailed history; blood tests (hormonal, biochemical, sugar).
The changes that occur in the body often go unnoticed by the person himself, and yet, if you pay attention to them in time and take appropriate measures, you can prevent most serious diseases. It is almost impossible to do this through an independent anamnesis. To do this, it is important to monitor your health and undergo a comprehensive examination at least once a year.
You understand that modern man is constantly faced with a number of problems that in one way or another undermine his body:
- poor ecology (the ecology of the entire planet is under threat)
- increased risk of stressful situations (unstable situation in the country, worries at work, at home, etc.)
- general bustle (especially in large cities)
- poor nutrition (we replace a full lunch with quick snacks: coffee, tea, cookies or a hamburger, a hot dog, a slice of pizza with cola from a local fast food chain, and some are not used to eating at work)
All this can disrupt the natural energy metabolism in the body. They occur against a background of subtle symptoms and contribute to the development of metabolic syndrome.
Metabolic syndrome in women: what is it?
This pathology is not a separate disease. Metabolic syndrome includes a combination of the following four serious diseases:
- diabetes mellitus type 2;
- hypertension;
- coronary heart disease;
- obesity.
All of these diseases are serious on their own, but taken together they become even more dangerous. That's why doctors call metabolic syndrome the "deadly quartet." Without adequate treatment, the pathology often leads to serious complications and even death. Therefore, it is very important to diagnose metabolic syndrome in women in a timely manner. What this is most often becomes known to women during menopause. And many women associate their malaise with menopause. Therefore, people consult a doctor already in the later stages of pathology development, when changes in the cardiovascular system are noticeable. But with the help of competent treatment, it is still possible to stop the progression of health problems. Although it is believed that the pathology cannot be completely cured.
Why does a man with metabolic syndrome need a urologist?
The fact is that the “components” of metabolic syndrome (obesity, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance) often “lead” to erection problems. That is why a urologist is able to assess a man’s overall health by just asking him one question: “What is the quality of your sex life?”
There are numerous studies worldwide that confirm this connection. For example, in a study by Italian urologists it was proven that the prevalence of erection problems (erectile dysfunction) among patients with metabolic syndrome was 26.7%. Turkish scientists examined 393 men in the urology department and found metabolic syndrome in 40% of them, and erectile dysfunction in 69%. The results of Finnish studies also demonstrate a high prevalence of erectile dysfunction among patients with metabolic syndrome (76.2%). Moreover, problems with erection begin to occur in men with metabolic syndrome quite early - at the age of about 40 years.
Metabolic syndrome in women: description
This set of changes in health is associated with metabolic disorders. The main one is the development of cell insensitivity to insulin. As a result, this hormone ceases to perform its functions, and glucose is not absorbed by the tissues. This leads to pathological changes in all organs, especially the brain.
The main function of insulin is to trigger the mechanism for transporting glucose into the cell. But if the receptors involved in this remain insensitive to this hormone, the process is disrupted. As a result, glucose is not absorbed, more insulin is produced, and they accumulate in the blood.
In addition, metabolic syndrome in women is characterized by an increase in the level of “bad” cholesterol and triglycerides due to impaired fat metabolism. There is also an excess amount of uric acid and hormonal imbalance. As a result of these changes, blood pressure increases, obesity appears, and heart function is disrupted.
All these changes develop in the body gradually. Therefore, it is not immediately possible to diagnose metabolic syndrome in women. Signs of it are detected when changes affect the functioning of many organs. But first, due to poor nutrition and a sedentary lifestyle, the sensitivity of cells to insulin is disrupted. As a result, the pancreas begins to produce even more of this hormone to provide the cells with glucose. A large amount of insulin in the blood leads to metabolic disorders, especially the process of fat absorption. Obesity develops and blood pressure rises. And excess glucose in the blood leads to diabetes mellitus, as well as to the destruction of the protein membrane of cells, which causes premature aging.
What are the health hazards?
If the metabolism of carbohydrates and lipids in the body is not normalized at the initial level, then systemic damage to the arteries develops. Syndrome X is one of the main risk factors for acute disorders of cerebral and coronary circulation, hypertensive crises, cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral and cardiac ischemia.
Lesions of the digestive system occur in the form of fatty liver, decreased bile secretion, and impaired intestinal motor function. Decreased vision in patients develops due to diabetic damage to the retinal vessels. The filtration ability of the kidneys weakens, and protein is found in the urine. Progression of nephropathy leads to renal failure.
The lower extremities may suffer from both atherosclerotic disorders (intermittent claudication) and diabetic polyneuropathy (non-healing ulcers, loss of sensation). When these processes are severe, gangrene occurs, leading to the need for amputation.
Sharp fluctuations in blood sugar in uncompensated diabetes cause comatose states, which can be life-threatening.
Causes of metabolic syndrome in women
Pathological changes in the body with this pathology are associated with cell insensitivity to insulin. It is this process that causes all the symptoms that characterize metabolic syndrome in women. The causes of insulin resistance can vary.
- Most often, the pathology occurs due to excessive consumption of carbohydrate and fatty foods. As a result, a lot of glucose and fatty acids enter the blood. They do not have time to be absorbed and are deposited in the tissues. Therefore, obesity develops. And fatty acids cause changes in cells that impair insulin sensitivity.
- Oddly enough, low-calorie diets also lead to metabolic disorders. The body stores fat tissue, which makes glucose less absorbed.
- Lack of physical activity causes a slowdown in all metabolic processes. Especially because of this, the absorption of fats, which are deposited in the subcutaneous tissue and on the internal organs, is disrupted.
- Sometimes metabolic syndrome in women can be caused by a genetic predisposition. In this case, with a sedentary lifestyle or poor diet, obesity quickly develops.
- Some drugs can cause cells to become insensitive to insulin. These are corticosteroids, thyroid-stimulating hormones, oral contraceptives and some hypoglycemic agents.
- Frequent stress and prolonged mental stress disrupt the process of hormone production. This often affects the production of insulin and the sensitivity of cells to it.
- Hormonal imbalances often lead to the development of metabolic syndrome in menopausal women. This is due to decreased estrogen production.
- Circulatory disorders, increased blood pressure or oxygen deprivation of the brain also reduce the sensitivity of cells to insulin.
Symptoms of pathology
The disease develops slowly. Symptoms increase gradually and in the initial stages do not have a negative impact on a person’s health and lifestyle.
Glucose is the basic cellular “fuel”; it provides energy for all metabolic processes in the body. When insulin resistance develops, a person's blood contains enough glucose, but it does not enter the cells, and they lack nutrients. This causes symptoms characteristic of metabolic syndrome:
- Psychological symptoms: bad mood, attacks of aggressiveness, irritability. These manifestations are associated with insufficient supply of glucose to the neurons of the brain.
- Picky eating and sweet tooth. This symptom is caused by a lack of glucose in the cells.
- Chronic fatigue, decreased performance, as a lack of glucose leads to a lack of energy.
- Constant thirst, which is caused by the accumulation of glucose in the blood.
How does metabolic syndrome manifest?
The pathology develops unnoticed, and recently it appears more and more often in adolescence. But many of its manifestations are not noticed at the initial stages. Therefore, patients often turn to a doctor when serious disturbances in the functioning of internal organs and systems are already observed. How can one determine in time that metabolic syndrome is developing in women? Symptoms of pathology may be:
- increased fatigue, loss of strength, decreased performance;
- with a long break in eating, a bad mood appears, even aggression;
- you constantly want sweets, eating carbohydrates improves your condition and improves your mood;
- a rapid heartbeat appears, and then - pain in the heart;
- headaches often occur and blood pressure rises;
- Nausea, dry mouth and increased thirst may occur;
- Digestion slows down, constipation appears;
- Symptoms of pathology of the autonomic nervous system develop - tachycardia, increased sweating, impaired coordination of movements, and others.
There are also external signs of this pathology. An experienced doctor can diagnose metabolic syndrome in women at first glance. Photos of such patients show a common sign for all: abdominal obesity. This means that fat accumulates mainly in the abdominal area. And not only in the subcutaneous tissue, but also around the internal organs, which further disrupts their functioning. It is believed that abdominal obesity develops if a woman's waist circumference exceeds 88 centimeters.
You may also notice red spots on the neck and upper chest. Their appearance is associated with vasospasm due to increased blood pressure or stress.
Diagnosis of the disease
The presence of metabolic syndrome is indicated by abdominal-visceral obesity, in which fat is deposited mainly above the waist, that is, male-type obesity.
Diagnosis of the disease in children
Metabolic syndrome in children is asymptomatic, and its signs begin to form only during school years, when the child begins to move less. At this time, a blood test showing an increase in lipids and lipoproteins in the blood helps to identify the disease. Another sign of the disease is a persistent increase in blood pressure.
A prerequisite for making a diagnosis is the insensitivity of receptor cells to insulin. This factor allows the endocrinologist to prescribe a diagnostic set of studies, during which other clinical signs are collected.
Metabolic syndrome in children is characterized by the presence of certain symptoms, which together sooner or later lead to the development of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Obesity, characterized by the deposition of fat in the anterior abdominal cavity, on the torso above the waist, as well as on the shoulder girdle, neck and face.
- Significant reduction in cell sensitivity to insulin.
- Diabetes mellitus type II.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Increased levels of lipids and lipoproteins in the blood, as well as uric acid.
- Increased body hair growth in girls.
- Blood clotting disorders.
- Renal dysfunction.
Diagnosis of the disease in women
Metabolic syndrome in women at an early stage also does not manifest itself with any external signs. However, their absence only means that the disease is actively progressing from the inside, affecting the cells of the body.
The main signs of metabolic syndrome in women are the following manifestations:
- weight gain due to fat deposition in the anterior abdominal cavity;
- increased appetite and need for sweet foods;
- dry mouth and thirst;
- constipation;
- arterial hypertension;
- headaches accompanied by dizziness;
- increased heart rate and shortness of breath;
- heartache;
- feeling of weakness and increased irritability;
- increased sweating at night;
- hair growth on the body and face;
- menstrual irregularities;
- infertility.
When making a final diagnosis, the attending physician takes into account the following diagnostic criteria:
- hereditary predisposition;
- gynecology, including the onset of the first menstruation, its duration and intensity of discharge, previous gynecological diseases, as well as the number of pregnancies and their outcome;
The diagnosis is made based on the following studies:
- biochemical blood test;
- blood clotting test;
- a test carried out using glucose powder, which allows you to determine the body’s susceptibility to this substance;
- determination of hormone levels in the blood;
- heart examination;
- a study to determine the ratio of fat and muscle tissue in the body;
- consultations with specialists, including an endocrinologist and gynecologist.
Diagnosis of the disease in men
Metabolic syndrome in men is determined based on the following criteria:
- obesity, characterized by the deposition of fat in the anterior abdominal wall;
- blood glucose content over 6.1 mmol per 1 liter, provided the test is taken on an empty stomach;
- arterial hypertension;
- reducing high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels;
- increased triglyceride levels;
- problems with erection;
- infertility.
Complications and consequences of metabolic syndrome
This is a chronic pathology with a severe clinical course. Without proper treatment, metabolic syndrome in women leads to serious consequences. Most often, vascular dysfunction causes myocardial infarction or stroke. Atherosclerosis, thrombophlebitis, or chronic coronary heart disease may also develop.
And improper treatment of type 2 diabetes leads to the development of its insulin-dependent form. Long-term increases in blood glucose levels cause blindness, premature aging, and disruption of peripheral vascular function. Gout or fatty liver disease may also develop. Such patients usually have reduced immunity, so they often suffer from colds, bronchitis and pneumonia.
If metabolic syndrome develops in women of reproductive age, it can cause infertility. After all, disturbances in this pathology affect not only carbohydrate and fat metabolism. All organs and tissues suffer, and hormonal imbalances are often observed. Polycystic ovary syndrome, endometriosis, decreased libido, and menstrual irregularities may develop.
Prevention
Predisposition to the disease is genetically determined. Despite this, it is still possible to avoid the development of a dangerous pathology. To do this, you should lead a healthy lifestyle. In particular, it is important to take care of quality nutrition and sufficient physical activity. You should eat at least 4 times a day. Portions should be small. Vegetables and fruits should predominate in food. Movement is life. To achieve normal shape, you don't have to go to the gym or run in the morning. It is enough to get to work on foot, take evening walks, use the steps instead of the elevator. It will be useful to sign up for a swimming pool.
During work, it is recommended to take short breaks to charge. This is especially true if professional duties are performed at the computer. For prevention purposes, it is recommended to undergo a course of physiotherapy or massage. This will help speed up your metabolism. After 40 years of age, you should regularly measure your blood cholesterol levels. This will allow you to control the situation. In case of the slightest deviations, it will be possible to immediately proceed to their correction.
Diagnosis of metabolic syndrome
Typically, patients with such symptoms first come to the general practitioner. After examination and medical history, the patient is referred to an endocrinologist for further examination and selection of treatment methods. Questioning the patient allows us to determine the characteristics of lifestyle and nutrition, and the presence of chronic diseases. In addition, the endocrinologist performs an external examination of the patient: measures waist circumference and calculates body mass index. But metabolic syndrome in women is not determined only by these signs. Diagnosis of pathology also involves laboratory tests. Most often, this is done by blood and urine tests. The presence of metabolic syndrome is indicated by the following indicators:
- elevated triglyceride levels;
- decreased concentration of high-density lipoproteins;
- increased levels of bad cholesterol;
- fasting glucose level is at least 5.5 mmol/l;
- high concentrations of insulin and leptin;
- protein molecules and increased levels of uric acid are found in the urine.
In addition, other examination methods are used. Glucose tolerance tests, blood clotting tests, and 24-hour blood pressure monitoring may be performed.
The doctor may prescribe an ultrasound of the thyroid gland, an MRI of the adrenal glands or pituitary gland, and an ECG of the heart. An important indicator is also the patient’s hormonal background.
Historical reference
Until recently (until the middle of the 20th century), such a concept did not exist at all. For the first time, J. Vague spoke about a similar phenomenon, who, when separating two types of obesity (android, also known as abdominal in the shape of an “apple” and genoid in the shape of a “pear”), revealed a direct pattern of abdominal obesity with the development of diabetes mellitus, coronary heart disease and gout.
41 years later, in 1988, G. Reaven coined the concept of “syndrome X,” which combines several disorders:
- insulin resistance;
- compensatory hyperinsulinemia;
- abdominal obesity;
- elevated triglyceride levels;
- low high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol;
- arterial hypertension (AH).
Moreover, he considered the main “culprits” for the development of syndrome X to be insulin resistance and compensatory hyperinsulinemia, which contribute to excess weight gain, leading to abdominal obesity.
Based on these research works, in 2004, the All-Russian Scientific Society of Cardiology (VNOK) decided to combine the following symptoms into one term “metabolic syndrome”:
- abdominal obesity (provided that the waist circumference in men is more than 102 cm, and in women 88 cm);
- high triglyceride levels (more than 150 mg/dL or 1.69 mmol/L);
- low HDL cholesterol (in men 39 mg/dL or 1.04 mmol/L, and in women 50 mg/dL or 1.29 mmol/L);
- arterial hypertension (more than 130 or 85 mm Hg);
- plasma glucose level (110 mg/dL or 6.1 mmol/L).
But not everyone completely agrees with them.
The International Diabetes Federation accepts abdominal obesity as the main criterion for MS, in the presence of which any 2 of the following signs are detected:
- high triglyceride levels;
- lowering cholesterol levels;
- arterial hypertension (AH);
- When taking a blood test, fasting hyperglycemia is detected
The World Health Organization (WHO) considers the main symptom of metabolic syndrome to be insulin resistance with elevated blood sugar levels and the presence of any two signs:
- abdominal obesity;
- AG;
- increased triglyceride levels;
- lowering HDL cholesterol;
- microalbuminuria (urine analysis reveals kidney pathology, which subsequently develops into kidney failure)
As you can guess, there are some disagreements in the process of diagnosing metabolic syndrome, because it is not known for certain what can be considered the foundation for the development of these processes that fall under this definition. It is the combination of certain factors that matters. Therefore, some “liberties” are allowed in its diagnosis.
Principles of treatment
Each patient requires an individual approach. Treatment of metabolic syndrome in women is prescribed depending on blood counts, degree of obesity and the presence of concomitant diseases. Its main goals should be to reduce body weight, increase cell sensitivity to insulin, normalize metabolic processes and blood pressure, correct hormonal levels and improve the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Most often, the following methods are used for treatment:
- a special diet for metabolic syndrome in women is a mandatory and most effective way to lose weight and normalize metabolic processes;
- the patient is also recommended to change lifestyle by increasing physical activity;
- Various medications are used to correct disturbances in the functioning of internal organs;
- For women with this pathology, psychological support and maintaining a positive attitude are very important.
Additionally, the patient can use other methods. With the help of traditional medicine recipes, metabolism is normalized, body weight is reduced, and blood circulation is improved. It is effective to treat metabolic syndrome in women in a sanatorium. The principles of physiotherapy used there improve carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, calm the nervous system, and normalize blood pressure. The most effective for these purposes are balneotherapy, massage, drinking mineral waters, and electrotherapy.
Main reasons
Insulin performs various functions in the body. But its main task is to contact receptors located in the membrane of each cell. After this, the transport of glucose from the intercellular space into the cell begins.
In other words, insulin helps glucose enter the cell. If the receptors do not respond to insulin for any reason, glucose begins to accumulate in the blood. The development of metabolic syndrome is based on insulin insensitivity, that is, insulin resistance. This phenomenon can be caused by various reasons.
Genetic predisposition
In some people, insulin insensitivity is genetic. The genes responsible for the development of metabolic syndrome are located on chromosome 19. Mutations in this case can cause:
- cells do not have enough receptors that are responsible for communicating with insulin;
- receptors become insensitive to insulin;
- the immune system itself begins to produce antibodies that block insulin-sensitive receptors;
- The pancreas produces abnormal insulin.
There is a theory that decreased insulin sensitivity is the result of evolution.
It is this property that helps the body better survive hunger. But modern people, when consuming high-calorie foods, develop obesity and, as a consequence, metabolic syndrome. Diet high in fat and carbohydrates
It is the most important factor in the development of MS. Saturated fatty acids, which come with animal fats, lead to obesity. In addition, fatty acids can cause serious changes in the cell membrane, making them insensitive to the action of insulin. And an excessively high-calorie diet causes glucose and various acids to enter the blood in large quantities. Their excess is deposited in fat cells, subcutaneous fat, and tissues, which also causes a decrease in insulin sensitivity.
Other reasons include:
- Sedentary lifestyle. With a decrease in physical activity, the speed of all metabolic processes decreases. As a result, fatty acids block the entry of glucose into the cell and reduce the sensitivity of the cell membrane to insulin.
- Long-term hypertension. In this case, peripheral circulation is disrupted.
- Addiction to a low-calorie diet. If the calorie content of the daily diet is less than 300 kcal, this causes irreversible metabolic disorders. The body begins to save, builds up reserves, which leads to severe fat deposition.
- Stress. Prolonged mental stress leads to disruption of the nervous regulation of organs and tissues. This leads to disruptions in the production of hormones, including insulin.
- Long-term use of insulin antagonist drugs, such as glucagon, corticosteroids, oral contraceptives. These drugs reduce the absorption of glucose into tissues, which causes a decrease in insulin sensitivity.
- Insulin overdose in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. If the dose is incorrectly selected, a large amount of insulin accumulates in the blood. As a result, the receptors begin to get used to it. Insulin resistance in this case is a kind of protection of the body from high concentrations of insulin.
- Hormonal disorders. In women, with increased testosterone production and decreased estrogen, fat begins to accumulate in a male pattern. As a result, the functioning of blood vessels is disrupted, and arterial hypertension may appear.
- A decrease in the level of thyroid hormones during hypothyroidism can also cause increased levels of lipids in the blood and the development of insulin resistance.
- Age-related changes in men. With age, testosterone production begins to decrease, which can cause insulin resistance, hypertension, and obesity.
Drugs for the treatment of metabolic syndrome
Drug treatment is prescribed depending on the severity of the symptoms of the pathology. Most often, drugs are used to normalize lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, to increase cell sensitivity to insulin, as well as to lower blood pressure and improve heart function. Sometimes medications are used to normalize hormonal levels. Medicines are selected by the doctor individually after a full examination.
- To treat lipid metabolism disorders, drugs from the group of statins and fibrates are prescribed. These may be Rosuvastatin, Lovastatin, Fenofibrate.
- To improve the absorption of glucose by cells and increase their sensitivity to insulin, special products and vitamins are needed. These are “Metformin”, “Glucophage”, “Siofor”, “Alfa-Lipon” and others.
- If metabolic syndrome develops in menopausal women, hormonal therapy is used. These may be drugs containing estradiol and drospirenone.
- To normalize blood pressure and improve heart function, ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers or diuretics are used. The most common drugs are Captopril, Felodipine, Bisoprolol, Losartan, Torsemide and others.
Often, treatment of metabolic syndrome in women with medications is aimed at weight loss. In this case, drugs are used that block appetite and improve the psychological state of a woman when she refuses food. This could be, for example, the drug Fluoxetine. Another group of anti-obesity drugs allows you to quickly remove fats from the intestines, preventing them from being absorbed into the blood. This is Orlistat or Xenical. If you have metabolic syndrome, it is undesirable to use such popular anti-obesity drugs as Prozac, Reduxin, Sibutramine, as well as modern dietary supplements without consulting a doctor. They can cause serious side effects.
Diagnostics
To understand what is happening to a person, it is necessary to consult several doctors who can not only confirm or refute the diagnosis, but also develop a special treatment program for a particular person.
Typically, the patient first turns to a therapist, who makes a preliminary diagnosis by collecting relevant information and ordering tests. After receiving the results of the examination, the person receives a referral to an endocrinologist, who conducts his examination and collates the previously obtained results. It assesses the level of risk and predicts further success in treatment. In order for the recovery process to be complete, a nutritionist is involved in this process, who develops a special individual dietary method.
The changes occurring in the body, as a rule, are very indicative, but only at the level of laboratory research.
Elevated levels may be detected in the patient's blood:
- triglycerides (1.7 mmol/l),
- cholesterol (above 3.0 mmol/l),
- uric acid (from 415 µmol/l and above),
- blood sugar (more than 5.6-6.1 mmol/l),
- reduced high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels
In urine:
- presence of protein components in urine
This happens as a result of excessive obesity, when the internal organs of a person are also covered with fat. Triglycerides are “simple” fats devoid of cholesterol (one of the stages of cholesterol conversion). Some of them can be synthesized independently, through the liver, and the other large part enters the body from the outside with food. Fat, just like glucose, is energy, as well as the building material of cells (their membranes), which is necessary for their development and further regeneration. Fat is also consumed by muscle tissue. All its surpluses are “safely” stockpiled.
If there is a violation of lipid metabolism (in other words, fat metabolism) and the presence of internal obesity, unconsumed fats enter the blood, penetrating the portal vein. As soon as fats and their half-life products enter the portal vein, the body decides to eliminate them and remove them from the body. As a result, the load on the kidneys increases, which try to cleanse the blood of excess fatty components and remove it all with urine.
If protein molecules are found in the urine, this directly indicates that some changes have already occurred in the kidneys and they cannot filter properly. This may indicate the onset of diabetes or hypertension.
Let us say right away that during the examination no one will be able to diagnose you with “metabolic syndrome”.
And all because such a disease simply does not exist in ICD-10 (WHO from 1998). This concept includes a certain part of the symptoms and abnormalities in which certain diseases can develop, including diabetes mellitus.
Therefore, the diagnosis prescribes a dual examination result, for example, hypertension, having code I 10, obesity (of such and such a degree), having code E 66.9. At the same time, all the symptoms and signs identified as a result of the anamnesis and other studies are recorded in the medical record.
If MS is suspected, the patient is asked to undergo a series of tests and undergo an initial examination, during which:
- Anthropometric measurements are carried out (to identify the type of obesity), and I also determine the weight, height and age of the patient (to identify body mass index)
- When determining the mass fraction of abdominal fat, as well as when studying the pituitary gland and adrenal glands, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques are used.
- An oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is performed to identify impaired carbohydrate metabolism (in case of insulin resistance) and an intravenous glucose tolerance test (IVGTT)
- When arterial hypertension is detected, blood pressure is measured and its fluctuations throughout the day are subsequently recorded.
- When taking a blood test in her serum, the following is determined: the amount of cholesterol; triglycerides; HDL cholesterol; LDL cholesterol; uric acid. The presence of microalbuminuria, which is a unique marker of vascular damage in diabetic conditions, is also recorded.
- An ultrasound may be prescribed to assess the health of the thyroid gland.
- As part of the laboratory study, the patient’s hormonal levels are also assessed
Lifestyle with metabolic syndrome
In order to improve metabolic processes and increase cell sensitivity to insulin, it is very important to increase the patient’s physical activity. But when playing sports, you must follow several rules, then the treatment of obesity will be effective:
- you need to choose a sport that would bring you pleasure, since you need to do it in a good mood;
- training should be daily for at least an hour;
- loads need to be increased gradually, you should not overwork;
- Do not exercise if you have high blood pressure or serious problems with your heart or kidneys.
What workouts will help people with metabolic syndrome? For women under 50 years old, anaerobic exercise and strength exercises are suitable. This includes jogging, exercise equipment, squats, fast swimming, and aerobics. After 50 years, it is better to take up Nordic walking, swimming, calm dancing, and cycling.
The importance of lifestyle adjustments in the treatment of MS
In order for the treatment of this pathology to bring a positive result, it is important to 100% change your lifestyle and nutritional culture. Regular exercise and a low-carbohydrate diet are an effective combination that will help speed up metabolism and increase cell sensitivity to insulin.
Physical activity
Regular physical therapy exercises contribute to the effective burning of fat reserves, accelerating metabolic processes, increasing the sensitivity to insulin of all tissues and organs, and producing a large amount of endorphins (hormones of happiness that improve mood and help control appetite).
Physical therapy is the key to higher productivity and rejuvenation of the body.
When playing sports, follow a few simple rules that will allow you to deal with obesity problems as effectively as possible:
- Training should be on a regular basis. When playing sports, remember self-discipline, since your health depends on the correct approach to physical activity. Train 6 days a week for an hour. Also, exercise should be enjoyable - playing sports by force is not recommended. For this reason, it is necessary to choose the workout that is right for you.
- When choosing a sport, consider your age and physical capabilities. For example, a person over 50 years old should prefer walking or Nordic walking. But young people can jog. Swimming in the pool and cycling are ideal for any age. Also, the listed sports have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
- Consider contraindications for health reasons. Thus, doctors recommend temporarily abandoning physical activity if there is protein in the blood or high blood pressure.
Strength and cardio exercises are the most effective in the fight against obesity, especially if they are regularly alternated. Anaerobic, that is, strength exercises, are performed at a fast pace, during exercise you have to make significant efforts.
Such loads are well suited for young people, but are contraindicated for those who have problems with the cardiovascular system. At first, the duration of such training should not exceed 15 minutes a day, but with each subsequent week you can increase the duration by 5-10 minutes.
Aerobic exercise, or cardio, is performed at a lower intensity and intensity. But they improve the functioning of the lungs and heart, and such activities also help burn subcutaneous fat. Such training includes dancing, exercise on a treadmill, or an exercise bike. The continuation of cardio training at the very beginning should not exceed 15 minutes, over time it can be increased.
Proper nutrition for metabolic syndrome
Weight loss is the main goal of treatment for this pathology. But in order not to harm your health even more, weight loss should be gradual. It is believed that the body perceives without stress a loss of 3% of the initial mass per month. This is approximately 2-4 kilograms. If you lose weight faster, metabolic processes will slow down even more. Therefore, it is recommended that a woman pay close attention to the selection of her diet. It is advisable that the diet be compiled individually by a doctor. In this case, the degree of obesity, the presence of complications, and the patient’s age will be taken into account.
The diet for metabolic syndrome in women should contain few carbohydrates and fats. You need to give up confectionery, baked goods and baked goods, sweets, fatty meats and fish, canned foods, rice, bananas, raisins, refined fats and sugary drinks. The diet should contain green vegetables, unsweetened fruits, lean meat, fish and dairy products, whole grain bread, buckwheat, and barley. In addition, the following rules must be observed:
- You need to eat in small portions, but do not allow long breaks between meals;
- Products are best boiled, stewed or baked;
- All food must be chewed thoroughly;
- food should not be washed down;
- you need to limit your salt intake;
- It is recommended to keep a food diary.
The story of a patient with metabolic syndrome: “Now I am a healthy person”
Narrated by Nadezhda Sergeeva, 57 years old. Weight before weight loss was 169 kg, weight two years after weight loss started - 79 kg
— In 2011, I became a participant in the program “Let Them Talk” — then, with a height of 169 cm, I weighed 169 kg. I was diagnosed with “arterial hypertension” and “type 2 diabetes mellitus”; my blood pressure went off scale over 220 mmHg.
It was very difficult to move: I couldn’t walk well, my back hurt badly, and life was boring and uninteresting. In order to get to the kitchen, I had to rest twice, because... shortness of breath began. I couldn’t go outside at all and spent all my time in the apartment.
The children brought me food and did all the housework (laundry, cooked, washed the floors). I couldn’t even get into the bathtub and wash myself. And then, on the program, Andrei Malakhov introduced me to Mikhail Gavrilov, the doctor who saved my life.
How did my weight loss begin? With self-love. It took me a long time to learn how to take care of myself, pamper myself, and take care of my health. This was the basis on which my treatment and diet were built. While losing weight, I managed to get rid of bad eating habits and acquire new, healthy ones. I learned to choose foods and stopped forcing myself to eat foods I didn’t like.
Two years have passed since then. Today my weight is 79 kg. My blood pressure has returned to normal (it’s now 70/110), my blood sugar is normal. Basically, I am a healthy person now.
Nadezhda Sergeeva: photo after losing weight, weight 79 kg
Back to contents
Prevention of metabolic syndrome
It is believed that most modern women are predisposed to this pathology. Therefore, you need to know how to behave in order to prevent the development of metabolic syndrome:
- eat right, don’t starve or follow low-calorie diets;
- move more, play sports;
- regularly undergo massage and physiotherapy;
- after 40 years, monitor cholesterol and blood glucose levels;
- give up bad habits and fast food.
This pathology now occurs in every third person. It is especially important to monitor your weight for women over 50 years of age, since metabolic syndrome greatly disrupts the functioning of all organs. Therefore, when the first symptoms of pathology appear, you need to consult a doctor for help. Moreover, not only examination and selection of an individual diet are important, but also psychological support.
What does a man with metabolic syndrome look like?
- His “beer belly” is growing (abdominal obesity occurs when fat accumulation is concentrated in the torso and abdomen). At the same time, fatty tissue grows not only under the skin layer, but also begins to surround and compress internal organs. In addition, the fat itself turns into a separate endocrine organ and begins to secrete substances that cause inflammation and the formation of blood clots.
- A man's waist circumference exceeds 102 cm.
- Red spots periodically appear on the neck and chest due to vasospasm and increased blood pressure: “upper” pressure readings exceed 130 mmHg. Art., “lower” indicators – 85 mm Hg. Art.
There is also laboratory diagnostics for obesity in men: for this, a doctor (endocrinologist, urologist, cardiologist) can prescribe the necessary tests.
How to normalize cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood
With metabolic syndrome, patients usually have poor results on blood tests for cholesterol and triglycerides. There is little “good” cholesterol in the blood, and “bad” cholesterol, on the contrary, is elevated. Triglyceride levels are also elevated. All this means that the vessels are affected by atherosclerosis, a heart attack or stroke is not far off. Blood tests for cholesterol and triglycerides are collectively called a lipid profile. Doctors love to talk and write, they say, I’m sending you to get tested for your lipid profile. Or worse - the lipid spectrum is unfavorable. Now you will know what it is.
To improve blood test results for cholesterol and triglycerides, doctors usually prescribe a low-calorie diet and/or statin medications. At the same time, they pretend to be smart, trying to look impressive and convincing. However, a starvation diet does not help at all, and pills help, but cause significant side effects. Yes, statins improve cholesterol blood test results. But whether they reduce mortality is not yet a fact... there are different opinions... However, the problem of cholesterol and triglycerides can be solved without harmful and expensive pills. Moreover, it may turn out to be easier than you think.
A low-calorie diet usually does not normalize cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood. Moreover, in some patients, test results even worsen. This happens because a low-fat “starvation” diet is overloaded with carbohydrates. Insulin converts the carbohydrates you eat into triglycerides. But it’s precisely these very triglycerides that I would like to have less in my blood. Your body cannot tolerate carbohydrates, which is why metabolic syndrome has developed. If you do not take action, it will smoothly turn into type 2 diabetes or suddenly end in a cardiovascular catastrophe.
They won't beat around the bush for long. The problem of triglycerides and cholesterol is perfectly solved by a low-carbohydrate diet. The level of triglycerides in the blood normalizes after 3-4 days of following it! Get tested and see for yourself. Cholesterol improves later, after 4-6 weeks. Get your blood tested for cholesterol and triglycerides before starting your “new life,” and then again. See if a low carb diet actually helps! At the same time, it normalizes blood pressure. This is the real prevention of heart attack and stroke, and without the painful feeling of hunger. Blood pressure and heart supplements are a good addition to your diet. They cost money, but the expense is worth it because you will feel much more alert.
Development mechanism
The pathological process is triggered by physical inactivity and poor nutrition.
They lead to a decrease in the sensitivity of receptors that interact with insulin. To provide insulin-insensitive cells with glucose, the pancreas tends to produce more of this hormone, resulting in an increase in its level in the blood - hyperinsulinemia. This is not a harmless condition - it results in disturbances in fat metabolism and vascular function, obesity develops and blood pressure rises.
Glucose is not absorbed by the cells of the body, its excess remains in the blood, which is called “hyperglycemia”. An imbalance in the concentration of glucose outside and inside the cell contributes to metabolic disorders and the appearance of free radicals, the main adverse effect of which is damage to the cell membrane and premature aging.
Clinical manifestations
The disease does not begin acutely - at an early stage it proceeds gradually, almost asymptomatically from the outside, but is very active inside the body - even in the absence of external symptoms, metabolic disorders in the cells are progressing more and more.
The main symptoms of metabolic syndrome are:
- increased body weight, accompanied by the accumulation of subcutaneous fatty tissue in the anterior abdominal wall; the waist circumference will be more than 80 cm;
- excessively good appetite, selectivity in food (constantly craving sweets);
- dry mouth, thirst;
- tendency to constipation;
- increase in blood pressure to 140/90 mm Hg. Art. and more frequent, occurring unnoticed (determined by chance) or with headache and dizziness;
- palpitations, tachycardia;
- pain in the heart area;
- severe general weakness, fatigue, irritability;
- increased sweating, especially at night;
- shortness of breath on exertion;
- increased hair growth in places atypical for women - on the face, limbs, chest area;
- irregular menstrual cycle;
- inability to conceive (pregnancy does not occur within 12 months of unprotected sexual activity).
Why do you need nutritional adjustments?
When a person has prediabetes, i.e. the glucose concentration is above the standard value, but diabetes cannot yet be diagnosed.
It is in this case that to correct impaired glucose tolerance, adherence to certain dietary rules, lifestyle and weight loss can help.
If you reduce the amount of “light” carbohydrates consumed in food, reduce the calorie content of dishes, play sports and increase physical activity, you can correct the situation and stop the development of metabolic syndrome.
Prevention and prognosis
To avoid the formation of problems such as obesity and metabolic syndrome, you should strictly adhere to the following simple preventive recommendations:
- complete renunciation of addictions;
- complete and balanced nutrition;
- maintaining a moderately active lifestyle;
- avoiding emotional exhaustion;
- taking only those medications prescribed by the attending physician;
- timely treatment of endocrine diseases;
- Regularly undergoing a full preventive examination in the clinic with visits to all clinicians.
If all treatment and preventive recommendations are followed, metabolic syndrome will have a favorable prognosis. However, late detection of pathology almost always leads to the formation of the above consequences.
Classification
Based on the pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome, several degrees of severity are distinguished:
- initial - in this case, patients develop metabolic dysglycemia, when the functioning of the pancreas remains optimal. Insulin concentration is normal or slightly increased. Diabetes and cardiovascular disorders do not develop;
- moderate - differs in that glucose tolerance is already beginning to develop and there are malfunctions in the organ that produces insulin. The blood glucose level is higher than normal, but does not reach critical values;
- severe - in such situations, the patient is diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus, and there are also symptoms of a pronounced dysfunction of the pancreas.
Metabolic syndrome
Hormones and androgen deficiency syndrome: norms and deviations
The state of men's health largely depends on the level of free testosterone (FT). The maximum concentration of the hormone is reached at the age of 18-20, then the levels stabilize. The lower bar should not fall below 8 nmol/liter up to 50 years old, and below 6 nmol/liter at 60-70 years old.
According to statistics, 13% of men under 50 years of age have testosterone levels below the normal level. By the age of 80, this figure already covers 60% of men. Statistics show only part of the problem, since it includes only those patients who themselves went to medical institutions.
Young people 16-20 years old experience the downside of high testosterone levels. They are energetic, active, they are haunted by a constant feeling of hunger, while young men with high testosterone eat everything in a row and in large quantities, but remain thin and lean. At this age, guys' libido is off the charts, they think about sex all the time and are ready to have it day and night.
Until the age of 30, hormonal levels are relatively stable. A man is sexually active, makes a career, starts a family, earns money, works a lot. Over time, everything begins to change imperceptibly: after work you don’t want to go anywhere - it’s much more pleasant to lie down. The wife is not as attractive as she used to be, and sex has ceased to be an event. Often, complete sexual cooling is a mutual phenomenon according to the principle “she doesn’t want it and I don’t need it.” Moreover, the age of the spouses who find themselves in such a situation often does not exceed 35 years. The reason for everything is androgen deficiency syndrome (ADS) in men. The main danger of pathology is that its manifestations are not limited only to lack of strength and apathy.
Metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance: what is the connection?
If a person has this condition, insulin resistance develops, because no longer produces this peptide hormone. With its help, glucose is utilized, which enters the body during meals.
If a person has an insulin-dependent form of diabetes (type 1 diabetes), the pancreas cannot cope with sufficient production of the hormone. For treatment, medications are prescribed that promote the utilization of insulin in the liver; they also help the muscles become less sensitive to the insulin that is available.
If drug therapy is insufficient, insulin injections are prescribed. The required dosage is selected only by a specialist.
It is important to know that hormone activity is very high. They take part in the body’s absorption of all types of components (protein, fat, carbohydrates). If there is a malfunction in one hormonal chain, the entire metabolism is immediately disrupted.
Complications
In the absence of adequate, timely treatment, metabolic syndrome can develop into serious diseases, which often cause death in patients:
- myocardial infarction and other forms of coronary heart disease;
- diabetes;
- acute cerebrovascular accidents (stroke);
- gout;
- secondary immunodeficiency, against which bronchitis, pneumonia and other infectious diseases often develop;
- obstructive sleep apnea syndrome.
Symptoms
The peculiarity of this disease is that it develops slowly, the clinical manifestations increase gradually and in the initial stages of the development of the disease do not affect the person’s health and lifestyle.
Metabolic syndrome in men and women has the following first signs:
- frequent mood changes;
- attacks of aggression or irritability;
- change in taste preferences;
- increased craving for sweets;
- chronic fatigue syndrome;
- decreased ability to work;
- constant thirst, which makes it necessary to drink large amounts of liquid, as well as frequently visit the toilet to empty the bladder.
As metabolic syndrome develops, the symptoms will worsen, causing the following to appear in the clinical picture:
- obesity of the abdominal type, i.e. accumulation of fatty tissue in the abdominal area. The waist circumference for men will be above 94 centimeters, and for women - more than 80 centimeters;
- persistent increase in blood pressure above 139/89 millimeters of mercury;
- attacks of severe dizziness and headache;
- flashing “flies” before the eyes;
- dry mouth;
- shortness of breath not only during vigorous physical activity, but also at rest;
- increased appetite;
- decreased potency in men;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle and hypertrichosis in females;
- male and female infertility;
- tachycardia and pain in the heart area;
- the appearance of red spots in the chest and neck, which is caused by arterial hypertension;
- impaired renal function;
- profuse sweating;
- nausea without vomiting;
- stool disorder, which results in constipation;
- drowsiness;
- sleep apnea syndrome;
- lack of coordination;
- the appearance of stretch marks on the abdomen and thighs;
- tremor of the limbs.
Metabolic syndrome and arterial hypertension, in combination with the above symptoms, should be applied to both adults and children.
Signs
The disease develops slowly, so at the initial stage its manifestations are invisible, but later the following symptoms are diagnosed:
- bad mood, aggression during periods of hunger;
- excessive fatigue;
- increased heart rate;
- pain in the heart area;
- headache;
- attacks of nausea, loss of coordination;
- dry mouth, constant feeling of thirst;
- bowel dysfunction (constipation);
- excessive sweating, especially at night.
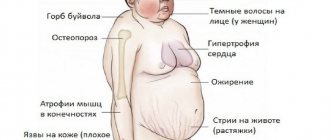
External signs of the disease are significant fat deposits.
With metabolic syndrome, a person has a large belly, fat deposits in the shoulder girdle, as well as other parts of the body
High blood pressure, which often accompanies metabolic syndrome, is manifested by redness of the neck and chest.
Laboratory examination diagnoses:
- elevated cholesterol levels;
- the presence of protein in the urine;
- increase in uric acid;
- high glucose level.
Features of the clinical picture in childhood and pregnancy
In pregnant women, disturbances in uteroplacental blood flow are observed, the risk of complications during childbirth increases, and babies are often born overweight.
Children with this disease are overweight, they experience rapid breathing, heart rhythm disturbances, and problems with sexual development.
Women have menopause, men have androgen deficiency
The content of the article
The condition, which in women refers to menopause, in men is called androgen deficiency or hypogonadism. Unlike the fair sex, whose ovaries simply stop producing eggs and sex hormones in normal quantities during menopause, which leads to infertility, the stronger half of humanity produces the main male hormone testosterone until old age. True, its norms also begin to decline with age. Some people don’t have enough androgens at the age of 30. And unlike women, many men remain fertile into old age.
Hypogonadism in men does not have such periods as the female menopause, which is divided into the premenopausal period, menopause itself and menopause. Also, male menopause has no age limits, so it is not predictable.
Most women, knowing that menopause is imminent, prepare for this event in advance: they increase their immunity, change their diet, get more rest, and take hormone replacement medications. Men, as a rule, do not think about this topic, although their androgen deficiency syndrome occurs much earlier than women's autumn. Signs of hypogonadism are a “potbelly”, a swollen torso and subcutaneous fat deposits on the sides. The consequence of a lack of androgen hormones is apathy, a dull look, and rapid fatigue.
Minus 30 kg: how to live and what to do if you have metabolic syndrome
“Eat less, move more” and other ways to become slimmer that will not help here. Our author Sasha Zhukovskaya talks about her battle with a diagnosis of insulin resistance.
I'm 12, summer 2000. With a height of 164 cm, I jumped from 50 kg to 74 in a year. But neither I nor my family yet know how seriously we are in trouble - we are thoughtfully walking around the clothing market in the not yet - we always buy jeans from the same women. Cool, Turkish. The saleswoman, out of habit, brings several pairs: she remembers me and my figure well. But (wow!) nothing fits on me. She calmly takes out a few more jeans a size larger. What if the manufacturer's size range has changed? Also by. So we get to size 30, the largest, she doesn’t have any more. My mom notices that I'm probably pushing too hard on milk and buns. Actually, at that moment I realized that I weighed more than normal.
Realizing that I was much plumper than others my age, I looked up in home medical reference books what obesity is and what BMI is. I calculated my body mass index and felt sad. The manuals did a good job of explaining obesity, but they didn't describe a single cause that could be understood beyond the long-winded "overeating." But what kind of overeating is there when the family has barely made ends meet all their lives.
I tried to regulate my diet - refuse salads or hot food at family holidays, have dinner no later than six in the evening, drink more water. I found all these useful tips for losing weight in books; not everyone had the Internet back then. It didn’t help - the weight only crawled up. In the eleventh grade, I already weighed 85 kilograms with a height of 165.
At school, boys made fun of me because I was fat. There were no too cruel jokes, they didn’t bully me, but they didn’t perceive me as a girl. And I was worried that girls were friends with me so that they would look better against my background.
Attacks of narcissism were replaced by attacks of anger and reluctance to be fat. Until I was twelve, I looked completely different and weighed much less: I well remembered that state and “that” myself. “Current” me was a stranger to me. But then school ended. I moved to another city and my worries were forgotten: it turned out that being overweight does not interfere with dressing cool, going on dates and enjoying life. I thought that I might never be able to lose weight, and if I didn’t take it for granted right now, I would suffer. I started buying cool things for myself and came to terms with my 16 English size and 52 Russian size.
It was then that my weight reached the critical point at that time - 95 kilograms. I was 23 years old. This figure shocked me, and despite my previous unsuccessful experience of losing weight, I tried again. What happened: Zumba, strength training, circuit training, massages and wraps, LPG and even laser lipolysis. I managed to lose about 15 kilograms, but they came back very quickly, in less than six months, although I did not give up classes and massage. It’s interesting that those around me didn’t understand why I was fighting with weight. After all, “it suits me that way.”
The endocrinologists I contacted ordered tests for thyroid hormones, found everything in order and sent me home. “Well, just eat less and move more,” I was told by about ten different doctors whom I visited over the years. Thank you.
This year I turned 30, by June my weight reached 105 kg. The hips were more than 120 cm, the waist - 130 cm! I told myself: “******!!!! (Wow)". We need to do something about this.
I started with mommy forums. In general, this is a place where you can find recommendations for all possible doctors - mothers develop the maximum number of health problems during pregnancy, and then their children also need to be treated. These superwomen know who is the best in the city to treat tooth decay, who will save you from hair loss, obesity, depression and colic. That’s how I found my endocrinologist, Yulia. "Enchantress!" - the forum chirped about her.
The doctor realized that I was an advanced case as soon as she saw me. Tests and my food diary showed that I have a serious disorder called metabolic syndrome. Otherwise - insulin resistance.
What it is?
To put it simply, it’s a metabolic disorder that makes you gain weight and you can’t stop it in any way. And scientifically speaking, with this syndrome, the peripheral tissues of our body lose sensitivity to insulin, the main hormone responsible for lipid metabolism.
Medicine doesn’t know exactly how and why this happens: inflammation, if you suffer from it on your legs and don’t really treat it, genetic pathologies, stress overeating, which no one stopped in time.
The hormone insulin is produced by the pancreas. We mostly hear about it as a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. I didn’t even know how omnipotent this hormone was and how much it affected metabolism. Insulin also delivers glucose to tissue cells, synthesizes fatty acids that the body needs, and stops lipolysis - the breakdown of fats. If too much insulin is produced, as in metabolic syndrome, it accumulates in the blood, and the body ceases to part with the accumulated fat. In the future, if the disorder progresses and insulin levels rise, the body loses tolerance to glucose. You begin to uncontrollably crave sweets and cannot stop until you have eaten all the chocolates within a 100-meter radius. If nothing is done here, diabetes or fatty liver disease may develop, a disease that leads to cirrhosis.
Only a doctor can make a diagnosis and determine exactly how advanced your syndrome is. Do not read sites from the first search line and do not take any medications until you have visited an endocrinologist.
How to suspect you have metabolic syndrome:
- you are often hungry;
- to fill yourself up, you need not a plate, but a whole frying pan of fried potatoes;
- you can’t imagine your life without sweets, you can’t even stand a day without them;
- you have a very full stomach and waist, and fat is mainly deposited there (waist is more than 80 cm in volume)
- you have dry skin on your hands, on the bends of your elbows and knees, darkened skin on your knuckles;
- hair loss is inexplicable (inexplicable - this means that you are not pregnant or have not recently given birth to a child, and this is not seasonal hair loss, but regular)
- sleep poorly and are awake mostly at night.
How your endocrinologist will determine it: he will prescribe general and biochemical blood tests, tests for thyroid hormones, insulin, glucose and the HOMA index, cholesterol, triglycerides and leptin (the hormone responsible for appetite), check whether the ovaries are in order and sex hormones - he will refer you to find out this from a gynecologist. My doctor also sent me to check my liver to see if there were any signs of fatty hepatosis. This can be found out by doing an ultrasound.
I couldn’t find anything sensible on the Internet about insulin resistance, except for two or three articles on Wikipedia, so I tortured both the treating endocrinologist and doctors I knew from other areas. I learned about Pubmed (a database created by the US National Library of Medicine - editor's note) and read studies about insulin there. So it became clear that I cannot lose weight precisely because of the syndrome: no matter what I eat, the body perceives it as non-carbohydrate food. For the body, I am “starving”, and we are in hell, pain, panic. Therefore, instead of seeing that I actually eat enough carbohydrates, my brain asks for more and more.
With metabolic syndrome, “eat less, move more” does not work without outside intervention - you need to take medications prescribed by your doctor, sometimes even do IVs.
With the start of treatment, hunger decreases and it becomes easier to tolerate the therapeutic diet. But plump girls who don’t even know they are sick will be told by Facebook weight loss experts, random Instagram commentators and relatives that they are just lazy assholes who don’t go to the gym and eat pizza for days. Yes, I really ate for days, and this process cannot be stopped with one effort of will. You cannot instill a love for sports through humiliation. You can’t call people lazy creatures, it’s better to help them. Treatment is needed, and not only for excessive appetite and cravings for sweets - medications help the body understand where it has taken a wrong turn and help enhance the breakdown of fats.
How is metabolic syndrome treated (and where do the kilograms go)
The doctor prescribes medications depending on the tests: to suppress uncontrollable appetite, to reduce insulin and glucose levels in the blood, vitamins and amino acids that help metabolism - for example, alpha-lipoic acid, Omega-3, B vitamins. He may prescribe medications that are administered intravenously or by drip, for example, hepatoprotectors.
Next, the already familiar “diet and sports” to everyone who has ever lost weight. The diet will need to be followed throughout your life. The drugs are usually stopped and checked to see how the body copes on its own. If everything is in order, diet and activity will be enough to prevent history from repeating itself. If the tests show that insulin has increased, you will need to take the medicine again. Older people usually need to take medications for life. Nothing has been canceled for me yet and will not be canceled until next summer.
The diet is based on the principles of the insulin index of foods. It means how much insulin levels in the blood will increase if you consume this product. As a basis, the researchers took 100 grams of the highest insulin product - white bread.
A sample “prohibited” list looks like this:
- anything starchy: potatoes, beets, white rice, cornflakes and cornmeal products;
- everything flour and butter: goodbye bread and burgers;
- sweets (logical, we need to regulate insulin!) and sweet fruits (bananas, dates);
- carbonated drinks and alcohol.
I have compiled a table of the insulin index of foods for myself and will share it with you with great pleasure.
The point of the diet is to eat those foods and dishes that will not cause frantic production of insulin in the body. I was first prescribed a strict diet, which would help reconfigure the pancreas to properly produce insulin. When on a strict diet, you can’t even eat harmless grains like buckwheat, only vegetables, water and cottage cheese. And no sugar, of course.
I started treatment in July of this year. In the first month of taking the medication, my body went crazy, and out of habit, I drank soda, it was hot, and ate cookies. Do not do it this way! In August, I pulled myself together and started that same strict diet. My cravings for sweets began to wane, as did my appetite. I noticed that I can no longer eat a whole piece of chicken fillet, I only manage half. In October, other changes became noticeable - my tastes in food changed greatly, I was drawn to vegetables that I never liked to eat, to fruits that I had been indifferent to all my life (apples). With the end of the strict stage of the therapeutic diet, I expected that I would pounce on potatoes with mayonnaise, my favorite cookies and chocolate, but nothing like that - I crunched on my carrots, just like a month ago. I stopped frying and started stewing or boiling everything. Indifference to sweets has reached such a scale that I don’t even eat sweets that lie in front of my eyes on the table. My husband buys himself chocolate, but I have no desire to eat it.
I didn't believe that this could be cured. I didn’t believe that medications would help, that diet and exercise would have any effect. I only started going to the gym in October, and before that I was limited to longer walks with the dog. Well, like all overweight people, I thought that I needed to lose weight first, and only then go to the gym.
Advertising for sporting goods (hello, Reebok and other titans of the industry) seems to say that sports are for the fit and slim. By some miracle I overcame this stereotype and still went. Maybe it was because at my gym there are a lot of people with different body shapes.
You just need to come to the gym and take a trainer to help. He will make sure you do everything right. There are also dance or aerobic activities. If you don’t feel like it, buy a bicycle so that your body gets used to it and loves movement.
What's the result?
It's December now. Over the course of 5 months of treatment, I lost more than 30 kilograms and moved from size 54-56 to size 46. I started another Instagram to show what I eat - diet restrictions turned on my imagination, and I invent salads from various healthy vegetables and fruits on the go. On Pubmed, I read various studies on foods that insulin-resistant people can and cannot eat, and added the information I found to my tablet. I started smiling and taking pictures more often. It’s difficult to describe my husband’s reaction—he’s shocked. For a while he watched me quietly crawl towards my goal, and then he signed up for the gym with me.
The most surprising thing about all this is how little information there is about this problem, how little it has been studied. We only know that we must adhere to proper nutrition, but we don’t know what to do if we eat right all our lives, and our weight increases.
I hope my story will help some of you think deeply and delve into the origins of excess weight: go to an endocrinologist, gynecologist and therapist, you may also need a psychologist. It's not scary at all. It's scary when you don't know what to do with it.
Metabolic syndrome and its treatment: an understanding test
Time limit: 0
Navigation (job numbers only)
0 of 8 tasks completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Information
You have already taken the test before. You can't start it again.
The test is loading...
You must log in or register in order to begin the test.
You must complete the following tests to start this one:
results
Correct answers: 0 out of 8
Time's up
Categories
- No category 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- With answer
- With a viewing mark
- Task 1 of 8
1.
What is a sign of metabolic syndrome:
Correct Of all the above, only hypertension is a sign of metabolic syndrome. If a person has fatty liver disease, then he probably has metabolic syndrome or type 2 diabetes. However, fatty liver is not officially considered a sign of MS.
False Of all the above, only hypertension is a sign of metabolic syndrome. If a person has fatty liver disease, then he probably has metabolic syndrome or type 2 diabetes. However, fatty liver is not officially considered a sign of MS.
- Task 2 of 8
2.
How is metabolic syndrome diagnosed using cholesterol tests?
Correct The official criterion for diagnosing metabolic syndrome is only reduced “good” cholesterol.
False The official criterion for diagnosing metabolic syndrome is only low “good” cholesterol.
- Task 3 of 8
3.
What blood tests should be taken to assess the risk of a heart attack?
Right
Wrong
- Task 4 of 8
4.
What normalizes triglyceride levels in the blood?
Correct The main remedy is a low-carbohydrate diet. Physical exercise does not help normalize blood triglyceride levels, except in professional athletes who train 4-6 hours a day.
Incorrect The main remedy is a low-carbohydrate diet. Physical exercise does not help normalize blood triglyceride levels, except in professional athletes who train 4-6 hours a day.
- Task 5 of 8
5.
What are the side effects of statin cholesterol medications?
Right
Wrong
- Task 6 of 8
6.
What are the real benefits of taking statins?
Right
Wrong
- Task 7 of 8
7.
What are safe alternatives to statins?
Right
Wrong
- Task 8 of 8
8.
What medications help with insulin resistance, the main cause of metabolic syndrome?
Correct You can only take metformin as prescribed by your doctor. The rest of the listed pills help you lose weight, but cause severe side effects and destroy your health. They do much more harm than good.
Incorrect You can only take metformin as prescribed by your doctor. The rest of the listed pills help you lose weight, but cause severe side effects and destroy your health. They do much more harm than good.
Possible negative consequences of MS if left untreated
One example of such a situation is the so-called metabolic syndrome, which has become widespread in the world in recent years. Its prevalence is especially widespread in developed countries, where the lifestyle of the population is often characterized by excessive calorie consumption and insufficient physical activity. Taken together, these and some other negative factors can lead to the development of a disease such as metabolic syndrome.
The syndrome itself is not a disease, but a complex of various disorders of the normal functioning of the human body, which together can lead to quite serious problems.
Among the most common negative consequences of metabolic syndrome are cardiovascular diseases, including some of the most dangerous - myocardial infarction, the development of diabetes and stroke.
In addition, depending on the individual characteristics of a person, metabolic syndrome can provoke the occurrence of fatty liver hepatosis, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), dysfunction of the genitourinary system in men, gout and other dangerous diseases. Thus, the possible negative consequences are quite dangerous, and therefore it will be useful to understand what metabolic syndrome is and how it can be dealt with.
Spa treatment
Patients who do not have contraindications (they are similar to those for physiotherapeutic procedures) can be referred to sanatorium-resort treatment. Local sanatoriums or resorts specializing in balneotherapy are preferred - Borjomi, Essentuki, Polyana Kvasova, Berezovsky Mineral Waters, Feodosia and others. It is important to ensure that the sanatorium specialists have the opportunity to adjust the patient’s glucose-lowering therapy, since blood sugar levels may fluctuate during treatment.