There are no women who are not at least somewhat concerned about the condition of their breasts. There may be physiological reasons for this - concern for the health of the newborn, when there is an understanding of the value of mother's milk for him and the relationship with this condition of the mammary glands. Or aesthetic ones, for women involved in the modeling business or simply among well-groomed ladies seeking to present themselves effectively. What to do if frightening discharge from the nipples suddenly appears. From both at once, or from one.
Main types of discharge
Usually transparent and yellow discharge from the mammary glands when pressed does not always indicate the development of pathological processes. But brown and bloody ones are already a sign of a serious illness, which will be the reason for immediate medical examination. So, discharge from the chest, in addition to yellow secretion, is as follows:
- Transparent. If this process occurs without changes in the glands, then such a manifestation can be caused by stress, the presence of hormonal imbalance, taking contraceptives, and the like.
- White ones are often observed during pregnancy, as well as in the first few months after completion of lactation. They are considered the norm. In other cases, the appearance of white secretion against the background of pressure indicates galactorrhea, which is caused by increased production of estrogens and an increase in prolactin. Sometimes such manifestations are associated with pathological changes in the pituitary gland, as well as with dysfunction of the thyroid gland.
- Green ones are a clear sign of mastopathy. The consistency of the discharge will be thick and slimy. They will certainly be accompanied by compaction in the glands, general pain in the chest, and fever.
- Brown ones are caused by bleeding occurring in the milk ducts, and are also provoked by the development of mastopathy and malignancy. The usually dark and in some cases black tint is caused by the presence of blood.
- Bloody discharge is one of the most serious symptoms, which may indicate the development of a malignant tumor or intraductal papilloma. It should be taken into account that spotting red discharge may occur due to chest injuries.
- Purulent secretion is usually caused by an inflammatory infectious process. In this case, patients experience fever along with pain, redness of the skin in the nipple area, swelling and swelling of the breasts.
How fluid is released from the breast
Fluid from the mammary glands is more often released when pressure is applied.
Non-dairy secretions come out of the same channels as milk. Each nipple has about 10 holes. Fluid from the mammary glands, when pressed, may protrude from one or more tubules on one or both breasts.
The discharge is thick and watery, of various colors - from transparent and white to black and bloody. All this depends on the reasons that caused the appearance of fluid from the nipples.
Mammologists believe that the likelihood of breast discharge increases with age and the number of pregnancies a woman has had. However, problems can also arise in a girl who has not given birth.
The presence of discharge may indicate the appearance of a benign or malignant neoplasm. Moreover, cancer diseases often occur without the release of fluid. Therefore, in most cases, when nipples leak, the problem indicates less dangerous health problems than cancer. However, you should still visit a doctor.
Physiological causes of pathology
Yellow discharge from the mammary glands when pressed can occur for the following reasons: physiological and pathological. The first type includes:
- Bearing the fetus. During pregnancy, the breast prepares for the birth of the baby, as well as for feeding it. During this period, the glands seem to be training to produce milk and then remove it. A similar process occurs in the last trimester. The increased tone of the uterus stimulates the release of yellowish fluid from both glands.
- Some time after finishing feeding. The symptom may persist for the next three years. This depends on the woman’s age, and, in addition, on the number of pregnancies she has had.
- Because of an abortion. The presence of discharge and its duration are determined by the exact period at which the artificial termination of pregnancy was performed. In such a situation, discharge can disturb the patient from several days to a whole month.
- When using contraceptives. Oral contraceptives contain hormones that stimulate lactation. Discharge may disappear after complete discontinuation of such contraceptives. They need to be replaced with some alternative type. But this must be done according to the doctor’s recommendation.
Among other things, yellow discharge from the mammary glands when pressed is possible during therapy with hormonal medications, as well as due to the use of antidepressants. The cause may also be too tight bras or physical overload.
What should not be done if there is discharge from the mammary glands?
At the first appearance of discharge, you should avoid several actions that negatively affect the condition of the mammary glands:
- take medications without a specialist’s prescription;
- wear tight underwear;
- make warm compresses and other traditional medicine procedures;
- take a hot shower or bath;
- use hormonal medications, including contraceptives, before visiting a doctor;
- squeeze out the liquid yourself.
Any prohibited actions can lead to a worsening of the condition and can also provoke complications.
Pathological causes of the disease
The main factors that provoke yellow discharge from the mammary glands:
- Ductectasia is a disease characterized by a process of pathological expansion of the ducts, which are called subareolar canals. This disease is typical for women after forty, since its main cause is age-related changes in the body. The disease does not pose a health hazard, but only with timely treatment. Otherwise, serious consequences cannot be ruled out.
- Chest injury (we are talking about blows, bruises). If this happens without violating the integrity of the skin, then within two days a small part of the liquid substance can be easily squeezed out of the nipple.
- Presence of intraductal papilloma. This is a benign papillary tumor that occurs in the duct near the nipple. Due to the development of formation, a thick liquid is released, which can sometimes even contain blood impurities.
- Mastitis or abscess. In this case, the area of the gland may become inflamed. The cause can be a bacterial infection; in most situations, the provocateur is Staphylococcus aureus. Against the background of an abscess, pus accumulates in the breast tissue.
- Galactorrhea is the discharge of yellow colostrum from the nipples, which has nothing to do with feeding. Most often, the main cause is an increase in the level of prolactin in the blood (with the development of hyperprolactinemia) or an increase in the level of estrogen.
- Fibrous cystic mastopathy, in which a dense area of tissue appears in the mammary gland. This condition is dangerous because it can later degenerate into cancer.
- The presence of a malignant neoplasm (breast cancer) - a tumor that forms unnoticed due to uncontrolled cell division. Yellow discharge occurs due to pressure and can be observed from both glands or only from one.
- Paget's disease involves the presence of a malignant tumor involving the nipple or nipple circle. The disease is extremely dangerous and requires prompt diagnosis and treatment.
White shade
White discharge more often appears during pregnancy or lactation. If their occurrence is not associated with these processes, then fluid from the breast may be released as a result of the development of a disease such as galactorrhea, in which spontaneous leakage of milk occurs. This pathology can be observed not only in women, but also in men, although it is diagnosed in them very rarely.
Galactorrhea mainly occurs in women who have recently weaned their child. As a rule, it disappears on its own after 6–7 months. However, if during this period a woman becomes ill with inflammatory or infectious diseases, there is a high risk of serious complications (mastopathy, oncology, etc.).
Important! If your lactation has stopped, but white discharge periodically appears from your breasts over the course of several months, and the glands themselves become painful, you should immediately visit a doctor. All these signs indicate a complicated course of galactorrhea and the need for special treatment.
White secretion released from the mammary glands can also indicate the following pathological conditions:
- Impaired functionality of the pituitary gland.
- Hyperthyroidism/hypothyroidism.
- Kidney failure.
- Cystic lesions of the ovaries.
- Mastopathy.
- Oncology.
How should pathology be diagnosed?
When yellow discharge appears from the breasts in women, it is imperative to make an appointment with a mammologist. The doctor will most likely refer the patient to undergo procedures such as mammography and breast ultrasound. You will also need to do galactography (a type of mammography), which is an X-ray examination of the milk ducts, which involves the injection of a contrast agent into them. Among other things, the following may also be prescribed:
- Taking a blood test for prolactin along with sex hormones.
- Thyroid examination.
- Conducting a cytological analysis of breast discharge.
Generalization of the result will help the doctor determine the diagnosis, and at the same time, further therapeutic techniques.
What types of nipple discharge are there?
The discharge varies, which indicates the nature of the disease. It is normal to discharge milk in the form of milk during pregnancy or after childbirth. However, the rest of the discharge is pathological and has a different color, consistency, smell, taste (you just shouldn’t try them). The secret could be:
- Thick or liquid.
- Watery or slimy.
- With a subtle odor or fetid.
- White, yellow, greenish, dark green, black, brown, with blood.
- Transparent, opaque or translucent.
A milky white secretion can be secreted in both sexes. This may be a form of galactorrhea - prolactemia. It develops due to:
- Pathologies of the thyroid gland.
- Changes in climatic conditions.
- Frequent flights.
- Disorders of the pituitary-hypothalamar system.
Galactorrhea can be recognized by white or clear thick discharge from both breasts.
Other secretions may include:
- Transparent discharge. If they are not accompanied by pain, then there is no need to worry. They can occur during active physical activity, during menstruation, when wearing the wrong bra, or when taking contraceptives.
- Dark green, almost black discharge often occurs during menopause, when the breast ducts become deformed and change. The pain may not bother you. You should consult a doctor, who most often detects ectasia (plasmacytic mastitis), a disease that can lead to cancer.
- Bloody discharge often occurs with chest injuries. It should be treated with the help of doctors, otherwise the injury may abscess, leading to cystadenopapilloma or intraductal papilloma.
- Brownish-green discharge often occurs with fibrocystic disease or mastopathy. At the same time, the glands swell, causing a feeling of fullness in the chest. This requires drug treatment.
go to top
Treatment of pathology
Timely treatment of yellow discharge from the breast with pressure will help achieve positive results. Depending on the diagnosis, it can be conservative, but surgical intervention is also possible.
Pathologies such as mastitis and abscess are cured with antibiotics and by opening purulent cavities. If ductectasia is present, the patient will definitely require surgery. In its process, the affected ducts in the gland are removed.
Diagnosis and treatment
What will the doctor prescribe if nipple discharge appears?
Expert opinion
Many women neglect regular examinations by a mammologist, and when they discover a “ball” in their breasts during a self-examination, they postpone a visit to the doctor for as long as possible, hoping that the lump will resolve on its own. All this can lead to the development of various diseases, including those accompanied by secersation.
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category Oksana Anatolyevna Gartleb
An examination by a doctor when discharge from the nipples appears is strictly necessary, because taking care of your health is not only the prevention of diseases, but also the timely detection of problems in the body. When you see a doctor, you will need to try to answer important questions:
- When did the discharge first appear?
- What color and consistency are they?
- Is breast discharge accompanied by other symptoms, such as pain?
- Was the appearance of discharge preceded by any trauma to the mammary glands?
You also need to inform the doctor about taking any medications and oral contraceptives, if such a fact occurs.
It is advisable to schedule a visit to the doctor if you have a regular menstrual cycle in phase 1 on days 5-7, in the absence of regular menstruation at any time.
Prescription of treatment for discharge from the mammary glands.
Basic examinations that the doctor will prescribe if discharge from the chest appears:
- manual examination - palpation of the mammary glands in a standing and lying position;
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands;
- mammography (for routine examinations once every 2 years after 40 years);
- cytological analysis of secreted fluid or puncture biopsy;
- tests to determine the level of hormones and tumor markers, a detailed general blood test;
- consultation with a gynecologist and endocrinologist.
The choice of the appropriate therapeutic strategy depends on the disease causing the nipple discharge.
In some cases, drug therapy can be supplemented by taking dietary supplements. For example, if there is swelling of the mammary glands in the second half of the menstrual cycle and slight discharge from the nipples appears, the mammologist may recommend taking evening primrose oil “Gynocomfort”. It blocks the excessive production of prolactin, which is often the cause of seceration. The product was developed by specialists from the pharmaceutical company VERTEX and has the necessary documents and certificates.
Surgical intervention
Surgical intervention is also required if intraductal papilloma is found. The affected area should be removed. The removed particles are subjected to histological examination to reliably exclude the malignant nature of the papilloma. For Paget's disease, a mastectomy is prescribed, which involves removing the affected gland. Next, chemotherapy sessions are prescribed.
Preventive actions
As a preventative measure, it is recommended to undergo a breast ultrasound once a year.
The only effective way to prevent the formation of pathological discharge from the mammary glands is to undergo regular preventive examinations:
- Consultation with a mammologist at least 1 year a year.
- At least 1-2 times a year, if necessary, conduct an examination with a gynecologist more often.
- Mammography. It is recommended for women over 35 years of age to be performed at intervals of 2 years.
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the mammary glands is performed annually for nulliparous women or up to 35 years of age.
Additionally, you can conduct a complete preventive medical examination, which will allow you to identify serious diseases at the initial stages of development. Early diagnosis significantly increases the likelihood of successful recovery and reduces the risk of complications.
How does discharge occur?
Milk Ducts
Women's breasts contain milk ducts, which are located between the fibrous and fatty tissue. Each canal has an opening at the top of the nipple. All women have an individual number of ducts, but the maximum number can reach up to fifteen. Through the milk ducts, not only milk and colostrum are produced, but also physiological secretion.
In the absence of diseases or the influence of external negative factors, the following condition is inherent in whitish, transparent discharge from the mammary glands:
- scanty and abundant;
- thick and watery;
- viscous or slimy.
Any uniform consistency of secretion from the canals is normal, but only against the background of a transparent shade of liquid and a small volume. If there is too much discharge, it is not recommended to postpone a visit to the mammologist.
For a certain condition, there are indicators of the norm of physiological secretion:
- Scanty, thick (one or two drops). It is noted when pressing on the chest in young girls and nulliparous women a few days before menstruation and during increased sexual arousal.
- Not very abundant, liquid. Characteristic of older women and women who have given birth, but the appearance of thick liquid is possible.
- Viscous. Colostrum occurs during gestation, breastfeeding, and for several years after cessation of lactation (individual indicator).
Competent diagnostics
Pathological processes in the mammary gland are the sphere of influence of the mammologist. When contacting him, you will be assigned:
- mammography;
- microscopy and culture of breast discharge;
- ultrasonography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- CT;
- clinical blood test;
- cytological examination;
- tests for the level of various hormones in the body;
- radiography;
- ductography;
- biopsy, etc.
These diagnostic methods allow you to examine the structure of the mammary gland, assess the degree of its functionality, identify the presence of an inflammatory or infectious process, and also eliminate the risk of developing a cancerous tumor.
In addition, the doctor will listen to the patient, analyze her complaints, trace her medical history, and find out about cases of malignant neoplasms in the woman’s family.
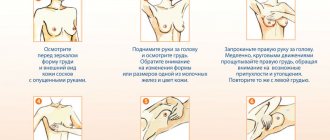
He will then conduct a thorough contact examination of the breast. The concentration and appearance of the discharged fluid will be assessed, as well as the presence of blood in it. The specialist will carefully examine the condition of the breast itself. First of all, he will check for compliance with the norm the size, shape, color, type of nipple, its color and the severity of any changes.
If there are nodules, lumps or painful tumors in the patient’s mammary gland, he will conduct a differential diagnosis.
After lactation
The non-dairy nature of fluid from the nipples after a woman has stopped breastfeeding is characterized by the following characteristics:
- The first months. The appearance of milk is allowed, the production of which should disappear on its own after 2-3 months. It is advisable to gradually wean the baby from breastfeeding.
- One year later. Some women may experience fluid from their nipples for up to a year. In some cases, the doctor prescribes special medications (Bromocriptine, Parlodel, Dostinex).
There is no need to panic if fluid comes out when you press on your nipples after feeding. For some time, prolactin is produced in large quantities, so the appearance of white discharge from the nipples will be noted until the body gradually returns to prenatal normal.
Main manifestations
The main manifestations of mastopathy include:
- green discharge from the glands;
- spotting (in advanced stages);
- aching, dull pain before the onset of menstruation;
- breast swelling;
- compactions that can be detected upon palpation;
- increase in the size of lymph nodes.
Mastopathy is a benign change in gland tissue that is directly dependent on neurohumoral regulation. This means that the factors in the development of this disease are both pathologies caused by disturbances in the functioning of nervous regulation (neuroses, stress, depression), and changes in the hormonal balance and homeostasis of the body.
Causes of discharge
The causes of yellow discharge from the mammary glands when pressed can be due to many factors. Secretion in pregnant women is considered safe during the entire period of pregnancy and after the birth of the child. In the first weeks of pregnancy, colostrum may appear from the nipples, which sometimes takes on a yellowish tint. After childbirth and complete completion of feeding, lactation continues for three years due to the production of a hormone such as prolactin.
After an abortion or miscarriage, discharge may also appear due to hormonal imbalance in the body. When hormones return to normal, secretion stops. Hormonal changes provoke the formation of fluid in the breasts several days before menstruation. It is usually transparent in color, there is no smell and does not cause trouble. The nature of the discharge is determined only by a mammologist after studying the tests and symptoms. A clear fluid may be released when a woman is aroused. This is normal. Adolescents face this problem during puberty, when scant secretion from the mammary glands appears.
The norm is a transparent discharge that appears in parallel with the following actions:
When blood pressure drops, clear fluid may appear from the mammary glands. Mammography and taking antidepressants are two more provocateurs of discharge. All this does not go beyond the norm if there is no pain.
All causes of discharge from the mammary glands are divided into two main groups: physiological and pathological. Physiological causes include those causes that are not symptoms of any disease. These include pregnancy, in the initial stages a transparent substance appears from the nipples, and at a later stage the secretion becomes white, colostrum is added to it.
Physiological reasons
Stopping breastfeeding is also a physiological cause of secretion from the mammary glands. Changes in a woman's hormonal levels can also cause discharge from the breasts, especially during puberty in girls, before menstruation, and in women during menopause. The formation of secretion from the breast is possible due to irritation of the nipples during arousal or tight underwear, which will stop after the cause of stimulation is eliminated. The use of drugs that provoke an increase in prolactin also causes discharge from the mammary glands. Sometimes taking birth control affects the release of fluid from the nipples.
Pathological causes
Pathological discharge is more serious in nature, and therefore requires the attention of a specialist to this problem and further treatment of the disease. They may be the following pathologies or diseases:
- Ectasia or inflammation of the milk ducts, when thick secretions block the milk ducts and cause them to become inflamed. Instead of treatment, surgery is required.
- Mastitis is accompanied by the release of purulent fluid from the mammary glands, and the melting of the mammary tissue occurs. Treatment is only surgical.
- A breast abscess occurs when an infection gets through cracks in the nipples or trauma to the breast. The cause may also be stagnation of milk in the breast due to incomplete expression, or hypothermia of the mammary glands. With this disease, purulent accumulations form, which collect in capsules and, when pressed on the mammary gland, come out.
- Injury to the mammary gland may be accompanied by bloody secretion, provided the skin is intact.
- Intraductal papilloma is a type of benign tumor. It is characterized by brown discharge and is treated surgically.
- Paget's disease is a form of breast cancer associated with a change in the structure of the nipple, in which secretion from the breast is possible and the mammary gland is removed.
- Galactorrhea is a pathology caused by hormonal imbalance. With it, the fluid output is similar to breast milk.
- Fibrocystic mastopathy provokes the formation of cysts in the mammary glands. The disease often develops into cancer and is treated conservatively. Green, brown and black secretions may appear from the nipples.
- Breast cancer is an oncological disease characterized by the appearance of dense areas in the breast and enlarged lymph nodes.
When should you see a doctor?
There are a number of symptoms, if they occur, you should immediately contact a specialist:
- discharge bothers you for more than two days;
- they contain an admixture of blood;
- the secretion comes out of only one mammary gland;
- the discharge has a thick consistency;
- peeling appears on the skin of the nipple;
- loss of symmetry (increase in size, formation of dense knots);
- the color of the nipple and the area around it changes;
- pain appears in the chest.
Discharge from the mammary glands when pressed, as well as any changes in this area should not be ignored. Timely visits to the doctor, diagnosis, and therapy will help avoid complications and serious illnesses.
Prevention
To prevent the development of breast diseases it is necessary:
- Maintain optimal body weight and daily physical activity
- Maintain proper diet and sleep
- Avoid blows, bruises, cuts, punctures and other damage to the chest and décolleté area.
- Do not neglect natural feeding
- Give up bad habits, minimize the number of stressful situations
- Limit from excessive use of hormonal drugs
- Be examined by a mammologist twice a year
It is equally important to regularly self-palpate the glands. If there are neoplasms, they can be most clearly felt during menstruation. In everyday life, it is better to use comfortable underwear made of natural fabric. The bra should support the breasts, not compress them.
The listed recommendations have a positive effect on hormonal levels, help strengthen the immune system, and minimize the risk of pathological discharge from the mammary glands.
The development of female breasts begins during puberty and is closely related to the ratio of hormones such as estrogens, progesterone and prolactin. Milk production begins in the ducts and lobules of the mammary gland during pregnancy. Each nipple has holes through which it comes out. If discharge of a different type appears from the mammary glands, then special attention must be paid to this. Often this phenomenon is a sign of a serious illness. The color and smell of the released liquid matters. A mammologist will help determine the cause of the discharge.
- Diseases that cause nipple discharge
- Types of discharge from the mammary glands
- What to do if there is discharge from the nipples
- Diagnosis of diseases
- Prevention of breast diseases
Early discharge
But there are patients in whom yellow discharge from the breast is recorded at an earlier date - at the fourteenth or sixteenth week. But there have been cases where it is likely that a clear and liquid secretion will appear in an even earlier period of pregnancy - in the fifth or sixth week. Such a physiological process, given the woman’s condition, is absolutely normal, so there is no need to panic.
Prevention of breast diseases
For the purpose of prevention, every woman should be examined by a mammologist once a year. It is also recommended to regularly conduct preventive gynecological examinations and promptly treat diseases of the endocrine system.
Breast self-examination plays an important role, which should be performed once a month. It allows you to detect lumps and external changes in the condition of the mammary glands at an early stage.
It is necessary to avoid hypothermia and chest injuries, stress, and uncontrolled use of medications.
Video: How to do a breast self-examination
The mammary glands take part in lactation and are therefore important for any woman. Discharge from them is either a normal condition or a sign of pathology, judging by the state of health. Yellow discharge from the mammary glands when pressed is considered more of a deviation than normal. Especially if they are painful and bring other changes in the overall picture. In some cases, such symptoms can be observed in men and adolescents; they mean that there is an inflammatory process or some kind of abnormality in the mammary glands.
Purulent mastitis
This is an inflammatory pathology of the mammary glands with damage to interstitial or glandular tissue. This disease manifests itself as hyperthermia, swelling and tenderness of tissues, chills, and the formation of cavities in the chest with pus. The disease develops as a result of intensive proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms in the tissues of the gland. In most cases, inflammation is caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Pathogens can also be Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli, streptococci, tuberculous mycobacteria, and enterobacteria. The main complaints of patients are that their chest hurts and their temperature rises. Green discharge from the breast also occurs when pressure is applied.
What could it be?
The first alarming symptom that indicates a possible disease is discharge from the mammary gland, which occurs when pressed and independently.
The causes of discharge are:
- Physiological: at birth - engorgement of the glands with the release of colostrum, the period of pregnancy and lactation, when the gland produces milk, residual discharge after the end of feeding.
- Pathological—hormonal disorders in the body, age-related changes, inflammatory diseases of the mammary glands, tumors.
Diagnosis of diseases
Before the examination, the doctor finds out how long ago the discharge appeared, whether it is formed constantly or periodically, whether the woman has pain, whether there have been injuries to the breast, whether the woman has used hormonal drugs.
The diagnosis is established by palpation of the mammary gland, ultrasound, mammography, ductography (X-ray using a contrast agent injected into the ducts). The most accurate results are obtained when examined 2-3 days after the end of menstruation. In the second phase of the cycle, breast swelling occurs, which causes errors in the results.
If oncology is suspected, a puncture is performed (sampling of fluids or tissues from the affected area of the gland). The contents are examined under a microscope to detect atypical cells.
Video: Diagnosis of breast diseases
General information
Nipple discharge occurs as a result of the formation of secretory fluid in the milk ducts. This can occur both during normal physiological processes and during various pathological conditions of the body.
The fluid appears spontaneously or when the nipple is squeezed. This depends on the individual structural features of the mammary glands of each woman. The discharge may occur in one gland or both. Their consistency can be thick or watery. Colored discharge with an unpleasant odor requires special attention.
Types and nature of discharge
Discharge from the nipples outside of gestation and lactation indicates pathology of the mammary glands
Based on the color of the secretion released from the nipples, the doctor is able in most cases to guess the correct diagnosis and stage of development of the disease. Types and nature of discharge:
- The green shades of the secreted secretion are given by pus, which is actively secreted during the development of mastitis.
- Brown discharge indicates the development of a tumor or cyst in the mammary gland. If the liquid has a rich and dark shade, this indicates a large size of the neoplasm that has damaged the capillaries.
- Some women may experience small amounts of transparent masses before menstruation; this is considered normal.
- The yellow or cream-colored secretion is actively produced and secreted after childbirth and in the first days of motherhood.
This is colostrum. If a yellow secretion is released before menstruation and is accompanied by painful sensations, the development of mastopathy can be assumed. Black discharge from the nipple occurs mainly in stages 3-4 of breast cancer - Black color indicates the neglect of the condition and the disintegration of a malignant neoplasm (breast cancer).
- Interspersed with blood in the secretion indicates the development of malignant tumors or damage to blood vessels against the background of the growth of a benign formation.
- Purulent masses are released during the development of the inflammatory process inside the ducts of the mammary glands, and are often observed with mastitis. Such discharge with bloody patches is dangerous; in most cases, this indicates the development of malignant tumors.
The amount of secretion secreted can be insignificant or abundant when a woman needs to use special sanitary pads for her breasts.
Do not squeeze the contents out of the breast; this can injure the delicate tissue of the mammary glands and increase secretion production.
Negative symptoms of secretion formation
In order not to miss the initial stage of a serious illness, you should be attentive to your own health. The following signs should alert you:
- If six months after the baby has been weaned, yellowish drops spontaneously appear from the breast, although the woman is sure that there is no pregnancy.
- If a girl has never been pregnant, and she has foul-smelling colostrum or discharge of a greenish, brownish hue, mixed with blood or pus.
Any pain or discomfort should alert a woman. This condition can develop due to the inflammatory process in the tissues and ducts of the breast.
The liquid may be released spontaneously or only when pressed. In the presence of abundant spontaneous discharge, a benign tumor of the pituitary gland may be detected. With mammary duct papilloma, the discharge sometimes resembles colostrum in appearance.