Stagnation of bile (cholestasis) occurs for many reasons. Tumors, stones, and functional disorders can become obstacles to the secretion. Stagnant processes are not the norm. Long-term bile retention leads to irreversible changes in the composition of the secretion and structure of the gallbladder, and after a few years to cholelithiasis, cirrhosis or fibrosis of the liver. That is why it is important to listen to your body, and if signs of bile stagnation appear, consult a doctor.
Functions of bile in the human body
Bile production occurs in the liver, but most of it is stored in the gallbladder, which holds 30 to 60 ml of bile. Sometimes it is concentrated, and its content increases from 5 to 20 times.
Bile performs the functions:
- Digestive . Helps complete absorption of fats, to some extent proteins and carbohydrates. Bile salts break down fats into small particles, which creates good conditions for the work of the lipase enzyme, which speeds up the digestion process.
- Activator . Bile salts act as an accelerator for water-soluble enzymes.
- Solvent . Serves as a good medium for the interaction of fats and fat-breaking enzymes.
- Absorbent . Helps absorb various substances due to the actions of bile salts.
- Suction . Fats are made soluble in the watery contents of the intestinal canal and become suitable for absorption. Iron, calcium, vitamins are digested and absorbed faster with the help of bile salts.
- Outputting . With the help of bile, heavy metals and bile pigments are removed from the body.
- Stimulating . Bile salts stimulate peristalsis.
- Choleretic . Bile acts as its own stimulant. Its salts are the most powerful choleretic agents. They are absorbed from the intestines, transported to the liver and stimulate further bile secretion.
Bile helps maintain a suitable pH of the contents of the duodenum, neutralizes the acidity of the stomach, and prevents the harmful effects of acids on the mucous membrane.
Prevention
Measures to prevent bile stagnation include following the rules of a healthy diet and an active lifestyle. Walking for 40 minutes a day will reduce the risk of congestion several times. For the purpose of prevention, it is necessary to visit a gastroenterologist annually. Early diagnosis of abnormalities will allow timely treatment to begin and prevent the disease from progressing.
Diet and nutrition
You can take diet No. 5 as the basis for your daily diet. This is a complete and balanced diet, excluding large amounts of fat, salt, fried foods, and alcoholic beverages. The products used as part of the diet are beneficial for the liver, are easily digestible and do not cause spasm of the walls of the bladder and ducts.
This includes dietary meat, lean fish, sweet fruits, and low-fat dairy products. Despite the benefits of fresh vegetables, you should not eat them in large quantities. This can cause stool retention and place additional stress on the liver. The recommended drinks are weak tea and rosehip decoction.
Exercises for bile stagnation
In the absence of physical activity, all processes in the body slow down, including the excretion of bile. To prevent bile stagnation, you need to perform simple exercises:
- turns the body in different directions;
- alternately bending the legs at the knees and raising the opposite arm to the elbow;
- in a lying position, pulling your bent legs to your chest.
It is not advisable to bend over; sudden movements can deform the gallbladder. Movements must be performed smoothly, at a slow pace.
Massage for bile stagnation
A specialized treatment procedure is prescribed by a doctor after a detailed examination of the patient. You can use self-massage techniques on your own. A kind of internal massage is performed using exercises.
To do this, you need to lie on your back, bend your knees. Place your hands on your stomach, while protruding (inhale) and retract the anterior abdominal wall (exhale). Regular implementation of this exercise and other recommendations improves the flow of bile through the biliary tract and prevents stagnation in the gallbladder.
https://youtu.be/2IjeFhJv_hA
Causes of bile stagnation
Cholestasis is a phenomenon in which bile cannot pass from the liver to the duodenum. The most common cause of cholestasis is gallstone disease, in which stones form in the gallbladder or its ducts.
The second most common cause is a kink in the gallbladder. It can be congenital or acquired. The deformed organ is not able to perform its functions in full and cannot excrete the entire volume of bile. In third place is parasitic liver damage. With helminthic infestations, when roundworms enter the biliary tract, the outflow of bile is disrupted.
Other reasons:
- Duodenal dyskinesia. It occurs as a result of a violation of the tone of the bile ducts or gallbladder.
- The influence of stress, neuroses, disorders in the autonomic nervous system.
- Dyskinesia of the gallbladder.
- Dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi.
- Pregnancy.
- Binge eating.
- Cholangitis.
- Alcoholism.
https://youtu.be/iZgEt0xDvbM
What is the danger of bile stagnation
Bile plays an important role in the digestion process. It promotes the breakdown and digestion of fats received from food, activates pancreatic enzymes, reduces the acidity level of gastric juice, without it fat-soluble vitamins are not absorbed.
When the flow of bile into the duodenum is disrupted, excess cholesterol is retained in the body, provoking the development of atherosclerosis. Failure of glycogen synthesis from glucose becomes a prerequisite for the appearance of diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
Stagnation of bile in the gallbladder causes inflammation of this organ, often triggering the formation of sand and stones. If cholestasis is not treated in time, it will provoke other pathologies:
- dyspepsia associated with insufficient breakdown and digestion of food;
- cholecystitis, turning into cirrhosis of the liver - due to the development of bacterial microflora;
- osteoporosis and vitamin deficiency due to insufficient absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D).
Prolonged stagnation of bile leads to an increase in the level of bilirubin and its re-entry into the blood. The resulting bilirubinemia causes intoxication in the body.
Types of cholestasis
In medicine, there are 2 types of cholestasis:
- Intrahepatic. The etiology of the development of the disease is located inside the liver.
- Extrahepatic. This type is based on mechanical disorders of the extrahepatic ducts.
Cholestasis can have an acute stage or take a chronic form.
Intrahepatic cholestasis has its own characteristics and develops for the following reasons:
- acute hepatitis;
- alcoholic liver disease;
- primary biliary cholangitis;
- viral hepatitis B or C;
- taking medications that affect the liver;
- oral contraceptives;
- increased hormonal levels during pregnancy;
- development of cancer affecting the liver.
Extrahepatic development occurs due to:
- stones in the bile duct;
- narrowing of the bile duct;
- pancreatic cancer;
- cancer in the bile ducts;
- pancreatitis.
Causes
Stagnation of bile can be caused by a mechanical obstruction:
- stones blocking the ducts;
- enlarged lymph nodes, which are located at the gates of the liver;
- a tumor localized in the pancreas or near the duodenal papilla;
- common bile duct cyst;
- swelling of the walls of the ducts due to inflammation;
- accumulations of helminths during parasitic infections.
The most common cause of cholestasis is alcoholic liver damage and drug intoxication caused by long-term use of toxic drugs. Congestion accompanies diseases that impair the motility of the biliary tract:
- viral hepatitis;
- biliary dyskinesia;
- duodenal diverticula;
- cholangitis, cholelithiasis;
- hepatic artery aneurysm;
- Caroli syndrome;
- bending of the gallbladder;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- Mirizzi syndrome;
- sepsis;
- Byler's disease.
A greater risk of cholestasis occurs when infected with bacterial infections caused by endotoxins.
Risk factors
In women, stagnation of bile provokes pregnancy. In later stages, the gallbladder is not completely emptied, resulting in bile stagnation. Contraceptive drugs also have a negative impact.
Other predisposing factors are:
- transition to parenteral nutrition;
- condition after liver transplant surgery;
- heart failure with damage to the right ventricle;
- immunodeficiency due to HIV infection;
- blood diseases;
- disturbances of intestinal microflora.
People who violate the principles of proper nutrition and lead a sedentary lifestyle are at risk.
How does cholestasis develop?
Cholestasis is a decrease or cessation of bile flow. When the disease occurs, the movement of digestive fluid produced by the liver into the duodenum is disrupted. When the flow of bile stops, pigment bilirubin goes into the bloodstream and accumulates there, which is why cholestasis develops.
Normally, bilirubin combines with bile in the liver and passes through the bile ducts into the digestive tract, where it is excreted from the body. Most bilirubin is excreted through feces, and less through urine.
Diagnostic measures
Cholestasis syndrome in children and adults is difficult to identify due to weak signs at the initial stage. Patients consult a doctor when bile stagnation is already long-term or complicated. After the interview and examination, the patient will have to undergo tests and undergo a series of instrumental examinations. Measures for diagnosing biliary stasis include:
- Blood test for free bilirubin and other biochemical indicators of liver function.
- Urine test for urobilin.
- Examination of stool to identify parasites.
- Ultrasound, which allows you to see defects in the structure and functionality of the bile reservoir and its ducts, the presence of sediments and stones.
- X-ray with contrast.
- Duodenal intubation, examining the condition of the sphincters, contractility of the bile ducts. Allows you to study the production of bile and its composition.
Features of bile stagnation in pregnant women
Some women experience itching in their arms and legs during pregnancy. The reason for its appearance is intrahepatic cholestasis during pregnancy, in which a large number of hormones affect the normal flow of bile. Stagnation of bile (symptoms and treatment in adults and pregnant women have their own characteristics) manifests itself in the last trimester, when the growth of hormones reaches its peak.
The gallbladder holds the bile needed to break down fats during digestion. Stopping the flow of bile causes a buildup of bile acids that enter the bloodstream.
This is facilitated by estrogen and progesterone, pregnancy hormones. Women who are pregnant with twins, have liver problems before pregnancy, or have a genetic predisposition to the disease are more likely to experience cholestasis.
The disease creates risks for the unborn child:
- lack of oxygen to the fetus during pregnancy and childbirth;
- the possibility of a stillborn fetus;
- increased load on the child’s liver.
Women with cholestasis should be under close medical attention.
Prevention and prognosis
To ensure that adults and children do not have problems with bile stagnation, the following general preventive measures are recommended:
- maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle;
- rational use of medications prescribed by the clinician;
- complete and balanced nutrition;
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- early diagnosis and complex therapy of ailments leading to such a disorder;
- Regular visits to all specialists for preventive examinations - this is especially necessary for persons with a genetic predisposition to bile stagnation.
Timely detection, adequate and comprehensive therapy, as well as compliance with the recommendations of the attending physician are the key to a favorable outcome of the disease, namely complete recovery or stable remission. The occurrence of complications in the form of cirrhosis, renal failure and internal hemorrhages is extremely rare.
https://youtu.be/h7j7b0GL1SE
Bile stagnation after gallbladder removal
If the gallbladder is diseased or removed, it will not absorb fat and release cholesterol in the required amount. The liver will produce bile, but instead of sending it to the gallbladder for storage, it will send it directly through ducts to the small intestine.
Over time, the body will adapt to the loss of the bladder, but at the initial stage problems arise:
- Postcholecystectomy diarrhea . 20% of people who have their bladder removed develop diarrhea. This occurs due to the large flow of bile that passes through the small intestine. Over time, the process is restored and normalized.
- Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction . After surgery, pain occurs in the upper abdomen, often after eating. The cause is the sphincter of Oddi, a valve found in the small intestine that regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juices. The dysfunction occurs because it does not relax properly. Over time, subject to changes in eating habits, the pain goes away and the passage of bile normalizes.
Symptoms
The severity of clinical manifestations is influenced by several factors, including:
- etiological factor;
- severity of toxic damage to hepatocytes or bile duct cells;
- age category of the patient.
The main symptoms of bile stagnation are:
- constant nausea, rarely leading to vomiting;
- belching with an unpleasant odor;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- pain, heaviness and discomfort in the area under the right ribs;
- sleep disorder;
- heartburn;
- bad breath;
- coating of the tongue with a coating that has a white or yellow tint;
- violation of the act of defecation, namely diarrhea;
- irradiation of pain in the back;
- increased sweating;
- weakness and lethargy;
- cholelithiasis, in which the formation of stones in the gallbladder or bile ducts is noted.
If the disease occurs in the icteric form, then the above symptoms are supplemented by the following signs:
- acquisition of a yellowish tint by the skin, visible mucous membranes and sclera;
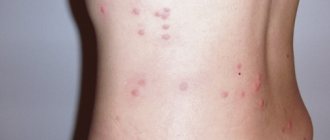
- unexplained rashes;
- skin itching of varying severity;
- discoloration of feces;
- darkening of urine;
- constant thirst.
In cases of chronic disease, the presence of:
- xanthoma and xanthelasm - are small nodules with a yellow or brown tint, localized in the chest, back, elbows, and eyelids;
- skin hyperpigmentation;
- increased bleeding;
- twilight vision disorders;
- decreased bone density, which makes a person susceptible to frequent fractures, including pathological ones;
- muscle weakness;
- male and female infertility;
- significant reduction in body weight.
It is advisable to apply all symptoms to both adults and children.
Yellow color of the face and mucous membranes due to stagnation of bile
Symptoms of cholestasis, where does it hurt?
Symptoms of cholestasis include:
- dark urine;
- light-colored stool with an unpleasant odor;
- general itching.
Stagnation of bile (symptoms and treatment in adults require increased attention) affects the excess of bilirubin deposited in the skin. Changed skin color indicates the appearance of jaundice, and dark urine appears due to excess bilirubin secreted by the kidneys. Itching is caused by bile products accumulated in the skin.
The stool becomes light-colored because the passage of bilirubin into the intestines is blocked. It accumulates a lot of fat because bile can't get into the intestines to help digest it. Fatty deposits in feces create an unpleasant odor.
Symptoms of cholestasis due to the causes of liver disorders:
- altered blood vessels visible in the skin, in the form of stars, cobwebs;
- accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
Symptoms of cholestasis due to causes outside the liver:
- intermittent pain in the upper right abdomen, sometimes radiating to the right shoulder;
- enlarged gallbladder.
Stagnation of bile in adults predetermines other symptoms: loss of appetite, fever.
Symptoms of stagnation
Cholestatic syndrome is always accompanied by manifestations characteristic of impaired liver function. The main symptom that immediately makes you think about the problem is discomfort in the right hypochondrium. When pressed, the liver feels thick and painful. In parallel with this, skin itching occurs. The shade of urine changes - it becomes darker in color, as well as feces, which, on the contrary, becomes lighter in color.
It is possible to determine that the outflow of bile is disrupted by other signs:
- frequently recurring attacks of nausea, belching and vomiting;
- yellowing of the skin, outer membranes of the eyes (in severe cases);
- unpleasant odor from the mouth.
When the gallbladder spasms, bile is thrown into the upper parts of the digestive tract. This leads to attacks of heartburn and bitterness in the mouth. To prevent bile from the stomach from disturbing digestion, doctors recommend refraining from heavy dinners.
Most people who experience cholestasis syndrome complain of lack of appetite, dry mouth, and bitter belching. If the skin condition suddenly worsens - dandruff, allergic rashes or small subcutaneous rashes appear, this sign should also be a reason to pay attention to the functioning of the liver and biliary system.
Consequences and complications
Impaired bile flow leads to the development of chronic liver disease, which makes its treatment difficult. Cholesteric disease can be complicated by osteoporosis, bone fractures, and a deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins. Stagnation of bile leads to abnormally elevated lipid levels, which increases the risk of cardiovascular disease.
The risk of portal hypertension increases, which leads to varicose veins of the esophagus, stomach, cirrhosis of the liver, and enlarged spleen.
Symptoms
Stagnation of bile negatively affects the condition of the entire digestive tract. But cholestasis is usually detected in the later stages, when the bile becomes thick and complications develop. After all, the pathology progresses slowly, and the symptoms are often similar to those of other diseases. At first, the patient feels a slight decrease in performance, drowsiness, absent-mindedness, and a slowdown in digestion processes.
Other signs of bile stagnation gradually appear:
- decreased appetite;
- the appearance of bitterness in the mouth;
- heartburn;
- nausea, belching or vomiting;
- bowel dysfunction;
- the stool becomes lighter and has a putty-like consistency;
- darkening of urine;
- increase in liver size;
- yellowing of the skin, characteristic color of the whites of the eyes;
- itching, especially severe on the skin of the hands and feet;
- sleep disturbance;
- aching pain in the right hypochondrium;
- attacks of sharp pain in the liver.
The main symptom of bile stasis is yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes.
Diagnostics and examinations
When diagnosing cholestasis in people, the doctor tries to determine whether the cause is in the liver or outside the liver based on symptoms and physical examination findings.
Diagnosis stages:
- Doctor's assessment.
- Blood analysis.
- Visual test using ultrasound (if the results of the blood test reveal abnormalities).
- Liver biopsy (if necessary).
Elevated levels of bilirubin, cholesterol, and fatty acids indicate the presence of a disease, but not the cause of its occurrence. An ultrasound examination is done if blood results reveal abnormalities, and computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging may also be performed in addition to or instead of ultrasound.
If the cause of cholestasis lies in the liver, then a biopsy is suggested. When bile ducts are blocked, accurate imaging is required.
To do this, follow the following steps:
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. During the procedure, a flexible viewing tube is inserted through the mouth into the small intestine, through which a contrast agent is delivered to the bile, pancreas, and ducts. X-rays are then taken.
Stagnation of bile. Having identified the symptoms in the hospital, the doctor can prescribe treatment.
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography . MRI of the biliary tract is performed with a special method, in which the fluid in the ducts appears light, and the surrounding tissues appear dark.
- Endoscopic ultrasonography . Using an ultrasound probe passed through the mouth into the small intestine, a complete internal picture is obtained.
Diagnostics
Stagnation of bile in the liver requires a whole range of laboratory and instrumental diagnostic measures. However, first of all, the gastroenterologist should independently perform several manipulations:
- study the medical history - this will help in finding the pathological cause of bile stagnation;
- analyze your life history - this should include information regarding nutrition, addiction to bad habits and taking medications;
- conduct a thorough physical examination, which must necessarily include palpation of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity, while the doctor pays attention to the patient’s reaction when touching the area of the right hypochondrium. In addition, it is very important to assess the condition of the skin, mucous membranes and sclera;
- interview the patient in detail - this will allow the clinician to draw up a complete symptomatic picture.
The most diagnostic information is provided by the following laboratory tests:
- blood biochemistry;
- general clinical analysis of blood and urine;
- tests to determine enzyme activity;
- microscopic examination of biopath;
- coprogram.
However, the basis of diagnosis is instrumental procedures, including:
- endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography;
- ultrasonography of the liver and gallbladder;
- percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography;
- MRCP and PET;
- biopsy;
- CT and MRI.
MRCP
Stagnation of bile should be differentiated from those diseases that have similar symptoms:
- viral and drug-induced hepatitis;
- cholangitis and pericholangitis;
- intrahepatic formations;
- cholangiocarcinoma;
- choledocholithiasis;
- parasitic infestations;
- atresia of the bile ducts;
- primary sclerosing cholangitis;
- metastasis of cancer to the liver or gallbladder.
Treatment of cholestasis in adults
Therapy is prescribed depending on the type of cholestasis:
- If the bile ducts are blocked, endoscopy or surgery is prescribed.
- When bile is blocked in the liver, various treatments are prescribed depending on the underlying cause.
- Cholestyramine is prescribed to relieve itching.
If the cause of the disease is hepatitis, then cholestasis disappears after treating the hepatitis with antiviral drugs. If medications are the suspected cause, they are discontinued. People with cholestasis are advised to avoid consuming substances that are toxic to the liver, such as alcohol and medications.
If the liver is not severely damaged, then it is suggested to take vitamin K, which improves blood clotting. Calcium and vitamin D supplements are often prescribed for cholestasis. The first-line drug for cholestatic pruritus is cholestyramine.
For the treatment of cholestasis, hepatoprojectors of animal and plant origin are used:
| Name of the drug | Mode of application |
| Progepar | Use 1–2 tablets. 3 times a day |
| Hepatosan | The dosage regimen is prescribed by the doctor, depending on the disease |
| Ornithine | Prescribed for hepatitis, cirrhosis, the dosage is prescribed by the doctor |
| Phosphogliv | Wide spectrum of action, prescribed 2 capsules 3 times a day, treatment lasts up to 6 months. |
| Karsil, herbal preparation, active substance – milk thistle | Prescribed 3 times a day, 4 tablets. |
When treating pregnant women, all drugs should be prescribed only as directed by a doctor. Bisphosphonates have been used successfully to treat bone mineral density, which is impaired in cholestasis.
Complex treatment
When treating the problem, diet No. 5 is recommended.
A set of therapeutic measures is prescribed by a doctor after accurately identifying the causes and characteristics of the pathology. Treatment of bile stagnation is aimed at improving its outflow, normalizing the contractile activity of the ducts and the functionality of the gastrointestinal tract, and reducing the influence of provoking factors. Medicines, herbal remedies, and physiotherapy methods are used. It is mandatory to follow diet No. 5. If conservative therapy does not alleviate the patient’s condition, then drainage, dilation of the ducts, and surgical stenting are performed, often by laparoscopy. In severe cases, it is recommended to remove the gallbladder.
Medicines for cholestasis
It will not be possible to eliminate bile stagnation without medication. The doctor prescribes drug treatment individually, based on the clinical picture of the disease and the presence of background ailments and contraindications in the patient. Funds are prescribed in combination. The regimen includes the following drugs:
- Choleretic: Allohol tablets;
- Holosas syrup.
- "No-shpa";
- "Levomycetin";
- "Gepabene";
- "Galstena";
Massage sessions
Therapeutic abdominal massage will only bring benefits.
To prevent bile from stagnating and spasms disappear, you can massage the abdomen. The movements are concentrated mainly in the place of projection of the gallbladder - the area of the right hypochondrium. The session consists of stroking, rubbing, vibration movements in a clockwise direction and light pressure. Massage is prohibited in case of inflammation, the presence of stones, tumors, digestive dysfunctions, high temperature, pain.
Massage and gymnastics are permissible only in the remission phase of the disease, and if discomfort occurs, the procedures should be stopped.
Therapeutic exercise and diet
A sedentary lifestyle reduces the dynamics of the biliary tract. Light daily exercise combined with breathing will help improve the muscle tone of the abdomen and bile reservoir and help normalize the outflow of liver secretions. Among them are turns of the body, slight bends, lifting the legs from a position lying on the left side, “scissors”, walking in place with raising the knees, rolling from heels to toes.
A diet for stagnation of bile in the gallbladder excludes fatty, fried, spicy, salty foods, baked goods and alcohol from the diet. Porridge with water, lean fish and meat, legumes, and fermented milk products are shown. The diet should be enriched with fruits and vegetables, nuts, vegetable oils, and seafood. It is advisable to eat small portions of 4-5 rubles. in a day. You can drink green and weak black tea, still mineral water. The same diet is indicated for a removed gallbladder.
Folk remedies against bile stagnation
Traditional medicine offers an infusion of oats to treat the problem.
Alternative medicine recipes will help alleviate the condition of a patient with cholestasis. To improve bile flow and eliminate inflammation, decoctions of oats, knotweed, immortelle, mint, corn silk, sweet clover, arnica, rose hips, and barberry root are used. You can purchase special herbal infusions at the pharmacy. Bile is better removed if you drink apple, carrot or beet juice half an hour before meals and take mummy tablets dissolved in water for 2 weeks. To improve the patency of the bile ducts and prevent parasitic infestations, traditional healers recommend eating pumpkin seeds. You can remove bile from the body at home using the blind probing method. On an empty stomach, the patient drinks a solution of magnesia and lies down on a heating pad placed under the left side.
Diet
If liver function is impaired, fractional meals are required. Fats should be excluded from the diet, especially refractory fats, smoked meats, sausages, semi-finished products, and canned foods.
Products that need to be included in the diet:
- Yogurt.
- Spinach
- Blueberries, cherries, tomatoes, sweet peppers, pumpkin.
- Sea kale, green leafy vegetables.
- Red wine or red grapes.
Diet example for 1 day
Breakfast:
- 3/4 cup oatmeal.
- 1 medium sized banana.
- 1 cup skim milk.
- Freshly brewed coffee.
Dinner:
- 2 slices whole grain bread.
- 85 g turkey breast.
- 30 g low-fat cheese.
- A slice of tomato with green leaf lettuce.
- 1 apple.
Dinner:
- 100 g tilapia.
- 150 g brown rice with 1 teaspoon oil.
- A handful of spinach.
- 2 crackers.
- 1/2 cup low-fat yogurt with fruit of choice.
Snack:
- 28 g almonds.
- 1 cup low-fat (1%) cottage cheese
- 10 low-fat crackers.
What complications can there be from the disease?
If the outflow of bile is disrupted, normal and complete breakdown and absorption of fats does not occur. They enter the bloodstream in an unprocessed form, which will lead to disruption of the functions of various organs, primarily to the development of diabetes. The development of atherosclerosis is also often caused by the accumulation of bile, since it contains cholesterol. During stagnation, excess of this substance is not removed from the body, causing sclerotic changes in the condition of the blood vessels. When bile stagnates in the gallbladder, the likelihood of stone formation in this organ increases.
Currently reading: What is gallbladder dyskinesia - causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
If bile is not removed in a timely manner, the gallbladder and liver ducts suffer; as a result of inflammation, liver tissue changes in them with the development of necrosis in certain areas of the parenchyma. Delayed medical care and lack of treatment can lead to conditions such as:
- The development of gastritis as a result of the accumulation of bilirubin and general intoxication of the body.
- Vitamin deficiency - due to metabolic disorders.
- Provoke diseases of cholecystitis and cholangitis.
- Cause cholelithiasis.
- Lead to a serious complication in the form of liver cirrhosis.
- Impair liver function and lead to liver failure.
- Disturbance in the condition of the skeletal system with the development of osteoporosis.
- The last stages of the disease with the occurrence of stagnation of bile in the gallbladder can lead to death.
To prevent the development of such complications, it is necessary to follow the recommendations of specialists and follow all the rules for preventing such changes in the gallbladder.
Massage
Massage is contraindicated in the acute form of the disease, with pancreatitis. Massaging should begin from the back area. Basic techniques: rubbing, stroking, kneading the body. The back is massaged for at least 15 minutes, then proceed to the surface of the chest.
Movements should be soft and gentle. Massage this part for at least 5 minutes, and then move to the epigastric area. Basic techniques: stroking, careful, gentle rubbing. If there is no pain, you can massage the abdominal muscles.
There are several special massage techniques:
- Methodology according to Ogulov.
- Dubrovsky massage.
- Visceral massage.
Symptoms and therapy
At an early stage, the disease manifests itself with typical symptoms inherent in gallbladder diseases. The chronic form is expressed specifically:
- bloating;
- temperature increase;
- severe pain on the left side.
Therapy is carried out depending on the symptoms. Spasms and pain are relieved, medications are prescribed to improve the outflow of mucus. The doctor recommends physiotherapeutic methods and a set of special physical exercises. In rare cases, surgery is performed to correct the situation.
Tubazh with mineral water
The procedure is not recommended for cholelithiasis, hepatic colic, or severe liver damage. The procedure is carried out in the morning, on an empty stomach.
Methodology:
- Drink 250 ml of still mineral water. To enhance the effect, you can add 1 tbsp. l. vegetable oil.
- Lie on your right side, place a heating pad filled with warm water under your stomach.
- After 1.5 hours, you should turn over to the other side, leaving the heating pad in its original position.
- Empty your bowels and return to a lying position so that the water completely cleanses the small intestine.
Tubage is carried out no more than once a week. On this day after the procedure, you should not eat heavy, fatty, spicy foods, or drink alcohol.
Stagnation of bile. Treatment of bile stasis with folk remedies
Traditional methods of treatment are acceptable to use, but these are not the main methods for treating bile stagnation.
Top 8 folk methods alleviate the patient’s condition:
- performing abdominal exercises and a special massage method
- drinking a decoction based on mint, rose hips, and corn silk
- the use of anti-inflammatory, choleretic herbs: peppermint, buckthorn bark, watch, St. John's wort, wormwood, immortelle
- drink a decoction of aloe, calendula, ginseng, yarrow, mint, coriander
- tubage
- heated unrefined vegetable oil
- eating a piece of lard
- Beet juice will help remove excess bile
Subscribe to our Yandex Zen channel!
Bile stasis is treated at home in one of the following ways:
- choleretic herbs
- sunflower oil
- salted lard with garlic
- beet juice
- pumpkin seed
- corn silk
Herbs: immortelle, St. John's wort, dandelion roots, corn silk, rose hips are sold in the pharmacy. Prepare and take according to the indicated recipe.
Take 0.5 cups of sunflower oil During the day, drink rosehip decoction.
Lard and garlic are eaten without bread, then the right side is warmed on a heating pad, and a rosehip infusion is drunk throughout the day.
the beets until half cooked and squeeze out the juice. Drink in large sips 30 minutes before meals.
Pumpkin seeds are hulled and consumed raw.
Choleretic drugs
Stagnation of bile (symptoms and treatment in adults require the use of choleretic drugs) is treated with drugs that enhance bile formation and help the release of bile into the duodenum. Depending on the mechanism of their action, anti-inflammatory drugs are divided into two groups: those that enhance the formation of bile and those that promote its excretion.
Allohol
A choleretic drug containing dry bile, dry garlic and nettle leaves, and activated carbon. Contraindicated for people with individual intolerance to components, peptic ulcers, liver dystrophy. During pregnancy and lactation, use only on the recommendation of a doctor.
The drug is taken 3-4 times a day, after meals. The dose is calculated by the attending physician. It is not recommended to take it for more than 3 months.
Nikodin
A choleretic drug that enhances the secretion of bile and facilitates its release into the intestines. The active ingredient is hydroxymethylnicotinamide. Recommended for dyskinesia, cholecystitis, reactive hepatitis. Use with caution for cholestasis. Daily intake from 500 to 1000 mg is divided into 3-4 times.
Hofitol
A herbal preparation containing artichoke leaves. Recommended for hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, cholecystitis, biliary dyskinesia.
It has many contraindications for various types of diseases. The dose depends on the patient's age. During pregnancy, the drug is prescribed strictly as directed by the doctor.
Symptoms of pathology
Stagnation of bile in the gallbladder can go unnoticed for a long time. The intensity of the manifestations depends on the characteristics of the patient’s body and the reasons for the failure of the kinetics of the cystic ducts. Stagnation of bile in a child is most often caused by congenital characteristics, genetics and poor nutrition, helminthic infestations and viruses, although the signs of pathology do not differ from adults. Symptoms of stagnant processes in the bile reservoir:
- itchy skin;
- discoloration of feces;
- dark urine;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- spasmodic or aching pain under the right rib;
- dryness and bitter taste in the mouth;
- belching;
- heartburn;
- nausea and vomiting;
- yellowness of the skin and sclera;
- bad breath.
Homeopathy
Homeopathic medicines are available for the treatment of cholestasis.
These include choleretic agents for the treatment of chronic hepatitis, anti-inflammatory herbal remedies:
- Kumivit.
- Galstena.
- Hepel.
- Polyphytohol.
In treatment, herbal preparations are used containing: peppermint, stinging nettle, licorice. The combination of elecampane root, rose hips and hawthorn fruits, tansy flowers affects metabolic processes in the liver and enhances the choleretic effect.
Reviews
A pathology such as bile stagnation occurs in every fifth adult. This is due to poor nutrition, people’s passion for diets and fast food, an abundance of stress, and a sedentary lifestyle. For many, this pathology is not accompanied by any serious disorders of the liver and gallbladder. Therefore, they use herbal choleretic agents. And not only doctor’s consultations, but also reviews from other patients help you choose them.
Irina I periodically experience pain in the right hypochondrium and indigestion. Since I have chronic gastritis, I take a lot of medications to improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. After an ultrasound, they found biliary dyskinesia. They prescribed the choleretic Ursofalk. I liked the drug, I really feel light after it, my intestinal function has improved.
Tatyana After the diet, she began to notice heaviness in her stomach and pain on the right side. I consulted a doctor, she advised me how to remove bile stagnation. I drank Holosas, Gepabene and began to adhere to proper nutrition. Now I eat little by little 6 times a day. After about a month everything got better.
Lydia A special diet and taking Allochol help me cope with bile stagnation. As soon as I notice that heaviness has appeared on the right side, I immediately switch to dairy and plant foods and drink Allochol. After about 2-3 weeks, there are no longer any signs of bile stagnation.
Surgical treatment
Surgical resolution of cholestasis is carried out using cholecystectomy. Traditional surgery is performed in an open manner. No more than 5–8% of patients are exposed to it.
The rest of the patients undergo surgery using a laparoscopic technique, which provides low trauma, a good cosmetic effect, and postoperative complications rarely occur. To treat patients with obstructive jaundice, percutaneous endobiliary interventions are performed under ultrasound and fluoroscopy control.
Nutrition
Nutritional treatment ranks first in the treatment of cholestasis. To correct the stagnation process, use the Pevzner diet - No. 5. The main goal of such nutrition is to reduce the load on the biliary tract, in particular on the gallbladder and liver.
The principles of diet No. 5 are:
We also recommend reading:
How to treat the gallbladder
- fractional meals - up to 7 times a day in small portions and at the same time;
- prolonged hunger and overeating are prohibited;
- exclusion of fried and fatty foods;
- limiting the intake of hot and cold food (the temperature of food should be no more than 60 degrees and no lower than 45 degrees);
- cooking - only by steaming and in the oven, by stewing and boiling;
- if a crust forms after baking the product, remove it and do not consume it;
- exclusion of alcohol and carbonated drinks from the diet;
- Fermented milk products are only allowed to be consumed if they have a low fat content.
The diet should be complete and balanced. Snacking on the go, abuse of junk food (fast food) are factors that can cause an exacerbation of the disease. To monitor the course of cholestasis, you can keep a diary, in which it is recommended to record the foods introduced into the diet and the body’s reaction to their use.
Forbidden food
If you neglect the principles of a healthy diet during bile stagnation, drug treatment will not bring the desired recovery. It is recommended to completely exclude the following foods from the diet:
- fresh bread, bakery products, confectionery;
- chocolate and products prepared with its addition, ice cream;
- cooking fat;
- sorrel, garlic, onion;
- fermented milk products with a high percentage of fat content;
- rich broth of meat, fish, mushrooms;
- pure mushrooms (fried, steamed, stewed), legumes;
- hard and sharp cheese;
- smoked meats, canned fish;
- fatty meat, fish;
- radish and radish;
- vegetables and fruits with sour taste;
- spices, hot sauce;
- high strength coffee and tea;
- cabbage;
- sausage, sausages.
Despite such a large list of prohibited foods, there are many useful ones that have a positive effect on the body and the course of the disease.
Allowed food
The diet of a patient with cholestasis is compiled on an individual basis. Not only the features of the development of the underlying disease are taken into account, but also concomitant pathological conditions in the body associated with the biliary tract.
Only lean meat is allowed
The following foods should predominate in the diet:
- natural juice, compote, coffee with added milk, unfortified tea, jelly;
- vegetable broth soup with pasta and cereals;
- lean meat (poultry, etc.);
- fruits and vegetables (except prohibited ones);
- honey, jam;
- low-fat cheese, low-fat cottage cheese, sour cream in small quantities;
- bread made from rye or wheat flour (unsweetened dough).
If you adhere to proper nutrition and take medications prescribed by your doctor, you can get rid of stagnation in the bile ducts in a short time.
Traditional recipes for bile stagnation
Stagnation of bile, the symptoms and treatment of which involve the use of herbs, can be treated with the help of choleretic plants.
Dandelion
Dandelion root is a safe natural remedy. It increases urine production, serves as a natural laxative, and cleanses the liver. Young leaves have the greatest healing power. But it is also useful in dried form.
Recipe:
- Plant roots 1 tbsp. Brew in hot water, boil in 250 g of water for 5 minutes.
- Cool, strain, take 3 times a day, ¼ cup, diluted with water.
St. John's wort
Tincture of St. John's wort flowers helps with biliary dyskinesia, hepatitis, and bile stagnation.
How to cook:
- 1 tbsp. l. herbs are poured into 200 ml of water and boiled for 10–15 minutes.
- The settled and strained solution is diluted with water and drunk 1/3 cup every 30 minutes throughout the day. before meals.
Decoction of St. John's wort and immortelle
To prepare the decoction you need:
- Take 4 parts St. John's wort and 4 parts immortelle inflorescences. Fill with hot water.
- Boil for 15 minutes. Then cool and strain.
- Take ¼ glass, diluted with water, 2-3 times a day before meals.
Peppermint
For colic in the liver, you should drink tea brewed with peppermint leaves. Selected, washed leaves are brewed fresh or dried. You can drink throughout the day, 4–5 times.
Corn silk
They have a pronounced choleretic effect. Prescribed for cholecystitis, cholestasis. It is used internally in the form of a decoction, which is prepared from 10 grams of raw materials and 200 ml of water. Take 40 ml every 4 hours.
Oat infusion
Cleansing the liver with oats has been known since ancient times.
To do this, prepare a decoction:
- Whole grains, not flakes, of washed oats are poured into 1.5 liters of boiled water, boiled for 30 minutes.
- It is left to stand and then used as a remedy. You should drink 1 tbsp. half an hour before meals for 1 month.
Camomile tea
Enhances bile formation and is used for cholecystitis and cholestasis. A decoction of chamomile flowers is made at the rate of 1 tbsp. l. for 200 ml of water. Drink ½ or 1/3 glass 3 times a day after meals.
Rose hip
A decoction of rose hips is prepared as follows:
- 100 g of berries are poured into 400 ml of water, boiled for 2-3 minutes, and then left for 2-3 hours. Drink the decoction instead of water throughout the day. For pancreatitis, drinking the decoction is not recommended.
Rosehip extract can be bought at the pharmacy, it is sold under the name Holosas. Helps well with bile duct dyskinesia.
Wild strawberry
The plant helps the body free itself from bile stagnation. An infusion is prepared from the leaves and roots. The plant is poured with boiling water and infused like tea. You can use dry wild strawberries. The tea can be infused in a thermos and drunk several times throughout the day.
Beet
Beetroot juice prevents the formation of gallstones. To do this, beet juice is diluted with carrot juice in a 1:2 ratio. We start drinking with a small dose, 1 tsp, gradually increasing the amount of juice drunk to 120 ml per day.
Sauerkraut juice
The vitamin-rich juice has a choleretic effect. It is taken during the acute period of cholestasis and for prevention. Start drinking juice 1 tbsp. l. per day, gradually increasing the dose to 300 ml. You should drink it before meals, for 2-3 months.
Most adults who do not ignore the symptoms and undergo treatment in the early stages get rid of bile stagnation. In the future, prevention and a healthy lifestyle will help maintain the liver in normal condition.
Author: Belyaeva Anna
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
https://youtu.be/fY5-dmYGyCY
Treatment methods
Therapy begins with eliminating the cause of bile stagnation - conservative treatment of concomitant diseases or surgical removal of obstacles to the outflow of secretions. With any chosen method, a diet is indicated. This is 6 meals a day with a fat limit of up to 40 g per day. It should be balanced and contain at least 120 g of protein. Animal fats need to be replaced with vegetable fats, since they are absorbed in the intestines without bile acids.
Food should be boiled, baked, steamed and always warm. Spicy, fatty, fried foods, and alcohol should be excluded from the menu. Before meals, you can drink decoctions of choleretic herbs and mineral water, but in small quantities. For some patients, the doctor may prescribe tubage. It can be done at home using sorbitol or mineral water.
Operation
Stagnation of bile in the gallbladder or ducts as a result of blockage is a dangerous condition that can lead to serious consequences. If it is impossible to quickly get rid of stagnation without surgery, the removal of bile is restored surgically. The choice of method depends on the reason:
- papillectomy – excision of growths in the area of the duodenal papilla;
- dissection of the bile duct during its stenosis (stricture) eliminates obstruction;
- removal of stones, balls of parasites;
- expansion of the duct with self-expanding stents;
- choledochotomy - opening of the common bile duct with the imposition of a fistula;
- drainage of a cyst or abscess.
If the gallbladder is damaged, it is usually opened or completely removed - cholecystectomy.
Medicines
Medicines for cholestasis are prescribed to remove stagnation of bile and get rid of unpleasant symptoms:
- Hepatoprotectors (Karsil, Ademethionine) - improve liver function and restore its cells.
- Ursodeoxycholic acid preparations (Ursosan, Ursodez), choleretic agents (Allohol) - stimulate the production and excretion of bile.
- Cytostatic agents (Methotrexate) – prevent the division of tumor cells.
- Antihistamines (Tavegil, Suprastin) – relieve itching.
- Antispasmodics (No-Shpa, Papaverine) – relieve pain.
The duration of use and dosage are determined by the attending physician. The use of medications without medical supervision is prohibited.
Folk remedies
At home, you can prepare healing decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs according to folk recipes. They will help eliminate cholestatic syndrome and relieve inflammation. Knotweed, corn silk, yarrow, sweet clover and other herbs can be bought at the pharmacy and brewed like tea. But you shouldn’t abuse them; they can bring not only benefits, but also harm. One remedy can act differently on different organisms, so you should not use them without consulting your doctor.
Juices from apples, carrots, and beets have a good effect. They must be freshly squeezed. The drink may contain one component, but more often they drink a mixture of juices - they can be mixed in equal quantities. For the juice to be beneficial, you need to drink it an hour after eating, but not more than 150 ml. Oat decoction has a good effect. It's easy to prepare: 1 tbsp. l. pour 2 tbsp. boiling water, cook for 30 minutes. Take 20 minutes before meals throughout the day.
What should you not eat if you have bile stagnation?
The main thing in nutrition when bile stagnation is to exclude fried and fatty foods, cold foods and soups. It's better to make friends with a steamer and oven. Since fats cause disease, avoid oils.
- Meat (not allowed)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Pork 17.96 25.14 1.24 294.27 kcal (1231 kJ) Mutton 17.11 17.37 1.29 221.83 kcal (928 kJ) Duck 17.16 27.90 0.64 290.13 kcal (1214 kJ) Goose 19.30 41.20 0.00 447.00 kcal (1871 kJ) - By-products (not allowed)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Liver 19.46 4.10 2.90 119.70 kcal (501 kJ) Kidneys 15.17 3.25 0.56 105.09 kcal (439 kJ) Brain 10.69 7.16 0.46 132.25 kcal (553 kJ) Stomach 21.45 6.90 0.30 106.00 kcal (443 kJ) Language 15.42 12.13 0.91 171.27 kcal (716 kJ) - Fish and seafood (not allowed)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Sturgeon 16.62 10.80 0.02 160.67 kcal (672 kJ) Salmon 20.92 12.32 0.31 189.93 kcal (795 kJ) Beluga 19.48 2.14 0.02 108.40 kcal (453 kJ) Stellate sturgeon 17.45 10.90 0.00 169.25 kcal (708 kJ) Trout 20.22 7.67 0.38 149.72 kcal (626 kJ) Salmon 21.57 12.86 0.63 195.63 kcal (818 kJ) Som 20.52 6.83 11.12 173.50 kcal (726 kJ) Carp 17.90 3.67 0.19 105.85 kcal (443 kJ) Crab sticks 7.69 1.81 10.85 91.54 kcal (383 kJ) Black caviar 22.00 10.58 1.51 189.18 kcal (791 kJ) Red caviar 30.60 13.73 1.35 244.75 kcal (1024 kJ) - Smoked meats, canned food, sausages (not allowed)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Smoked sausage 17.03 39.65 1.97 427.27 kcal (1788 kJ) Raw smoked sausage 19.94 43.66 2.26 499.51 kcal (2090 kJ) Spikes 12.40 27.49 0.44 272.17 kcal (1139 kJ) Sausages 11.07 23.54 2.25 255.21 kcal (1068 kJ)) Doctor's sausage 13.91 21.39 1.43 g 250.36 kcal (1048 kJ) Korean 14.07 33.71 1.04 366.56 kcal (1534 kJ) Stew 14.58 19.29 0.27 238.85 kcal (999 kJ) Saira in oil 18.28 21.02 0.37 256.44 kcal (1073 kJ) Smoked fish 23.45 10.61 0.04 189.89 kcal (794 kJ) Salty fish 28.58 10.55 0.29 213.74 kcal (894 kJ) Pickled vegetables 0.72 0.00 5.40 25.28 kcal (105 kJ) Canned vegetables 3.21 2.85 5.21 76.67 kcal (320 kJ) including green peas Olives and olives 0.99 15.71 1.98 155.43 kcal (650 kJ) Sun-dried tomatoes 6.76 5.60 27.43 182.15 kcal (762 kJ) Canned artichokes 3.37 2.29 10.87 67.00 kcal (280 kJ) - Vegetables, mushrooms (not allowed)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Radish 1.37 0.19 3.81 22.78 kcal (95 kJ) Radish 2.14 0.30 5.83 33.72 kcal (141 kJ) Turnip 1.99 0.46 5.61 28.92 kcal (121 kJ) Onion 2.72 0.45 8.74 44.41 kcal (185 kJ) Garlic 6.67 0.64 23.02 122.53 kcal (512 kJ) White cabbage 1.80 0.05 5.44 27.90 kcal (116 kJ) raw Tomatoes 2.23 1.31 5.23 37.56 kcal (157 kJ) and tomato paste Mushrooms 4.09 2.53 3.95 60.58 kcal (253 kJ) any Eggplant 0.96 0.70 5.58 30.91 kcal (129 kJ) Asparagus 3.67 2.14 4.32 46.09 kcal (192 kJ) Bell pepper 1.30 0.00 7.20 26.50 kcal (110 kJ) after heat treatment - Fruits, berries (not allowed)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Figs 0.70 0.20 12.00 54.00 kcal (226 kJ) Raspberries 2.52 0.68 10.56 53.14 kcal (222 kJ) Cowberry 0.69 0.37 8.73 41.43 kcal (173 kJ) Grape 1.11 0.72 17.50 73.17 kcal (306 kJ) Cranberry 0.86 0.29 13.69 62.90 kcal (263 kJ) Orange 1.64 0.46 9.47 42.34 kcal (177 kJ) Kiwi 1.40 0.99 9.66 52.42 kcal (219 kJ) Lemon 1.27 0.24 5.02 34.46 kcal (144 kJ) Ginger 7.52 5.43 60.33 86.70 kcal (362 kJ) Date fruit 5.62 1.45 57.00 252.21 kcal (1055 kJ) Mandarin 0.80 0.20 7.50 38.00 kcal (159 kJ) Pear 0.40 0.30 10.30 47.00 kcal (196 kJ) Melon 0.87 0.60 8.26 41.02 kcal (171 kJ) Persimmon 0.60 0.30 7.40 33.00 kcal (138 kJ) - Dairy and fermented milk products (not allowed)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Salty cheese 19.50 18.80 0.00 247.00 kcal (1033 kJ) Serum 3.91 0.67 5.36 41.83 kcal (175 kJ) Cream 2.42 19.76 16.39 298.08 kcal (1247 kJ) fat percentage is more than 6% Ryazhenka 2.95 3.43 4.07 64.50 kcal (269 kJ) fat percentage is more than 6% Cottage cheese 15.28 4.35 3.73 121.82 kcal (509 kJ) fat percentage is more than 6% Milk 3.26 3.45 5.53 68.15 kcal (285 kJ) fat percentage is more than 6% - Soups, broths (not allowed)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Fish broth 4.83 0.90 0.32 28.08 kcal (117 kJ) Meat broth 4.70 1.87 0.49 34.19 kcal (143 kJ) Mushroom broth 0.75 0.15 0.45 7.44 kcal (31 kJ) Sorrel soup 2.44 2.74 4.25 43.64 kcal (182 kJ) Spinach soup 3.08 3.79 6.64 50.17 kcal (210 kJ) Bean soup 3.15 2.13 2.71 65.55 kcal (274 kJ) Any okroshka 4.75 1.92 2.11 47.44 kcal (198 kJ) - Flour products (not allowed)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Paste 10.44 7.11 48.23 299.78 kcal (1254 kJ) with any fatty sauces and tomato dressing Pasta 9.60 2.12 56.27 279.07 kcal (1168 kJ) with the addition of products from the prohibited list Fried pies 6.60 9.35 32.20 242.35 kcal (1014 kJ) Puff pastry products 5.86 20.01 38.70 359.78 kcal (1506 kJ) Pastry products 7.20 7.14 45.16 242.76 kcal (1016 kJ) Donuts 6.43 14.25 41.22 320.11 kcal (1339 kJ) fried in oil Pancakes 6.15 8.25 28.09 207.84 kcal (870 kJ) Fresh bread 5.25 2.40 49.05 252.00 kcal (1054 kJ) Pizza 9.77 13.85 24.48 261.83 kcal (1096 kJ) - Cereals, legumes, seeds (not allowed)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Beans 13.70 1.80 33.04 206.48 kcal (864 kJ) Peas 17.14 1.56 40.80 246.44 kcal (1031 kJ) Mash 21.89 1.51 48.93 288.47 kcal (1207 kJ) Chickpeas 17.27 4.89 48.88 303.45 kcal (1270 kJ) Beans 7.62 0.27 12.94 91.11 kcal (381 kJ) Lentils 19.36 1.70 40.03 249.74 kcal (1045 kJ) Nuts 14.79 64.18 11.92 675.68 kcal (2828 kJ) any Sunflower seeds 20.70 52.90 3.40 580.00 kcal (2427 kJ) Pumpkin seeds 23.51 44.60 10.78 549.92 kcal (2301 kJ) - Fats and eggs (not allowed)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Margarine 0.14 60.96 0.31 538.16 kcal (2252 kJ) Melted butter 0.23 76.18 1.35 890.06 kcal (3725 kJ) Palm oil 0.00 99.97 0.00 894.67 kcal (3745 kJ) Unrefined oil 0.01 99.66 0.00 898.47 kcal (3761 kJ) unrefined Salo 2.76 84.43 1.03 771.46 kcal (3229 kJ) Eggs 12.71 11.51 0.70 100.00 kcal (418 kJ) fried - Sauces, spices, herbs (not allowed)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Spinach 2.86 1.78 2.39 21.21 kcal (88 kJ) only as decoration or to add flavor to dishes Rhubarb 0.68 0.06 2.28 15.00 kcal (62 kJ) only as decoration or to add flavor to dishes Sorrel 1.49 0.14 3.81 22.88 kcal (95 kJ) only as decoration or to add flavor to dishes Friese 2.40 2.18 6.98 32.43 kcal (135 kJ) only as decoration or to add flavor to dishes Arugula 2.46 0.67 2.31 26.06 kcal (109 kJ) only as decoration or to add flavor to dishes Ketchup 1.81 0.52 18.48 86.15 kcal (360 kJ) Mayonnaise 1.80 48.89 5.14 473.75 kcal (1983 kJ) Mustard 7.26 8.95 11.83 159.51 kcal (667 kJ) Horseradish 2.70 3.13 11.19 83.24 kcal (348 kJ) Ground black pepper 10.08 3.77 37.08 234.27 kcal (980 kJ) Vinegar 20.00 60.00 8.00 30.00 kcal (125 kJ) Adjika 1.38 3.05 7.82 63.97 kcal (267 kJ) Green onions 2.49 0.08 4.33 20.57 kcal (86 kJ) Chilli 1.82 0.19 8.75 37.39 kcal (156 kJ) Wassabi 3.16 5.73 20.19 140.60 kcal (588 kJ) Ginger 1.89 0.73 14.82 73.87 kcal (309 kJ) - Drinks (not allowed)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Coffee 4.53 2.76 8.32 70.57 kcal (295 kJ) Cocoa 25.07 15.00 23.07 359.33 kcal (1504 kJ) Black strong tea 3.44 1.79 8.86 59.72 kcal (249 kJ) Hibiscus 1.33 0.42 6.07 28.12 kcal (117 kJ) Chicory 4.27 0.66 45.48 212.15 kcal (888 kJ) All carbonated drinks, cold drinks 0.00 0.00 9.95 45.17 kcal (189 kJ) Alcohol 0.74 0.92 3.22 236.90 kcal (991 kJ) even with a slight degree Hot chocolate 5.56 5.76 76.00 384.00 kcal (1607 kJ) Green tea 4.47 1.45 7.64 55.82 kcal (233 kJ) Stevia leaves 0.02 0.00 37.10 181.49 kcal (759 kJ) Whey 1.08 0.18 6.93 29.17 kcal (122 kJ) Juices 0.51 0.08 10.40 46.93 kcal (196 kJ) freshly pressed, industrial juices Carob 4.76 0.76 66.47 240.92 kcal (1008 kJ) - Sweets (not allowed)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Chocolate 6.83 31.26 48.11 512.70 kcal (2146 kJ) Butter creams 6.13 13.17 35.59 285.13 kcal (1193 kJ) Ice cream 4.25 13.23 23.97 233.15 kcal (975 kJ) Halva 12.16 30.46 48.05 502.56 kcal (2103 kJ) Souffle 5.56 8.91 41.05 263.42 kcal (1102 kJ) Chewing gum 0.00 0.00 70.00 170.00 kcal (711 kJ) Muesli bars 4.00 8.00 64.00 360.00 kcal (1506 kJ) Sesame candies 7.60 33.00 75.00 627.40 kcal (2626 kJ) Popcorn 7.51 12.16 56.88 366.09 kcal (1532 kJ) Hematogen 6.24 4.59 73.94 361.76 kcal (1514 kJ) Waffles 5.22 22.82 60.79 468.23 kcal (1960 kJ) Chuck-chuck 6.45 22.07 55.12 456.05 kcal (1909 kJ) Sherbet 6.74 11.73 62.66 384.62 kcal (1610 kJ) Condensed milk 6.56 7.87 49.01 308.58 kcal (1291 kJ) Kozinaki 11.84 31.75 38.69 494.17 kcal (2068 kJ) Jam 0.99 0.16 60.89 248.99 kcal (1042 kJ) Honey 1.02 0.23 76.39 307.17 kcal (1285 kJ)
Signs of gallbladder pathology
Poor bile flow requires immediate treatment. Therefore, if you have the following symptoms, you should consult a gastroenterologist or hepatologist:
- Pain in the right side, under the ribs. These sensations come in varying degrees of severity, for example, with stones in the gall bladder, the pain becomes more intense. If there is a bend in the bladder or cholecystitis, the pain is less pronounced. Pain appears after eating food, especially fatty, spicy foods or fried and smoked foods, also after physical activity (cycling, jogging, jumping, etc.) or after nervous strain.
- The tongue becomes covered with a yellow coating. Some pathologies provoke the release of bile into the esophagus and into the oral cavity, for example, cholelithiasis or tumor formations. Depending on the cause, the color of the plaque can range from light yellow to slightly greenish.
- Feeling of bitterness in the mouth. It occurs after bile enters the esophagus and oral cavity, due to diseases such as cholecystitis, biliary dyskinesia, the presence of stones in the gall bladder and cancer processes.
- Yellowness that occurs on the skin and mucous membranes. Some diseases contribute to the entry of bile acid into the blood system (cholelithiasis, chronic cholecystitis and tumors, along with which there is a poor outflow of bile).
- Discolored stool . They occur together with pain in the right side under the ribs, the manifestation of jaundice and other symptoms characteristic of pathologies of the biliary system. However, stool discoloration may be a consequence of taking medications or not following a diet.
- Dark colored urine. It is a signal of problems in the biliary system, but sometimes the color of urine changes depending on the medications taken and foods consumed.
In a child, symptoms of poor bile flow appear in the same way as in adults. treatment .
Sample menu for bile stagnation for a week
| Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | Day 5 | Day 6 | Day 7 | |
| 7.00 - first breakfast | Oatmeal porridge with dried fruits, black tea | Steamed omelette with tomato, unsweetened tea | Rice casserole, tea | Soft-boiled egg, applesauce, herbal tea | Milk noodle soup, milk tea | Oatmeal pancakes with sour cream, soft-boiled egg, compote | Lazy dumplings with sour cream, tea |
| 10.00 - second breakfast | Fruit mousse, biscuits | Vegetable puree | Baked apples | Crackers, compote | Cheesecakes with sour cream | Kissel, toast with cheese | Low-fat cottage cheese |
| 13.00 - lunch | Vegetable soup, oven-baked chicken, dried fruit compote | Stuffed cabbage rolls, vegetable borscht, jelly | Vegetable soup with buckwheat, steamed meatballs, compote | Boiled turkey meat, pea puree, sauerkraut, peach juice | Potato soup, boiled fish, jelly | Vegetable soup with noodles, steamed cutlets, rosehip broth | Vegetable soup, noodle soup with meat, jelly |
| 16.00 - afternoon tea | Rose hip decoction, cookies | Applesauce, oatmeal cookies | Vegetable Salad | Dried biscuit, low-fat kefir | Carrots and apples in salad | Fruit juice and cookies | Banana |
| 19.00 - dinner | Mashed potatoes, steamed minced fish cutlet, tea | Buckwheat with beef, rosehip decoction | Pilaf with meat, kefir | Buckwheat with butter, bread with butter and cheese, jelly | Mashed potatoes with meat, kefir | Rice porridge with milk and butter, bread and butter, a piece of cheese | Semolina porridge with milk, herbal tea |
If following a diet does not bring the expected relief of symptoms, additional treatment will be required. Read about possible methods in this article and remember, self-medication can be dangerous to your health. It is better to take any action after consulting a doctor.
Gallbladder massage for congestion
Contraindications for massage during bile stagnation are:
- peritonitis;
- acute forms of inflammation of the liver and liver;
- pancreatitis.
Massage of the gallbladder during stagnation of bile allows you to relieve pain that occurs during inflammation and increases blood circulation in the area of the organ. The treatment cycle includes 12 massages, which are performed every other day.
The massage is carried out according to the following method:
- On the back are carried out:
- stroking and pressing along all lines of the back;
- Long muscles are kneaded with fingertips;
- pincer kneading with the tips of the thumbs;
- massage with circular movements using the base of the palm;
- Zones D6-D10, at the site of innervation of the liver and bladder, are massaged in particular detail;
- knead the broad back muscles;
- Gently massage the trapezius muscle; chopping and tapping movements should not be used.
- On the neck:
- ironing, pressing and kneading are used;
- The collar area is massaged thoroughly.
- On the surface of the sternum:
- The patient is placed on his back and the pectoral muscles are kneaded, smoothed and squeezed.
- On the abdominal area:
- gently stroke the belly in a circle;
- wring out fabrics;
- rub the rectus abdominis muscles;
- knead;
- rub the edges of the costal arches with your thumbs downwards;
- Use line rubbing with the edges of the palms.
Menu (Power Mode)
With hypotonic dyskinesia of the bladder, the “choleretic” diet must be followed constantly and, if followed correctly, complications ( cholecystitis , cholangitis , cholelithiasis) can be prevented. It is advisable to include vegetables (in any form) and fruits, vegetable oils in every meal. In order to enhance the motility of the gallbladder and reduce cholesterol, you need to consume various oils: corn, sunflower, flaxseed, olive. Be sure to include bran in its natural form or pre-steamed in all dishes (in the absence of diarrhea). It is better to eat whole grains and dried fruits daily. At night you need to consume fresh kefir. Below is a one-day menu, but based on it you can create a diet for a week.
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Treatment
A positive result in the treatment of various stagnant processes can be achieved by following a well-thought-out integrated approach. Treatment should be based solely on drug therapy and a fairly strict diet.
Treatment is prescribed by a gastroenterologist or hepatologist or surgeon. If necessary, the doctor will refer you to other specialists for additional advice.
To effectively treat cholestasis, a specialist prescribes the following categories of medications:
- Modern hepatoprotectors are medications that effectively protect and restore the liver. Among the most effective drugs are Heptral, Essentiale, as well as Silibor, Gepabene.
- Various antispasmodics that relieve spasms in the bile ducts and adjacent ducts. Due to this, pain is effectively relieved. To remove such spasms, doctors prescribe No-shpa, regular Spazmolgon, Riabal.
- If there is debilitating pain in the area of the right hypochondrium, various painkillers are prescribed - Ketanov or the weaker Ibuprofen.
- Important cholekinetics are prescribed to significantly improve the flow of bile juice. Optimal results can be achieved through the use of drugs such as Holosas, Cholecystokinin, Xylitol;
- Antibacterial drugs. Biseptol, Metronidazole are prescribed when inflammatory processes are detected in the bile ducts and adjacent bile ducts.
- Antihistamines. The main purpose of these products is to eliminate itching. For this purpose, doctors prescribe Tavegil and Suprastin.
- If required, various types of antipruritic external therapy - ointments, gels and creams - can be prescribed.
In particularly advanced situations, the patient is prescribed special duodenal intubation. The event is intended for washing the ducts with medicinal mineral warm water.
If conservative methods do not bring positive results, the doctor may prescribe surgery to remove stones, dilate the ducts, and often remove the bile-producing organ.
Important! Only an experienced doctor can prescribe a medicine, as well as a particular procedure. Self-medication is extremely unacceptable.
Diagnosis of disorders in the outflow of bile
Symptoms indicating poor bile flow suggest the presence of pathology. Only a gastroenterologist can confirm the diagnosis and determine the cause.
After collecting anamnesis and examination, the patient will receive a referral for research.
This:
- General analysis and blood biochemistry;
- urine and feces examinations;
- glucose level assessment;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity;
- X-ray (with or without isotopes).
They will allow:
- Assess the functioning of the digestive organs.
- See their structure, mechanical barriers that prevent the normal secretion of bile.
- Identify the inflammatory process, elevated cholesterol and sugar levels.
When there are no serious deviations, the gastroenterologist may recommend lifestyle adjustments.
If the patient followed the recommendations, but the disease did not subside, a more in-depth examination will be required, including:
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) or CT (computed tomography) of the abdominal cavity.
- Allergy tests.
- Genetic research.
- Analysis of duodenal contents (from the duodenum).
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopic examination.
- Cholescintigraphy.
In severe cases, a liver biopsy is required for histological and cytological tissue analysis. Patients with suspected carcinoma (a type of cancer) often undergo this procedure.
Finding the cause of cholestasis often takes a long time. In some cases, it is not possible to determine the factor that caused the problem.
Why is this condition dangerous?
Stagnation of bile secretion without proper treatment can lead to a number of complications. Such consequences may include:
- diarrhea;
- severe itching;
- poor absorption of fats and vitamins, resulting in exhaustion;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- liver failure;
- inflammation due to the addition of bacterial microflora;
- sepsis;
- formation of stones in the bladder and blockage of the ducts;
- softening of bone tissue (osteomalacia) due to cholestasis over a very long time.
Bile stagnation during pregnancy can be a serious condition for both mother and baby.
Cholestasis triggers the development of cholecystitis, osteoporosis, liver failure, and cirrhosis. Crystals form in the gallbladder and stones form. Blockage of the ducts by them is accompanied by unbearable pain. Delay may result in the death of the patient.
Although most cases of the problem during pregnancy are not dangerous, serious complications are possible:
- premature birth;
- fetal distress of the fetus (oxygen starvation, which has consequences for normal development);
- stillbirth;
- After childbirth, the risk of liver cancer, diabetes and thyroid disease increases.
List of permitted products. What can you eat if you have bile stagnation?
- Meat and poultry (possible)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Veal 19.67 2.18 0.38 100.21 kcal (419 kJ)) steam, boil, grind, chop Rabbit meat 20.80 9.64 0.48 171.51 kcal (717 kJ) steam, boil, grind, chop Beef 20.56 12.90 1.95 197.40 kcal (826 kJ) no fat Chicken 18.49 12.85 0.26 189.79 kcal (794 kJ) without skin Turkey 20.05 3.77 0.33 116.97 kcal (489 kJ) without skin horsemeat 28.23 10.74 0.03 168.63 kcal (705 kJ) - Fish and seafood (possible)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Hake 16.80 2.29 0.18 87.66 kcal (366 kJ) Pollock 16.20 1.39 0.02 79.54 kcal (332 kJ) can be boiled, baked (after boiling) Zander 18.60 6.81 0.10 86.58 kcal (362 kJ) Tuna 22.51 1.29 0.83 101.69 kcal (425 kJ) Cod 16.84 1.47 0.69 83.50 kcal (349 kJ) Fresh oysters 10.60 2.31 5.83 85.65 kcal (358 kJ) Squid 19.25 2.66 1.44 106.99 kcal (447 kJ) in small quantities Shrimps 19.02 1.76 0.57 94.73 kcal (396 kJ) in small quantities Salmon 19.02 1.76 0.57 94.73 kcal (396 kJ) only as a snack - Vegetables (possible)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Potato 2.09 0.35 17.36 80.69 kcal (337 kJ) can be boiled and baked Cauliflower 2.50 0.30 5.40 30.00 kcal (125 kJ) can be boiled and baked Chinese cabbage 1.19 0.19 2.43 14.97 kcal (62 kJ) can be boiled and baked Pumpkin 1.20 0.27 6.96 30.48 kcal (127 kJ) can be boiled and baked Zucchini 1.24 1.02 6.02 28.73 kcal (120 kJ) can be boiled and baked Carrot 21.15 0.15 8.25 36.50 kcal (152 kJ) can be boiled and baked Sea kale 1.50 5.02 2.61 66.71 kcal (279 kJ) Avocado 2.17 16.87 5.84 183.20 kcal (766 kJ) Green beans 2.67 0.23 4.04 27.73 kcal (116 kJ) steamed or baked Broccoli 3.27 0.67 4.66 34.32 kcal (143 kJ) boiled or steamed Celery 1.58 0.56 4.37 30.26 kcal (126 kJ) boiled or steamed - Fruits, berries (possible)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Soft sweet apples 0.39 0.39 9.86 46.27 kcal (193 kJ) raw, baked, ground Banana 2.19 0.90 21.65 99.77 kcal (417 kJ) no more than 1 pc. in a day Prunes 2.43 0.97 57.06 238.98 kcal (1000 kJ) Watermelon 1.23 0.79 8.31 35.51 kcal (148 kJ) up to two pieces per day Dried melon 1.33 0.05 76.05 288.50 kcal (1207 kJ) Dried papaya 1.04 0.60 65.55 300.07 kcal (1256 kJ) Dried apricots 5.15 1.19 52.23 229.02 kcal (958 kJ) - Dairy and fermented milk products (possible)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Low-fat sour cream 2.90 2.00 4.80 53.00 kcal (221 kJ) Mild cheeses 7.20 22.00 2.00 231.50 kcal (969 kJ) in small quantities Kefir 2.95 1.00 4.00 37.68 kcal (157 kJ) fat content up to 2% Yogurt 3.52 2.00 11.59 85.50 kcal (357 kJ) no artificial additives Cottage cheese 17.62 2.23 2.81 101.39 kcal (424 kJ) fat content up to 2% Milk 3.23 2.14 5.06 61.47 kcal (257 kJ) fat content up to 2% Curdled milk 2.85 2.00 4.32 52.15 kcal (218 kJ) fat content up to 2% Chees Feta 15.80 20.89 2.08 252.78 kcal (1058 kJ) in small quantities - Soups, broths (possible)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Vegetable soups 3.01 1.99 5.72 50.28 kcal (210 kJ) with the addition of potatoes, zucchini, pumpkin, carrots Cereal soups 5.37 1.36 6.03 54.61 kcal (228 kJ) with buckwheat, semolina, rice. You can cook noodle soup Fruit soups 0.57 0.06 12.64 51.89 Kcal (213 kJ) Milk soups with pasta 2.89 2.92 12.28 85.43 kcal (357 kJ) Borscht with low-fat broth 1.00 1.00 6.00 38.00 kcal (159 kJ) Vegetable cabbage soup 1.96 2.05 4.31 34.24 kcal (143 kJ) Beetroot 2.03 2.11 8.66 58.24 kcal (243 kJ) Pea soup 4.09 2.63 8.34 69.94 kcal (292 kJ) Soup with pearl barley 2.09 3.04 3.29 47.86 kcal (200 kJ) - Flour products (possible)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Paste 10.00 1.10 71.50 344.00 kcal (1439 kJ) You can add any products from the list of permitted products to the paste. Bread made from bran or rye flour 5.32 1.50 44.25 189.38 kcal (792 kJ) Crackers 10.96 4.98 66.71 355.44 kcal (1487 kJ) Galette cookies 9.14 8.89 65.36 393.31 kcal (1646 kJ) Dried sponge cake 6.94 7.61 52.16 299.08 kcal (1251 kJ) Wheat slices 12.70 2.25 70.30 355.00 kcal (1486 kJ) Crispbreads with no artificial additives 10.05 2.76 55.41 301.20 kcal (1260 kJ) Bran 12.00 2.88 43.52 255.00 kcal (1067 kJ) - Cereals, legumes, seeds (possible)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Buckwheat 5.16 1.94 26.15 128.30 kcal (537 kJ) You can use water or milk (milk is diluted 50% with water). Oatmeal 8.89 4.93 43.63 253.23 kcal (1060 kJ) You can use water or milk (milk is diluted 50% with water). Rice 5.99 1.51 57.09 263.80 kcal (1104 kJ) You can use water or milk (milk is diluted 50% with water). Muesli 9.95 7.60 61.36 342.45 kcal (1433 kJ) that do not contain prohibited additives Cereals 11.80 6.15 57.50 326.48 kcal (1366 kJ) Bulgur 3.10 0.20 14.10 83.00 kcal (347 kJ) Couscous 9.09 2.18 57.09 286.98 kcal (1201 kJ) Millet porridge 3.20 1.60 17.60 95.00 kcal (397 kJ) Flax seed 21.48 38.57 15.59 497.43 kcal (2082 kJ) - Fats and eggs (ok)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Butter 1.44 73.30 1.94 678.69 kcal (2841 kJ) no more than 30 g per day Vegetable oil 0.22 93.82 1.12 856.59 kcal (3585 kJ) past refining (no more than 15 g per day). The oil is used as a salad dressing Olive oil 0.25 91.66 0.39 845.93 kcal (3541 kJ) in small quantities Eggs 11.96 10.72 1.39 144.34 kcal (604 kJ) omelette, boil them - Sauces, spices, herbs (possible)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Milk sauce 2.04 6.47 6.42 85.06 kcal (356 kJ) Vegetable sauce 2.88 2.36 7.13 62.09 kcal (259 kJ) Sour cream sauce 2.09 9.43 5.57 134.34 kcal (562 kJ) Salt 13.39 20.62 12.22 252.91 kcal (1058 kJ) no more than 10 g per day Dill 3.44 0.85 7.88 46.85 kcal (196 kJ) Parsley 3.62 0.04 8.03 46.13 kcal (193 kJ) Vanillin 0.13 4.76 33.93 297.77 kcal (1246 kJ) Cinnamon 3.84 2.01 54.18 246.23 kcal (1030 kJ) Soy sauce 5.18 0.07 21.45 36.87 kcal (154 kJ) in small quantities Iceberg 1.34 0.58 3.38 23.79 kcal (99 kJ) in small quantities Korn 1.49 0.20 1.71 16.45 kcal (68 kJ) in small quantities Romano 1.95 0.75 2.42 19.75 kcal (82 kJ) in small quantities - Drinks (possible)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Black tea with lemon or milk 0.76 0.69 4.42 23.79 kcal (99 kJ) You can sweeten it slightly. In addition to sugar, it is allowed to add xylitol to tea. Rosehip in the form of decoction 0.19 0.00 4.59 28.67 kcal (120 kJ) Juices 0.51 0.08 10.40 46.93 kcal (196 kJ) after diluting with water Ground compotes from dried fruits and fresh fruits 0.80 0.14 15.50 65.00 kcal (272 kJ) Jelly 2.80 0.02 20.30 81.00 kcal (339 kJ) Kissel 0.35 0.16 35.78 141.19 kcal (591 kJ) with a little added sugar Morse 0.32 0.19 9.95 41.42 kcal (173 kJ) with a little added sugar - Sweets (possible)
Product Proteins, (g) Fats, (g) Carbohydrates, (g) Calorie content, kilocalories Note Boiled and baked fruits and berries 2.86 1.78 2.39 21.21 kcal (88 kJ) main condition: they should not be sour Boiled and baked fruits and berries 0.91 0.90 19.29 84.04 kcal (351 kJ) Marmalade 1.19 0.82 73.26 297.51 kcal (1245 kJ) Lollipops 0.47 1.66 80.31 340.10 kcal (1423 kJ) Soft caramels 3.60 9.60 59.80 324.00 kcal (1356 kJ) without seeds, sesame and nuts Biscuit 6.94 7.61 52.16 299.08 kcal (1251 kJ) no more than one piece per day Permitted fruit puree 1.36 0.44 13.83 71.09 kcal (297 kJ) Gingerbread 4.85 4.76 68.39 345.84 kcal (1447 kJ) 1 per day Turkish Delight 1.33 1.58 79.24 356.00 kcal (1490 kJ) if there are no nuts Nougat 3.60 21.20 64.90 458.00 kcal (1917 kJ) if there are no nuts
How to treat congestion in the gallbladder and ducts?
The sooner it is possible to identify bile stagnation, the easier it is to eliminate this condition. In later stages, surgical removal of the gallbladder may be required. But if the root cause is not eliminated, after removal the bile will begin to stagnate in the ducts, which will lead to further problems.
This disease can be completely cured in the early stages. Further prevention will help (nutrition, auxiliary therapy, physical activity) to prevent disturbances in the functioning of the liver and gall bladder.
Another article on this topic: Diseases of the small intestine: symptoms and signs of the disease
Diet for bile stagnation
No medicine will help if the patient does not reconsider his diet.
To prevent bile from stagnating, it is necessary to consume choleretic products:
- Lean meat and fish, chicken eggs.
- Dairy products.
- Fresh vegetables and herbs.
- Herbal teas.
- Porridge, grain products.
Don't give up meat and switch to a plant-based diet. Meat is one of those foods that requires a large amount of bile to digest. If you remove it from the diet, it will lead to thickening and worsening of the outflow of bile.
It is worth excluding those foods that increase the load on the liver and cause spasm of the bile ducts:
- Alcohol, coffee.
- Fried food.
- Smoked meats, pickled vegetables, canned food.
- Pastries and sweets.
- Fatty broths, lard.
Frequent split meals will help remove congestion: bile will be released every time food enters the stomach, and will not accumulate.
Drug treatment
To eliminate poor bile flow and related problems, various drugs are used. The doctor prescribes:
- Antispasmodics that eliminate spasm of the bile ducts (Odeston, No-Shpa, Baralgin).
- Mild sedatives to neutralize the effects of stress.
- Choleretic - to improve the flow of bile. Prescribed with caution, contraindicated in the presence of stones. This group of drugs includes Allohol, Holosas, Cholenzym, Chofitol, etc.
Massage for a patient with a tendency to stagnation of bile will help improve its outflow. Physiotherapeutic treatment is used for the same purpose. But these manipulations are carried out in the remission stage.
Treatment of bile stasis with folk remedies
These methods are best used as auxiliary methods, and only after examination. Self-administration of choleretic drugs in the presence of stones can lead to complete blockage of the bile ducts. This entails serious deterioration in health and even death.
Herbal remedies will help eliminate the difficult passage of condensed bile in the absence of stones. Corn silk, dandelion, rose hips, mint, barberry, and dill are especially effective. You need to drink them half an hour before meals.
You can consume flaxseed oil on an empty stomach - it will improve the flow of bile, normalize liver function, and eliminate spasms.
An hour after meals, drink freshly squeezed juices. A mixture of beetroot, apple and carrot in equal proportions is especially effective. To feel the therapeutic effect, you need to take them for at least a month.
What to do
Accumulation and stagnation of bile occurs due to a number of factors. Therefore, before treating the reflux of bile into the stomach, it is necessary to find out the cause of the development of the pathology. Medical care for the disease includes several areas:
- diagnostic measures;
- diet;
- conservative therapy;
- alternative methods.
A systematic, comprehensive approach allows you to cope with the problem and helps prevent the development of relapse of reflux.
Attention!
If there are tumors or stones in the gallbladder, doctors discuss radical intervention and decide whether and when surgery is necessary.
Diagnostics
If biliary reflux is suspected, the doctor ascertains the medical history, examines the patient, and prescribes general clinical and instrumental examinations. The release of bile into the stomach is characterized by symptoms that are quickly determined by a specialist based on objective data. Questioning the patient allows you to find out about the duration of the disease, signs of pathology that characterize excessive accumulation and penetration of bile into the upper sections. The gastroenterologist recommends additional diagnostic methods:
- A blood test - general and biochemical - to identify signs of inflammation, thickening of bile, liver dysfunction.
- Carrying out FGDS with histological sampling of material. During fibrogastroscopy, you can see a lot of mucus, a strong release of secretions, determine the degree of damage to the mucosa and the extent of the process with the development of duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum), esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus).
- Detection of the pathogenic pathogen Helicobacter pylori using various tests - PCR, ELISA, urease diagnostics.
- Performing pH testing to determine the level of stomach acidity.
- X-ray with barium contrast.
If the patient has symptoms of damage to parenchymal organs, an ultrasound is prescribed. The method allows you to study the structure of organs and their function, and check for the presence of additional formations.
How can you suspect that you have bile stagnation?
The insidiousness of gallbladder diseases is that they occur for a long time without pronounced symptoms. Therefore, obvious signs of bile stagnation usually appear several months or even years after the onset of the disease.
Possible symptoms of stagnation of bile in the gallbladder:
- feeling of heaviness, pain in the right hypochondrium;
- discomfort after eating fatty and fried foods, alcohol;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- jaundiced skin tone;
- nausea, occasional vomiting mixed with bile.
Usually the symptoms of bile stagnation are mild. Most often, chronic moderate pain appears in the area of the right hypochondrium. They should alert you and force you to undergo ultrasound diagnostics.
Important! Timely treatment at the first signs of bile stagnation in the gallbladder prevents the formation of stones and avoids the need for surgical interventions in the future.
If your relatives had cholelithiasis or they had to undergo cholecystectomy and other similar operations due to diseases of the biliary tract, be especially attentive to your health and diet. Although hereditary predisposition to gallstone disease has not been officially proven, it is well known to specialists who have been monitoring patients with gallstones for decades.
Help with stagnant processes
Such unpleasant symptoms of impaired bile flow must be eliminated not only with the help of medications, but also by performing special gymnastic exercises and adhering to a diet.
Very often, a violation of the outflow of bile acid appears after eating certain foods, so you should first figure out how to choose the right diet:
- meals are divided into 5-6 times a day, in small portions;
- It is forbidden to eat food immediately before bedtime;
- It is forbidden to eat dishes that are too hot or cold, only warm ones;
- exclude fried dishes, soups with fatty meat and fish;
- steam, bake or boil food;
- Milk products, including fermented milk, are introduced into the daily diet.
What foods can restore the normal flow of bile?
You can relieve unpleasant symptoms by consuming certain foods that promote the flow of bile:
- Vegetable oils - corn, olive, sunflower. Any of them is used in salads, cereals, added to soups and other ready-made dishes. To improve the flow of bile, it is recommended to take olive or sunflower oil in the morning, 1 teaspoon before breakfast. However, the opinion of doctors on this issue is not clear.
- Bran is useful both for cleansing the body and for improving the flow of bile juice.
- A good prevention and treatment would be the consumption of steamed and baked vegetables or broths based on vegetables, with their help the processes of formation of bile juice are improved. Eating vegetables daily will prevent the appearance of gallstones and bile stagnation.
- If the outflow of bile is difficult, it is recommended to include pears, oranges, lemons, prunes, watermelon and melon in your diet.
- Freshly prepared juices from fruits and vegetables: juice from cabbage, beets and lingonberries most effectively prevents stagnation.
- Chicory leaves or root.
- Turmeric.
- To prevent symptoms and the disruption of bile outflow itself, it is recommended to add all kinds of greens (parsley, dill, spinach, etc.) to dishes.
- Avocado copes with cholesterol, which leads to the normal functioning of the biliary system.
All of the above is taken not only during illness, but also as preventive measures.
However, if you have gallstones, you should consult a specialist, otherwise excessive consumption of a particular product may harm the body. To make it easier to create your own menu, here is an example:
- 08.00 - steam omelette of two proteins; oatmeal (buckwheat can be used); a small slice of bread, not strong tea;
- 11.30 - cottage cheese or a piece of cottage cheese casserole; biscuits (no more than 3 pieces); chamomile or rosehip tea;
- 13.00 - soup with vegetable broth; a piece of bread; porridge made from rice or wheat cereals; steam cutlets (not fatty); compote;
- 15.30 - fruits (salad); weak tea without sugar;
- 18.00 - fish, low-fat varieties, stewed without frying; mashed potatoes; a piece of bread; a glass of low-fat kefir (sour milk).
The main condition of the diet menu is a variety of dishes, as well as the complete exclusion of prohibited foods.
Exercise to improve bile flow
Gymnastics is an important component in the treatment of impaired bile outflow; with its help, the respiratory abilities of the diaphragm develop, blood circulation improves, as well as the condition of the gallbladder and intestines.
You should do physical exercises to drain bile in the morning, before eating. One exercise is repeated at least 5 times:
- Take a position lying on your back, arms along the body, legs straight - while inhaling, we blow out the stomach as much as possible, while exhaling, we pull it back in.
- Without changing position, bend your legs at the knees - while inhaling, you should raise your knees to your stomach and touch them with your forehead, and while exhaling, take the same position.
- Without changing the initial position of the body, touch the floor with bent knees, first on the right side, then on the left.
- While lying on your back, raise your legs up and perform movements similar to walking.
Gymnastics
Gymnastic exercises help develop diaphragmatic breathing, stimulate blood circulation, and improve the condition of the intestinal and gall muscles. It is better to do exercises in the morning, before breakfast. The number of repetitions should reach 5 times. Exercises:
- Lie on your back and breathe with your diaphragm. Inhaling - we blow out the stomach, exhaling - we draw in.
- Lying on your back, legs bent at the knees. Inhaling, we pull our legs towards our stomach and touch them with our heads. Exhaling, we return to the starting position.
- Starting position as in task No. 2. We turn our legs bent at the knees first to the right, then to the left.
- Lying on your back, raise your bent legs up and imitate steps.
Return to contents
Consequences: what does impaired bile secretion lead to?
If there is a lack of bile, fats consumed with food (animal and vegetable) do not undergo emulsification , i.e., they do not acquire the ability to dissolve in liquid.
Another article on this topic: Causes of black stool, what does it mean?
The lack of bile leads to the fact that a number of intestinal digestive enzymes cease to be produced. As a result, pure fat enters the bloodstream, causing:
- Cholesterol is not excreted - on the contrary, it is deposited on the walls of blood vessels at an increased rate, narrowing their lumen. This leads to increased blood pressure, thrombus formation, and blockage of blood vessels.
- Glucose is not transformed into glycogen. The result is the development of diabetes mellitus.
- The body stops absorbing fat-soluble vitamins, which provokes vitamin deficiency and decreased activity of the immune system. The amount of calcium absorbed also decreases, which leads to osteoporosis.
A congestive gallbladder is a prerequisite for severe complications. The longer bile is in the gallbladder, the more viscous it becomes. Bile salts precipitate, forming stones.
At a minimum, inflammation of the gallbladder develops, but in most cases, regular stagnation leads to the appearance of cholelithiasis and subsequent removal of the bladder.
Acidity in the intestines increases, hence fermentation and inflammation of the small and large intestines, intoxication.
But the most dangerous complication occurs when poor flow of bile is observed in the liver ducts: this causes the death of hepatocytes.
Reasons for violation
Liver diseases such as cirrhosis or hepatitis lead to a violation of the choleretic properties.
Bile is produced in the small channels of the liver, and immediately the bile ducts help in its movement. The common bile duct is inextricably linked with the pancreas; secretory fluid flows through it to the duodenum. Any area of biliary movement may experience disruption. Violation of the choleretic property occurs for several reasons:
- failure in the contraction of the walls of the gallbladder and bile ducts leads to a deterioration in the organ’s ability to push bile;
- compression of an organ caused by the inflammatory process of neighboring organs, pregnancy, uncharacteristic location of the internal organs, heavy load, injury;
- cholesterol content in bile that is higher than normal leads to lipid metabolism disorders;
- increased hormonal levels during pregnancy, when taking hormonal pills, menopause leads to a disorder in the synthesis of fatty acids;
- restriction and monotony in nutrition leads to limited outflow;
- liver diseases (cirrhosis, hepatitis);
- the reduced content of complex lipids prevents the thickening of bile;
- inflammatory, allergic process of the gallbladder.
The disease has no clear age restrictions; problems with bile can occur in both adults and children. It occurs as a result of taking medications, poor diet and illness.
Return to contents
Treatment measures
Therapy is aimed at alleviating the patient's condition. It includes drug treatment, a strict diet and exercise. In addition, physical procedures (electrophoresis, laser therapy) may be prescribed. Treatment with mineral waters is prescribed according to the type: for hypertonic, drink lightly carbonated water, for hypotonic, drink highly carbonated water. Resort-type sanatoriums with a focus on curing digestive diseases help.
Diet therapy
With dyskinesia, adherence to proper dietary nutrition is important. It is recommended to restore the regimen - eat every 3-4 hours, increase the number of meals to 5 times a day. When a person does not eat for a long time, the bile stagnates in the gallbladder, acquires a thick consistency and its movement along the paths becomes constrained and difficult, which has a negative effect on the hypotonic and hypertonic types.
Food portions should be small in size, as it is better to eat more often. Eating too much increases the secretion of bile, which can negatively affect the functioning of organs throughout the body. Food should be low-fat, low-calorie, and always warm. Avoid eating contrasting foods (cold and hot) to prevent increased contraction of the bile ducts.
Problems with the gallbladder will require adherence to a dietary diet.
If you are not bothered by acute symptoms, you are allowed to occasionally indulge in your favorite treats, but it is recommended to use them with caution. In the case when there is a strong period of exacerbation of the disease, it is important to follow a strict diet - fatty, spicy, salty foods, smoked meat and fish, fast food (pizza, hot dog, shawarma) are prohibited.
Medicines
The treatment regimen for dyskinesia is selected by the doctor according to the type. With the hypertensive type, the task is to get rid of the contraction of the bile ducts. Antispasmodic drugs (“Drotaverine” tablets, “Spazoverine”) are prescribed first. They help reduce pain and increase the flow of bile into the small intestine. For the hypotonic type of dyskinesia, antispasmodic and then choleretic medications are prescribed to improve the outflow of bile (Artibel, Cynarix, immortelle herb). The medications are homeopathic and harmless. Contraindication: presence of gallstones. For both types, enzyme preparations are prescribed, which are taken to improve the digestion of food, which have a beneficial effect on the bile ducts, which need to be restored.
Gymnastics for dyskinesia
Physical exercises (exercises, gymnastic exercises) have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, blood circulation in the body, and the muscles of the gallbladder. Exercises are done on an empty stomach, at least 5-6 approaches at a time. Here are examples:
- Belly breathing. Inhale - the stomach grows, exhale - the stomach falls. Do 4-5 such breathing tasks.
- Lie on your back, bend your knees, pressing them to your stomach. The upper part of the body rises, reaching the head to the knees. Minimum 5 lifts.
- Doing a “bicycle” - moving your legs as if a bicycle were moving both forward and in the opposite direction. Do as much as possible of this important and beneficial exercise.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods are used as a complement to the main therapy. A correctly selected valuable composition can reduce pain during exacerbations and stop some painful manifestations in the body. Infusions and decoctions of herbs such as immortelle, oregano, mint, and chamomile tea are used. Below are some examples of preparing decoctions and infusions.
https://youtu.be/AWK_QakvWm4
For hypotonic type:
- Decoction of immortelle herb. 2-3 tbsp. l. pour 250 ml of boiling water and place in a water bath for 20-30 minutes. Let cool and strain the resulting liquid; drink 0.5 cups before meals. Treatment is long-term.
For hypertensive type:
- Mint infusion. 2 tsp. pour a glass of boiling water, leave for 30 minutes, strain. Drink 3 tbsp. l. before meals, twice a day. The course of treatment is 2-3 weeks.
For both types of dyskinesia:
- Chamomile tea. Prepare as regular tea and drink at any time of the day.
General rules
Bile is continuously secreted by the liver, between meals it accumulates in the gallbladder, and after meals it enters the duodenum.
Disorders of the biliary system (dyskinesia) are associated with uncoordinated, excessive or insufficient contraction of the gallbladder, ducts and ductal sphincters. Stagnation of bile in the gallbladder is caused by dyskinesia of the hypotonic type, in which there is insufficient reduction of bile, and a small amount of bile enters the digestive tract, which disrupts the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract (intestinal motility is inhibited, the absorption of vitamins , calcium , iron , which in turn leads to the development various diseases.
This condition is functional and can be caused by constant consumption of fatty and spicy foods, breaks between meals, nervous experiences, hormonal disorders ( menopause ) and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. However, functional disorders can contribute to the appearance of organic pathology of the liver, pancreas, biliary system or duodenum. Stagnation of bile can cause an inflammatory process in the gallbladder - dyskinesia in most cases precedes cholecystitis , since prolonged disturbances in bladder emptying lead to excessive growth of pathogenic flora in the intestine, which leads to infection of the gallbladder.
cholesterol content . In the bladder, the process of bile thickening occurs, and it becomes more saturated with cholesterol. It can be said that hypotonic dysfunction promotes the loss of cholesterol crystals. At the initial stages, ultrasound reveals thick bile (biliary sludge), which indicates a violation of its physicochemical properties. During this period, it is important to normalize bile secretion; if the changes are not eliminated, the formation of microliths begins.
Olive oil
One of the treatment methods is to cleanse the bile ducts and gallbladder in a medical facility by duodenal lavage with warm mineral water or the administration of a 20% sorbitol solution. This procedure reduces spasm of the sphincters and increases the flow of bile. You can carry out so-called “blind probing” at home once a week. To carry it out, use olive oil (drink 30 ml on an empty stomach) or xylitol (20 g of powder per 50 ml of water). After consuming them, the patient should lie down in bed with a heating pad applied to the liver area. It is forbidden to perform tubing if there are stones in the bladder or ducts, since the procedure may dislodge stones that will cause blockage of the ducts.
If there is poor outflow of bile, the patient is bothered by constant aching pain in the right hypochondrium, which can intensify or weaken. Nausea and vomiting , constipation , bitterness in the mouth , weakness and fatigue are also noted
To eliminate stagnation, choleretics ( Holosas , Holagol , Allochol , Cholenzym , Liobil , Decholin , Biliton , Kholamine , Suprakol ) are prescribed, which stimulate the bile-forming function of the liver and cholekinetics, which increase the tone of the bladder ( Sorbitol , Mannitol , Xylitol , Berberine sulfate (barberry leaf extract) , Flamin (immortelle extract), Holosas (rose hip extract) Treatment necessarily involves a balanced diet.
A special diet has been developed for stagnation of bile in the gallbladder - this is a variant of Table No. 5 Diet No. 5L/F (lipotropic-fat). It is aimed at stimulating bile secretion, improving bile circulation and intestinal motor function. It also has a lipotropic effect (prevents fatty liver) and helps remove cholesterol from the body. It is prescribed not only for hypomotor dyskinesia, but also after cholecystectomy in the presence of bile stasis syndrome.
This is a complete diet with a physiological content of proteins, carbohydrates (simple carbohydrates are limited), but a high content of fats (due to vegetable ones containing polyunsaturated fatty acids) and enriched with lipotropic substances.
Basic principles of nutrition:
- Vegetable oils in the diet make up 50% of the total amount of fats; if calculated more accurately, their amount should be 1.0-1.2 g per kg of the patient’s weight.
- Contains lipotropic products (cottage cheese, egg whites, fish, lean meat).
- A large number of vegetables, fruits and wheat bran have been introduced.
- Food is cooked in water (steam) and baked; frying is excluded.
- Grinding food is not necessary.
- Fractional meals (up to 5-6 times).
- Salt is limited to 8 g.
- Liquids up to 1.5-2 liters.
- Easily digestible carbohydrates (sweets, sugar, honey, jams, preserves), which cause bile stagnation, are limited.
- Extractives and cholesterol, spices, whole milk, and animal fats are limited.
As already mentioned, this condition requires frequent and split meals (this improves the flow of bile), as well as including choleretic foods in the diet so that bile enters the intestines in a timely manner. After all, the main function of bile is digestive. The main components of bile are involved in the digestion of fats, making them available for further action by pancreatic lipase. The excretory function is also important (removal of bile pigments, excess cholesterol, bacterial toxins, heavy metal salts and drug metabolites from the body).
List of products that have a choleretic effect:
- Vegetable oils. They are rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, phospholipids, vitamin E.
- Unsaturated fatty acids (arachidonic, linoleic) are part of cell membranes, help normalize cholesterol metabolism, participate in the synthesis of prostaglandins, which dilute bile, and increase the contractility of the gallbladder.
- It is important to use vegetable oils without heat treatment for salad dressings. Eating vegetables with vegetable oil gives a double effect; moreover, it is safe to use compared to consuming oil with spoons (contraindicated in case of cholelithiasis).
- Almost all vegetables, fruits, and berries stimulate bile secretion and also relieve constipation. This point is important, since daily bowel movements have a tonic effect on the bile ducts. The most pronounced effect is found in oranges, avocados, tangerines, melons, watermelons, prunes, pears, lemons, and among vegetables - dill, rhubarb, spinach.
- Juices - cabbage, beetroot, lingonberry.
- Wheat bran (30 g per day). They are steamed with boiling water and, once swollen, added to all dishes, 2 tablespoons three times a day. Bran improves the flow of bile and reduces the likelihood of stone formation, since it reduces the cholesterol content in bile.
- Egg yolks.
- Turmeric.
This list of choleretic food products can be supplemented with herbs that enhance contractions and eliminate stagnation of bile: calamus, barberry, lingonberry, immortelle, oregano, coriander, dandelion, knotweed, rowan, caraway, thyme, chicory, rose hips, chicory.
Healing herbs
It must be remembered that choleretic products must be included in the diet carefully, taking into account their tolerance. This is especially true for gallstone disease. If consuming them causes pain or increases bitterness in the mouth (which can be observed in the presence of cholecystitis), then this product is excluded from the diet.
Sometimes, if the bladder is insufficiently emptied, a magnesium diet is recommended, which is based on Table No. 5 , enriched with products containing magnesium: wholemeal bread and bran bread, wheat bran products, buckwheat and millet cereals, bran decoction, vegetables and fruits, dried fruits.
Typically, biliary dyskinesia of the hypotonic type is accompanied by constipation , in this regard, Diet No. 3 with an increase in the amount of choleretic products can be effective. This is a complete diet that can be constantly followed and includes foods that enhance intestinal motility and bowel movements (vegetables, fruits, baked goods with bran, cereals, fermented milk drinks, bran.). As you can see, the composition of the diets is very similar.
Also excluded are products that increase fermentation and rotting (fried foods, legumes, carbohydrates, fatty foods). On an empty stomach it is recommended to drink water with honey, juices, and at night: kefir, infusions of dried fruits (prunes, dried apricots) and then eat steamed fruits and fresh fruits.
Impaired bile outflow treatment
In each individual case, treatment will be different, since the characteristics of the body, the duration of the disease, and its stage influence the doctor’s prescription.
The main goal before therapy is to understand where the disease came from, remove the main annoying symptoms, and improve the patient’s condition so that he can live a full life and not suffer. After this, a careful selection of medications takes place based on previously completed tests. In complex treatment, one cannot do without vitamins, which restore the lack of necessary substances in the body and increase overall immunity. Therapy to get rid of itching is mandatory, since it makes it impossible to live normally and rest at night. To restore liver function, special drugs are offered that affect cells and restore their function. Eliminating the disease at the cellular level is most effective, since the work occurs inside the tissues, ridding the body of microorganisms. It is necessary to take medications that are designed to get rid of excess toxins that poison the entire body.
Classification of congestion in the bile ducts
Accumulation and stagnation of bile can be:
- Spicy. Symptoms appear suddenly and the condition worsens rapidly. In this case, there is a high risk of serious complications and premature death of the person.
- Chronic. It manifests itself gradually, serious disorders in the body occur several months and even years after the onset of the disease.
Congestion can be intrahepatic or extrahepatic . In the first case, the ducts inside the liver are blocked, in the second, problems appear with the gallbladder and the ducts that deliver bile to the intestines.
The disease can have an icteric (yellow discoloration of the skin and sclera of the eyes) or anicteric form.
Depending on the characteristics of the disease, bile stasis occurs:
- Dissociative, when individual components of bile stagnate.
- Partial – it is caused by a decrease in the amount of bile.
- Total – when the transportation of bile through the ducts is disrupted.
Depending on the characteristics of the disease, the correct treatment tactics and the possibility of a full recovery depend.
Fully or partially limited products
- Extractive dishes (broths), spicy vegetables and herbs with a high content of essential oils: horseradish, parsnips, celery, onions, garlic, shallots, katran, oregano, marjoram, savory, rosemary, basil, radishes, turnips, radish.
- Fatty meat and fish, goose and duck meat, smoked meats, fish caviar, salted fish, refractory fats and lard, sausages, all types of canned food.
- By-products (internal organs of animals due to their high cholesterol content).
- Hard-boiled and fried eggs, which are difficult to digest.
- Fresh bread, pastry, fried pastries (pies, pancakes, pancakes), cakes, pastries, puff pastry.
- Whole fat milk and cream.
- Hot sauces.
- Carbonated and alcoholic drinks, coffee, chocolate, cocoa.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| peas | 6,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 60 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| chickpeas | 19,0 | 6,0 | 61,0 | 364 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
| marinated mushrooms | 2,2 | 0,4 | 0,0 | 20 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| almond | 18,6 | 57,7 | 16,2 | 645 |
Snacks | ||||
| potato chips | 5,5 | 30,0 | 53,0 | 520 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| vareniki | 7,6 | 2,3 | 18,7 | 155 |
| dumplings | 11,9 | 12,4 | 29,0 | 275 |
Bakery products | ||||
| buns | 7,9 | 9,4 | 55,5 | 339 |
Confectionery | ||||
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| shortbread dough | 6,5 | 21,6 | 49,9 | 403 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| cream 35% (fat) | 2,5 | 35,0 | 3,0 | 337 |
| whipped cream | 3,2 | 22,2 | 12,5 | 257 |
Meat products | ||||
| fatty pork | 11,4 | 49,3 | 0,0 | 489 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Eggs | ||||
| hard-boiled chicken eggs | 12,9 | 11,6 | 0,8 | 160 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| salmon caviar granular | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| salmon | 19,8 | 6,3 | 0,0 | 142 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| salmon | 21,6 | 6,0 | — | 140 |
| trout | 19,2 | 2,1 | — | 97 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| whiskey | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,4 | 235 |
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
| cognac | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 239 |
| liquor | 0,3 | 1,1 | 17,2 | 242 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| cola | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 42 |
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| sprite | 0,1 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 29 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Stagnation of bile in cats and dogs: causes, signs and treatment
The first place among the causes of bile stagnation in pets is occupied by parasitic and helminthic infestations, namely: opisthorchiasis, alveococcosis and echinococcosis.
Other causes of cholestasis in animals include cancer of the liver and gall bladder, cholelithiasis, poisoning and infectious diseases.
You can suspect bile stagnation in a dog or cat based on the following signs:
- yellowness of the sclera, mucous membranes and skin;
- increased appetite or refusal to eat;
- weight loss;
- stool discoloration;
- darkening of urine;
- increased bleeding of wounds;
- lethargy and drowsiness.
Treatment of cholestasis in cats and dogs follows the same principles as in humans. First of all, you need to eliminate the cause - remove parasites and worms, remove stones or tumors of the gallbladder and tract.
Drug therapy involves the use of antispasmodics, painkillers, choleretic and enzyme preparations.
Advice from a gastroenterologist
The disease causes discomfort and disrupts a person’s usual way of life. Therefore, the patient’s natural desire is to get rid of reflux and its associated symptoms.
To achieve an effective treatment result, gastroenterologists advise:
- Adhere to the diet and nature of your diet, exclude from the menu foods that provoke bile reflux.
- Reduce the impact of stress factors and other negative causes.
- Treat concomitant diseases in a timely manner.
- Include regular moderate physical activity.
- Stabilize your weight.
- Follow the recommendations of a specialist on taking medications.
- Give up bad habits - alcohol and smoking.
Pathology of the digestive system, which is accompanied by the entry of bile into the upper sections, can be successfully treated thanks to modern methods of diagnosis and treatment. However, the main condition on the path to recovery is the joint work of the doctor and the patient.
What will help avoid bile stagnation?
Physical activity will not only improve the flow of bile from the gallbladder, but also strengthen the body as a whole. Thus, it is recommended not only to exercise, but also to take a daily walk in the fresh air, attend a swimming pool or dance classes.
An equally important condition is a diet that excludes unhealthy foods, alcoholic drinks, and drinking strong coffee.
If you consult a specialist in a timely manner, without the presence of cancer, treatment always gives positive results. Following all the recommendations, both in nutrition and in taking medications for the outflow of bile, will help get rid of the problems that have arisen.
Author: Daria Tyutyunnik, doctor, especially for moizhivot.ru
https://youtu.be/XHwYhGODlrY
Causes of congestion
All possible causes of bile stagnation in the liver are divided into three main groups. Here we can note a general dysfunction of organs and the main biliary tract, various diseases, as well as unfavorable environmental factors.
Stagnation of bile in the liver often occurs for reasons such as:
- Improperly structured and unbalanced nutrition - long-term fasting, overeating, lack of fluids, eating a large number of spicy and fried foods.
- Seasonal exacerbation of chronic pathologies in the digestive system or failure after a diet.
- Major changes in diet.
- Significant psycho-emotional disturbances.
- Pathologies in the pelvic organs.
- Food poisoning and intestinal pathogenic infections.
- Acute and chronic gastritis and ulcers.
- Bad habits – smoking and drinking.
- Long-term use of medications - hormonal medications, anti-inflammatory drugs and antibacterial drugs.
- Leading a sedentary, mostly sedentary lifestyle.
- The presence of congenital pathologies of the gallbladder.
- General genetic predisposition.
- Food allergies and manifestations of atopic dermatitis.
- Pregnancy.
- Endocrine health problems - obesity and diabetes.
Stagnation of bile juice in the liver can occur in the postoperative period when the gallbladder is removed.